Submitted:
26 March 2024
Posted:
27 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Attacks
- DoS HTTP Unbearable Load King (HULK): It serves as a web server DDoS tool that primarily intended for research purposes, aiding penetration testers in assessing server efficiency. Security specialists use HULK to identify vulnerabilities in their security measures against DDoS attacks and address them proactively, mitigating potential exploits by malicious actors. The tool generates multiple distinctive requests at irregular intervals from the same host, executing a DDoS attack and attempting to thwart the network’s defense mechanisms by avoiding predictable attack patterns [17].
- DoS GoldenEye: GoldenEye, akin to an HTTP flood, constitutes a DDoS attack strategically crafted to inundate web servers’ resources. It achieves this by incessantly soliciting single or multiple URLs from numerous source-attacking machines. GoldenEye introduces dynamic alterations to the generated requests, employing randomization of user agents, referrers, and nearly all pertinent parameters. To prolong the connection, GoldenEye incorporates a URL suffix, facilitating request bypass through several Content Delivery Network (CDN) systems, commonly known as No Cache. As the server reaches its limits of concurrent connections, legitimate requests from other users become unresponsive [18].
2.2. Intrusion Detection Systems
2.3. Feature Selection
- Information Gain: It is one of the most used feature selection techniques for resizing datasets for anomaly detection. This technique consists of, through entropy calculation, ranking the attributes by assigning a “weight” to them, ranging from 0 to 1, depending on the degree of relevance of the attributes. This attribute selection technique is based on[6] filters. Entropy is used to infer the distribution of the characteristics of the features analyzed. Right after calculating the entropy, the gain formula is applied to obtain the weights of features.
