Submitted:
28 March 2024
Posted:
28 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Retrieving Flavonoids’ Structures
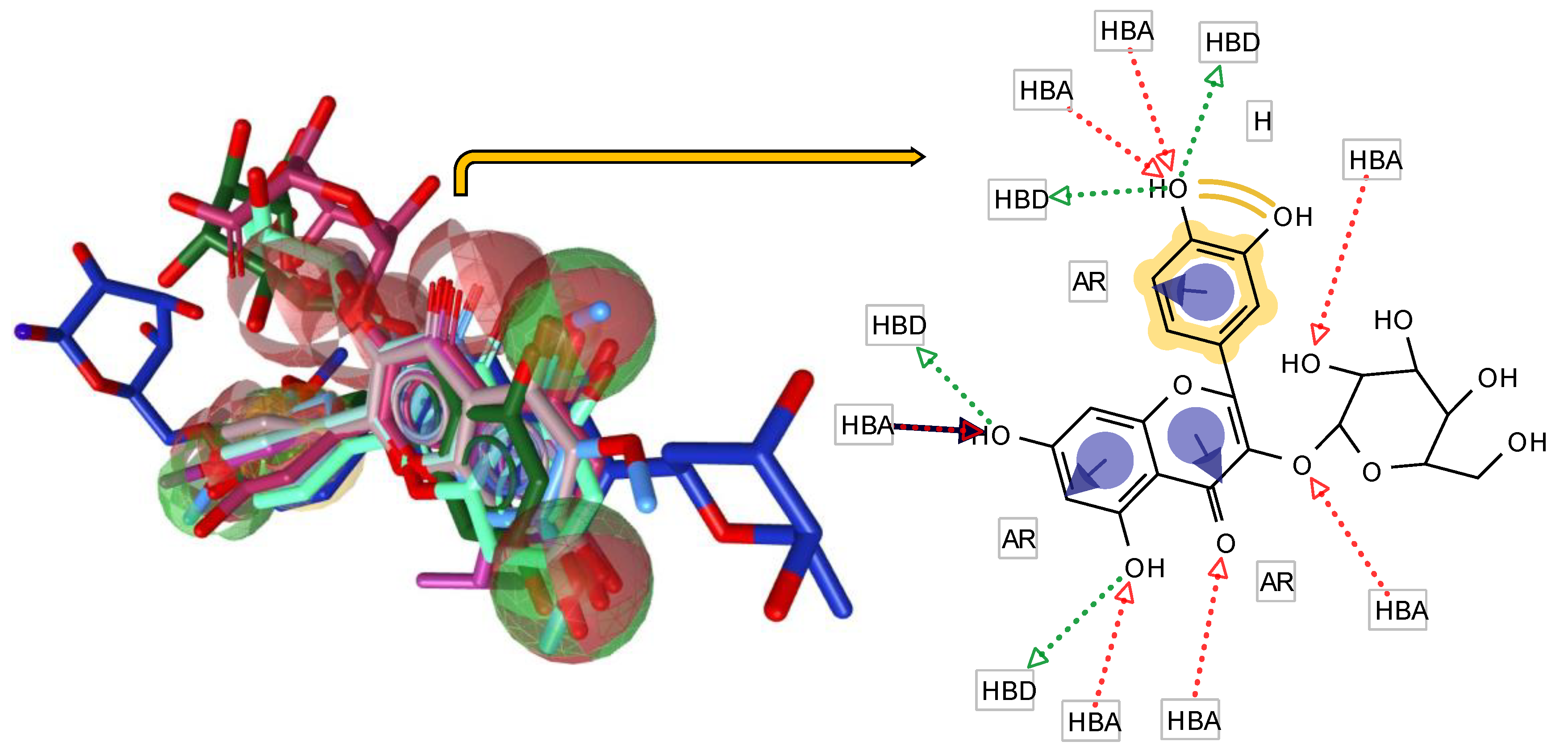
Establishing Pharmacophore Model
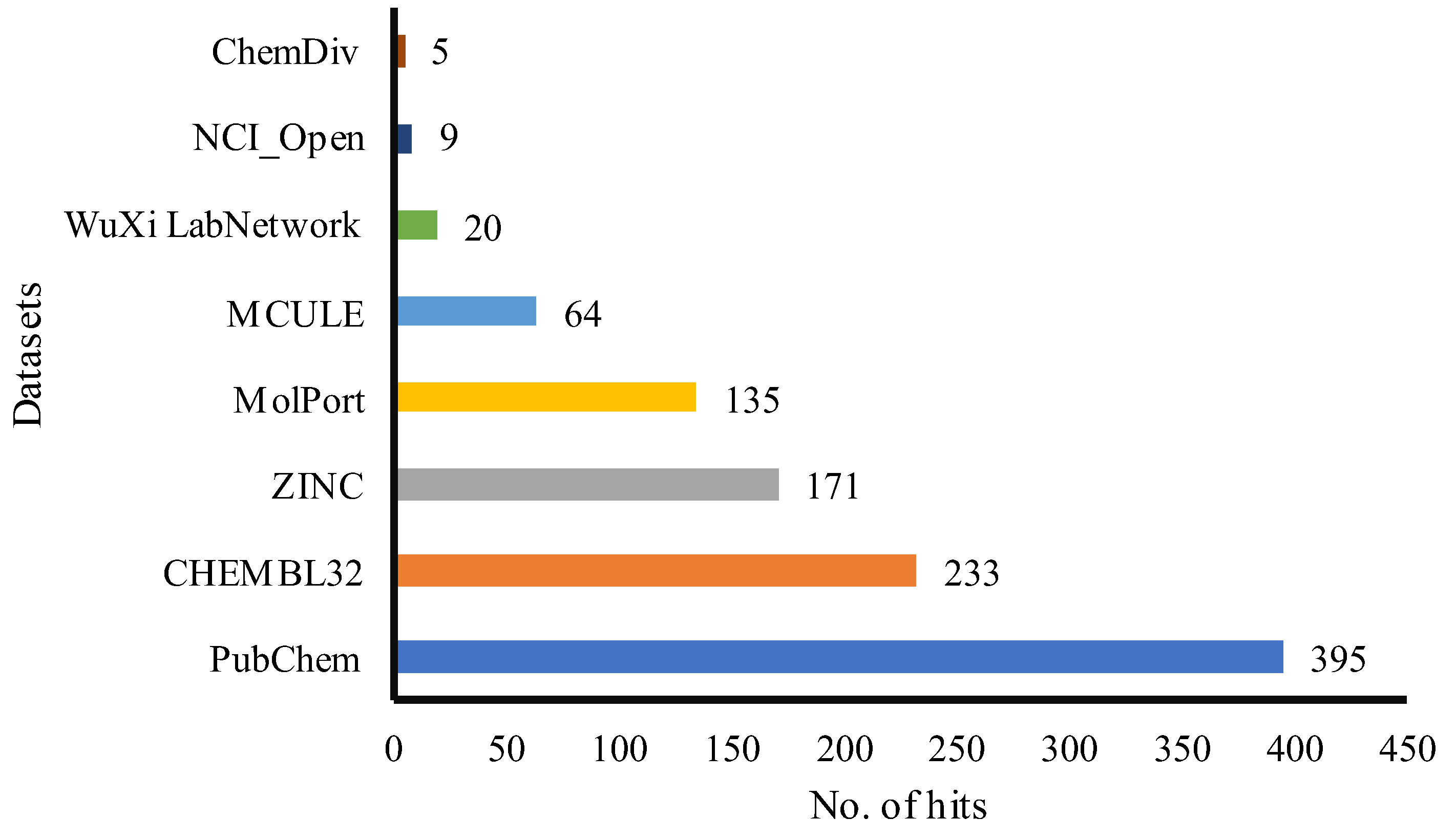
Screening Large Chemical Database
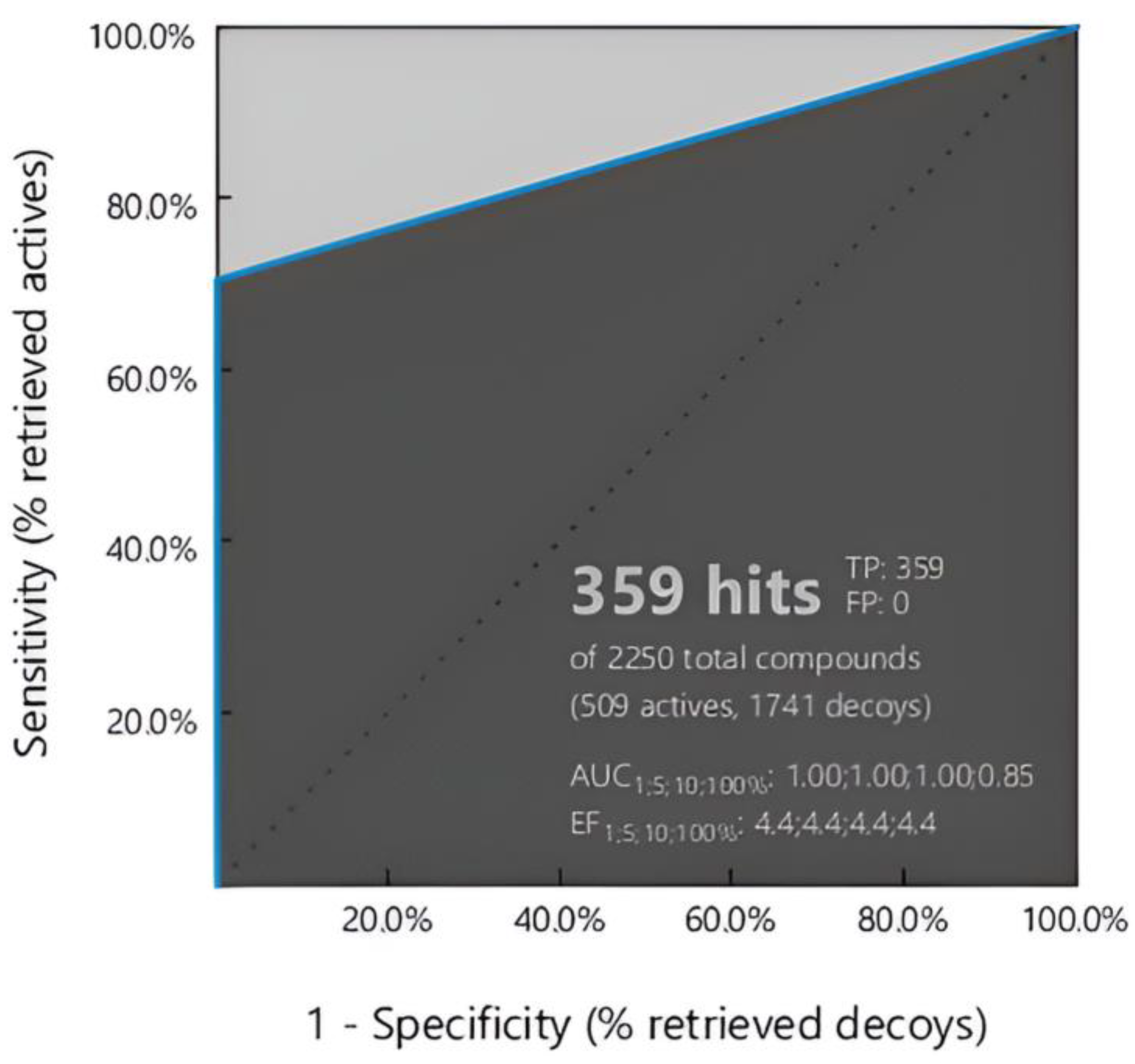
Creating Chemical Libraries and Assessing Model Precision
Establishing a Predictive QSAR Equation
Multicollinearity Measurement
Principal Component Analysis
Applicability Domain (AD) Assessment
3. Results
Flavonol-Based Pharmacophore Models
Virtual Screening
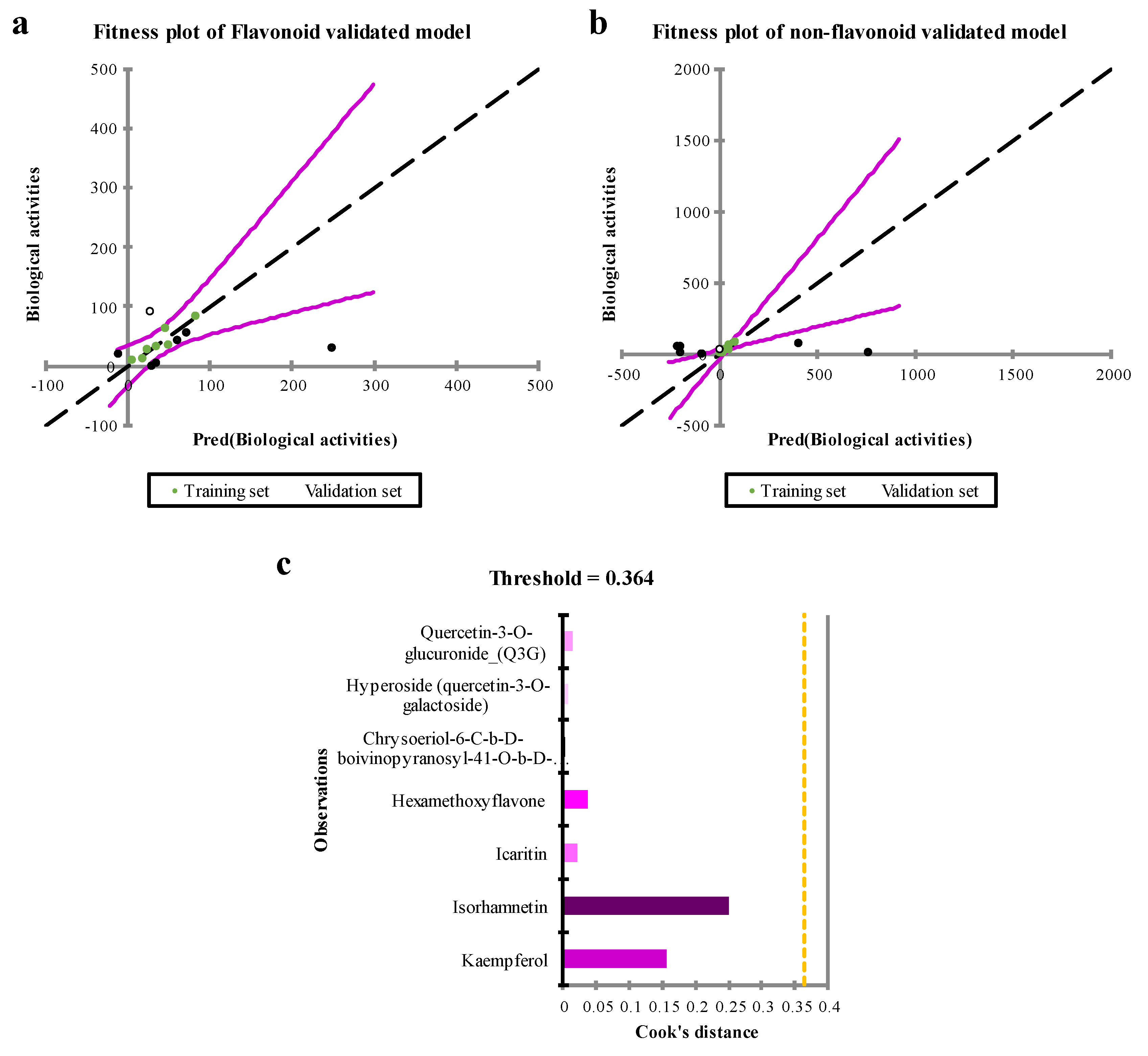
The QSAR Model
Applicability Domain (AD) Analysis

PCA Measure of the Predictors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khani, H.; Ghorbani, M.; Nojoomi, F.; Mohebbi, A. Honey Bee Dry Venom Reduces Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Secretion in PLC/PRF/5 Cell Line. International Journal of Medical Laboratory 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A.; Lorestani, N.; Tahamtan, A.; Kargar, N.L.; Tabarraei, A. An Overview of Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Secretion Inhibitors. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, W.J.; Papatheodoridis, G. V.; Lok, A.S.F. Hepatitis B. The Lancet 2023, 401, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. Trends in Mortality of Liver Disease Due to Hepatitis B in China from 1990 to 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Chin Med J (Engl) 2022, 135, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Kazim, S.N. HBV CccDNA A Culprit and Stumbling Block for the Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Its Presence in Hepatocytes Perplexed the Possible Mission for a Functional Cure. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 24066–24081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbato, J.M.; Avihingsanon, A.; Singh, K.P.; Zhao, W.; Deleage, C.; Rosen, E.; Cottrell, M.L.; Rhodes, A.; Dantanarayana, A.; Tumpach, C.; et al. HIV DNA Persists in Hepatocytes in People with HIV-Hepatitis B Co-Infection on Antiretroviral Therapy. EBioMedicine 2023, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevola, R.; Beccia, D.; Rosato, V.; Ruocco, R.; Mastrocinque, D.; Villani, A.; Perillo, P.; Imbriani, S.; Delle Femine, A.; Criscuolo, L.; et al. HBV Infection and Host Interactions: The Role in Viral Persistence and Oncogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Behnampour, N.; Shahramian, I.; Moradi, A. Association of HLADQ-B1 Polymorphisms in Three Generations of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Virus Res 2023, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Behnampour, N.; Shahramian, I.; Moradi, A. Mutations in the S Gene of Hepatitis B Virus in Three Generations of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afraie, M.; Moradi, G.; Zamani, K.; Azami, M.; Moradi, Y. The Effect of Hepatitis B Virus on the Risk of Pregnancy Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Virol J 2023, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.L.; Chen, M.X.; Adu-Gyamfi, E.A.; Geng, L.H.; Fu, L.J.; Wan, Q.; Ding, Y. Bin Maternal Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Pregnancy Outcomes of Freeze-Thaw Embryo Transfer. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2323495–e2323495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufon, K.A.; Meriki, H.D.; Kwenti, T.E.; Tony, N.J.; Malika, E.; Bolimo, A.F.; Kouanou, Y.S.; Nkuo-Akenji, T.; Anong, D.N. HBV Transmission Risk Assessment in Healthcare Workers, Household and Sexual Contacts of HBV Infected Patients in the Southwest Region of Cameroon. Oman Med J 2019, 34, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.J.; Lok, A.S.; Zoulim, F. New Perspectives on Development of Curative Strategies for Chronic Hepatitis B. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2023, 21, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunnaike, M.; Das, S.; Raut, S.S.; Sultana, A.; Nayan, M.U.; Ganesan, M.; Edagwa, B.J.; Osna, N.A.; Poluektova, L.Y. Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: New Approaches towards Cure. Biomolecules 2023, Vol. 13, Page 1208 2023, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.; Blank, A.; Voronkova, N.; Stepanova, T.; Sagalova, O.; Chulanov, V.; Osipenko, M.; Morozov, V.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Bulevirtide in Combination with Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis D Virus Coinfection (MYR202): A Multicentre, Randomised, Parallel-Group, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2023, 23, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Han, B.; Zhang, W.; Wu, W. Clinical Effects of NTCP-Inhibitor Myrcludex B. J Viral Hepat 2021, 28, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, A.; Markert, C.; Hohmann, N.; Carls, A.; Mikus, G.; Lehr, T.; Alexandrov, A.; Haag, M.; Schwab, M.; Urban, S.; et al. First-in-Human Application of the Novel Hepatitis B and Hepatitis D Virus Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex B. J Hepatol 2016, 65, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis D with the Entry Inhibitor Myrcludex B: First Results of a Phase Ib/IIa Study. J Hepatol 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Hou, J.; Asselah, T.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Zoulim, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Janczewska, E.; Nahass, R.G.; Bourgeois, S.; Buti, M.; et al. Randomised Phase 2 Study (JADE) of the HBV Capsid Assembly Modulator JNJ-56136379 with or without a Nucleos(t)Ide Analogue in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Gut 2023, 72, 1385–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdette, D.; Hyrina, A.; Song, Z.; Beran, R.K.; Cheung, T.; Gilmore, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Capsid Assembly Modulator for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2023, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amblard, F.; Chen, Z.; Wiseman, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, P.; Salman, M.; Verma, K.; Azadi, N.; Downs-Bowen, J.; Tao, S.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Highly Potent HBV Capsid Assembly Modulators (CAMs). Bioorg Chem 2023, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Gong, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Long, G.; Li, H.; Xiao, F.; Lu, M.J.; Hu, Y.; et al. A Novel Phthalazinone Derivative as a Capsid Assembly Modulator Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Expression. Antiviral Res 2024, 221, 105763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezanezhadi, M.; Mohebbi, A.; Askari, F.S.; Hosseini, S.D.; Tabarraei, A. Hepatitis B Virus Reverse Transcriptase Polymorphisms between Treated and Treatment-Naïve Chronically Infected Patients. Virusdisease 2019, 30, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conners, E.E.; Panagiotakopoulos, L.