Submitted:
28 March 2024
Posted:
29 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
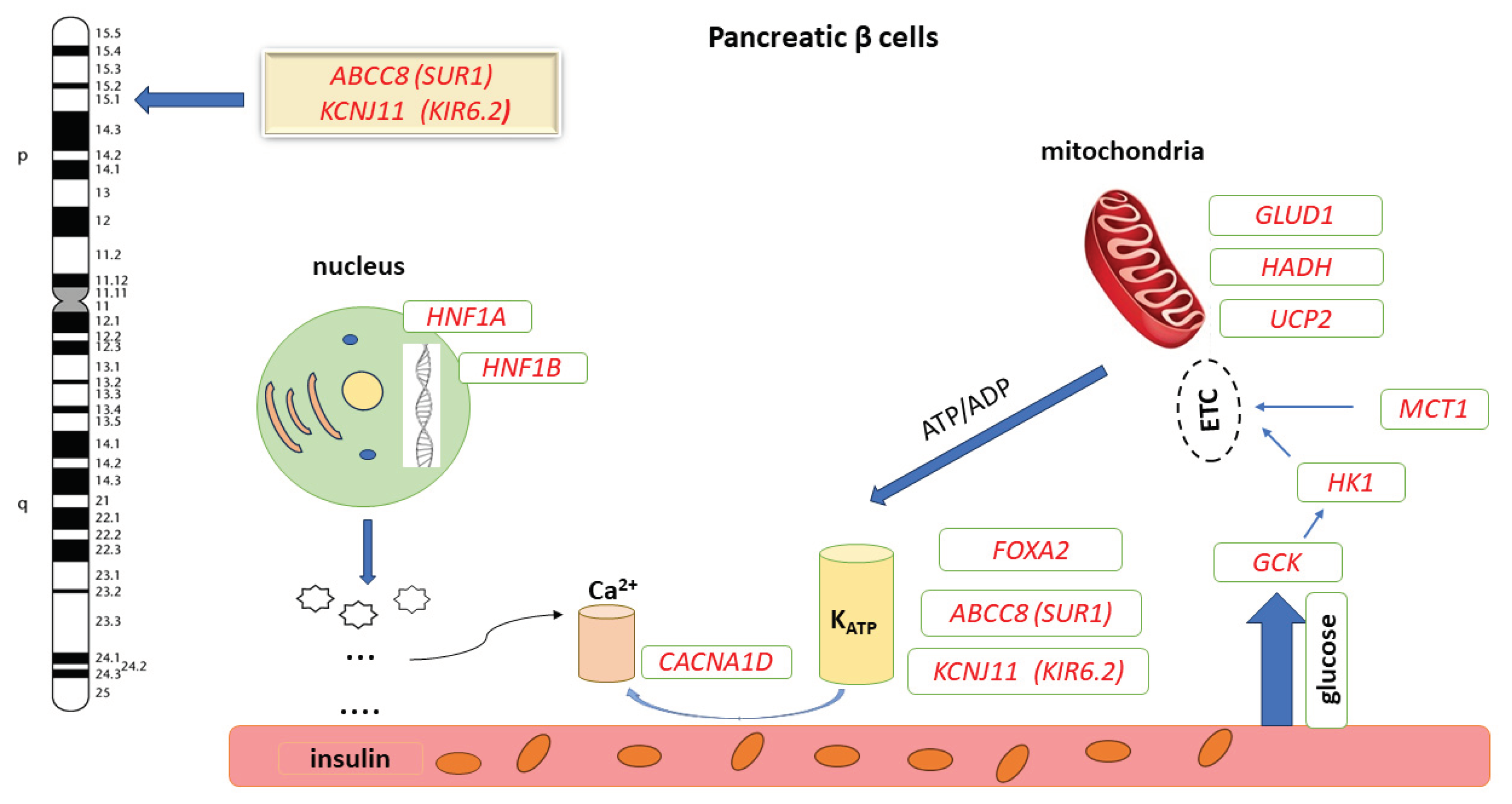
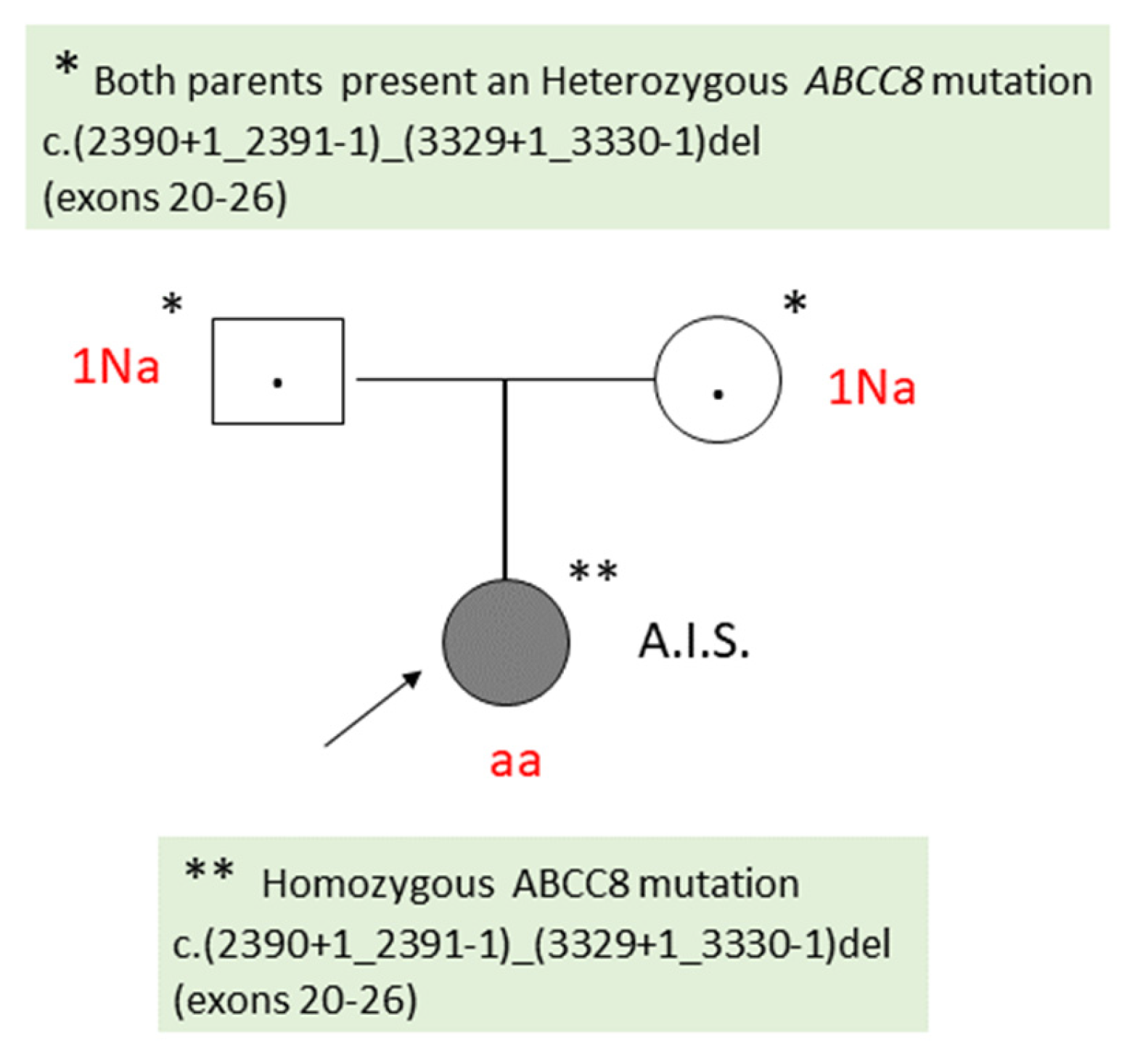
2.1. Patient 1
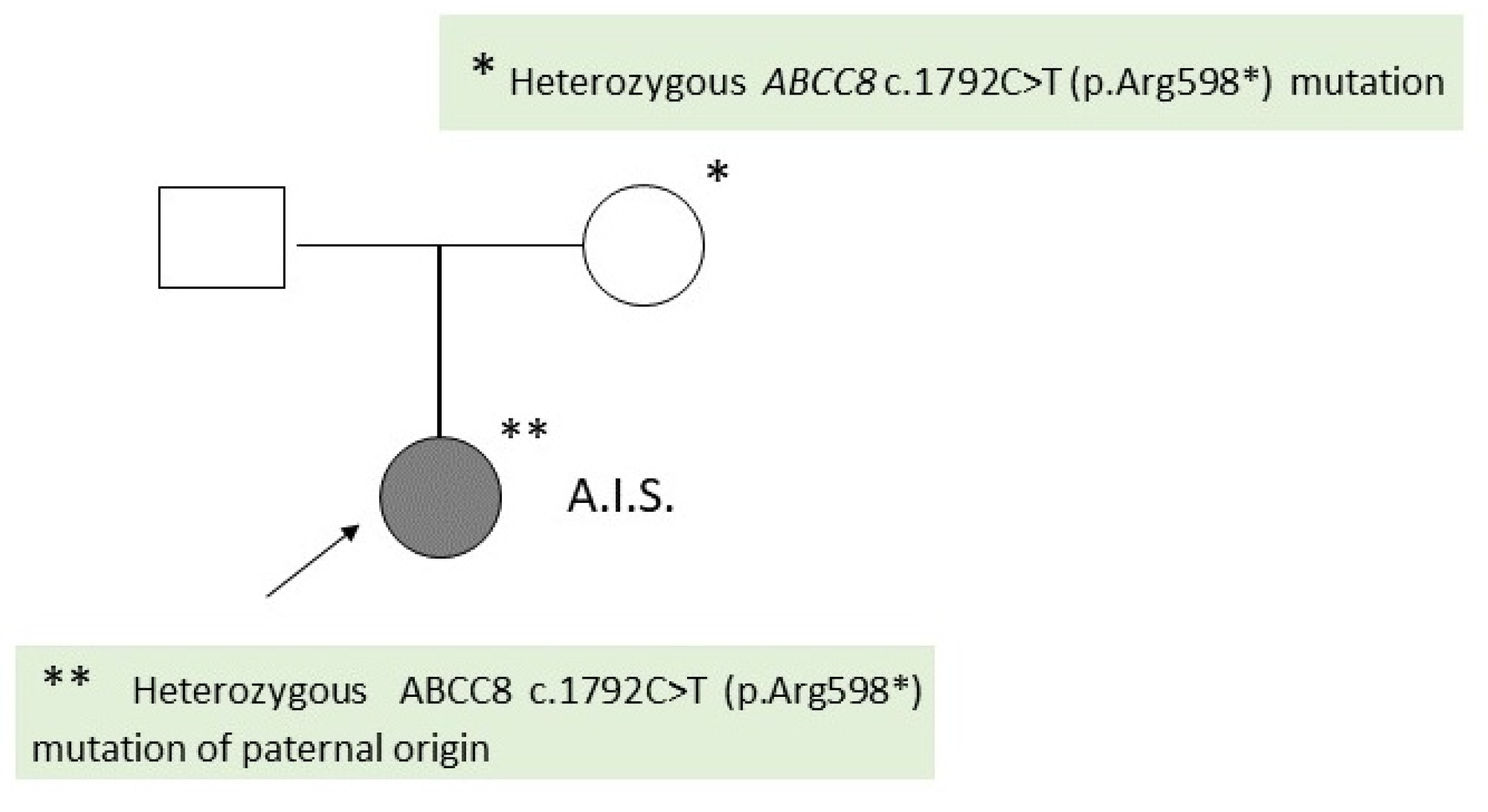
2.2. Patient 2
3. Discussion
4. Genetic Counseling
5. Material and Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Vora, S.; Chandran, S.; Rajadurai, V.S.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in infancy: Current concepts in diagnosis and management. Indian Pediatr. 2015, 52, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.R.; Flanagan, S.E.; James, C.; Shield, J.; Ellard, S.; Hussain, K. Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. Arch Dis Child. 2009, 94, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Santos, F.; Simões, H.; Castro-Feijóo, L.; Rodríguez, P.C.; Fernández-Marmiesse, A.; Fiaño, R.S.; Rego, T.; Carracedo. ; Conde, J.B. Congenital hyperinsulinism in two siblings with ABCC8 mutation: same genotype, different phenotypes. Arq. Bras. de Endocrinol. Metabol. 2018, 62, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OMIM—Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Available online: https://www.omim.org/, (accessed on 9 March 2024).