- OneR: It is a simple attribute classification algorithm [21]. It consists of creating a rule for each attribute in the training data and selecting the attributes with the lowest error. It treats all numerically valued attributes as continuous and uses a direct method to divide the set’s range of values into several disjoint ranges. This is one of the most primitive techniques and produces simple rules based on just one resource [22].
- PCA: Principal component analysis (PCA) is a standard technique for most modern data analysis because it is a simple, non-parametric method for extracting relevant information from disorganized data sets. Simply and effectively, it can show how to resize the data set to improve processing. PCA generates new features using the existing features in a dataset, looking for the features that have underlays and are relevant at the same time [23].
- Symmetrical Uncert: Symmetric uncertainty is a commonly used technique in attribute selection to resize data sets in anomaly detection. This technique is based on the calculation of entropy and the ranking of attributes, assigning weights that vary from 0 to 1 according to their relevance. After calculating the entropy, we apply the gain formula to obtain the weights of the features, indicating their importance. [24].
- Correlation Attribute: The Attribute Correlation technique is used to measure the statistical relationship between pairs of attributes in a data set. It calculates the correlation between attributes to determine whether they are linearly related and to what degree. The correlation coefficient is a measure that varies from -1 to 1, indicating the direction sign (positive or negative) and strength (magnitude) of the relationship between attributes. This technique can be applied to identify highly correlated attributes, which may indicate redundancy or overlapping information. By removing or combining highly correlated attributes, we can