Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
21 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Survivin and Cancer
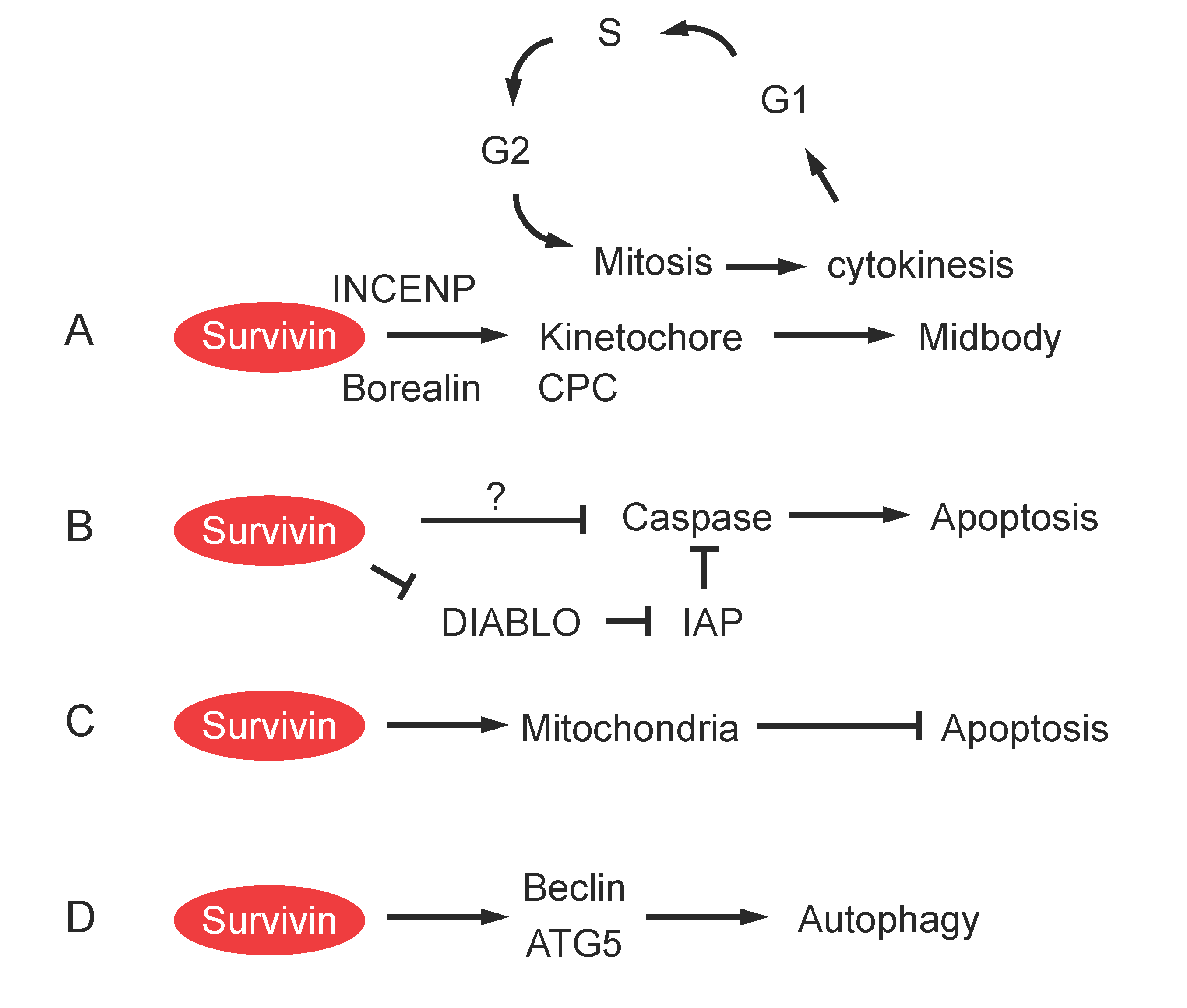
Role of Survivin in Cell Division
Role of Survivin in Apoptosis
Role of Survivin in Mitochondrial Function and Autophagy
Survivin Localization
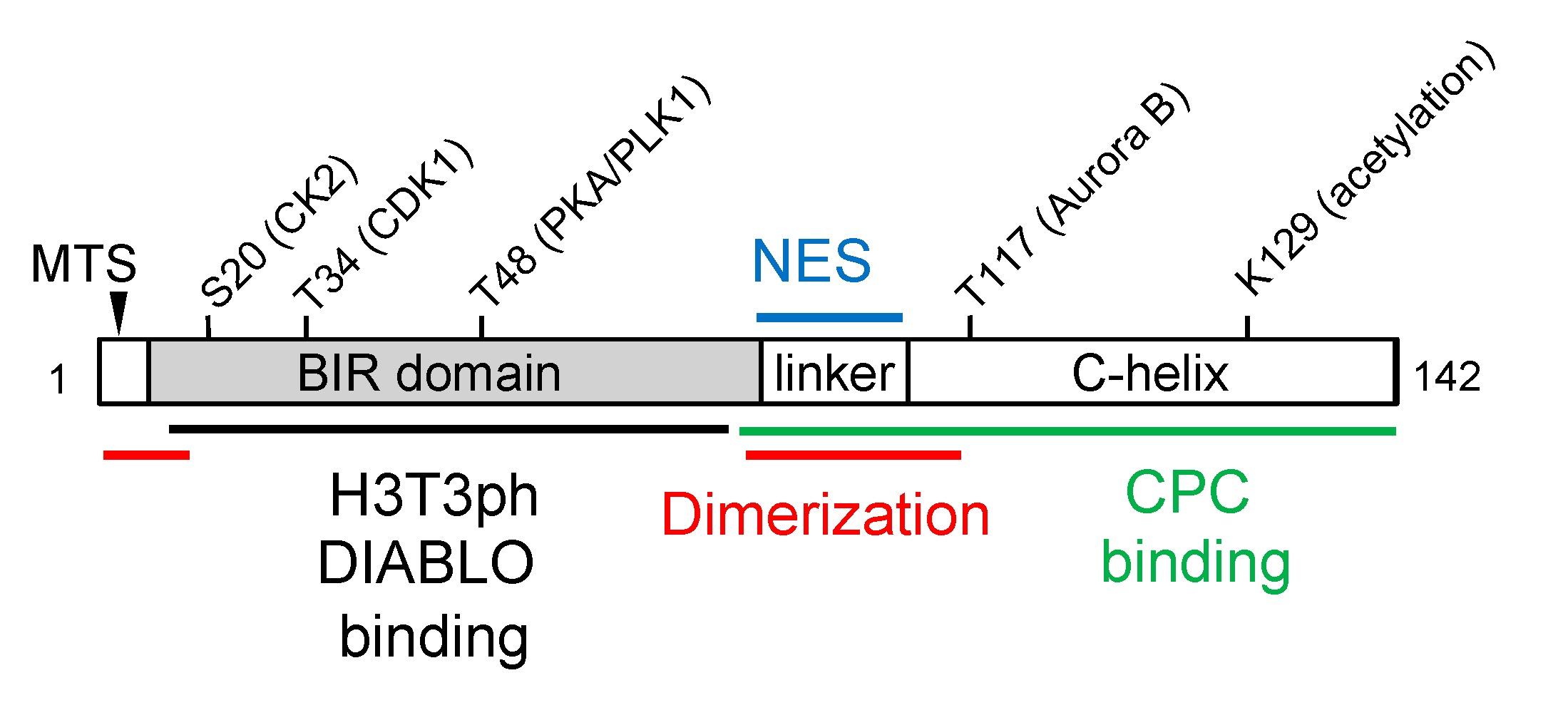
Survivin Protein Structure and Post-Translational Modification
Therapeutic Strategies to Target Survivin
Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, K.; Iwamoto, S.; Gon, G.; Nohara, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Tanigawa, N. Expression of survivin and its relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast. Clin Cancer Res 2000, 6, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, C.; Lohmann, C.M.; Cotsonis, G.; Lawson, D.; Santoianni, R. Survivin expression in ovarian carcinoma: correlation with apoptotic markers and. Mod Pathol 2003, 16, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarela, A.I.; Verbeke, C.S.; Ramsdale, J.; Davies, C.L.; Markham, A.F.; Guillou, P.J. Expression of survivin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis and cell cycle regulatory. Br J Cancer 2002, 86, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowski, P.; Kuhnel, T.; Muhr-Wilkenshoff, F.; Heine, B.; Stein, H.; Hopfner, M.; Germer, C.T.; Scherubl, H. Prognostic value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell. Br J Cancer 2003, 88, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Dong, Y.; Ohno, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Tokuda, M. Survivin expression and its correlation with cell proliferation and prognosis in epithelial ovarian tumors. Int J Oncol 2002, 21, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Kuwabara, Y.; Mitani, M.; Shinoda, N.; Sato, A.; Toyama, T.; Mitsui, A.; Nishiwaki, T.; Moriyama, S.; Kudo, J.; et al. Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: correlation with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer 2001, 95, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oparina, N.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Faldt Beding, A.; Parris, T.; Helou, K.; Karlsson, P.; Einbeigi, Z.; Bokarewa, M.I. Prognostic Significance of BIRC5/Survivin in Breast Cancer: Results from Three Independent Cohorts. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonini, G.; Vincenzi, B.; Santini, D.; Scarpa, S.; Vasaturo, T.; Malacrino, C.; Coppola, R.; Magistrelli, P.; Borzomati, D.; Baldi, A.; et al. Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of survivin in 67 surgically resected pancreatic cancer patients. Br J Cancer 2005, 92, 2225–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Yie, S.M.; Wu, S.M.; Chen, S.; Lou, B.; He, X.; Ye, S.R.; Xie, K.; Rao, L.; Gao, E.; et al. Detection of survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in the peripheral blood of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Clin Exp Metastasis 2009, 26, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, S.M.; Lou, B.; Ye, S.R.; He, X.; Cao, M.; Xie, K.; Ye, N.Y.; Lin, R.; Wu, S.M.; Xiao, H.B.; et al. Clinical significance of detecting survivin-expressing circulating cancer cells in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens-Beumer, I.J.; Zeestraten, E.C.; Benard, A.; Christen, T.; Reimers, M.S.; Keijzer, R.; Sier, C.F.; Liefers, G.J.; Morreau, H.; Putter, H.; et al. Clinical prognostic value of combined analysis of Aldh1, Survivin, and EpCAM expression in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2014, 110, 2935–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Jiao, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Huo, Z. Clinical and prognostic significance of HIF-1alpha, PTEN, CD44v6, and survivin for gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2014, 9, e91842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Hanna, D.L.; Zhang, W.; Mendez, A.; Yang, D.; El-Khoueiry, R.; Matsusaka, S.; Sunakawa, Y.; Stremitzer, S.; Parekh, A.; et al. Cytokeratin-20 and Survivin-Expressing Circulating Tumor Cells Predict Survival in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients by a Combined Immunomagnetic qRT-PCR Approach. Mol Cancer Ther 2015, 14, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, J.; Canovas, P.; Islam, A.; Altieri, D.C.; Doxsey, S.J. Survivin modulates microtubule dynamics and nucleation throughout the cell cycle. Mol Biol Cell 2006, 17, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianani, R.; Jarboe, E.; Orlicky, D.; Frost, M.; Bobak, J.; Lehner, R.; Shroyer, K.R. Expression of survivin in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic colonic mucosa. Hum Pathol 2001, 32, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarti, A.; Zhai, G.G.; Zhang, M.; Malhotra, R.; Latham, D.E.; Delaney, M.A.; Robe, P.; Nestler, U.; Song, Q.; Loeffler, J. Survivin enhances radiation resistance in primary human glioblastoma cells via caspase-independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7494–7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, F.; Hoffmann, J.; Distel, L.; Herrmann, M.; Noisternig, T.; Papadopoulos, T.; Sauer, R.; Rodel, C. Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 4881–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren, A.G.; Wong, L.; Pakusch, M.; Fowler, K.J.; Burrows, F.J.; Vaux, D.L.; Choo, K.H. Survivin and the inner centromere protein INCENP show similar cell-cycle localization and gene knockout phenotype. Curr Biol 2000, 10, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E.M.; Pollefeyt, S.; Steiner-Mosonyi, M.; Luo, W.; Devriese, A.; Lupu, F.; Bono, F.; Leducq, N.; Dol, F.; Schaeffer, P.; et al. Deficiency of survivin in transgenic mice exacerbates Fas-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial pathways. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, G.; Adida, C.; Altieri, D.C. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 1997, 3, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Otevrel, T.; Gao, Z.; Ehrlich, S.M.; Fields, J.Z.; Boman, B.M. Evidence that APC regulates survivin expression: a possible mechanism. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 8664–8667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.; Pelus, L.M. Regulation of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis family member survivin in normal cord. Blood 2001, 98, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.; Pelus, L.M. Survivin, a cancer target with an emerging role in normal adult tissues. Mol Cancer Ther 2006, 5, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Conway, E.M.; Kang, C.; Winoto, A. Essential role of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, in T cell development, maturation, and homeostasis. J Exp Med 2004, 199, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Bakal, C.; Shahinian, A.; Elia, A.; Wakeham, A.; Suh, W.K.; Duncan, G.S.; Ciofani, M.; Rottapel, R.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C.; et al. Survivin loss in thymocytes triggers p53-mediated growth arrest and p53-independent cell death. J Exp Med 2004, 199, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletic, A.V.; Jellusova, J.; Cato, M.H.; Lee, C.R.; Baracho, G.V.; Conway, E.M.; Rickert, R.C. Essential Role for Survivin in the Proliferative Expansion of Progenitor and Mature B Cells. J Immunol 2016, 196, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Nishimura, W.; Devor-Henneman, D.; Kusewitt, D.; Wang, H.; Holloway, M.P.; Dohi, T.; Sabo, E.; Robinson, M.L.; Altieri, D.C.; et al. Postnatal expansion of the pancreatic beta-cell mass is dependent on survivin. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Schroer, S.; Choi, D.; Chen, P.; Okada, H.; Woo, M. Perinatal survivin is essential for the establishment of pancreatic beta cell mass in mice. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, K.; Okada, H.; Wang, R.; Woo, M. Survivin is required for beta-cell mass expansion in the pancreatic duct-ligated mouse model. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; de Bruin, A.; Caldas, H.; Fangusaro, J.; Hayes, J.; Conway, E.M.; Robinson, M.L.; Altura, R.A. Essential role for survivin in early brain development. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 6962–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, E.; Wittkopf, N.; Gunther, C.; Leppkes, M.; Okada, H.; Watson, A.J.; Podstawa, E.; Backert, I.; Amann, K.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Loss of Survivin in Intestinal Epithelial Progenitor Cells Leads to Mitotic Catastrophe and Breakdown of Gut Immune Homeostasis. Cell Rep 2016, 14, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ambrosini, G.; Chu, E.Y.; Plescia, J.; Tognin, S.; Marchisio, P.C.; Altieri, D.C. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature 1998, 396, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Altieri, D.C. Transcriptional analysis of human survivin gene expression. Biochem J 1999, 344 Pt 2, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaira, V.; Lee, C.W.; Goel, H.L.; Bosari, S.; Languino, L.R.; Altieri, D.C. Regulation of survivin expression by IGF-1/mTOR signaling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asanuma, H.; Torigoe, T.; Kamiguchi, K.; Hirohashi, Y.; Ohmura, T.; Hirata, K.; Sato, M.; Sato, N. Survivin expression is regulated by coexpression of human epidermal growth factor. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 11018–11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, L.; Perez-Rosado, A.; Artiga, M.J.; Camacho, F.I.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, N.; Ruiz-Ballesteros, E.; Mollejo, M.; Martinez, B.; Cuadros, M.; et al. Expression of the NF-kappaB targets BCL2 and BIRC5/Survivin characterizes small. J Pathol 2005, 206, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Greene, M.I. EGFR enhances Survivin expression through the phosphoinositide 3 (PI-3) kinase. Exp Mol Pathol 2005, 79, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Bisi, J.; Strum, J.; Liu, L.; Carrick, K.; Graham, K.M.; Treece, A.L.; Hardwicke, M.A.; Dush, M.; Liao, Q.; et al. Regulation of survivin by ErbB2 signaling: therapeutic implications for. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.J.; Plescia, J.; Clevers, H.; Fearon, E.R.; Altieri, D.C. Survivin and molecular pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Lancet 2003, 362, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Raskett, C.M.; Prudovsky, I.; Altieri, D.C. Molecular dependence of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer on a notch-survivin signaling axis. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 5273–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Feldmann, G.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, N.; Comerford, S.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Anders, R.A.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D. Elucidation of a universal size-control mechanism in Drosophila and mammals. Cell 2007, 130, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlckova, K.; Ondrusova, L.; Vachtenheim, J.; Reda, J.; Dundr, P.; Zadinova, M.; Zakova, P.; Pouckova, P. Survivin, a novel target of the Hedgehog/GLI signaling pathway in human tumor cells. Cell Death Dis 2016, 7, e2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, S.N.; Markant, S.L.; Esparza, L.A.; Garcia, G.; Terry, D.; Huang, J.M.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Li, X.N.; Grant, G.A.; Crawford, J.R.; et al. Survivin as a therapeutic target in Sonic hedgehog-driven medulloblastoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3770–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Hughes, D.; Petrovic, V.; Major, M.L.; Park, H.J.; Tan, Y.; Ackerson, T.; Costa, R.H. Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25, 10875–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; McGuirk, M.; Hockenberry, T.N.; Wu, Q.; Ashar, H.; Black, S.; Wen, S.F.; Wang, L.; Kirschmeier, P.; Bishop, W.R.; et al. Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and participates in. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2613–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Liu, T.; Samadashwily, G.; Li, F.; Grossman, D. Survivin repression by p53, Rb and E2F2 in normal human melanocytes. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, M.; Plescia, J.; Leav, I.; Li, J.; Languino, L.R.; Altieri, D.C. Endogenous tumor suppression mediated by PTEN involves survivin gene silencing. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 4954–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Zheng, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Xu, X.; Cao, L.; Luhasen, T.; Lee, M.H.; Xiao, C.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Chen, W.; et al. Interplay among BRCA1, SIRT1, and Survivin during BRCA1-associated tumorigenesis. Mol Cell 2008, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Span, S.W.; Ferreira, C.G.; Kruyt, F.A.; Giaccone, G. CRM1-mediated nuclear export determines the cytoplasmic localization of the antiapoptotic protein Survivin. Exp Cell Res 2002, 275, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahotka, C.; Wenzel, M.; Springer, E.; Gabbert, H.E.; Gerharz, C.D. Survivin-deltaEx3 and survivin-2B: two novel splice variants of the apoptosis inhibitor survivin with different antiapoptotic properties. Cancer Res 1999, 59, 6097–6102. [Google Scholar]
- Caldas, H.; Honsey, L.E.; Altura, R.A. Survivin 2alpha: a novel Survivin splice variant expressed in human malignancies. Mol Cancer 2005, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola, G.; Vela, E.; Fernandez-Figueras, M.T.; Isamat, M.; Munoz-Marmol, A.M. Exonization of Alu-generated splice variants in the survivin gene of human and non-human primates. J Mol Biol 2007, 366, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, H.; Jiang, Y.; Holloway, M.P.; Fangusaro, J.; Mahotka, C.; Conway, E.M.; Altura, R.A. Survivin splice variants regulate the balance between proliferation and cell death. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1994–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noton, E.A.; Colnaghi, R.; Tate, S.; Starck, C.; Carvalho, A.; Ko Ferrigno, P.; Wheatley, S.P. Molecular analysis of survivin isoforms: evidence that alternatively spliced variants do not play a role in mitosis. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, A.; Kroupis, C.; Dimas, K. Association of survivin splice variants with prognosis and treatment of breast cancer. World J Clin Oncol 2014, 5, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ackermann, E.J.; Bennett, C.F.; Rothermel, A.L.; Plescia, J.; Tognin, S.; Villa, A.; Marchisio, P.C.; Altieri, D.C. Pleiotropic cell-division defects and apoptosis induced by interference with survivin function. Nat Cell Biol 1999, 1, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lens, S.M.; Wolthuis, R.M.; Klompmaker, R.; Kauw, J.; Agami, R.; Brummelkamp, T.; Kops, G.; Medema, R.H. Survivin is required for a sustained spindle checkpoint arrest in response to lack of tension. Embo J 2003, 22, 2934–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, G.; Kauw, J.J.; Medema, R.H.; Lens, S.M. Survivin mediates targeting of the chromosomal passenger complex to the centromere and midbody. EMBO Rep 2006, 7, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.E.; Ghenoiu, C.; Xue, J.Z.; Zierhut, C.; Kimura, H.; Funabiki, H. Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 2010, 330, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Dai, J.; Daum, J.R.; Niedzialkowska, E.; Banerjee, B.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Gorbsky, G.J.; Higgins, J.M. Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis. Science 2010, 330, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, Y.; Honda, T.; Tanno, Y.; Watanabe, Y. Two histone marks establish the inner centromere and chromosome bi-orientation. Science 2010, 330, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheatley, S.P.; Carvalho, A.; Vagnarelli, P.; Earnshaw, W.C. INCENP is required for proper targeting of Survivin to the centromeres and the anaphase spindle during mitosis. Curr Biol 2001, 11, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, M.A.; Lan, W.; Powers, S.E.; McCleland, M.L.; Kuang, J.; Stukenberg, P.T. Aurora B kinase exists in a complex with survivin and INCENP and its kinase activity is stimulated by survivin binding and phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell 2002, 13, 3064–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babkoff, A.; Cohen-Kfir, E.; Aharon, H.; Ronen, D.; Rosenberg, M.; Wiener, R.; Ravid, S. A direct interaction between survivin and myosin II is required for cytokinesis. J Cell Sci 2019, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Welm, A.; Bishop, J.M. Cell division and cell survival in the absence of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 15100–15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, E.; Plescia, J.; Wilkinson, J.C.; Duckett, C.S.; Altieri, D.C. Acute ablation of survivin uncovers p53-dependent mitotic checkpoint functions and control of mitochondrial apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasula, S.M.; Ashwell, J.D. IAPs: what’s in a name? Mol Cell 2008, 30, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, D.; Kim, P.J.; Blanc-Brude, O.P.; Brash, D.E.; Tognin, S.; Marchisio, P.C.; Altieri, D.C. Transgenic expression of survivin in keratinocytes counteracts UVB-induced apoptosis and cooperates with loss of p53. J Clin Invest 2001, 108, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc-Brude, O.P.; Mesri, M.; Wall, N.R.; Plescia, J.; Dohi, T.; Altieri, D.C. Therapeutic targeting of the survivin pathway in cancer: initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 2003, 9, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Cetraro, P.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; MacKenzie, A.; Abadia-Molina, F. A Review of the Current Impact of Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins and Their Repression in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. IAP family proteins--suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, S.J.; Renatus, M.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, C.; Fesik, S.W.; Liddington, R.C.; Salvesen, G.S. Structural basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell 2001, 104, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Park, Y.C.; Rich, R.L.; Segal, D.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. Structural basis of caspase inhibition by XIAP: differential roles of the linker versus the BIR domain. Cell 2001, 104, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Shiozaki, E.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Wu, Q.; Datta, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Shi, Y. Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell 2001, 104, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.; Deveraux, Q.; Tamm, I.; Welsh, K.; Assa-Munt, N.; Salvesen, G.S.; Reed, J.C. A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 7787–7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nakabayashi, Y.; Takahashi, R. Ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein promotes proteasomal degradation of caspase-3 and enhances its anti-apoptotic effect in Fas-induced cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 8662–8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yao, X.; Wu, M. Direct interaction between survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the anti-apoptotic activity of survivin during taxol-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 23130–23140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Kelly, A.E.; Funabiki, H.; Patel, D.J. Structural basis for recognition of H3T3ph and Smac/DIABLO N-terminal peptides by human Survivin. Structure 2012, 20, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 2000, 102, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, A.M.; Ekert, P.G.; Pakusch, M.; Silke, J.; Connolly, L.M.; Reid, G.E.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.J.; Vaux, D.L. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 2000, 102, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeish, I.A.; Lopes, R.; Bell, S.J.; McKay, T.R.; Fernandez, M.; Lockley, M.; Wheatley, S.P.; Lemoine, N.R. Survivin interacts with Smac/DIABLO in ovarian carcinoma cells but is redundant in Smac-mediated apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 2005, 302, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunajova, L.; Cash, E.; Markus, R.; Rochette, S.; Townley, A.R.; Wheatley, S.P. The N-terminus of survivin is a mitochondrial-targeting sequence and Src regulator. J Cell Sci 2016, 129, 2707–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohi, T.; Beltrami, E.; Wall, N.R.; Plescia, J.; Altieri, D.C. Mitochondrial survivin inhibits apoptosis and promotes tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest 2004, 114, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townley, A.R.; Wheatley, S.P. Mitochondrial survivin reduces oxidative phosphorylation in cancer cells by inhibiting mitophagy. J Cell Sci 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohi, T.; Xia, F.; Altieri, D.C. Compartmentalized phosphorylation of IAP by protein kinase A regulates cytoprotection. Mol Cell 2007, 27, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivadeneira, D.B.; Caino, M.C.; Seo, J.H.; Angelin, A.; Wallace, D.C.; Languino, L.R.; Altieri, D.C. Survivin promotes oxidative phosphorylation, subcellular mitochondrial repositioning, and tumor cell invasion. Sci Signal 2015, 8, ra80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuchner, J.