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Spradling, P.R.; Hagan, L.M.; Harris, A.M.; Rogers-Brown, J.S.; Wester, C.; Nelson, N.P. Screening and Testing for Hepatitis B Virus Infection: CDC Recommendations — United States, 2023. MMWR. Recommendations and Reports 2023, 72, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareifopoulos, N.; Lagadinou, M.; Karela, A.; Kyriakopoulou, O.; Velissaris, D. Neuropsychiatric Effects of Antiviral Drugs. Cureus 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An Overview. J Nutr Sci 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi, M.; Salavatiha, Z.; Gogoi, U.; Mohebbi, A. An Overview of Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Flavonoids and Their Mechanisms of Action. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2024, 14, 1356003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Sun, G.; Guo, W.; Huang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhao, F.; Hu, K. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Quercetin in Human Hepatoma Cell Lines. Virol Sin 2015, 30, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, M.K.; Ahmed, S.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Abdelwahid, M.A.S.; Arbab, A.H.; Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Al-Oqail, M.M. Novel Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Euphorbia Schimperi and Its Quercetin and Kaempferol Derivatives. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29100–29110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.K.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; …, A.H.A.-S.P. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Flavonoid Myricetin-3-O-Rhamnoside along with Quercetin from Guiera Senegalensis Leaves; Elsevier, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J.T.; Agudelo, I.; Alejandro Ricco, R.; Vicenta Cavallaro, L.; Campos, R.; Parlar, A.; Mex Alvarez, R. The Infusion of Baccharis Spicata (Lam.) Baill (Asteraceae) Has Antiviral Activity against Hepatitis B Virus without Cytotoxic Effects against Several Cell Lines. In blacpma.ms-editions.clJT Ortega, I Agudelo, RA Ricco, LV Cavallaro, RH CamposBoletín Latinoamericano y del Caribe de Plantas Medicinales y, 2024•blacpma.ms-editions.cl. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Bolton, E.E.; Chen, J.; Fu, G.; Gindulyte, A.; Han, L.; He, J.; He, S.; Shoemaker, B.A.; et al. PubChem Substance and Compound Databases. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, D1202–D1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.L.; Patricia Bento, A.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrian-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL Database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D Pharmacophores Derived from Protein-Bound Ligands and Their Use as Virtual Screening Filters. J Chem Inf Model 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, A. Ligand-Based 3D Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation of Potential Smoothened Inhibitors. J Mol Model 2023, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, M.K.