Submitted:
20 March 2024
Posted:
20 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Models and Their Governing Equations
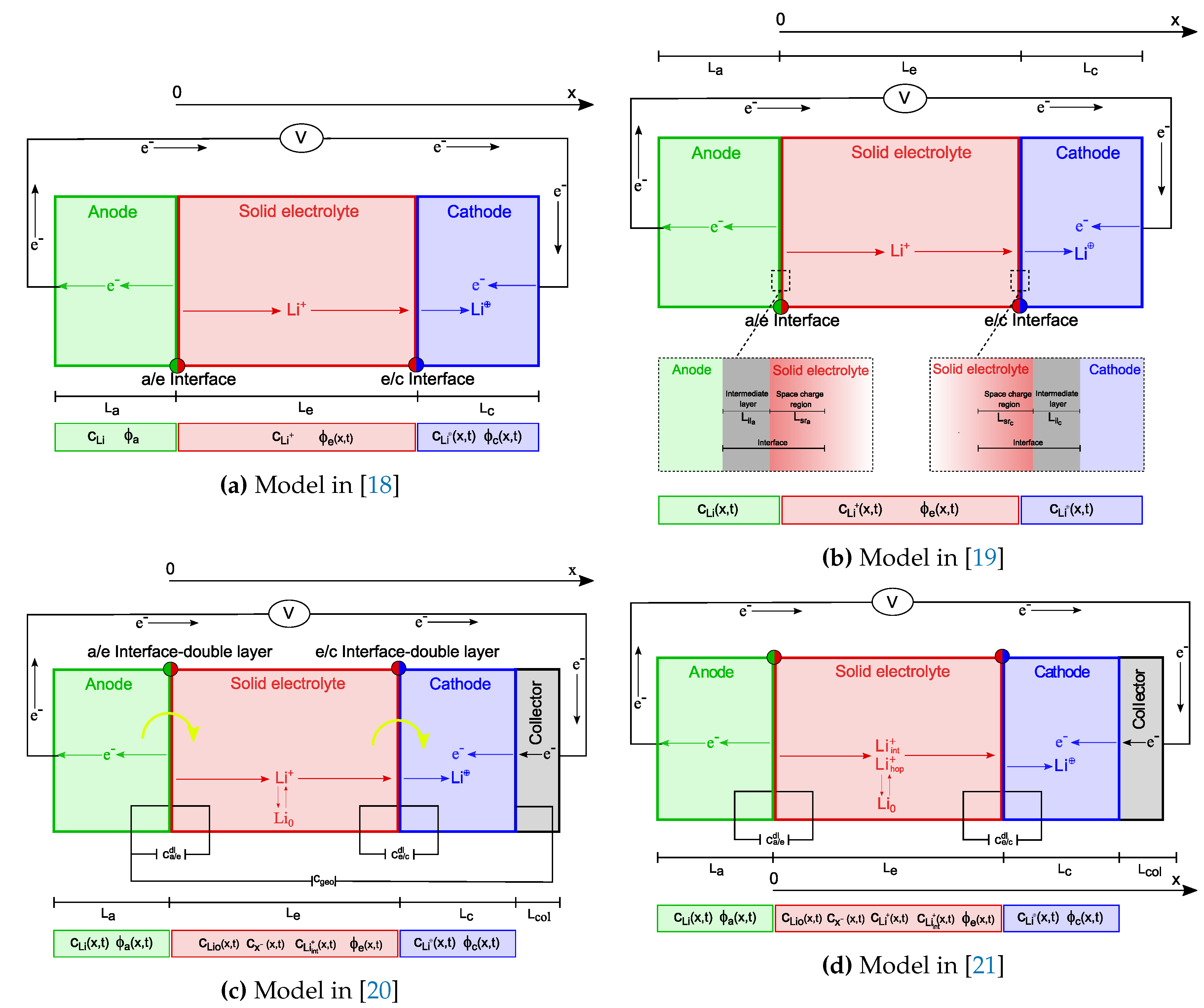
2.1. One-Dimensional Single-Ion Conduction Models [18]
2.2. An Advanced Framework for Solid Electrolyte Intercalation Batteries [19]
2.3. An Advanced All-Solid-State Li-Ion Battery Model [20]
2.4. Two-Mechanisms Model for All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries
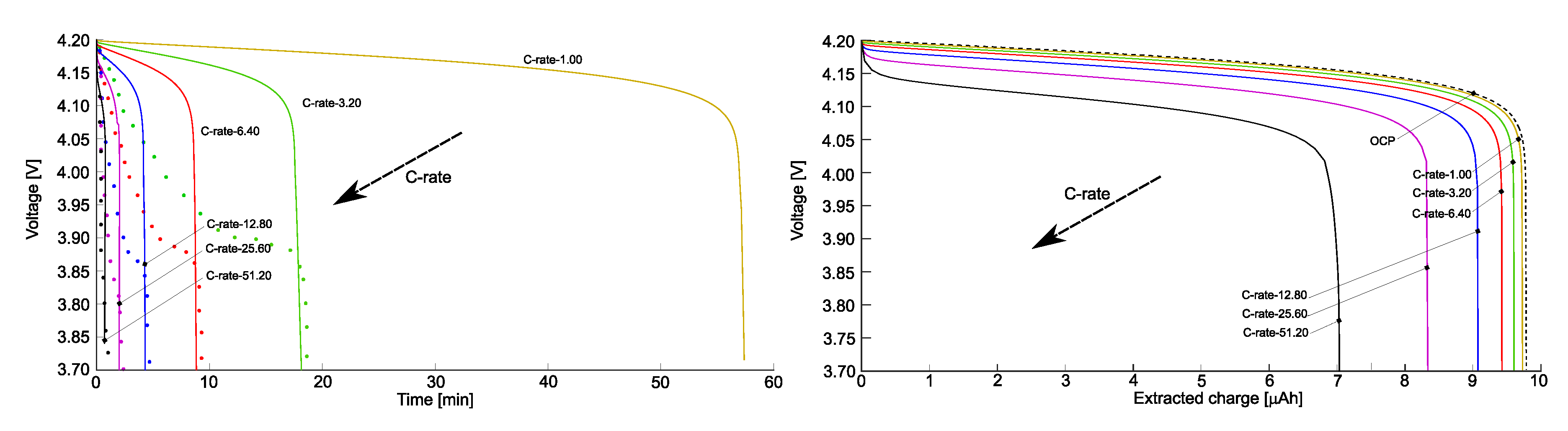
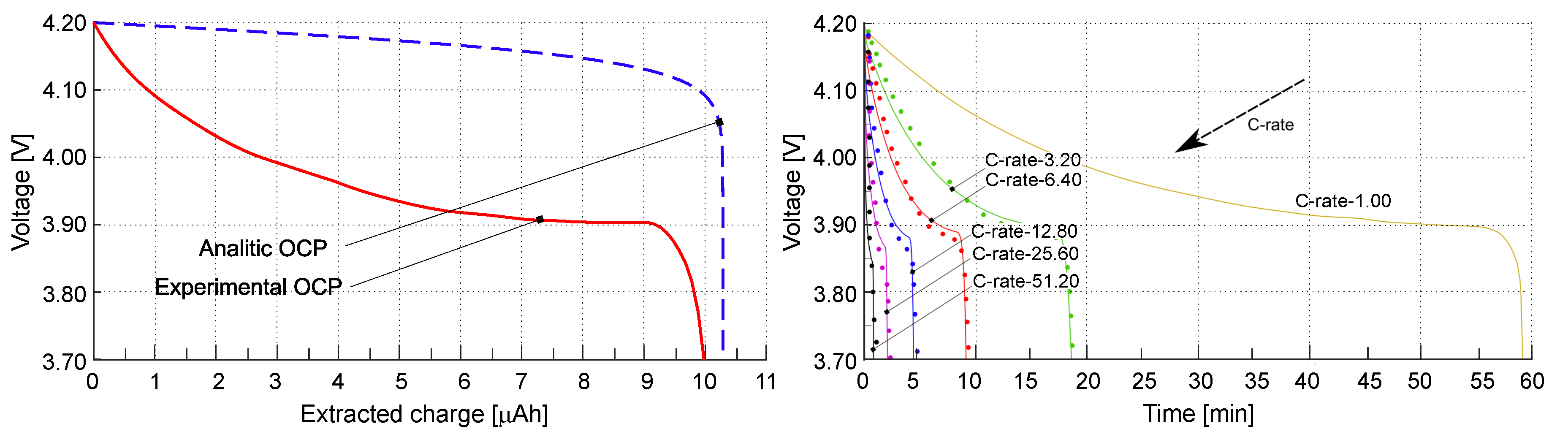
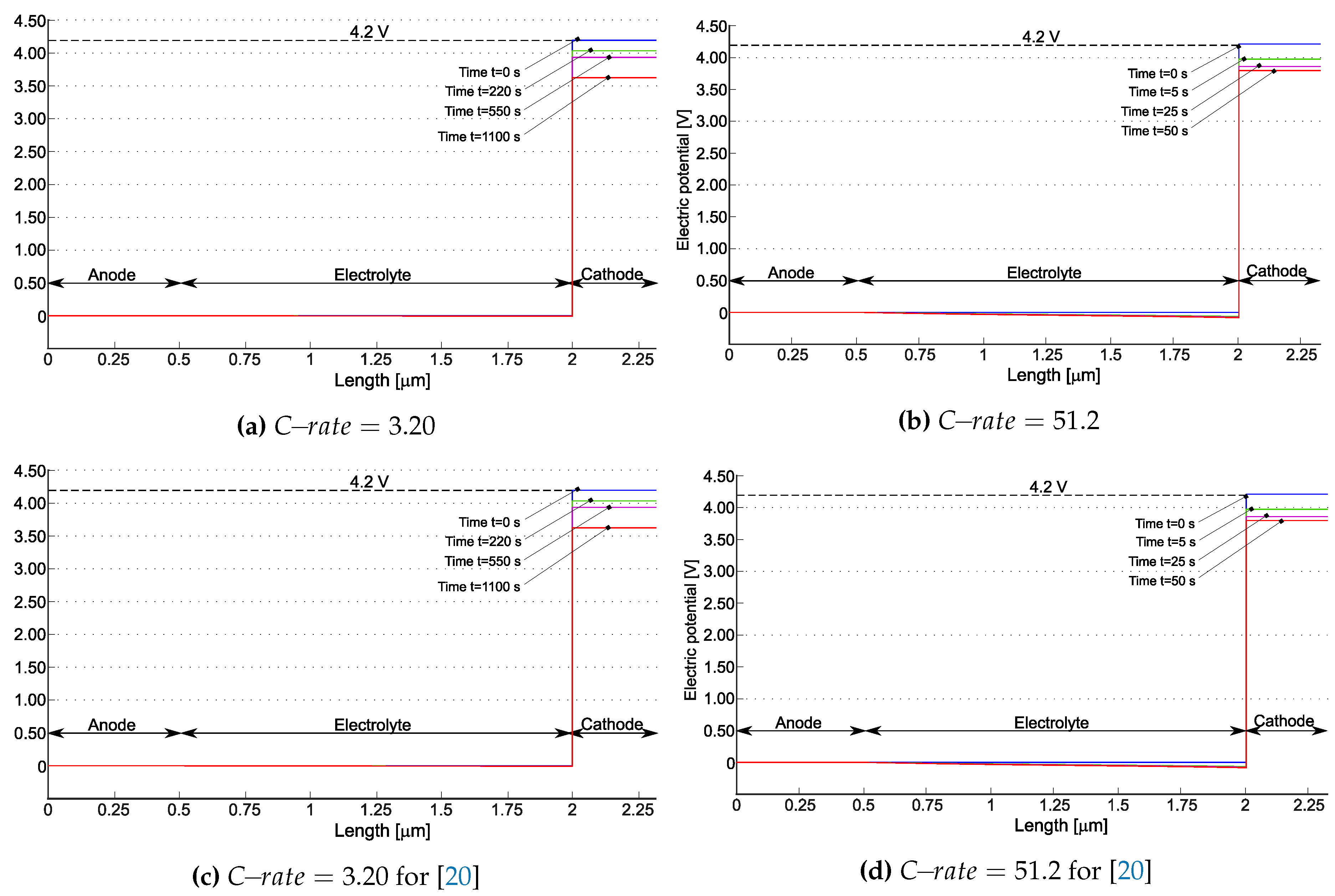
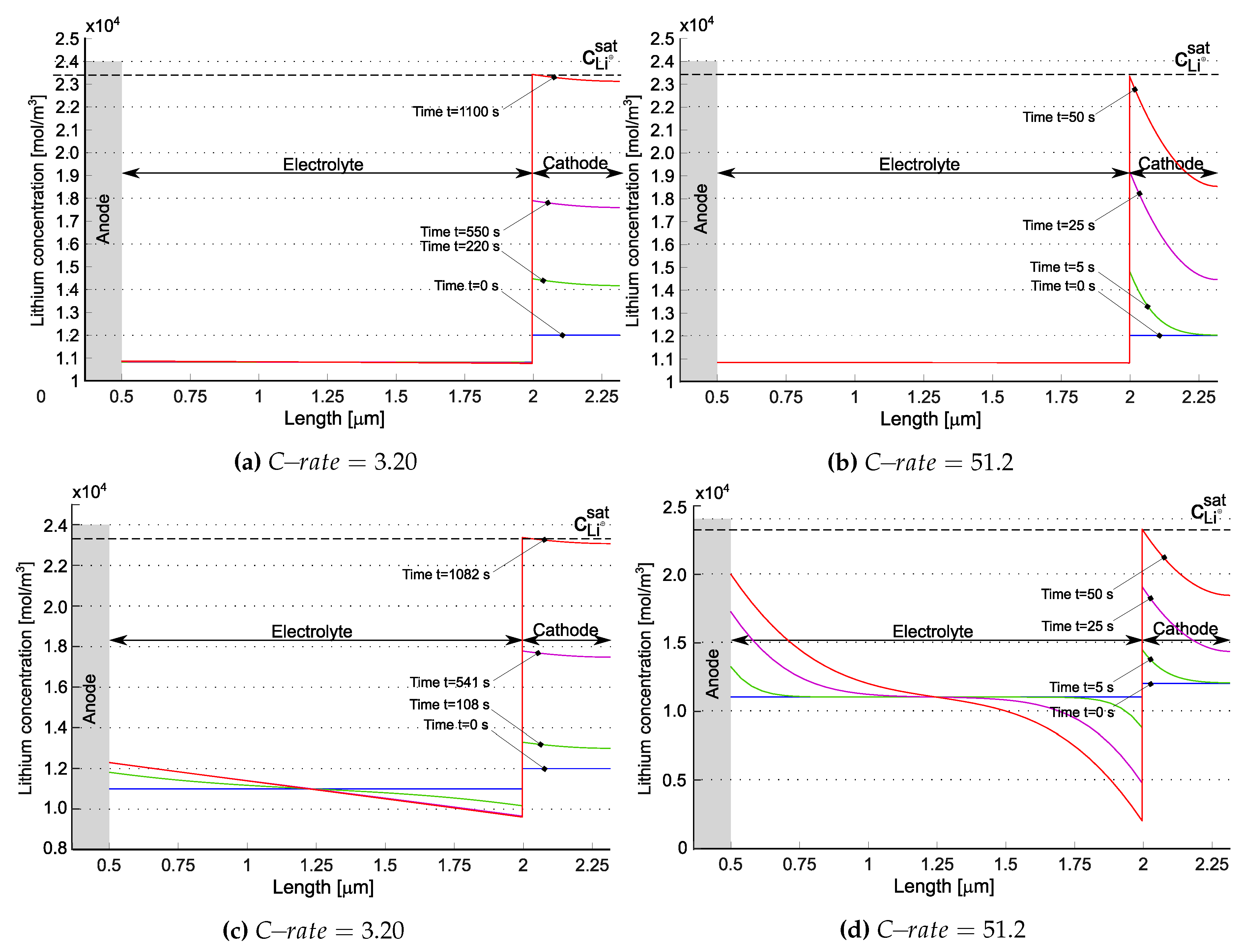
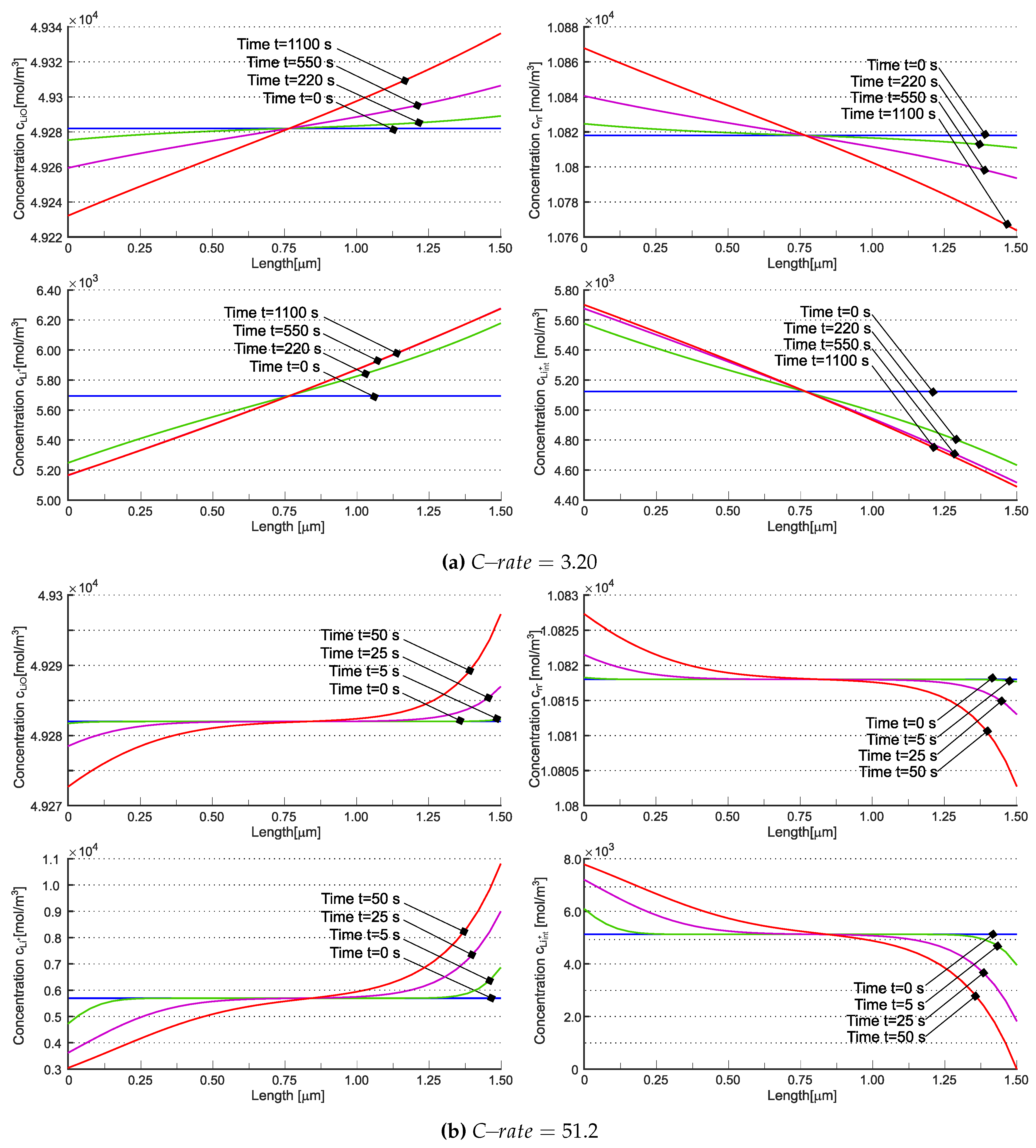
3. Benchmark Comparison
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Appendix A Analytical OCP Simulations
References
- Schnell, J.; Günther, T.; Knoche, T.; Vieider, C.; Köhler, L.; Just, A.; Keller, M.; Passerini, S.; Reinhart, G. All-solid-state lithium-ion and lithium metal batteries – paving the way to large-scale production. J POWER SOURCES 2018, 382, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Kotobuki, M.; Song, S.; Lai, M.; Lu, L. Review on solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. J POWER SOURCES 2018, 389, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazioli, D.; Magri, M.; Salvadori, A. Computational modeling of Li-ion batteries. COMPUT MECH 2016, 58, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Monroe, C.W. Multiscale Lithium-Battery Modeling from Materials to Cells. ANNU REV CHEM BIOMOL 2020, 11, 277–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, M.; Armstrong, D.; Brown, Z.; Bu, J.; Castell, M.; Chen, P.; Cocks, A.; Corr, S.; Cussen, E.; Darnbrough, E.; et al. 2020 roadmap on solid-state batteries. J PHYS ENERGY 2020, 2, 032008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhanagopalan, D.; Qian, D.; McGilvray, T.; Wang, Z.; Camino, F.; Graetz, J.; Dudney, N.; Meng, Y. Interface limited lithium transport in solidstate batteries. J PHYS CHEM LETT 2014, 5, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, T.; Raijmakers, L.; Vezhlev, E.; Wu, B.; Schuelli, T.; Danilov, D.; Wei, Y.; Eichel, R.; et al. Interface Aspects in All-Solid-State Li-Based Batteries Reviewed. ADV ENERGY MATER 2021, 2003939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Li, A.