reduce the dimensionality of the dataset and improve the efficiency of AD algorithms [25]. This technique has its objectives well defined during its execution, which are the extraction of the most relevant information in a dataset, the reduction of the size of the data set, preserving only the important data for detecting attacks, and finally carrying out a data simplification.
3. Literature Review
3.1. Method of Selection
3.2. Discussion and Open Issues
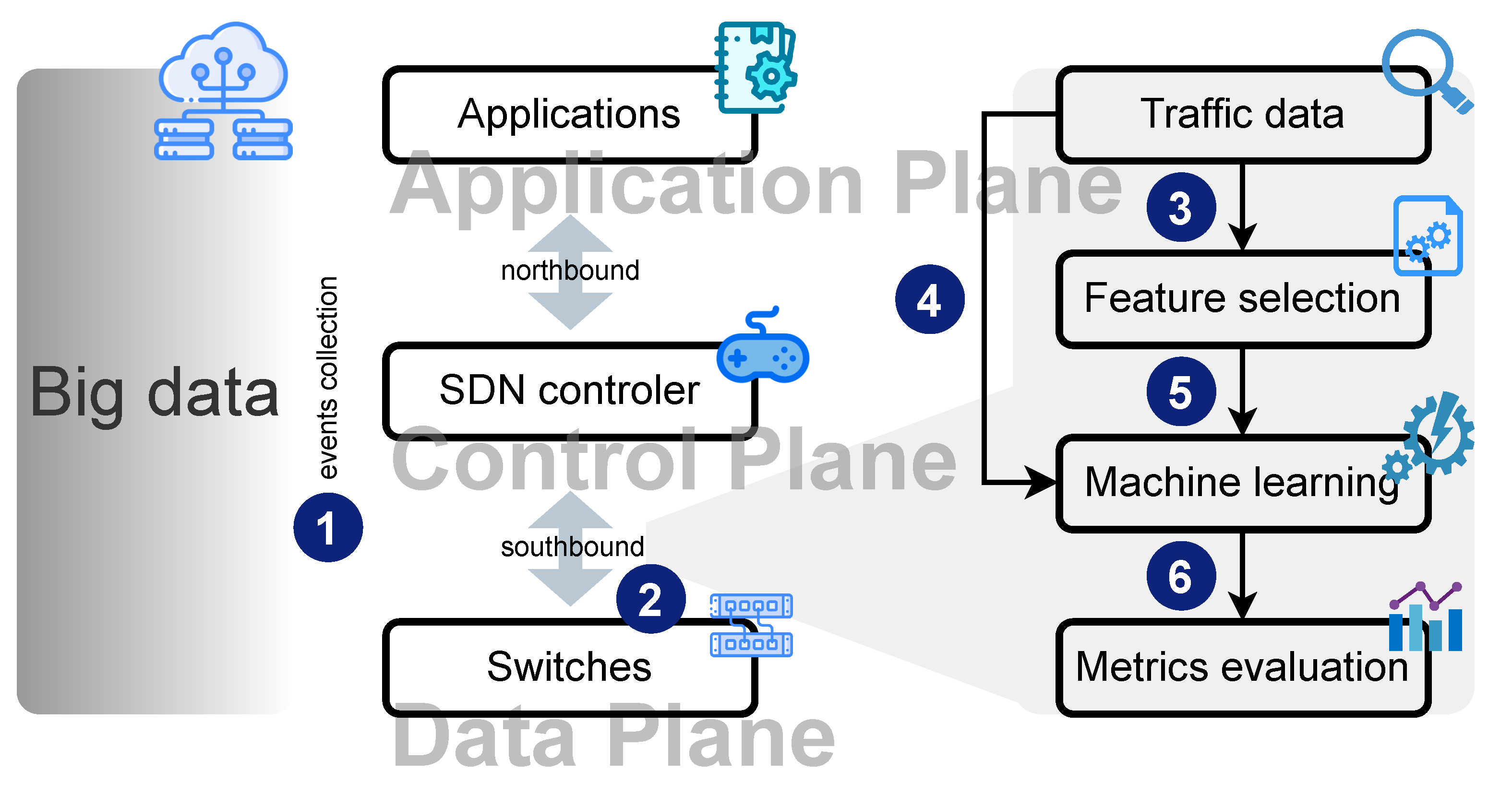
4. Assessment Methodology
4.1. Assessment Model
4.2. Dataset and Sets of Features Analyzed
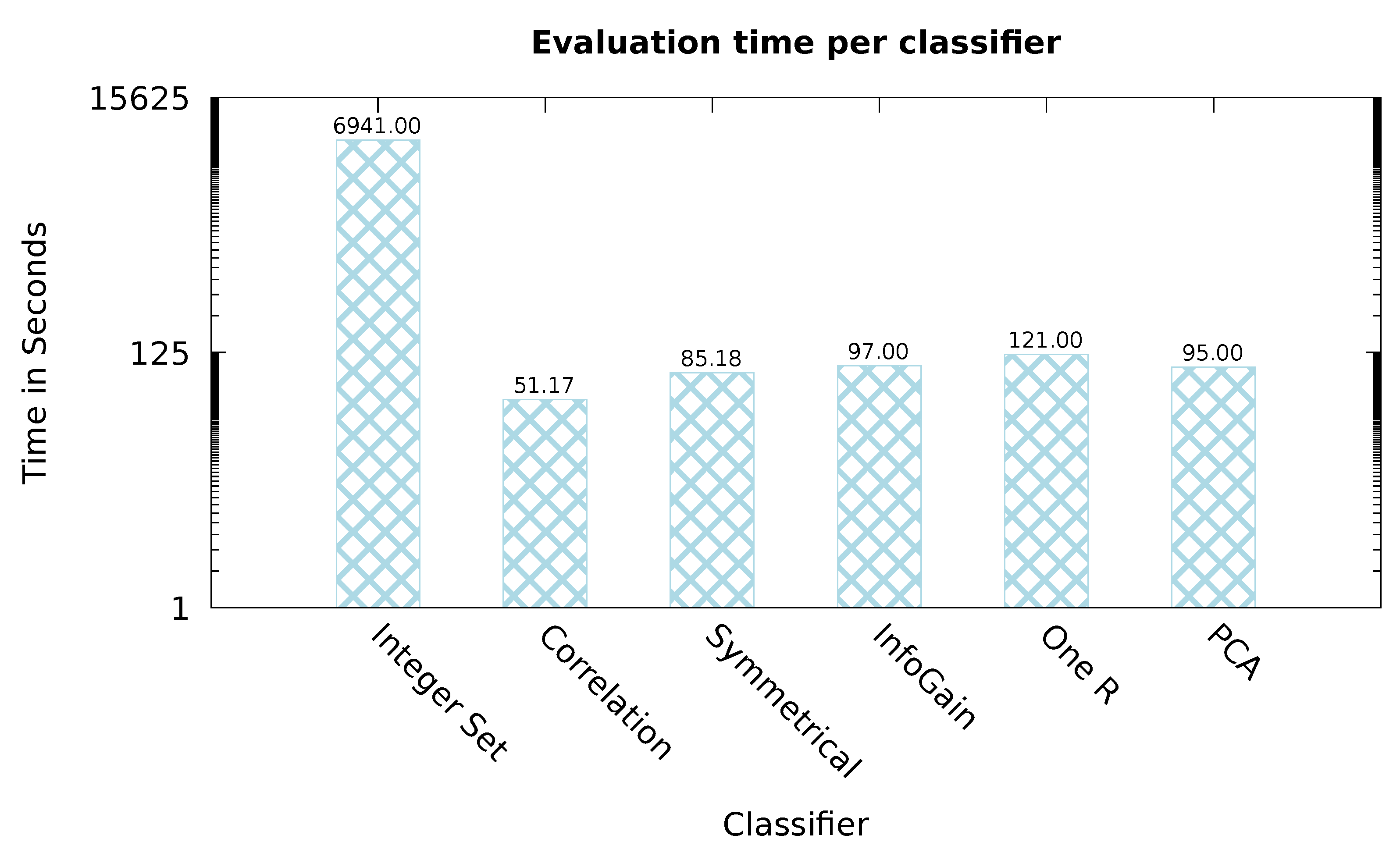
5. Performance Assessment
5.1. Evaluation of the Entire Dataset
5.2. Evaluation Using Feature Selection
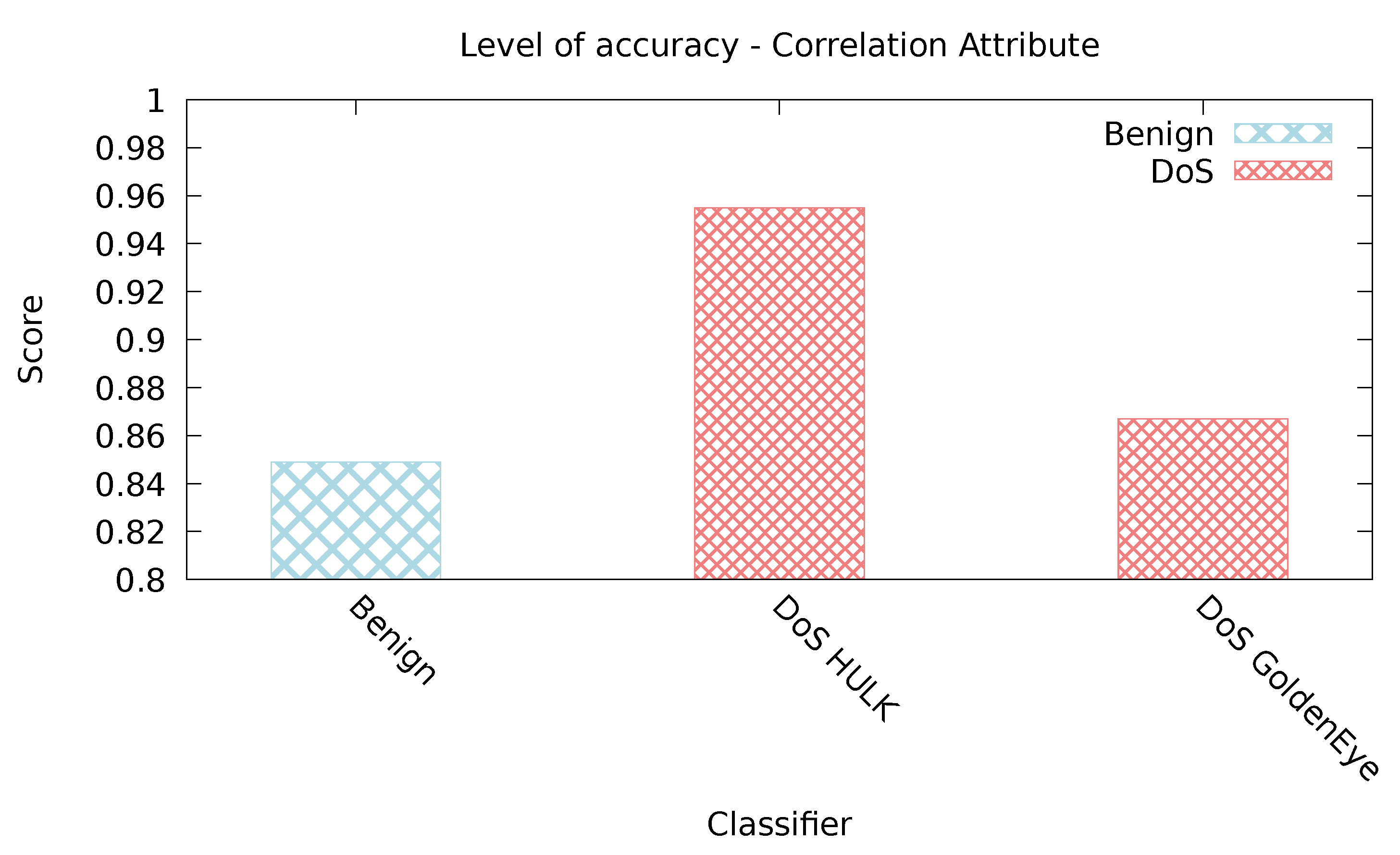
5.2.1. Correlation Attribute
5.2.2. Symmetrical Uncert
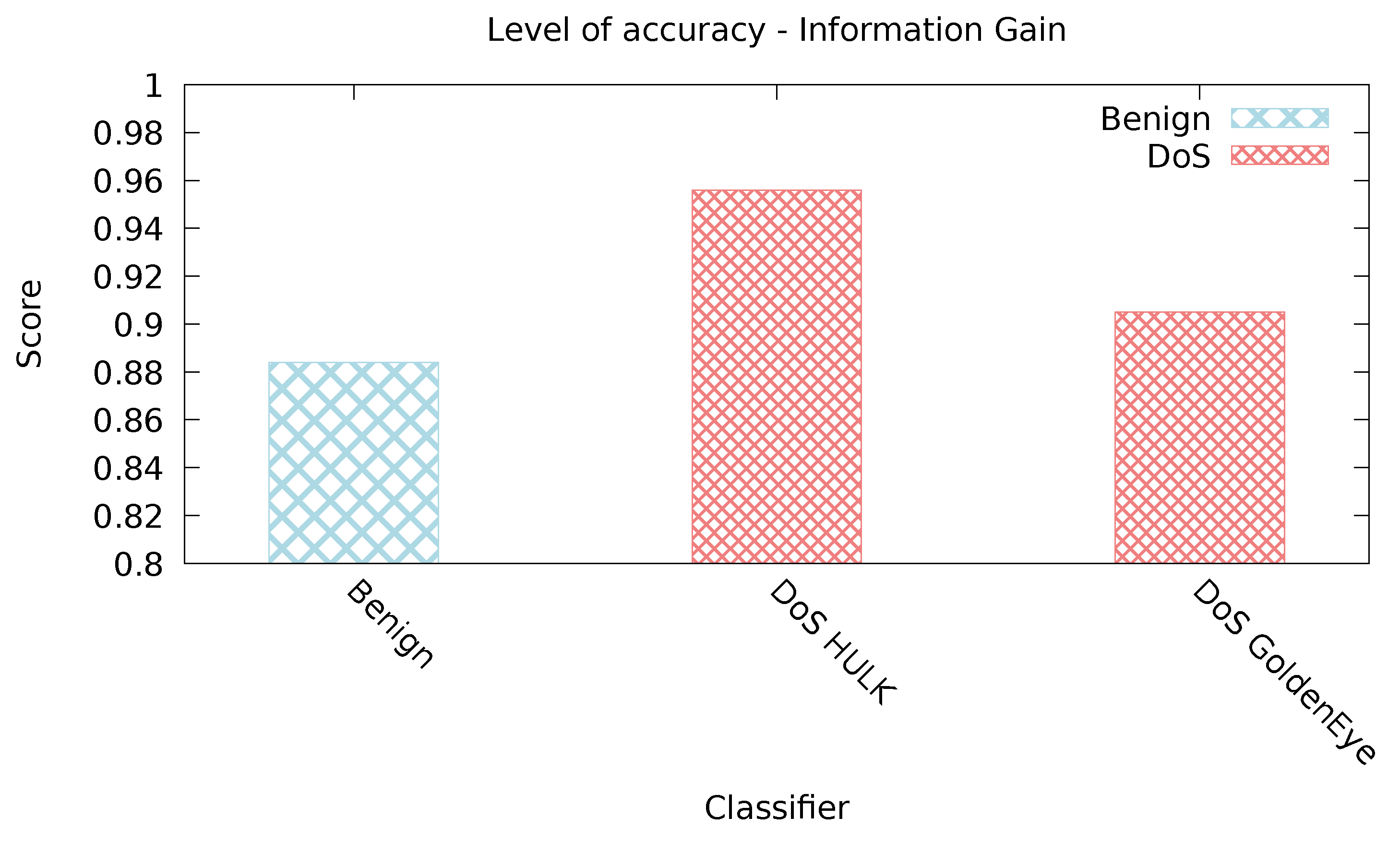
5.2.3. InfoGain Classifier
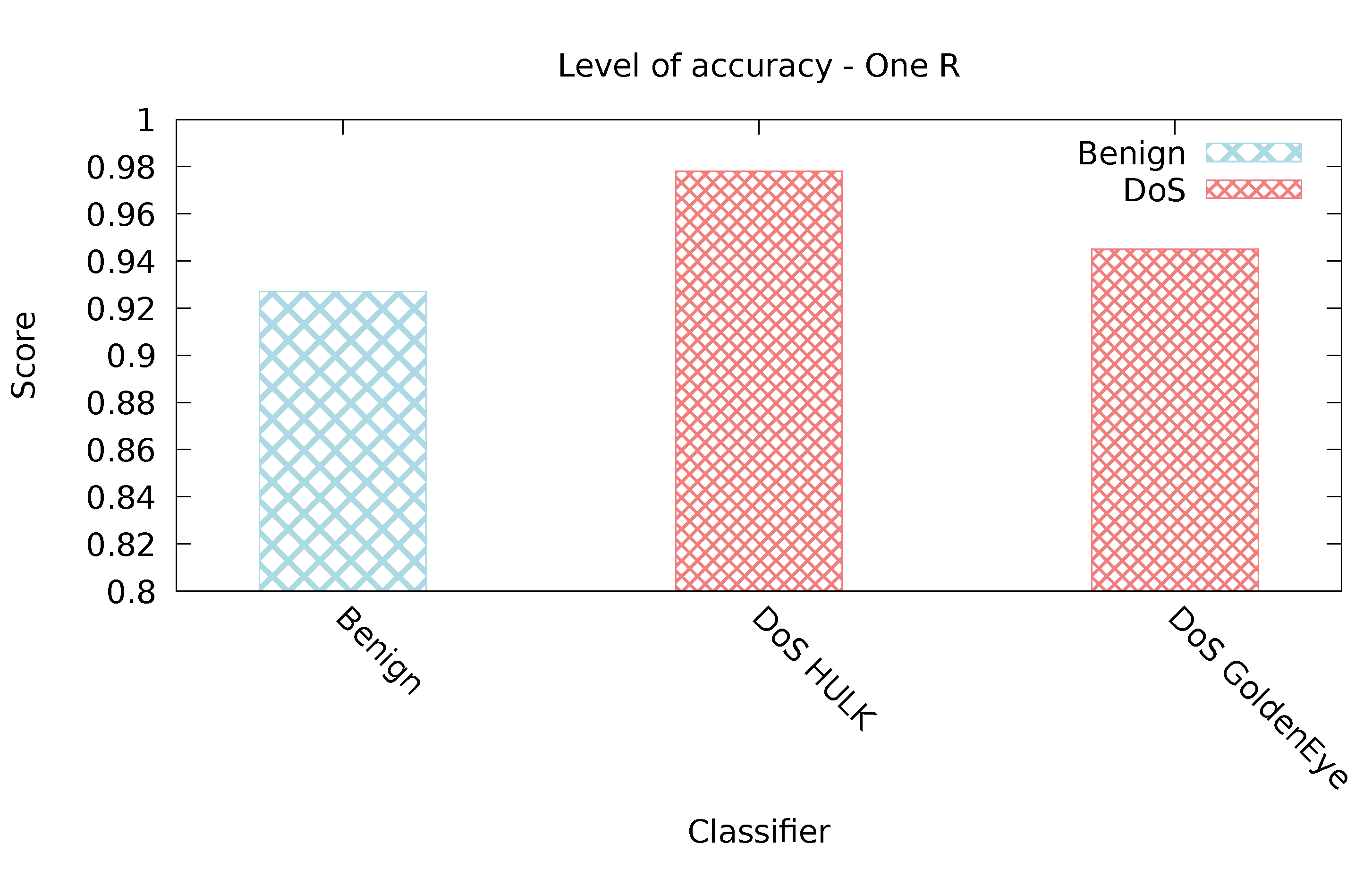
5.2.4. OneR Classifier
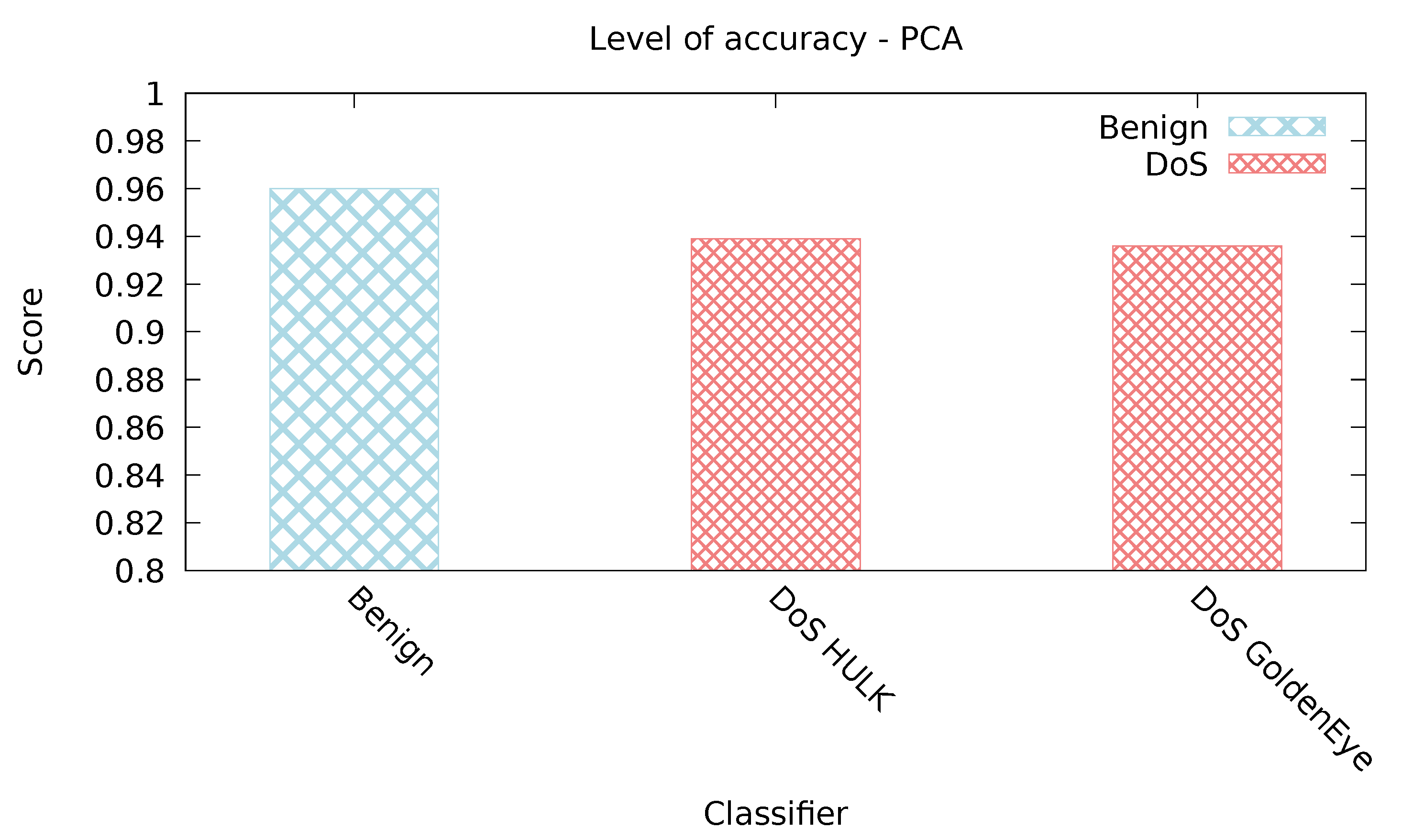
5.2.5. PCA Classifier
5.3. Discussion of Results
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- do Prado, P.F.; Peixoto, M.L.M.; Araújo, M.C.; Gama, E.S.; Gonçalves, D.M.; Silva, M.V.S.; Immich, R.; Madeira, E.R.M.; Bittencourt, L.F., Mobile Edge Computing for Content Distribution and Mobility Support in Smart Cities. In Mobile Edge Computing; Mukherjee, A.; De, D.; Ghosh, S.K.; Buyya, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 473–500. [CrossRef]
- Akabane, A.T.; Immich, R.; Pazzi, R.W.; Madeira, E.R.M.; Villas, L.A. Exploiting Vehicular Social Networks and Dynamic Clustering to Enhance Urban Mobility Management. Sensors 2019, 19, 3558. [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.L.; Wickboldt, J.A.; Lunardi, R.C.; Dalmazo, B.L.; Granville, L.Z.; Gaspary, L.P.; Bartolini, C.; Hickey, M. A solution for identifying the root cause of problems in IT change management. 12th IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM 2011) and Workshops, 2011, pp. 586–593. [CrossRef]
