1. Introduction
Burn injuries represent a significant global health issue, disproportionately affecting pediatric populations in the African region. Worldwide and in the Pan-American area, they rank as the third leading cause of accidental injury and death in children aged 1 to 4 years, and the second in Europe, highlighting the critical need for effective burn care strategies [
1]. Children’s unique physiological attributes, including their thinner skin and the rapid growth phase, exacerbate the risk of deep tissue damage, protracted healing, and significant scarring from burn injuries [
2]. Among combustions, partial-thickness (II/1) burns are characterized by the damage of both the epidermis and the papillary layer of the dermis, necessitating an intricately balanced approach to care [
3,
4]. These injuries not only demand acute medical intervention to facilitate wound closure but also a holistic strategy to address potential functional, esthetic, psychological, and social impacts, underscoring the complexity of pediatric burn management [
5].
Historically, the treatment of burns, particularly in children, has focused on preventing infection and promoting healing, due to their vulnerability to pathogens and the catastrophic consequences of infections in burn wounds. Traditional agents include silver sulfadiazine (SSD) and iodine-based products, which have been staples in burn care [
6,
7]. However, concerns over toxicity, resistance, and healing impairment have driven the search for alternative remedies. Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (Polyhexanide or PHMB in short) is a polymer-based, broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent. PHMB consists of repeating basic biguanide units linked by hexamethylene hydrocarbon chains, resulting in a cationic and amphipathic structure, which has garnered attention for its potential to alter burn care. Notably, PHMB exhibits potent activity against a plethora of pathogens including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida albicans, positioning it as a key instrument in combating wound infections - a prevalent complication of that can significantly delay healing processes [
8]. Furthermore, there is minimal evidence of resistance development against PHMB, making it a sustainable option for long-term use in healthcare settings [
9].
In exploring strategies to address infection control and mitigate antimicrobial resistance, it is important to consider the mechanisms through which drugs exert their effects. A body of research has focused on the PHMB, investigating its ability to preferentially target bacteria over host cells. Contrary to the conventional understanding that PHMB disrupts microbial membranes [
10], a study has revealed its capability to penetrate bacterial cells, leading to inhibited cell division and DNA condensation [
11]. Therefore, it proposes an alternative mechanism of antimicrobial action, potentially involving DNA interaction. Further analysis demonstrated that PHMB forms nanoparticles upon interaction with bacterial chromosomal DNA, and its bacterial growth inhibitory effects can be attenuated by co-application with the DNA-binding agent Hoechst 33258, supporting the notion of a DNA-targeted antimicrobial mechanism. Interestingly, while PHMB is capable of entering mammalian cells, it appears to be sequestered within endosomes and prevented from accessing the nucleus, highlighting a differential impact on bacterial versus mammalian DNA [
11].
These previous findings accentuate a distinct antimicrobial mechanism by which PHMB selectively interacts with and condenses bacterial chromosomes. Particularly, the absence of reported resistance to PHMB suggests this mechanism could represent a promising avenue for antimicrobial development, circumventing common pathways of resistance [
8,
11]. Beyond its germicide properties, it has been observed to support wound healing, possibly through establishing moist microenvironments and minimizing inflammation [
12,
13]. Lastly, PHMB can be incorporated into various forms, such as gels, solutions, creams, and impregnated dressings, allowing for flexible application based on the wound's needs. On a side note; it is also frequently utilized as a hot tub and swimming pool algicide, although, chlorine might be a superior disinfectant for water [
14].
While PHMB is promising, comprehensive studies specifically targeting pediatric burn patients are somewhat limited, necessitating cautious extrapolation of data from adult and in vitro studies [
15,
16]. Although generally well-tolerated, PHMB can cause allergic contact dermatitis in some individuals, therefore, monitoring and patient-specific considerations are crucial [
17]. PHMB's use in certain jurisdictions may face regulatory limitations or require specific approvals, impacting its availability and usage in pediatric burn care. Depending on the healthcare setting, the cost of PHMB formulations compared to traditional interventions may ultimately affect its adoption and widespread use.
Scientific literature, while affirming PHMB's antimicrobial prowess, seldom ventures into its direct implications on healing timelines or how it influences critical outcomes such as scar formation, functional impairment, or pain management. Moreover, the interaction of PHMB with patient-specific factors—age, Total Body Surface Area (TBSA) affected, frequency of dressing changes, and the interval between injury occurrence and treatment commencement—remains underexplored. These factors are pivotal in the context of pediatric burns, where they can significantly dictate the trajectory of healing and recovery. For instance, the TBSA affected by burns, a critical measure of burn severity, has been directly linked to the risk of infection and length of hospital stay, thereby indirectly affecting healing outcomes.
Addressing this knowledge gap, our study embarks on a comprehensive evaluation of PHMB’s efficacy in pediatric II/1 burn management. We aim to scrutinize its influence on the time to reepithelialization (TTRE), a primary metric of healing while dissecting how this influence is modulated by intrinsic patient metrics and wound characteristics. Through this inquiry, we aspire to illuminate the multifaceted role of PHMB in pediatric burn care, extending beyond its antimicrobial function to encompass its contributions to overall healing efficacy, safety profile, and compatibility with broader treatment strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
This retrospective multi-center cohort study was conducted in accordance with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines [
18]. The research setting was two Hungarian tertiary pediatric burn units (at the Universities of Pécs and Szeged), recognized for their comprehensive burn care and rehabilitation services. The study period spanned from 17 October 2023 to 15 February 2024, allowing for the evaluation of short-term and intermediate healing outcomes.
2.2. Participants
The cohort comprised 27 pediatric patients, aged 1 to 13 years, diagnosed with II/1 partial-thickness burns covering between 1 and 10% TBSA. Half of the patients were admitted in Pécs and the other half in Szeged. Inclusion criteria were: (1) patients’ age below 18 years, (2) confirmed diagnosis of II/1 burns, (3) treatment initiation within 24 hours of injury, and (4) consent for PHMB application. Exclusion criteria included (1) known hypersensitivity to PHMB, (2) presence of full-thickness burns, (3) receiving skin grafts, (4) missing photo-documentation, (5) absence on follow-up examinations before complete healing, (6) and concurrent injuries or diseases requiring systemic interventions.