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. A review of mechanics-related material damages in all-solid-state batteries: Mechanisms, performance impacts and mitigation strategies. NANO ENERGY 2020, 70, 104545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.K.; Qi, Y. Simulation of the Effect of Contact Area Loss in All-Solid-State Li-Ion Batteries. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2017, 164, 3512–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.; Hogg, B.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M. Li plating as unwanted side reaction in commercial Li-ion cells – A review. J POWER SOURCES 2018, 384, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porz, L.; Swamy, T.; Sheldon, B.; Rettenwander, D.; Frömling, T.; Thaman, H.; Berendts, S.; Uecker, R.; Carter, W.; Chiang, Y. Mechanism of Lithium Metal Penetration through Inorganic Solid Electrolytes. ADV ENERGY MATER 2017, 7, 1701003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishvan, S.; Fleck, N.; McMeeking, R.; Deshpande, V. Growth rate of lithium filaments in ceramic electrolytes. ACTA MATER 2020, 196, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wei, S.; Li, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y. Recent Progress of the Solid-State Electrolytes for High-Energy Metal-Based Batteries. ADV ENERGY MATER 2018, 8, 1702657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Luan, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Liu, H. Single Lithium-Ion Conducting Solid Polymer Electrolyte with Superior Electrochemical Stability and Interfacial Compatibility for Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries. ACS APPL MATER INTER 2020, 12, 7249–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ou, J.; Li, M.; Luo, D.; Dou, H.; Li, Z.; Amine, K.