Submitted:
21 March 2024
Posted:
22 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Pharmacokinetics
2. Mechanisms of Action
2.1. Complex I Inhibition
2.2. AMPK-Dependent Mechanisms
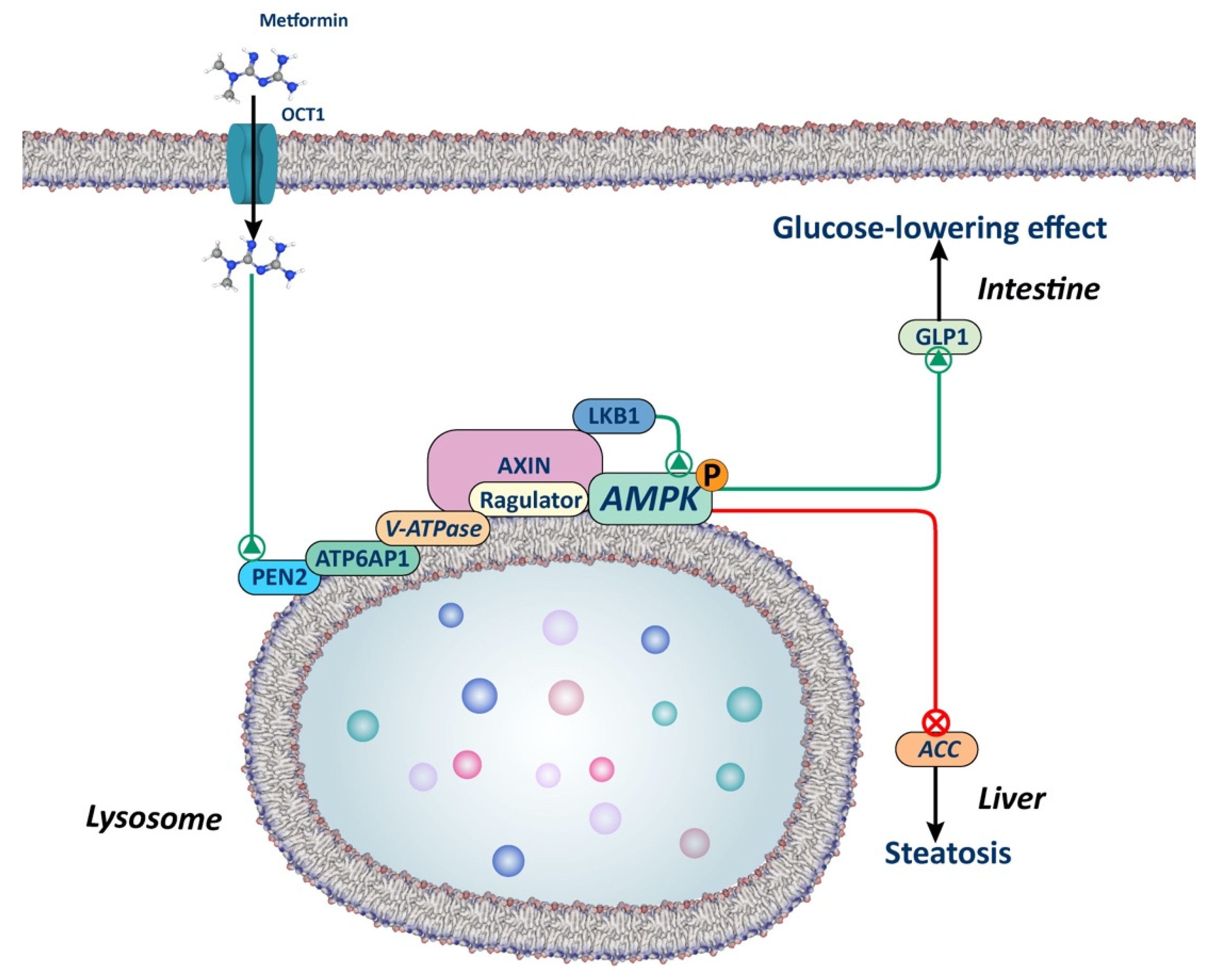
2.2.1. AMPK-Dependent Lysosomal Pathway
2.3. AMPK-Independent Mechanisms
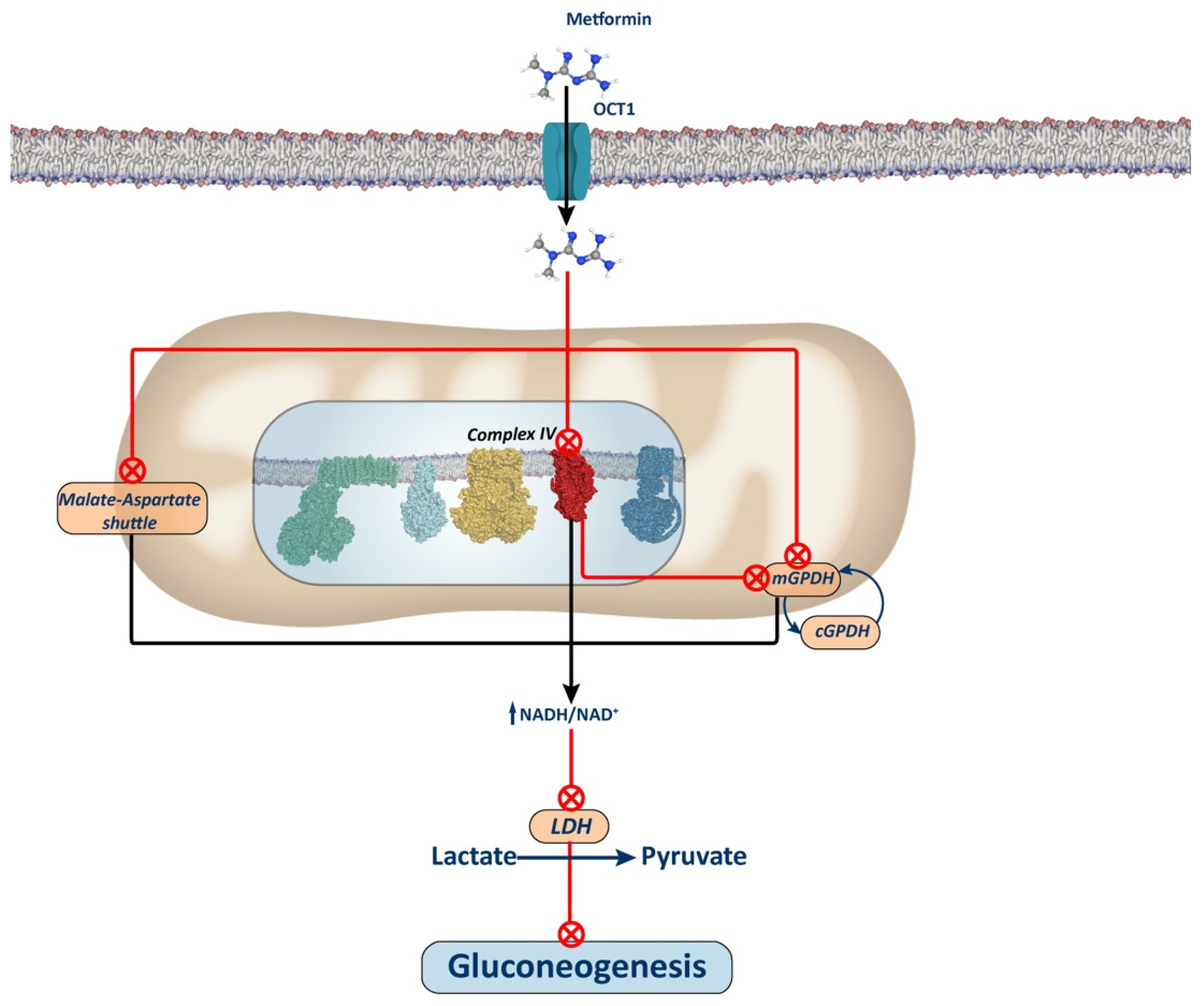
2.4. Complex IV Inhibition
2.5. Epigenetic Effects of Metformin
2.5.1. Histone Acetylases
2.5.2. Histone Deacetylases
2.5.3. DNA Methylation
2.6. Effects of Metformin on microRNAs
2.7. Effects of Metformin on the Microbiota
3. Metformin and Cancer
3.1. Breast Cancer
3.1.1. Clinical Studies
3.1.2. Animal Studies
3.1.3. In Vitro Studies
3.2. Colorectal Cancer
3.2.1. Clinical Studies
3.2.2. Animal Studies
3.2.3. In Vitro Studies
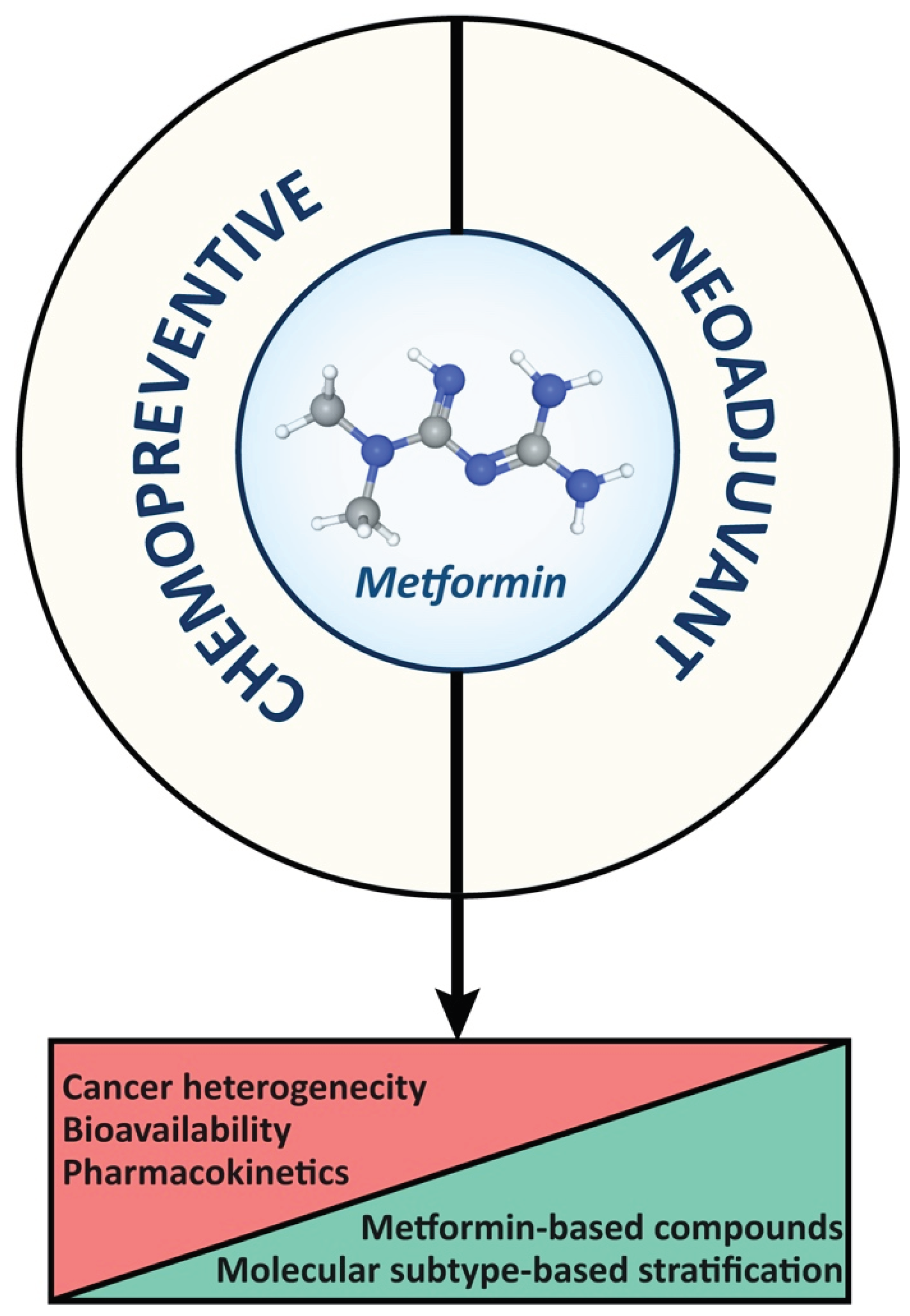
4. Future Perspectives and Improvements in Cancer Therapy
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: 21st List 2019 Available online:. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/325771 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Ahmad, E.; Sargeant, J.A.; Zaccardi, F.; Khunti, K.; Webb, D.R.; Davies, M.J. Where Does Metformin Stand in Modern Day Management of Type 2 Diabetes? Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical Overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Understanding the Glucoregulatory Mechanisms of Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2019, 15, 569–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inzucchi, S.E.; Lipska, K.J.; Mayo, H.; Bailey, C.J.; McGuire, D.K. Metformin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raičević, B.; Janković, S. Predictors of Gastrointestinal Complaints in Patients on Metformin Therapy. Open Med (Wars) 2023, 18, 20230871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Bertrand, L.; Pollak, M.; Viollet, B. Metformin: From Mechanisms of Action to Therapies. Cell Metab 2014, 20, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundal, R.S.; Krssak, M.; Dufour, S.; Laurent, D.; Lebon, V.; Chandramouli, V.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Schumann, W.C.; Petersen, K.F.; Landau, B.R.; et al. Mechanism by Which Metformin Reduces Glucose Production in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree-Green, M.; Bergman, B.C.; Cengiz, E.; Fox, L.A.; Hannon, T.S.; Miller, K.; Nathan, B.; Pyle, L.; Kahn, D.; Tansey, M.; et al. Metformin Improves Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity in Youth With Type 1 Diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2019, 104, 3265–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Barzilai, N.; Simonson, D.C. Mechanism of Metformin Action in Obese and Lean Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetic Subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991, 73, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hother-Nielsen, O.; Schmitz, O.; Andersen, P.H.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Pedersen, O. Metformin Improves Peripheral but Not Hepatic Insulin Action in Obese Patients with Type II Diabetes. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989, 120, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, L.A.; Hartline, L.; Liu, Z.; Barrett, E.J. Metformin Improves Skeletal Muscle Microvascular Insulin Resistance in Metabolic Syndrome. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2022, 322, E173–E180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, E.; Montori-Grau, M.; Wahli, W.; Palomer, X.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. Striking a Gut–Liver Balance for the Antidiabetic Effects of Metformin. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2023, 44, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, G. Site-Specific Uncoupling and Inhibition of Oxidative Phosphorylation by Biguanides. II. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1969, 172, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, E. Metformin-Induced Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibition: Facts, Uncertainties, and Consequences. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaMoia, T.E.; Butrico, G.M.; Kalpage, H.A.; Goedeke, L.; Hubbard, B.T.; Vatner, D.F.; Gaspar, R.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Cline, G.W.; Nakahara, K.; et al. Metformin, Phenformin, and Galegine Inhibit Complex IV Activity and Reduce Glycerol-Derived Gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2122287119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madiraju, A.K.; Erion, D.M.; Rahimi, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Braddock, D.T.; Albright, R.A.; Prigaro, B.J.; Wood, J.L.; Bhanot, S.; MacDonald, M.J.; et al. Metformin Suppresses Gluconeogenesis by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Glycerophosphate Dehydrogenase. Nature 2014 510:7506 2014, 510, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Metformin: Update on Mechanisms of Action and Repurposing Potential. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2023 19:8 2023, 19, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoia, T.E.; Shulman, G.I. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Metformin Action. Endocr Rev 2021, 42, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejuela, M.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Menendez, J.A.; Pernas, S. Metformin and Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi Thent, Z.; Hannim Zaidun, N.; Fairuz Azmi, M.; Senin, M.; Haslan, H.; Salehuddin, R. Is Metformin a Therapeutic Paradigm for Colorectal Cancer: Insight into the Molecular Pathway? Curr Drug Targets 2016, 18, 734–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.A.W.; Jiang, A.A.; Toh, E.M.S.; Ng, C.H.; Ong, Z.H.; Peng, S.; Tham, H.Y.; Sundar, R.; Chong, C.S.; Khoo, C.M. Metformin and Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression. Int J Colorectal Dis 2020, 35, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewski, S.; Siegel, P.M.; St-Pierre, J. Metabolic Profiles Associated With Metformin Efficacy in Cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Col, N.F.; Ochs, L.; Springmann, V.; Aragaki, A.K.; Chlebowski, R.T. Metformin and Breast Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis and Critical Literature Review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012, 135, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.H.; Satkunam, M.; Pond, G.R.; Steinberg, G.R.; Blandino, G.; Schunemann, H.J.; Muti, P. Association of Metformin with Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Patients with Type II Diabetes: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2018, 27, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, M.R.; Doran, E.; Halestrap, A.P. Evidence That Metformin Exerts Its Anti-Diabetic Effects through Inhibition of Complex 1 of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain. Biochemical Journal 2000, 348, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.B.; Sundelin, E.I.; Jakobsen, S.; Gormsen, L.C.; Munk, O.L.; Frøkiær, J.; Jessen, N. [11C]-Labeled Metformin Distribution in the Liver and Small Intestine Using Dynamic Positron Emission Tomography in Mice Demonstrates Tissue-Specific Transporter Dependency. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1724–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Giacomini, K.M. Transporters Involved in Metformin Pharmacokinetics and Treatment Response. J Pharm Sci 2017, 106, 2245–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Metformin. Clin Pharmacokinet 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossmann, H.H.; Lutz, O.M.D. Pharmacology of Metformin - An Update. Eur J Pharmacol 2019, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.D.; Dzierlenga, A.L.; Nelson, N.R.; Li, H.; Werts, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Cherrington, N.J. Mechanism of Altered Metformin Distribution in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3305–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormsen, L.C.; Sundelin, E.I.; Jensen, J.B.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Munk, O.L.; Christensen, M.M.H.; Brøsen, K.; Frøkiær, J.; Jessen, N. In Vivo Imaging of Human 11C-Metformin in Peripheral Organs: Dosimetry, Biodistribution, and Kinetic Analyses. J Nucl Med 2016, 57, 1920–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshawi, A.; Agius, L. Low Metformin Causes a More Oxidized Mitochondrial NADH/NAD Redox State in Hepatocytes and Inhibits Gluconeogenesis by a Redox-Independent Mechanism. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 2839–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wondisford, F.E. Metformin Action: Concentrations Matter. Cell Metab 2015, 21, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, C.; Bailey, C.J. Accumulation of Metformin by Tissues of the Normal and Diabetic Mouse. Xenobiotica 1994, 24, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Goswami, S.; Giacomini, K.M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Metformin Pathways: Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2012, 22, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellakis, M. Why Metformin Should Not Be Used as an Oxidative Phosphorylation Inhibitor in Cancer Patients. Chemotherapy 2023, 68, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mir, M.Y.; Nogueira, V.; Fontaine, E.; Avéret, N.; Rigoulet, M.; Leverve, X. Dimethylbiguanide Inhibits Cell Respiration via an Indirect Effect Targeted on the Respiratory Chain Complex I. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli Esposti, M. Inhibitors of NADH-Ubiquinone Reductase: An Overview. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998, 1364, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, H.R.; Jones, A.J.Y.; Pollak, M.N.; Hirst, J. Effects of Metformin and Other Biguanides on Oxidative Phosphorylation in Mitochondria. Biochem J 2014, 462, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, H.R.; Blaza, J.N.; Yin, Z.; Chung, I.; Pollak, M.N.; Hirst, J. Structural Basis of Mammalian Respiratory Complex I Inhibition by Medicinal Biguanides. Science 2023, 379, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foretz, M.; Hébrard, S.; Leclerc, J.; Zarrinpashneh, E.; Soty, M.; Mithieux, G.; Sakamoto, K.; Andreelli, F.; Viollet, B. Metformin Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis in Mice Independently of the LKB1/AMPK Pathway via a Decrease in Hepatic Energy State. J Clin Invest 2010, 120, 2355–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.W.; Hughey, C.C.; Lantier, L.; Sundelin, E.I.; Peggie, M.; Zeqiraj, E.; Sicheri, F.; Jessen, N.; Wasserman, D.H.; Sakamoto, K. Metformin Reduces Liver Glucose Production by Inhibition of Fructose-1-6-Bisphosphatase. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Chu, Q.; Xie, J.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B.; Birnbaum, M.J. Biguanides Suppress Hepatic Glucagon Signalling by Decreasing Production of Cyclic AMP. Nature 2013, 494, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Ross, F.A.; Hawley, S.A. AMPK: A Nutrient and Energy Sensor That Maintains Energy Homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakhill, J.S.; Scott, J.W.; Kemp, B.E. AMPK Functions as an Adenylate Charge-Regulated Protein Kinase. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2012, 23, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.J.; Lamia, K.A.; Vasquez, D.; Koo, S.-H.; Bardeesy, N.; Depinho, R.A.; Montminy, M.; Cantley, L.C. The Kinase LKB1 Mediates Glucose Homeostasis in Liver and Therapeutic Effects of Metformin. Science 2005, 310, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-M.; Seo, W.-Y.; Song, K.-H.; Chanda, D.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, D.-K.; Lee, M.-W.; Ryu, D.; Kim, Y.-H.; Noh, J.-R.; et al. AMPK-Dependent Repression of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via Disruption of CREB.CRTC2 Complex by Orphan Nuclear Receptor Small Heterodimer Partner. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 32182–32191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G.; Detaille, D.; Guigas, B. Role of Mitochondria in the Mechanism(s) of Action of Metformin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 442419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcock, C.; Wyre, N.D.; Bailey, C.J. Subcellular Distribution of Metformin in Rat Liver. J Pharm Pharmacol 1991, 43, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-S.; Li, M.; Ma, T.; Zong, Y.; Cui, J.; Feng, J.-W.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lin, S.