2.3. Intervention
All participants received sterile, preserved 0.04% PHMB gel (LAVANID® 2, SERAG-WIESSNER, Naila, Germany) topical application as part of their wound care regimen. The treatment protocol entailed cleaning the wound with sterile saline, and bullectomy, followed by PHMB application and dressing with a versatile wound contact layer. We utilized a woven cotton paraffine-impregnated net (Grassolind®, HARTMANN GROUP, Heidenheim, Germany), or a similarly paraffine-impregnated, fine-meshed gauze, containing 0,5 % chlorhexidine as well (Bactigras®, Smith+Nephew, Watford, England, UK). They are capable of covering large body surfaces without causing hypersensitive reactions. Adjunct medications, including analgesia with a synthetic opioid; 0.1-0.2 mg/kg nalbuphine injection (Nubain, ALTAMEDICS GmbH, Cologne, Germany), and sedation with midazolam (Dormicum, Egis Gyógyszergyár Zrt, Budapest, Hungary) were administered based on clinical indications and parental consent.
2.4. Outcome Measures
TTRE was the primary endpoint, defined as the number of days from injury to the wound's closure. Complete wound closure was defined as a new, continuous, shiny, layer of epithelium developing on the wound’s entire surface. Secondary outcomes included the incidence of wound infections, the number of dressing changes (therefore, to get the total amount of dressings applied, the initial dressing has to be added to the number of reapplications), length of hospital stay (LOS), and any reported complications. Patient and wound metrics—age, sex, burn-affected TBSA, the depth, location, and severity of combustions, time since injury, and prehospital treatments—were meticulously recorded during the first meetings and summarized in Microsoft Excel 2021 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). Injuries and their healing progression were photo-documented on the initial and each follow-up examination. No data point was missing for any of the included patients.
2.5. Statistical Evaluation
Descriptive statistics were calculated for all endpoints using means, standard deviations (SD), medians, interquartile ranges (IQR), 25th percentiles (IQR25), 75th percentiles (IQR75), counts, and ranges. Correlations were calculated via Pearson’s coefficient. Statistical comparison was conducted with Chi2- and Fischer’s Exact tests (in cases of discrete variables) and Mann-Whitney U test (when analyzing continuous outcomes) using Python 3.9.16. with numpy, pandas, and scikit-learn libraries. Differences were deemed significant when p ≤ 0.05. For the burn localization analysis, Kruskal-Wallis tests were used, due to non-normal distribution and small sample sizes. Linear regression, random forest, and deep learning models were trained to predict TTRE, utilizing Pytorch 2.0. Their efficacy was validated by mean squared errors (MSE) which indicates the average squared difference between the estimated values and the actual value of TTRE, with a lower MSE representing a better fit. Additionally, the R² score, which can range from -∞ to 1, provides a measure of how well the observed outcomes are replicated by the model, based on the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model.
3. Results
Our study ventured on a meticulous examination of 27 pediatric patients - 14 managed at Pécs and 13 at Szeged, Hungary - treated with PHMB for II/1 burns. This cohort was characterized by a male-predominant gender distribution (66% male, 33% female) and an age range from 1 to 13 years (mean: 3.74, SD: 4.73), similar to international reports [
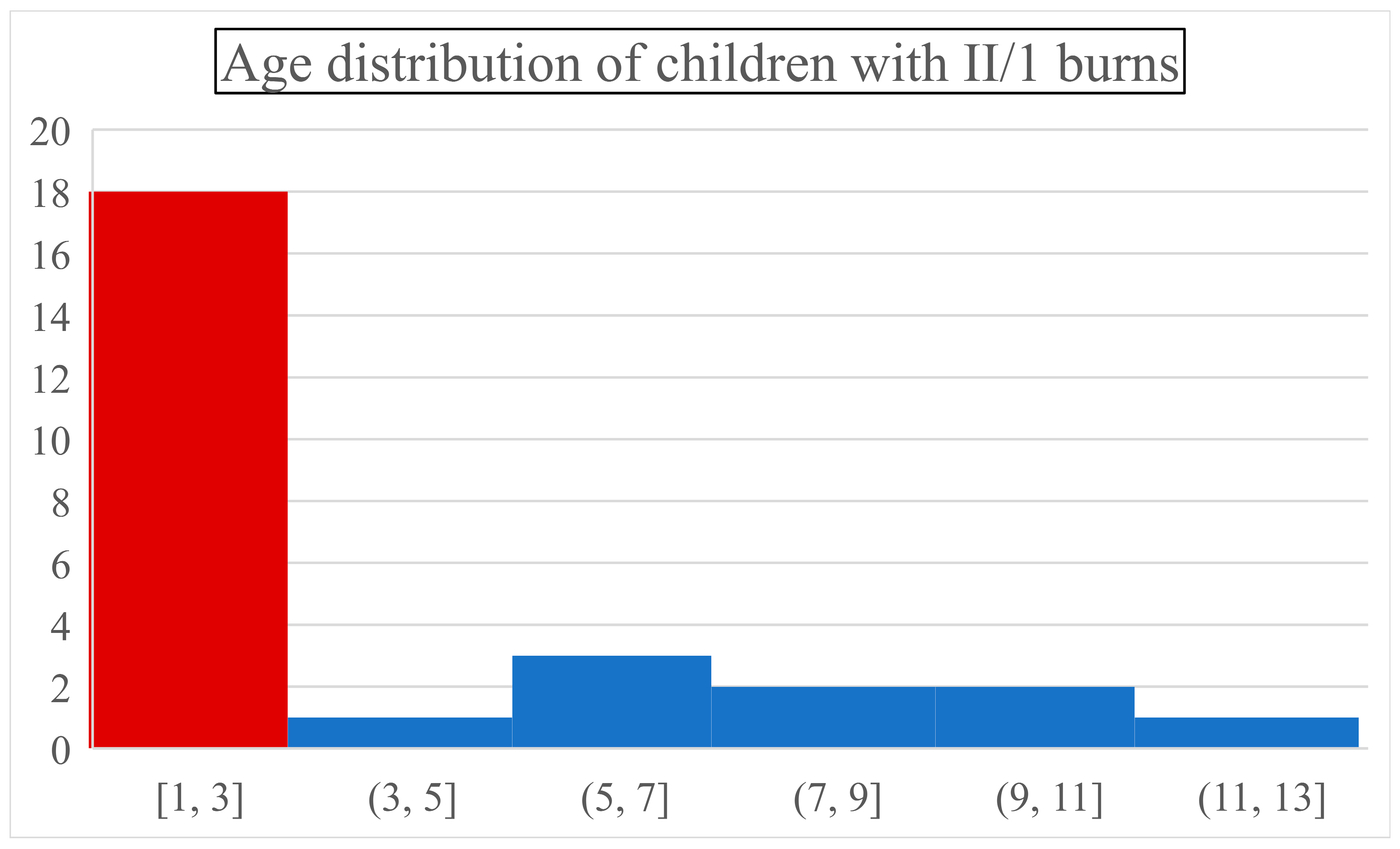
1]. An important observation was that combustion incidence peaked in infants (44% were ≤ one-year-olds) and toddlers (two and three-year-olds together represented 22% of children). Below the age of three, a child was around nine times more likely to suffer a thermal injury than in any upcoming 3-year interval (
Figure 1.). After the first three critical years (66% of all cases), the incidence dropped drastically and became steady.