- Gϋemes, M.; Rahman, S.A.; Kapoor, R.R.; Flanagan, S.; Houghton, J.A.L.; Misra, S.; Oliver, N.; Dattani, M.T.; Shah, P. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia in children and adolescents: Recent advances in understanding of pathophysiology and management. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 577–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- States, L.J.; Davis, J.C.; Hamel, S.M.; Becker, S.A.; Zhuang, H. 18F-6-Fluoro-l-Dopa PET/CT Imaging of Congenital Hyperinsulinism. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 51S–56S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, A.G.; Melikian, M.; Globa, E.; Detlefsen, S.; Rasmussen, L.; Petersen, H.; Brusgaard, K.; Rasmussen, A.H.; Mortensen, M.B.; Christesen, H.T. The difficult management of persistent, non-focal congenital hyperinsulinism: A retrospective review from a single, tertiary center. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020, 21, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, K. Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Neoreviews. 2021, 22, e230–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournet, J.-C.; Mayaud, C.; de Lonlay, P.; Gross-Morand, M.-S.; Verkarre, V.; Castanet, M.; Devillers, M.; Rahier, J.; Brunelle, F.; Robert, J.-J.; et al. Unbalanced Expression of 11p15 Imprinted Genes in Focal Forms of Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Association with a Reduction to Homozygosity of a Mutation in ABCC8 or KCNJ11. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, E.; Mitteer, L.; Boodhansingh, K.; Becker, S.A.; McKnight, H.; Boyajian, L.; Ackermann, A.M.; Kalish, J.M.; Bhatti, T.R.; States, L.J.; et al. Case Report: Two Distinct Focal Congenital Hyperinsulinism Lesions Resulting From Separate Genetic Events. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 699129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, K.E.; Becker, S.; Boyajian, L.; Shyng, S.-L.; MacMullen, C.; Hughes, N.; Ganapathy, K.; Bhatti, T.; Stanley, C.A.; Ganguly, A. Genotype and Phenotype Correlations in 417 Children With Congenital Hyperinsulinism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E355–E363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSheikh, A.; Shyng, S.-L. KATP channel mutations in congenital hyperinsulinism: Progress and challenges towards mechanism-based therapies. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1161117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, S.; Urbanska, K.; Biel, N.; Bielak, M.J.; Tarkowska, A.; Piekarski, R.; Prokurat, A.I.; Pacholska, M.; Ben-Skowronek, I. Congenital Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia—A Review and Case Presentation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewat, T.I.; Johnson, M.B.; Flanagan, S.E. Congenital Hyperinsulinism: Current Laboratory-Based Approaches to the Genetic Diagnosis of a Heterogeneous Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roženková, K.; Güemes, M.; Shah, P.; Hussain, K. The Diagnosis and Management of Hyperinsulinaemic Hypoglycaemia. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 7, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Salomon-Estebanez, M.; Shah, P.; Nicholson, J.; Cosgrove, K.E.; Dunne, M.J. Therapies and outcomes of congenital hyperinsulinism-induced hypoglycaemia. Diabet. Med. 2018, 36, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Ge, J.; Zhang, M.; Hussain, K.; Guan, Y.; Cheng, R.; Xi, L.; Zheng, Z.; Ren, S.; Luo, F. Genotype and phenotype analysis of a cohort of patients with congenital hyperinsulinism based on DOPA-PET CT scanning. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- http://gnomad.broadinstitute.org, (accesed on 7 March 2024).