-C. Metformin Activates AMPK through the Lysosomal Pathway. Cell Metab 2016, 24, 521–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-S.; Jiang, B.; Li, M.; Zhu, M.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Li, T.Y.; Liang, Y.; Lu, Z.; et al. The Lysosomal V-ATPase-Ragulator Complex Is a Common Activator for AMPK and MTORC1, Acting as a Switch between Catabolism and Anabolism. Cell Metab 2014, 20, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Tian, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Qu, Q.; Yu, Y.; et al. Low-Dose Metformin Targets the Lysosomal AMPK Pathway through PEN2. Nature 2022, 603, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madiraju, A.K.; Qiu, Y.; Perry, R.J.; Rahimi, Y.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zhang, D.; Camporez, J.-P.G.; Cline, G.W.; Butrico, G.M.; Kemp, B.E.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Gluconeogenesis via a Redox-Dependent Mechanism in Vivo. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1384–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisson, D.; Vohl, M.C.; St-Pierre, J.; Hudson, T.J.; Gaudet, D. Glycerol: A Neglected Variable in Metabolic Processes? Bioessays 2001, 23, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.C. Glycerol Utilization and Its Regulation in Mammals. Annu Rev Biochem 1977, 46, 765–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saheki, T.; Iijima, M.; Li, M.X.; Kobayashi, K.; Horiuchi, M.; Ushikai, M.; Okumura, F.; Meng, X.J.; Inoue, I.; Tajima, A.; et al. Citrin/Mitochondrial Glycerol-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Double Knock-out Mice Recapitulate Features of Human Citrin Deficiency. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 25041–25052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migoya, E.M.; Bergeron, R.; Miller, J.L.; Snyder, R.N.K.; Tanen, M.; Hilliard, D.; Weiss, B.; Larson, P.; Gutierrez, M.; Jiang, G.; et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Administered in Combination with Metformin Result in an Additive Increase in the Plasma Concentration of Active GLP-1. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2010, 88, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logie, L.; Harthill, J.; Patel, K.; Bacon, S.; Hamilton, D.L.; Macrae, K.; McDougall, G.; Wang, H.-H.; Xue, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Cellular Responses to the Metal-Binding Properties of Metformin. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdieri, L.; Gatla, H.; Vancurova, I.; Vancura, A. Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase by Metformin Induces Protein Acetylation in Prostate and Ovarian Cancer Cells. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 25154–25166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, S.C.; Ellison, G.C.; Melton, P.E.; Newsholme, P.; Mamotte, C.D.S. Epigenetic Effects of Metformin: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018, 20, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Wang, S.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. PPP1R3C Mediates Metformin-Inhibited Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Metabolism 2019, 98, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Joven, J.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin Targets Histone Acetylation in Cancer-Prone Epithelial Cells. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 3355–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdone, L. Histone Acetylation in Gene Regulation. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 2006, 5, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyàs, E.; Verdura, S.; Llorach-Parés, L.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Joven, J.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Brunet, J.; Nonell-Canals, A.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; et al. Metformin Is a Direct SIRT1-Activating Compound: Computational Modeling and Experimental Validation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caton, P.W.; Nayuni, N.K.; Kieswich, J.; Khan, N.Q.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Corder, R. Metformin Suppresses Hepatic Gluconeogenesis through Induction of SIRT1 and GCN5. J Endocrinol 2010, 205, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, G.; Li, G. Metformin Activates AMPK/SIRT1/NF-ΚB Pathway and Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction to Drive Caspase3/GSDME-Mediated Cancer Cell Pyroptosis. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; He, R.-R.; Liu, B. Mitochondrial Sirtuin 3: New Emerging Biological Function and Therapeutic Target. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8315–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X. SIRT1 and Energy Metabolism. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2013, 45, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Cacicedo, J.M.; Ruderman, N.; Ido, Y. SIRT1 Modulation of the Acetylation Status, Cytosolic Localization, and Activity of LKB1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, 27628–27635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmaszyk, A.; Mikołajczak, P.; Dworacka, M. Sirtuin 1 as the Mechanism of Action of Agents Used in the Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacotherapy. Eur J Pharmacol 2021, 907, 174289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Luo, G.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Qian, Y.; Fan, C. Pharmacological Activation of SIRT1 by Metformin Prevented Trauma-Induced Heterotopic Ossification through Inhibiting Macrophage Mediated Inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol 2021, 909, 174386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Shao, Y.; Wu, C.; Ma, X.; Lv, C.; Wang, Q. Metformin Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Enhances Autophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease via AMPK/SIRT1-FoxO1 Pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2020, 500, 110628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felgueiras, R.; Neto, A.C.; Rodrigues, A.R.; Gouveia, A.M.; Almeida, H.; Neves, D. Anti-Oxidant Effect of Metformin through AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α/SIRT3– Independent GPx1 Expression in the Heart of Mice with Endometriosis. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig 2022, 43, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, Y.J.; Choi, H.C. Metformin Mitigates Stress-Induced Premature Senescence by Upregulating AMPKα at Ser485 Phosphorylation Induced SIRT3 Expression and Inactivating Mitochondrial Oxidants. Mech Ageing Dev 2022, 206, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; He, J.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yue, Z.; Shao, X.; Cheng, J.; Wang, T.; Mou, S. AMPK Activation Coupling SENP1-Sirt3 Axis Protects against Acute Kidney Injury. Molecular Therapy 2023, 31, 3052–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Bian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Zhao, Y. Metformin Promotes in Vitro Maturation of Oocytes from Aged Mice by Attenuating Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress via SIRT3-Dependent SOD2ac. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, W.-N.; Xue, Y.-N.; Zhang, L.-C.; Zhang, J.-J.; Lu, S.-Y.; Yan, X.-Y.; Yu, H.-M.; Su, J.; Sun, L.-K. SIRT3 Aggravates Metformin-Induced Energy Stress and Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Exp Cell Res 2018, 367, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Verdura, S.; García, R.Á.-F.; Stursa, J.; Werner, L.; Blanco-González, E.; Montes-Bayón, M.; Joven, J.; Viollet, B.; et al. Metformin Regulates Global DNA Methylation via Mitochondrial One-Carbon Metabolism. Oncogene 2018, 37, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Men, Y.; Lu, L.; Geng, T.; Zhou, J.; Mitsuhashi, A.; Shozu, M.; Maihle, N.J.; Carmichael, G.G.; Taylor, H.S.; et al. Metformin Alters DNA Methylation Genome-Wide via the H19/SAHH Axis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Schrader, S.; Perfilyev, A.; Martinell, M.; Ahlqvist, E.; Ling, C. DNA Methylation Partially Mediates Antidiabetic Effects of Metformin on HbA1c Levels in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2023, 202, 110807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calzón, S.; Perfilyev, A.; Männistö, V.; de Mello, V.D.; Nilsson, E.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Ling, C. Diabetes Medication Associates with DNA Methylation of Metformin Transporter Genes in the Human Liver. Clin Epigenetics 2017, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooten, N.N.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Dluzen, D.F.; Zhang, Y.; Bernier, M.; Zonderman, A.B.; Becker, K.G.; Gorospe, M.; Cabo, R.; Evans, M.K. Metformin-mediated Increase in DICER1 Regulates MicroRNA Expression and Cellular Senescence. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirsoy, İ.H.; Ertural, D.Y.; Balci, Ş.; Çınkır, Ü.; Sezer, K.; Tamer, L.; Aras, N. Profiles of Circulating MiRNAs Following Metformin Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J Med Biochem 2018, 37, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Rovira, O.; Guerra, E.; Esteve, E.; Xifra, G.; Martínez, C.; Ricart, W.; Rieusset, J.; et al. Profiling of Circulating MicroRNAs Reveals Common MicroRNAs Linked to Type 2 Diabetes That Change with Insulin Sensitization. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.C.K.; Than, W.H.; Kwan, B.C.H.; Lai, K.B.; Chan, R.C.K.; Teoh, J.Y.C.; Ng, J.K.C.; Chow, K.M.; Cheng, P.M.S.; Law, M.C.; et al. Adipose and Plasma MicroRNAs MiR-221 and 222 Associate with Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and New Onset Diabetes after Peritoneal Dialysis. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, B.; Song, J.; Chaudhari, K.; Yang, S.-H.; Zhang, G.J.; Sun, X.; Taylor, H.S.; et al. Let-7 Underlies Metformin-Induced Inhibition of Hepatic Glucose Production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2122217119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S. MiR-140-5p Aggravates Insulin Resistance via Directly Targeting GYS1 and PPP1CC in Insulin-Resistant HepG2 Cells. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2021, 14, 2515–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimoradi, N.; Firouzabadi, N.; Fatehi, R. How Metformin Affects Various Malignancies by Means of MicroRNAs: A Brief Review. Cancer Cell Int 2021, 21, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Stratigou, T.; Tsagarakis, S. Metformin and Gut Microbiota: Their Interactions and Their Impact on Diabetes. Hormones 2019, 18, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Kamyshnyi, A. Effects of Metformin on the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Mol Metab 2023, 77, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, J.; Feng, S.; Huang, C.; Wang, H.; Huo, F.; Liu, H. Akkermansia Muciniphila, Which Is Enriched in the Gut Microbiota by Metformin, Improves Cognitive Function in Aged Mice by Reducing the Proinflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-6. Microbiome 2023, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lou, X.; Jiang, C.; Ji, X.; Tao, X.; Sun, J.; Bao, Z. Gut Microbiota Is Correlated with Gastrointestinal Adverse Events of Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silamiķele, L.; Silamiķelis, I.; Ustinova, M.; Kalniņa, Z.; Elbere, I.; Petrovska, R.; Kalniņa, I.; Kloviņš, J. Metformin Strongly Affects Gut Microbiome Composition in High-Fat Diet-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mouse Model of Both Sexes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021, 12, 626359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, N.T.; Differding, M.K.; Zhang, M.; Maruthur, N.M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J.; Yeh, H.-C. Metformin Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Function and Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Perdigones, C.M.; Muñoz-Garach, A.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, M.D.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut Microbiota of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Gastrointestinal Intolerance to Metformin Differs in Composition and Functionality from Tolerant Patients. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 145, 112448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xie, C.