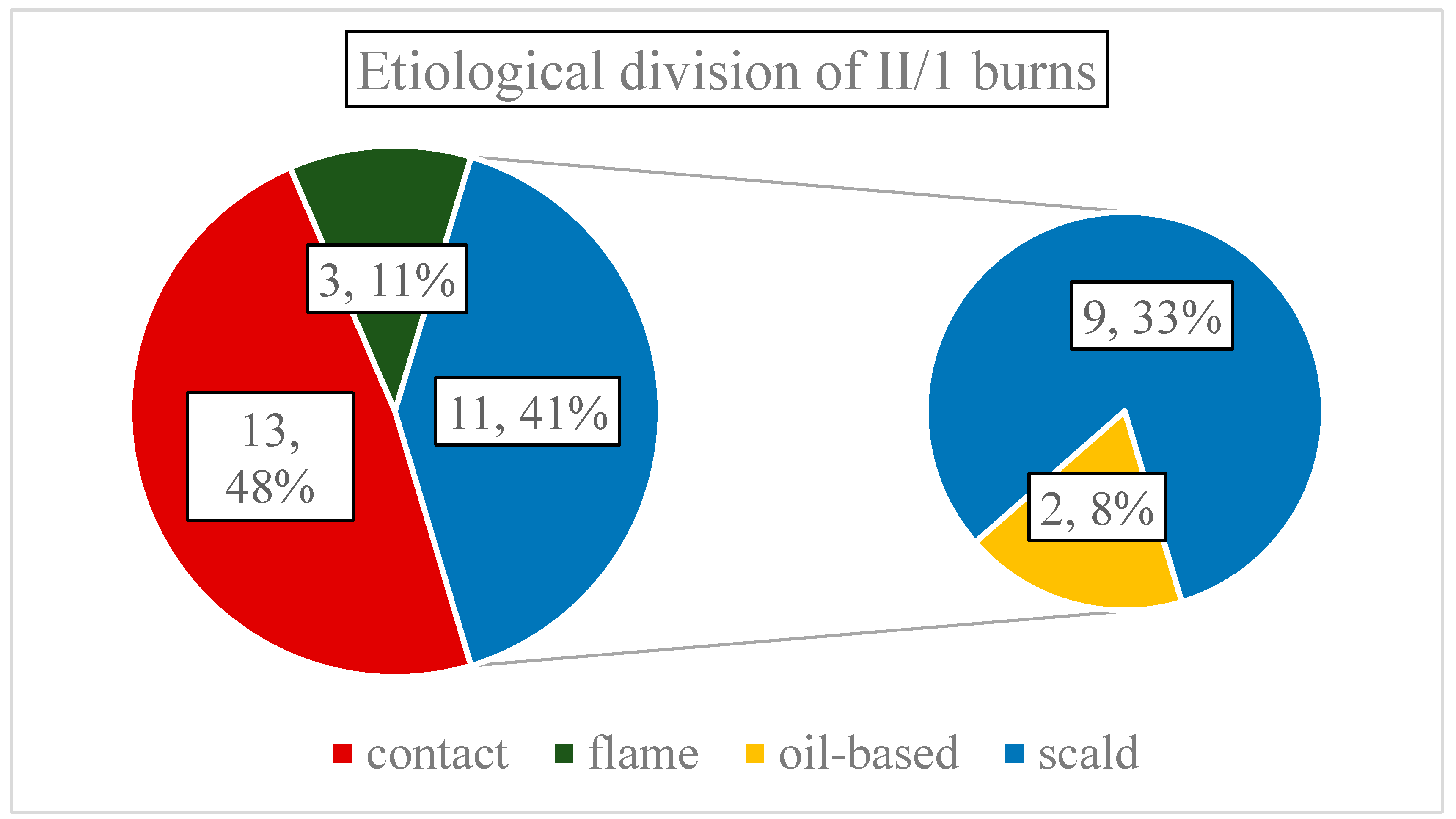
Average surface of thermal wounds was 2.87% TBSA (SD:1.33, range: 1-7.5%), and etiologically distributed as follows: 13 contact- (48.15%), 11 scalding- (40.74%), and three flame injuries (11.11% of all cases) (
Figure 2.). Scalding-type burns were oil-based two times. It is important to mention that only two patients had larger than 5% TBSA injuries, therefore, most burns were small in area. Regarding depth, a single combustion was classified as mixed depth - containing small islands of deep partial-thickness (II/2) burns, penetrating the reticular dermis - the rest were solely II/1.
