1. Introduction
In the absence of building energy audits, property or building management depends solely on electric bills and electrical drawings to approximate power use. Electricity audits fail to include usage patterns and factors that lead to abnormal increases in consumption. Comprehending energy consumption patterns based on visual, analytical, and behavioral observations is challenging due to the large amount of data provided by a real-time energy monitoring system, the diverse range of equipment and appliances installed, and the unique preferences of building occupants. This limitation hinders effective decision making. The popularity of artificial intelligence (AI) and adaptation of machine learning (ML) methods has offered tools in energy savings, but no one stands out from these options [
1]. Conversely, input parameters varies depending on the purpose of prediction and forecastiong – primarily driven to save on operational cost. Prophet algorithm [
2] for shopping malls and office buildings was applied on the effects of holidays and weather in power consumption trend analysis and prediction. Related researches include [
3] using dynamic and static and hybrid data analysis in buildings, Related research such as [
4] using K-means and [
5] using k-shape and random forest (KS-RF), to classify users according to power consumption behavior based on grid demand. A seasonal approach of educational building consumption from daily usage was limited to descriptive analysis through data cleaning and visualization [
6], while [
7] used Independent Component Analysis (ICA) to determine factors affecting consumption. A comprehensive review of building energy consumption prediction employing various neural network and regression methods, published between 2015 to 2022, was conducted by Borowski and Zwolińska [
8]. The researchers [
8] utilized artificial neural networks (ANN) and support vector machines (SVM) to forecast the amount of energy used for cooling in a hotel building. This prediction was based on hourly data of weather conditions and the number of people present in the facility. The hourly forecast was not suitable for [
9], as it necessitated the use of a combined 10-hour interval time series model and neural network to accurately anticipate building load consumption. Another study of [
10], referenced as [
10], employed Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to preprocess the inputs of a backpropagation neural network. It was utilized to forecast the cooling demand of ice storage systems. With the addition of Classification Regression Tree (CART), a model was derived in [
11] to predict the consumption of air conditioning water system based on load, and water flow temperature and flow rate. The air conditioning starting time in factory setting was the focus of [
12] in their effort to manage energy from their prediction model based on memory loop neural networks, with air condition capacity and climate as inputs. The goal of these papers is to achieve energy savings with ANN and sensor-based data collection system, as common methodologies [
13].
According to [
14], about 15% to 20% of the nationwide electric power consumption is attributed to buildings, and that 49% to 51% of energy consumption in educational buildings is due to air conditioning systems [
15,
16]. Based on study [
17], each degree setback saves 5-7% and each degree increase in ambient temperature increases consumption by 11-23%. The need for energy monitoring and a system to model cooling electrical appliances electricity consumption to determine indoor thermal and air quality conditions at steady state power condition of air conditioning unit (ACU) are the motivations in the pursuance of this research. Specifically, this paper aims to: (1) measure and calculate the real-time electrical power consumption of building room’s air-conditioning units and indoor dry bulb temperature, relative humidity, and carbon dioxide (CO
2) levels, and (2) derive a model to identify significant relationships and patterns among power and the aforementioned indoor environmental and air quality conditions. Input parameters that could affects power consumption, as discussed in other researches such as, building materials (e.g. wall, ceiling, floor, door) [
18,
19], geographical location, geometrical configuration, other sources and configurations of energies [
20] and electrical loads [
21], occupant-related variables (e.g., comfort index, personal preference), and space control devices (i.e., components and electrical loads accuracy) [
22], and other disturbances, such as outdoor weather [
23]– parameters affecting thermal comfort will not be considered in this paper. Related to this, the characteristics and quality of supplied power of the electric distributor nor standby generator set, as presented in [
24] will not be covered in this paper. This research undertaking and direction can help practice and promote energy sustainability of an organization, specifically its Building Management and Energy Management Teams implement behavioral change among all building occupants, tenants, and guests, and objective use of data to practice efficient electricity consumption performance and improvements.