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Basudan, O.A.; Herqash, R.N. The Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Sea Buckthorn Is Attributed to Quercetin, Kaempferol and Isorhamnetin. Biomed Rep 2022, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. Icaritin Inhibits the Expression of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Hepatoma Cell Lines through Post-Transcriptional Regulation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Ren, F.; Yang, X. Anti-HBV Therapeutic Potential of Small Molecule 3, 5, 6, 7, 3′, 4′-Hexamethoxyflavone in Vitro and in Vivo. Virology 2021, 560, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Guo, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; Dong, J.-X. New Anti-HBV C-Boivinopyranosyl Flavones from Alternanthera Philoxeroides. Molecules 2016, 21, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Wu, N.; Shen, C.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y.; Han, J.; et al. Hyperoside Nanocrystals for HBV Treatment: Process Optimization, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2016, 42, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, G. In Vivo and in Vitro Antiviral Activity of Hyperoside Extracted from Abelmoschus Manihot (L) Medik. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007, 28, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.X.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.J.; Rong, X.Y.; Jing, S.; Xie, Y.H.; Huang, D.F.; Zhao, C. Luteolin-7-O-Glucoside Present in Lettuce Extracts Inhibits Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Production and Viral Replication by Human Hepatoma Cells in Vitro. Front Microbiol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.W.; Geng, C.A.; Jiang, F.Q.; Ma, Y.B.; He, K.; Zhou, N.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.J. Chemical Constituents of Swertia Yunnanensis and Their Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, C.A.; Chen, J.J. The Progress of Anti-HBV Constituents from Medicinal Plants in China. Nat Prod Bioprospect 2018, 8, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.L.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, H.L.; Chang, C.G.; Chen, C.F.; Chang, C.; Hsieh, M.T. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Effects of Wogonin Isolated from Scutellaria Baicalensis. Planta Med 2000, 66, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhao, L.; You, Q.; Yang, Y.; Gu, H.; Song, G.; research, N.L.-A. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Wogonin in Vitro and in Vivo. Antiviral Res 2007, 74, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Parvez, M.K.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Abdelwahid, M.A.S.; Alhowiriny, T.A.; Al-Rehaily, A.J. Novel Anti-hepatitis B Virus Flavonoids Sakuranetin and Velutin from Rhus Retinorrhoea. Mol Med Rep 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Ren, J.H.; Su, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, S.T.; Zhang, C.R.; Chen, J. Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Activity of Swertisin Isolated from Iris Tectorum Maxim. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 257, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, T.; Han, X.; Yuan, H.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Virology, X.W.