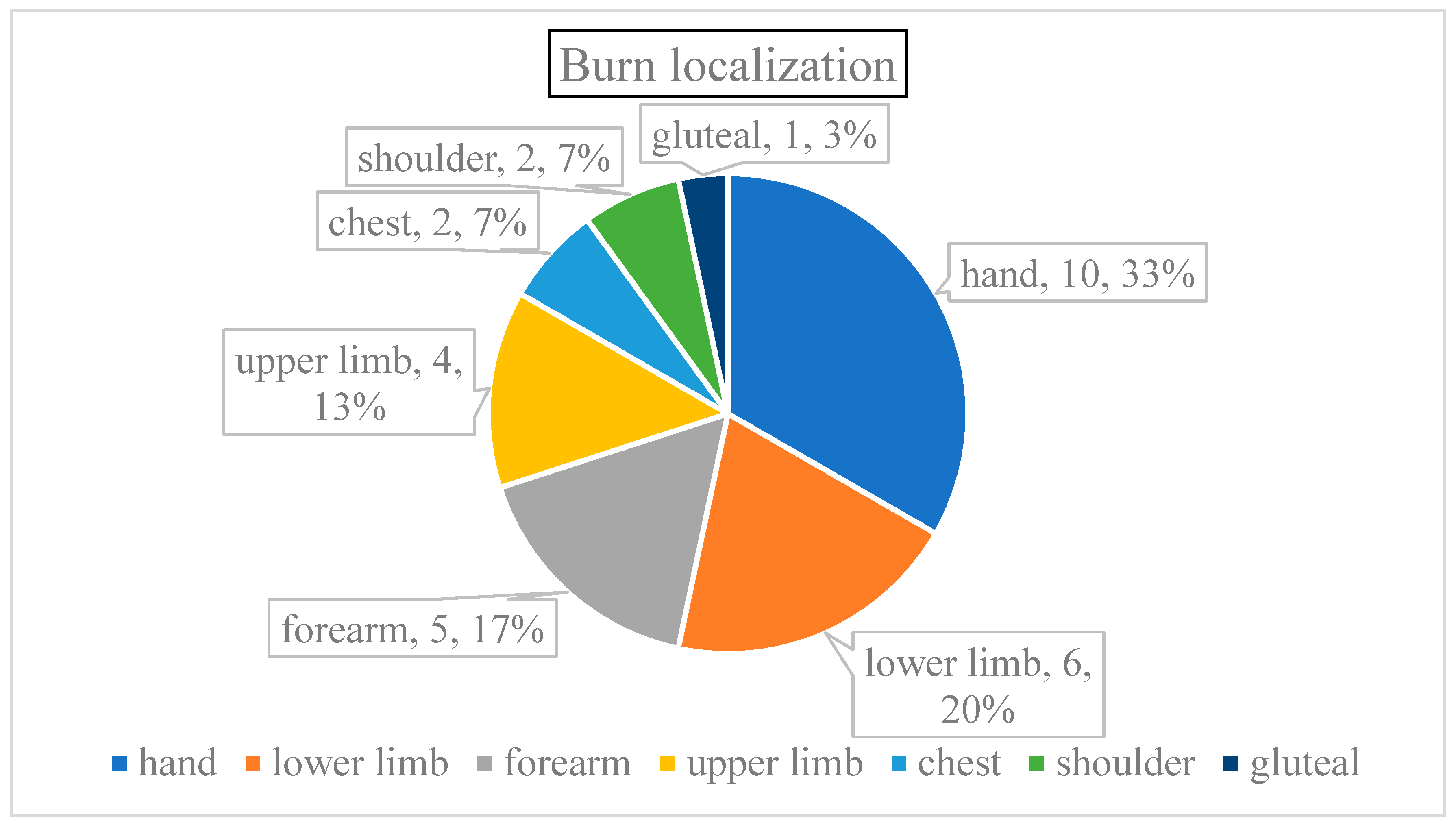
Burn localization was more varied. Six patients had multiple regions damaged (22.22% of all cases); the burn affected both upper and lower limbs of four patients and the chest was injured along with a shoulder in two children (
Figure 3). The majority of injuries involved the upper limb (70% of all cases), especially the hands (46% of each scenario), followed by the incidence on the lower extremities (23%), and lastly, the trunks (7%).
Prehospital management can be summarized by discussing the time elapsed between the injury and hospital arrival, which averaged 3.48 hours, caused by a few outliers. Consequently, median and IQR25 times were both one hour with an IQR75 of 3.5 hours, skewing the distribution left, and generally towards rapid transit times. However, prehospital cold therapy (running water or cooling gels) was only applied in four out of five cases (81.5% received it) while any kind of analgesia was only administered for every third child (33.3% got painkillers). Regrettably, the absence of prehospital care negatively correlated with age, therefore most children who did not receive any intervention were below three years old. Cold treatment was only skipped in children under two years (mean age: 1.2 years) and while protocols generally lacked pain management, those who received it were also older (mean age of 5 years) compared to untreated patients (mean age of 3.1 years).
