1. Introduction
“Tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies” refers to the crustal material fabrics and compositions and structural deformations that can reflect the geological environment and physicochemical conditions of different structures under the action or control of tectonic stress field and the different types of tectonorock, mineral, and geochemical element assemblages formed therefrom as well as their zoning characteristics [
1]. Based on different research levels and scales, Fang
et al. (2021) divided structure lithofacies into five levels, i.e., (1) tectonic structure lithofacies; (2) regional structure lithofacies; (3) ore field structure lithofacies; (4) deposit structure lithofacies; and (5) ore-body structure lithofacies [
2]. Lv
et al. (1998, 2001, 2020) proposed structure deformation lithofacies [
3,
4,
5], which combines structures and constructions and is mainly applicable to the ore field-deposit level [
6]. Through zoning and deformation screening of structure lithofacies and combined research of macroscopic and microscopic tectofacies, Fang
et al. (2021) identified 9 zoning structure styles of vertical tectofacies in the metallogenic system of Sn-Cu-W mineralized concentration area in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, providing a theoretical basis for the deep prospecting and buried structure lithofacies prediction of this area [
2]. By structure-alteration lithofacies mapping method, Han
et al. (2011) studied the diapiric structure of copper ore deposit of Fengshan Block in Yimen County, Yunnan Province, carried out prospecting on deep orebody, and made a breakthrough in ore prospecting. This shows that the study on tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies can not only reveal the metallogenetic process, but provide an important basis for ore prediction [
1].
Located in the southwestern margin of the Yangtze Plate (
Figure 1a), the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn metallogenic province is bounded by the Anninghe fault (SN strike) on the west, the Weining-Shuicheng fault (NW strike) on the northeast, and Mile-Shizong fault (NE strike) on the southeast, respectively. So far, over 500 Pb-Zn deposits (spots) have been found there [
7,
8], which mainly exist in carbonate formation and are controlled by tectonic and altered carbonates [
9,
10]. As one of the representative deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn metallogenic province, the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit has a typical feature that ore body exists in “black/fracture zone” [
11] (
Figure 1b). “Black/fracture zone”, as the main ore-bearing geologic body of deposit, is controlled by F
15, F
1 and other major strike-slip faults of the ore area [
10], and can be divided by composition into two types, i.e., the “black/fracture zone” mainly composed by Upper Sinian Dengying Formation (Zb
d) dolomitic breccia or fragments (referred to as R1) and that mainly composed by Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation (∈
1q) black gray calcareous fine sandstone, siltstone, and calcareous shale breccia or fragments (referred to as R2). The R1 type, which mainly consists of ore-controlling and ore-bearing structures [
12,
13], has been concerned by many scholars [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. At present, there are mainly three opinions on the relationship between “black/fracture zone” and ore forming: (1) the product of paleokarst cave deposit [
19]; (2) the product of slump breccia, diagenetic breccia, tectonic breccia, and karst breccia formed by gravity flow [
20] (but effects during and after metallogenic epoch are not distinguished in this opinion); (3) tectonic genesis [
12] believe that “black/fracture zone” is the fracture zone formed by tensile fracture structure and carbonized by the reformation and superimposition of ore-forming fluid rich in organic carbon; Kong
et al. (2022) believe that “black/fracture zone” is controlled by minus flower structure composed by NW-W and N-W faults [
11]; Han
et al. (2022) believe that “black/fracture zone” is under the combined control of minus flower structure and diapir structure [
10].
It is found through preliminary field investigation that the “black/fracture zone” is composed of multiple types of tectonite, but the material compositions, textures, structures, mineral assemblages, geochemical characteristics, and the zoning rules of structure-alteration lithofacies of different types of tectonite remain unclear. Therefore, this paper makes a systematic study on the petrography, geochemistry, and fluid inclusions of structure-alteration lithofacies of R1 type “black/fracture zone” which is closely related to the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit and ore forming by structure-alteration lithofacies mapping method [
1,
2] in combination with alteration lithofacies prospecting method [
21], and discusses the lithofacies zoning rule and forming mechanism of the “black/fracture zone” of the deposit, thus providing theoretical and practical basis for deep prospecting in the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
2. Geological Characteristics of the Deposit
The strata exposed in the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit (
Figure 1b) mainly include Upper Sinian Dengying Formation (Zb
d), Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation (∈
1q), Lower Cambrian Canglangpu Formation (∈
1c), and Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation (∈
1l). Dengying Formation, the major ore-bearing horizon, can be divided into 8 members and 13 layers, of which the fourth to the eighth members are the main ore-bearing horizons. Fault structures which develop in the deposit can be divided into four orders [
17]: first-order structures, including F
1 and F
15, NWW-approx. EW striking, which are dextral shear-tension and tension-shear faults formed under the NW-SE principal compressive stress in the early stage (metallogenic epoch) and sinistral shear and shear-compression faults formed under the compressive stress in the late stage and control the distribution of the deposit; second-order structures, a series of N-W faults derived from first-order structures (F
3, F
8, F
6, F
100, and F
5) which are dextral tension and tension-shear faults in the early stage (metallogenic epoch) and sinistral compression and compression-shear faults in the late stage and generally control single ore body; third and fourth-order structures are subordinated faults which control the occurrence of veins.
The deposit consists of 1# and 2# ore bodies, of which the 2# ore body is smaller in scale and occurs as veins [
22] while the 1# ore body, with NWW strike, NE dip, and SE pitch, is the main body of the deposit. The 1# ore body includes five blocks (
Figure 1b,c), of which Block I is located between F
15 and F
25, with NWW strike and SW dip (locally NE dip at an angle of 62°~82°), and appears in long strip in plane while is bead-like in section; Block II is located between F
25 and F
8, with NW strike and NE dip (locally SW dip at an angle of 58°~84°), and takes the shape of a rhombus in plane while is columnar in section; Block III is located between F
8 and F
9, with NW strike and NE dip at an angle of 56°~80°, and takes the shape of a rhombus in plane while is columnar in section; Block IV is located between F
9 and F
6, with NW strike and NE dip (locally SW dip at an angle of 60°~88°), and takes a pod-like shape in plane while is columnar in section; and Block V is located between F
6 and F
5, with NW strike and NE dip (locally SW dip at an angle of 70°~88°), and takes the shape of a rhombus in plane while is columnar in section. Ore minerals are mainly sphalerite, followed by gelenite and pyrite and supplemented by a small amount of lead and zinc oxides such as sardinianite, bonamite, hydrozincite, and willemite, and metallic minerals like chalcopyrite and malachite. Gangue minerals are mainly dolomite, calcite, and quartz. Ore structures mainly include massive structure, brecciated structure, stockwork-like structure, and fine-veined structure. Ore textures mainly include granular texture, metasomatic texture, metasomatic relict texture, exsolution texture, common-border texture and intersertal texture. The types of wall-rock alteration are simple, mainly including carbonatization (dolomitization and calcilization), carbonization, silicification, and pyritization.
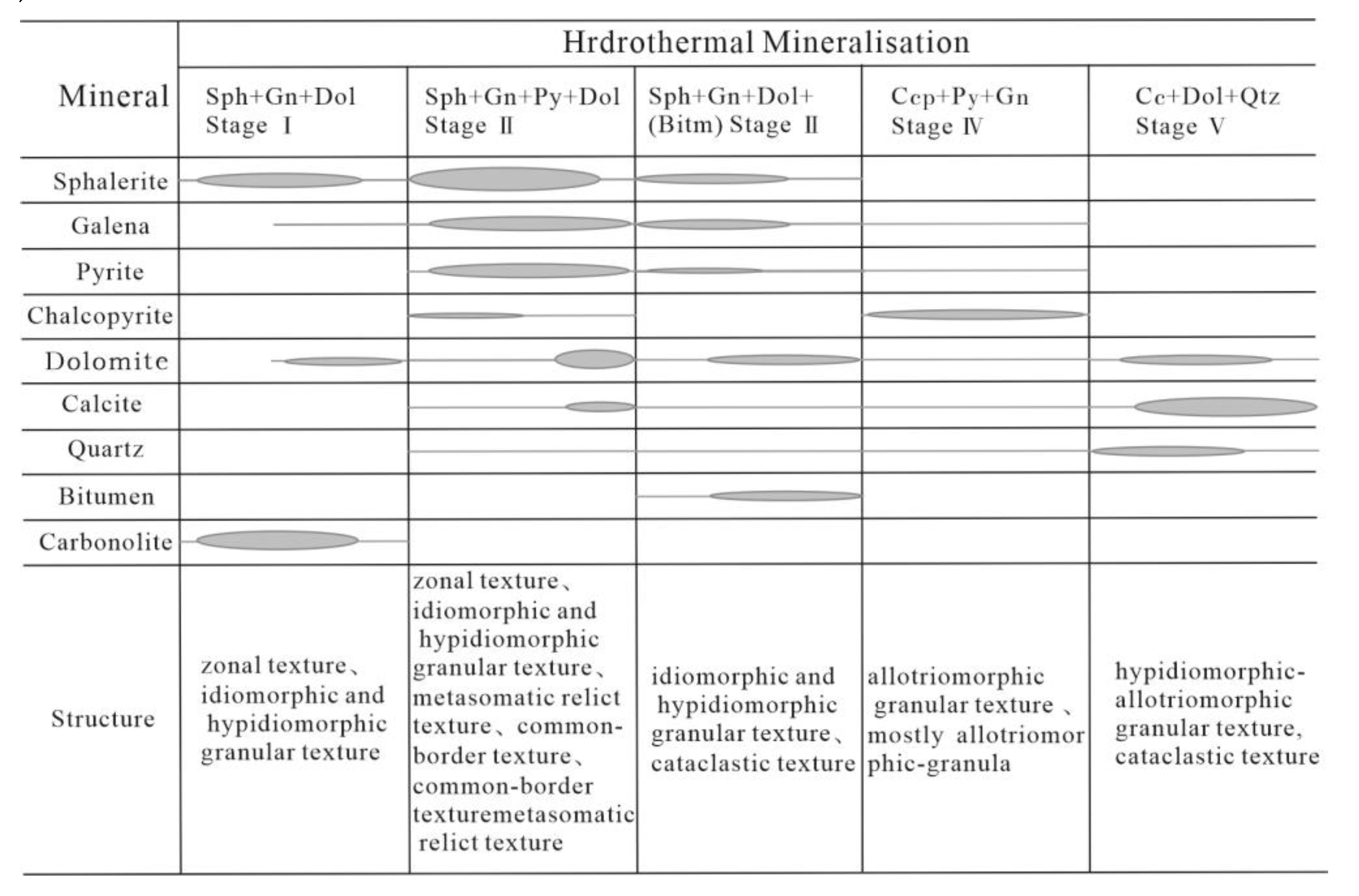
Through field studies and laboratory identification of (polished) thin sections and based on the symbiotic relationship, textures, structures, interpenetration, and other characteristics of minerals, the hydrothermal mineralization epoch of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit can be divided into five stages (
Figure 2):
(I) “marmatite + galena + dolomite” stage, in which sphalerite is brownish black or dark brown and has idiomorphic- hypidiomorphic textures, galena is iron-rich, and galena and dolomite are brecciated and cemented by late-stage sphalerite and other sulfides; (II) “sphalerite + galena + pyrite + dolomite” stage, the major metallogenic stage of the deposit in which sphalerite is mostly brown, metasomatic solution texture, metasomatic relict texture, exsolution texture, and zonal texture are common, and galena and pyrite have coarse particles; (III) “sphalerite + galena + dolomite + (bitumen)” stage, in which sphalerite is light yellow, and sphalerite, galena, and dolomite occur as veins and typically break early-stage sulfides; (IV) “chalcopyrite + pyrite + galena” stage, in which chalcopyrite, pyrite, and galena are mostly allotriomorphic-granular; and (V) “calcite + dolomite + quartz” stage, in which calcite, dolomite, and quartz all occur as veins and calcite vein encapsulated by early-stage bitumen can be seen.
3. Analysis Method
(1) Based on the research content and method of structure-alteration lithofacies mapping [
21], a typical section is selected for 1: 200 structure-alteration lithofacies mapping, the distribution range of alteration zone is determined, the altered lithofacies is zoned in details, and the tectonite and mineralized alteration assemblage types and typical textural and structural characteristics of various alteration lithofacies zones are analyzed by field sketching of typical geological phenomena; and the correlation between the zoning of alteration lithofacies and the spatial distribution of ore bodies and that between the mineralization scale (intensity) and the zoning of structure-alteration lithofacies are determined.
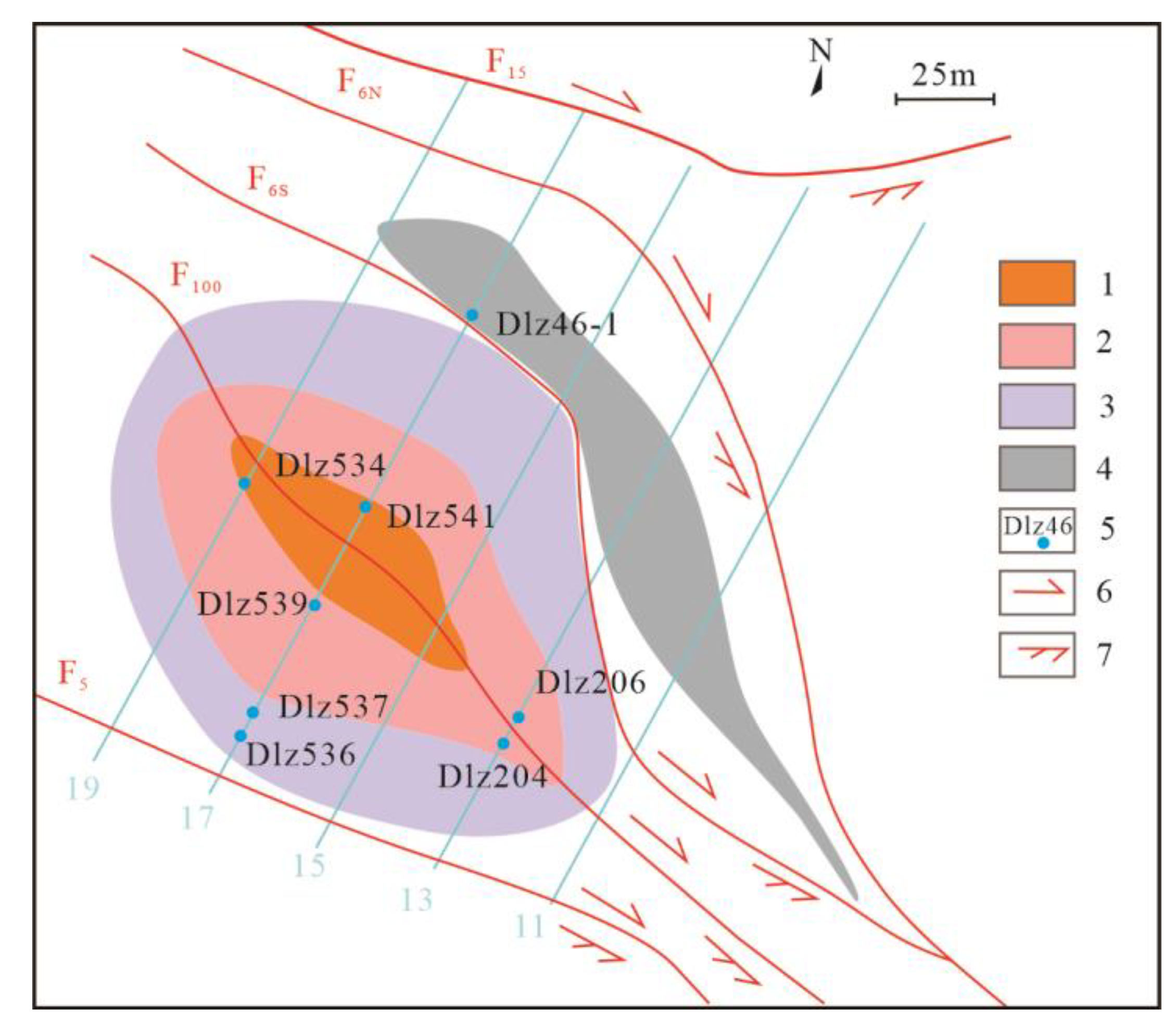
(2) To clarify the variation of physico-chemical conditions of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of “black/fracture zone” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, sphalerite, calcite, and other minerals in the major metallogenic stage (Stage II) of the metallogenic epoch of different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies in R1 “black/facture zone” in 1,944m level (
Figure 3) are selected fro the study on fluid inclusions.
