Submitted:
23 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Analyze the relationship between dataset composition and both overall and ethnicity-specific model performance.
- Quantify the extent to which dataset rebalancing can mitigate bias in age estimation models.
- Determine whether dataset rebalancing alone is sufficient or if it should be combined with other bias mitigation techniques.
- Target bias: Biases inherent to the target subject, such as gender, ethnicity, makeup, and facial expression.
- Guess bias: Biases introduced by the people guessing the apparent age, which can be influenced by their own age and gender.
2. Materials and Methods
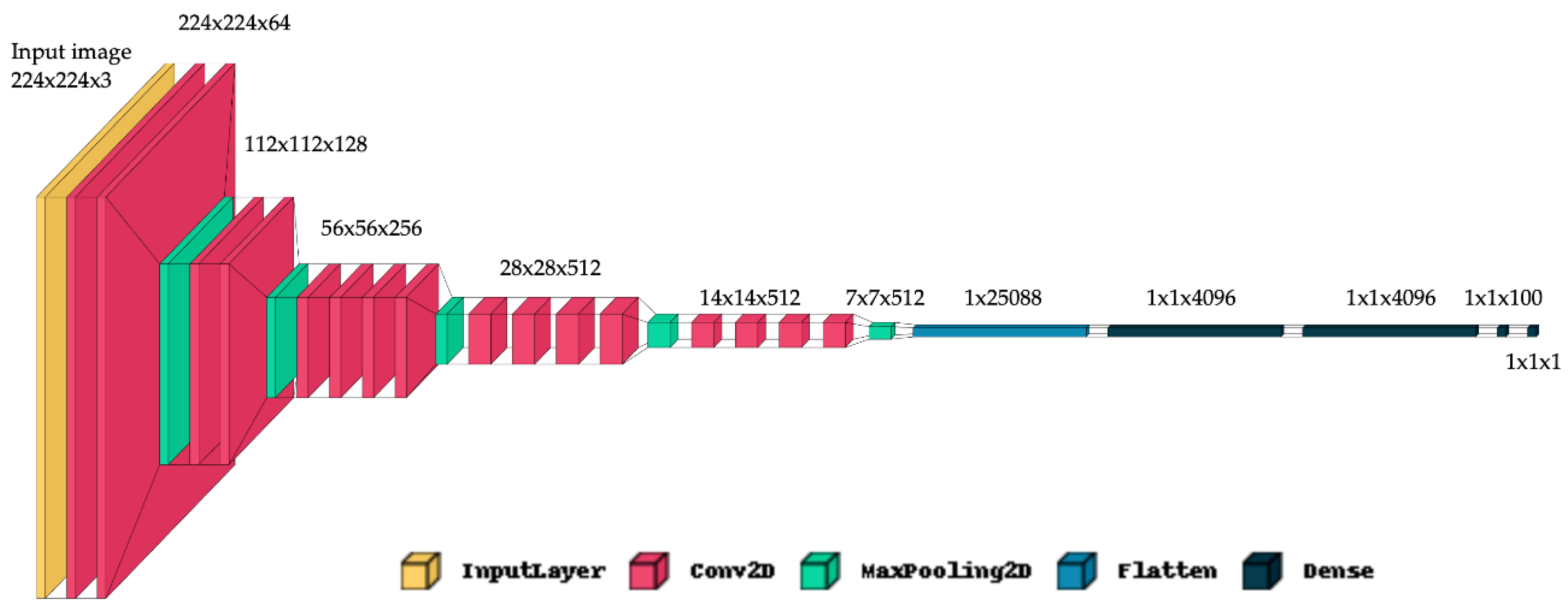
- VGG19 and ResNet50 are known for their deep architectures, allowing them to capture intricate features through multiple layers of convolutions. This depth can be advantageous in learning hierarchical representations of facial features relevant to age.
- MobileNetV2 is chosen for its efficiency and suitability for mobile and embedded applications, offering a balance between computational efficiency and performance, which is valuable for practical deployment scenarios.
- VGG16 offers a simpler architecture compared to VGG19 but still maintains strong performance in various computer vision tasks, making it a reliable benchmark in our comparative analysis.
- Learning Rate: Ranging from 0.1 to 0.000001, to find a balance between convergence speed and fine-grained model adjustments. Lower rates allow for finer adjustments during training, potentially leading to better generalization.
- Batch Size: Explored from 16 to 128, balancing between computational efficiency and gradient noise reduction. Larger batch sizes often accelerate training but can lead to poorer generalization compared to smaller batches.
- Number of Epochs: Explored from 30 to 100, considering the trade-off between model convergence and overfitting. More epochs may capture complex patterns but risk overfitting, especially with limited data.
3. Results
- represents the MAE for the j-th group (White, Black, or Asian).
- is the mean MAE across the three groups.
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michalski, D; Yiu, S. Y.; Malec, C. The Impact of Age and Threshold Variation on Facial Recognition Algorithm Performance Using Images of Children. Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics (ICB), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 20-23 Feb. 2018; 217-224.
- Srinivas, N.; Ricanek, K.; Michalski, D.; Bolme, D. S.; King, M. Face recognition algorithm bias: Performance differences on images of children and adults. Proceedings of the EEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, June 16-20, 2019.