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Xia, J.; Chen, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Intestinal FXR Mediate the Clinical Benefits of Metformin. Nat Med 2018, 24, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive Impact of Non-Antibiotic Drugs on Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin in Cancer Treatment and Prevention. Annu Rev Med 2015, 66, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Morgan, E.; Rumgay, H.; Mafra, A.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Gralow, J.R.; Cardoso, F.; Siesling, S.; et al. Current and Future Burden of Breast Cancer: Global Statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast 2022, 66, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Colorectal Cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and Mortality Estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Today Available online:. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garczorz, W.; Kosowska, A.; Francuz, T. Antidiabetic Drugs in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Hajjar, A.; Cryns, V.L.; Trentham-Dietz, A.; Gangnon, R.E.; Heckman-Stoddard, B.M.; Alagoz, O. Breast Cancer Risk for Women with Diabetes and the Impact of Metformin: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Med 2023, 12, 11703–11718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerba, F.; Chatziioannou, A.C.; Jasbi, P.; Robinot, N.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Trolat, A.; Vozar, B.; Hartman, S.J.; Scalbert, A.; Bonanni, B.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles of Metformin in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Pooled Analysis of Plasmas from Two Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. J Transl Med 2022, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikermane, S.G.; Sharma, M.; Abughosh, S.M.; Aparasu, R.R.; Trivedi, M. V.; Johnson, M.L. Dose-Dependent Relation between Metformin and the Risk of Hormone Receptor-Positive, Her2-Negative Breast Cancer among Postmenopausal Women with Type-2 Diabetes. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2022, 195, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfling, L.L.; Støer, N.C.; Andreassen, B.K.; Ursin, G.; Botteri, E. Low-Dose Aspirin, Statins, and Metformin and Survival in Patients with Breast Cancers: A Norwegian Population-Based Cohort Study. Breast Cancer Research 2023, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Cao, L.; Yin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, W. Prognostic Value of Metformin in Cancers: An Updated Meta-Analysis Based on 80 Cohort Studies. Medicine 2022, 101, E31799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, F.; Rajati, F.; Sarokhani, D.; Bavandpour, M.; Moradinazar, M. The Relationship between Metformin Consumption and Cancer Risk: An Updated Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Int J Prev Med 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, O.H.Y.; Suissa, S. Metformin and Cancer: Solutions to a Real-World Evidence Failure. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essa, N.M.; Salem, H.F.; Elgendy, M.O.; Gabr, A.; Omran, M.M.; Hassan, N.A.; Tashkandi, H.M.; Harakeh, S.; Boshra, M.S. Efficacy of Metformin as Adjuvant Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, Vol. 11, Page 5505 2022, 11, 5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Amirabadizadeh, A.; Aramjoo, H.; Llorens, S.; Roshanravan, B.; Saeedi, F.; Talebi, M.; Shakibaei, M.; Samarghandian, S. Impact of Metformin on Cancer Biomarkers in Non-Diabetic Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Current Oncology 2021, 28, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, H.; Bellerba, F.; Macis, D.; Bertelsen, B.E.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A.; Aristarco, V.; Viste, K.; Mellgren, G.; Di Cola, G.; Costantino, J.; et al. Effect of Metformin and Lifestyle Intervention on Adipokines and Hormones in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Pooled Analysis from Two Randomized Controlled Trials. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serageldin, M.A.; Kassem, A.B.; El-Kerm, Y.; Helmy, M.W.; El-Mas, M.M.; El-Bassiouny, N.A. The Effect of Metformin on Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicities in Non-Diabetic Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomised Controlled Study. Drug Saf 2023, 46, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Coleman, N.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Janku, F.; Rodon, J.; Pant, S.; Dumbrava, E.E.I.; Fu, S.; Hong, D.S.; et al. Phase I Study of MTORC1/2 Inhibitor Sapanisertib (CB-228/TAK-228) in Combination with Metformin in Patients with MTOR/AKT/PI3K Pathway Alterations and Advanced Solid Malignancies. Cancer Research Communications 2024, 4, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashraheel, S.S.; Kheraldine, H.; Khalaf, S.; Moustafa, A.E. Al Metformin and HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 162, 114676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tong, Y.; Hong, J.; Huang, O.; Wu, J.; He, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, K. Neoadjuvant Docetaxel, Epirubicin, and Cyclophosphamide with or without Metformin in Breast Cancer Patients with Metabolic Abnormality: Results from the Randomized Phase II NeoMET Trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2023, 197, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K, S.; A, T.; A, G.; L, H.; H, G.; DD, S.; LG, E.; L, K.; E, K. The Combined Treatment with Ketogenic Diet and Metformin Slows Tumor Growth in Two Mouse Models of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Res Sq 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Castillo, V.; López-Urrutia, E.; Villanueva-Sánchez, O.; Ávila-Rodríguez, M.A.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Cortés-González, C.; López-Camarillo, C.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.J.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. Targeting Metabolic Remodeling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer in a Murine Model. J Cancer 2017, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, F.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, J.; Lyu, S.; Song, Q. Metformin Inducing the Change of Functional and Exhausted Phenotypic Tumor-Infiltrated Lymphocytes and the Correlation with JNK Signal Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer : Targets and Therapy 2022, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Suo, H.