- Shenfield, A.; Day, D.; Ayesh, A. Intelligent intrusion detection systems using artificial neural networks. ICT Express 2018, 4, 95–99.
- Jose, S.; Malathi, D.; Reddy, B.; Jayaseeli, D. A survey on anomaly based host intrusion detection system. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 2018, 1000, 012049.
- Stiawan, D.; Idris, M.Y.B.; Bamhdi, A.M.; Budiarto, R.; others. CICIDS-2017 dataset feature analysis with information gain for anomaly detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132911–132921.
- Elsayed, M.; Le-Khac, N.A.; Azer, M.; Jurcut, A. A Flow Based Anomaly Detection Approach with Feature Selection Method Against DDoS Attacks in SDNs. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking 2022, PP, 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Neto, E.P.; Silva, F.S.D.; Schneider, L.M.; Neto, A.V.; Immich, R. Seamless MANO of multi-vendor SDN controllers across federated multi-domains. Computer Networks 2021, 186, 107752. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.; Neto, E.; Immich, R.; Fontes, R.; Neto, A.; Rodriguez, F.; Rothenberg, C.E. dh-aes-p4: On-premise encryption and in-band key-exchange in P4 fully programmable data planes. 2021 IEEE Conference on Network Function Virtualization and Software Defined Networks (NFV-SDN), 2021, pp. 148–153. [CrossRef]
- Dalmazo, B.L.; Marques, J.A.; Costa, L.R.; Bonfim, M.S.; Carvalho, R.N.; da Silva, A.S.; Fernandes, S.; Bordim, J.L.; Alchieri, E.; Schaeffer-Filho, A.; others. A systematic review on distributed denial of service attack defense mechanisms in programmable networks. International Journal of Network Management 2021, 31, e2163.
- Illy, P.; Kaddoum, G.; Kaur, K.; Garg, S. ML-based IDPS Enhancement With Complementary Features For Home IoT networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management 2022, PP, 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Paxson, V. An analysis of using reflectors for distributed denial-of-service attacks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review 2001, 31, 38–47.