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Obexer, P.; Ausserlechner, M.J. BIRC5/Survivin enhances aerobic glycolysis and drug resistance by altered regulation of the mitochondrial fusion/fission machinery. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.K.; Cheng, Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, J.M. Interaction of Beclin 1 with survivin regulates sensitivity of human glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 2010, 584, 3519–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, D.; Yousefi, S.; Schmid, I.; Zlobec, I.; Perren, A.; Friis, R.; Simon, H.U. ATG5 is induced by DNA-damaging agents and promotes mitotic catastrophe independent of autophagy. Nat Commun 2013, 4, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Chan, H.H.; Chen, S.H.; Sarvagalla, S.; Chen, P.S.; Coumar, M.S.; Cheng, S.M.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Leung, E.; et al. BIRC5/Survivin is a novel ATG12-ATG5 conjugate interactor and an autophagy-induced DNA damage suppressor in human cancer and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1296–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuchner, J.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Obexer, P.; Ausserlechner, M.J. BIRC5/Survivin as a target for glycolysis inhibition in high-stage neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colnaghi, R.; Connell, C.M.; Barrett, R.M.; Wheatley, S.P. Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 33450–33456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauer, S.K.; Bier, C.; Habtemichael, N.; Stauber, R.H. The Survivin-Crm1 interaction is essential for chromosomal passenger complex localization and function. EMBO Rep 2006, 7, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauber, R.H.; Rabenhorst, U.; Rekik, A.; Engels, K.; Bier, C.; Knauer, S.K. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and the biological activity of mouse survivin are regulated by an active nuclear export signal. Traffic 2006, 7, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knauer, S.K.; Bier, C.; Schlag, P.; Fritzmann, J.; Dietmaier, W.; Rodel, F.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Kovacs, A.F.; Doring, C.; Hansmann, M.L.; et al. The survivin isoform survivin-3B is cytoprotective and can function as a chromosomal passenger complex protein. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temme, A.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Hendruschk, S.; Gunes, S.; Weigle, B.; Schakel, K.; Schmitz, M.; Bachmann, M.; Schackert, G.; Rieber, E.P. Nuclear localization of Survivin renders HeLa tumor cells more sensitive to apoptosis by induction of p53 and Bax. Cancer Lett 2007, 250, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connell, C.M.; Colnaghi, R.; Wheatley, S.P. Nuclear survivin has reduced stability and is not cytoprotective. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 3289–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, E.; Murai, Y.; Matsui, K.; Isizawa, S.; Cheng, C.; Masuda, M.; Takano, Y. Survivin expression in tumor cell nuclei is predictive of a favorable prognosis in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Lett 2001, 163, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.M.; O’Driscoll, L.; Purcell, R.; Fitz-Simons, N.; McDermott, E.W.; Hill, A.D.; O’Higgins, N.J.; Parkinson, M.; Linehan, R.; Clynes, M. Prognostic importance of survivin in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 2003, 88, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vischioni, B.; van der Valk, P.; Span, S.W.; Kruyt, F.A.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Giaccone, G. Nuclear localization of survivin is a positive prognostic factor for survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 2004, 15, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Yasufuku, K.; Nakajima, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Chiyo, M.; Yoshida, S.; Suzuki, M.; Sekine, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Agamy, G.; et al. Nuclear Survivin in pN2 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Prognostic and Clinical Implications. Eur Respir J 2008.