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Lu, S.; Jin, F.; Cao, Y. Metformin Plays an Antitumor Role by Downregulating Inhibitory Cells and Immune Checkpoint Molecules While Activating Protective Immune Responses in Breast Cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 118, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilinyi, R.; Czompa, A.; Czegledi, A.; Gajtko, A.; Pituk, D.; Lekli, I.; Tosaki, A. The Cardioprotective Effect of Metformin in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: The Role of Autophagy. Molecules : A Journal of Synthetic Chemistry and Natural Product Chemistry 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alvarez, R.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lamb, R.; Hulit, J.; Howell, A.; Gandara, R.; Sartini, M.; Rubin, E.; Lisanti, M.P.; Sotgia, F. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Breast Cancer Cells Prevents Tumor Growth: Understanding Chemoprevention with Metformin. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurzhan, S.; Bekezhankyzy, Z.; Ding, H.; Berdigaliyev, N.; Sergazy, S.; Gulyayev, A.; Shulgau, Z.; Triggle, C.R.; Aljofan, M. The Effect of Different Glucose Concentrations on the Antiproliferative Activity of Metformin in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewski, S.; Klimcakova, E.; Johnson, R.M.; Tabariès, S.; Annis, M.G.; McGuirk, S.; Northey, J.J.; Chénard, V.; Sriram, U.; Papadopoli, D.J.; et al. PGC-1α Promotes Breast Cancer Metastasis and Confers Bioenergetic Flexibility against Metabolic Drugs. Cell Metab 2017, 26, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzer, A.; German, N.J.; Gonzalez-Herrera, K.N.; Asara, J.M.; Haigis, M.C.; Struhl, K. Metformin and Phenformin Deplete Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Glycolytic Intermediates during Cell Transformation and NTPs in Cancer Stem Cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 10574–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.; Bi, M.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Han, Z.Q.; Han, X.; Wang, H.Y.; Sun, G.P.; Liu, H. Metformin Induces Apoptosis via a Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway in Human Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. Exp Ther Med 2016, 11, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, S. Metformin Inhibits Human Breast Cancer Cell Growth by Promoting Apoptosis via a ROS-Independent Pathway Involving Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Pivotal Role of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD). Cellular Oncology 2018, 41, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.L.; Wang, B.F.; Liang, B.B.; Zhang, L.; Pan, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.H.; Zhang, S.Q.; et al. A ROS/Akt/NF-ΚB Signaling Cascade Mediates Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion in Human Breast Cancer Cells. World J Oncol 2022, 13, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Liu, W.; Tala, T.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; et al. Metformin Suppresses Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting KLF5 for Degradation. Cell Discovery 2017 3:1 2017, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, F.; Momeni, A.; Ramezani, M.; Ansari, Y.; Moghbelinejad, S. Metformin Caused Radiosensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells through the Expression Modulation of MiR-21-5p/SESN1axis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2023, 24, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Haugrud, A.B.; Schaefer, M.A.; Messerli, S.M.; Miskimins, W.K. Ability of Metformin to Deplete NAD+ Contributes to Cancer Cell Susceptibility to Metformin Cytotoxicity and Is Dependent on NAMPT Expression. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1225220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; Li, S.F.; Wei, R.; Jiang, Z. Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. J Diabetes Res 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, T.; Walts, Z.L.; Steinwandel, M.; Lipworth, L.; Murff, H.J.; Zheng, W.; Warren Andersen, S. Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Cancer Risk. JAMA Netw Open 2023, 6, e2343333–e2343333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berster, J.M.; Göke, B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus as Risk Factor for Colorectal Cancer. Arch Physiol Biochem 2008, 114, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Rui, D.; Nie, S.; Xiang, H. Metformin Therapy and Risk of Colorectal Adenomas and Colorectal Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehdev, A.; Shih, Y.C.T.; Vekhter, B.; Bissonnette, M.B.; Olopade, O.I.; Polite, B.N. Metformin for Primary Colorectal Cancer Prevention in Patients with Diabetes: A Case-Control Study in a US Population. Cancer 2015, 121, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovic, M.C.; Mikulic, D.; Bilic-Curcic, I.; Mrzljak, A. How Far along Are We in Revealing the Connection between Metformin and Colorectal Cancer? World J Gastroenterol 2021, 27, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.C.; Ferrara, A.; Achacoso, N.; Ehrlich, S.F.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Habel, L.A. A Cohort Study of Metformin and Colorectal Cancer Risk among Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2018, 27, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.S.; Park, C.H.; Eun, C.S.; Park, D. Il; Han, D.S. Metformin Use and the Risk of Colorectal Adenoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 32, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.; Hu, C.; Tsakiridis, T.; Santana-Davila, R.; Lu, B.; Erasmus, J.J.; Doemer, A.J.; Videtic, G.M.M.; Coster, J.; Yang, A.X.; et al. Addition of Metformin to Concurrent Chemoradiation in Patients With Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The NRG-LU001 Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2021, 7, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Chen, B.E.; Gelmon, K.A.; Whelan, T.J.; Ennis, M.; Lemieux, J.; Ligibel, J.A.; Hershman, D.L.; Mayer, I.A.; Hobday, T.J.; et al. Effect of Metformin vs Placebo on Invasive Disease-Free Survival in Patients With Breast Cancer: The MA.32 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujalte Martin, M.; Borchiellini, D.; Thamphya, B.; Guillot, A.; Paoli, J.B.; Besson, D.; Hilgers, W.; Priou, F.; El Kouri, C.; Hoch, B.; et al. TAXOMET: A French Prospective Multicentric Randomized Phase II Study of Docetaxel Plus Metformin Versus Docetaxel Plus Placebo in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer 2021, 19, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akce, M.; Farran, B.; Switchenko, J.M.; Rupji, M.; Kang, S.; Khalil, L.; Ruggieri-Joyce, A.; Olson, B.; Shaib, W.L.; Wu, C.; et al. Phase II Trial of Nivolumab and Metformin in Patients with Treatment-Refractory Microsatellite Stable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J Immunother Cancer 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, M.