- Sharafaldin, I.; Lashkari, A.H.; Ghorbani, A.A. Toward generating a new intrusion detection dataset and intrusion traffic characterization. ICISSp 2018, 1, 108–116.
- Torres, G.; Liu, C. Can data-only exploits be detected at runtime using hardware events? A case study of the Heartbleed vulnerability. In Proceedings of the Hardware and Architectural Support for Security and Privacy 2016; ACM, New York, NY, United States, 2016; pp. 1–7.
- Basnet, R.B.; Shash, R.; Johnson, C.; Walgren, L.; Doleck, T. Towards Detecting and Classifying Network Intrusion Traffic Using Deep Learning Frameworks. J. Internet Serv. Inf. Secur. 2019, 9, 1–17.
- Alieyan, K.; ALmomani, A.; Manasrah, A.; Kadhum, M.M. A survey of botnet detection based on DNS. Neural Computing and Applications 2017, 28, 1541–1558.
- Mahjabin, S. Implementation of DoS and DDoS attacks on cloud servers. Periodicals of Engineering and Natural Sciences (PEN) 2018, 6, 148–158.
- Charlier, J.; Singh, A.; Ormazabal, G.; State, R.; Schulzrinne, H. SynGAN: Towards generating synthetic network attacks using GANs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.09899 2019.
- Kumar, V.; Sangwan, O.P. Signature based intrusion detection system using SNORT. International Journal of Computer Applications & Information Technology 2012, 1, 35–41.
- Dalmazo, B.L.; Vilela, J.P.; Curado, M. Triple-Similarity Mechanism for alarm management in the cloud. Computers & Security 2018, 78, 33–42. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, G.; Singh, R. Optimization of sentiment analysis using machine learning classifiers. Human-centric Computing and information Sciences 2017, 7, 1–12.
- NOVAKOVIĆ, J.; STRBAC, P.; BULATOVIĆ, D. TOWARD OPTIMAL FEATURE SELECTION USING RANKING METHODS AND CLASSIFICATION ALGORITHMS. Yugoslav Journal of Operations Research 2011, 21, 119–135.