-. Discovery and Mechanism of Action of Novel Baicalein Modified Derivatives as Potent Antihepatitis Agent. Virology 2017, 507, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembower, D.E.; Lin, Y.M.; Flavin, M.T.; Chen, F.C.; Korba, B.E. Robustaflavone, a Potential Non-Nucleoside Anti-Hepatitis B Agent. Antiviral Res 1998, 39, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, M.; Xue, T.C. ; Gao B ERK1/2-HNF4α Axis Is Involved in Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibition of HBV Replication. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2020, 41, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Hu, J.; Shu, W.; Gao, B.; Disease, S.X.-C.D. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Opposes HBV-Induced Incomplete Autophagy by Enhancing Lysosomal Acidification, Which Is Unfavorable for HBV Replication. nature.comL Zhong, J Hu, W Shu, B Gao, S XiongCell Death & Disease, 2015•nature.com 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.Y.; Zhao, K.J.; Wang, J.B.; Ma, Z.J.; Xiao, X.H. Green Tea Polyphenol, Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate, Possesses the Antiviral Activity Necessary to Fight against the Hepatitis B Virus Replication in Vitro. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2014, 15, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gu, W.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Xing, G.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, W. Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus via Farnesoid X Receptor Alpha. J Nat Med 2016, 70, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.H.; Sun, C.P.; Huang, H.C.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, H.K.; Huang, C. Epigallocatechin Gallate Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Human Liver Chimeric Mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 2018, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Tao, M.H.; Hung, T.M.; Chen, J.C.; Lin, Z.J.; Huang, C. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Entry of Hepatitis B Virus into Hepatocytes. Antiviral Res 2014, 111, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukuda, S.; Watashi, K.; Hojima, T.; Isogawa, M.; Iwamoto, M.; Omagari, K.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Kojima, S.; Sugiyama, M.; et al. A New Class of Hepatitis B and D Virus Entry Inhibitors, Proanthocyanidin and Its Analogs, That Directly Act on the Viral Large Surface Proteins. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Chen, D. Biflavanones, Flavonoids, and Coumarins from the Roots of Stellera Chamaejasme and Their Antiviral Effect on Hepatitis B Virus. Chem Biodivers 2008, 5, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Uwai, K.; Taguchi, R.; Chayama, K.; Sakaguchi, T.; Narita, R.; Yao, W.L.; Takeuchi, F.; Otakaki, Y.; et al. Rosmarinic Acid Is a Novel Inhibitor for Hepatitis b Virus Replication Targeting Viral Epsilon RNA-Polymerase Interaction. PLoS One 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki-Utsubo, C.; Indrasetiawan, P.; Fukano, K.; Muramatsu, M.; Artanti, N.; Hanafi, M.; Hotta, H.; Kameoka, M. Amentoflavone Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Infection via the Suppression of PreS1 Binding to Host Cells. Microbiol Immunol 2023, 67, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, H.