Submitted:
26 March 2024
Posted:
26 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
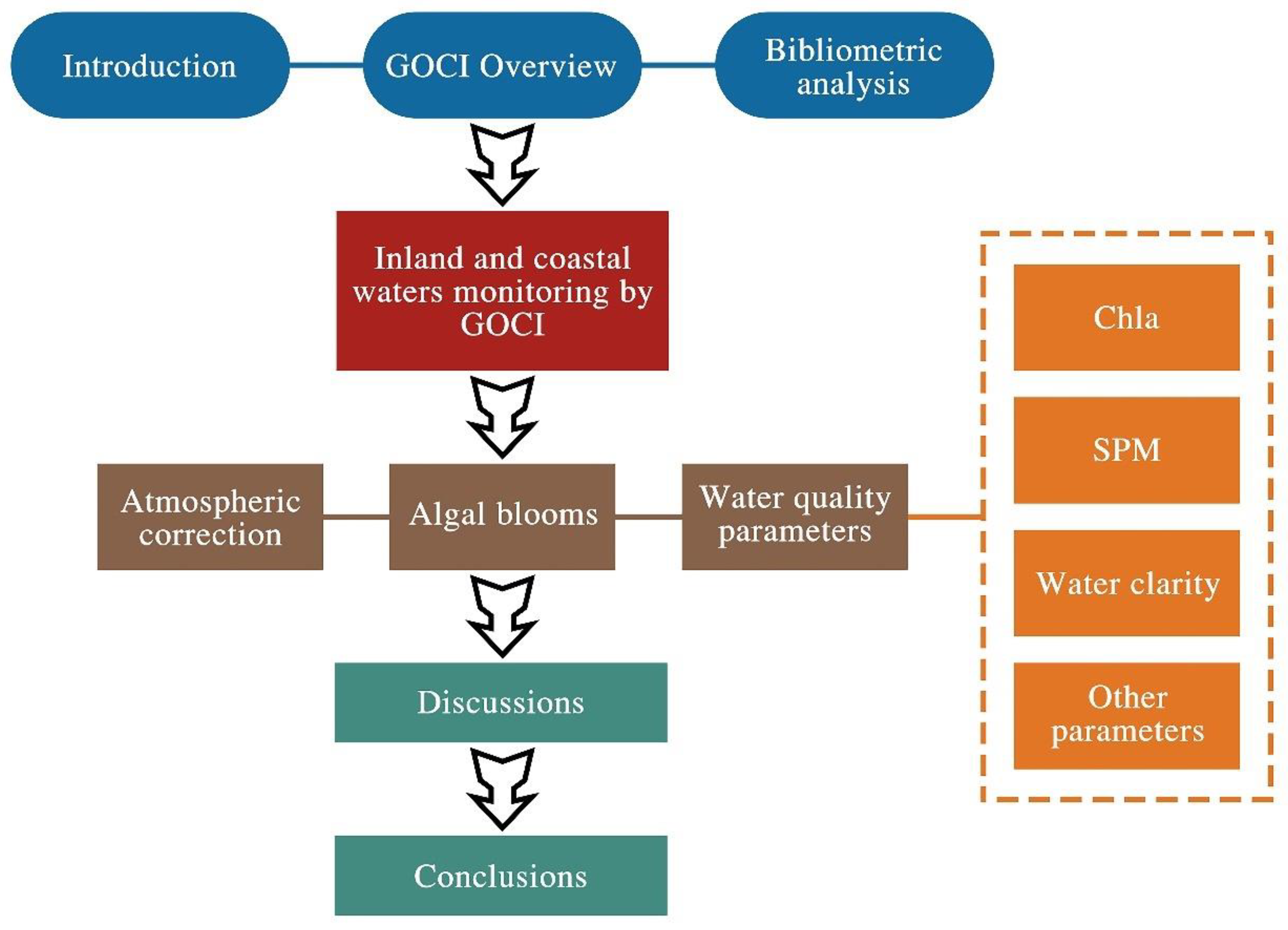
1. Introduction
2. GOCI Overview
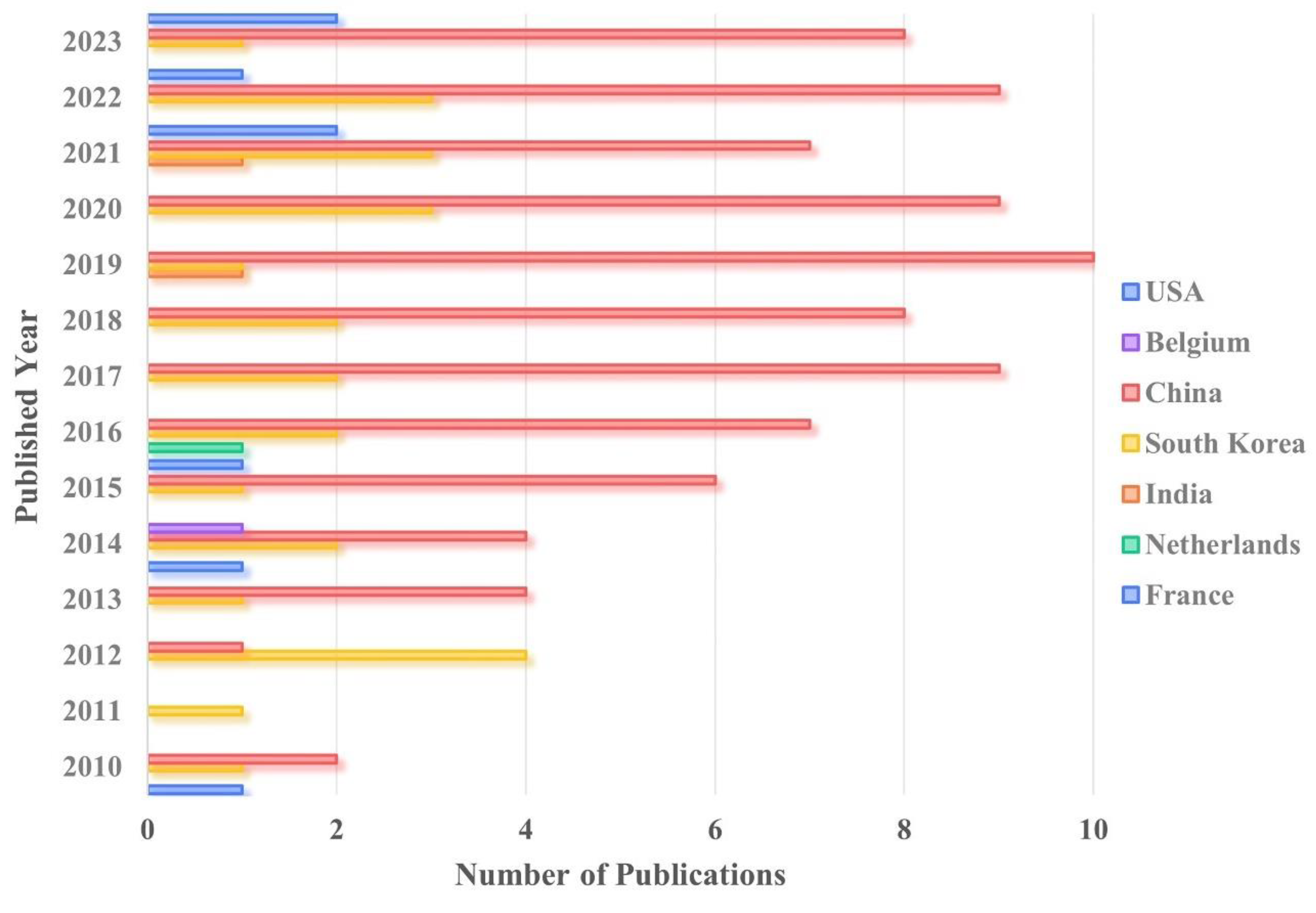
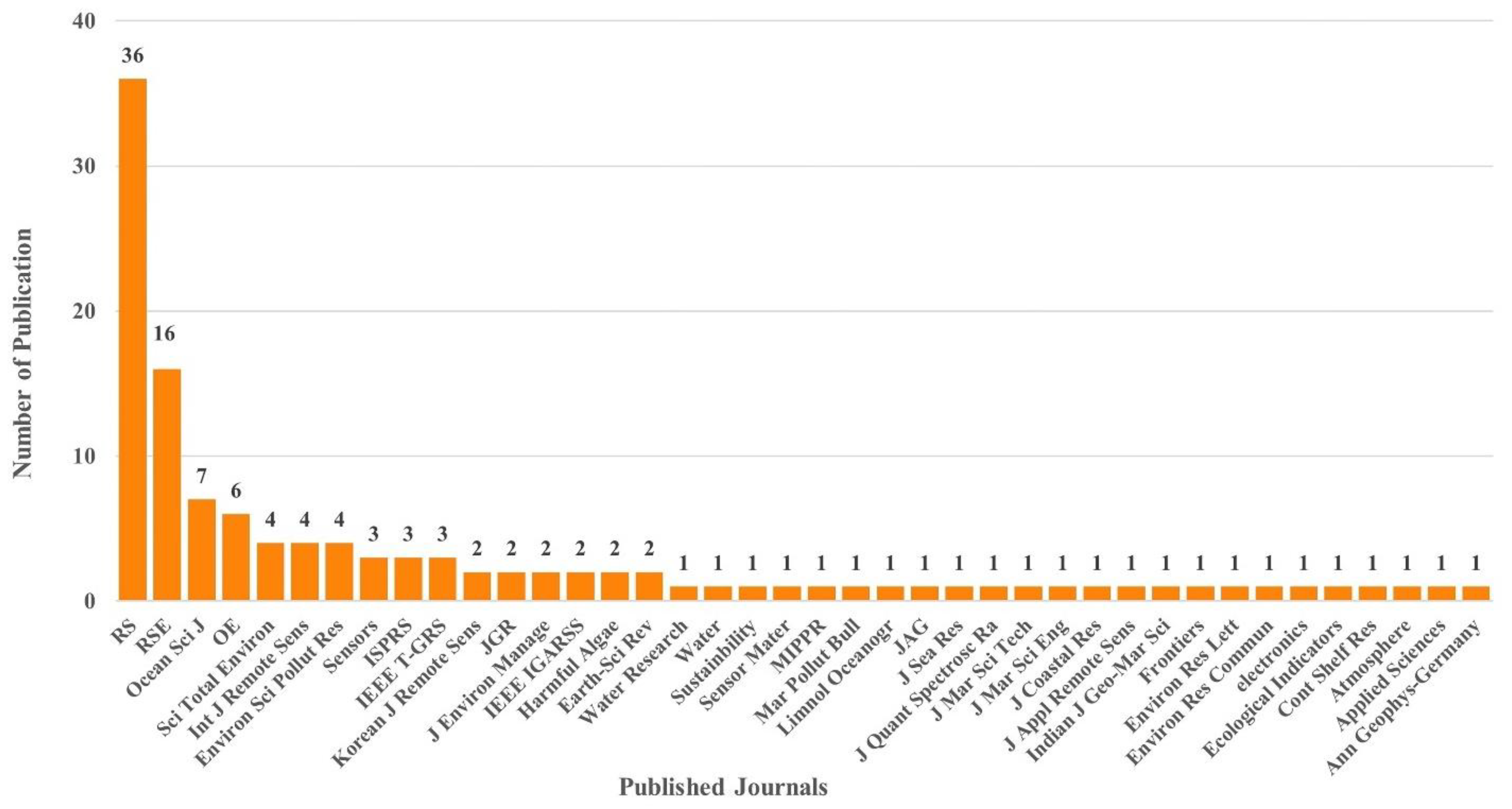
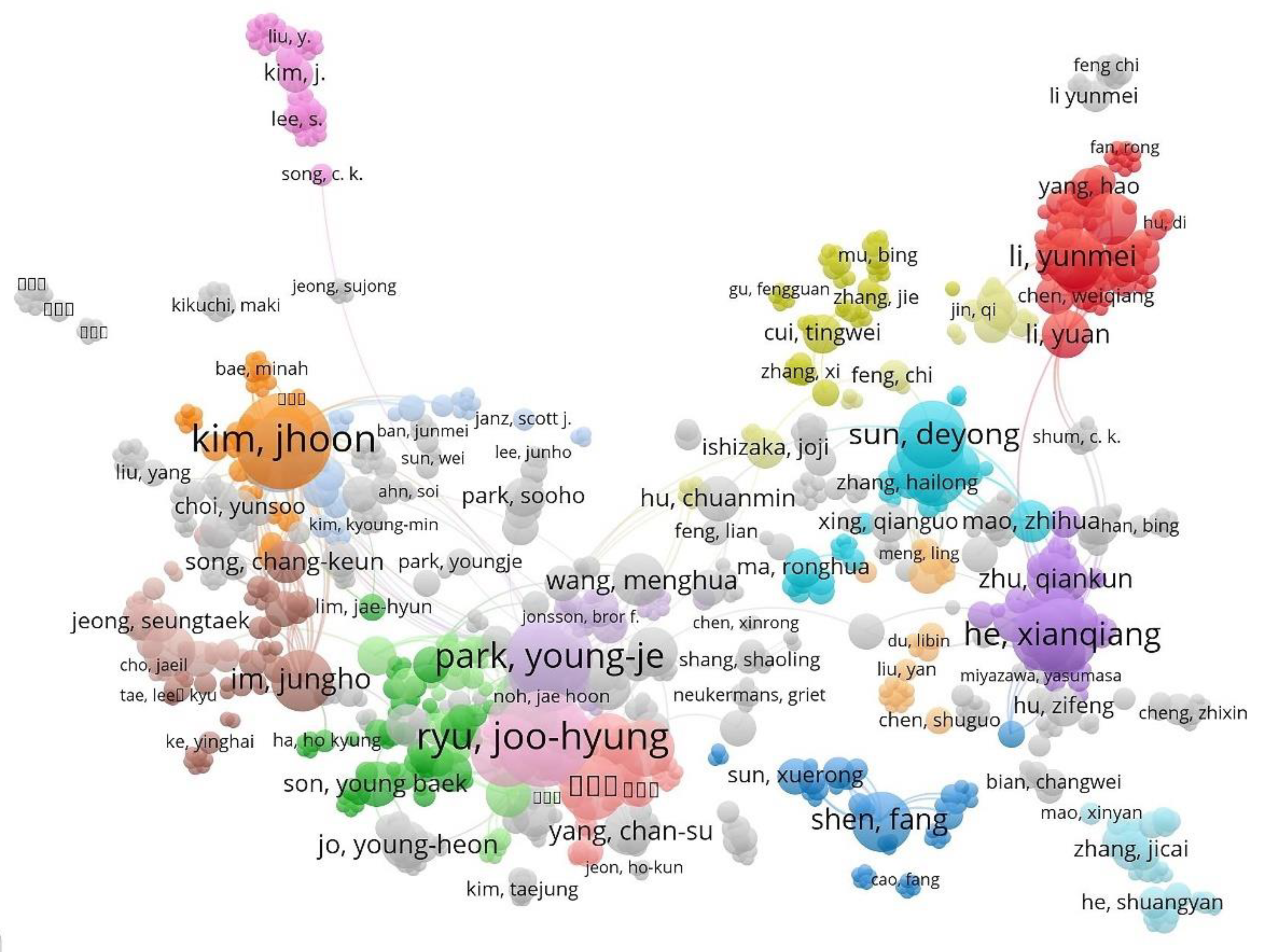
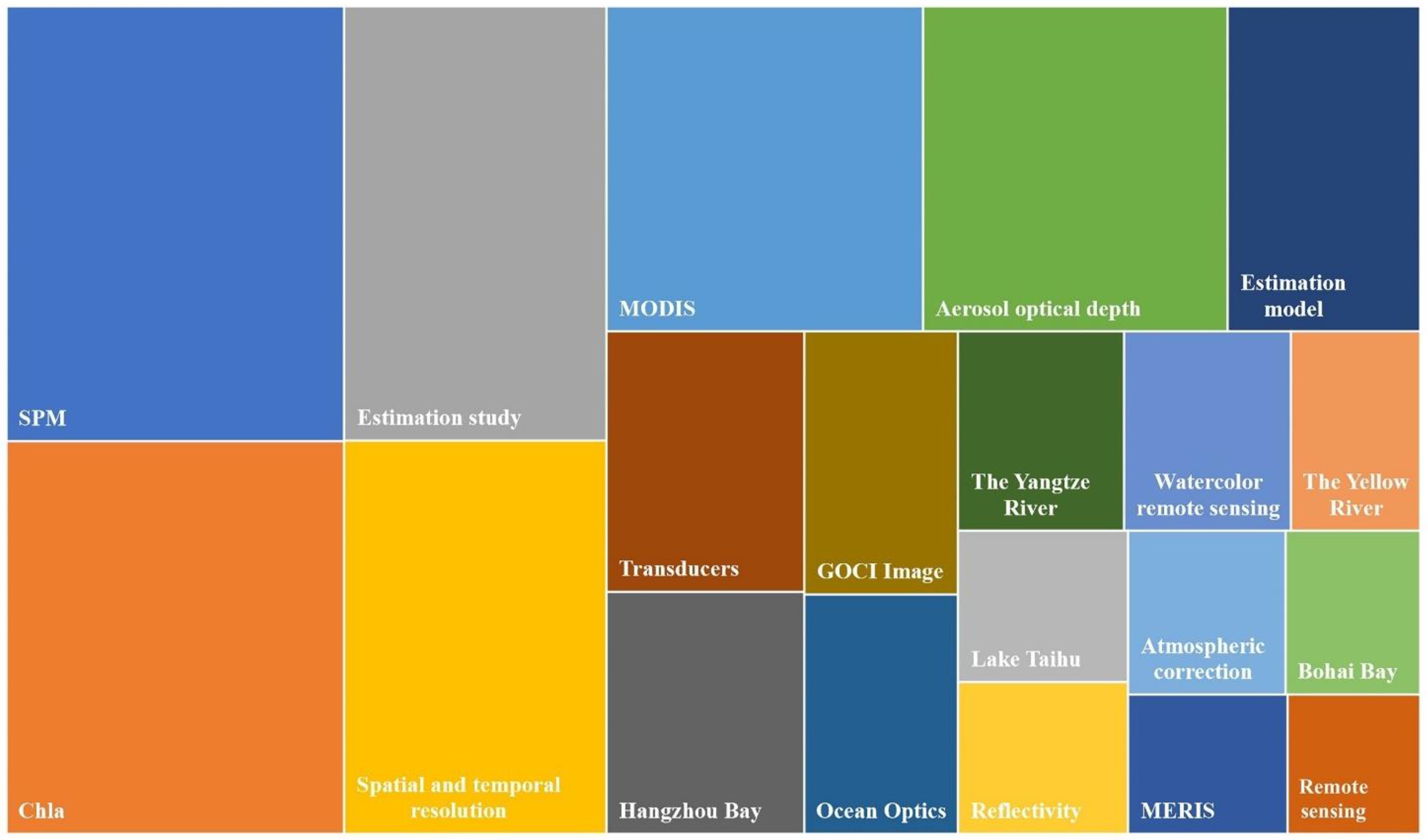
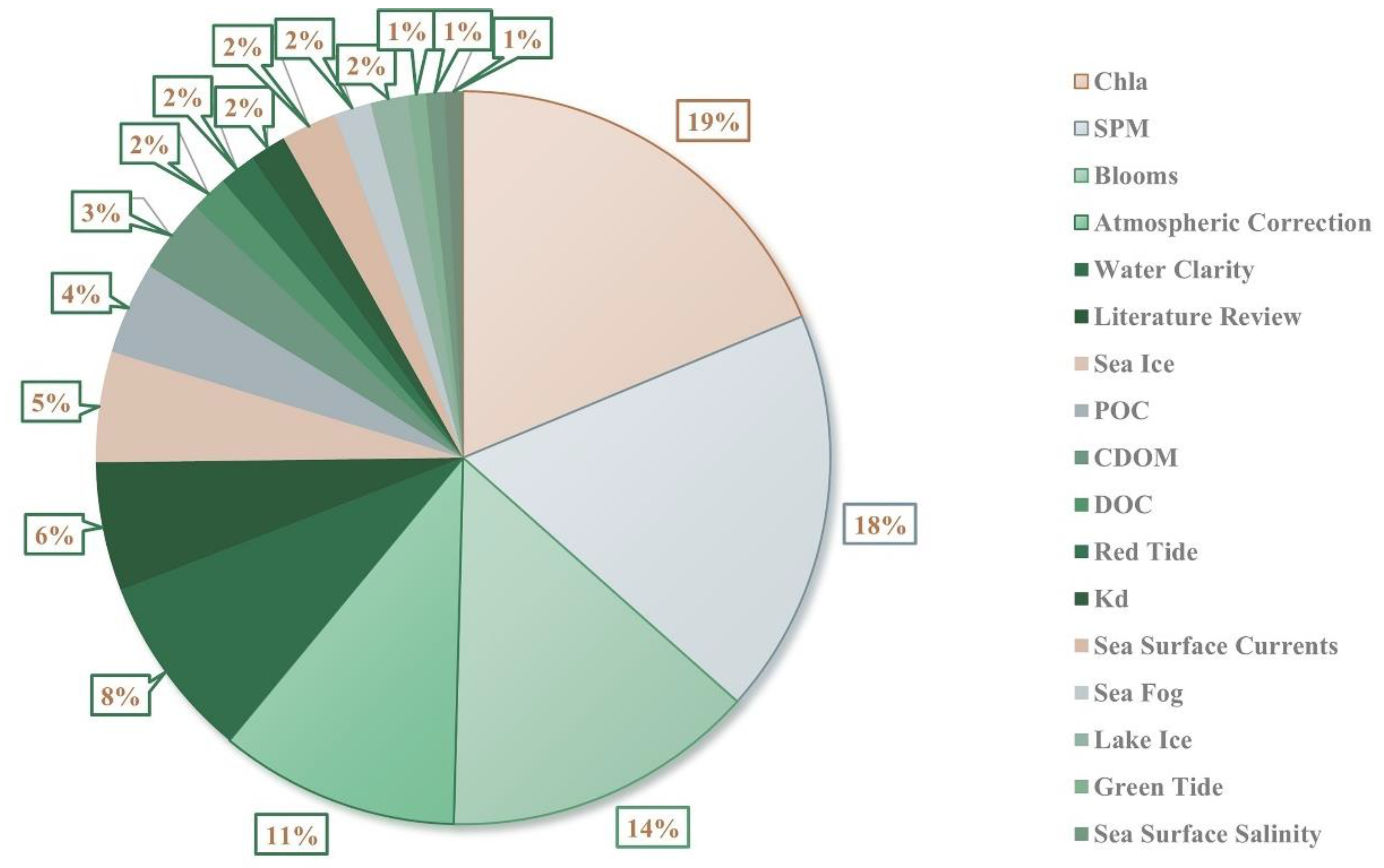
3. Bibliometric Analysis
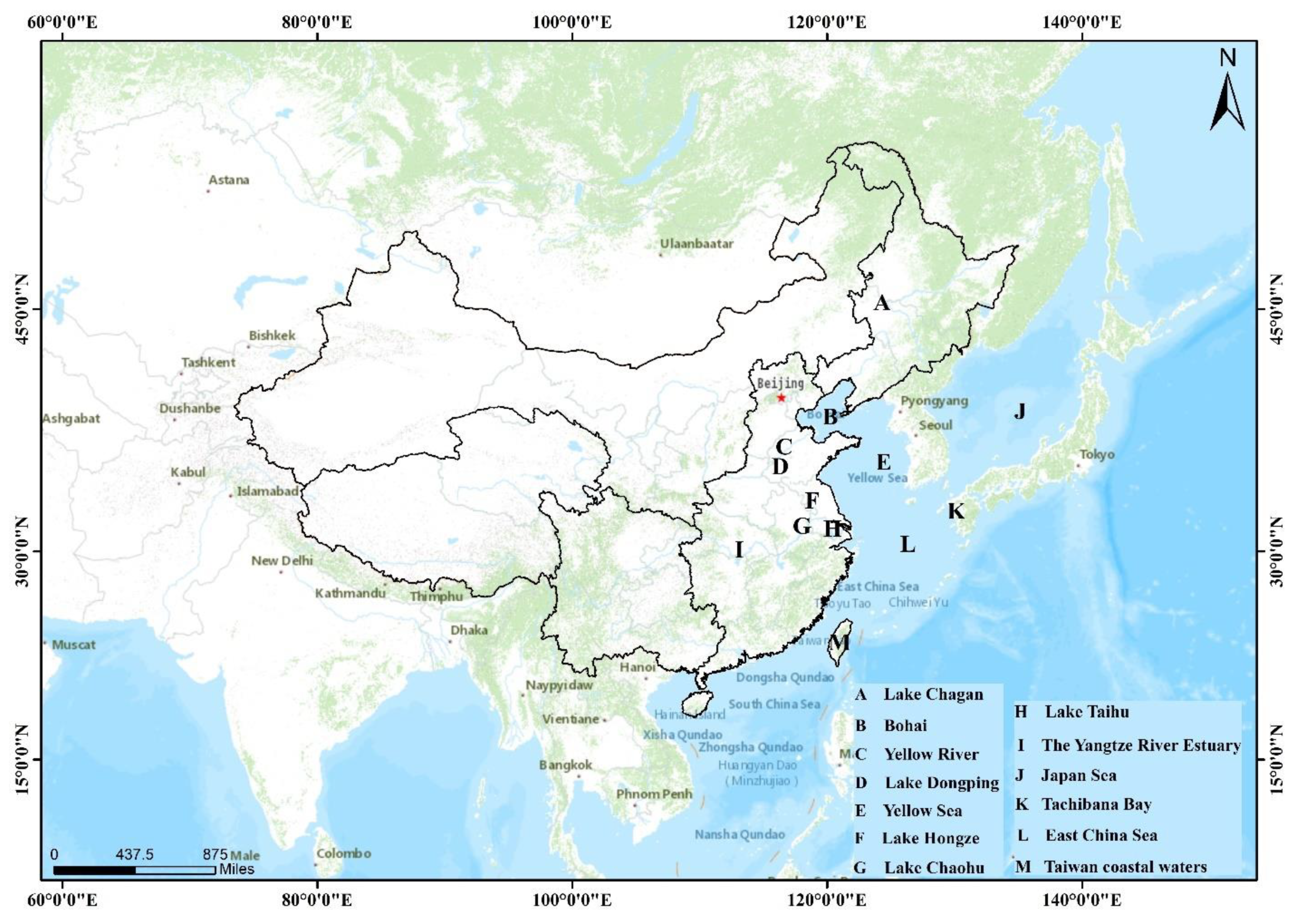
4. Inland and Coastal Waters Monitoring by GOCI
4.1. Atmospheric Correction over Inland and Coastal Waters
4.2. Algal Blooms
4.3. Water Quality Parameters
4.3.1. Chla
4.3.2. SPM
4.3.3. Water Clarity
4.3.4. Other Parameters
5. Discussions
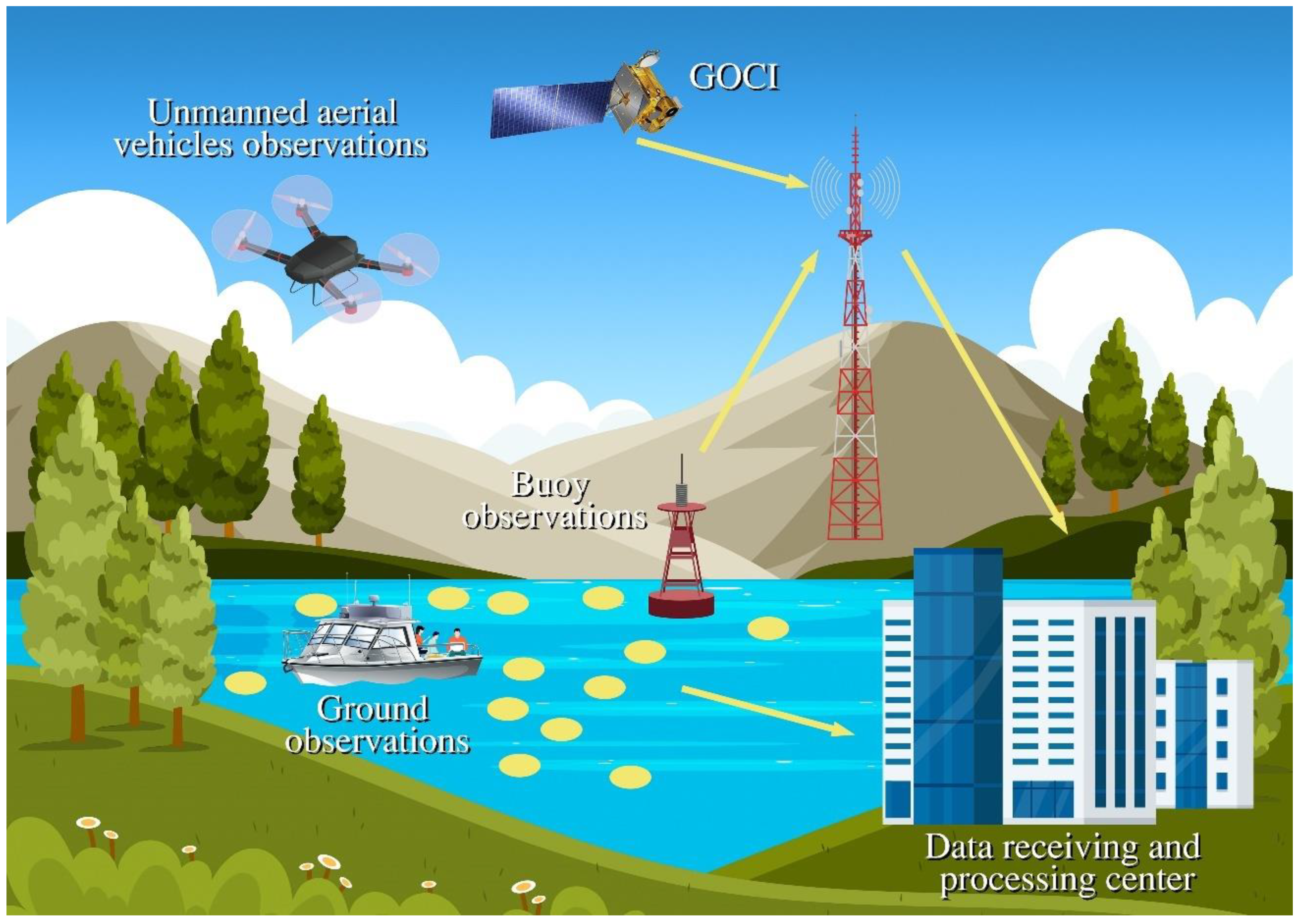
5.1. Integrating Geostationary Ocean Color Satellites, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, and Ground Collaborative Observation
5.2. Fusion of Geostationary Ocean Color Satellites with Other Satellite Products
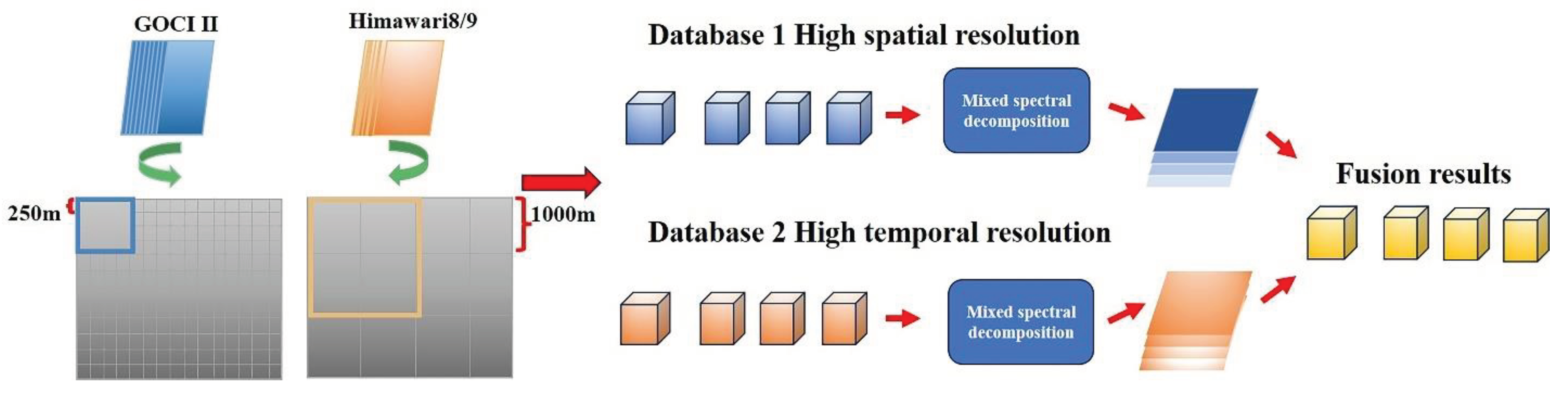
5.3. Improving Spectral, Spatial, and Temporal Resolution of Geostationary Ocean Color Sensors
5.3.1. Improving Spectral Resolution
5.3.2. Improving Spatial Resolution
5.3.3. Improving Temporal Resolution
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Author Contribution
Data Availability Statement
Conflict of interest
References
- Schofield, O.; Arnone, R.A.; Bissett, W.P.; Dickey, T.D.; Davis, C.O.; Finkel, Z.; Oliver, M.; Moline, M.A. Watercolors in the coastal zone: What can we see? 2004.
- Shi, J.; Shen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Field Radiometric Calibration of a Micro-Spectrometer Based on Remote Sensing of Plateau Inland Water Colors. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color 1. Limnology and oceanography 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Morel, A.Y. Remote assessment of ocean color for interpretation of satellite visible imagery: A review. 2012.
- Sathyendranath, S. Reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group. IOCCG Project Office, Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, IOCCG Rep 2000, 3, 140. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, T.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J. Retrieval of atmospheric and oceanic properties from MERIS measurements: A new Case-2 water processor for BEAM. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2007, 28, 5627–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyryliuk, D.; Kratzer, S. Evaluation of Sentinel-3A OLCI products derived using the Case-2 Regional CoastColour processor over the Baltic Sea. Sensors 2019, 19, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F.; Li, H.; Li, J. High-frequency and tidal period observations of suspended particulate matter in coastal waters by AHI/Himawari-8. Opt Express 2020, 28, 27387–27404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Bi, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, F.; Lyu, H.; Dong, X.; Cai, X. Utilization of GOCI data to evaluate the diurnal vertical migration of Microcystis aeruginosa and the underlying driving factors. J Environ Manage 2022, 310, 114734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouw, C.B.; Greb, S.; Aurin, D.; DiGiacomo, P.M.; Lee, Z.; Twardowski, M.; Binding, C.; Hu, C.; Ma, R.; Moore, T.; et al. Aquatic color radiometry remote sensing of coastal and inland waters: Challenges and recommendations for future satellite missions. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 160, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Nam, W.H. A systematic review and quantitative meta-analysis of the relationships between driving forces and cyanobacterial blooms at global scale. Environ Res 2023, 216, 114670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Song, C.; Cao, Z.; Xue, K.; Lu, S.; Chen, T.; Liu, K. Monitoring inland water via Sentinel satellite constellation: A review and perspective. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2023, 204, 340–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovis, W.A.; Clark, D.; Anderson, F.; Austin, R.; Wilson, W.; Baker, E.; Ball, D.; Gordon, H.; Mueller, J.; El-Sayed, S. Nimbus-7 Coastal Zone Color Scanner: system description and initial imagery. Science 1980, 210, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conkright, M.; Gregg, W. Comparison of global chlorophyll climatologies: In situ, CZCS, Blended in situ-CZCS and SeaWiFS. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2003, 24, 969–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cracknell, A.P. The development of remote sensing in the last 40 years. 2018, 39, 8387–8427.