- Gupta, V.; Mittal, M. KNN and PCA classifier with autoregressive modelling during different ECG signal interpretation. Procedia Computer Science 2018, 125, 18–24.
- al kaaf, H.; Ali, A.; Shamsuddin, S.; Hassan, S. Feature selection for malicious android applications using Symmetrical Uncert Attribute Eval method. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2020, 884, 012060. [CrossRef]
- Gnanambal, S.; Thangaraj, M.; Meenatchi, V.; Gayathri, V. Classification algorithms with attribute selection: an evaluation study using WEKA. International Journal of Advanced Networking and Applications 2018, 9, 3640–3644.
- Zainudin, A.; Akter, R.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.M. Towards Lightweight Intrusion Identification in SDN-based Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems. 2022 27th Asia Pacific Conference on Communications (APCC), 2022, pp. 610–614. [CrossRef]
- AlMasri, T.; Snober, M.A.; Al-Haija, Q.A. IDPS-SDN-ML: An Intrusion Detection and Prevention System Using Software-Defined Networks and Machine Learning. 2022 1st International Conference on Smart Technology, Applied Informatics, and Engineering (APICS), 2022, pp. 133–137. [CrossRef]
- Sampath, N.; Jerlin, M.; Krithika, L.; Anitha, A. Intrusion Detection in Software Defined Networking using Genetic Algorithm. 2020 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Information Technology and Engineering (ic-ETITE), 2020, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Acharya, I.; Papalkar, D.; Joseph, M. Top-Performing Unifying Architecture for Network Intrusion Detection in SDN Using Fully Convolutional Network. 2023 5th International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), 2023, pp. 1340–1344. [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, D.; Amanowicz, M. A study on flow features selection for malicious activities detection in software defined networks. 2018 International Conference on Military Communications and Information Systems (ICMCIS), 2018, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Janabi, A.H.; Kanakis, T.; Johnson, M. Overhead Reduction Technique for Software-Defined Network Based Intrusion Detection Systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66481–66491. [CrossRef]
- Friha, O.; Ferrag, M.A.; Shu, L.; Maglaras, L.; Choo, K.K.; Nafaa, M. FELIDS: Federated Learning-based Intrusion Detection System for Agricultural Internet of Things. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 2022, 165. [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Rahman, M.M. Flow Based Anomaly Detection in Software Defined Networking: A Deep Learning Approach With Feature Selection Method. 2018, pp. 630–635. [CrossRef]
- Matsa, L.S.; Zodi-Lusilao, P.G.A.; Bhunu-Shava, P.F. Forward Feature Selection for DDoS Detection on Cross-Plane of Software Defined Network Using Hybrid Deep Learning. 2021 3rd International Multidisciplinary Information Technology and Engineering Conference (IMITEC), 2021, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Abou El Houda, Z.; Khoukhi, L. A Hierarchical Fog Computing Framework for Network Attack Detection in SDN. ICC 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2022, pp. 4366–4371. [CrossRef]
- Scaranti, G.F.; Carvalho, L.F.; Barbon, S.; Proença, M.L. Artificial Immune Systems and Fuzzy Logic to Detect Flooding Attacks in Software-Defined Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100172–100184. [CrossRef]
- El Houda, Z.A.; Brik, B.; Khoukhi, L. Ensemble Learning for Intrusion Detection in SDN-Based Zero Touch Smart Grid Systems. 2022 IEEE 47th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), 2022, pp. 149–156. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Sarac, K. Mitigating Evasion Attacks on Machine Learning based NIDS Systems in SDN. 2021 IEEE 7th International Conference on Network Softwarization (NetSoft), 2021, pp. 268–272. [CrossRef]