- https://clinvarminer.genetics.utah.edu/submissions-by-variant/NM_000352.6%28ABCC8%29%3Ac.1792C%3ET%20%28p.Arg598Ter%29, (accesed on 7 March 2024).
- Damaj, L.; le Lorch, M.; Verkarre, V.; Werl, C.; Hubert, L.; Nihoul-Fékété, C.; Aigrain, Y.; de Keyzer, Y.; Romana, S.P.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; et al. Chromosome 11p15 Paternal Isodisomy in Focal Forms of Neonatal Hyperinsulinism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4941–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vroede, M.; Bax, N.; Brusgaard, K.; Dunne, M.J.; Groenendaal, F. Laparoscopic Diagnosis and Cure of Hyperinsulinism in Two Cases of Focal Adenomatous Hyperplasia in Infancy. PEDIATRICS 2004, 114, e520–e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; Saint-Martin, C.; Ribeiro, M.-J.; Vaury, C.; Verkarre, V.; Arnoux, J.-B.; Valayannopoulos, V.; Gobrecht, S.; Sempoux, C.; Rahier, J.; et al. ABCC8 and KCNJ11 molecular spectrum of 109 patients with diazoxide-unresponsive congenital hyperinsulinism. J. Med Genet. 2010, 47, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, I.; Schanze, I.; Felgendreher, I.M.; Barthlen, W.; Vogelgesang, S.; Mohnike, K.; Zenker, M. Integration of genomic analysis and transcript expression of ABCC8 and KCNJ11 in focal form of congenital hyperinsulinism. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1015244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, V.B.; Guemes, M.; Nessa, A.; Alam, S.; Shah, P.; Gilbert, C.; Senniappan, S.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ellard, S.; Hussain, K. Clinical and histological heterogeneity of congenital hyperinsulinism due to paternally inherited heterozygous ABCC8/KCNJ11 mutations. Eur J Endocrinol. 2014, 171, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Ying, L.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, B.; Yao, R.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, T.; et al. Genetic variants of ABCC8 and clinical manifestations in eight Chinese children with hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, N.; Ahamed, A.; Unnikrishnan, A.G.; Kumar, H.; Ellard, S. Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus due to an ABCC8 mutation: a case report. . 2014, 15, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A; Cheng, J.; Sheng, H.; Wen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, C., Shao, Y.; Li, C., Liu, L.; Li, X. Clinical Management and Gene Mutation Analysis of Children with Congenital Hyperinsulinism in South China. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2019, 11, 400–409.