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q. ; Li K Anti-Hepatitis B Virus and Anti-Cancer Activities of Novel Isoflavone Analogs. Eur J Med Chem 2013, 62, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.J.; Liu, S.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chou, S. Antiviral Activity of Chemical Compound Isolated from Artemisia Morrisonensis against Hepatitis B Virus in Vitro. Antiviral Res 2014, 101, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, J.; Ren, F.; Xu, H.; Tan, M.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J. Nobiletin, a Novel Inhibitor, Inhibits HBsAg Production and Hepatitis B Virus Replication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 523, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, X. Baicalin Benefits the Anti-HBV Therapy via Inhibiting HBV Viral RNAs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2017, 323, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.C.; Ng, L.T.; Cheng, P.W.; Chiang, W.; Lin, C.C. Antiviral Activities of Extracts and Selected Pure Constituents of Ocimum Basilicum. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2005, 32, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ying, G.; Wu, S.; Wu, F.; Chen, Z. In Vitro Inhibition Effects of Hepatitis B Virus by Dandelion and Taraxasterol. Infect Agent Cancer 2020, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.C.; Huang, T.J.; Lin, E.H.; Huang, C.H.; Chou, C.H. Antihepatitis B Virus Constituents of Solanum Erianthum. Nat Prod Commun 2012, 7, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. Pharmit: Interactive Exploration of Chemical Space. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W442–W448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, A.; Askari, F.S.; Sammak, A.S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Najafimemar, Z. Druggability of Cavity Pockets within SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein and Pharmacophore-Based Drug Discovery. Future Virol 2021, 16, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A.; Naderi, M.; Sharifian, K.; Behnezhad, F.; Mohebbi, M.; Gholami, A.; Askari, F.S.; Mirarab, A.; Monavari, S.H. Computational-Aided Reproposing Drug(s) and Discovery for Potential Antivirals Targeting Hepatitis B Virus Capsid Protein; 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriwaki, H.; Tian, Y.S.; Kawashita, N.; Takagi, T. Mordred: A Molecular Descriptor Calculator. J Cheminform 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, A.; Consonni, V.; Pavan, M.; Todeschini, R. DRAGON Software: An Easy Approach to Molecular Descriptor Calculations. Match 2006, 56, 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Afgan, E.; Nekrutenko, A.; Grüning, B.A.; Blankenberg, D.; Goecks, J.; Schatz, M.C.; Ostrovsky, A.E.; Mahmoud, A.; Lonie, A.J.; Syme, A.; et al. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2022 Update. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, W345–W351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenberg, D.; Team, on behalf of T.G.; Coraor, N.; Team, on behalf of T.G.; Von Kuster, G.; Team, on behalf of T.G.; Taylor, J.; Team, on behalf of T.G.; Nekrutenko, A.; Team, on behalf of T.G. Integrating Diverse Databases into an Unified Analysis Framework: A Galaxy Approach. Database 2011, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Askari, F.S.; Shaddel, R.; Mirarab, A.; Oladnabi, M. QSAR Modeling of a Ligand-Based Pharmacophore Derived from Hepatitis B Virus Surface Antigen Inhibitors. Acta Microbiol Bulg 2022, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Mohebbi, A.; Ghorbanzadeh, T.; Naderifar, S.; Khalaj, F.; Askari, F.S.; Salehnia Sammak, A. A Fragment-Based Drug Discovery Developed on Ciclopirox for Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein: An in Silico Study. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0285941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, A.; Kar, S.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Computational Modeling of Human Serum Albumin Binding of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Employing QSAR, Read-Across, and Docking. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, P. Das; Tripathi, I.P.; Dwivedi, M.K. QSAR Study of Some Anti-Hepatitis B Virus Agents Comprising 4-Aryl-6-Chloro-Quinolin-2-Ones and 5-Aryl-7-Chloro-1, 4-Benzodiazepines; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nasution, M.A.F.; Stephanie, F.; Tambunan, U.S.F. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Simulation of Flavonoids as Smoothened Protein Inhibitor of Hedgehog Signaling Pathways. AIP Conf Proc 2019, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, F.S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Parhiz, J.; Hassanpour, M.; Mohebbi, A.; Mirshafiey, A. Digging for the Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12 Inhibitors: A Pharmacophore-Based and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Future Virol 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekawati, M.M.; Fardiansyah Nasution, M.A.; Siregar, S.; Rizki, I.F.; Tambunan, U.S.F. Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Simulation of Terpenoid Compounds as the Inhibitor of Sonic Hedgehog Protein for Colorectal Cancer Therapy. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 2019, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hădărugă, D.I. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships (QSAR) in Flavonoid Compound Class. Journal of Agroalimentary Processes and Technologies 2009, 15, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, C.E. Identifying Candidate Flavonoids for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Network-Based Strategy. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 892559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Pan, F.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Y.; Tian, W.; Peng, W.; Liu, J. Virtual Screening Strategy for Anti-DPP-IV Natural Flavonoid Derivatives Based on Machine Learning. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
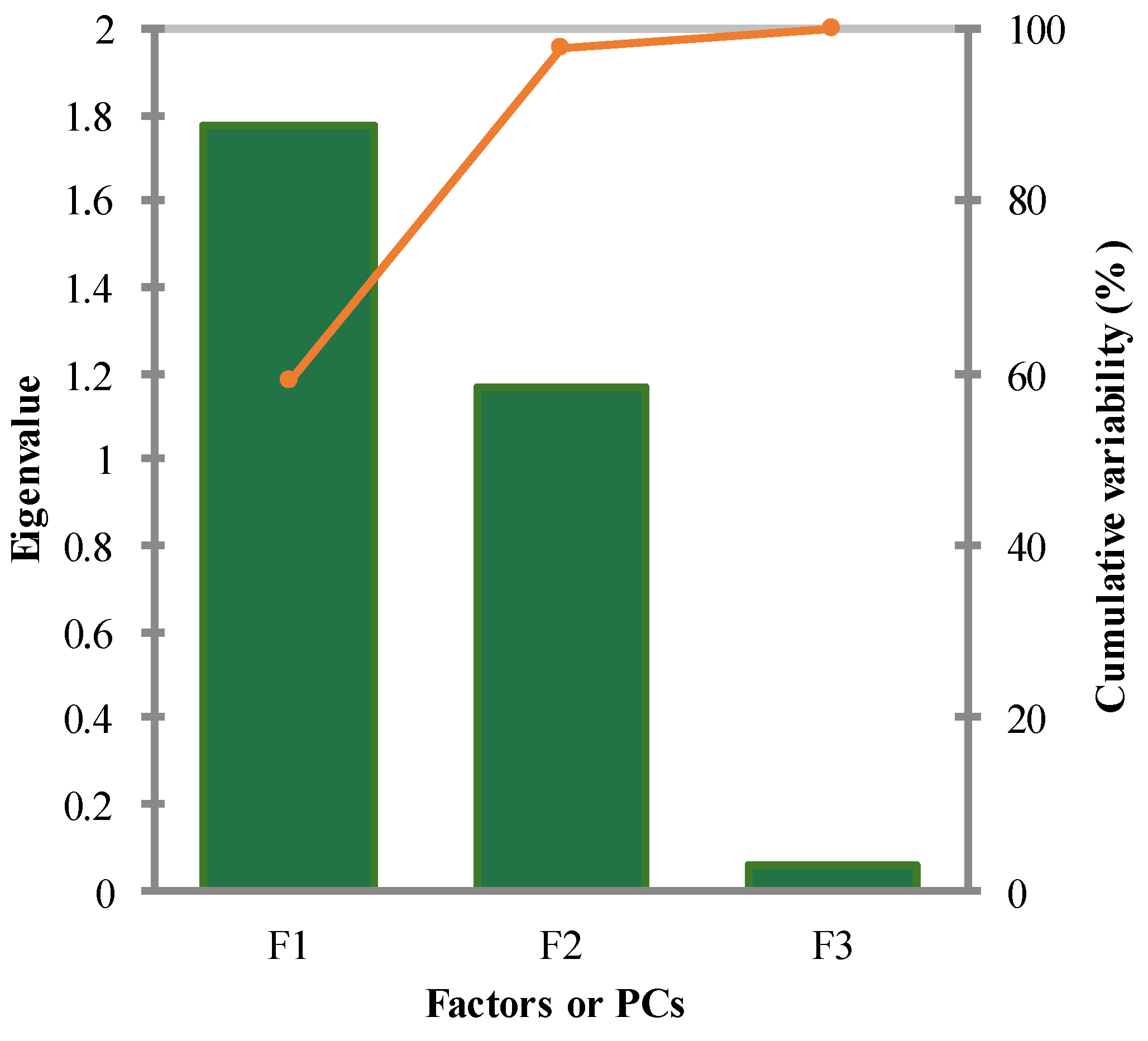
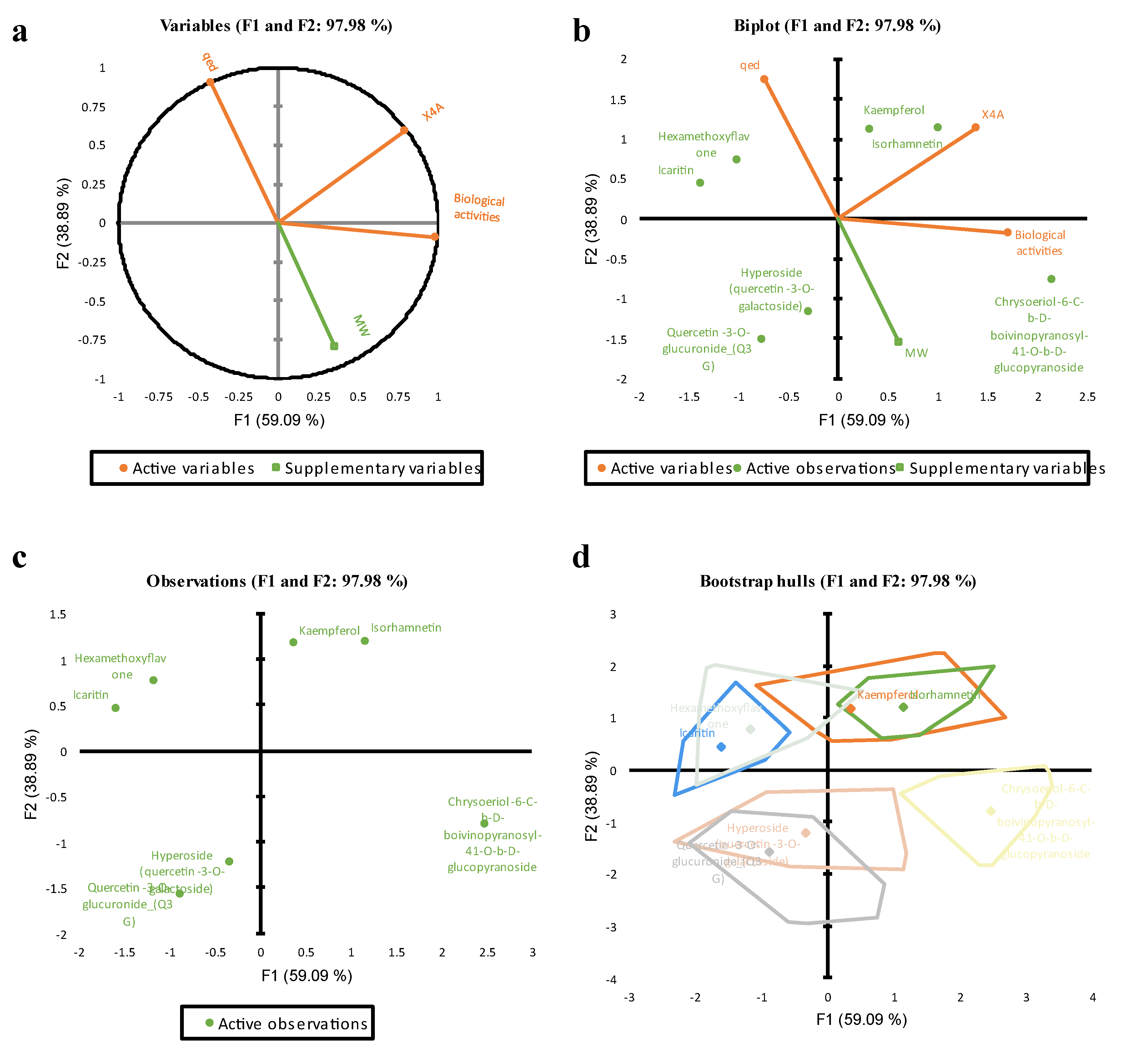
| Nbr. of variables | Variables | MSE | R² | Adjusted R² | Akaike's AIC | Schwarz's SBC | Amemiya's PC |
| 2 | X4A / qed | 102.80 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 67.48 | 69.40 | 0.17 |
| The best model for the selected selection criterion is displayed in blue | |||||||
| Source | DF | Sum of squares | Mean squares | F | Pr > F |
| X4A | 1 | 5610.79 | 5610.79 | 54.58 | < 0.0001 |
| qed | 1 | 3280.34 | 3280.34 | 31.91 | 0.00 |
| Non-flavonoid test set | Flavonoid validation test set | ||||
| Statistic | Training set | Validation set | Statistic | Training set | Validation set |
| Observations | 14.00 | 7.00 | Observations | 14.00 | 7.00 |