- Jiang, L.; Wang, M. Improved near-infrared ocean reflectance correction algorithm for satellite ocean color data processing. Opt Express 2014, 22, 21657–21678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, F.; Wei, X. Fusion of Landsat-8/OLI and GOCI Data for Hourly Mapping of Suspended Particulate Matter at High Spatial Resolution: A Case Study in the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary. Remote Sensing 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, J.; Davis, C.; Erb, A.; Hu, C.; Gatebe, C.; Jordan, C.; Lee, Z.; Mannino, A.; Mouw, C.; Schaaf, C.; et al. Coastal Observations from a New Vantage Point. Eos 2016, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, C.; Nukapothula, S. Atmospheric Correction of GOCI Using Quasi-Synchronous VIIRS Data in Highly Turbid Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, W. The NIR-SWIR combined atmospheric correction approach for MODIS ocean color data processing. Optics express 2007, 15, 15722–15733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, M. Detection of turbid waters and absorbing aerosols for the MODIS ocean color data processing. Remote Sensing of Environment 2007, 110, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Sharma, R.; Thapliyal, P.; Gangwar, R.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, R. Geostationary satellite-based observations for ocean applications. Current Science 2019, 117, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products. Remote sensing of environment 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Shen, W.; Xie, Y. MODIS-based monitoring of spatial distribution of trophic status in 144 key lakes and reservoirs of China in summer of 2018. J. Lake Sci 2021, 33, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, F.; Li, P. Assessment of Normalized Water-Leaving Radiance Derived from GOCI Using AERONET-OC Data. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Song, Q.; Duan, H. Remote Estimation of Water Clarity and Suspended Particulate Matter in Qinghai Lake from 2001 to 2020 Using MODIS Images. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lin, C.; Ma, R.; Cao, Z. Remote Sensing Estimation of Lake Total Phosphorus Concentration Based on MODIS: A Case Study of Lake Hongze. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.; Tschudi, M.; Pacifici, F.; Liu, Y. Validation of Suomi-NPP VIIRS sea ice concentration with very high-resolution satellite and airborne camera imagery. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2017, 130, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Román, M.O.; Csiszar, I.; Vermote, E.F.; Wolfe, R.E.; Hook, S.J.; Friedl, M.; Wang, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Miura, T. Land and cryosphere products from Suomi NPP VIIRS: Overview and status. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2013, 118, 9753–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hao, X.; Zhang, B.; Zou, C.-Z.; Cao, C. Assessment of the Reprocessed Suomi NPP VIIRS Enterprise Cloud Mask Product. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, L. VIIRS-derived ocean color product using the imaging bands. Remote Sensing of Environment 2018, 206, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-S.; Lee, S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Choi, J.-K.; Ryu, J.-H. Decadal measurements of the first Geostationary Ocean Color Satellite (GOCI) compared with MODIS and VIIRS data. Remote Sensing 2021, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Mao, K.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, L.; Shen, X.; Qin, Z. An algorithm for retrieving land surface temperatures using VIIRS data in combination with multi-sensors. Sensors (Basel) 2014, 14, 21385–21408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.M.; Jeffrey, H.; Gorter, H.; Anderson, P.; Clark, C.; Holmes, A.; Feldman, G.C.; Patt, F.S. SeaHawk: an advanced CubeSat mission for sustained ocean colour monitoring. In Proceedings of the Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XX; 2016; pp. 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Arino, O.; Gross, D.; Ranera, F.; Leroy, M.; Bicheron, P.; Brockman, C.; Defourny, P.; Vancutsem, C.; Achard, F.; Durieux, L. GlobCover: ESA service for global land cover from MERIS. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium; 2007; pp. 2412–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Doerffer, R.; Schiller, H. The MERIS Case 2 water algorithm. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2007, 28, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rast, M.; Bezy, J.; Bruzzi, S. The ESA Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer MERIS a review of the instrument and its mission. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1999, 20, 1681–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.L.; Henson, S.A.; Lamquin, N.; Clerc, S.; Donlon, C. Assessing the Effect of Tandem Phase Sentinel-3 OLCI Sensor Uncertainty on the Estimation of Potential Ocean Chlorophyll-a Trends. Remote Sensing 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in case II waters using MODIS and MERIS data—successes and challenges. Environmental Research Letters 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, X. Evaluation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance Products from Multiple Ocean Color Missions in Highly Turbid Water (Hangzhou Bay). Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstone, G.H.; Pardo, S.; Dall'Olmo, G.; Brewin, R.J.W.; Nencioli, F.; Dessailly, D.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Casal, T.; Donlon, C. Performance of Ocean Colour Chlorophyll a algorithms for Sentinel-3 OLCI, MODIS-Aqua and Suomi-VIIRS in open-ocean waters of the Atlantic. Remote Sensing of Environment 2021, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuzé, J.; Bréon, F.; Devaux, C.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Lafrance, B.; Maignan, F.; Marchand, A.; Nadal, F.; Perry, G. Remote sensing of aerosols over land surfaces from POLDER-ADEOS-1 polarized measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2001, 106, 4913–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, M.; Deuzé, J.; Bréon, F.; Hautecoeur, O.; Herman, M.; Buriez, J.; Tanré, D.; Bouffies, S.; Chazette, P.; Roujean, J.-L. Retrieval of atmospheric properties and surface bidirectional reflectances over land from POLDER/ADEOS. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 1997, 102, 17023–17037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, H. ADEOS overview. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 1999, 37, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, Y.; Murakami, H.; Ogata, K.; Kachi, M. A quasi-physical sea surface temperature method for the split-window data from the Second-generation Global Imager (SGLI) onboard the Global Change Observation Mission-Climate (GCOM-C) satellite. Remote Sensing of Environment 2021, 257, 112347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, A.; Campbell, J.W.; Hooker, S.B.; Steinmetz, F.; Ogata, K.; Hirata, T.; Higa, H.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Isada, T.; Suzuki, K. Performance of JAXA’s SGLI standard ocean color products for oceanic to coastal waters: chlorophyll a concentration and light absorption coefficients of colored dissolved organic matter. Journal of Oceanography 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Okamura, Y.; Mokuno, M.; Amano, T.; Yoshida, J. First year on-orbit calibration activities of SGLI on GCOM-C satellite. In Proceedings of the Earth observing missions and sensors: Development, implementation, and characterization V; 2018; pp. 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.; Liu, M.; Guan, L. Simulation of Thermal Infrared Brightness Temperatures from an Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner Onboard a New Generation Chinese Ocean Color Observation Satellite. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heales, C.J.; Lloyd, E. Play simulation for children in magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Sciences 2022, 53, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Kumar, R.; Stoffelen, A. Validation of ocean surface winds from the OCEANSAT-2 scatterometer using triple collocation. Remote sensing letters 2013, 4, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, R.; Arora, R.; Rao, M.V.; Thyagarajan, K. OCEANSAT 2: mission and its applications. In Proceedings of the GEOSS and Next-Generation Sensors and Missions; 2006; pp. 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Kumar, P.; Pal, P.K. Assimilation of Oceansat-2-scatterometer-derived surface winds in the weather research and forecasting model. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2011, 50, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, D.-E.; Choi, S.-Y.; Kwon, O.-S. OSMI-1 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through ER stress and NF-κB signaling in colon cancer cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 11073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher, K.; Buchkremer, R. Measuring online sensory consumer experience: introducing the Online Sensory Marketing Index (OSMI) as a structural modeling approach. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 2022, 17, 751–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamquin, N.; Mazeran, C.; Doxaran, D.; Ryu, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J. Assessment of GOCI radiometric products using MERIS, MODIS and field measurements. Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 287–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Jang, L.-H.; Lim, J.; Khim, B.-K.; Jo, Y.-H. Sargassum detection using machine learning models: A case study with the first 6 months of GOCI-II imagery. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.; Quartly, G.D.; Shutler, J.; Miller, P.I.; Yoshikawa, Y. Estimation of ocean surface currents from maximum cross correlation applied to GOCI geostationary satellite remote sensing data over the Tsushima (K orea) S traits. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2016, 121, 6993–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduan, J.D.; Washburn, L. High-frequency radar observations of ocean surface currents. Annual review of marine science 2013, 5, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.; Neukermans, G.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Jolivet, D. Challenges and opportunities for geostationary ocean colour remote sensing of regional seas: A review of recent results. Remote Sensing of Environment 2014, 146, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Han, H.-J.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.-J.; Ahn, Y.-H. Overview of geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) and GOCI data processing system (GDPS). Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Whitman, P.; Vandermeulen, R.; Hu, C.; Mannino, A.; Salisbury, J.; Efremova, B.; Conmy, R.; Coffer, M.; Salls, W.; et al. Assessing potential of the Geostationary Littoral Imaging and Monitoring Radiometer (GLIMR) for water quality monitoring across the coastal United States. Mar Pollut Bull 2023, 196, 115558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, J.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Park, K.-S. Characterization of spatial and temporal variation of suspended sediments in the Yellow and East China Seas using satellite ocean color data. GIScience & Remote Sensing 2014, 51, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Hu, C. Evaluation of remote sensing algorithms for cyanobacterial pigment retrievals during spring bloom formation in several lakes of East China. Remote Sensing of Environment 2012, 126, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, M.; Feng, L.; Zhao, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentrations in a highly turbid eutrophic lake using a classification-based MODIS land-band algorithm. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2019, 12, 3769–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Kratzer, S.; Wang, J.; Shi, T.; Hu, Z.; Yang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhou, Q. Estimating ultraviolet reflectance from visible bands in ocean colour remote sensing. Remote Sensing of Environment 2021, 258, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Hu, C. Diurnal changes of a harmful algal bloom in the East China Sea: Observations from GOCI. Remote Sensing of Environment 2014, 140, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Quantitative Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in the Bohai–Yellow Sea Using GOCI Surface Reflectance Products. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Choi, J.K.; Park, Y.J.; Han, H.J.; Ryu, J.H. Application of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) to estimates of ocean surface currents. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2014, 119, 3988–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Sun, G. Geostationary ocean color imager and application progress. Marine environmental science 2014, 33, 966–971. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Huang, D. Applications of geostationary satellite data in the study of ocean and coastal short-term processes: Two cases in the East China Sea. In Remote Sensing of Ocean and Coastal Environments; Elsevier: 2021; pp. 139–154.