- Hashemian, S.; Esfehani, R.J.; Karimdadi, S.; Ghaemi, N.; Eshraghi, P.; Gonabadi, N.M.; Sahebkar, A.; Vakili, R.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Genotyping of ABCC8, KCNJ11, and HADH in Iranian Infants with Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D.; Bryan, J. Neonatal Diabetes and Congenital Hyperinsulinism Caused by Mutations in ABCC8/SUR1 are Associated with Altered and Opposite Affinities for ATP and ADP. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrand, J.; Busiah, K.; Vaivre-Douret, L.; Fauret, A.L.; Berdugo, M.; Cavé, H.; Polak, M. Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus. Front Pediatr. 2020, 8, 540718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, J.S.; Jacobson, D.A. Channeling dysglycemia: ion-channel variations perturbing glucose homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, D.; Familial Hyperinsulinism. 2003 Aug 19 [updated 2019 Mar 21]. In: Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1375/, (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Nestorowicz, A.; Glaser, B.; Wilson, B.A.; Shyng, S.-L.; Nichols, C.G.; Stanley, C.A.; Thornton, P.S.; Permutt, M.A. Genetic Heterogeneity in Familial Hyperinsulinism. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, D.; Hawton, K.; Senniappan, S. Congenital hyperinsulinism: recent updates on molecular mechanisms, diagnosis and management. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 35, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, C.A. Perspective on the Genetics and Diagnosis of Congenital Hyperinsulinism Disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ackermann, A.M.; Boodhansingh, K.E.; Bhatti, T.R.; Liu, C.; Schug, J.; Doliba, N.; Han, B.; Cosgrove, K.E.; Banerjee, I.; et al. Functional and Metabolomic Consequences of KATP Channel Inactivation in Human Islets. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, B.; Blech, I.; Krakinovsky, Y.; Ekstein, J.; Gillis, D.; Mazor-Aronovitch, K.; Landau, H.; Abeliovich, D. ABCC8 mutation allele frequency in the Ashkenazi Jewish population and risk of focal hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Anesthesia Analg. 2011, 13, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, I.; Salomon-Estebanez, M.; Shah, P.; Nicholson, J.; Cosgrove, K.E.; Dunne, M.J. Therapies and outcomes of congenital hyperinsulinism-induced hypoglycaemia. Diabet. Med. 2018, 36, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, X.; Ji, L. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of ABCC8 Nonneonatal Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Miller, T.; Houghton, J.; Munyard, P.; Kumar, Y.; Puvirajasinghe, C.; Giri, D. Congenital hyperinsulinism due to compound heterozygous mutations in ABCC8 responsive to diazoxide therapy. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Patient A.I.S. | Patient D.M.S. |
|---|---|---|
| Histologic type | Diffuse CHI | Focal CHI |
| The result of the patient’s genetic testing | Homozygous ABCC8 c.(2390+1_2391-1)_(3329+1_3330-1)del (exons 20-26) | Heterozygous ABCC8 c.1792C>T (p.Arg598*) |
| The result of genetic testing of the patient’s parents |
Both parents: Heterozygous ABCC8 c.(2390+1_2391-1)_(3329+1_3330-1)del (exons 20-26) |
Father: Heterozygous ABCC8 mutation c.1792C>T (p.Arg598*) Mother: normal result |
| Gender | F | F |
| Family history | no | no |
| Gestation | Term (38 weeks) | Term (38 weeks) |
| Parents’ consanguinity | No | No |
| Birth weight | 3140 g | 2700g |
| Onset of symptoms | 1st day | 3rd day |
| Persistent hypoglycaemia | 13-32mg/dL | 17-45 mg/dL |
| Insulin plasma level | ↑ (41,45 uUI/ mL; normal value: 3-25 uUI/ mL) | 15.28 uUI/ ml (normal value: 3-25 uUI/ml) |
| C- peptid plasma level | ↑ (4,92 ng/ mL; normal value: 0,2-4.4 ng/ mL) | 2,2 ng/ ml (normal value: 0,9-7,1 ng/mL |
| hGH | ↑ (133,67 uUI/mL ; normal value: 0-5 uUI/ mL) | Normal value |
| Thyroid hormones | Normal value | Normal value |
| Cortisol plasma level | Normal value | ↓ (2,27 µg/ dL(normal value: 4,3-22,4 µg/dL) |
| ACTH | Not performed | ACTH < 5 pg/mL (normal value: 5 -46 pg/ mL) |
| Macrosomia | No | No |
| Neurological manifestations | No | Tonic-clonic seizures Generalized hypotonia |
| Perinatal asphyxia | Yes | No |
| Transfontanelle ultrasonography |
Bilateral subependymal hemorrhage | Not performed |
| Brain CT | Not performed | Patologic |
| Abdominal IRM | normal | Normal |
| EEG | normal | Hypsarrhythmia |
| Diazoxide responsiveness | No | No |
| (18)F-DOPA PET/CT | Not indicated | Not performed yet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