- El Houda, Z.A.; Hafid, A.S.; Khoukhi, L. A Novel Machine Learning Framework for Advanced Attack Detection using SDN. 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2021, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Mbasuva, U.; Zodi, G.A.L. Designing Ensemble Deep Learning Intrusion Detection System for DDoS attacks in Software Defined Networks. 2022 16th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication (IMCOM), 2022, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, D.; Munadi, R.; Purwanto, Y. DDoS Attack Detection in Software Defined Network using Ensemble K-means++ and Random Forest. 2020 3rd International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), 2020, pp. 164–169. [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, G.; Primya, T.; Subashini, G.; Senthilkumar, V.; Gomathi, S. Hybrid Intrusion Detector using Deep Learning Technique. 2021 International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), 2021, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Amarudin.; Ferdiana, R.; Widyawan. New Approach of Ensemble Method to Improve Performance of IDS using S-SDN Classifier. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communication, Networks and Satellite (COMNETSAT), 2022, pp. 463–468. [CrossRef]
- Abdulqadder, I.H.; Zou, D.; Aziz, I.T.; Yuan, B. Enhanced Attack Aware Security Provisioning Scheme in SDN/NFV Enabled over 5G Network. 2018 27th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (ICCCN), 2018, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Suresh, G.M.; Madhavu, M.L. AI Based Intrusion Detection System Using Self-Adaptive Energy Efficient BAT Algorithm for Software Defined IoT Networks. 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), 2020, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, S.; Metia, R.; Girija, P.; Baranitharan, K.; Indirani, M.; R, M. Detection of DDoS Attacks using Artificial Gorilla Troops Optimizer based Deep Learning Model. 2023 Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Energy (ICAIS), 2023, pp. 385–391. [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.Y.; Cho, S. Explaining Deep Learning-Based Traffic Classification Using a Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 4738–4751. [CrossRef]
| 1 | CIC Dataset download: http://205.174.165.80/CICDataset/CIC-IDS-2017/
|
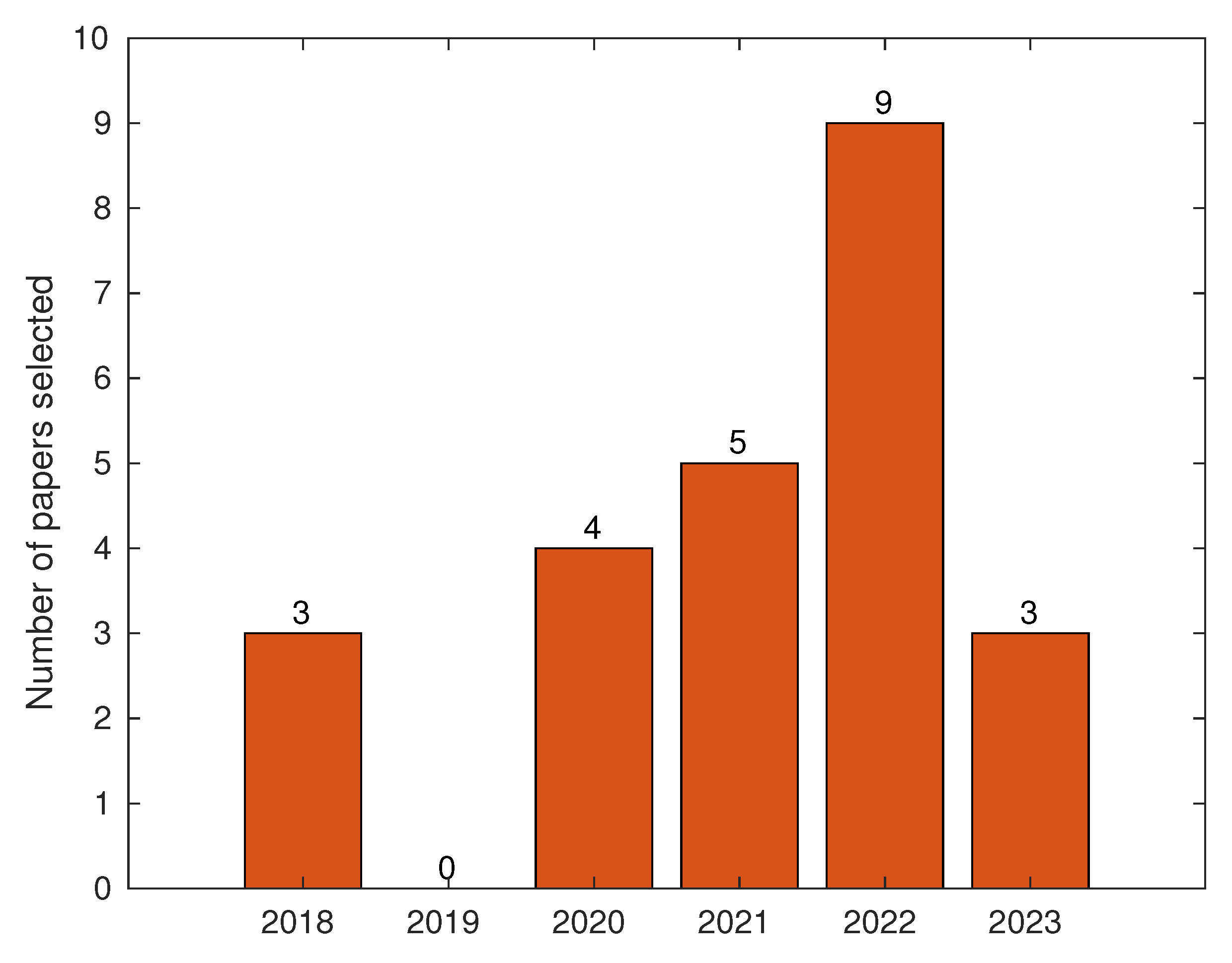

| Inclusion Criteria | |
|---|---|
| IC | Published as a full paper in a conference, magazine or journal. |
| Exclusion Criteria | |
| EC | The paper was not published between 2018 and 2023. |
| Results | Total |
|---|---|
| IEEE Xplore Search | 31 |
| Excluded by EC | 5 |
| Not satisfied IC | 1 |
| Selected papers | 24 |
| File name | Traffic type | numbers of occurrences |
|---|---|---|
| Monday- | ||
| WorkingHours.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 529,918 |
| Tuesday- | ||
| WorkingHours.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 432,074 |
| SSH-Patator | 5.897 | |
| FTP-Patator | 7,938 | |
| Wednesday- | ||
| WorkingHours.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 440,031 |
| DoS Hulk | 231,073 | |
| DoS GoldenEye | 10,293 | |
| DoS Slowloris | 5,796 | |
| DoS Slowhttptest | 5,499 | |
| Heatbleed | 11 | |
| Thursday-WorkingHours-Morning- | ||
| WebAtacks.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 168,186 |
| Web Attack-Brute Force | 1,507 | |
| Web Attack-Sql Injection | 21 | |
| Web Attack-XSS | 652 | |
| Thursday-WorkingHours- | ||
| Afternoon- | ||
| Infiltration.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 288,566 |
| Infiltration | 36 | |
| Friday-WorkingHours- | ||
| Morning.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 189,067 |
| Bot | 1,966 | |
| Friday-WorkingHours-Afternoon- | ||
| PortScan.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 127,537 |
| PortScan | 158,930 | |
| Friday-WorkingHours-Afternoon | ||
| -DDos.pcap_ISCX.csv | Benign | 97,718 |
| DDos | 128,07 | |
| Total de Registros | 2,830,743 |
| Attack name | TP | FP |
|---|---|---|
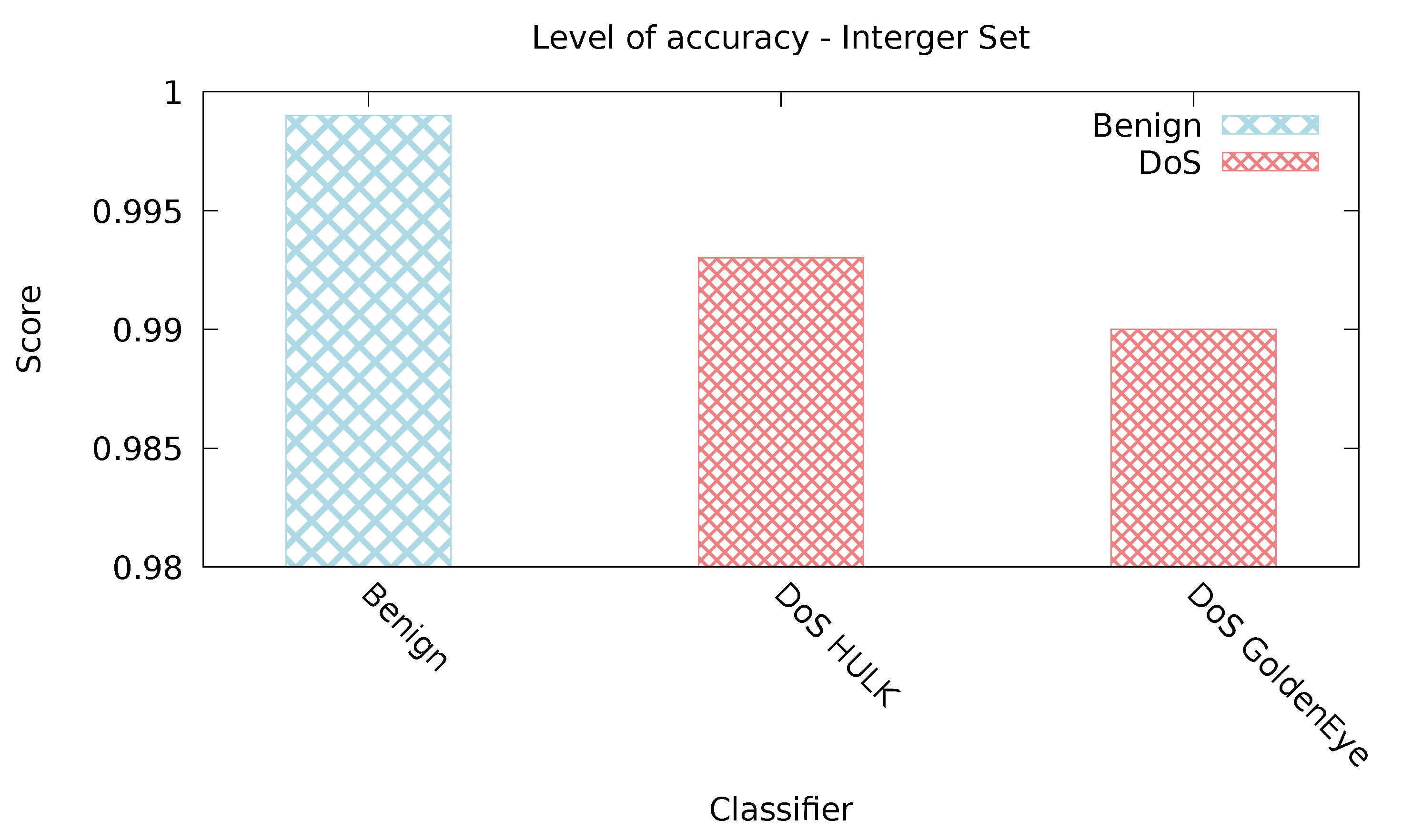
| Benign | 0.996 | 0.002 |
| Dos Hulk | 0.999 | 0.004 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 0.988 | 0 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 131626 | 501 | 25 |
| DoS Hulk | 47 | 69056 | 0 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 35 | 2 | 3103 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 306107 | 1783 | 408 |
| DoS Hulk | 53238 | 108217 | 31 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 1070 | 3273 | 2851 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 301481 | 6804 | 13 |