- Albiero, V.; Bowyer, K. W. Is face recognition sexist? no, gendered hairstyles and biology are, arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.06989 2020.
- Albiero, V.; Zhang, K.; Bowyer, K. W. How does gender balance in training data affect face recognition accuracy. Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Houston, TX, USA, 2020; 1-10.
- Terhörst, P.; Kolf, J. N.; Huber, M.; Kirchbuchner, F.; Damer, N.; Moreno, A. M.; Fierrez, J.; Kuijper, A. A Comprehensive Study on Face Recognition Biases Beyond Demographics. IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society 2022, 3, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, P.; Bussche, A.V.D. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A Practical Guide, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 141–187. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, A. M.; Ricanek, K.; Patterson, E. A review of the literature on the aging adult skull and face: Implications for forensic science research and applications. Forensic Science International 2007, 172, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulu, R.; Tapamo, J. R.; Adewumi, A. O. Age estimation via face images: a survey. J. Image Video Proc. 2018, 2018, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, E.K.; Valliappan, R.; Patrick, T. Facial Age Estimation Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Overview. Big Data Cogn. Conput. 2022, 6, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Age Detection using Facial Images: traditional Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning, towardsdatascience.com. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/age-detection-using-facial-images-traditional-machine-learning-vs-deep-learning-2437b2feeab2 (Accessed on 18 Jun 2024).
- Andraz, P.; Vitomir, S.; Klemen, G. Analysis of Race and Gender Bias in Deep Age Estimation Models. Proceedings of the 8th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2021.
- Kimmo, K.; Jungseock, J. FairFace: Face Attribute Dataset for Balanced Race, Gender, and Age. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1908.04913 2019.
- Abdolrashidi, A.; Minaei, M.; Azimi, E. Age and Gender Prediction From Face Images Using Attentional Convolutional Network. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010.03791 2020.
- Sathyavathi, S.; Baskaran, K. R. An Intelligent Human Age Prediction from Face Image Framework Based on Deep Learning Algorithms. Information Technology and Control 2023, 52, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, J. S.; Wahyono. Age Estimation on Human Face Image Using Support Vector Regression and Text-Based Features. Intl. Journal of Adv. Comp. Science and Applications 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Clapes, A.; Bilici, O.; Temirova, D.; Avots, E.; Anbarjafari, G.; Escalera, S. From Apparent to Real Age: Gender, Age, Ethnic, Makeup, and Expression Bias Analysis in Real Age Estimation. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, June 18-22, 2018; 2373-2382.
- Xing, J.; Li, K.; Hu, W.; Yuan, C.; Ling, H. Diagnosing deep learning models for high accuracy age estimation from a single image. Pattern Recognition 2017, 66, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, J. C. S.; Ozcinar, C.; Marjanovic, M.; Baró, X.; Anbarjafari, G.; Escalera, S. On the effect of age perception biases for real age regression. Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, Lille, France, 2019; 1-8.
- UTKFace, github.io. Available online: https://susanqq.github.io/UTKFace/ (Accessed on 19 Jun 2024).
- APPA-REAL, chalearnlap.cvc.uab.cat. Available online: https://chalearnlap.cvc.uab.cat/dataset/26/description/ (Accessed on 19 Jun 2024).
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556 2014. [CrossRef]
- Kaiming, H.; Xiangyu, Z.; Shaoqing, R.; Jian, S. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385 2015. [CrossRef]