2. Materials and Methods
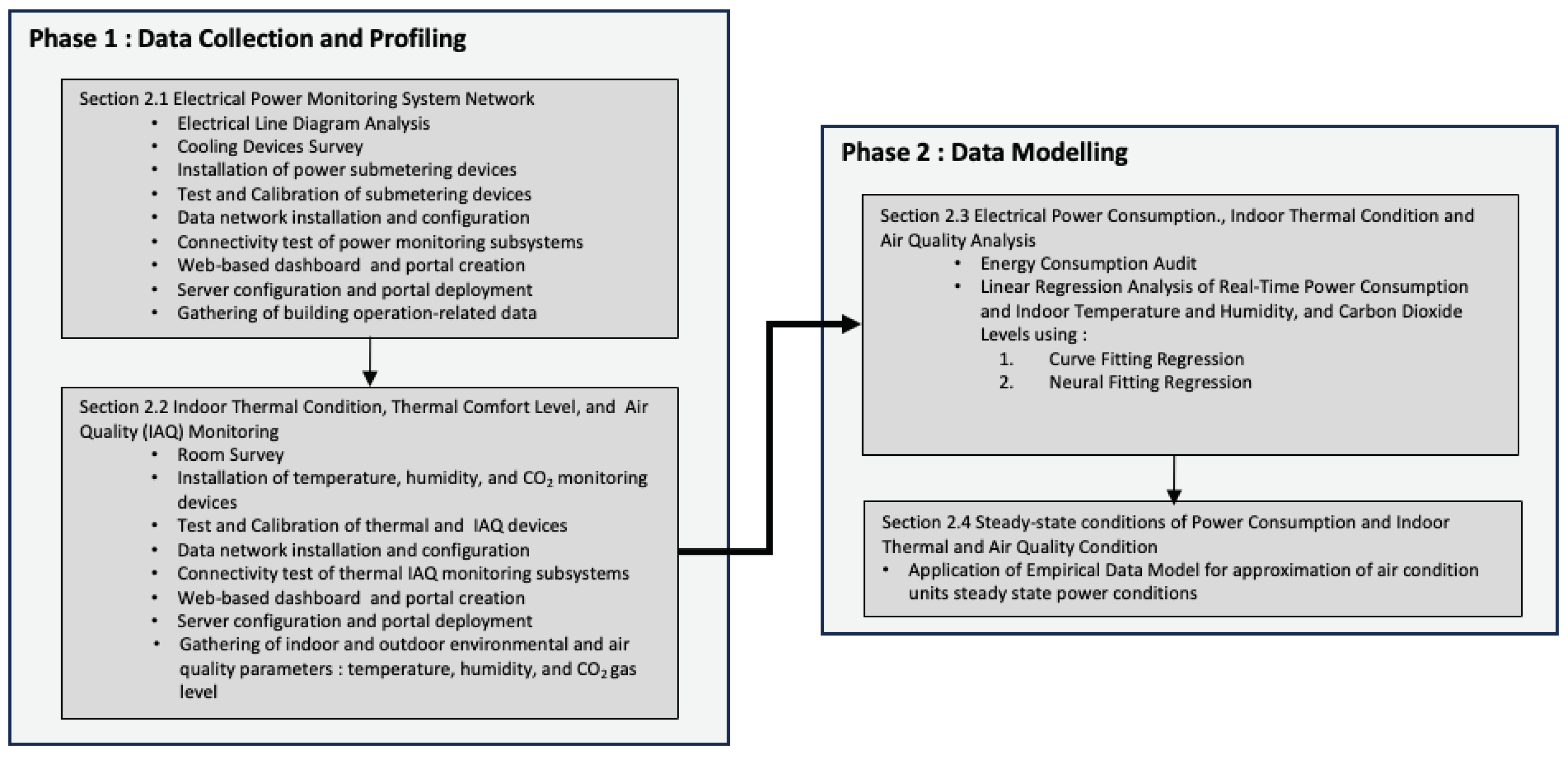
Energy consumption studies include two phases: data collection and profiling and data modeling.