| Sum of weights | 14.00 | 7.00 | Sum of weights | 14.00 | 7.00 |
| DF | 11.00 | 4.00 | DF | 11.00 | 4.00 |
| R² | 0.87 | 0.00 | R² | 0.87 | 0.03 |
| Adjusted R² | 0.85 | Adjusted R² | 0.85 | ||
| MSE | 102.80 | 217498.45 | MSE | 102.80 | 13862.97 |
| RMSE | 10.14 | 466.37 | RMSE | 10.14 | 117.74 |
| MAPE | 28.44 | 2971.25 | MAPE | 28.44 | 4965.21 |
| DW | 1.19 | DW | 1.19 | ||
| AIC | 67.48 | AIC | 67.48 | ||
| SBC | 69.40 | SBC | 69.40 | ||
| PC | 0.20 | PC | 0.20 | ||
| Press | 838.87 | Press | 838.87 | ||
| Q² | 0.90 | 0.00 | Q² | 0.90 | 0.00 |
| Validation set | Descriptor | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-value | P-value | Lower Bound | Upper Bound |
| Flavonoid | X4A | 0.82 | 0.03 | 25.93 | < 0.0001 | 0.75 | 0.88 |
| qed | -0.62 | 0.03 | -19.17 | < 0.0001 | -0.70 | -0.55 | |
| Non-flavonoid | X4A | 0.82 | 0.03 | 25.93 | < 0.0001 | 0.75 | 0.88 |
| qed | -0.62 | 0.03 | -19.17 | < 0.0001 | -0.70 | -0.55 |
| Observation | Biological activities | Pred(Biological activities) | Residual | Std. residual | Std. dev. on pred. (Mean) | Adjusted Pred. |
| Kaempferol | 34.96 | 48.75 | -13.79 | -1.36 | 4.22 | 51.64 |
| Isorhamnetin | 63.28 | 46.64 | 16.64 | 1.64 | 4.36 | 42.87 |
| Icaritin | 10.00 | 5.73 | 4.27 | 0.42 | 4.65 | 4.59 |
| Hexamethoxyflavone | 11.37 | 19.13 | -7.76 | -0.77 | 3.83 | 20.42 |
| Chrysoeriol-6-C-b-D-boivinopyranosyl-41-O-b-D-glucopyranoside | 83.26 | 82.51 | 0.75 | 0.07 | 6.11 | 82.08 |
| Hyperoside (quercetin-3-O-galactoside) | 32.30 | 35.47 | -3.17 | -0.31 | 4.13 | 36.10 |
| Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide_(Q3G) | 26.13 | 23.08 | 3.05 | 0.30 | 5.16 | 22.01 |
| Proanthocyanidin | 20.00 | -11.17 | 31.17 | 3.07 | 9.65 | -11.17 |
| Amentoflavone | 90.20 | 26.77 | 63.43 | 6.26 | 5.45 | 26.77 |
| Rosmarinic acid | 30.00 | 249.24 | -219.24 | -21.62 | 27.91 | 249.24 |
| Sakuranetin | 43.69 | 60.05 | -16.36 | -1.61 | 10.03 | 60.05 |
| Oolonghomobisflavan C (OHBF-C) | 4.30 | 35.25 | -30.95 | -3.05 | 6.31 | 35.25 |
| Luteolin 7-O-glucuronide | 55.51 | 72.27 | -16.76 | -1.65 | 4.89 | 72.27 |
| Isovitexin | 0.09 | 29.80 | -29.71 | -2.93 | 3.69 | 29.80 |
| Observation | Biological activities | Pred(Biological activities) | Residual | Std. residual | Std. dev. on pred. (Mean) | Adjusted Pred. |
| Kaempferol | 34.96 | 48.75 | -13.79 | -1.36 | 4.22 | 51.64 |
| Isorhamnetin | 63.28 | 46.64 | 16.64 | 1.64 | 4.36 | 42.87 |
| Icaritin | 10.00 | 5.73 | 4.27 | 0.42 | 4.65 | 4.59 |
| Hexamethoxyflavone | 11.37 | 19.13 | -7.76 | -0.77 | 3.83 | 20.42 |
| Chrysoeriol-6-C-b-D-boivinopyranosyl-41-O-b-D-glucopyranoside | 83.26 | 82.51 | 0.75 | 0.07 | 6.11 | 82.08 |
| Hyperoside (quercetin-3-O-galactoside) | 32.30 | 35.47 | -3.17 | -0.31 | 4.13 | 36.10 |
| Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide_(Q3G) | 26.13 | 23.08 | 3.05 | 0.30 | 5.16 | 22.01 |
| PHAP | 73.50 | 405.98 | -332.48 | -32.79 | 51.55 | 405.98 |
| Nobiletin | 33.90 | 6.23 | 27.67 | 2.73 | 4.59 | 6.23 |
| Linalool | 7.10 | 765.39 | -758.29 | -74.79 | 100.32 | 765.39 |
| Betulinic acid | 50.00 | -213.33 | 263.33 | 25.97 | 33.84 | -213.33 |
| Ursolic acid | 7.10 | -198.67 | 205.77 | 20.29 | 32.05 | -198.67 |
| Taraxasterol | 56.29 | -196.63 | 252.92 | 24.95 | 31.98 | -196.63 |
| Solamargine | 1.57 | -88.09 | 89.66 | 8.84 | 19.57 | -88.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