| DoS Hulk | 457 | 160507 | 522 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 2002 | 3908 | 1284 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 129673 | 2215 | 207 |
| DoS Hulk | 13581 | 55307 | 4 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 619 | 286 | 2223 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 130842 | 1106 | 97 |
| DoS Hulk | 8703 | 60329 | 0 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 297 | 179 | 2635 |
| Class | Benign | DoS Hulk | DoS GoldenEye |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 12957 | 2654 | 69 |
| DoS Hulk | 3382 | 65713 | 0 |
| DoS GoldenEye | 558 | 1574 | 1008 |
| Method | Benign | Dos Hulk | DoS GoldenEye | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | FP | TP | FP | TP | FP | |
| Correlation Attribute | 0.993 | 0.322 | 0.670 | 0.016 | 0.396 | 0.001 |
| Symmetrical Uncert | 0.978 | 0.015 | 0.994 | 0.034 | 0.178 | 0.001 |
| Info Gain | 0.981 | 0.225 | 0.8 | 0.018 | 0.699 | 0.001 |
| One R | 0.99 | 0.137 | 0.873 | 0.01 | 0.839 | 0.001 |
| PCA | 0.978 | 0.071 | 0.951 | 0.951 | 0.321 | 0 |
Short Biography of Authors
 |
Iuri A. Mundstock is a master’s student in the Graduate Program in Computing (PPGComp) at the Federal University of Rio Grande (FURG). He received a bachelor’s degree in Computer Engineering in 2024 from the Federal University of Rio Grande, Brazil. His primary interests are focused on security and feature extraction methods. |
 |
Yuri Santo is a Ph.D. student in Graduate Program in Computer Science (PPGCC) at the Federal University of Para, Brazil. Yuri received a Master’s degree in Computer Science in 2023 from the Federal University of Para, Brazil. His main research interests include Internet of Things, Federated Learning models, Open Radio Access Network, and data security and privacy. |
 |
Thiago L. T. Silveira holds a D.Sc. degree in Computer Science (2019) from the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS), Porto Alegre, Brazil, and a M.Sc. degree in Computer Science (2016), and B.Sc. degrees in Information Systems (2015) and Computer Science (2013) from the Federal University of Santa Maria (UFSM), Santa Maria, Brazil. Thiago is currently an Assistant Professor at UFRGS. His interests are computer vision, pattern recognition, and signal processing. |
 |
Roger Immich is a Professor at the Digital Metropolis Institute (IMD) of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte (UFRN). He earned his Ph.D. in Informatics Engineering from the University of Coimbra, Portugal (2017). He was a visiting researcher at the University of California at Los Angeles, United States (UCLA) in 2016/2017, a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute of Computing of the University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in 2018/2019, and a Visiting Professor of University of Málaga (UMA), Spain, in 2021. His research interests encompass various areas, including Smart Cities, IoT, 5G, Quality of Experience, as well as Cloud and Fog computing. |
 |
Andre Riker is a computer scientist who holds a bachelor’s and master’s degree in computer science. He received his Ph.D. degree in information science and technology from the University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, in 2019. He is currently Assistant Professor with the Computer Science Faculty, Federal University of Pará, Brazil. His main research interests include Internet of Things, optimization models, federated learning models, and data security and privacy. |
 |
Bruno L. Dalmazo received his Ph.D. degree in Information Science and Technology from the University of Coimbra in 2018. He completed his Master’s degree in Computer Science in 2011 at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Bruno also received a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science in 2008 from the Federal University of Santa Maria, Brazil. Currently, he holds the position of Associate Professor at the Center for Computational Sciences of the Federal University of Rio Grande - FURG, working both in undergraduate and graduate programs. His primary research interests involve network traffic prediction, as well as security and privacy in software-defined network environments. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