(3) Typical samples, 40 pieces in total, are selected from different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones to carry out geochemical test in China Nonferrous Metals Northwest Mineral Geological Test Center. Of all the samples, 8 pieces are subjected to major element test by ICP-ACE, and 36 pieces from different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level are subjected to trace element test by ICP-MS.
4. Analysis Results
4.1. Zoning Characteristics of Tectonite-Mineralized Alteration Lithofacies
As a special geologic body of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, “black/fracture zone” has a close relation with ore forming [
13], and its formation is under the control of the strike-slip of F
1 and F
15 (
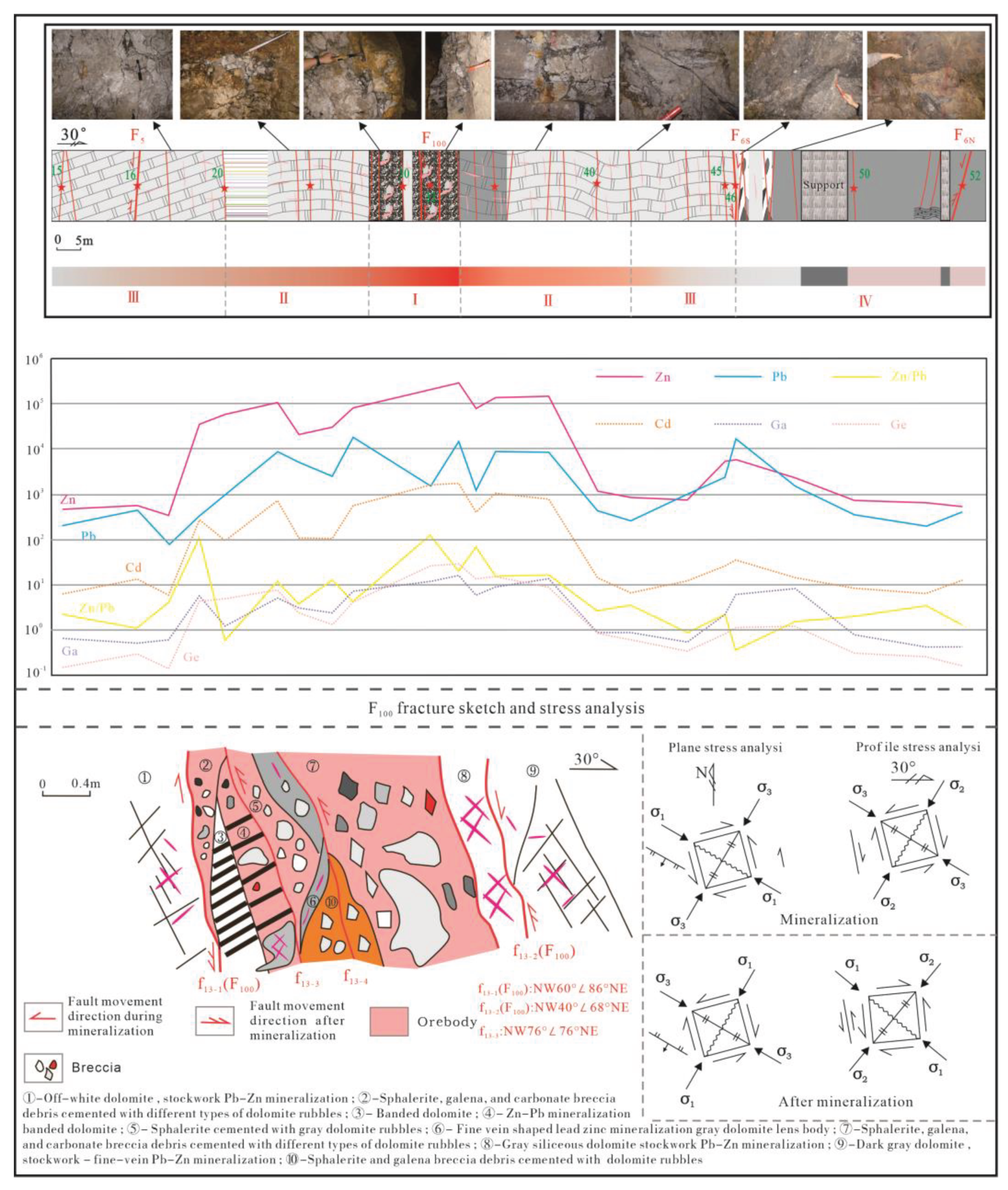
Figure 1b). R1 “black/fracture zone” is distributed within the 2~15# prospecting lines in the east of the mine on the surface and in both the west and the east of the mine below the elevation of 2,000m; R2 “black/fracture zone” is distributed to the west of the 9# prospecting line in the west of the mine and located above the elevation of 2,050m, which is 7m wide at its narrowest and 166m at its widest location, and within the zone, no breccia structure has ever developed and the existing structure is mainly cataclastic. R1 is the major ore-bearing type of “black/fracture zone”. In this paper, R1 “black/fracture zone” of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit is taken as an example for 1: 200 detailed mapping of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies, and it is found that the tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies of R1 “black/fracture zone” presents an obvious zonation.
R1 “black/fracture zone” of the 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level is located between F
6N and F
5, second-order structures of the deposit, and with F
100 as the center, four types of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies have developed in succession outward from the center, i.e., ① brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone; ② stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; ③ veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; and ④ fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone (
Table 1). The characteristics of the facies zones are as follows:
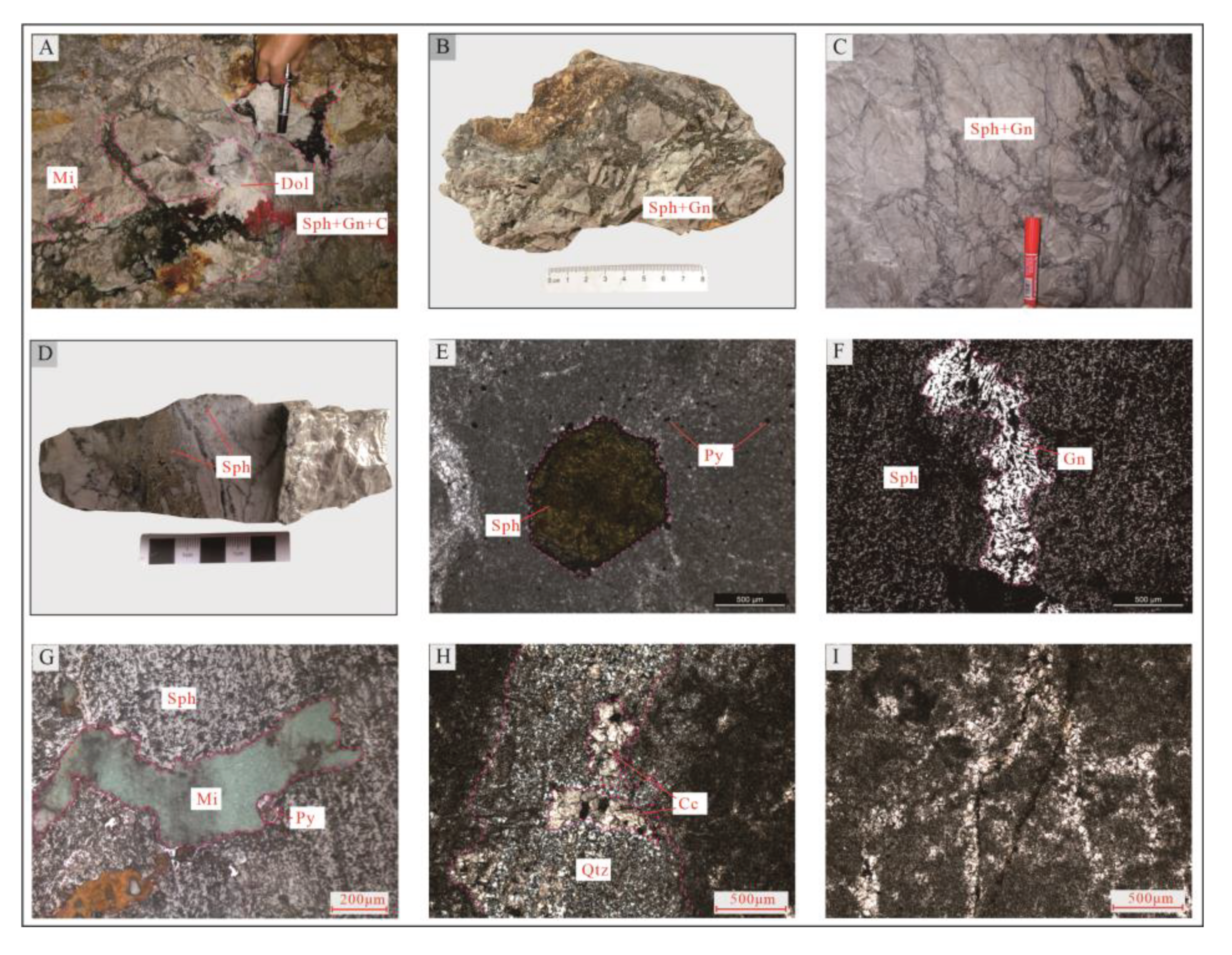
①- Brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone (
Table 1): It takes F
100 as the center (
Figure 4), and its tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies assemblage is complex breccia + sphalerite + galena + chalcopyrite + dolomite. The tectonite is complex breccia, and mineralized and complex breccia is located within F
100 and at its footwall and has the ore-controlling characteristics of an extensional structure. The complex breccia generally comprises more than 5 kinds of rubbles (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5A–F), e.g., the rubles of dark gray dolomite (
Figure 5A), caesious siliceous dolomite (
Figure 5A), gray dolomite (
Figure 4B), off-white dolomite (
Figure 5A,C), banded dolomite (
Figure 4), rhyolite (
Figure 5D), and tuff (
Figure 5E,F), which reflect its source complexity. In addition to the dolomite of host rocks, there is pyroclastic rock in the depth and overlying collapsed dolomite, which is greatly different from typical fault breccia; the cement includes sphalerite, galena, hydrothermal dolomite, carbonate breccia debris, etc. Sphalerite, which is mostly brownish black and yellowish brown and mainly cement, is scattered or sparsely disseminated in small amount in dolomite rubbles, and mainly has idiomorphic and hypidiomorphic granular textures (
Figure 5A, C, D). Galena has hypidiomorphic and allotriomorphic granular textures (
Figure 5E,F), metasomatic sphalerite shows metasomatic relict textures (
Figure 5E), galena and chalcopyrite have common-border textures, and metasomatic pyrite shows metasomatic relict textures (
Figure 5F). Bitumen is filled along the fractures of dolomite rubbles, covers chalcopyrite, galena, and pyrite, and shows poikilitic textures (
Figure 5G). Carbonatization is mainly dolomitization, and the dolomite in dolomite rubbles and cement shows secondary enlargement textures (
Figure 5H,I), which reflects strong dolomitization and hydrothermal activities in these zones.
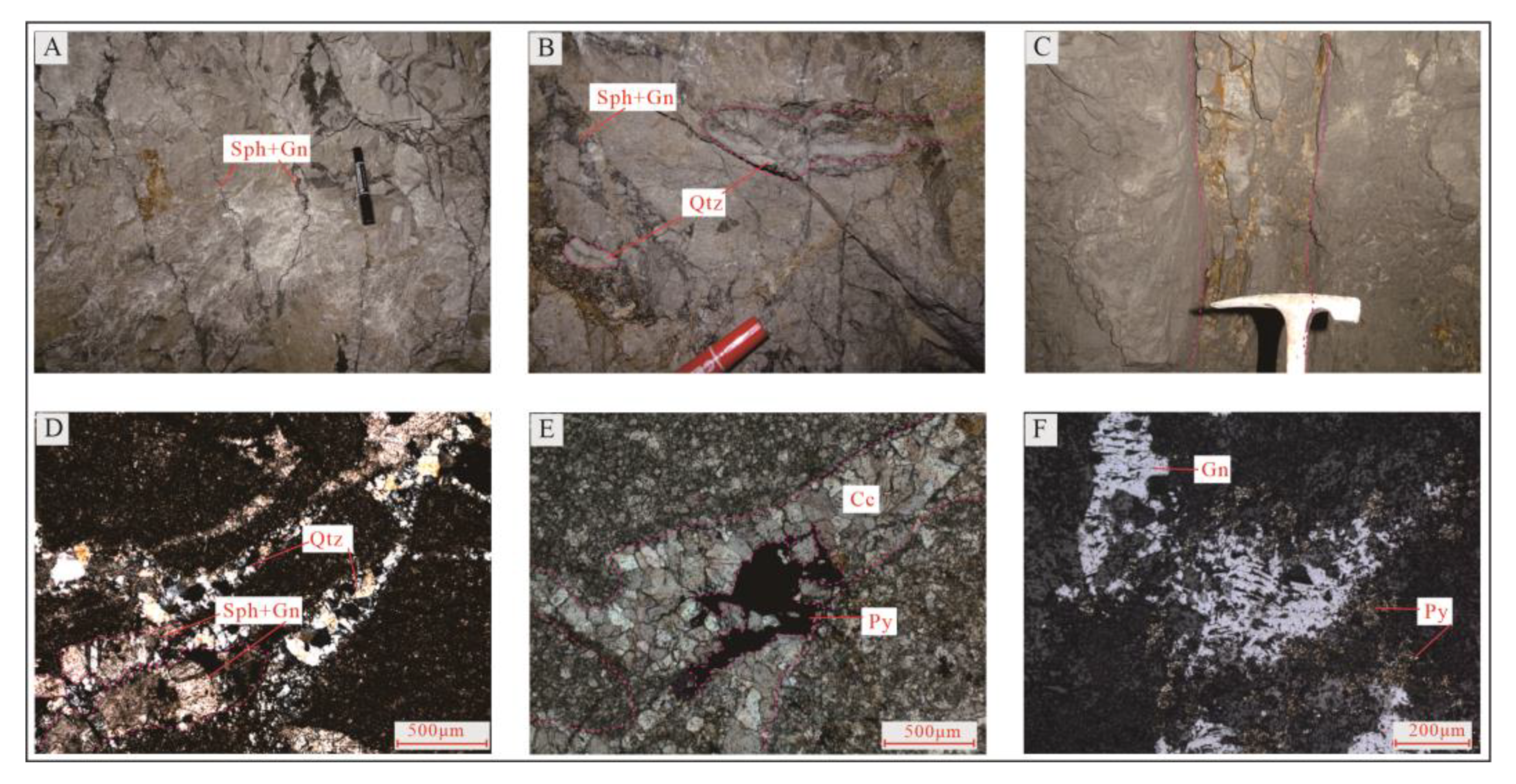
②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone: Its tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies assemblage is simple breccia + sphalerite + galena + quartz + dolomite, mainly including gray dolomite and carbonized dolomite debris, sphalerite, and galena cemented with dolomite rubbles (
Figure 6A–C) which have stockwork-like or brecciated structure. A small amount of veined and lumpy malachite can be seen in cement (
Figure 6A,G), which is filled along sphalerite fractures. It is the product after the metallogenic epoch, which, however, reflects copper mineralization in the metallogenic epoch of the zone. Rubbles are angular-subangular and can be collaged (
Figure 6B,C); under hydrothermal effect, rubbles are corroded and become bay-shaped (
Figure 6B); the compositions of rubbles are consistent with those of wall rocks. Sphalerite is mainly yellowish-brown and shows hypidiomorphic-allotriomorphic granular textures (
Figure 6D,E), and galena shows allotriomorphic granular textures and is filled along sphalerite fractures (
Figure 6F). Copper mineralization mainly involves malachite, which is associated with sphalerite, galena, and pyrite. Silicification, significantly stronger than that of facies zone ①, mainly involves fine-granular quartz stringer with vein width of approximately 1mm (
Figure 6H). Carbonatization mainly involves dolomite, which is lumpy and associated with sphalerite and galena (
Figure 6A), followed by calcite, which shows stockwork-like or veined structure and some of which is metasomatized by quartz and presents metasomatic relict textures.
③- Veined pyrite-sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone: Its tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies assemblage is dolomitic cataclasite + pyrite + sphalerite and galena + quartz + calcite. Rock fragments are mainly cataclasite (
Figure 7A–C), with fracture density up to 3-5/20cm. Fawn-tawny sphalerite and galena shows allotriomorphic granular textures, generally filled along fractures (
Figure 7A,B). Silicification tends to be intensified, and quartz is lumpy (
Figure 7B) and veined (
Figure 7D), with the maximum vein width of approximately 5cm. Carbonatization mainly involves calcite, which is stockwork-like, fine-veined, and lumpy (
Figure 7D,E). Allotriomorphic granular pyrite is filled along fractures of idiomorphic granular calcite lumps, or is metasomatized by galena and shows metasomatic relict textures (
Figure 7F).