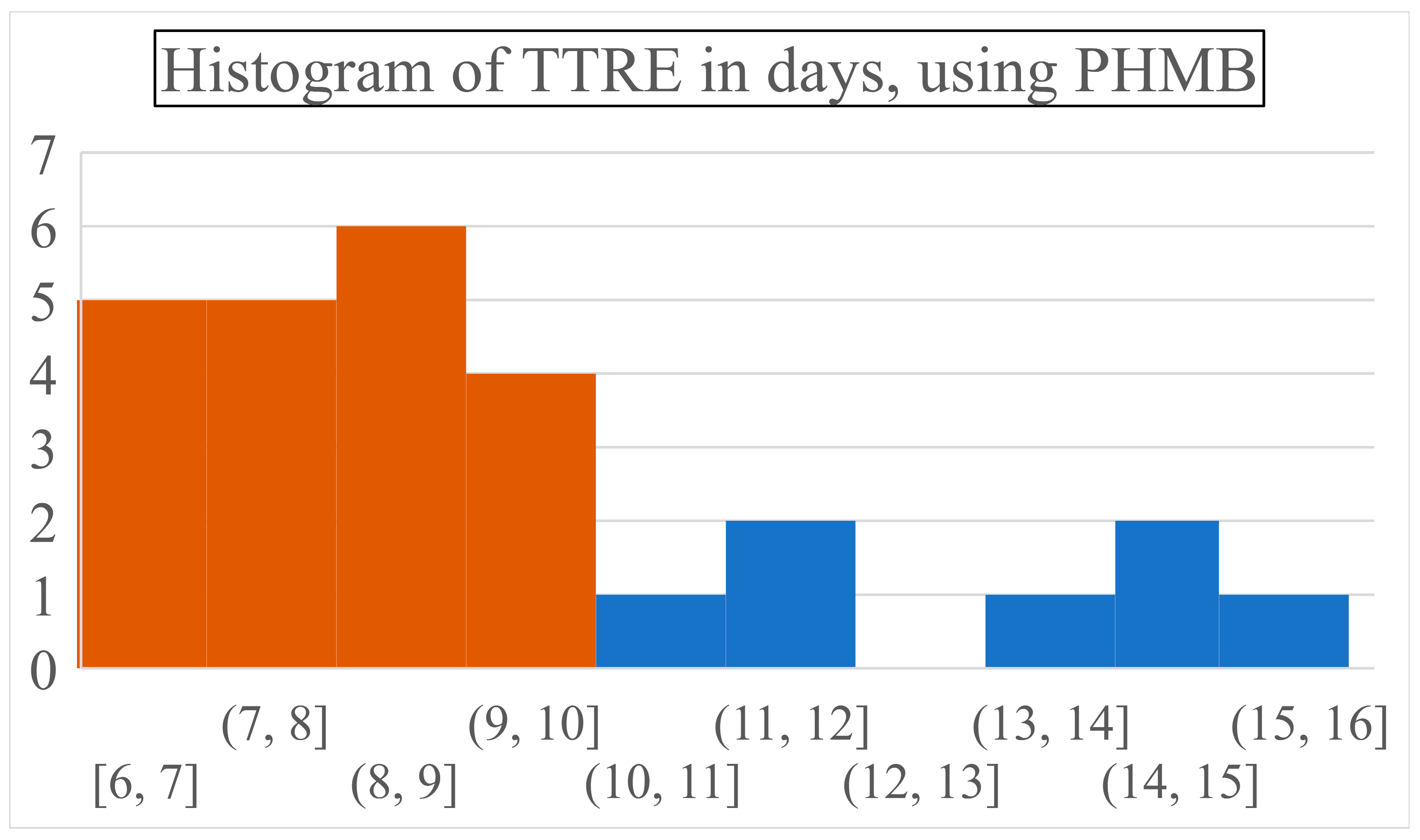
PHMB required 8.78 days to achieve complete wound closure (SD: 2.64, range: 6-15 days) while necessitating 2.37 dressing changes on average (SD: 1.6, range: 1-6 times) (
Figure 4).
Most patients healed between the 6
th and 9
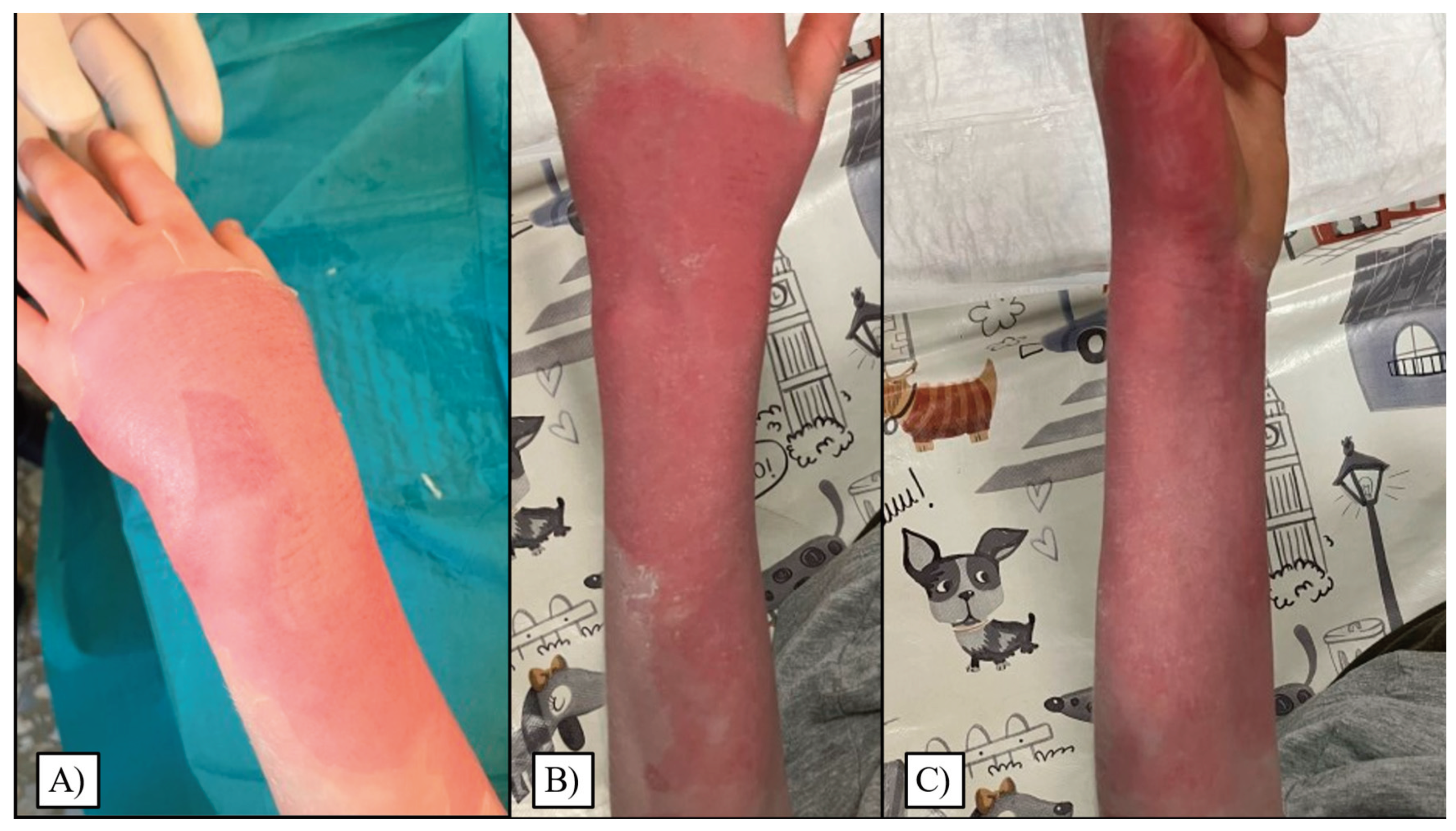
th days, with around 18% of children recovering on each of these days. On later days, again steadily, approximately 5% of patients recuperated entirely. Visual representations of the most common wound site after injury, and subsequent to reepithelialization can be seen in
Figure 5.