- Howard, A. G.; Zho, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Hartwig, A. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861 2017. [CrossRef]
- ImageNet. Available online: https://www.image-net.org (Accessed on 19 Jun 2024).
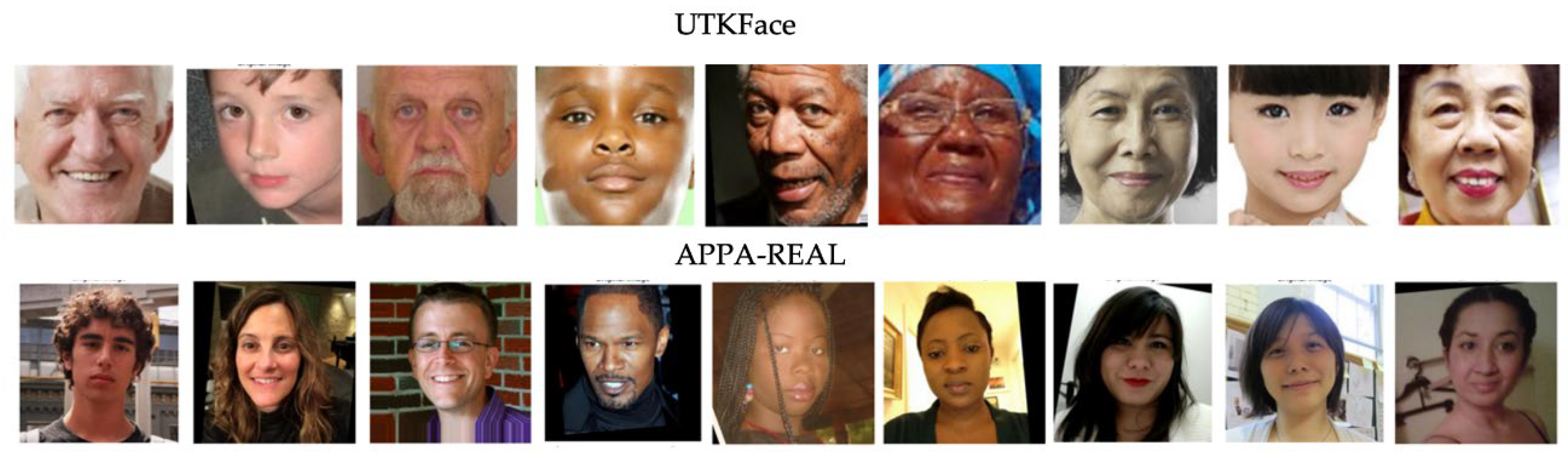



| Paper | Methodologies | Datasets | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analysis of Race and Gender Bias in Deep Age Estimation Models [11] | The authors employ two pre-trained age estimation models: WideResNet: Two variants trained on UTKFace (WideResNet-UTK) and IMDB-WIKI (WideResNet-IMDB) datasets. FaceNet: Based on the FaceNet architecture and fine-tuned on the IMDB-WIKI dataset. The evaluation involves partitioning the datasets into subgroups based on gender, race, and combined gender-race categories. The models’ performance is assessed using Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) metrics |
UTKFace APPA-REAL |
Gender Bias: The study finds that age estimation tends to be more accurate for male subjects than females across both datasets, particularly with the WideResNet models. The authors suggest that makeup usage among females might contribute to this discrepancy. Race Bias: While performance differences are observed across race groups, these variations are inconsistent between the two datasets. This suggests that other factors, such as image quality and pose, might have a more significant impact than race on age estimation accuracy. Gender-Race Subgroup Analysis: The analysis of combined gender-race subgroups reveal some exceptions to the general trends. For instance, male subjects perform worse than females in the Asian group on the UTKFace dataset. |
| FairFace: Face Attribute Dataset for Balanced Race, Gender, and Age [12] | The authors use a ResNet-34 architecture to train their models. They compare the performance of models trained on FairFace with models trained on other existing datasets, such as UTKFace, LFWA+, and CelebA. The evaluation involves cross-dataset classification and testing on novel datasets collected from Twitter, online media outlets, and a protest activity study. | The authors primarily use the YFCC-100M Flickr dataset, a large publicly available image dataset. They also incorporate images from other sources like Twitter and online newspapers. The dataset is carefully balanced across seven racial groups: White, Black, Indian, East Asian, Southeast Asian, Middle East, and Latino. It contains 108,501 facial images, each labeled with race, gender, and age group. | The results demonstrate that the model trained on FairFace consistently outperforms models trained on other datasets across various metrics, including accuracy and consistency across different racial groups. The FairFace model shows less than 1% accuracy discrepancy between male/female and White/non-White classifications for gender. In contrast, other models exhibit significant biases, particularly towards the male and White categories. |
| Age and Gender Prediction From Face Images Using Attentional Convolutional Network [13] | The proposed framework consists of two main components: Residual Attention Network (RAN): This network uses attention mechanisms to focus on important facial regions for age and gender prediction. It consists of attention modules that adaptively weight features as the network goes deeper. ResNet Model: This model is a residual convolutional network (ResNet) used for gender classification. The predicted gender is then concatenated with the features from the RAN for age prediction. The final prediction is obtained by ensembling the outputs of the RAN and ResNet models. |
UTKFace | The authors evaluate their model on the UTKFace dataset and compare its performance with individual models (RAN and ResNet) and previous work. The ensemble model outperforms both individual models in terms of gender and age prediction accuracy. It also achieves a higher gender classification accuracy than the previous work. |