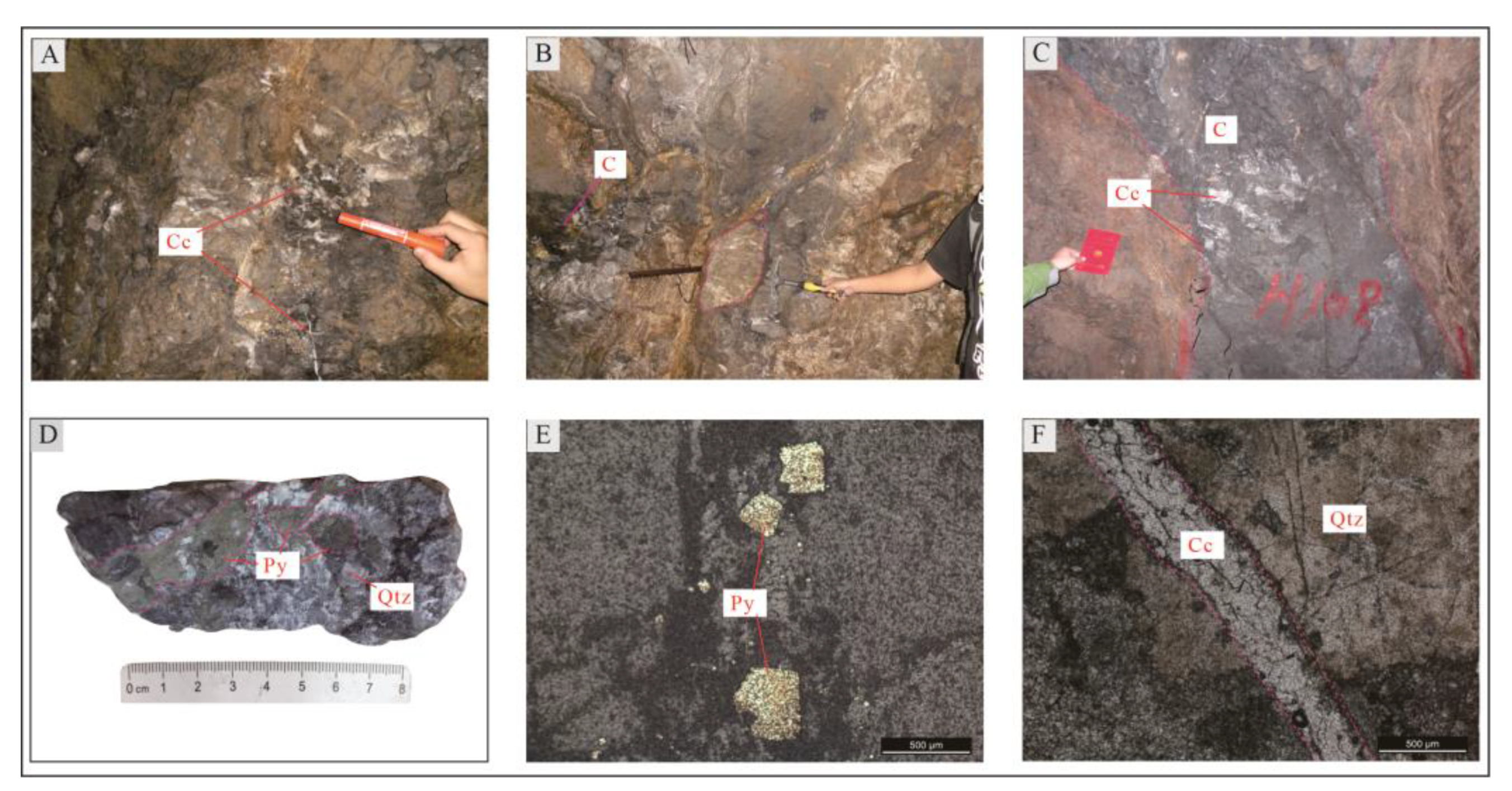
④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone: Located in F
6, it is controlled by F
6S and F
6N. Its tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies assemblage is carbonized dolomite + quartz + calcite + pyrite + (sphalerite and galena) (
Figure 8), with off-white dolomite lens interbedded at the position close to wall rocks (
Figure 8B). Sphalerite and galena are distributed sporadically, and lumpy pyrite is scattered (
Figure 8D, E) and shows idiomorphic-allotriomorphic granular textures (
Figure 8E). Quartz is lumpy (
Figure 8D), and silicified dolomite is formed locally (
Figure 8F) owing to strong silicification. This zone is rich in carbon, which is its most typical feature and reflects the reduction environment.
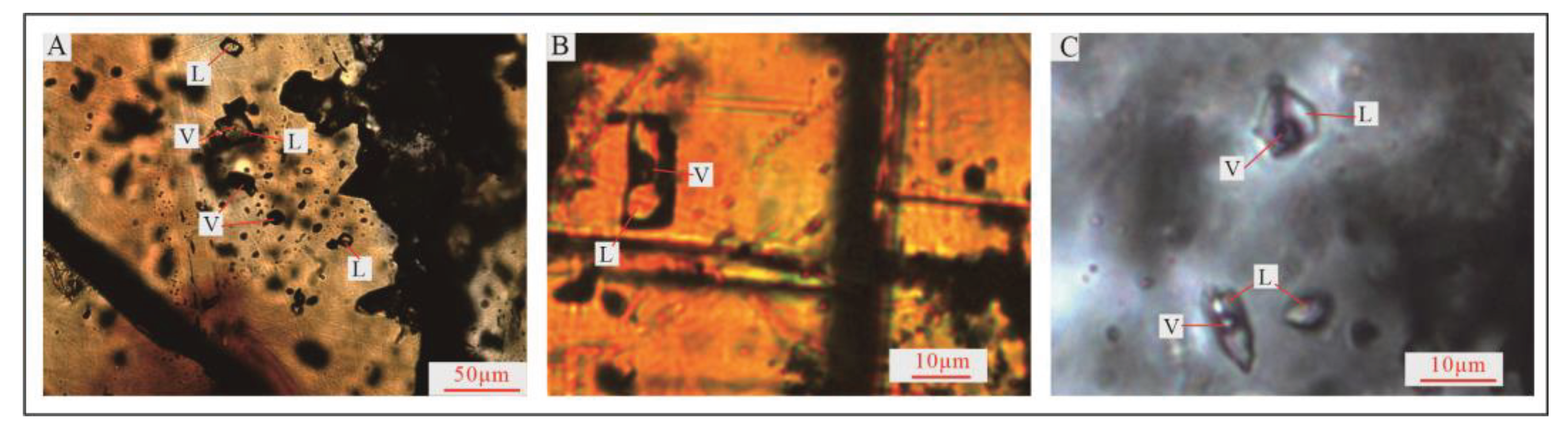
4.2. Characteristics of Fluid Inclusions
Most inclusions are gas-liquid two-phase inclusions (
Figure 9A–C), and some sphalerite contains a small amount of pure gas and pure liquid inclusions (
Figure 9A). The homogenization temperature of gas-liquid two-phase inclusions is measured, and the salinity and the fluid density are calculated by the Bodnor’s empirical formula (1993) and Liu Bin and Shen Kun’s empirical formula (1999), respectively [
23,
24].
The characteristics of liquid inclusions of various tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones are as follows (
Table 2): For Zone ①, the homogenization temperature is 177.5~267.8℃ (mean value of 225.0℃), the salinity is 8.55~14.57% NaCl
eqv (mean value of 12.00% NaCl
eqv), and the fluid density is 0.88~0.97g/cm
3 (mean value of 0.93g/cm
3); for Zone ②, the homogenization temperature is 146.3~288.5℃ (mean value of 211.6℃), the salinity is 6.59~17.79% NaCl
eqv (mean value of 13.60% NaCl
eqv), and the fluid density is 0.88~1.01g/cm
3 (mean value of 0.96g/cm
3); for Zone ③, the homogenization temperature is 168.1~221.4℃ (mean value of 197.9℃), the salinity is 7.17~13.29% NaCl
eqv (mean value of 11.40% NaCl
eqv), and the fluid density is 0.92~1.04g/cm
3 (mean value of 0.95g/cm
3); and for Zone ④, the homogenization temperature is 186.0~211.4℃ (mean value of 200.5℃), the salinity is 9.47~12.28% NaCl
eqv (mean value of 10.70% NaCl
eqv), and the fluid density is 0.93~0.96g/cm
3 (mean value of 0.95g/cm
3).
It can be seen that the homogenization temperature decreases from Zone ① to Zone ④, the salinity increases from Zone ① to Zone ② and then decreases to Zones ③ and ④, and the fluid density has little change on the whole.
4.3. Geochemical Characteristics
4.3.1. Major Element Characteristics
Through comparative study on the major elements of tectonite of various tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones, it is found that the SiO
2 and Al
2O
3 contents and the CaO/MgO mole ratio tend to increase with the gradual weakening of mineralization from Zone ① to Zone ④ while the CaO and MgO contents tend to decrease. The SiO
2 content is the lowest in Zone ①, and the quartz content increases gradually from Zone ① to Zone ④ (
Table 3). Both the CaO and the MgO contents tend to decrease from Zone ① to Zone ④, indicating that the migration of Ca
2+ and Mg
2+ ions occurs in tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones under the hydrothermal effect, while the CaO/MgO mole ratio tends to increase with the drift away from the center of ore body, indicating that with the migration and precipitation of ore-forming fluid, Mg
2+ ions are gradually consumed and the ratio of Ca
2+ gradually increases in the fluid. Strong dolomitization occurs in Zone ① while calcilization dominates in Zone ④ (
Table 3), which is consistent with the study results of the tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies profiles.
4.3.2. Trace Element Characteristics
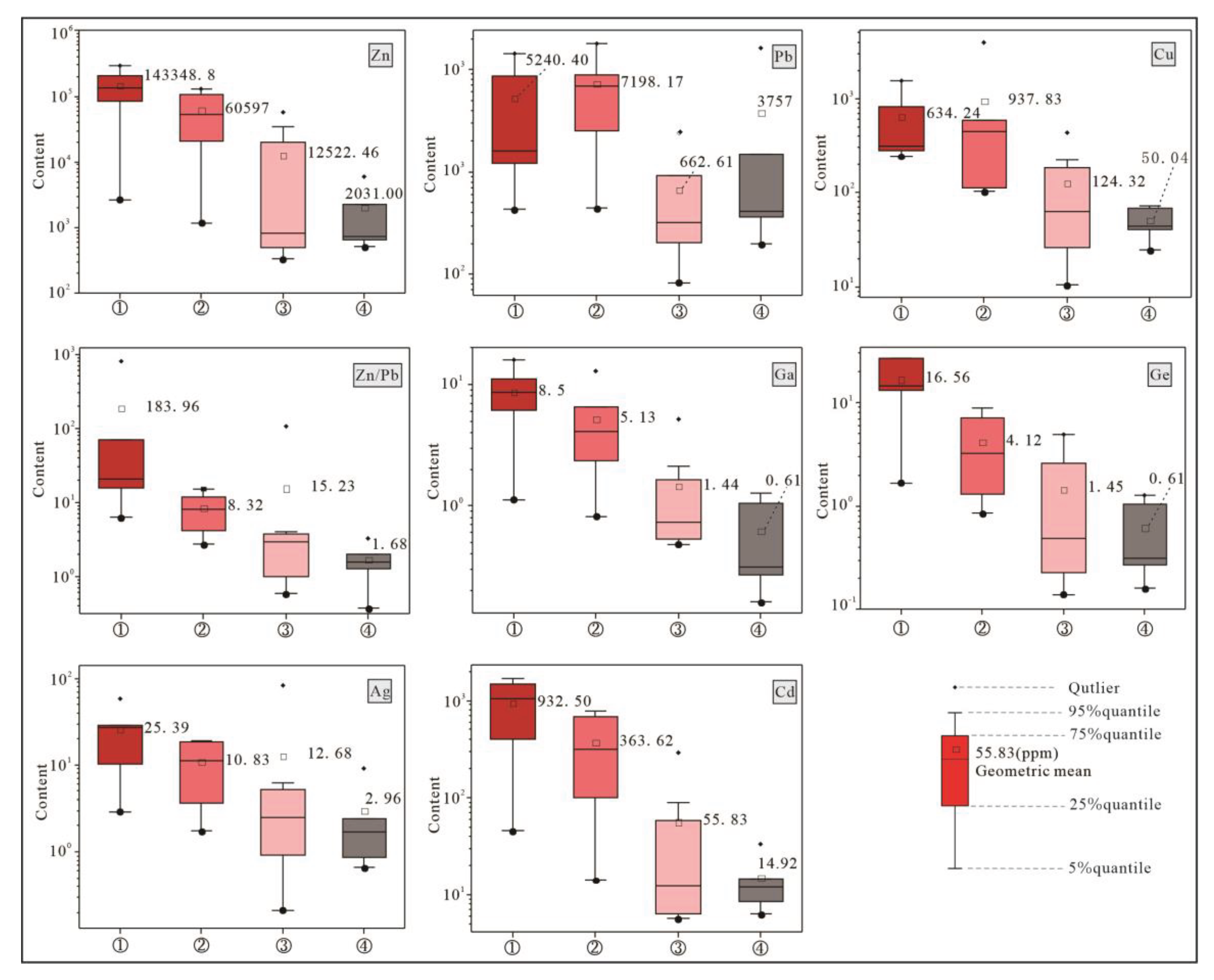
The study on trace elements (
Table 4,
Figure 2, 4 and 10) shows that the contents of Zn, Ge, Ga, Cd, and Ag decrease from tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones ① to ④. Zn, Pb, and Cu are more enriched in Zones ① and ② than in ③ and ④; Ge, Ga, Cd, and Ag are mainly enriched in Zones ① and ②, and when the exceptional value of Ag content (83.9ppm) in Zone ③, which makes the mean value of Ag content in Zone ③ slightly higher than that in Zone ②, is ignored, the Ag content in Zone ② (mean value of 10.83) is obviously higher than that in Zone ③ (mean value of 2.51). The ratio of Zn/Pb can reflect the migration direction of ore-forming fluid [
25]. Zn/Pb ratio in Zone ① is obviously higher than that in Zones ②, ③, and ④ (
Figure 10), indicating that the center of ore-forming fluid is in Zone ①. Both the change rule of the content of a single element and that of the ratio of elements reflect that hydrothermal fluid is likely to be originated from Zone ①, and migrates to Zones ②, ③, and ④ in succession.