- Chen, J.; He, X.; Quan, W.; Ma, L.; Jia, M.; Pan, D. A statistical analysis of residual errors in satellite remote sensing reflectance data from oligotrophic open oceans. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2021, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Comparison of atmospheric correction algorithms for TM image in inland waters. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2008, 29, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, L.-Q.; Chen, X.-L. Evaluation on the atmospheric correction methods for water color remote sensing by using HJ-1A/1B CCD image-taking Poyang Lake in China as a case. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2013, 33, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Lee, B.; Oh, I.S. Development of atmospheric correction algorithm for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, J.; Mannino, A.; Franz, B.; Kim, W. Uncertainties in the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Remote Sensing Reflectance for Assessing Diurnal Variability of Biogeochemical Processes. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dou, T.; Yang, B. A review of research on retrieving the concentration of suspended particulate matter and chlorophyll-a in lake based on GOCI images. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering 2017, 28, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Han, B.; Jamet, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, T. Evaluation of Four Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for GOCI Images over the Yellow Sea. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-H.; Park, Y.-J. Estimating Water Reflectance at Near-Infrared Wavelengths for Turbid Water Atmospheric Correction: A Preliminary Study for GOCI-II. Remote Sensing 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, W.; Lee, B.; Oh, I.S. Vicarious calibration of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. Opt Express 2015, 23, 23236–23258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyens, C.; Jamet, C.; Ruddick, K.G. Spectral relationships for atmospheric correction. II. Improving NASA's standard and MUMM near infra-red modeling schemes. Opt Express 2013, 21, 21176–21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, F.; Verhoef, W. An improved spectral optimization algorithm for atmospheric correction over turbid coastal waters: A case study from the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary and the adjacent coast. Remote Sensing of Environment 2017, 191, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Huang, N.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Cui, Q. Using geostationary satellite ocean color data to map the diurnal dynamics of suspended particulate matter in coastal waters. Remote Sensing of Environment 2013, 133, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Tian, L. Atmospheric correction under cloud edge effects for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager through deep learning. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2023, 201, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Shanmugam, P.; Park, Y.-J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F.; Wang, D.; Huang, H. Atmospheric correction of geostationary satellite ocean color data under high solar zenith angles in open oceans. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Yu, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, L.; Xing, Q. Monitoring the Dissipation of the Floating Green Macroalgae Blooms in the Yellow Sea (2007–2020) on the Basis of Satellite Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, Z.; Xiaoli, C.; Sen, W.; Xinxin, Y. Analysis of the Causes of Cyanobacteria Bloom: A Review. Journal of Resources and Ecology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gower, J.F.R.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Brando, V.E. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Progress in Oceanography 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, J.P.; Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C.; Corcoran, A.A.; Hubbard, K.A.; Muhlbach, E.; Sharp, W.C.; Brand, L.E.; Kelble, C.R. Remote detection of cyanobacteria blooms in an optically shallow subtropical lagoonal estuary using MODIS data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Z.; Bilal, M.; He, Y. Remote sensing estimation of phytoplankton absorption associated with size classes in coastal waters. Ecological Indicators 2021, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water research 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sakib, M.H.; Rashid, A.H.A.; Yang, C.S. Comparing performance of inter-sensor NDVI for the detection of floating macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea. 2021.