Figure 1 shows the beginning phase of creating suitable electrical power, indoor temperature, and air quality monitoring devices. These systems are essential for collecting real-time power consumption, indoor temperature and humidity, and CO
2 levels. Following parameters will determine the dependent variables for the system model reflecting their impact on ACU electrical power consumption: In addition to data collection devices, network setups allow monitoring devices to be connected, data stored, and accessed as needed.
Phase 2 analyzes data gathered from Phase 1, using energy audit findings to compare with the model. Electrical schematics, past electricity billings, appliance electrical requirements, and external temperature and humidity are examined in audit reports. Phase 1 data will be utilized to assess electrical usage, indoor and outdoor temperature and humidity, humidity and heat indeces, and air quality. Multiple regression modeling, including linear (i.e., curve fitting) and non-linear (i.e., neural network fitting) methods will be used in this investigation. Regression analysis indicates elements that may significantly increase power usage.
2.1. Electrical Power and Indoor Air Quality Monitoring Monitoring System Network
Building power consumption is measured, recorded, and tracked by an energy consumption monitoring system. Each floor's air conditioning and ventilating electrical distribution panel connects to its power submetering component. Remote power consumption sub-metering modules employ Arduino Mega 2560 [
25] connected to a Raspberry Pi 3B+ over a Local Area Network (LAN). Circuit breaker power consumption, room temperature, humidity, and CO
2 gas sensors are measured in real time. Each floor's electrical distribution panel has a circuit breaker for each network appliance (ACU, outlets, lighting). In Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) monitoring modules, Si7021 sensors measure temperature and humidity while CCS811 sensors measure CO
2. IAQ monitors will only be deployed in defined places because outdoor environmental variables (temperature, humidity, CO