Moreover, distinct etiologies governed wound closure times as well, which in turn were directly linked to different age groups. Contact burns were most prevalent, primarily in the youngest (median age: 1, range: 1-8 years), who regenerated at the fastest rate (TTRE: 8.08, SD: 1.71, range: 6-11 days). Injuries via scalding were next in chronological and incidence order – albeit they presented the widest age range (median age: 3, range: 1-13 years) and reepithelialization distribution (TTRE: 9.36, SD: 3.17 range= 6-15 days). Least frequent were the flame wounds (median age: 8, range: 6-10) with marginally the most extended healing (TTRE: 9.67, SD: 4.04 days, range: 6-14 days).
Prolonged healing times reasonably correlated with more dressing changes (r=0.706), larger burned TBSA% (r=0.626), and longer LOS (r=0.463) the most. Older age was also slightly associated with prolonged recovery (r=0.302). Remarkably, delayed intervention had only minimal impact on healing times (r=0.249). Localization also affected recuperation times, although not significantly (p=0.081). Fascinatingly, while the healing time of the hands and the whole upper limb healed quite fast, (mean TTRE: 7.60 and 7.75, respectively), when only the forearm was injured, it required 10.4 days on average to regenerate. While the trunk and shoulders took similar times to reepithelialize (8 and 7.5 days, respectively), the lower limbs’ recuperation took noticeably longer time (average TTRE: 11.43 days).
A linear regression model developed to predict TTRE, based on factors like age, sex, TBSA affected, transport time, and the prehospital usage of cold therapy or analgesia produced the following evaluation metrics: MSE: 3.017 and R²: -0.358. In this case, a negative R² value suggests that the simulation did not effectively capture the variability in TTRE, highlighting the complexity of predicting healing times based solely on the variables provided. Furthermore, additional, more sophisticated models were trained and deployed, although, performed inferior on this task (random forest MSE: 3.68, R²: -0.66; deep learning model MSE: 4.93, R²: -1.22).
Captivatingly, three instances of significant difference were found between patients who received analgesia and those who did not. Paradoxically, analgesia seemed to prolong healing times (TTRE was 11.33 days for those who received it as opposed to 7.5 days for those who did not, with a p-value of 0.0005) along with increasing dressing changes (n= 3.66 vs 1.72 times, p = 0.0077). However, these last two observations can probably be explained by the significant difference in their mean TBSA (3.61 vs 2.50 %, p=0.0474), further emphasizing the role of surface area as a burn regeneration influencing factor.
Lastly, LOS was 0.96 days on average (SD: 1.73, range 0-7 days). However, it is important to mention that only six children (22% of the cohort) spent the night at the hospitals, therefore, most of the patients could be treated in an ambulatory manner. Admissions were necessary due to larger than 5% TBSA burns, mixed depth injury, or social reasons. No complications were reported or observed during the study.
An extensive collection of study metrics can be assessed in
Table 1.
4. Discussion
In this comprehensive analysis, our study systematically investigated the effectiveness of PHMB in treating II/1 burns among a pediatric cohort of 27 patients from two Hungarian medical centers. This research offers a profound insight into the demographic distribution, etiology, and treatment outcomes associated with pediatric burns, reflecting a noteworthy male predominance (2 out of 3 patients were boys) and a notable susceptibility in children aged three years and below to thermal injuries (approximately 9 times higher frequency than other age groups). The incidence peak in infants and toddlers underscores a critical need for heightened awareness and preventive strategies in this vulnerable age interval. Male predisposition is attributed to higher activity levels and risk-taking behavior. Our finding aligns with broader patterns observed in burn statistics worldwide [
19,
20].
Our findings elucidate the predominance of contact burns, accounting for half of the injuries, followed by scalding and flame injuries, with the observation that scalding burns were predominantly water-based. Despite the varying etiologies, the majority of burns were minor in terms of TBSA affected, suggesting that most incidents involved limited exposure to the causative agent. In terms of initial care, the study revealed that while the majority were promptly treated with cold therapy, only a third received analgesia prior to hospital admission, suggesting an area for potential improvement in early burn care protocols. This discrepancy also raises considerations about the standardization and accessibility of prehospital care for pediatric burn victims, particularly the youngest who are most at risk. Targeted educational programs for parents and caregivers, focusing on the most common mechanisms of burns in this population, could considerably reduce the incidence of pediatric burns.