- Shinohara, E.T.; Gonzalez, A.; Massion, P.P.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Freyer, A.S.; Olson, S.J.; Andersen, J.J.; Shyr, Y.; Carbone, D.P.; et al. Nuclear survivin predicts recurrence and poor survival in patients with resected nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Oka, K.; Noda, S.E.; Katoh, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Itoh, J.; Itoh, H.; Ishiuchi, S.; Sakurai, H.; et al. Nuclear survivin expression predicts poorer prognosis in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2008. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, S.F.; Weinell, A.; Molitor, M.; Stenner, M.; Semrau, R.; Drebber, U.; Weissenborn, S.J.; Speel, E.J.; Wittekindt, C.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; et al. Nuclear survivin expression is associated with HPV-independent carcinogenesis and is an indicator of poor prognosis in oropharyngeal cancer. Br J Cancer 2008, 98, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; McNiff, J.M. Nuclear expression of survivin portends a poor prognosis in Merkel cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 2008, 21, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, P.; Griss, S.; Arnold, C.N.; Horsch, D.; Goke, R.; Arnold, R.; Heine, B.; Stein, H.; Zeitz, M.; Scherubl, H. Nuclear survivin is a powerful novel prognostic marker in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor disease. Neuroendocrinology 2005, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantalat, L.; Skoufias, D.A.; Kleman, J.P.; Jung, B.; Dideberg, O.; Margolis, R.L. Crystal structure of human survivin reveals a bow tie-shaped dimer with two unusual alpha-helical extensions. Mol Cell 2000, 6, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdecia, M.A.; Huang, H.; Dutil, E.; Kaiser, D.A.; Hunter, T.; Noel, J.P. Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement. Nat Struct Biol 2000, 7, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchmore, S.W.; Chen, J.; Jakob, C.; Zakula, D.; Matayoshi, E.D.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Ng, S.C.; Altieri, D.C. Crystal structure and mutagenic analysis of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein survivin. Mol Cell 2000, 6, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Nettesheim, D.; Liu, Z.; Olejniczak, E.T. Solution structure of human survivin and its binding interface with Smac/Diablo. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, Q.P.; Cao, K.; Li, H.Y.; Iglesias, P.A.; Zheng, Y. Chromosome alignment and segregation regulated by ubiquitination of survivin. Science 2005, 310, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaprakash, A.A.; Klein, U.R.; Lindner, D.; Ebert, J.; Nigg, E.A.; Conti, E. Structure of a Survivin-Borealin-INCENP core complex reveals how chromosomal passengers travel together. Cell 2007, 131, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.M.; Osborne, T.P.; Wheatley, S.P. Phosphorylation of survivin at threonine 34 inhibits its mitotic function and enhances its cytoprotective activity. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, D.S.; Grossman, D.; Plescia, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Villa, A.; Tognin, S.; Marchisio, P.C.; Altieri, D.C. Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 13103–13107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, S.P.; Barrett, R.M.; Andrews, P.D.; Medema, R.H.; Morley, S.J.; Swedlow, J.R.; Lens, S.M. Phosphorylation by aurora-B negatively regulates survivin function during mitosis. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, R.M.; Colnaghi, R.; Wheatley, S.P. Threonine 48 in the BIR domain of survivin is critical to its mitotic and anti-apoptotic activities and can be phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colnaghi, R.; Wheatley, S.P. Liaisons between survivin and Plk1 during cell division and cell death. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 22592–22604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Holloway, M.P.; Ma, L.; Cooper, Z.A.; Riolo, M.; Samkari, A.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Chin, Y.E.; Altura, R.A. Acetylation directs survivin nuclear localization to repress STAT3 oncogenic activity. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 36129–36137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, T.; Kita, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Mori, M.; Amino, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Tominaga, F.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kinoyama, I.; Matsuhisa, A.; et al. YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, induces regression of. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 8014–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, T.; Okamoto, I.; Suzuki, M.; Nakahara, T.; Yamanaka, K.; Hatashita, E.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Ono, K.; Nakagawa, K. Radiosensitizing effect of YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, in. Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14, 6496–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Shuda, M.; Guastafierro, A.; Feng, H.; Toptan, T.; Tolstov, Y.; Normolle, D.; Vollmer, L.L.; Vogt, A.; Domling, A.; et al. Survivin is a therapeutic target in merkel cell carcinoma. Sci Transl Med 2012, 4, 133ra156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaros, T.G.; Stockwin, L.H.; Mullendore, M.E.; Smith, B.; Morrison, B.L.; Newton, D.L. The "survivin suppressants" NSC 80467 and YM155 induce a DNA damage response. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2012. [CrossRef]