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, F.; Xue, Y. Effects of Metformin on CD133+ Colorectal Cancer Cells in Diabetic Patients. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragagnoli, A.C.; Araujo, R.L.C.; Ferraz, M.W.; dos Santos, L.V.; Abdalla, K.C.; Comar, F.; Santos, F.A.; Oliveira, M.A.; Carvalheira, J.B.C.; Cárcano, F.M.; et al. Metformin plus Lrinotecan in Patients with Refractory Colorectal Cancer: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. British Journal of Cancer 2021 124:6 2021, 124, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, V.C.; Braghiroli, M.I.; Faria, L.D.; Bariani, G.; Alex, A.; Bezerra Neto, J.E.; Capareli, F.C.; Sabbaga, J.; Lobo dos Santos, J.F.; Hoff, P.M.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of Metformin Combined With 5-Fluorouracil in Patients With Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2016, 15, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.J.; Seo, Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Yoon, J.P.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Hong, S.P.; Cheon, J.H.; et al. Effects of Metformin on Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells Depend on Alterations in Glutamine Metabolism. Scientific Reports 2018 8:1 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, R. V.; Mackenzie, E.D.; Boulahbel, H.; Frezza, C.; Heiserich, L.; Tardito, S.; Bussolati, O.; Rocha, S.; Hall, M.N.; Gottlieb, E. HIF-Independent Role of Prolyl Hydroxylases in the Cellular Response to Amino Acids. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzi, F.; Mogavero, A.; Varinelli, L.; Belfiore, A.; Manenti, G.; Caccia, C.; Volpi, C.C.; Beznoussenko, G. V.; Milione, M.; Leoni, V.; et al. MIF/CD74 Axis Is a Target for Novel Therapies in Colon Carcinomatosis. Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research 2017, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, G.; Hardie, D.G.; Pearson, E.R. The Mechanisms of Action of Metformin. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Yoneda, K.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; et al. Metformin Suppresses Azoxymethane-Induced Colorectal Aberrant Crypt Foci by Activating AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Mol Carcinog 2010, 49, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimoto, A.; Endo, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Hosono, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nakajima, N.; Nagashima, Y.; Wada, K.; Nakagama, H.; et al. Metformin Suppresses Intestinal Polyp Growth in ApcMin/+ Mice. Cancer Sci 2008, 99, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaafar, D.K.; Zaitone, S.A.; Moustafa, Y.M. Role of Metformin in Suppressing 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine-Induced Colon Cancer in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Mice: Effect on Tumor Angiogenesis and Cell Proliferation. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Suhaimi, N.A.; Phyo, W.M.; Yap, H.Y.; Choy, S.H.Y.; Wei, X.; Choudhury, Y.; Tan, W.J.; Tan, L.A.P.Y.; Foo, R.S.Y.; Tan, S.H.S.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Bioenergetics in Colorectal Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 2017, 16, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangia-Makker, P.; Yu, Y.; Vasudevan, A.; Farhana, L.; Rajendra, S.G.; Levi, E.; Majumdar, A.P.N. Metformin: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Recurrent Colon Cancer. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, K.; Okabayashi, K.; Seishima, R.; Ishida, T.; Shigeta, K.; Tsuruta, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Kitagawa, Y. Metformin Inhibits the Development and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. Med Oncol 2022, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraiyarasan, S.; Adefuye, M.; Manjunatha, N.; Ganduri, V.; Rajasekaran, K. Colon Cancer and Obesity: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakikhani, M.; Dowling, R.J.O.; Sonenberg, N.; Pollak, M.N. The Effects of Adiponectin and Metformin on Prostate and Colon Neoplasia Involve Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2008, 1, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algire, C.; Moiseeva, O.; Deschênes-Simard, X.; Amrein, L.; Petruccelli, L.; Birman, E.; Viollet, B.; Ferbeyre, G.; Pollak, M.N. Metformin Reduces Endogenous Reactive Oxygen Species and Associated DNA Damage. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2012, 5, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharping, N.E.; Menk, A. V.; Whetstone, R.D.; Zeng, X.; Delgoffe, G.M. Efficacy of PD-1 Blockade Is Potentiated by Metformin-Induced Reduction of Tumor Hypoxia. Cancer Immunol Res 2017, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadfield, L.A.; Saigal, A.; Szamosi, J.C.; Hammill, J.A.; Bezverbnaya, K.; Wang, D.; Gautam, J.; Tsakiridis, E.E.; Di Pastena, F.; McNicol, J.; et al. Metformin-Induced Reductions in Tumor Growth Involves Modulation of the Gut Microbiome. Mol Metab 2022, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachem, A.; Makhlouf, C.; Binger, K.J.; de Souza, D.P.; Tull, D.; Hochheiser, K.; Whitney, P.G.; Fernandez-Ruiz, D.; Dähling, S.; Kastenmüller, W.; et al. Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Promote the Memory Potential of Antigen-Activated CD8+ T Cells. Immunity 2019, 51, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogavero, A.; Maiorana, M.V.; Zanutto, S.; Varinelli, L.; Bozzi, F.; Belfiore, A.; Volpi, C.C.; Gloghini, A.; Pierotti, M.A.; Gariboldi, M. Metformin Transiently Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation as a Result of Either AMPK Activation or Increased ROS Production. Sci Rep 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, K.A.; Van Wickle, J.; Hill, R.B.; Marchese, A.