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. A review of composite solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: fundamentals, key materials and advanced structures. CHEM SOC REV 2020, 49, 8790–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielefeld, A.; Weber, D.; Janek, J. Microstructural modeling of composite cathodes for all solid state batteries. J PHYS CHEM C 2019, 123, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Han, W. Recent advances in inorganic solid electrolytes for lithium batteries. FRONT ENERGY RES 2014, 2, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, S.; Guy-Bouyssou, D.; Bouillon, P.; Le Cras, F.; Delacourt, C. Charge/Discharge Simulation of an All-Solid-State Thin-Film Battery Using a One-Dimensional Model. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2012, 159, A104–A115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstorfer, M.; Funken, S.; Jacob, T. An advanced model framework for solid electrolyte intercalation batteries. PHYS CHEM CHEM PHYS 2011, 13, 12817–12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raijmakers, L.; Danilov, D.; Eichel, R.; Notten, P. An advanced all-solid-state Li-ion battery model. ELECTROCHIM ACTA 2020, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabras, L.; Danilov, D.; Subber, W.; Oancea, V.; Salvadori, A. A two-mechanism and multiscale compatible approach for solid state electrolytes of (Li-ion) batteries. J ENERGY STORAGE 2022, 48, 103842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Grazioli, D.; Geers, M. Governing equations for a two-scale analysis of Li-ion battery cells. INT J SOLIDS STRUCT 2015, 59, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhaylov, M.; Ganser, M.; Klinsmann, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Guz, I.; McMeeking, R. An elementary 1-dimensional model for a solid state lithium-ion battery with a single ion conductor electrolyte and a lithium metal negative electrode. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2019, 123, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Grazioli, D.; Geers, M.; Danilov, D.; Notten, P. A multiscale-compatible approach in modeling ionic transport in the electrolyte of (Lithium ion) batteries. J POWER SOURCES 2015, 293, 892–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Grazioli, D.; Magri, M.; Geers, M.; Danilov, D.; Notten, P. On the role of saturation in modeling ionic transport in the electrolyte of (Li-ion) batteries. J POWER SOURCES 2015, 294, 696–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, D.; Niessen, R.; Notten, P. Modeling All-Solid-State Li-Ion Batteries. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2011, 158, A215–A222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.; Newman, J. The use of mathematical modeling in the design of Lithium/polymer battery systems. ELECTROCHIM ACTA 1995, 40, 2191–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, T.; Doyle, M.; Newman, J. Simulation and Optimization of the Dual Lithium Ion Insertion Cell. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 1994, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; Bosco, E.; Grazioli, D. A computational homogenization approach for Li-ion battery cells. Part 1 - Formulation. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2014, 65, 114–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A. Multiscale modelling and numerical simulation of rechargeable Lithium ion batteries: concepts, methods and challenges. RSC ADVANCES 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Sastry, A.; Park, J. Study on microstructures of electrodes in Lithium-ion batteries using variational multi-scale enrichment. J POWER SOURCES 2016, 315, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Rucci, A.; Brandell, D.; Frayret, C.; Gaberscek, M.; Jankowski, P.; Johansson, P. Boosting Rechargeable Batteries R&D by Multiscale Modeling: Myth or Reality? CHEM REV 2019, 119, 4569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purkayastha, R.; McMeeking, R. An integrated 2-D model of a Lithium ion battery: the effect of material parameters and morphology on storage particle stress. COMPUT MECH 2012, 50, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, A.; McMeeking, R.; Grazioli, D.; Magri, M. A coupled model of transport-reaction-mechanics with trapping. Part I - small strain analysis. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2018, 114, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arricca, M.; Cabras, L.; Serpelloni, M.; Bonanno, C.; McMeeking, R.M.; Salvadori, A. A coupled model of transport-reaction-mechanics with trapping, Part II: Large strain analysis. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2023, 181, 105425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, L. A Cahn-Hilliard-type theory for species diffusion coupled with large elastic-plastic deformations. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2012, 60, 1983–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHoff, R. Thermodynamic in material science; CRC Press - Taylor and Francis, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shell, S. Thermodynamics and statistical mechanics: an integrated approach; Cambridge University Press, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bohn, E.; Eckl, T.; Kamlah, M.; McMeeking, R. A Model for Lithium Diffusion and Stress Generation in an Intercalation Storage Particle with Phase Change. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2013, 160, A1638–A1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, C.; Rejovitzky, E.; Anand, L. A Cahn-Hilliard-type phase-field theory for species diffusion coupled with large elastic deformations: Application to phase-separating Li-ion electrode materials. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2014, 70, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, A.; Guduru, P.; Chason, E. Analytical solutions for composition and stress in spherical elastic–plastic Lithium-ion electrode particles containing a propagating phase boundary. INT J SOLIDS STRUCT 2015, 69-70, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefont, A.; Argoul, F.; Bazant, M. Analysis of diffuse-layer effects on time-dependent interfacial kinetics. J