| An Intelligent Human Age Prediction from Face Image Framework Based on Deep Learning Algorithms [14] | The proposed framework combines a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) with a Cuckoo Search (CS) algorithm. Preprocessing: Images are converted to grayscale, histogram equalized, and denoised. Face Edge Detection: Gabor filters are used to extract facial edges. Feature Extraction: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is employed to reduce dimensionality and extract relevant features. Age Estimation: A DCNN, specifically ResNet, is used for age prediction. The CS algorithm optimizes the model’s weights to improve accuracy. |
UTKFace FGNet CACD |
The authors evaluate their model using various metrics, including Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), Pearson correlation coefficient, precision, recall, F1-score, and computation time. The proposed DCNN-CS model outperforms other methods like CNN, DNN, LSTM, and SVR in terms of accuracy and computational efficiency. |
| Age Estimation on Human Face Image Using Support Vector Regression and Texture-Based Features [15] | The proposed framework consists of the following steps: Preprocessing: Images are resized and converted to grayscale. Feature Extraction: Three texture-based feature extraction methods are used: Local Binary Pattern (LBP), Local Phase Quantization (LPQ), and Binarized Statistical Image Features (BSIF). The authors also experiment with combinations of these methods. Feature Reduction: Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is applied to reduce the dimensionality of the extracted features. Age Estimation: Support Vector Regression (SVR) is used to predict age based on the extracted features. |
Face-age UTKFace |
The authors evaluate their model using Mean Absolute Error (MAE). They experiment with different image sizes, feature extraction methods, and PCA dimensions. The best results are achieved using a combination of BSIF and LPQ features with a PCA dimension of 70, resulting in an MAE of 9.766 for the first age rounding strategy and 9.754 for the second strategy. |
| Age estimation via face images: a survey [8] |
This study investigates methods for facial age estimation, discussing validation challenges and approaches. Techniques include dataset splitting with rotational exclusion, density-preserving sampling, cross-validation, and bootstrap strategies. It explores k-fold cross-validation and leave-one-out (LOO) strategies. Moreover, it examines multi-manifold metric learning and hierarchical models for age estimation. |
FG-NET MORPH Gallagher’s web collected database YGA LHI HOIP Iranian face database |
The study emphasizes comprehensive approaches and stresses the importance of validation strategies to avoid overfitting and enhance generalization. The paper summarizes recent studies, evaluation protocols, datasets, age estimation approaches, and feature extraction methods, offering a comprehensive overview of age estimation research. |
| From apparent to real age: gender, age, ethnic, makeup, and expression bias analysis in real age estimation [16] | The study examines real age estimation in facial still images, focusing on the transition from apparent to real age. It enriches the APPA-REAL dataset with attributes like gender, ethnicity, makeup, and facial expression. Experiments with a basic Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) illustrate the influence of apparent labels on real age prediction. Bias correction on CNN predictions reveals consistent biases introduced by attributes, suggesting potential for enhanced age recognition performance. | APPA-REAL | The study suggests using apparent labels for training improves real age estimation compared to training with real ages alone. Bias correction on CNN predictions enhances age recognition performance. The analysis reviews state-of-the-art methods, emphasizing the importance of addressing biases. |