- Sun, X.; Wu, M.; Xing, Q.; Song, X.; Zhao, D.; Han, Q.; Zhang, G. Spatio-temporal patterns of Ulva prolifera blooms and the corresponding influence on chlorophyll-a concentration in the Southern Yellow Sea, China. Sci Total Environ, 2018; 640-641, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.T.M.; Park, Y.-G.; Choi, J.M. Divergence Observation in a Mesoscale Eddy during Chla Bloom Revealed in Submesoscale Satellite Currents. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.H.; Kim, W.; Son, S.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Park, Y.J. Remote quantification of Cochlodinium polykrikoides blooms occurring in the East Sea using geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI). Harmful Algae 2018, 73, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Huan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Hu, C.; Wang, S.; He, Y. Remote-Sensing Estimation of Phytoplankton Size Classes From GOCI Satellite Measurements in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2017, 122, 8309–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Chlorophyll-a concentration inversion and distribution with GOCI images in the Changjiang Estuary. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Spatial Atmospheric Marine Environmental Optics (SAME 2023); 2023; pp. 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-K.; Min, J.-E.; Noh, J.H.; Han, T.-H.; Yoon, S.; Park, Y.J.; Moon, J.-E.; Ahn, J.-H.; Ahn, S.M.; Park, J.-H. Harmful algal bloom (HAB) in the East Sea identified by the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Tang, R.; Sun, X.; Liu, D. Simple methods for satellite identification of algal blooms and species using 10-year time series data from the East China Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, Z.; Liu, C. Detecting harmful algal blooms using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) data in Bohai Sea, China. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Modeling of Ecosystems for Sustainability XII; 2015; pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yimin, L.; Zhenyu, T.; Chen, Y.; Feng, H.; Di, M.; Juhua, L.; Hongtao, D. Extraction of Algal Blooms in Dianchi Lake Based on Multi-Source Satellites Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Advances in Earth Science 2022, 37, 1141. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Baek, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Jo, Y.-H. GOCI-II based sea surface salinity estimation using machine learning for the first-year summer. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2022, 43, 6605–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Han, L. Hourly remote sensing monitoring of harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Taihu Lake based on GOCI images. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28, 35958–35970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-S.; Park, K.-A.; Micheli, F. Derivation of Red Tide Index and Density Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Choi, B.-J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.-G. Tracing floating green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using GOCI satellite data and Lagrangian transport simulations. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Min, J.-E.; Ryu, J.-H. Detecting massive green algae (Ulva prolifera) blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) data. Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Long-term spatial variation of algal blooms extracted using the U-net model from 10 years of GOCI imagery in the East China Sea. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 321, 115966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Li, Z.; Bilal, M.; Wang, S.; Sun, D.; Chen, Y. Automatic method to monitor floating macroalgae blooms based on multilayer perceptron: case study of Yellow Sea using GOCI images. Opt Express 2018, 26, 26810–26829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Shi, Z.; An, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, Y. A novel spectral-unmixing-based green algae area estimation method for GOCI data. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 10, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Ma, R.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; Hu, M.; Xiong, J. Monitoring fractional floating algae cover over eutrophic lakes using multisensor satellite images: MODIS, VIIRS, GOCI, and OLCI. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Visser, P.M.; Ma, R. Diurnal changes of cyanobacteria blooms in Taihu Lake as derived from GOCI observations. Limnology and Oceanography 2018, 63, 1711–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J. Drinking water treatment residuals from cyanobacteria bloom-affected areas: Investigation of potential impact on agricultural land application. Sci Total Environ 2020, 706, 135756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Wang, W. Classifying diurnal changes of cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu to identify hot patterns, seasons and hotspots based on hourly GOCI observations. J Environ Manage 2022, 310, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Cai, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Zeng, S.; Bi, S.; Wang, G. Contributions of meteorology and nutrient to the surface cyanobacterial blooms at different timescales in the shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 894, 165064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Mu, M.; Li, Y. Tempo-spatial dynamics of water quality and its response to river flow in estuary of Taihu Lake based on GOCI imagery. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2017, 24, 28079–28101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Harding, L.W. Retrieval of diffuse attenuation coefficient in the Chesapeake Bay and turbid ocean regions for satellite ocean color applications. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2009; 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Becker, B.L. Remote sensing estimation of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in optically shallow waters. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2017, 128, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Jing, C.; Rui, L. A method of water quality analysis: chlorophyll a concentration estimation of Dongping Lake based on GOCI image. Environmental Protection 2017, 45, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zha, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Developing a two-step retrieval method for estimating total suspended solid concentration in Chinese turbid inland lakes using Geostationary Ocean Colour Imager (GOCI) imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2015, 36, 1385–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020; 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, S.; Cui, T.; Lai, Q.; Bao, Y.; Diao, R.; Yue, Y.; Hao, Y. Improving remote sensing retrieval of water clarity in complex coastal and inland waters with modified absorption estimation and optical water classification using Sentinel-2 MSI. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2021, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, M.; Lü, C. Analysis on Diurnal Variation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration of Taihu Lake Based on Optical Classification with GOCI Data. Guang pu xue yu Guang pu fen xi= Guang pu 2016, 36, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, T.W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Wei, J.W.; Mu, B.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Liu, R.J.; Chen, X.Y. Remote sensing of chlorophyll a concentration in turbid coastal waters based on a global optical water classification system. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2020, 163, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Cao, Z.; Chu, Q.; Jing, Y. Optimized remote sensing estimation of the lake algal biomass by considering the vertically heterogeneous chlorophyll distribution: Study case in Lake Chaohu of China. Sci Total Environ 2021, 771, 144811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Moon, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J.; Ishizaka, J. Evaluation of chlorophyll retrievals from Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) for the North-East Asian region. Remote Sensing of Environment 2016, 184, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A global approach for chlorophyll-a retrieval across optically complex inland waters based on optical water types. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomets, T.; Toming, K.; Paavel, B.; Kutser, T. Evaluation of remote sensing and modeled chlorophyll-a products of the Baltic Sea. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2022, 16, 046516–046516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, M.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Jiang, L.; Xue, K.; Xiong, J.; Hu, M. A decade-long chlorophyll-a data record in lakes across China from VIIRS observations. Remote Sensing of Environment 2024, 301, 113953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Park, K.-A. Application of Deep Learning for Speckle Removal in GOCI Chlorophyll-a Concentration Images (2012–2017). Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, H.; Song, K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Remote chlorophyll-a estimates for inland waters based on a cluster-based classification. Sci Total Environ 2013, 444, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, F.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, Z. Assessment of satellite-based chlorophyll-a retrieval algorithms for high solar zenith angle conditions. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2017, 11, 012004–012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, L. Assessment of the Number of Valid Observations and Diurnal Changes in Chl-a for GOCI: Highlights for Geostationary Ocean Color Missions. Sensors 2020, 20, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuno, Y.; Makio, K.; Koike, K. Chlorophyll-a Estimation in Tachibana Bay by Data Fusion of GOCI and MODIS Using Linear Combination Index Algorithm. Advances in Remote Sensing 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Park, K.-A. Application of deep learning for speckle removal in goci chlorophyll-a concentration images (2012–2017). Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Bai, Y.; Li, H.; He, X.; Gong, F.; Li, T. Fluorescence Line Height Extraction Algorithm for the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, S.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, X.; Li, P. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a Concentration Using GOCI Data in Sediment-Laden Turbid Waters of Hangzhou Bay and Adjacent Coastal Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2023, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Chen, M. A Weighted Algorithm Based on Normalized Mutual Information for Estimating the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Remote Sensing 2015, 7, 11731–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shi, K.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, A.x.; Sun, D.; Xu, L.; Zou, J.; Chen, X. Satellite observation of hourly dynamic characteristics of algae with Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) data in Lake Taihu. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 159, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Loiselle, S.A.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, L.; Shang, L. A new three-band algorithm for estimating chlorophyll concentrations in turbid inland lakes. Environmental Research Letters 2010, 5, 044009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Shi, L.; Ji, G. an expanded three band model to monitor inland optically complex water using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Frontiers in Remote Sensing 2022, 3, 803884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulong, G.; Changchun, H.; Yunmei, L.; Chenggong, D.; Lingfei, S.; Yuan, L.; Weiqiang, C.; Hejie, W.; Enxiang, C.; Guangxing, J. Hyperspectral reconstruction method for optically complex inland waters based on bio-optical model and sparse representing. Remote Sensing of Environment 2022, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from GOCI and GOCI-II Data in Optically Complex Lakes. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Bowers, D.G.; Mitchelson-Jacob, E.G. Estimating suspended sediment concentrations from ocean colour measurements in moderately turbid waters; the impact of variable particle scattering properties. Remote Sensing of Environment 2005, 94, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Xue, K.; Shen, M. Effect of Satellite Temporal Resolution on Long-Term Suspended Particulate Matter in Inland Lakes. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Dong, C. Spatio-temporal Analysis of suspended sediment Concentration in the Yongjiang Estuary Based on GOCI. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; 2018; p. 032017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, L. High Temporal Resolution Monitoring of Suspended Matter Changes from GOCI Measurements in Lake Taihu. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zou, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Li, R. Suspended particle size retrieval based on geostationary ocean color imager (GOCI) in the Bohai Sea. Journal of Coastal Research 2016, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; et al. An approach for retrieval of horizontal and vertical distribution of total suspended matter concentration from GOCI data over Lake Hongze. Sci Total Environ 2020, 700, 134524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; He, X.; Chen, T.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, P. Retrieval of total suspended particulate matter in highly turbid Hangzhou Bay waters based on geostationary ocean color imager. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2017, 2017; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Padial, A.A.; Thomaz, S.M. Prediction of the light attenuation coefficient through the Secchi disk depth: empirical modeling in two large Neotropical ecosystems. Limnology 2008, 9, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Moon, J.-E.; Gallegos, S. Development of suspended particulate matter algorithms for ocean color remote sensing. Korean Journal of Remote Sensing 2001, 17, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, J.-E.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Ryu, J.-H.; Shanmugam, P. Development of ocean environmental algorithms for Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Korean Journal of Remote Sensing 2010, 26, 189–207. [Google Scholar]
- Ruddick, K.; Vanhellemont, Q.; Yan, J.; Neukermans, G.; Wei, G.; Shang, S. Variability of suspended particulate matter in the Bohai Sea from the geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI). Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sensing of Environment 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Pan, D.; He, X.; Bai, Y. Diurnal Variability of Turbidity Fronts Observed by Geostationary Satellite Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J.; Ryu, J.-H.; Choi, J.-K.; Ahn, J.-H.; Min, J.-E.; Son, Y.-B.; Lee, S.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Ahn, Y.-H. Initial validation of GOCI water products against in situ data collected around Korean peninsula for 2010–2011. Ocean Science Journal 2012, 47, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanto, E.; Tang, J.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Ishizaka, J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kiyomoto, Y.; Yamada, K.; Chiang, C. Empirical ocean-color algorithms to retrieve chlorophyll-a, total suspended matter, and colored dissolved organic matter absorption coefficient in the Yellow and East China Seas. Journal of oceanography 2011, 67, 627–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. Retrieval of Suspended Matter Concentration and Reconstruction of Missing Data Based on GOCI in Bohai and Yellow Sea. Ocean University of China 2013.