ELECTROANAL CHEM 2001, 500, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, M.; Chu, K.; Bayly, B. Current-voltage relations for elecrochemical thin films. SIAM J APPL MATH 2005, 65, 1463–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Danilov, D.; Xie, J.; Raijmakers, L.; Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Notten, P. Degradation mechanisms of C6/LiFePO4 batteries: experimental analyses of calendar aging. ELECTROCHIM ACTA 2016, 190, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Danilov, D.; Gao, L.; Yang, Y.; Notten, P. Degradation mechanisms of C6/LiFePO4 batteries: experimental analyses of cycling-induced aging. ELECTROCHIM ACTA 2016, 210, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.; Faulkner, L. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Famprikis, T.; Canepa, P.; Dawson, J.; Islam, M.S.; Masquelier, C. Fundamentals of inorganic solid-state electrolytes for batteries. Nature Materials 2019, 18, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabras, L.; Serpelloni, M.; Salvadori, A. Electro-chemo-mechanics of solid state batteries with lithium plating and stripping. FRONT MATER 2022, 9, 1052617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganser, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Kamlah, M.; McMeeking, R. A finite strain electro-chemo-mechanical theory for ion transport with application to binary solid electrolytes. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2019, 125, 681–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, A.; Guduru, P.; Chason, E. A continuum model of deformation, transport and irreversible changes in atomic structure in amorphous Lithium–silicon electrodes. ACTA MATER 2015, 98, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, G.; Nadimpalli, S.; Sethuraman, V.; Bower, A.; Guduru, P. Measurement and modeling of the mechanical and electrochemical response of amorphous Si thin film electrodes during cyclic lithiation. J MECH PHYS SOLIDS 2014, 62, 276–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magri, M.; Boz, B.; Cabras, L.; Salvadori, A. Quantitative