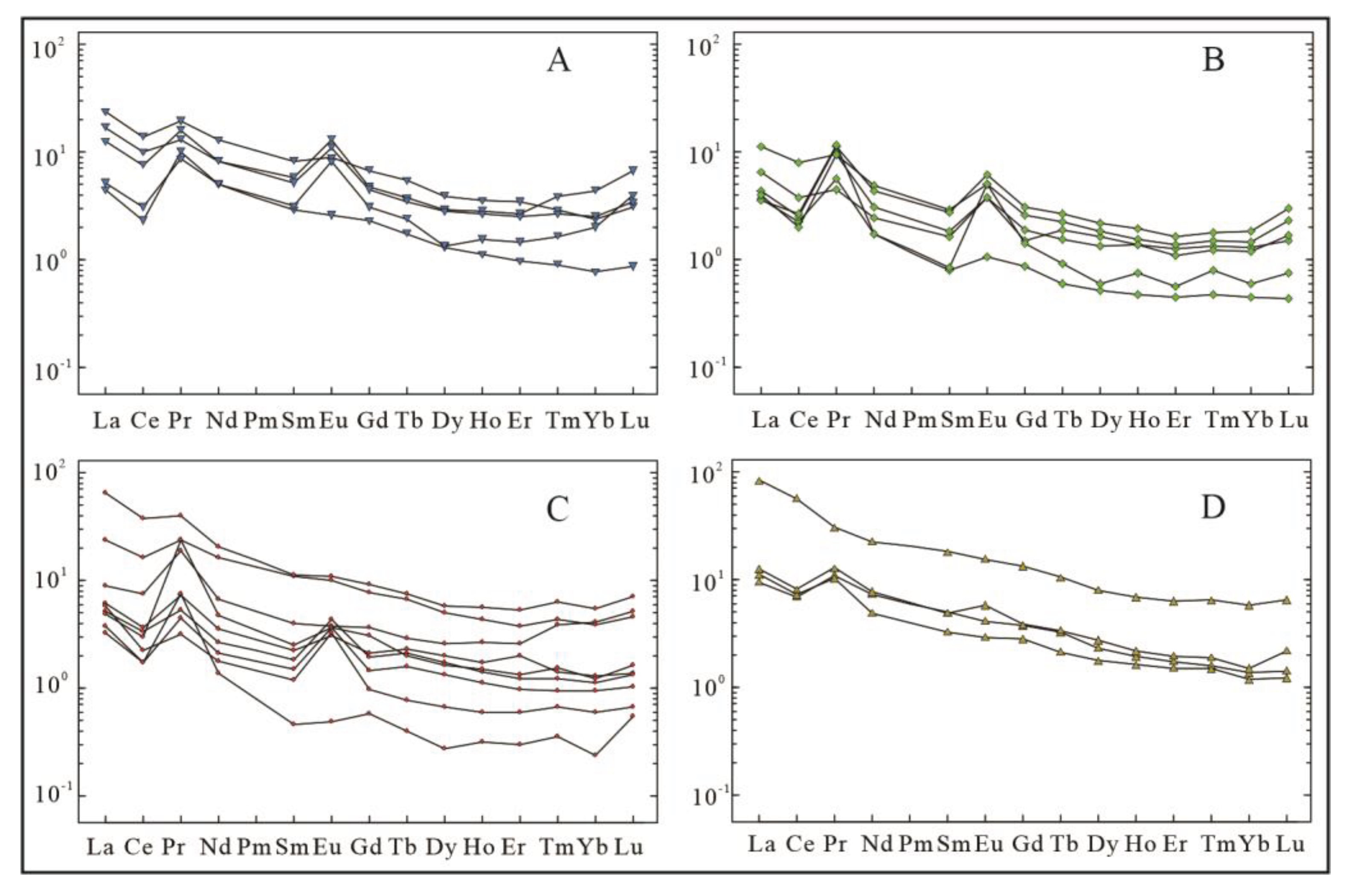
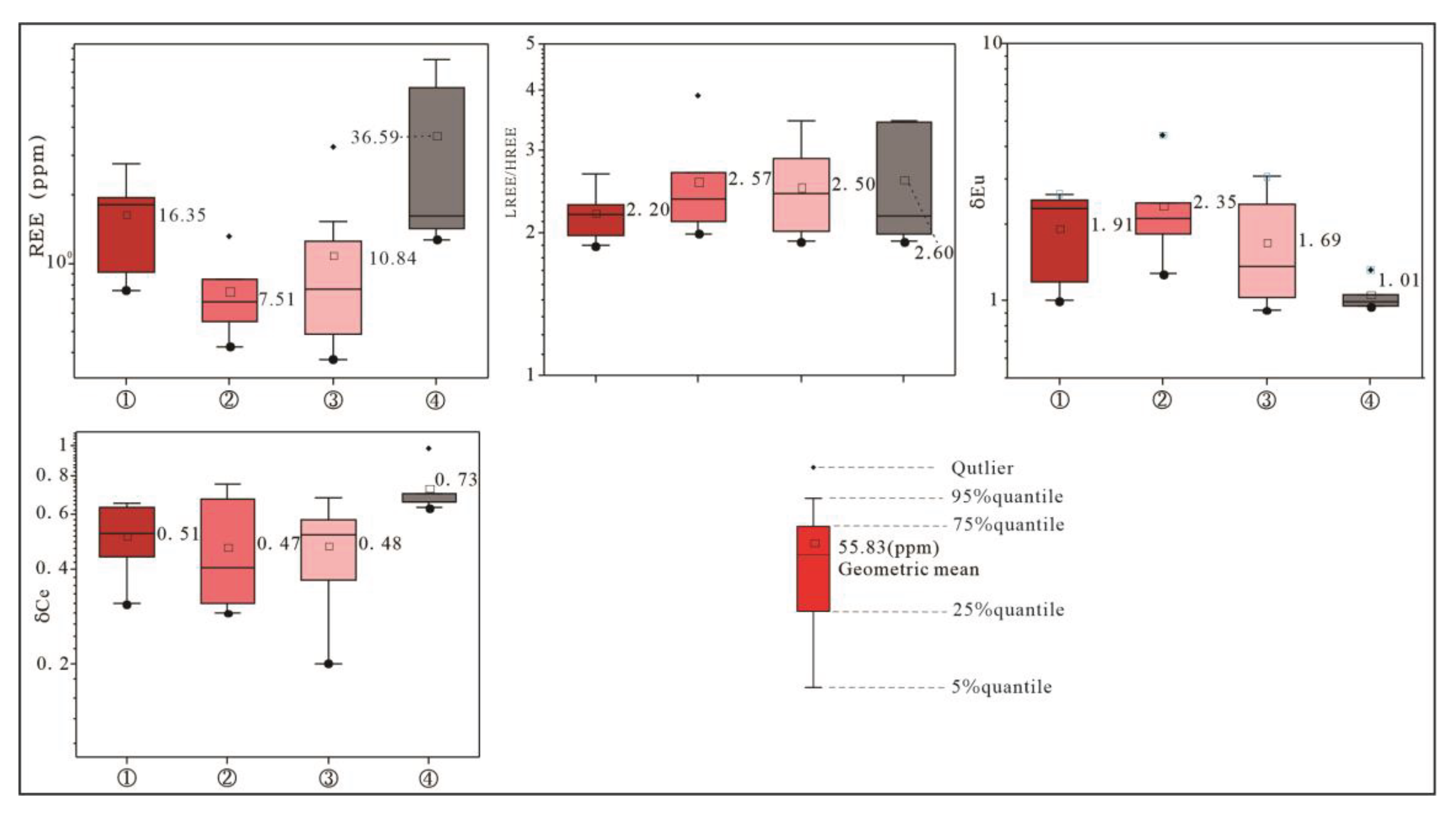
4.3.3. Rare Earth Element (REE) Characteristics
Brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone (①) (
Figure 9A and
Figure 10A,
Table 4): total REE content (∑REE) of 7.59~27.52 (mean value of 16.35), low dip towards the right, LREE/HREE of 1.98~2.66 (mean value of 2.20), Eu showing positive anomaly (δEu=1.00~2.61, mean value of 1.91), Ce showing negative anomaly (δCe=0.31~0.65, mean value of 0.51); stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone (②) (
Figure 9B and
Figure 10B,
Table 4): total REE content (∑REE) of 4.92~13.17 (mean value of 7.51), low dip towards the right, LREE/HREE of 1.99~3.90 (mean value of 2.57), Eu showing positive anomaly (δEu=1.27~4.42, mean value of 2.35), Ce showing negative anomaly (δCe=0.31~0.75, mean value of 0.47); veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone (③) (
Figure 9C and
Figure 10C,
Table 4): total REE content (∑REE) of 3.76~15.38 (mean value of 10.84), low dip towards the right, LREE/HREE of 1.92~3.16 (mean value of 2.50), Eu showing positive anomaly (δEu=0.92~3.05, mean value of 1.69), Ce showing negative anomaly (δCe=0.20~0.68, mean value of 0.48); fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone (④) (
Figure 9D and
Figure 10D,
Table 4): total REE content (∑REE) of 12.75~79.56 (mean value of 36.59), LREE/HREE of 1.92~3.46 (mean value of 2.60), Eu showing weak negative anomaly-positive anomaly (δEu=0.95~1.32, mean value of 1.06), Ce showing negative anomaly (δCe=0.63~0.98, mean value of 0.73).
5. Discussion
5.1. Element Characteristics and Significance of Tectonite-Mineralized Alteration Lithofacies Zones
Studies indicate that Zn, Pb, Cu, Ga, Ge, Cd, Ag, and other metallogenic elements show obvious immigration in various tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones. The contents of Zn, Pb, Cu, Ga, Ge, Cd, Ag, and other metallogenic elements are obviously higher in Zones ① and ② than in Zones ③ and ④, and the Zn/Pb ratio decreases gradually from Zone ① to Zone ④, which reflects the migration of ore-forming fluid from Zone ① to Zone ④.
The total REE content (∑REE) in various tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone” is higher than that in host rocks (0.92~10.64ppm, mean value of 2.82ppm) [
26], but it is impossible for a carbonate formation to leach out REE-rich ore-forming fluid [
27], which indicates that REEs are provided by REE-rich ore-forming fluid in addition to host rocks. With similar ionic radius, Y has similar geochemical behavior with REE and Sm [
28,
29,
30], so the variation trend of Y, REE, and Sm can be utilized to distinguish ore-forming fluids from different sources [
26,
31]. In the Y-∑REE and Y-Sm diagrams (Figure 13), the data projections of tectonite in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones have a good linear relation with those of Sinian Dengying Formation dolomite, basal Huili Group, and overlying Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation clasolite, and the correlation coefficients are 0.86 and 0.90, respectively, reflecting that they are closely related in genesis and have a certain clustering tendency, where complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone (①) and fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone (④) are close to the distribution range of basement strata and overlying Cambrian strata while stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone (②) and veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone (③) are close to that of Sinian Dengying Formation strata of host rocks. Studies on S, Pb, Sr, Zn, and other isotopes [
26,
32] show that metallogenic materials of the deposit, which have the characteristics of a crust source type, mainly come from basement strata, Sinian Dengying Formation, and overlying strata. Therefore, ore-forming fluid may have run through REE-rich basal Huili Group and overlying Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation strata and extracted metallogenic materials. The REE pattern and the LREE/HREE ratio can be used to discuss hydrothermal source and hydrothermal evolution [
31]. The LREE/HREE ratio increases gradually from Zone ① to Zone ④ (
Figure 11), indicating out-migration of ore-forming fluid from Zone ①, relative LREE enrichment, and gradually enhanced fractional distillation.
Figure 11.
Chondrite distribution modes of rare earth elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. A- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; B- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; C- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; D- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 11.
Chondrite distribution modes of rare earth elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. A- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; B- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; C- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; D- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 12.
Box diagrams of rare earth elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 12.
Box diagrams of rare earth elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 13.
Y-∑REE and Y-Sm change chart of different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. Note: The data of basement strata (Huili Group) are from 3433]; the data of Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation are from [
34]; and the data of Sinian Dengying Formation are from [
36].
Figure 13.
Y-∑REE and Y-Sm change chart of different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. Note: The data of basement strata (Huili Group) are from 3433]; the data of Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation are from [
34]; and the data of Sinian Dengying Formation are from [
36].
Sensitive to redox environment, Eu and Ce are often used to reflect the environment of deposit formation. Sverjensky (1984) and Bau (1992) find through study that temperature plays an important role in anomaly of Eu: when temperature is high enough (generally above 250℃), Eu
3+ in fluid is apt to be reduced to Eu
2+ which is easier to replace Ca
2+, leading to positive anomaly of Eu in carbonate minerals; when temperature falls (generally below 250℃), Eu
3+ dominates in fluid, leading to negative anomaly of Eu [
28,
35]. At a moderate temperature and in moderate reduction conditions, both Eu
2+ and Eu
3+ occupy a considerable proportion in fluid, so that positive anomaly, no anomaly, and negative anomaly of Eu all appear in the formed minerals [
36,
37,
38,
39]. Through study on REE characteristics of submarine high-temperature hydrothermal system, Ding
et al. (2000) find obvious positive Eu anomaly in the system [
40]. Eu anomaly may be affected by either metallogenic hydrothermal fluid or compositions of tectonite [
41]. Various tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone” mainly comprise carbonatite of Sinian Dengying Formation which is characterized by negative Eu anomaly [
26], but different degrees of positive Eu anomaly occurs in these zones, apparently indicating that positive Eu anomaly in these zones are mainly affected by ore-forming fluid. Strong positive Eu anomaly occurs in all Zones ①, ②, and ③, and the positive Eu anomaly in Zones ① and ② (1.93 after anomaly value of 4.42 deducted) is higher than that in Zone ③ while weak positive and negative anomalies occur in Zone ④, reflecting the existence of high-temperature ore-forming fluid participating in ore forming. From Zone ① to Zone ④, temperature falls from medium-high to medium-low temperature, which agrees with the results of temperature measurement of fluid inclusions. Ce anomaly is affected by redox conditions, and with high oxygen fugacity, Ce
3+ in solution is apt to be oxidized to Ce
4+, leading to negative Ce anomaly in minerals precipitating from metallogenic hydrothermal fluid. The δCe values of Zones ①, ②, and ③ are close, lower than that of Dengying Formation dolomite of host rocks (mean value of 0.78) [
26], while the value of Zone ④ (mean value of 0.73) is close to that of Dengying Formation dolomite of host rocks (mean value of 0.78) [
26], reflecting the existence of oxidizing fluid participating in ore forming.
To sum up, Zones ① and ② are where enriched precipitation of metallogenic elements occurs, and Zone ① is the mineralization center. Ore-forming fluid flows through REE-rich basement strata and overlying Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation and migrates from Zone ① to Zone ④, with gradually stronger fractionation of REE and gradually lower metallogenic temperature, reflecting the existence of oxidizing fluid participating in ore forming.
5.2. Zoning Mechanism of Tectonite-Mineralized Alteration Lithofacies
The Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit is located between the Puduhe fault and the Xiaojiang fault, and a widely-distributed intracontinental strike-slip structure system with obvious zoning and diversity has been formed in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn mineralization concentrated area under the collision of Indo-China Block and Yangtze Plate during the Indo-Chinese Epoch [
10]; sinistral strike-slip movement of approx. SN striking Anninghe, Puduhe, and Xiaojiang deep major faults occurs under the uniform action of NW-SE structural stress fields [
10]; and dextral strike-slip occurs to the NWW-approx. EW striking F
1 and F
15 faults of the deposit which present dextral shear-tension and tension-shear, and the derived dextral tension-shear secondary faults F
8, F
9, F
6, and F
5, second-order folds, interlayer faults, and other assemblages (
Figure 14A,B) control the single ore body (
Figure 14).
Studies show that outward from the mineralization center (ore shoot) are brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone (①), stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone (②), veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone (③), F
6S, fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone (④), and F
6N, successively (
Figure 4 and
Figure 14A). Controlled by F
100 (F
5) of second-order structure of the deposit, Zone ① is the center of hydrothermal activity where complex breccia and shoot are often formed (
Figure 14A,B); complex breccia comprises fault and hydrothermal-origin rubbles, mainly including overlying collapsed rubbles, rubbles formed from hydrothermal corrosion, rubbles of wall rocks, and deep-source rubbles, some of which, with good roundness, have the characteristics of rheonorphic breccia [
42] and are the evidence for diapirism (cryptoexplosion). Zone ② is controlled by the subordinate structure derived from the second-order structure of the deposit, and the rubbles here are mainly wall rock rubbles with little migration; mineralization here is weaker than that in Zone ①; stockwork-like and veined structures dominate the zone. In Zone ③, pyritization and calcilization dominate and ore bodies are filled in brecciated or stockwork-like form. In Zone ④, calcilization, pyritization, silicification, and carbonization are significantly enhanced. In Zone ①, dolomitization is the strongest while silicification is relatively weak. The homogenization temperature of ore-forming fluid decreases from Zone ① to Zone ④. From the perspective of the entire deposit, fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone (④) controls the type and grade of ores; in the west of Zone ④ is ore block V with relatively low grade dominated by brecciated, stockwork-like, and veined ores while in the east are ore blocks III, II, and I with higher grade dominated by lumpy, brecciated, and stockwork-like ores [
43]. Therefore, Zones ①, ②, and ③ are the main places where ore body occurs while Zone ④ acts as a partition layer and plays a role in the reduction of S.
The ore-forming fluid of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit is the Ca
2+-Na
+-Cl
--SO
42- type [
26,
44] with high Na/K mole ratio (greater than 1), low Na/Ca mole ratio (smaller than 4), and low F/Cl mole ratio [
45], and is basin brine [
46,
47]. The solubility of chloride complex of elements Zn and Pb is 1 – 6 orders of magnitude higher than that of hydrosulfide complex [
48,
49], and fluid inclusions, however, contain a large amount of Cl
- ions, so the elements Zn and Pb should have migrated mainly in the form of chloride complex. The content and the proportion of anion SO
42- decrease gradually while those of Cl
- increase from the early to the late stage of mineralization, reflecting the consumption of SO
42- and the release of Cl
- in the ore-forming process. The study on S isotopes shows that the sulfides of the deposit are formed mainly through thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR) [
50]. The analysis of gas phase compositions of fluid inclusions shows that the redox parameter R (0.052→0.175→0.283) tends to increase gradually from the early to the late stage of mineralization; fluid inclusions often contain CH
4 and other reducing gases [
50]; the study on H-O isotopes shows that they are distributed along the reaction line of basin brine and organic matters. These all reflect that organic matters or reducing fluid rich in organic matters participates in reactions in the ore-forming process. Based on the textures of ore body, the contact relation of ore body with wall rocks, alteration characteristics, and ore-forming fluid characteristics, Yuan Bo
et al. (2014) believe that the deposit is the product of the mixing of reductant-rich (reducing) fluid and metal and sulfate-rich (oxidizing) fluid [
50]. Therefore, the main mechanism of sulfide precipitation should be the mixing of Cl
- and SO
42--rich high-temperature oxidizing fluid which contains metallogenic elements and reducing fluid.