Through our review of wound healing dynamics under PHMB treatment, an average of 8.78 days was observed for complete wound closure, with a direct correlation between longer healing times and the number of dressing changes, as well as the percentage of TBSA affected. Associations between older age and prolonged recovery, although slight, along with the minimal impact of delayed intervention on healing times, present intriguing avenues for further investigation into the biological and environmental factors influencing burn recovery. As most patients could be treated ambulatory, a remarkably short 0.96 days of average LOS was required to treat the children. Minimal hospitalization alleviates children’s distress associated with the medical environment, reduces their risk of hospital-acquired infections, and liberates medical staff and resources. Its efficiency in healing, devoid of any reported complications, presents PHMB as a viable alternative to traditional treatments, which have often been criticized for their cytotoxicity and potential to postpone wound healing [
6].
Complexities of predicting healing times were highlighted by the challenges encountered in developing an effective linear regression model, as evidenced by negative R-squared values in our predictive analyses. Consequently, this accentuates the multifaceted nature of burn healing, which may not be fully captured through conventional statistical models. Interestingly, analgesia administration was associated with longer healing times and an increased number of dressing changes, a finding that, while seemingly paradoxical, may reflect more severe burns among recipients necessitating more intensive treatment. Therefore, this observation prompts a deeper inquiry into the relationship between pain management strategies and wound-healing processes in pediatric burn patients.
Lastly, the absence of complications reported in our study is encouraging but also warrants a broader review of the long-term outcomes of PHMB-treated burns. It is necessary to investigate how these children fare in terms of scar formation, functional mobility, and psychological impact compared to those treated with traditional methods.
When juxtaposed with literature on SSD and other alternatives, PHMB's attributes—broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, low cytotoxicity, and a favorable profile for wound healing—suggest its potential as a superior option in specific contexts of pediatric burn care [
21]. In contrast, SSD needed 14.74 days using a weighted average (mean ranges: 12.75-16 days) when applied to similar-depth injuries- although, the authors did not report TBSA in these trials [
22,
23]. Additionally, hydrofiber dressings [
22], hydrogels [
23], biosynthetic porcine xenografts, and hydrocolloid coverings [
24] required 14.0, 12.42, 12.24, and 11.21 days for reepithelialization on average, respectively. Zinc-hyaluronan gel achieved slightly superior results to PHMB, requiring only 7.9 days for wound closure, however, it was only applied to the facial region, which has enhanced capillarization and regenerative capabilities [
25]. Nevertheless, the broader adoption of PHMB necessitates further investigation, particularly in direct comparison to these traditional agents, to understand its place fully within the spectrum of burn treatments.
Limitations of our study, including its small sample size and the observational design, necessitate cautious interpretation of the results. The potential for selection bias and the inability to establish causality highlight the need for larger, randomized controlled trials to validate our findings and explore the mechanistic underpinnings of PHMB's efficacy in burn management. Future research should aim to expand the demographic and etiological spectrum of pediatric burn patients studied, incorporating a broader range of burn severities in addition to sizes and therapeutic modalities. Additionally, investigating the long-term outcomes of PHMB treatment, including scar formation and functional impairment, will be crucial in comprehensively evaluating its role in pediatric burn care.
In summary, this study sheds light on significant aspects of pediatric burn injuries and their management, presenting PHMB as a promising agent in the therapeutic arsenal. However, it also lays bare the complexities of burn care in children, urging further exploration into optimized treatment protocols, prehospital care standardization, and the intricacies of wound healing. Through continued research and innovation, we can aspire to significantly improve outcomes for pediatric burn victims, paving the way for more effective, tailored approaches to burn prevention and care.
5. Conclusions
Our study underscores PHMB's potential in pediatric burn care, showcasing its swift efficacy in wound closure with minimal need for dressing changes (2.37 times) and remarkably short hospital stays (0.96 days) on average. Mean wound closure times utilizing PHMB were approximately 8.78 days, with healing times extending with larger burn sizes and older age. Intriguingly, analgesia administration was associated with longer healing periods and more dressing changes, suggesting a complex interplay between pain management and wound healing. It also unearthed a stark demographic trend: children under three face the highest risk of burn injuries, spotlighting an urgent need for targeted prevention. Another concerning discovery was the inconsistent prehospital care, particularly the scarce use of cold therapy or analgesia immediately post-injury in infants and toddlers. Advocacy for comprehensive educational initiatives emerges, aimed at arming caregivers and responders with essential skills for immediate burn treatment.