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.H.; Paull, D.; Gao, J. Application of the geostationary ocean color imager to mapping the diurnal and seasonal variability of surface suspended matter in a macro-tidal estuary. Remote Sensing 2016, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-K.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, B.R.; Eom, J.; Moon, J.-E.; Ryu, J.-H. Application of the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) to mapping the temporal dynamics of coastal water turbidity. Remote Sensing of Environment 2014, 146, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Diurnal Changes Monitoring and Analysis of the Total Suspended Matters in Bohai Sea Using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; 2019; p. 012036. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, J.; Dong, Q.; Song, Q.; Ding, J. Retrieval of total suspended matter concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment 2010, 114, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Gong, F.; Huang, H.; Pan, D. Simulation of Sedimentation in Lake Taihu with Geostationary Satellite Ocean Color Data. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Shulman, I. Hourly turbidity monitoring using Geostationary Ocean Color Imager fluorescence bands. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukushkin, A.S. Long-term seasonal variability of water transparency in the surface layer of the deep part of the Black Sea. Russian Meteorology and Hydrology 2014, 39, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, Z.; Bilal, M.; Sun, D. Remote sensing of water turbidity in the eastern China seas from geostationary ocean colour imager. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2020, 41, 4080–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Dingfeng, Y.; Xiaoyan, L.; Qian, Y.; Yingying, G. Research on remote sensing retrieval and diurnal variation of Secchi disk, depth of Jiaozhou Bay based on GOCI. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources 2021, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Gao, J.; Sun, D.; Tian, M. Monitoring Water Transparency in Shallow and Eutrophic Lake Waters Based on GOCI Observations. Remote Sensing 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Bilal, M. Variations of transparency derived from GOCI in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Optics Express 2018, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, T.J.; Perez-Losada, J.; Schladow, S.G.; Reuter, J.E.; Jassby, A.D.; Goldman, C.R. Water clarity modeling in Lake Tahoe: Linking suspended matter characteristics to Secchi depth. Aquatic Sciences 2006, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, B.K.; Reifel, K.M.; Tiffany, M.A.; Watts, J.M.; Hurlbert, S.H. Spatial and temporal patterns of transparency and light attenuation in the Salton Sea, California, 1997–1999. Lake and Reservoir Management 2007, 23, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, J.M.; Lyubchich, V.; Zhang, Q. Patterns and Trends in Secchi Disk Depth over Three Decades in the Chesapeake Bay Estuarine Complex. Estuaries and Coasts 2019, 42, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, D.; Cheng, W.; Gai, Y.; Yao, H.; Yang, L.; Pan, S. Monitoring multi-temporal and spatial variations of water transparency in the Jiaozhou Bay using GOCI data. Mar Pollut Bull 2022, 180, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi disk depth: A new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility. Remote sensing of environment 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Hu, J.-W.; Tian, L.; Yu, D.-F.; Gao, H.; Yang, L.; An, D.-Y. Comparative study on transparency retrieved from GOCI under four different atmospheric correction algorithms in Jiaozhou Bay and Qingdao Coastal area. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M. Global daily gap-free ocean color products from multi-satellite measurements. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2022, 108, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; Yue, X.; Ye, Z. A Novel Remote Sensing Algorithm for Estimating Diffuse Attenuation Coefficient in the BohaiSea and Yellow Sea. Guangxi Science 2016, 23, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Gong, F.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Bai, R.; Xu, Y. Using geostationary satellite ocean color data and superpixel to map the diurnal dynamics of water transparency in the eastern China seas. Ecological Indicators 2022, 142, 109219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pan, D.; Mao, Z. Water-transparency (Secchi Depth) monitoring in the China Sea with the SeaWiFS satellite sensor. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology VI; 2004; pp. 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Zhu, Q.; Hao, Z.; Gong, F. Recent changes of global ocean transparency observed by SeaWiFS. Continental Shelf Research 2017, 143, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Zheng, Y. Monitoring and understanding the water transparency changes of fifty large lakes on the Yangtze Plain based on long-term MODIS observations. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 221, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Lei, S.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Retrieval of Secchi Disk Depth in Turbid Lakes from GOCI Based on a New Semi-Analytical Algorithm. Remote Sensing 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Luyssaert, S.; Kaplan, L.A.; Aufdenkampe, A.K.; Richter, A.; Tranvik, L.J. The boundless carbon cycle. Nature Geoscience 2009, 2, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Laudon, H.; Jansson, M. Landscape regulation of bacterial growth efficiency in boreal freshwaters. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 2007, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-H.; Park, M.-O.; Kim, S.-W.; Han, I.-S.; Kim, W.; Park, Y.-J. Correlation between SST and CDOM during Summer Coastal Upwelling along the Southeast Coast of Korea. Journal of Coastal Research 2018, 1471–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, F.; Sokoletsky, L.; Sun, X. Validation and Calibration of QAA Algorithm for CDOM Absorption Retrieval in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuarine and Coastal Waters. Remote Sensing 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Huan, Y.; Mao, Z.; He, Y. Remote sensing estimation of colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) from GOCI measurements in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2020, 27, 6872–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cai, W.J.; He, X.; Zhai, W.; Pan, D.; Dai, M.; Yu, P. A mechanistic semi-analytical method for remotely sensing sea surface pCO2 in river-dominated coastal oceans: A case study from the East China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2015, 120, 2331–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.E.; Cai, W.-J.; Raymond, P.A.; Bianchi, T.S.; Hopkinson, C.S.; Regnier, P.A. The changing carbon cycle of the coastal ocean. Nature 2013, 504, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Tao, B.; Pan, D.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Gong, C. Satellite estimation of particulate organic carbon flux from Changjiang River to the estuary. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 223, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; Ciais, P.; Mackenzie, F.T.; Gruber, N.; Janssens, I.A.; Laruelle, G.G.; Lauerwald, R.; Luyssaert, S.; Andersson, A.J. Anthropogenic perturbation of the carbon fluxes from land to ocean. Nature geoscience 2013, 6, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lei, S.; Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; Zeng, S.; et al. Tracking spatio-temporal dynamics of POC sources in eutrophic lakes by remote sensing. Water Res 2020, 168, 115162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Shen, F.; Pan, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Satellite Observations of the Diurnal Dynamics of Particulate Organic Carbon in Optically Complex Coastal Oceans: The Continental Shelf Seas of China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2019, 124, 4710–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, N.; Obrador, B.; Alomar, C.; Pretus, J.L. Seasonality and landscape factors drive dissolved organic matter properties in Mediterranean ephemeral washes. Biogeochemistry 2012, 112, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Tzortziou, M.; Mannino, A. Remote sensing of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) stocks, fluxes and transformations along the land-ocean aquatic continuum: advances, challenges, and opportunities. Earth-Science Reviews, 2023; 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yunmei, L.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhu, A.x.; Song, T.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Shi, K. Tracing high time-resolution fluctuations in dissolved organic carbon using satellite and buoy observations: Case study in Lake Taihu, China. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2017, 62, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, H.d.R.; Xu, Q.; Ishizaka, J.; Carpenter, E.J.; Yager, P.L.; Goes, J.I. The influence of riverine nutrients in niche partitioning of phytoplankton communities–a contrast between the Amazon River Plume and the ChangJiang (Yangtze) River diluted water of the East China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 2018, 5, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, P.C.; Fischer, A.C.; Lewis-Brown, E.; Meredith, M.P.; Sparrow, M.; Andersson, A.J.; Antia, A.; Bates, N.R.; Bathmann, U.; Beaugrand, G. Impacts of the oceans on climate change. Advances in marine biology 2009, 56, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Goes, J.I.; do Rosario Gomes, H.; Lee, Z.; Noh, J.-H.; Wei, J.; Shang, Z.; Salisbury, J.; Mannino, A.; Kim, W. Estimates of diurnal and daily net primary productivity using the Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2022, 280, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, J.; Cao, Z.; Huang, H.; Gong, F. A Novel Multi-Candidate Multi-Correlation Coefficient Algorithm for GOCI-Derived Sea-Surface Current Vector with OSU Tidal Model. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Su, X.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, S.; Mao, Z.; He, Y. Remote sensing estimation of sea surface salinity from GOCI measurements in the southern Yellow Sea. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lee, K.-S. Capability of geostationary satellite imagery for sea ice monitoring in the Bohai and Yellow seas. Journal of Marine Science and Technology 2016, 24, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, F.; Zhang, R.; Tian-Kunze, X.; Han, B.; Zhu, L.; Cui, T.; Yang, Q. Sea Ice Thickness Retrieval Based on GOCI Remote Sensing Data: A Case Study. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, K.; Shao, D.; Xu, Y.; Gu, W. Monitoring the Characteristics of the Bohai Sea Ice Using High-Resolution Geostationary Ocean Color Imager (GOCI) Data. Sustainability 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, X. Dual-branch neural network for sea fog detection in geostationary ocean color imager. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.-K.; Kim, S.; Edwin, J.; Yang, C.-S. Sea fog identification from GOCI images using CNN transfer learning models. Electronics 2020, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.D.; Cherry, J.E.; Brown, D.; Bondurant, A.C.; Endres, K.L. Observation-derived ice growth curves show patterns and trends in maximum ice thickness and safe travel duration of Alaskan lakes and rivers. The Cryosphere 2020, 14, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D.A. Antarctic subglacial lake exploration: a new frontier in microbial ecology. The ISME Journal 2009, 3, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Galloway, A.W.; Powers, S.M.; Ozersky, T.; Woo, K.H.; Batt, R.D.; Labou, S.G.; O'Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Lottig, N.R. Ecology under lake ice. Ecology letters 2017, 20, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A review of remote sensing for water quality retrieval: Progress and challenges. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J. Dependence of relationship between inherent and apparent optical properties of water on solar altitude. Limnology and Oceanography 1984, 29, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T. Volume scattering function, average cosines, and the underwater light field. Limnology and oceanography 1991, 36, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, D.; Cunningham, A.; Dudek, A. Optical water type discrimination and tuning remote sensing band-ratio algorithms: Application to retrieval of chlorophyll and Kd (490) in the Irish and Celtic Seas. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2007, 73, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Deng, L.; Zeng, K. Diurnal variation of the diffuse attenuation coefficient for downwelling irradiance at 490 nm in coastal East China Sea. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Salama, M.S.; Shen, F.; Verhoef, W. Retrieval of the diffuse attenuation coefficient from GOCI images using the 2SeaColor model: A case study in the Yangtze Estuary. Remote Sensing of Environment 2016, 175, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Yuan, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Xu, T.; Shen, X.; Gao, C. Changes in global cloud cover based on remote sensing data from 2003 to 2012. Chinese Geographical Science 2019, 29, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS Journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Hong, S. Advancements of remote data acquisition and processing in unmanned vehicle technologies for water quality monitoring: An extensive review. Chemosphere 2023, 140198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Bao, F.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhong, S.; Yin, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z. Marine environmental monitoring with unmanned vehicle platforms: Present applications and future prospects. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 858, 159741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, H.; Kutser, T.; Han, Y.; Ma, R.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, P.; Jiang, C. Potential of Mie–fluorescence–Raman lidar to profile chlorophyll a concentration in inland waters. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57, 14226–14236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G. A ground-based remote sensing system for high-frequency and real-time monitoring of phytoplankton blooms. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 439, 129623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Woolway, R.I.; Shi, K.; Yang, X. Numerical simulation of thermal stratification in Lake Qiandaohu using an improved WRF-Lake model. Journal of Hydrology 2023, 618, 129184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.-M.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Y.-L. An Observing System Simulation Experiments framework based on the ensemble square root Kalman Filter for evaluating the concentration of chlorophyll a by multi-source data: A case study in Taihu Lake. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management 2014, 17, 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Lv, H.; Huang, C.; Li, Y. An inversion-based fusion method for inland water remote monitoring. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 9, 5599–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H. Ocean color estimation by Himawari-8/AHI. In Proceedings of the Remote sensing of the oceans and inland waters: Techniques, applications, and challenges; 2016; pp. 177–186. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, W. A novel multitemporal image-fusion algorithm: Method and application to GOCI and himawari images for inland water remote sensing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2020, 58, 4018–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shen, F.; Wei, X. Fusion of Landsat-8/OLI and GOCI data for hourly mapping of suspended particulate matter at high spatial resolution: A case study in the Yangtze (Changjiang) Estuary. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.-B.; Vannah, B.; Yang, Y.J. Comparative sensor fusion between hyperspectral and multispectral satellite sensors for monitoring microcystin distribution in Lake Erie. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2014, 7, 2426–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G. Optically based technique for producing merged spectra of water-leaving radiances from ocean color remote sensing. Applied Optics 2007, 46, 3856–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Zibordi, G.; Djavidnia, S. Merged series of normalized water leaving radiances obtained from multiple satellite missions for the Mediterranean Sea. Advances in Space Research 2009, 43, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V.; Chuprin, A.; Grant, M.; Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S. Assessing the fitness-for-purpose of satellite multi-mission ocean color climate data records: A protocol applied to OC-CCI chlorophyll-a data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2017, 203, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Duan, H.; Shen, M.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Liu, D.; Xiao, Q. Using VIIRS/NPP and MODIS/Aqua data to provide a continuous record of suspended particulate matter in a highly turbid inland lake. International journal of applied earth observation and geoinformation 2018, 64, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Miller, W.L. A new algorithm to retrieve chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) absorption spectra in the UV from ocean color. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2015, 120, 496–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Atmospheric correction of satellite ocean color imagery using the ultraviolet wavelength for highly turbid waters. Optics express 2012, 20, 20754–20770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werdell, P.J.; Bailey, S.W.; Franz, B.A.; Harding Jr, L.W.; Feldman, G.C.; McClain, C.R. Regional and seasonal variability of chlorophyll-a in Chesapeake Bay as observed by SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua. Remote Sensing of Environment 2009, 113, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, S.G.; Peters, S.W.; Gons, H.J. Remote sensing of the cyanobacterial pigment phycocyanin in turbid inland water. Limnology and oceanography 2005, 50, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Simis, S.G.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, K.; Lyu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, K. A four-band semi-analytical model for estimating phycocyanin in inland waters from simulated MERIS and OLCI data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2017, 56, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Fang, C.; Shang, Y.; Li, S.; Tao, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Remote estimation of phycocyanin concentration in inland waters based on optical classification. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 899, 166363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.S.; Pyo, J.; Kwon, Y.-H.; Duan, H.; Cho, K.H.; Park, Y. Drone-based hyperspectral remote sensing of cyanobacteria using vertical cumulative pigment concentration in a deep reservoir. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 236, 111517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Duan, H.; Baek, S.; Kim, M.S.; Jeon, T.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.H. A convolutional neural network regression for quantifying cyanobacteria using hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 233, 111350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Cao, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, T.; Song, K.; Lyu, L.; Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Duan, H. Microcystins risk assessment in lakes from space: Implications for SDG 6.1 evaluation. Water Research 2023, 245, 120648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Song, K.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Bi, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z. An OLCI-based algorithm for semi-empirically partitioning absorption coefficient and estimating chlorophyll a concentration in various turbid case-2 waters. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 239, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall'Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A simple semi-analytical model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in turbid waters: Validation. Remote Sensing of Environment 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Whitman, P.; Vandermeulen, R.; Hu, C.; Mannino, A.; Salisbury, J.; Efremova, B.; Conmy, R.; Coffer, M.; Salls, W. Assessing potential of the Geostationary Littoral Imaging and Monitoring Radiometer (GLIMR) for water quality monitoring across the coastal United States. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2023, 196, 115558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Gong, F.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, T. Atmospheric correction algorithm based on the interpolation of ultraviolet and shortwave infrared bands. Optics Express 2023, 31, 6805–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, X.; Luo, Q.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, E.; Cheng, R.; Fensholt, R.; Brandt, M. Mapping global lake dynamics reveals the emerging roles of small lakes. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Du, Y.; Lyu, L.; Du, J.; Shang, Y. Songhua River basin's improving water quality since 2005 based on Landsat observation of water clarity. Environmental Research 2021, 199, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Bi, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, F.; Lyu, H.; Dong, X.; Cai, X. Utilization of GOCI data to evaluate the diurnal vertical migration of Microcystis aeruginosa and the underlying driving factors. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 310, 114734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ani, C.J.; Baird, M.; Robson, B. Modelling buoyancy-driven vertical movement of Trichodesmium application in the Great Barrier Reef. Ecological Modelling 2024, 487, 110567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, L.; Tao, H.; Liu, G.; Fang, C.; Li, S.; Song, K. Re-estimating China's lake CO2 flux considering spatiotemporal variability. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology 2024, 19, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfield, C.K.; Wong, K.C. Mechanisms of sediment flux and turbidity maintenance in the Delaware Estuary. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011; 116. [Google Scholar]
- Uncles, R.; Elliott, R.; Weston, S. Observed fluxes of water, salt and suspended sediment in a partly mixed estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 1985, 20, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Abbreviations or symbols | Abbreviations or symbols | ||
| ABs AFAI AC CNKI Chla CDOM CBI DOC FAC FLH GABI GLI GLIMR HABs IEEE T-GRS ICWs JAG Int J Remote Sens ISPRS LCI MERIS MODIS NASA NIR NPP NDVI NRTI |
Algal blooms Alternative floating algae index Atmospheric correction China National Knowledge Infrastructure Chlorophyll a Colored dissolved organic matter Cyanobacterial bloom intensity Diffuse attenuation coefficient Dissolved organic carbon Floating algae cover Fluorescence line height Generalized algal bloom index algorithm Generation Global Imager Geostationary Littoral Imaging and Monitoring Radiometer Harmful algal blooms IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING Inland and coastal waters International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation International Journal of Remote Sensing ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Linear Combination Index Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer Instrument Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer National Aeronautics and Space Administration Near-infrared Net primary production Normalized difference vegetation index Normalized red tide index |
OSMI OE POC PC RF RI RS RSE Sci Total Environ SIA SIT SSCs SSS SDD SGLI SWIR SZA SPM SCI GOCI UV VIIRS WR YRE YOC |
Ocean Scanning Multispectral Imager Optics EXPRESS Particulate organic carbon Phycocyanin Random forest Rayleigh-corrected radiance Red tide index Remote sensing Remote Sensing of Environment Remote sensing reflectance Science of the Total Environment Sea ice area Sea ice thickness Sea surface currents Sea surface salinity Secchi disk depth Second Generation Global Imager Shortwave infrared Solar zenith angle Suspended particulate matter Synthetic chlorophyll index The Geostationary Ocean Color Imager Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Water Research Yalu River estuary Yellow and East China Sea Ocean Color |
| Number | Data | Spatial Resolution (m) | Temporal Resolution | Launched Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
CZCS SeaWiFS MODIS_TERRA MODIS_AQUA VIIRS Suomi NPP VIIRS NOAA-20 VIIRS NOAA-21 MERIS Sentinel-3A OLCI Sentinel-3B OLCI ADEOS ADEOS-Ⅱ SGLI HY-1A HY-1B HY-1C HY-1D HY-1E Oceansat-1 Oceansat-2 Oceansat-3 OSMI GOCI |
1000 1100,4500 250,500,1000 250,500,1000 375,750 375,750 375,750 300,1200 300 300 700 250,1000 250 250 250 250 250 100 360 360 360 1000 500 |
One day One day One day One day One day One day One day Three days <Two days <Two days Ten days Four days One day Three days/Seven days One day/Seven days One day/Three days One day/Three days One day/Three days Two days Two days One day/Three days Three days One hour |
1978 1997 1999 2002 2011 2017 2021 2002 2016 2018 1996 2002 2017 2002 2007 2018 2022 2023 1996 2009 2022 1999 2010 |
|
| 24 | GOCI-II | 250 | One hour | 2020 | |
| Bands | Center Wavelength/nm | Band Width/nm | Spectrum Type | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 |
412 443 490 555 660 680 745 865 |
20 20 20 20 20 10 20 40 |
VIS VIS VIS VIS VIS VIS NIR NIR |
1077 1199 1316 1223 1192 1093 1107 1009 |
| Band | Wavelength/nm | Bandwidth/nm | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9 B10 B11 B12 B13 |
380 412 443 490 510 555 620 660 680 709 745 865 PAN |
20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 10 10 20 40 483 |
CDOM CDOM, Chla Chla absorption maximum Chla, other pigments Chla, absorbing aerosol in ocean waters Turbidity, SPM Detect phytoplankton species Baseline of fluorescence signal, Chla, SPM Fluorescence signal Fluorescence base signal, AC, SPM AC, vegetation index AC, aerosol optical depth / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