investigation of the influence of electrode morphology in the electro-chemo-mechanical response of li-ion batteries. ELECTROCHIM ACTA 2022, 405, 139778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, A.; Zausch, J. Multiscale modeling of Li-ion batteries: thermal aspects. BEILSTEIN J NANOTECHNOL 2015, 6, 987–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, C.; Rejovitzky, E.; Anand, L. Diffusion-deformation theory for amorphous silicon anodes: the role of plastic deformation on elecrochemical performance. INT J SOLIDS STRUCT 2015, 67-68, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathiannasab, H.; Kashkooli, A.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z. Three-Dimensional Modeling of All-Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Synchrotron Transmission X-ray Microscopy Tomography. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2020, 167, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathiannasab, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z. Chemo-mechanical modeling of stress evolution in all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries using synchrotron transmission X-ray microscopy tomography. J POWER SOURCES 2021, 483, 229028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstorfer, M. A Discussion of the Cell Voltage during Discharge of an Intercalation Electrode for Various C-Rates Based on Non-Equilibrium Thermodynamics and Numerical Simulations. J ELECTROCHEM SOC 2019, 167, 013518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | The chemical potential in (16b) represents the entropy of mixing plus energetic interactions. The term is the reference value of the chemical potential that specifies the free energy in the absence of interaction and entropic contributions. The real valued constant in Eq. (16b) - termed the exchange parameter [38] - characterizes the energy of interaction between mobile guest species and insertion sites. If all of the interactions between mobile species and sites are the same, then and there is no energy of mixing: mixing is purely entropic. The contribution , emanating from the excess Gibbs energy [34,35], may lead to phase segregation [39,40,41]. |