- Giaccone, G.; Zatloukal, P.; Roubec, J.; Floor, K.; Musil, J.; Kuta, M.; van Klaveren, R.J.; Chaudhary, S.; Gunther, A.; Shamsili, S. Multicenter phase II trial of YM155, a small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in patients with advanced, refractory, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27, 4481–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.J.; Thomas, A.; Rajan, A.; Chun, G.; Lopez-Chavez, A.; Szabo, E.; Spencer, S.; Carter, C.A.; Guha, U.; Khozin, S.; et al. A phase I/II study of sepantronium bromide (YM155, survivin suppressor) with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 2013, 24, 2601–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Okamoto, I.; Miyazaki, M.; Morinaga, R.; Tsuya, A.; Hasegawa, Y.; Terashima, M.; Ueda, S.; Fukuoka, M.; Ariyoshi, Y.; et al. Phase I study of YM155, a novel survivin suppressant, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2009, 15, 3872–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Quinn, D.I.; Ferrari, A.; Ahmann, F.; Giaccone, G.; Drake, T.; Keating, A.; de Bono, J.S. A phase II study of YM155, a novel small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in castration-resistant taxane-pretreated prostate cancer. Ann Oncol 2012, 23, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Mita, A.; Lewis, L.D.; Garrett, C.R.; Till, E.; Daud, A.I.; Patnaik, A.; Papadopoulos, K.; Takimoto, C.; Bartels, P.; et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of YM155, a small-molecule inhibitor of survivin. J Clin Oncol 2008, 26, 5198–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Zhang, L.; Boufraqech, M.; Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, D.; Davis, S.; Rosenberg, A.; Ylaya, K.; Aufforth, R.; et al. Inhibition of Survivin with YM155 Induces Durable Tumor Response in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Cao, S.; Cheng, Q.; Keefe, J.T.; Rustum, Y.M.; Li, F. A novel small molecule FL118 that selectively inhibits survivin, Mcl-1, XIAP and cIAP2 in a p53-independent manner, shows superior antitumor activity. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Que, R.; Liu, C.; Ji, W.; Sun, B.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Survivin-targeted drug screening platform identifies a matrine derivative WM-127 as a potential therapeutics against hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2018, 425, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Heller, J.D.; Kuo, J.; Huang, R.C. Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid induces growth arrest and cellular apoptosis by inhibiting Cdc2 and survivin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 13239–13244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, D.; Ding, K.; Lu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J. GDP366, a novel small molecule dual inhibitor of survivin and Op18, induces cell growth inhibition, cellular senescence and mitotic catastrophe in human cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 2010, 9, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortugno, P.; Beltrami, E.; Plescia, J.; Fontana, J.; Pradhan, D.; Marchisio, P.C.; Sessa, W.C.; Altieri, D.C. Regulation of survivin function by Hsp90. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 13791–13796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plescia, J.; Salz, W.; Xia, F.; Pennati, M.; Zaffaroni, N.; Daidone, M.G.; Meli, M.; Dohi, T.; Fortugno, P.; Nefedova, Y.; et al. Rational design of shepherdin, a novel anticancer agent. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Tian, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, B.; Dong, P.; Watari, H.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Guo, Y.; et al. Ovarian Primary and Metastatic Tumors Suppressed by Survivin Knockout or a Novel Survivin Inhibitor. Mol Cancer Ther 2019, 18, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, W. Discovery of novel second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase mimetics as selective inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibitors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2014, 349, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, T.; Unno, Y.; Matsuno, K.; Sawada, J.; Ogo, N.; Tanaka, K.; Asai, A. Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the interaction between Survivin and Smac/DIABLO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010, 393, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Shin, I.; Park, S.H.; Kim, N.D.; Shin, I. An Inhibitor of the Interaction of Survivin with Smac in Mitochondria Promotes Apoptosis. Chem Asian J 2019, 14, 4035–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, M.D.; Sun, C.; Kunzer, A.; Sauer, D.; Sarris, K.; Hoff, E.; Yu, L.; Nettesheim, D.G.; Chen, J.; Jin, S.; et al. Discovery of a novel small molecule binding site of human survivin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2007, 17, 3122–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guvenc, H.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Joshi, K.; Kurt, H.; Banasavadi-Siddegowda, Y.K.; Mao, P.; Hong, C.; Yamada, R.; Kwon, C.H.; Bhasin, D.; et al. Impairment of glioma stem cell survival and growth by a novel inhibitor for Survivin-Ran protein complex. Clin Cancer Res 2013, 19, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chettiar, S.N.; Cooley, J.V.; Park, I.H.; Bhasin, D.; Chakravarti, A.; Li, P.K.; Li, C.; Jacob, N.K. Design, synthesis and biological studies of survivin dimerization modulators that prolong mitotic cycle. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 5429–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steigerwald, C.; Rasenberger, B.; Christmann, M.; Tomicic, M.T. Sensitization of colorectal cancer cells to irinotecan by the Survivin inhibitor LLP3 depends on XAF1 proficiency in the context of mutated p53. Arch Toxicol 2018, 92, 2645–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezov, A.; Cai, Z.; Freudenberg, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.; Thompson, T.; Murali, R.; Greene, M.I.; Wang, Q. Disabling the mitotic spindle and tumor growth by targeting a cavity-induced allosteric site of survivin. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.M.; Nagatomo, I.; Suzuki, E.; Mizuno, T.; Kumagai, T.; Berezov, A.; Zhang, H.; Karlan, B.; Greene, M.I.; Wang, Q. YAP modifies cancer cell sensitivity to EGFR and survivin inhibitors and is negatively regulated by the non-receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase 14. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, R.; Cheng, X.; Berezov, A.; Du, X.; Schon, A.; Freire, E.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Greene, M.I. Disabling TNF receptor signaling by induced conformational perturbation of tryptophan-107. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 10970–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, N.; Fuchigami, T.; Mizoguchi, T.; Yoshida, S.; Haratake, M.; Nakayama, M. Synthesis and characterization of radioiodinated 3-phenethyl-2-indolinone derivatives for SPECT imaging of survivin in tumors. Bioorg Med Chem 2018, 26, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Peery, R.C.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.T. Effective Targeting of the Survivin Dimerization Interface with Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, R.; Kyei-Baffour, K.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; de Andrade Horn, P.; Dai, M.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.T. Synthesis and Identification of a Novel Lead Targeting Survivin Dimerization for Proteasome-Dependent Degradation. J Med Chem 2020, 63, 7243–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.H.; Pedersen, L.O.; Becker, J.C.; Straten, P.T. Identification of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to the apoptosis inhibitor protein survivin in cancer patients. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 869–872. [Google Scholar]
- Hirohashi, Y.; Torigoe, T.; Maeda, A.; Nabeta, Y.; Kamiguchi, K.; Sato, T.; Yoda, J.; Ikeda, H.; Hirata, K.; Yamanaka, N.; et al. An HLA-A24-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope of a tumor-associated protein, survivin. Clin Cancer Res 2002, 8, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, R.; Mizutani, N.; Luo, Y.; Chiodoni, C.; Zhou, H.; Mizutani, M.; Ba, Y.; Becker, J.C.; Reisfeld, R.A. A DNA vaccine targeting survivin combines apoptosis with suppression of angiogenesis in lung tumor eradication. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodi, F.; Maherzi-Mechalikh, C.; Mougel, A.; Ben Hamouda, N.; Taboas, C.; Gueugnon, F.; Tran, T.; Nozach, H.; Marcon, E.; Gey, A.; et al. High Therapeutic Efficacy of a New Survivin LSP-Cancer Vaccine Containing CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-Cell Epitopes. Front Oncol 2018, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenstermaker, R.A.; Ciesielski, M.J.; Qiu, J.; Yang, N.; Frank, C.L.; Lee, K.P.; Mechtler, L.R.; Belal, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Hutson, A.D. Clinical study of a survivin long peptide vaccine (SurVaxM) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2016, 65, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahluwalia, M.S.; Reardon, D.A.; Abad, A.P.; Curry, W.T.; Wong, E.T.; Figel, S.A.; Mechtler, L.L.; Peereboom, D.M.; Hutson, A.D.; Withers, H.G.; et al. Phase IIa Study of SurVaxM Plus Adjuvant Temozolomide for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 2023, 41, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesielski, M.J.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Munich, S.A.; Orton, M.; Barone, T.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Fenstermaker, R.A. Antitumor cytotoxic T-cell response induced by a survivin peptide mimic. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010, 59, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Menges, M.; Veerapathran, A.; Coppola, D.; Gabrilovich, D.; Anasetti, C. Survivin-specific CD4+ T cells are decreased in patients with survivin-positive myeloma. J Immunother Cancer 2015, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.L.; Atkins, R.; Varadarajan, I.; Menges, M.; Edelman, J.; Baz, R.; Brayer, J.; Castaneda Puglianini, O.; Ochoa-Bayona, J.L.; Nishihori, T.; et al. Survivin Dendritic Cell Vaccine Safely Induces Immune Responses and Is Associated with Durable Disease Control after Autologous Transplant in Patients with Myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2023, OF1–OF11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