| Diagnosing deep learning models for high accuracy age estimation from a single image [17] | In this study, researchers explored age estimation from face images using deep learning. They examined training and evaluation procedures with deep learning models on two large datasets. They investigated three age estimation formulations, five loss functions, and three multi-task architectures. | Morph II WebFace |
The study significantly advances age estimation from face images using deep learning. Through systematic diagnosis, researchers pinpointed key factors affecting deep age estimation models, favoring a regression-based approach with Mean Absolute Error (MAE) loss. Their proposed deep multi-task learning architecture, addressing age, gender, and race simultaneously, outperformed other models. The final deep age estimation model surpassed previous solutions on Morph II and WebFace datasets. |
| On the effect of age perception biases for real age regression [18] | The paper proposes an end-to-end architecture for age estimation from still images using deep learning. It adapts the VGG16 model, pre-trained on ImageNet, to integrate face attributes like gender, race, happiness, and makeup levels during training. The architecture predicts both real and apparent age labels from facial images, considering human perception bias and attribute-based information. Training involves two stages: fine-tuning the last layers initially and then training the entire model end-to-end using the Adam optimization algorithm | APPA-REAL | The paper finds that incorporating face attributes into deep learning models notably enhances both real and apparent age estimation from facial images. Modifying the VGG16 model to include attributes like gender, race, happiness, and makeup levels during training yields superior performance over baseline models. Additionally, attribute-based analysis sheds light on how gender, race, happiness, and makeup influence age perception. |
| Name | Total number of samples | Gender | Race | Age Range | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | White | Black | Asian | Indian | Others | |||||
| UTKFace | 23,705 | 12,391 | 11,314 | 10,078 | 4,526 | 3,434 | 3,975 | 1,692 | 1 - 116 | ||
| APPA-REAL | 7,591 | 3,818 | 3,773 | 6,686 | 231 | 674 | 1 - 100 | ||||
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White 20% | 7,1603 | 7,1676 | 7,1663 | 7,0736 | 0,0440 |
| Black 60% | 6,7788 | 6,764 | 6,7813 | 6,9478 | 0,0828 |
| Asian 90% | 6,9338 | 6,956 | 6,9148 | 6,6874 | 0,1181 |
| Black 70% | 6,7632 | 6,7431 | 7,1447 | 6,8198 | 0,1740 |
| Black 30% | 6,7834 | 6,7537 | 7,2087 | 6,9303 | 0,1872 |
| White 10% | 6,8679 | 6,8687 | 7,1783 | 6,7177 | 0,1917 |
| Original | 6,4588 | 6,4241 | 6,4529 | 6,8593 | 0,1987 |
| Equal | 6,7129 | 6,4547 | 6,9672 | 6,5739 | 0,2189 |
| White 40% | 7,1286 | 7,153 | 7,3405 | 6,7528 | 0,2451 |
| Asian 50% | 6,6626 | 6,6547 | 7,1479 | 6,5305 | 0,2666 |
| White 70% | 7,3275 | 7,3464 | 7,625 | 6,9741 | 0,2666 |
| Asian 100% | 6,8969 | 6,8269 | 7,2377 | 7,5441 | 0,2938 |
| Black 10% | 6,7724 | 6,77 | 7,2787 | 6,5685 | 0,2988 |
| Asian 70% | 6,8689 | 6,9326 | 6,7004 | 6,2145 | 0,2991 |
| Black 40% | 7,1176 | 7,0839 | 7,7754 | 7,2036 | 0,3017 |
| Asian 10% | 6,6531 | 6,6385 | 7,2428 | 6,5518 | 0,3073 |
| Asian 40% | 6,7736 | 6,731 | 7,5072 | 6,927 | 0,3295 |
| White 30% | 7,1779 | 7,2144 | 7,49 | 6,6156 | 0,3650 |
| Black 90% | 6,8216 | 6,8529 | 7,2218 | 6,2795 | 0,3877 |
| Asian 30% | 6,8468 | 6,8523 | 7,4678 | 6,4999 | 0,3999 |
| Asian 60% | 7,1463 | 7,1156 | 8,0009 | 7,1076 | 0,4192 |
| Asian 20% | 6,7844 | 6,7327 | 7,733 | 6,9448 | 0,4303 |
| White 50% | 7,224 | 7,2357 | 7,9872 | 6,7413 | 0,5122 |
| White 60% | 7,6724 | 7,7254 | 8,1431 | 6,8498 | 0,5389 |
| Black 80% | 6,7672 | 6,762 | 7,7404 | 6,3828 | 0,5719 |
| Black 50% | 6,8294 | 6,845 | 7,7236 | 6,2425 | 0,6081 |