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Dwinell, M.B. Mitochondria-Targeted Drugs Stimulate Mitophagy and Abrogate Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 14891–14904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denise, C.; Paoli, P.; Calvani, M.; Taddei, M.L.; Giannoni, E.; Kopetz, S.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Pia, M.M.; Pettazzoni, P.; Sacco, E.; et al. 5-Fluorouracil Resistant Colon Cancer Cells Are Addicted to OXPHOS to Survive and Enhance Stem-like Traits. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41706–41721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X.; Shi, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, B. Metformin Enhances the Sensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells to Cisplatin through ROS-Mediated PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Gene 2020, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, W.W.; Weinberg, S.E.; Hamanaka, R.B.; Soberanes, S.; Sullivan, L.B.; Anso, E.; Glasauer, A.; Dufour, E.; Mutlu, G.M.; Scott Budigner, G.R.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Mitochondrial Complex I of Cancer Cells to Reduce Tumorigenesis. Elife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodaei, F.; Hosseini, S.M.; Omidi, M.; Hosseini, S.F.; Rezaei, M. Cytotoxicity of Metformin against HT29 Colon Cancer Cells Contributes to Mitochondrial Sirt3 Upregulation. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ung, T.T.; Li, S.; Lian, S.; Xia, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Do Jung, Y. Metformin Inhibits Lithocholic Acid-Induced Interleukin 8 Upregulation in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Suppressing ROS Production and NF-KB Activity. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Lanza-Jacoby, S. Metformin Decreases Growth of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Decreasing Reactive Oxygen Species: Role of NOX4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015, 465, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.H.; Pu, X.X.; Huang, M.J.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, J.M.; Lin, T.Y.; Lin, E.H. 5-Fluorouracil Upregulates the Activity of Wnt Signaling Pathway in CD133-Positive Colon Cancer Stem-like Cells. Chin J Cancer 2010, 29, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.C.; Ku, J.L. Metformin Increases Chemo-Sensitivity via Gene Downregulation Encoding DNA Replication Proteins in 5-Fu Resistant Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56546–56557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Metformin Attenuates Cells Stemness and Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Wnt3a/Β-catenin Pathway. Mol Med Rep 2019, 19, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Zielonka, J.; Ouari, O.; Lopez, M.; McAllister, D.; Boyle, K.; Barrios, C.S.; Weber, J.J.; Johnson, B.D.; Hardy, M.; et al. Mitochondria-Targeted Analogues of Metformin Exhibit Enhanced Antiproliferative and Radiosensitizing Effects in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 3904–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, A.; Wadhwani, A.; Sauraj; Roychowdhury, P. ; Kang, J.H.; Ko, Y.T.; Kuppusamy, G. WZB117 Decorated Metformin-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeting Breast Cancer Metabolism. Polymers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, R.; Jafari-Gharabaghlou, D.; Mirjafary, Z.; Saeidian, H.; Zarghami, N. Design and Optimization Various Formulations of PEGylated Niosomal Nanoparticles Loaded with Phytochemical Agents: Potential Anti-Cancer Effects against Human Lung Cancer Cells. Pharmacol Rep 2023, 75, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.; Sachan, R.; Alhayyani, S.; Al-abbasi, F.A.; Singh, R.; Anwar, F. Co-Drug Development of Gallic Acid and Metformin Targeting the pro-Inflammatory Cytokines for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2023, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citi, V.; Barresi, E.; Piragine, E.; Spezzini, J.; Testai, L.; Da Settimo, F.; Martelli, A.; Taliani, S.; Calderone, V. Anti-Proliferative Properties of the Novel Hybrid Drug Met-ITC, Composed of the Native Drug Metformin with the Addition of an Isothiocyanate H2S Donor Moiety, in Different Cancer Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solier, S.; Müller, S.; Cañeque, T.; Versini, A.; Mansart, A.; Sindikubwabo, F.; Baron, L.; Emam, L.; Gestraud, P.; Pantoș, G.D.; et al. A Druggable Copper-Signalling Pathway That Drives Inflammation. Nature 2023, 617, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailuno, G.; Baldassari, S.; Balboni, A.; Pastorino, S.; Zuccari, G.; Cortese, K.; Barbieri, F.; Drava, G.; Florio, T.; Caviglioli, G. Development of Biotinylated Liposomes Encapsulating Metformin for Therapeutic Targeting of Inflammation-Based Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, K.; Li, S.; Liu, T. Biomimetic Nanovesicle Co-Delivery System Impairs Energy Metabolism for Cancer Treatment. J Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torunoglu, S.T.; Zajda, A.; Tampio, J.; Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Huttunen, K.M. Metformin Derivatives - Researchers’ Friends or Foes? Biochem Pharmacol 2023, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, B.; Liu, X.; Ma, T. Carbonized Polymer Dots Derived from Metformin and L-Arginine for Tumor Cell Membrane- and Mitochondria-Dual Targeting Therapy. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 17922–17935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Zielonka, J.; Hardy, M.; Ouari, O.; Chitambar, C.R.; Dwinell, M.B.; Kalyanaraman, B. Synergistic Inhibition of Tumor Cell Proliferation by Metformin and Mito-Metformin in the Presence of Iron Chelators. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3518–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Deng, X.C.; Jin, X.K.; Zhang, S.M.; Wang, J.W.; Feng, J.; Chen, W.H.; Zhang, X.Z. Fused Cytomembrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Tumor-Specific Immunotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