| 4 |
is the valency of ion , equal to for cations. |
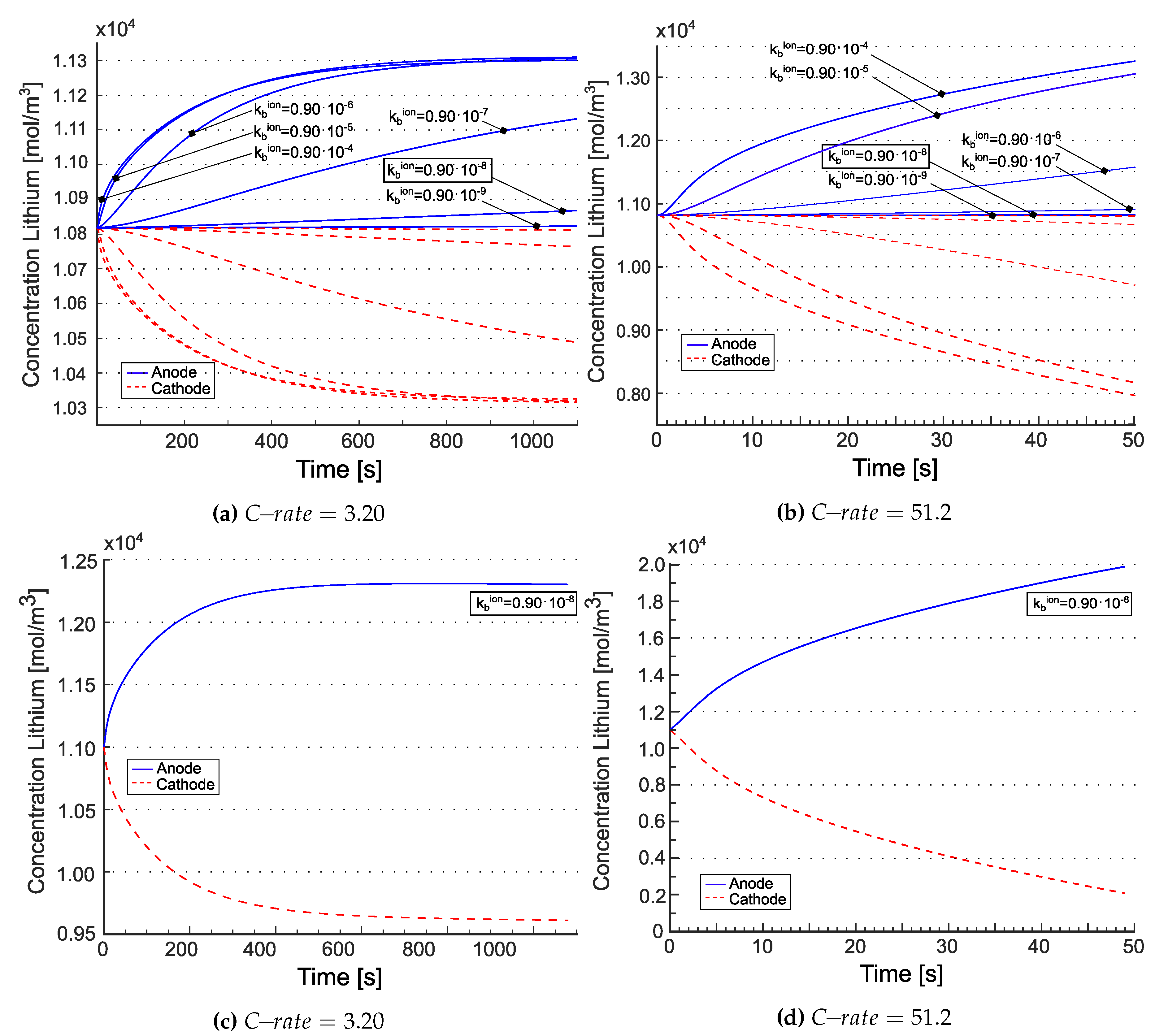
| 5 | This description of transport of vacancies, in a form analogous to liquid electrolytes, appears to be questionable and is replaced by a different formulation in the novel approach to be presented in Section 2.4
|
| 6 | The electro-neutrality condition is not used as a fundamental law. |
| Parameter | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | Temperature | ||
| Thickness of the anode | |||
| Thickness of the electrolyte | |||
| Thickness of the cathode | |||
| Thickness of the positive collector | |||
| A | Geometrical surface area | ||
| Maximum concentration of ions in the electrode | |||
| Electrical conductivities in the lithium anode | |||
| Electrical conductivities in the current collector | |||
| () | Lithium ion generation reaction rate constant for Equation (3) | ||
| Lithium ion recombination reaction rate constant for Equation (3) | |||
| () | Lithium ion generation reaction rate constant for Equation (35) | ||
| Lithium ion recombination reaction rate constant for Equation (35) | |||
| Double layer capacity per unit area of anode | |||
| Double layer capacity per unit area of cathode | |||
| - | Charge transfer coefficient for the negative electrode | ||
| - | Charge transfer coefficient for the positive electrode | ||
| Diffusion coefficient for ions in the electrolyte | |||
| Diffusion coefficient for ions in the electrolyte | |||
| Diffusion coefficient for ions in the cathode | |||
| Standard reaction rate constant for forward reaction in Equation (1) | |||
| Standard reaction rate constant for forward reaction in Equation (2) | |||
| - | Fraction of mobile ions in the electrolyte in equilibrium | ||
| Maximal lithium concentration in the electrolyte | |||
| – | Relative permittivity in the electrolyte |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