| White 90% | 8,2641 | 8,3888 | 8,039 | 6,9359 | 0,6191 |
| Black 100% | 6,8285 | 6,7755 | 8,1289 | 6,8429 | 0,6227 |
| White 80% | 7,6813 | 7,7504 | 8,1856 | 6,6583 | 0,6424 |
| Black 20% | 6,8741 | 6,8916 | 7,8781 | 6,2144 | 0,6831 |
| Asian 80% | 6,7975 | 6,7792 | 8,0498 | 6,4349 | 0,6944 |
| White 100% | 8,8956 | 9,1258 | 7,3192 | 6,9751 | 0,9432 |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | Black group compared to original | Black group compared to equal | Asian group compared to original | Asian group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 6,4588 | 6,4241 | 6,4529 | 6,8593 | 0,1987 | |||||||
| Equal | 6,7129 | 6,4547 | 6,9672 | 6,5739 | 0,2189 | 0,48% | 0,48% | 7,97% | -4,16% | |||
| 10% | 6,8679 | 6,8687 | 7,1783 | 6,7177 | 0,1917 | 6,41% | 6,41% | 6,92% | 11,24% | 3,03% | -2,06% | 2,19% |
| 20% | 7,1603 | 7,1676 | 7,1663 | 7,0736 | 0,0440 | 4,35% | 11,04% | 11,57% | 11,06% | 2,86% | 3,12% | 7,60% |
| 30% | 7,1779 | 7,2144 | 7,49 | 6,6156 | 0,3650 | 0,65% | 11,77% | 12,30% | 16,07% | 7,50% | -3,55% | 0,63% |
| 40% | 7,1286 | 7,153 | 7,3405 | 6,7528 | 0,2451 | -0,85% | 10,82% | 11,35% | 13,76% | 5,36% | -1,55% | 2,72% |
| 50% | 7,224 | 7,2357 | 7,9872 | 6,7413 | 0,5122 | 1,16% | 12,10% | 12,63% | 23,78% | 14,64% | -1,72% | 2,55% |
| 60% | 7,6724 | 7,7254 | 8,1431 | 6,8498 | 0,5389 | 6,77% | 19,69% | 20,26% | 26,19% | 16,88% | -0,14% | 4,20% |
| 70% | 7,3275 | 7,3464 | 7,625 | 6,9741 | 0,2666 | -4,91% | 13,81% | 14,36% | 18,16% | 9,44% | 1,67% | 6,09% |
| 80% | 7,6813 | 7,7504 | 8,1856 | 6,6583 | 0,6424 | 5,50% | 20,07% | 20,65% | 26,85% | 17,49% | -2,93% | 1,28% |
| 90% | 8,2641 | 8,3888 | 8,039 | 6,9359 | 0,6191 | 8,24% | 29,96% | 30,58% | 24,58% | 15,38% | 1,12% | 5,51% |
| 100% | 8,8956 | 9,1258 | 7,3192 | 6,9751 | 0,9432 | 8,79% | 41,38% | 42,06% | 13,42% | 5,05% | 1,69% | 6,10% |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | White group compared to original | White group compared to equal | Asian group compared to original | Asian group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 6,4588 | 6,4241 | 6,4529 | 6,8593 | 0,1987 | |||||||
| Equal | 6,7129 | 6,4547 | 6,9672 | 6,5739 | 0,2189 | 7,97% | 7,97% | 0,48% | -4,16% | |||
| 10% | 6,7724 | 6,77 | 7,2787 | 6,5685 | 0,2988 | 4,47% | 4,47% | 12,80% | 5,38% | 4,88% | -4,24% | -0,08% |
| 20% | 6,8741 | 6,8916 | 7,8781 | 6,2144 | 0,6831 | 8,23% | 13,07% | 22,09% | 7,28% | 6,77% | -9,40% | -5,47% |
| 30% | 6,7834 | 6,7537 | 7,2087 | 6,9303 | 0,1872 | -8,50% | 3,47% | 11,71% | 5,13% | 4,63% | 1,04% | 5,42% |
| 40% | 7,1176 | 7,0839 | 7,7754 | 7,2036 | 0,3017 | 7,86% | 11,60% | 20,49% | 10,27% | 9,75% | 5,02% | 9,58% |
| 50% | 6,8294 | 6,845 | 7,7236 | 6,2425 | 0,6081 | -0,67% | 10,86% | 19,69% | 6,55% | 6,05% | -8,99% | -5,04% |
| 60% | 6,7788 | 6,764 | 6,7813 | 6,9478 | 0,0828 | -12,20% | -2,67% | 5,09% | 5,29% | 4,79% | 1,29% | 5,69% |
| 70% | 6,7632 | 6,7431 | 7,1447 | 6,8198 | 0,1740 | 5,36% | 2,55% | 10,72% | 4,97% | 4,47% | -0,58% | 3,74% |
| 80% | 6,7672 | 6,762 | 7,7404 | 6,3828 | 0,5719 | 8,34% | 11,10% | 19,95% | 5,26% | 4,76% | -6,95% | -2,91% |
| 90% | 6,8216 | 6,8529 | 7,2218 | 6,2795 | 0,3877 | -6,70% | 3,65% | 11,92% | 6,67% | 6,17% | -8,45% | -4,48% |
| 100% | 6,8285 | 6,7755 | 8,1289 | 6,8429 | 0,6227 | 12,56% | 16,67% | 25,97% | 5,47% | 4,97% | -0,24% | 4,09% |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | White group compared to original | White group compared to equal | Black group compared to original | Black group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 6,4588 | 6,4241 | 6,4529 | 6,8593 | 0,1987 | |||||||
| Equal | 6,7129 | 6,4547 | 6,9672 | 6,5739 | 0,2189 | -4,16% | -4,16% | 0,48% | 7,97% | |||
| 10% | 6,6531 | 6,6385 | 7,2428 | 6,5518 | 0,3073 | -0,34% | -0,34% | -4,48% | 3,34% | 2,85% | 12,24% | 3,96% |
| 20% | 6,7844 | 6,7327 | 7,733 | 6,9448 | 0,4303 | 6,00% | 5,64% | 1,25% | 4,80% | 4,31% | 19,84% | 10,99% |