The comprehensive study presents that the metallogenic system of NE tectonic zones controls the metallogenic system of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit. Deep ore-forming fluid rich in Cl
- and SO
42-, driven by structures, migrates along the footwalls of NW-W and approx. E-W striking F
1 and F
15 and the NE-SW pitching main anticline of the derived secondary NWW-NW striking faults (F
25, F
8, F
9, F
6, F
5, etc.) (Wu Jianbiao
et al., 2022) while extracting Pb, Zn, Cu, and other metallogenic elements in the strata it flows through (
Figure 14); with the continuous gathering of ore-forming fluid, the fluid pressure increases and when it is higher than the lithostatic pressure and the tensile strength of wall rocks, diapirism (cryptoexplosion) occurs along NWW-NW striking faults (F
25, F
8, F
9, F
5, etc.), accompanied by rock breakage, spillover of volatile components, and abrupt pressure drop, forming complex breccia comprising dolomite which contains host rock, deep pyroclastic rock, and overlying collapsed dolomite. Meanwhile, deep ore-forming fluid starts to mix with the reducing fluid formed through meteoric water leaching of Jurassic-Cretaceous strata and carbonatite wall rock, initiating thermochemical sulfate reduction (TSR) and precipitating a large number of sulfides which are cemented with rubbles or filled in rock fractures, thus forming tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies assemblage subzones of “black/fracture zone” and different types of orebody clusters (
Figure 14A,B,
Table 1).
6. Conclusion
(1) Through analysis of ore-hosting tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies of R1 “black/fracture zone”, this paper establishes the identification marks, tectonite types, mineralized alteration types, and zoning characteristics and summarizes the zoning rule of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit. The tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones are divided into 4 types in succession outward from the mineralization center, i.e., ①- brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone, ②- stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone, ③- veined pyrite-sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone, and ④- fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone, of which Zones ①, ②, and ③ are the main places where ore body occurs while Zone ④ mainly acts as a partition layer.
(2) The homogenization temperature of ore-forming fluid decreases from Zone ① to Zone ④, the salinity increases from Zone ① to Zone ② and then decreases to Zones ③ and ④, and the fluid density has little change on the whole; the contents of Zn, Pb, Cu, Ga, Ge, Cd, Ag, and other metallogenic elements, the Zn/Pb ratio, and the CaO/MgO mole ratio decrease gradually from Zone ① to Zone ④; and REE fractionation, calcilization, silicification, and pyritization enhance gradually from Zone ① to Zone ④.
(3) The comprehensive study on the ore bodies and tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit and the fluid inclusions, major elements, trace elements, and rare earth elements in tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones with different structures indicates that diapirism (cryptoexplosion) of strike-slip structures and “black/fracture zone” is the key to ore forming; and the zoning mode of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit is established, bringing new thought, evidence, and inspiration for prospecting in the depth and on the periphery of the deposit.
Author Contributions
For L.X. (Lingjie Li): Conceptualization, Software, Investigation, Experiment, Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft. R.H. (Runsheng Han): Validation, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Supervision. J.W. (Jianbiao Wu): Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation. Z.F. (Zhixing Feng): Investigation, Experiment, Writing: Review & Editing.
Funding
This work was co-financed by This research project was jointly funded by the programs of the National Natural Science Foundation (Noes. 42172086,41572060, U1133602), the Program of ‘Yunling Scholar’ of Yunnan province (2014), Projects of Yunnan Engineering Laboratory of Mineral Resources Prediction and Evaluation (YM Lab) (2010) and Innovation Team of Yunnan province and KMUST (2008, 2012).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the helpful and useful suggestions of the editors and reviewers.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Han R S, Wang L, Fang W X, et al. Preliminary discussion on the piercing structural rock-mineralized altered rock phase zoning model of the Fengshan copper deposit in Yimen area, Yunnan. Geological Bulletin, 2011, 31(4): 495-504. (in Chinese).
- Fang W X, Wang S C, Jia R X et al. Theoretical innovation and technology research and development direction of large-scale structural petrographic mapping. Mineral exploration,2021,12(07):1488-1518. (in Chinese).
- Lv G X. Research on large-scale mapping of structural deformation and lithofacies traces and structural mineralization of Linglong-Jiaojiashi Au deposit. Acta Geosciences,1998, 19(2):10. (in Chinese).
- Lv G X, Guo T, Shu B, et al. Large-scale mapping of structural deformation lithofacies traces and geological prediction of hidden deposits - taking the Linglong-Jiaojia style gold deposit in Jiaodong as an example. Geological Bulletin of China,2001,(03):313-321.
- Lv G X, Zhang B L, Hu B Q, et al. Classification and application effects of lithofacies classification of ore field structural deformation. Geological Bulletin, 2020, 39(11):12.
- Zhang B L, Lv G X, Yu J G, et al. Research on tectonic deformation lithofacies classification based on deep geophysical information.Earth Science Frontiers, 2022,29(01):413-426 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Liu H C, Lin W D. Research on the regularity of Pb-Zn-Ag deposits in Northeast Yunnan. Yunnan University Press, 1999. (in Chinese).
- Cui Y L, Zhou J X, Huang Z L et al. Geology, geochemistry and genesis of the Pb-Zn deposit in Fule, Yunnan Province. Acta petrologica sinica, 2018, 34(1): 194-206. (in Chinese).
- Han R S, Zhang Y, Ren T, et al. Review of research on non-magmatic epithermal lead-zinc deposits hosted in carbonate rocks. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2020,45(04):29-40. (in Chinese).
- Han R S , Wu P , Zhang Y , et al. New progress in theoretical research on the mineralization theory of germanium-rich lead-zinc deposits in the Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou metallogenic area of Southwest Tethys . Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(2): 554-573.(in Chinese).
- Kong Z G, Zhang B C, Wu Y, et al. Research on the ore-controlling structural style and mineralization mechanism of the Daliangzi germanium-lead-zinc deposit in Sichuan [J]. Geoscience Frontiers, Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(1): 143. (in Chinese).
- Lin F C. New exploration into the origin of the Pb-Zn deposit in Daliangzi, Huidong, Sichuan . Mineral Deposits, 1994, 13(2): 126-136. (in Chinese).
- Liu Z P. Study on stable isotope geochemistry of Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Huidong, Sichuan . Chengdu University of Technology,2016. (in Chinese).
- Zhang J H. Mineralogical characteristics and genetic significance of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Huidong, Sichuan.Chengdu University of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese).
- Yuan B, Zhang C, Yu H, et al. Element enrichment characteristics: Insights from element geochemistry of sphalerite in Daliangzi Pb–Zn deposit, Sichuan, Southwest China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 186: 187-201.
- Liu W, Zhang X, Zhang J, et al. Sphalerite Rb-Sr dating and in situ sulfur isotope analysis of the Daliangzi lead-zinc deposit in Sichuan Province, SW China. Journal of Earth Science, 2018, 29(3): 573-586.
- Wu J B, Han R S, Feng Z X, Wu P, Gong H S, Ding T Z, Zhao Xinyue, Li L J,. F_(15) main controlling fault and its ore-controlling mechanism in Daliangzi Pb-Zn mining area in southwest Sichuan. Geological Bulletin Of China, 2022, 41 (10): 1869-1886.] (in Chinese).
- Li L J, Han R,Zhang Y,Wu J,Feng Z. Trace element signatures of sphalerite in the Sichuan Daliangzi Ge-rich Pb-Zn deposit and its implications for deep ore prospecting. Frontiers in Earth Science,2022.
- Wang Z J. Discussion on the sedimentary origin of ancient karst caves in Tianbaoshan and Daliangzi Pb-Zn mines. Geology and Exploration, 1985, 10: 10-17. (in Chinese).
- Hu J Z. New understanding of the metallogenic structure and metallogenic model of the Daliangzi lead-zinc-silver deposit in Huidong . Acta Geologica Sinica, 1993, (01): 40-68. (in Chinese).
- Han R S, W F, Hu Y Z, et al. Study on metallogenic structural dynamics and chronological constraints of Huize type (HZT) germanium-silver-lead-zinc deposit. Geotectonics and Mineralization, 2014, 38(4) : 758-771.(in Chinese).
- Wang Q, An Y L, Gu X X, et al. Enrichment rules of dispersed elements cadmium, germanium and gallium in Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2010, 30 (01): 78-84. (in Chinese).
- Bodnar R J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica acta, 1993, 57(3): 683-684.
- Liu B , Shen K . Thermodynamics of Full Body Inclusions. Beijing; Geological Publishing House. 1999, 44-114.(in Chinese).
- Zeng Q F. On hydrothermal mineralization conditions.Beijing: Science Press, 1986. (in Chinese).
- Wang H. Research on the mineralization of MVT Pb-Zn deposits in the Lianghui area, Sichuan, China. Kunming University of Science and Technology,2019. (in Chinese).
- Michard A. Rare earth element systematics in hydrothermal fluids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(3): 745-750.
- Bau M, Moeller P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite. Mineralogy and petrology, 1992, 45(3): 231-246.
- Cherniak D J, Zhang X Y, Wayne N K, et al. Sr, Y, and REE diffusion in fluorite[J]. Chemical Geology, 2001, 181(1-4): 99-111.
- Schönenberger J, Köhler J, Markl G. REE systematics of fluorides, calcite and siderite in peralkaline plutonic rocks from the Gardar Province, South Greenland. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1-2): 16-35.
- Liu S w, Shi S, Li R X, et al. Geochemistry study of rare earth elements in the May-uan Pb-Zn deposit in the northern margin of the Yangtze Plate. Mineral Deposits,2013,32(05):979-988 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Zhu C, Wang J, Zhang J, et al. Isotope geochemistry of Zn, Pb and S in the Ediacaran strata hosted Zn-Pb deposits in Southwest China. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 103274.
- Yin F G, Sun Z M, Ren G M, et al. Geological records of the Early-Mesoproterozoic orogeny in the southwestern margin of the Upper Yangtze Block. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(12):1917-1932.(in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Liu J Q, He L, He P. Geochemical characteristics and significance of the Qiongzhusi Formation in the eastern margin of the Kangdian Ancient Continent- Take as an examp-e the profile of Zincanggou in Zhaoyang District, Zhaotong City, Yunnan Province. Act-a Sedimentae Sinica,2021,39(05):1305-1319 (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Sverjensky D A. Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 67(1): 70-78.
- Constantopoulos J. Fluid inclusions and rare earth element geochemistry of fluorite from south-central Idaho. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(3): 626-636.
- Wang L Q, Cheng W B, Luo M C, et al. Study on the composition characteristics and genesis of metal sulfides and quartz rare earth elements in Meng Ya A Pb-Zn deposits, Xi Zang China. Geology of China, 2012,39(03):740-749. (in Chinese).
- Cao H W, Zhang S T, Gao Y Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements and their indicative significance in Linxi fluorite deposit, Neimenggu, China. Ge-ochimica,2014,43(02):131-140. (in Chinese).
- Song D H, Han R S, Wang M Z, et al. Main ore-controlling fault structural rock-lithofacies zoning model of Qingshan Pb-Zn deposit in northwest Guizhou. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(03): 376-390. (in Chinese).
- Ding Z J, Liu C Q, YAO S Z , et al. The composition of rare earth elements and their controlling factors in high-temperature fluids in submarine hydrothermal systems.Advances In Earth, 2000, 15(3): 307-312. (in Chinese).
- Zhao D, Han R S, Wang J S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in the Lehong large Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Yunnan.Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017,37(05):588-595. (in Chinese).
- Wang J C, Peng E S, Sun Z J. Classification of hydrodynamic breccia and its geological significance. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2000, 30(1): 18-23. (in Chinese).
- Yuan H. Mineralization-alteration lithofacies zoning mechanism and prospecting prediction of Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit, Sichuan. Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2021. (in Chinese).
- Wang J. Research on the positioning rules of large-scale Pb-Zn deposits in the southwestern margin of the middle and upper Yangtze Platform. China University of Geosciences, 2018. (in Chinese).
- Li F y. Research on the occurrence state and enrichment mechanism of dispersed elements in MVT lead-zinc deposits - taking the Tianbaoshan and Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposits in Sichuan as an example. Chengdu University of Technology, 2003. (in Chinese).
- Samson I M, Williams-Jones A E, Ault K M, et al. Source of fluids forming distal Zn-Pb-Ag skarns: Evidence from laser ablation–inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry analysis of fluid inclusions from El Mochito, Honduras. Geology, 2008, 36(12): 947-950.
- Hofstra A H, Meighan C J, Song X, et al. Mineral thermometry and fluid inclusion studies of the Pea Ridge iron oxide-apatite–rare earth element deposit, Mesoproterozoic St. Francois Mountains terrane, southeast Missouri, USA. Economic Geology, 2016, 111(8): 1985-2016.
- Reed M H, Palandri J. Sulfide mineral precipitation from hydrothermal fluids. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2006, 61(1): 609-631.
- Zhang Y. Fluid mixed mineralization mechanism of Huize super-large Pb-Zn deposit in Northeast Yunnan mining area.Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2016. (in Chinese).
- Yuan B, Mao Ji W, Yan X G, et al. Source and mineralization mechanism of Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit in Sichuan: S, C, H, O, Sr isotopes and sphalerite trace elements constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(01): 209-220. (in Chinese).
Figure 1.
(a) Structure of Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn mineralization concentrated area; (b) Geologic sketch of the Daliangzi Zinc-rich Pb-Zn deposit (slightly modified in 2022 based on the data of the mine and that provided by [
17]); (c) Cross section of A-B in the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit. Note: a-①-Yangtze plate; ②-Ganzi folded belt; ③-Yidun island arc belt; ④-Lanping block; ⑤-Sanjiang fold system; ⑥-Indian plate; b-1-Dolomite limestone of Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation; 2-Argillaceous limestone in upper member of Lower Cambrian Canglangpu Formation; 3-Quartz sandstone in lower member of Lower Cambrian Canglangpu Formation; 4-Shale in upper member of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 5-Quartz sandstone in lower member of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 6-Banded dolomite in the eighth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 7-Phosphorous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the seventh member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 8- Phosphorous dolomite in the 1
st layer of the seventh member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 9-Siliceous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the sixth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 10- Banded dolomite in the 1
st layer of the sixth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 11-Fine-grain siliceous dolomite in the fifth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 12-Nodular chert-bearing siliceous dolomite in the 4
th layer of the fourth member of Dengying Formation of Upper Island Arc Belt Series of Sinian System; 13-Pelitic-arenaceous dolomite in the 3
rd layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 14-Arenaceous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 15-Tabular silicalite in the 1
st layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 16-Arenaceous-pelitic dolomite in the third member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 17-Algae-bearing dolomite in the second member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 18-Ore block and No.; 19-“Black/fracture zone” and No.; 20-Rubber; 21-Fault movement direction during metallogenic epoch; 22-Fault movement direction after metallogenic epoch.
Figure 1.
(a) Structure of Sichuan-Yunnan-Guizhou Pb-Zn mineralization concentrated area; (b) Geologic sketch of the Daliangzi Zinc-rich Pb-Zn deposit (slightly modified in 2022 based on the data of the mine and that provided by [
17]); (c) Cross section of A-B in the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit. Note: a-①-Yangtze plate; ②-Ganzi folded belt; ③-Yidun island arc belt; ④-Lanping block; ⑤-Sanjiang fold system; ⑥-Indian plate; b-1-Dolomite limestone of Lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation; 2-Argillaceous limestone in upper member of Lower Cambrian Canglangpu Formation; 3-Quartz sandstone in lower member of Lower Cambrian Canglangpu Formation; 4-Shale in upper member of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 5-Quartz sandstone in lower member of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 6-Banded dolomite in the eighth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 7-Phosphorous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the seventh member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 8- Phosphorous dolomite in the 1
st layer of the seventh member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 9-Siliceous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the sixth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 10- Banded dolomite in the 1
st layer of the sixth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 11-Fine-grain siliceous dolomite in the fifth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 12-Nodular chert-bearing siliceous dolomite in the 4
th layer of the fourth member of Dengying Formation of Upper Island Arc Belt Series of Sinian System; 13-Pelitic-arenaceous dolomite in the 3
rd layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 14-Arenaceous dolomite in the 2
nd layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 15-Tabular silicalite in the 1
st layer of the fourth member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 16-Arenaceous-pelitic dolomite in the third member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 17-Algae-bearing dolomite in the second member of Upper Sinian Dengying Formation; 18-Ore block and No.; 19-“Black/fracture zone” and No.; 20-Rubber; 21-Fault movement direction during metallogenic epoch; 22-Fault movement direction after metallogenic epoch.