PHMB distinguished itself by facilitating healing without complications, challenging the status quo of traditional, sometimes cytotoxic, interventions. The research also beckons further exploration into PHMB's long-term impact compared to conventional methods. Ultimately, our investigation demands a holistic overhaul in pediatric burn management, combining prevention, prompt initial treatment, and innovative care strategies to safeguard our youngest and most vulnerable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.J., A.L., and T.Z.K.; methodology, A.G., A.G.L., A.L., H.N., and K.A.T.; software, A.L., and H.N.; validation, A.G., A.G.L., A.L., G.J., K.A.T., and T.Z.K.; formal analysis, A.G.L., A.L., and H.N.; investigation, A.G.L, G.J., K.A.T., and T.Z.K.; resources, J.G. and T.Z.K..; data curation, A.G.L., A.L., H.N., and K.A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A.; writing—review and editing, A.G., A.G.L., A.L., G.J., H.N., K.A.T, and T.Z.K.; visualization, H.N., A.G.L., and A.L.; supervision, A.G., G.J., K.A.T., and T.Z.K.; project administration, A.G., A.G.L., G.J., K.A.T., and T.Z.K.; funding acquisition, A.G., G.J., and K.A.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Surgical Division, Department of Pediatrics, Medical School, University of Pécs on November 21, 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient’s guardians to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
All data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adeloye, D.; Bowman, K.; Chan, K.Y.; Patel, S.; Campbell, H.; Rudan, I. Global and Regional Child Deaths Due to Injuries: An Assessment of the Evidence. J. Glob. Health 8, 021104. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.J. Skin. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, T.J.; Szymanski, K.D. Burn Evaluation and Management. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, R.; Sato, T.T. Initial Assessment and Management of Thermal Burn Injuries in Children. Pediatr. Rev. 2013, 34, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Rodríguez-Mercedes, S.; Grant, G.; Rencken, C.; Kinney, E.; Austen, A.; Hou, C.; Brady, K.; Schneider, J.; Kazis, L.; et al. Physical, Psychological, and Social Outcomes in Pediatric Burn Survivors Ages 5 to 18 Years: A Systematic Review. J. Burn Care Res. 2021, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadrup, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Loeschner, K. Toxicity of Silver Ions, Metallic Silver, and Silver Nanoparticle Materials after in Vivo Dermal and Mucosal Surface Exposure: A Review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2018, 98, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyneman, A.; Hoeksema, H.; Vandekerckhove, D.; Pirayesh, A.; Monstrey, S. The Role of Silver Sulphadiazine in the Conservative Treatment of Partial Thickness Burn Wounds: A Systematic Review. Burns J. Int. Soc. Burn Inj. 2016, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rippon, M.G.; Rogers, A.A.; Ousey, K. Polyhexamethylene Biguanide and Its Antimicrobial Role in Wound Healing: A Narrative Review. J. Wound Care 2023, 32, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessels, S.; Ingmer, H. Modes of Action of Three Disinfectant Active Substances: A Review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 2013, 67, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Ledwith, A.; Bamford, C.H.; Hann, R.A. Interaction of a Polymeric Biguanide Biocide with Phospholipid Membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1984, 769, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chindera, K.; Mahato, M.; Kumar Sharma, A.; Horsley, H.; Kloc-Muniak, K.; Kamaruzzaman, N.F.; Kumar, S.; McFarlane, A.; Stach, J.; Bentin, T.; et al. The Antimicrobial Polymer PHMB Enters Cells and Selectively Condenses Bacterial Chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, G.D.; Cavorsi, J.P.; Lee, D.K. Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB): An Addendum to Current Topical Antimicrobials. Wounds Compend. Clin. Res. Pract. 2007, 19, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical Impact Upon Wound Healing and Inflammation in Moist, Wet, and Dry Environments. | Semantic Scholar. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Clinical-Impact-Upon-Wound-Healing-and-Inflammation-Junker-Kamel/71a7f1dac6eba2349c0f31bf6b31884fa9dcf22d (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Romanowski, E.G.; Yates, K.A.; O’Connor, K.E.; Mah, F.S.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Kowalski, R.P. The Evaluation of Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (PHMB) as a Disinfectant for Adenovirus. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatkowski, A.; Drummer, N.; Andriessen, A.; Ulrich, D.; Pallua, N. Randomized Controlled Single Center Study Comparing a Polyhexanide Containing Bio-Cellulose Dressing with Silver Sulfadiazine Cream in Partial-Thickness Dermal Burns. Burns J. Int. Soc. Burn Inj. 2011, 37, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnich, K.E.; Stolarick, R.; Wilkins, R.G.; Chilson, G.; Pritt, S.L.; Unverdorben, M. The Effect of a Wound Care Solution Containing Polyhexanide and Betaine on Bacterial Counts: Results of an in Vitro Study. Ostomy. Wound Manage. 2012, 58, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sukakul, T.; Dahlin, J.; Pontén, A.; Antelmi, A.; Bruze, M.; Hamnerius, N.; Hauksson, I.; Isaksson, M.; Lejding, T.; Svedman, C. Contact Allergy to Polyhexamethylene Biguanide (Polyaminopropyl Biguanide). Contact Dermatitis 2021, 84, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolle, C.; Cambiaso-Daniel, J.; Forbes, A.A.; Wurzer, P.; Hundeshagen, G.; Branski, L.K.; Huss, F.; Kamolz, L.-P. Recent Trends in Burn Epidemiology Worldwide: A Systematic Review. Burns 2017, 43, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.; Gennaro, J.; von Saint Andre-von Arnim, A.; Stewart, B. Global Trends in Pediatric Burn Injuries and Care Capacity from the World Health Organization Global Burn Registry. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lőrincz, A.; Váradi, A.; Hegyi, P.; Rumbus, Z.; Tuba, M.; Lamberti, A.G.; Varjú-Solymár, M.; Párniczky, A.; Erőss, B.; Garami, A.; et al. Paediatric Partial-Thickness Burn Therapy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Life 2022, 12, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, D.M.; Foster, K.N.; Blome-Eberwein, S.A.; Twomey, J.A.; Herndon, D.N.; Luterman, A.; Silverstein, P.; Antimarino, J.R.; Bauer, G.J. Randomized Clinical Study of Hydrofiber Dressing with Silver or Silver Sulfadiazine in the Management of Partial-Thickness Burns. J. Burn Care Res. Off. Publ. Am. Burn Assoc. 2006, 27, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glat, P.M.; Kubat, W.D.; Hsu, J.F.; Copty, T.; Burkey, B.A.; Davis, W.; Goodwin, I. Randomized Clinical Study of SilvaSorb Gel in Comparison to Silvadene Silver Sulfadiazine Cream in the Management of Partial-Thickness Burns. J. Burn Care Res. Off. Publ. Am. Burn Assoc. 2009, 30, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, C.; St. Peter, S.D.; Lacey, S.; Beery, M.; Ward-Smith, P.; Sharp, R.J.; Ostlie, D.J. Biobrane versus Duoderm for the Treatment of Intermediate Thickness Burns in Children: A Prospective, Randomized Trial. Burns 2005, 31, 890–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lőrincz, A.; Lamberti, A.G.; Juhász, Z.; Garami, A.; Józsa, G. Management of Pediatric Facial Burns with Zinc-Hyaluronan Gel. Children 2022, 9, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).