| 30% | 6,8468 | 6,8523 | 7,4678 | 6,4999 | 0,3999 | -6,41% | -1,13% | -5,24% | 6,67% | 6,16% | 15,73% | 7,19% |
| 40% | 6,7736 | 6,731 | 7,5072 | 6,927 | 0,3295 | 6,57% | 5,37% | 0,99% | 4,78% | 4,28% | 16,34% | 7,75% |
| 50% | 6,6626 | 6,6547 | 7,1479 | 6,5305 | 0,2666 | -5,72% | -0,66% | -4,79% | 3,59% | 3,10% | 10,77% | 2,59% |
| 60% | 7,1463 | 7,1156 | 8,0009 | 7,1076 | 0,4192 | 8,84% | 8,12% | 3,62% | 10,76% | 10,24% | 23,99% | 14,84% |
| 70% | 6,8689 | 6,9326 | 6,7004 | 6,2145 | 0,2991 | -12,57% | -5,47% | -9,40% | 7,92% | 7,40% | 3,84% | -3,83% |
| 80% | 6,7975 | 6,7792 | 8,0498 | 6,4349 | 0,6944 | 3,55% | -2,11% | -6,19% | 5,53% | 5,03% | 24,75% | 15,54% |
| 90% | 6,9338 | 6,956 | 6,9148 | 6,6874 | 0,1181 | 3,92% | 1,73% | -2,51% | 8,28% | 7,77% | 7,16% | -0,75% |
| 100% | 6,8969 | 6,8269 | 7,2377 | 7,5441 | 0,2938 | 12,81% | 14,76% | 9,98% | 6,27% | 5,77% | 12,16% | 3,88% |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian 90% | 5,4808 | 5,7351 | 5,4583 | 5,0036 | 0,3015 |
| Asian 100% | 5,3499 | 5,6983 | 5,2564 | 4,7976 | 0,3677 |
| Asian 80% | 5,1197 | 5,5972 | 5,2153 | 4,0006 | 0,6807 |
| Asian 70% | 5,178 | 5,5635 | 5,2437 | 3,908 | 0,7170 |
| Original | 4,8925 | 5,3772 | 5,0445 | 3,6674 | 0,7401 |
| Asian 60% | 5,1361 | 5,7023 | 5,2071 | 3,877 | 0,7707 |
| Black 10% | 4,9504 | 5,4966 | 5,072 | 3,6505 | 0,7894 |
| White 10% | 5,028 | 5,5884 | 5,1332 | 3,7261 | 0,7926 |
| Asian 40% | 5,0608 | 5,6095 | 5,1833 | 3,7543 | 0,7934 |
| White 20% | 5,0549 | 5,6 | 5,1896 | 3,7361 | 0,7996 |
| Asian 50% | 5,2064 | 5,8149 | 5,2504 | 3,9063 | 0,8005 |
| Black 50% | 5,1155 | 5,5867 | 5,3529 | 3,7797 | 0,8024 |
| Asian 20% | 4,9849 | 5,5227 | 5,1505 | 3,6308 | 0,8183 |
| Black 30% | 5,2779 | 5,821 | 5,4611 | 3,8847 | 0,8408 |
| Asian 30% | 5,088 | 5,6537 | 5,2456 | 3,6904 | 0,8458 |
| Black 60% | 5,1542 | 5,6783 | 5,3728 | 3,7417 | 0,8501 |
| White 40% | 5,1123 | 5,7115 | 5,2279 | 3,7152 | 0,8503 |
| Equal | 4,9879 | 5,5465 | 5,1663 | 3,5711 | 0,8557 |
| White 50% | 5,152 | 5,7823 | 5,2317 | 3,7499 | 0,8582 |
| Asian 10% | 5,0262 | 5,6409 | 5,1295 | 3,6179 | 0,8588 |
| White 30% | 5,0891 | 5,6989 | 5,2045 | 3,6709 | 0,8634 |
| Black 70% | 5,1646 | 5,5988 | 5,5342 | 3,6896 | 0,8851 |
| Black 20% | 5,0512 | 5,6157 | 5,2732 | 3,5516 | 0,9031 |
| Black 90% | 5,2389 | 5,6447 | 5,6612 | 3,7357 | 0,9038 |
| Black 80% | 5,3513 | 5,8564 | 5,6689 | 3,8171 | 0,9203 |
| White 60% | 5,1887 | 5,8597 | 5,2998 | 3,6538 | 0,9362 |
| White 70% | 5,3421 | 6,0802 | 5,3782 | 3,7933 | 0,9565 |
| Black 40% | 5,3027 | 5,92 | 5,535 | 3,6802 | 0,9778 |
| Black 100% | 5,3681 | 5,7606 | 5,9055 | 3,7052 | 1,0048 |
| White 80% | 5,3377 | 6,1819 | 5,2886 | 3,7123 | 1,0209 |
| White 90% | 5,5117 | 6,4859 | 5,3614 | 3,7876 | 1,1066 |
| White 100% | 5,8152 | 7,1516 | 5,3912 | 3,803 | 1,3676 |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | Black group compared to original | Black group compared to equal | Asian group compared to original | Asian group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 4,8925 | 5,3772 | 5,0445 | 3,6674 | 0,7401 | |||||||
| Equal | 4,9879 | 5,5465 | 5,1663 | 3,5711 | 0,8557 | 3,15% | 3,15% | 2,41% | -2,63% | |||
| 10% | 5,028 | 5,5884 | 5,1332 | 3,7261 | 0,7926 | 0,76% | 0,76% | 3,93% | 1,76% | -0,64% | 1,60% | 4,34% |
| 20% | 5,0549 | 5,6 | 5,1896 | 3,7361 | 0,7996 | 0,21% | 0,96% | 4,14% | 2,88% | 0,45% | 1,87% | 4,62% |
| 30% | 5,0891 | 5,6989 | 5,2045 | 3,6709 | 0,8634 | 1,77% | 2,75% | 5,98% | 3,17% | 0,74% | 0,10% | 2,79% |
| 40% | 5,1123 | 5,7115 | 5,2279 | 3,7152 | 0,8503 | 0,22% | 2,97% | 6,22% | 3,64% | 1,19% | 1,30% | 4,04% |
| 50% | 5,152 | 5,7823 | 5,2317 | 3,7499 | 0,8582 | 1,24% | 4,25% | 7,53% | 3,71% | 1,27% | 2,25% | 5,01% |
| 60% | 5,1887 | 5,8597 | 5,2998 | 3,6538 | 0,9362 | 1,34% | 5,65% | 8,97% | 5,06% | 2,58% | -0,37% | 2,32% |
| 70% | 5,3421 | 6,0802 | 5,3782 | 3,7933 | 0,9565 | 3,76% | 9,62% | 13,07% | 6,62% | 4,10% | 3,43% | 6,22% |