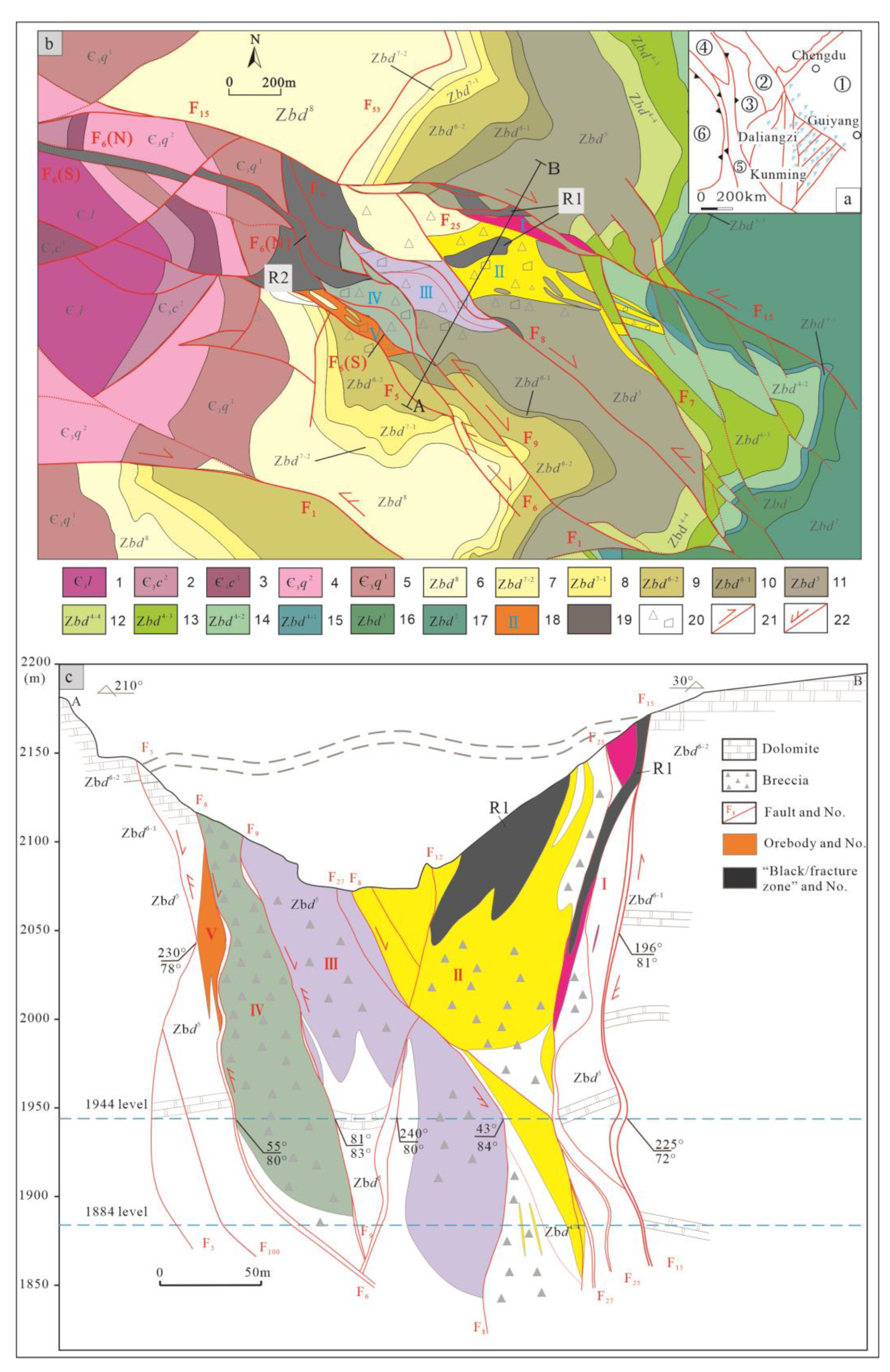
Figure 2.
Mineral formation sequence of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Figure 2.
Mineral formation sequence of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Figure 3.
Fluid inclusion sampling positions of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of “black/fracture zone” in 1,944m level. 1- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; 2- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; 3- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; 4- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone ; 5- Sample location and No. ; 6-Fault movement direction during mineralization; 7-Fault movement direction after mineralization.
Figure 3.
Fluid inclusion sampling positions of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of “black/fracture zone” in 1,944m level. 1- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; 2- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; 3- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; 4- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone ; 5- Sample location and No. ; 6-Fault movement direction during mineralization; 7-Fault movement direction after mineralization.
Figure 4.
Profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level. I- “Fracture zone”: complex breccia; II- “Fracture zone”: simple breccia; III- “Fracture zone”: dolomitic cataclasite; IV- “Black zone”: carbonized dolomite.
Figure 4.
Profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level. I- “Fracture zone”: complex breccia; II- “Fracture zone”: simple breccia; III- “Fracture zone”: dolomitic cataclasite; IV- “Black zone”: carbonized dolomite.
Figure 5.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone. A- Sphalerite, galena, and carbonate breccia debris cemented with different types of dolomite rubbles, including dark gray dolomite, caesious siliceous dolomite, gray dolomite, and off-white dolomite; B- Sphalerite, galena, carbonolite, and carbonatite cemented with gray dolomite and off-white dolomite rubbles; C- Sphalerite cemented with gray dolomite rubbles, in which scattered and sparsely disseminated sphalerite can be seen; D- Carbonized and dolomitized rhyolite rubbles (sampled from brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone in borehole ZK20-1); E- Perfectly round tuff rubbles; F- Sub-rounded tuff rubbles; G- Idiomorphic and hypidiomorphic granular sphalerite; H- idiomorphic granular sphalerite and metasomatic sphalerite showing metasomatic relict textures; I- Chalcopyrite and galena of common-border textures, chalcopyrite and metasomatic pyrite showing metasomatic relict textures; J- Bitumen, chalcopyrite, galena , and pyrite showing poikilitic textures; K- Secondary enlargement textures of dolomite; L- Sucrosic coarse-grain dolomite showing nodular structure with secondary enlargement textures. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Ccp- chalcopyrite; Py- pyrite; Bit- bitumen; Dol- dolomite.
Figure 5.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone. A- Sphalerite, galena, and carbonate breccia debris cemented with different types of dolomite rubbles, including dark gray dolomite, caesious siliceous dolomite, gray dolomite, and off-white dolomite; B- Sphalerite, galena, carbonolite, and carbonatite cemented with gray dolomite and off-white dolomite rubbles; C- Sphalerite cemented with gray dolomite rubbles, in which scattered and sparsely disseminated sphalerite can be seen; D- Carbonized and dolomitized rhyolite rubbles (sampled from brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies zone in borehole ZK20-1); E- Perfectly round tuff rubbles; F- Sub-rounded tuff rubbles; G- Idiomorphic and hypidiomorphic granular sphalerite; H- idiomorphic granular sphalerite and metasomatic sphalerite showing metasomatic relict textures; I- Chalcopyrite and galena of common-border textures, chalcopyrite and metasomatic pyrite showing metasomatic relict textures; J- Bitumen, chalcopyrite, galena , and pyrite showing poikilitic textures; K- Secondary enlargement textures of dolomite; L- Sucrosic coarse-grain dolomite showing nodular structure with secondary enlargement textures. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Ccp- chalcopyrite; Py- pyrite; Bit- bitumen; Dol- dolomite.

Figure 6.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone. A- Sphalerite, galena, dolomite, carbonolite, and carbonatite debris cemented with gray dolomite, showing brecciated textures, and lumpy dolomite associated with galena and sphalerite; B- Sphalerite and galena cemented with gray dolomite, showing stockwork-like or brecciated structure; C- Sphalerite and galena cemented with gray dolomite, showing stockwork-like structure; D- Veined and scattered yellowish-brown sphalerite; E- Idiomorphic granular sphalerite and pyrite scattered in dolomicrite; F- Galena filled along sphalerite fractures; G- Veined and lumpy malachite; H- Fine-grain quartz metasomatized calcite vein, showing metasomatic relict textures; I- Stockwork-like calcite vein. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Ccp- chalcopyrite; Py- pyrite; Bit- bitumen; Mi- malachite; Qtz- quartz; Dol- dolomite; Cc- calcite.
Figure 6.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone. A- Sphalerite, galena, dolomite, carbonolite, and carbonatite debris cemented with gray dolomite, showing brecciated textures, and lumpy dolomite associated with galena and sphalerite; B- Sphalerite and galena cemented with gray dolomite, showing stockwork-like or brecciated structure; C- Sphalerite and galena cemented with gray dolomite, showing stockwork-like structure; D- Veined and scattered yellowish-brown sphalerite; E- Idiomorphic granular sphalerite and pyrite scattered in dolomicrite; F- Galena filled along sphalerite fractures; G- Veined and lumpy malachite; H- Fine-grain quartz metasomatized calcite vein, showing metasomatic relict textures; I- Stockwork-like calcite vein. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Ccp- chalcopyrite; Py- pyrite; Bit- bitumen; Mi- malachite; Qtz- quartz; Dol- dolomite; Cc- calcite.
Figure 7.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone. A- Sphalerite and galena filled along dolomite fractures, showing stockwork-like textures; B- Sphalerite and galena filled along dolomite fractures and veined quartz; C- Cataclastic dolomite; D- Stockwork-like quartz and calcite; E- Lumpy calcite vein; F- Pyrite distributed along edge of galena. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Py- pyrite; Qtz- quartz; Cc- calcite.
Figure 7.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone. A- Sphalerite and galena filled along dolomite fractures, showing stockwork-like textures; B- Sphalerite and galena filled along dolomite fractures and veined quartz; C- Cataclastic dolomite; D- Stockwork-like quartz and calcite; E- Lumpy calcite vein; F- Pyrite distributed along edge of galena. Sph- sphalerite; Gn- galena; Py- pyrite; Qtz- quartz; Cc- calcite.
Figure 8.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of fine-veineded calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone. A- Lumpy and veined calcite in “black zone”; B- Lenticular dolomite in “black zone” and carbonolite filled along dolomite fractures; C- Lumpy calcite in “black zone”; D- Lumpy pyrite and quartz in “black zone”; E- Idiomorphic granular pyrite; F- Veined calcite cutting across silicified dolomite. Py- pyrite; Qtz- quartz; Cc- calcite; C- carbonolite.
Figure 8.
Typical field photos and microphotographs of fine-veineded calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone. A- Lumpy and veined calcite in “black zone”; B- Lenticular dolomite in “black zone” and carbonolite filled along dolomite fractures; C- Lumpy calcite in “black zone”; D- Lumpy pyrite and quartz in “black zone”; E- Idiomorphic granular pyrite; F- Veined calcite cutting across silicified dolomite. Py- pyrite; Qtz- quartz; Cc- calcite; C- carbonolite.
Figure 9.
Microscopic characteristics of liquid inclusions of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/facture zone”. A-Pure liquid, pure gas, and gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in sphalerite; B- Gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in sphalerite; C- Gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in calcite
Figure 9.
Microscopic characteristics of liquid inclusions of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/facture zone”. A-Pure liquid, pure gas, and gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in sphalerite; B- Gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in sphalerite; C- Gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in calcite
Figure 10.
Box diagrams of trace elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 10.
Box diagrams of trace elements in different tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of R1 “black/fracture zone”. ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone.
Figure 14.
A- Structural sketch of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones in 1,944m level of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit; B- Zoning pattern of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit (modified based on the studies of [
11,
17]). A: 1- Ore body and No.; 2- Ore shoot and No.; 3- Presumed ore shoot; 4- Fault movement direction during metallogenic epoch; 5- Fault movement direction after metallogenic epoch; 6- Strata and code; 7- Prospecting line No.; 8- Tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zone and No.; 9- Anticline. B: 1- Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 2- Sinian Dengying Formation; 3- Sinian Chengjiang Formation; 4- Huili Goup; 5- Migration direction of deep-source fluid; 6- Reducing fluid; 7- Boundary of parallel /angular unconformity contact; 8- Fault and No.; 9- Fault movement direction in metallogenic epoch; 10- Movement direction after metallogenic epoch; 11- ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; 12- ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; 13- ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; 14- ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone; 15- Deep-source ore-forming fluid. Note: 1- In Figure A, tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies is zoned based on the working section and that unzoned is the area not involved this time, and ore shoot takes the Zn+Pb content of 15% as the cutoff grade; 2- F100 and F5 are the same fault, and only appear as two faults in 1,944m level and 1,884m level, so only F5 is shown in Figure B.
Figure 14.
A- Structural sketch of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones in 1,944m level of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit; B- Zoning pattern of tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zones of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit (modified based on the studies of [
11,
17]). A: 1- Ore body and No.; 2- Ore shoot and No.; 3- Presumed ore shoot; 4- Fault movement direction during metallogenic epoch; 5- Fault movement direction after metallogenic epoch; 6- Strata and code; 7- Prospecting line No.; 8- Tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies zone and No.; 9- Anticline. B: 1- Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation; 2- Sinian Dengying Formation; 3- Sinian Chengjiang Formation; 4- Huili Goup; 5- Migration direction of deep-source fluid; 6- Reducing fluid; 7- Boundary of parallel /angular unconformity contact; 8- Fault and No.; 9- Fault movement direction in metallogenic epoch; 10- Movement direction after metallogenic epoch; 11- ①- Complex breccia-brecciated and stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization facies zone; 12- ②- Stockwork-like Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies zone; 13- ③- Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies zone; 14- ④- Fine-veined calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies zone; 15- Deep-source ore-forming fluid. Note: 1- In Figure A, tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies is zoned based on the working section and that unzoned is the area not involved this time, and ore shoot takes the Zn+Pb content of 15% as the cutoff grade; 2- F100 and F5 are the same fault, and only appear as two faults in 1,944m level and 1,884m level, so only F5 is shown in Figure B.
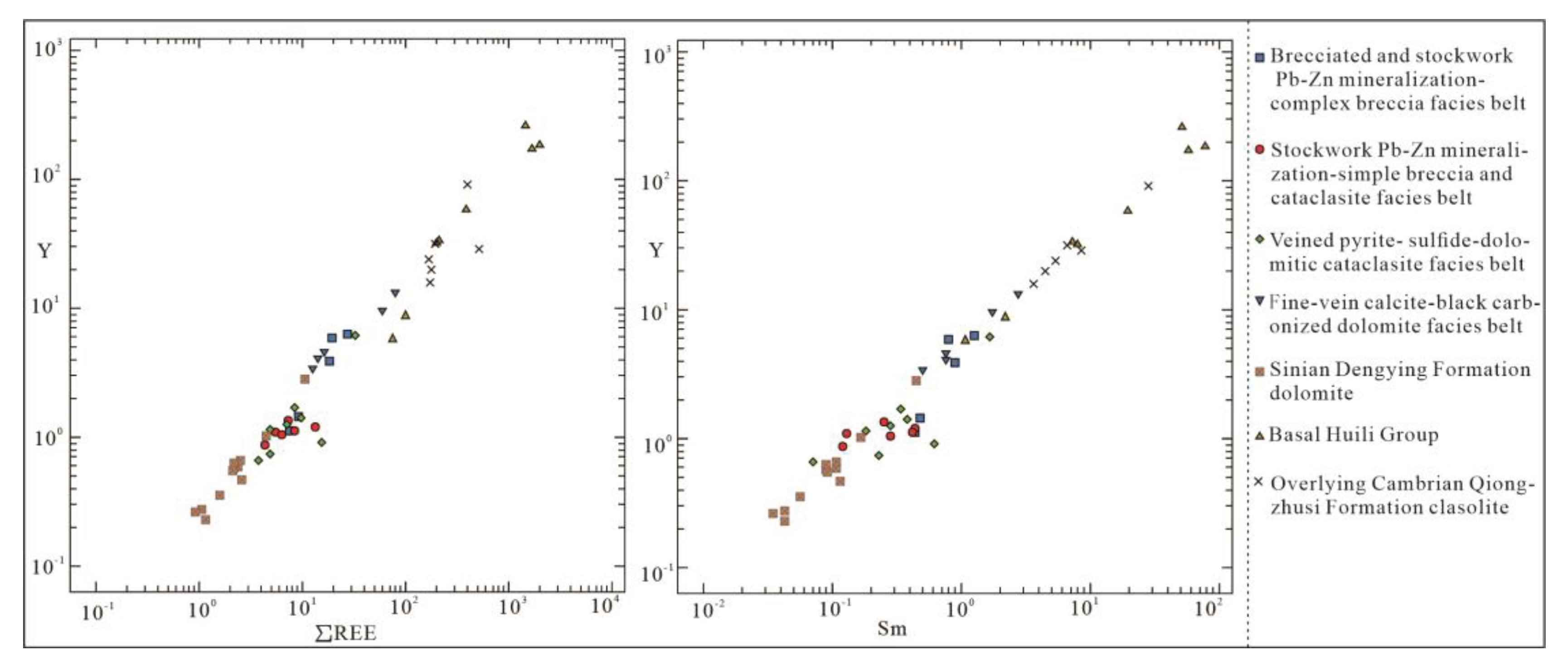
Table 1.