| 80% | 5,3377 | 6,1819 | 5,2886 | 3,7123 | 1,0209 | 1,67% | 11,46% | 14,97% | 4,84% | 2,37% | 1,22% | 3,95% |
| 90% | 5,5117 | 6,4859 | 5,3614 | 3,7876 | 1,1066 | 4,92% | 16,94% | 20,62% | 6,28% | 3,78% | 3,28% | 6,06% |
| 100% | 5,8152 | 7,1516 | 5,3912 | 3,803 | 1,3676 | 10,26% | 28,94% | 33,00% | 6,87% | 4,35% | 3,70% | 6,49% |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | White group compared to original | White group compared to equal | Asian group compared to original | Asian group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 4,8925 | 5,3772 | 5,0445 | 3,6674 | 0,7401 | |||||||
| Equal | 4,9879 | 5,5465 | 5,1663 | 3,5711 | 0,8557 | 2,41% | 2,41% | 3,15% | -2,63% | |||
| 10% | 4,9504 | 5,4966 | 5,072 | 3,6505 | 0,7894 | -1,83% | -1,83% | 0,55% | 2,22% | -0,90% | -0,46% | 2,22% |
| 20% | 5,0512 | 5,6157 | 5,2732 | 3,5516 | 0,9031 | 3,97% | 2,07% | 4,53% | 4,44% | 1,25% | -3,16% | -0,55% |
| 30% | 5,2779 | 5,821 | 5,4611 | 3,8847 | 0,8408 | 3,56% | 5,71% | 8,26% | 8,25% | 4,95% | 5,93% | 8,78% |
| 40% | 5,3027 | 5,92 | 5,535 | 3,6802 | 0,9778 | 1,35% | 7,14% | 9,72% | 10,09% | 6,73% | 0,35% | 3,06% |
| 50% | 5,1155 | 5,5867 | 5,3529 | 3,7797 | 0,8024 | -3,29% | 3,61% | 6,11% | 3,90% | 0,72% | 3,06% | 5,84% |
| 60% | 5,1542 | 5,6783 | 5,3728 | 3,7417 | 0,8501 | 0,37% | 4,00% | 6,51% | 5,60% | 2,38% | 2,03% | 4,78% |
| 70% | 5,1646 | 5,5988 | 5,5342 | 3,6896 | 0,8851 | 3,00% | 7,12% | 9,71% | 4,12% | 0,94% | 0,61% | 3,32% |
| 80% | 5,3513 | 5,8564 | 5,6689 | 3,8171 | 0,9203 | 2,43% | 9,73% | 12,38% | 8,91% | 5,59% | 4,08% | 6,89% |
| 90% | 5,2389 | 5,6447 | 5,6612 | 3,7357 | 0,9038 | -0,14% | 9,58% | 12,23% | 4,97% | 1,77% | 1,86% | 4,61% |
| 100% | 5,3681 | 5,7606 | 5,9055 | 3,7052 | 1,0048 | 4,32% | 14,31% | 17,07% | 7,13% | 3,86% | 1,03% | 3,76% |
| Dataset variations | Overall MAE | White Group MAE | Black Group MAE | Asian Group MAE | Standard deviation | MAE Change compared to previous | Compared to equal | Compared to original | White group compared to original | White group compared to equal | Black group compared to original | Black group compared to equal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 4,8925 | 5,3772 | 5,0445 | 3,6674 | 0,7401 | |||||||
| Equal | 4,9879 | 5,5465 | 5,1663 | 3,5711 | 0,8557 | -2,63% | -2,63% | 3,15% | 2,41% | |||
| 10% | 5,0262 | 5,6409 | 5,1295 | 3,6179 | 0,8588 | 1,31% | 1,31% | -1,35% | 4,90% | 1,70% | 1,69% | -0,71% |
| 20% | 4,9849 | 5,5227 | 5,1505 | 3,6308 | 0,8183 | 0,36% | 1,67% | -1,00% | 2,71% | -0,43% | 2,10% | -0,31% |
| 30% | 5,088 | 5,6537 | 5,2456 | 3,6904 | 0,8458 | 1,64% | 3,34% | 0,63% | 5,14% | 1,93% | 3,99% | 1,53% |
| 40% | 5,0608 | 5,6095 | 5,1833 | 3,7543 | 0,7934 | 1,73% | 5,13% | 2,37% | 4,32% | 1,14% | 2,75% | 0,33% |
| 50% | 5,2064 | 5,8149 | 5,2504 | 3,9063 | 0,8005 | 4,05% | 9,39% | 6,51% | 8,14% | 4,84% | 4,08% | 1,63% |
| 60% | 5,1361 | 5,7023 | 5,2071 | 3,877 | 0,7707 | -0,75% | 8,57% | 5,72% | 6,05% | 2,81% | 3,22% | 0,79% |
| 70% | 5,178 | 5,5635 | 5,2437 | 3,908 | 0,7170 | 0,80% | 9,43% | 6,56% | 3,46% | 0,31% | 3,95% | 1,50% |
| 80% | 5,1197 | 5,5972 | 5,2153 | 4,0006 | 0,6807 | 2,37% | 12,03% | 9,09% | 4,09% | 0,91% | 3,39% | 0,95% |
| 90% | 5,4808 | 5,7351 | 5,4583 | 5,0036 | 0,3015 | 25,07% | 40,11% | 36,43% | 6,66% | 3,40% | 8,20% | 5,65% |
| 100% | 5,3499 | 5,6983 | 5,2564 | 4,7976 | 0,3677 | -4,12% | 34,35% | 30,82% | 5,97% | 2,74% | 4,20% | 1,74% |
| Paper | Dataset | Overall MAE | Race | Standard deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | Black | Asian | ||||
| [11] [11] |
UTKFace | 9,79 | 7,71 | 9,56 | 0,931 | |
| APPA-REAL | 7,79 | 8,23 | 7,85 | 0,1948 | ||
| [18] | APPA-REAL | 7,356 | 7,40 | 7,73 | 6,59 | 0,4789 |
| [16] | APPA-REAL | 13,5774 | 13,6386 | 14,1607 | 12,4729 | 0,7055 |
| Our results | UTKFace | 5,4808 | 5,7351 | 5,4583 | 5,0036 | 0,3015 |
| Our results | APPA-REAL | 7,1603 | 7,1676 | 7,1663 | 7,0735 | 0,044 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