Characteristics of tectonite-mineralized facies belts of R1 “black/fracture zone”.
Table 1.
Characteristics of tectonite-mineralized facies belts of R1 “black/fracture zone”.
| Belt No. |
① |
② |
③ |
④ |
| tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies belts |
Brecciated and stockwork Pb-Zn mineralization-complex breccia facies belt |
Stockwork Pb-Zn mineralization-simple breccia and cataclasite facies belt |
Veined pyrite- sulfide-dolomitic cataclasite facies belt |
Fine-vein calcite-black carbonized dolomite facies belt |
| Tectonite type |
Fracture zone: complex breccia |
Fracture zone: simple breccia |
Fracture zone: dolomitic cataclasite |
“Black zone”: carbonized dolomite (clasolite) |
| Mineral assemblage |
Sphalerite + galena + chalcopyrite + dolomite |
Sphalerite + galena + quartz + dolomite and calcite |
Pyrite + sphalerite + galena + quartz + calcite |
Quartz + calcite + pyrite + (sphalerite and galena) |
| Ore fabric |
Brecciated structure; idiomorphic and hypidiomorphic granular texture, corrugation texture, metasomatic relict texture, common-border texture, poikilitic texture, secondary enlargement texture |
Brecciated structure, stockwork structure, veined structure; hypidiomorphic- allotriomorphic granular texture, metasomatic relict texture, common-border texture |
Mainly veined structure, stockwork structure; allotriomorphic granular texture, idiomorphic granular texture (calcite) |
Idiomorphic- allotriomorphic granular texture (pyrite) |
| Silicification |
Weak |
Visible quartz stringer with vein width of approx.. 1mm |
Lumpy and veined quartz with vein width up to 5cm |
Lumpy quartz or metasomatic calcite |
| Carbonatization |
Mainly dolomitization, lumpy and veined, secondary enlargement texture of dolomite visible |
Mainly fine-vein and stockwork calcite and lumpy dolomite |
Mainly stockwork-veined and lumpy calcite |
Mainly lumpy and stockwork calcite |
| Mineralization and alteration characteristics |
Lead-zinc mineralization, strong dolomitization, pyritization, copper mineralization (chalcopyrite), weak silicification |
Lead-zinc mineralization, moderate silicification, pyritization, copper mineralization (malachite), dolomitization, calcilization |
Weak lead-zinc mineralization, pyritization, calcilization, moderate silicification |
Carbonization, strong pyritization, silicification, strong calcilization |
Table 2.
microthermometers of fluid inclusions in each structural-mineralized altered lithofacies belt of the R1“Black-broken belt” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Table 2.
microthermometers of fluid inclusions in each structural-mineralized altered lithofacies belt of the R1“Black-broken belt” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Sample
Belt No |
lithofacies belt No |
tmineralization stage |
Size(μm) |
Type |
Gas-liquid ratio(%) |
homogenization temperature(℃) |
Homogeneous phase |
Freezing Point(℃) |
salinity%NaCleqv |
Minerals |
ρ(g/cm3) |
| DLZr-541 |
① |
Ⅱ |
8~11 |
L-V |
15~20 |
177.5~267.8 |
L |
-5.5~-8.9 |
8.55~12.51 |
Sp |
0.88~0.98 |
| DLZr-534 |
Ⅱ |
8~15 |
L-V |
10~16 |
197.6~263.1 |
L |
-7.5~-10.6 |
11.1~14.57 |
Sp |
0.91~0.97 |
| Average |
|
|
|
|
225 |
|
|
12.00 |
|
0.93 |
| DLZr-204 |
② |
Ⅱ |
11~15 |
L-V |
10~15 |
146.3~225.0 |
L |
-4.1~-11.2 |
6.59~15.96 |
Cc |
0.97~1.00 |
| DLZr-206 |
Ⅱ |
7~10 |
L-V |
10~25 |
177.0~288.5 |
L |
-7.8~-13.2 |
11.46~17.08 |
Sp |
0.88~1.01 |
| DLZr-539 |
Ⅱ |
13~17 |
L-V |
10~25 |
198.5~273.4 |
L |
-8.6~-14 |
12.39~17.79 |
Sp |
0.92~0.97 |
| Average |
|
|
|
|
211.6 |
|
|
13.6 |
|
0.96 |
| DLZr-536 |
③ |
Ⅱ |
7~15 |
L-V |
10~20 |
168.1~210.3 |
L |
-6.6~-10.5 |
9.98~14.46 |
Cc |
0.94~1.01 |
| DLZr-537 |
Ⅱ |
7~15 |
L-V |
13~17 |
197.8~221.4 |
L |
-4.5~-9.4 |
7.17~13.29 |
Sp |
0.92~0.95 |
| Average |
|
|
|
|
197.9 |
|
|
11.40 |
|
0.95 |
| DLZr-46-1 |
④ |
Ⅱ |
7~13 |
L-V |
10~20 |
186.0~211.4 |
L |
-6.1~-8.5 |
9.47~12.28 |
Cc |
0.93~0.96 |
| Average |
|
|
|
|
|
200.5 |
|
|
10.70 |
|
0.95 |
Table 3.
The main elements (wt%) of each structural rock-mineralized altered lithofacies belt in the R1 type““black/fracture zone”” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Table 3.
The main elements (wt%) of each structural rock-mineralized altered lithofacies belt in the R1 type““black/fracture zone”” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
| Sample No |
Rock name |
Tectonite-mineralized alteration lithofacies belts |
SiO2
|
Al2O3
|
TFe2O3
|
FeO |
MgO |
CaO |
Na2O |
K2O |
TiO2
|
MnO |
P2O5
|
LOI |
CaO+MgO |
CaO/MgO |
Sampling location |
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
8.09 |
0.19 |
1.23 |
0.77 |
20.59 |
28.69 |
0.086 |
0.027 |
0.015 |
0.044 |
0.079 |
40.27 |
49.28 |
1.00 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc609 |
Gray-black, tawny Cataclastic dolomite |
② |
23.41 |
1.55 |
3.59 |
0.42 |
15.41 |
22.55 |
0.046 |
0.26 |
0.056 |
0.041 |
0.31 |
32.6 |
37.96 |
1.05 |
the profile of 16# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc617 |
Gray-black, and tawny Cataclastic dolomite |
② |
66.93 |
4.64 |
2.27 |
1.03 |
4.26 |
8.49 |
0.1 |
1.44 |
0.24 |
0.028 |
0.5 |
10.95 |
12.75 |
1.42 |
the profile of 16# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
29.88 |
0.27 |
1.45 |
0.45 |
15.4 |
21.17 |
0.078 |
0.047 |
0.011 |
0.069 |
0.06 |
30.95 |
36.57 |
0.98 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
63.6 |
0.47 |
1.05 |
0.9 |
7.64 |
11.03 |
0.077 |
0.1 |
0.026 |
0.039 |
0.031 |
15.31 |
18.67 |
1.03 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
11.02 |
0.18 |
1.69 |
0.32 |
19.25 |
27.19 |
0.079 |
0.034 |
0.011 |
0.042 |
0.1 |
39.73 |
46.44 |
1.01 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-grained dolomite |
③ |
14.03 |
0.16 |
0.27 |
0.26 |
19.83 |
27.44 |
0.068 |
0.023 |
0.007 |
0.027 |
0.054 |
37.7 |
47.27 |
0.99 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc-49 |
Carbonized silicified dolomite |
④ |
74.67 |
8.13 |
3.06 |
0.77 |
2.31 |
2.99 |
0.1 |
2.7 |
0.46 |
0.038 |
0.28 |
4.61 |
5.3 |
0.92 |
the profile of 17# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
| DLZc500-1 |
Black carbonized dolomite crushed siltstone |
④ |
56.1 |
11.49 |
2.53 |
0.71 |
4.96 |
10.52 |
0.053 |
2.3 |
0.27 |
0.034 |
0.59 |
11.04 |
15.48 |
1.51 |
the profile of 0# prospecting line in 1,944m level |
Table 4.
Analysis Table of trace and rare earth elements (ppm) in each structural rock-mineralized altered lithofacies belt of the R1 type“Black-broken belt” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Table 4.
Analysis Table of trace and rare earth elements (ppm) in each structural rock-mineralized altered lithofacies belt of the R1 type“Black-broken belt” of the Daliangzi Pb-Zn deposit.
Sample
Belt No |
Rock name |
lithofacies belt No |
Cu |
Zn |
Pb |
Zn/Pb |
Ga |
Ge |
Ag |
Cd |
La |
Ce |
Pr |
Nd |
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
1526 |
2664 |
431 |
6.18 |
1.12 |
1.68 |
2.93 |
45.3 |
1.05 |
1.41 |
0.96 |
2.32 |
| DLZc-32 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
① |
309.20 |
207080 |
1592 |
809.51 |
11.03 |
26.80 |
28.62 |
1475.20 |
5.56 |
8.48 |
1.84 |
5.97 |
| DLZc-33 |
Dark gray-grayish white Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
817 |
289500 |
14279 |
20.27 |
15.8 |
26.6 |
57.8 |
1698 |
2.95 |
4.61 |
1.52 |
3.87 |
| DLZc-34 |
Fine-vein - brecciated |
① |
276 |
83800 |
1225 |
68.41 |
6.19 |
13.1 |
10.2 |
399 |
4.02 |
6.05 |
1.24 |
3.85 |
| DLZc-35 |
Gray dolomite |
① |
243 |
133700 |
8675 |
15.41 |
8.68 |
14.6 |
27.4 |
1045 |
1.22 |
1.88 |
0.82 |
2.36 |
| DLZc-23 |
The dolomite is layered, reticulated, and veined |
② |
113 |
104900 |
8875 |
11.82 |
5.37 |
7.16 |
18.8 |
674 |
0.86 |
1.37 |
0.54 |
0.81 |
| DLZc-24 |
Muddy Dolomite |
② |
587 |
20625 |
5036 |
4.10 |
2.88 |
2.38 |
6.28 |
100 |
1.54 |
2.28 |
0.42 |
1.15 |
| DLZc-26 |
Muddy cement dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
587 |
29980 |
2509 |
11.95 |
2.34 |
1.3 |
3.69 |
99.6 |
2.68 |
4.83 |
0.89 |
2.3 |
| DLZc-27 |
dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
3940 |
77300 |
17677 |
4.37 |
6.48 |
4.15 |
16.2 |
526 |
1.04 |
1.53 |
1.06 |
2.01 |
| DLZc-38 |
Gray dolomite |
② |
297 |
129600 |
8654 |
14.98 |
12.9 |
8.88 |
18.3 |
768 |
0.83 |
1.61 |
1.1 |
0.81 |
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white dolomite |
② |
103 |
1177 |
438 |
2.69 |
0.82 |
0.85 |
1.73 |
14.1 |
0.94 |
1.23 |
0.89 |
1.45 |
| DLZc-15 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
25.1 |
479 |
202 |
2.37 |
0.63 |
0.15 |
1.56 |
6.06 |
1.46 |
2.23 |
0.69 |
1.68 |
| DLZc-16 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
90.3 |
520 |
464 |
1.12 |
0.49 |
0.3 |
2.65 |
12.5 |
1.24 |
2.06 |
0.51 |
1.26 |
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
10.4 |
333 |
82.3 |
4.05 |
0.58 |
0.14 |
0.21 |
5.65 |
0.77 |
1.07 |
0.43 |
0.99 |
| DLZc-19 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
435 |
34225 |
323 |
105.96 |
5.21 |
4.29 |
4.17 |
287 |
0.9 |
1.06 |
0.72 |
0.65 |
| DLZc-20 |
Muddy Dolomite |
③ |
227 |
57700 |
98800 |
0.58 |
1.19 |
4.89 |
83.9 |
90.3 |
1.36 |
1.37 |
0.3 |
0.84 |
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
26.6 |
859 |
255 |
3.37 |
0.83 |
0.61 |
0.28 |
6.58 |
2.09 |
4.58 |
1.77 |
3.1 |
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
146 |
808 |
924 |
0.87 |
0.48 |
0.35 |
2.39 |
11.9 |
1.17 |
1.82 |
2.26 |
2.18 |
| DLZc-45 |
Gray-white. Gray dolomite |
③ |
34.17 |
5255.67 |
2388.00 |
3.51 |
2.10 |
0.83 |
6.28 |
26.63 |
5.59 |
10.12 |
2.28 |
7.63 |
| DLZc-46 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
71.9 |
5974 |
16332 |
0.37 |
5.91 |
1.05 |
9.12 |
33.3 |
15.5 |
22.9 |
3.77 |
9.56 |
| DLZc-49 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
69.25 |
2301.00 |
1485.50 |
1.58 |
7.94 |
1.27 |
2.45 |
14.60 |
19.80 |
34.75 |
2.88 |
10.52 |
| DLZc-50 |
Gray-black fine-vein dolomite |
④ |
43.6 |
721 |
359 |
2.01 |
0.78 |
0.31 |
0.86 |
8.48 |
2.26 |
4.25 |
1.05 |
3.42 |
| DLZc-51 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
④ |
24.35 |
645.50 |
197.00 |
3.20 |
0.42 |
0.27 |
0.66 |
6.25 |
2.99 |
4.98 |
1.23 |
3.60 |
| DLZc-52 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite , quartz |
④ |
41.1 |
514 |
416 |
1.24 |
0.42 |
0.16 |
1.72 |
12 |
2.64 |
4.44 |
0.98 |
2.3 |
Sample
Belt No
|
Rock name |
lithofacies belt No |
Sm |
Eu |
Gd |
Tb |
Dy |
Ho |
Er |
Tm |
Yb |
Lu |
Y |
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
0.44 |
0.15 |
0.47 |
0.065 |
0.33 |
0.063 |
0.16 |
0.023 |
0.13 |
0.02 |
1.12 |
| DLZc-32 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
① |
1.26 |
0.51 |
1.38 |
0.20 |
0.99 |
0.20 |
0.57 |
0.07 |
0.40 |
0.08 |
6.35 |
| DLZc-33 |
Dark gray-grayish white Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
0.89 |
0.76 |
0.98 |
0.14 |
0.74 |
0.16 |
0.44 |
0.098 |
0.74 |
0.17 |
3.92 |
| DLZc-34 |
Fine-vein - brecciated |
① |
0.79 |
0.64 |
0.92 |
0.13 |
0.71 |
0.15 |
0.41 |
0.067 |
0.43 |
0.09 |
5.94 |
| DLZc-35 |
Gray dolomite |
① |
0.48 |
0.47 |
0.63 |
0.089 |
0.34 |
0.087 |
0.24 |
0.042 |
0.34 |
0.10 |
1.43 |
| DLZc-23 |
The dolomite is layered, reticulated, and veined |
② |
0.12 |
0.061 |
0.18 |
0.022 |
0.13 |
0.027 |
0.074 |
0.012 |
0.075 |
0.01 |
0.87 |
| DLZc-24 |
Muddy Dolomite |
② |
0.25 |
0.22 |
0.31 |
0.071 |
0.42 |
0.078 |
0.21 |
0.034 |
0.22 |
0.04 |
1.36 |
| DLZc-26 |
Muddy cement dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
0.44 |
0.29 |
0.53 |
0.084 |
0.46 |
0.087 |
0.23 |
0.038 |
0.25 |
0.06 |
1.19 |
| DLZc-27 |
dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
0.42 |
0.36 |
0.64 |
0.1 |
0.56 |
0.11 |
0.27 |
0.045 |
0.31 |
0.08 |
1.12 |
| DLZc-38 |
Gray dolomite |
② |
0.13 |
0.29 |
0.29 |
0.034 |
0.15 |
0.043 |
0.093 |
0.02 |
0.1 |
0.02 |
1.10 |
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white dolomite |
② |
0.28 |
0.22 |
0.39 |
0.058 |
0.34 |
0.078 |
0.18 |
0.031 |
0.2 |
0.04 |
1.05 |
| DLZc-15 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
0.34 |
0.18 |
0.43 |
0.087 |
0.5 |
0.098 |
0.33 |
0.036 |
0.22 |
0.04 |
1.70 |
| DLZc-16 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.28 |
0.25 |
0.4 |
0.078 |
0.44 |
0.081 |
0.2 |
0.031 |
0.19 |
0.03 |
1.26 |
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
0.23 |
0.21 |
0.3 |
0.06 |
0.34 |
0.064 |
0.16 |
0.024 |
0.16 |
0.03 |
0.74 |
| DLZc-19 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.071 |
0.028 |
0.12 |
0.015 |
0.069 |
0.018 |
0.05 |
0.009 |
0.04 |
0.01 |
0.66 |
| DLZc-20 |
Muddy Dolomite |
③ |
0.18 |
0.19 |
0.2 |
0.029 |
0.17 |
0.034 |
0.1 |
0.017 |
0.1 |
0.02 |
1.16 |
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.61 |
0.22 |
0.75 |
0.11 |
0.65 |
0.15 |
0.43 |
0.099 |
0.69 |
0.13 |
0.91 |
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
0.38 |
0.21 |
0.63 |
0.075 |
0.41 |
0.084 |
0.22 |
0.039 |
0.21 |
0.04 |
1.41 |
| DLZc-45 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
1.65 |
0.57 |
1.61 |
0.25 |
1.26 |
0.25 |
0.63 |
0.11 |
0.66 |
0.12 |
6.10 |
| DLZc-46 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
1.73 |
0.63 |
1.91 |
0.28 |
1.45 |
0.32 |
0.88 |
0.16 |
0.93 |
0.18 |
9.52 |
| DLZc-49 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
2.79 |
0.91 |
2.74 |
0.40 |
2.05 |
0.39 |
1.05 |
0.17 |
0.99 |
0.17 |
12.95 |
| DLZc-50 |
Gray-black fine-vein dolomite |
④ |
0.76 |
0.24 |
0.77 |
0.12 |
0.59 |
0.11 |
0.29 |
0.041 |
0.23 |
0.04 |
4.05 |
| DLZc-51 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
④ |
0.76 |
0.34 |
0.79 |
0.13 |
0.70 |
0.12 |
0.33 |
0.05 |
0.26 |
0.06 |
4.55 |
| DLZc-52 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite,quartz |
④ |
0.5 |
0.17 |
0.58 |
0.08 |
0.45 |
0.092 |
0.25 |
0.038 |
0.2 |
0.03 |
3.36 |
Sample
Belt No
|
Rock name |
lithofacies belt No |
Cu |
Zn |
Pb |
Zn/Pb |
Ga |
Ge |
Ag |
Cd |
La |
Ce |
Pr |
Nd |
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
1526 |
2664 |
431 |
6.18 |
1.12 |
1.68 |
2.93 |
45.3 |
1.05 |
1.41 |
0.96 |
2.32 |
| DLZc-32 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
① |
309.20 |
207080 |
1592 |
809.51 |
11.03 |
26.80 |
28.62 |
1475.20 |
5.56 |
8.48 |
1.84 |
5.97 |
| DLZc-33 |
Dark gray-grayish white Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
817 |
289500 |
14279 |
20.27 |
15.8 |
26.6 |
57.8 |
1698 |
2.95 |
4.61 |
1.52 |
3.87 |
| DLZc-34 |
Fine-vein - brecciated |
① |
276 |
83800 |
1225 |
68.41 |
6.19 |
13.1 |
10.2 |
399 |
4.02 |
6.05 |
1.24 |
3.85 |
| DLZc-35 |
Gray dolomite |
① |
243 |
133700 |
8675 |
15.41 |
8.68 |
14.6 |
27.4 |
1045 |
1.22 |
1.88 |
0.82 |
2.36 |
| DLZc-23 |
The dolomite is layered, reticulated, and veined |
② |
113 |
104900 |
8875 |
11.82 |
5.37 |
7.16 |
18.8 |
674 |
0.86 |
1.37 |
0.54 |
0.81 |
| DLZc-24 |
Muddy Dolomite |
② |
587 |
20625 |
5036 |
4.10 |
2.88 |
2.38 |
6.28 |
100 |
1.54 |
2.28 |
0.42 |
1.15 |
| DLZc-26 |
Muddy cement dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
587 |
29980 |
2509 |
11.95 |
2.34 |
1.3 |
3.69 |
99.6 |
2.68 |
4.83 |
0.89 |
2.3 |
| DLZc-27 |
dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
3940 |
77300 |
17677 |
4.37 |
6.48 |
4.15 |
16.2 |
526 |
1.04 |
1.53 |
1.06 |
2.01 |
| DLZc-38 |
Gray dolomite |
② |
297 |
129600 |
8654 |
14.98 |
12.9 |
8.88 |
18.3 |
768 |
0.83 |
1.61 |
1.1 |
0.81 |
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white dolomite |
② |
103 |
1177 |
438 |
2.69 |
0.82 |
0.85 |
1.73 |
14.1 |
0.94 |
1.23 |
0.89 |
1.45 |
| DLZc-15 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
25.1 |
479 |
202 |
2.37 |
0.63 |
0.15 |
1.56 |
6.06 |
1.46 |
2.23 |
0.69 |
1.68 |
| DLZc-16 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
90.3 |
520 |
464 |
1.12 |
0.49 |
0.3 |
2.65 |
12.5 |
1.24 |
2.06 |
0.51 |
1.26 |
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
10.4 |
333 |
82.3 |
4.05 |
0.58 |
0.14 |
0.21 |
5.65 |
0.77 |
1.07 |
0.43 |
0.99 |
| DLZc-19 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
435 |
34225 |
323 |
105.96 |
5.21 |
4.29 |
4.17 |
287 |
0.9 |
1.06 |
0.72 |
0.65 |
| DLZc-20 |
Muddy Dolomite |
③ |
227 |
57700 |
98800 |
0.58 |
1.19 |
4.89 |
83.9 |
90.3 |
1.36 |
1.37 |
0.3 |
0.84 |
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
26.6 |
859 |
255 |
3.37 |
0.83 |
0.61 |
0.28 |
6.58 |
2.09 |
4.58 |
1.77 |
3.1 |
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
146 |
808 |
924 |
0.87 |
0.48 |
0.35 |
2.39 |
11.9 |
1.17 |
1.82 |
2.26 |
2.18 |
| DLZc-45 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
34.17 |
5255.67 |
2388.00 |
3.51 |
2.10 |
0.83 |
6.28 |
26.63 |
5.59 |
10.12 |
2.28 |
7.63 |
| DLZc-46 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
71.9 |
5974 |
16332 |
0.37 |
5.91 |
1.05 |
9.12 |
33.3 |
15.5 |
22.9 |
3.77 |
9.56 |
| DLZc-49 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
69.25 |
2301.00 |
1485.50 |
1.58 |
7.94 |
1.27 |
2.45 |
14.60 |
19.80 |
34.75 |
2.88 |
10.52 |
| DLZc-50 |
Gray-black fine-vein dolomite |
④ |
43.6 |
721 |
359 |
2.01 |
0.78 |
0.31 |
0.86 |
8.48 |
2.26 |
4.25 |
1.05 |
3.42 |
| DLZc-51 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
④ |
24.35 |
645.50 |
197.00 |
3.20 |
0.42 |
0.27 |
0.66 |
6.25 |
2.99 |
4.98 |
1.23 |
3.60 |
| DLZc-52 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite,quartz |
④ |
41.1 |
514 |
416 |
1.24 |
0.42 |
0.16 |
1.72 |
12 |
2.64 |
4.44 |
0.98 |
2.3 |
Sample
Belt No
|
Rock name |
lithofacies belt No |
Sm |
Eu |
Gd |
Tb |
Dy |
Ho |
Er |
Tm |
Yb |
Lu |
Y |
|
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
0.44 |
0.15 |
0.47 |
0.065 |
0.33 |
0.063 |
0.16 |
0.023 |
0.13 |
0.02 |
1.12 |
|
| DLZc-32 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
① |
1.26 |
0.51 |
1.38 |
0.20 |
0.99 |
0.20 |
0.57 |
0.07 |
0.40 |
0.08 |
6.35 |
|
| DLZc-33 |
Dark gray-grayish white Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
0.89 |
0.76 |
0.98 |
0.14 |
0.74 |
0.16 |
0.44 |
0.098 |
0.74 |
0.17 |
3.92 |
|
| DLZc-34 |
Fine-vein - brecciated |
① |
0.79 |
0.64 |
0.92 |
0.13 |
0.71 |
0.15 |
0.41 |
0.067 |
0.43 |
0.09 |
5.94 |
|
| DLZc-35 |
Gray dolomite |
① |
0.48 |
0.47 |
0.63 |
0.089 |
0.34 |
0.087 |
0.24 |
0.042 |
0.34 |
0.10 |
1.43 |
|
| DLZc-23 |
The dolomite is layered, reticulated, and veined |
② |
0.12 |
0.061 |
0.18 |
0.022 |
0.13 |
0.027 |
0.074 |
0.012 |
0.075 |
0.01 |
0.87 |
|
| DLZc-24 |
Muddy Dolomite |
② |
0.25 |
0.22 |
0.31 |
0.071 |
0.42 |
0.078 |
0.21 |
0.034 |
0.22 |
0.04 |
1.36 |
|
| DLZc-26 |
Muddy cement dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
0.44 |
0.29 |
0.53 |
0.084 |
0.46 |
0.087 |
0.23 |
0.038 |
0.25 |
0.06 |
1.19 |
|
| DLZc-27 |
dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
0.42 |
0.36 |
0.64 |
0.1 |
0.56 |
0.11 |
0.27 |
0.045 |
0.31 |
0.08 |
1.12 |
|
| DLZc-38 |
Gray dolomite |
② |
0.13 |
0.29 |
0.29 |
0.034 |
0.15 |
0.043 |
0.093 |
0.02 |
0.1 |
0.02 |
1.10 |
|
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white dolomite |
② |
0.28 |
0.22 |
0.39 |
0.058 |
0.34 |
0.078 |
0.18 |
0.031 |
0.2 |
0.04 |
1.05 |
|
| DLZc-15 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
0.34 |
0.18 |
0.43 |
0.087 |
0.5 |
0.098 |
0.33 |
0.036 |
0.22 |
0.04 |
1.70 |
|
| DLZc-16 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.28 |
0.25 |
0.4 |
0.078 |
0.44 |
0.081 |
0.2 |
0.031 |
0.19 |
0.03 |
1.26 |
|
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
0.23 |
0.21 |
0.3 |
0.06 |
0.34 |
0.064 |
0.16 |
0.024 |
0.16 |
0.03 |
0.74 |
|
| DLZc-19 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.071 |
0.028 |
0.12 |
0.015 |
0.069 |
0.018 |
0.05 |
0.009 |
0.04 |
0.01 |
0.66 |
|
| DLZc-20 |
Muddy Dolomite |
③ |
0.18 |
0.19 |
0.2 |
0.029 |
0.17 |
0.034 |
0.1 |
0.017 |
0.1 |
0.02 |
1.16 |
|
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
0.61 |
0.22 |
0.75 |
0.11 |
0.65 |
0.15 |
0.43 |
0.099 |
0.69 |
0.13 |
0.91 |
|
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
0.38 |
0.21 |
0.63 |
0.075 |
0.41 |
0.084 |
0.22 |
0.039 |
0.21 |
0.04 |
1.41 |
|
| DLZc-45 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
1.65 |
0.57 |
1.61 |
0.25 |
1.26 |
0.25 |
0.63 |
0.11 |
0.66 |
0.12 |
6.10 |
|
| DLZc-46 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
1.73 |
0.63 |
1.91 |
0.28 |
1.45 |
0.32 |
0.88 |
0.16 |
0.93 |
0.18 |
9.52 |
|
| DLZc-49 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
2.79 |
0.91 |
2.74 |
0.40 |
2.05 |
0.39 |
1.05 |
0.17 |
0.99 |
0.17 |
12.95 |
|
| DLZc-50 |
Gray-black fine-vein dolomite |
④ |
0.76 |
0.24 |
0.77 |
0.12 |
0.59 |
0.11 |
0.29 |
0.041 |
0.23 |
0.04 |
4.05 |
|
| DLZc-51 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
④ |
0.76 |
0.34 |
0.79 |
0.13 |
0.70 |
0.12 |
0.33 |
0.05 |
0.26 |
0.06 |
4.55 |
|
| DLZc-52 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite,quartz |
④ |
0.5 |
0.17 |
0.58 |
0.08 |
0.45 |
0.092 |
0.25 |
0.038 |
0.2 |
0.03 |
3.36 |
|
Sample
Belt No
|
Rock name |
lithofacies belt No |
∑REE |
LREE/HREE |
La/SmN |
Gd/YbN |
δEu |
δCe |
|
| DLZc-29 |
Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
7.59 |
2.66 |
1.50 |
2.92 |
1.00 |
0.31 |
|
| DLZc-32 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
① |
27.52 |
2.30 |
2.79 |
2.78 |
1.19 |
0.63 |
|
| DLZc-33 |
Dark gray-grayish white Cataclastic dolomite |
① |
18.07 |
1.98 |
2.08 |
1.07 |
2.48 |
0.52 |
|
| DLZc-34 |
Fine-vein - brecciated |
① |
19.49 |
1.88 |
3.20 |
1.73 |
2.29 |
0.65 |
|
| DLZc-35 |
Gray dolomite |
① |
9.10 |
2.19 |
1.60 |
1.50 |
2.61 |
0.44 |
|
| DLZc-23 |
The dolomite is layered, reticulated, and veined |
② |
4.29 |
2.68 |
4.51 |
1.94 |
1.27 |
0.47 |
|
| DLZc-24 |
Muddy Dolomite |
② |
7.24 |
2.14 |
3.87 |
1.14 |
2.41 |
0.67 |
|
| DLZc-26 |
Muddy cement dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
13.17 |
3.90 |
3.83 |
1.71 |
1.83 |
0.75 |
|
| DLZc-27 |
dolomitic cataclasite |
② |
8.53 |
1.99 |
1.56 |
1.67 |
2.12 |
0.31 |
|
| DLZc-38 |
Gray dolomite |
② |
5.52 |
2.58 |
4.02 |
2.34 |
4.42 |
0.34 |
|
| DLZc-40 |
Gray-white dolomite |
② |
6.33 |
2.11 |
2.11 |
1.57 |
2.04 |
0.29 |
|
| DLZc-15 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
8.32 |
1.92 |
2.70 |
1.58 |
1.44 |
0.53 |
|
| DLZc-16 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
7.05 |
2.06 |
2.79 |
1.70 |
2.28 |
0.62 |
|
| DLZc-17 |
Gray-white fine-vein dolomite |
③ |
4.83 |
1.97 |
2.11 |
1.51 |
2.44 |
0.44 |
|
| DLZc-19 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
3.76 |
3.45 |
7.97 |
2.42 |
0.92 |
0.30 |
|
| DLZc-20 |
Muddy Dolomite |
③ |
4.91 |
2.32 |
4.75 |
1.61 |
3.05 |
0.50 |
|
| DLZc-42 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
③ |
15.38 |
3.16 |
2.16 |
0.88 |
0.99 |
0.53 |
|
| DLZc-43 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
9.73 |
2.57 |
1.94 |
2.42 |
1.30 |
0.20 |
|
| DLZc-45 |
Gray-white dolomite |
③ |
32.72 |
2.54 |
2.13 |
1.96 |
1.06 |
0.68 |
|
| DLZc-46 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
60.20 |
3.46 |
5.64 |
1.66 |
1.06 |
0.70 |
|
| DLZc-49 |
Black dolomite |
④ |
79.56 |
3.43 |
4.47 |
2.24 |
0.99 |
0.98 |
|
| DLZc-50 |
Gray-black fine-vein dolomite |
④ |
14.17 |
1.92 |
1.87 |
2.70 |
0.95 |
0.66 |
|
| DLZc-51 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite |
④ |
16.29 |
1.99 |
2.49 |
2.48 |
1.32 |
0.63 |
|
| DLZc-52 |
Gray-white silicified dolomite,quartz |
④ |
12.75 |
2.17 |
3.32 |
2.34 |
0.96 |
0.66 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).