2 levels) vary less than indoor circumstances. Each RPi board has a 5V/2.5A DC supply. Web development requires installing a LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP) server on a Raspberry Pi to monitor and track power use every 5 minutes to preserve memory. Apache2 is the most used web server software. The server creates .html and .php documents based on the requested page. PHP is a server-side language for dynamic web programs. The Raspberry Pi will have Raspbian OS and phpMyAdmin for web-based database management. MATLAB is used for data analysis and processing.
Figure 2 illustrates the interconnectedness of the monitoring modules, computer server, database, remote monitoring devices, and LAMP server via a local area network. The data obtained from each power sub-metering module will be linked to both the local server and cloud for the purpose of data modeling, visualization, and analysis.
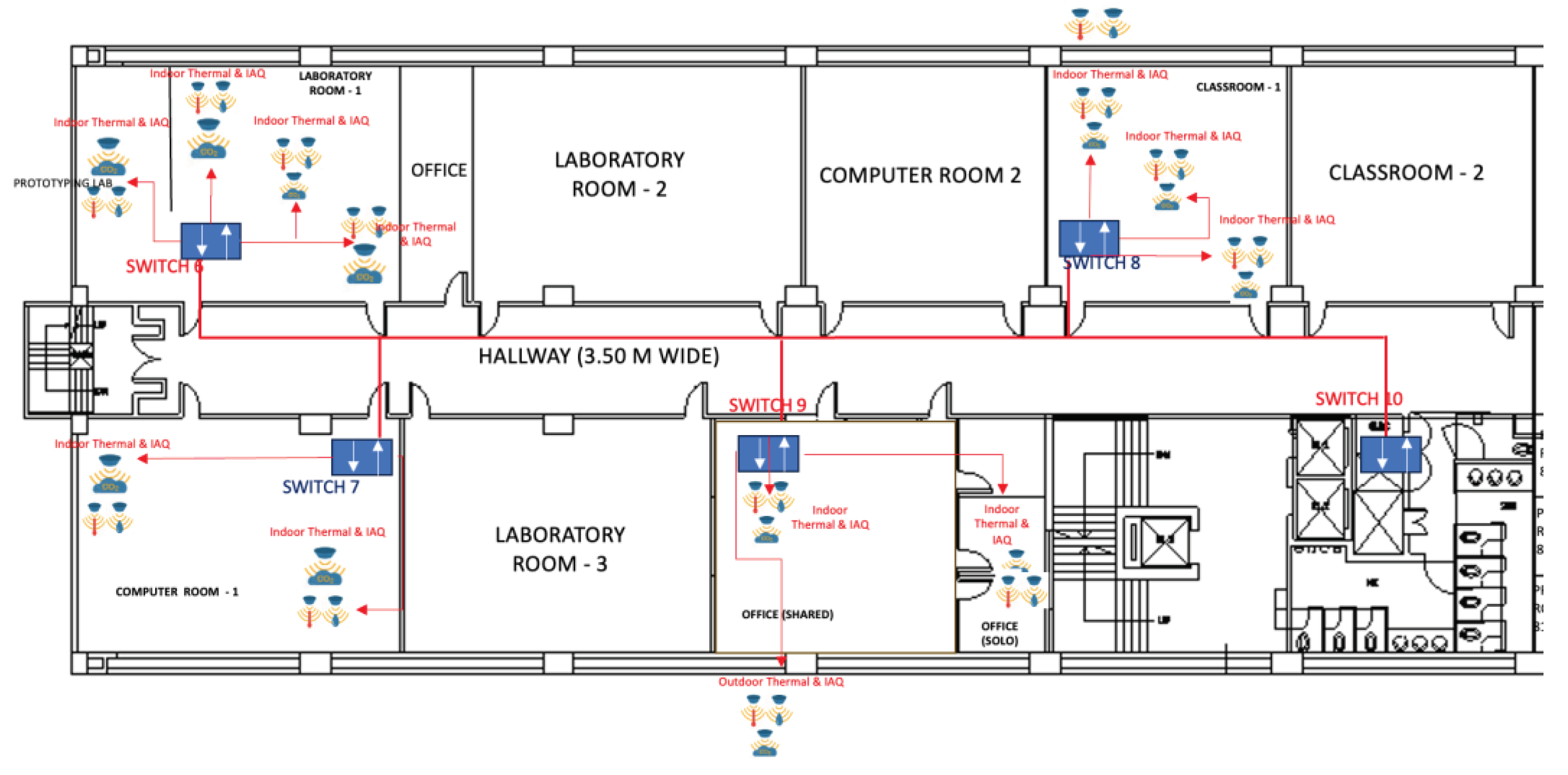
Figure 3 depicts the positioning of these sensors as an example. Typically, two sets of gas sensors would be positioned in the central area of each room, which has an average floor size of 69 m
2. This arrangement ensures comprehensive coverage of gas dispersion. Conversely, the thermal comfort level sensors, such as those measuring temperature and humidity, will be placed in a location within the room that is not near the ACU vents. Each instructional room is equipped with two (2) 2.5-horsepower split-type inverter air conditioning units.
2.2 Electrical Power Consumption Analysis Using Polynomial Curve and Neural Fitting Techniques
The ACU usage, indoor temperature, humidity, and CO
2 levels were recorded and documented every five (5) minutes over a duration of five (5) weeks, at an average outdoor temperature and relative humidity of 28°C and 67%, respectively [
26]. Only data collected during courses or office operations were used for curve fitting and analysis to correlate and model power usage with indoor temperature and air quality conditions. Five rooms with distinct purposes were chosen, including instructional facilities such as a 36-seater lecture room, a laboratory room, and a computer room, as well as office spaces with a maximum capacity of fifteen (15) people and a cubicle room designed for solo use. The operating duration of instructional classrooms normally spans from two (2) to eight (8) hours per day, whereas office spaces are frequently utilized for a period of eight (8) to ten (10) hours per day. During the process of data cleaning and normalization, only the numerical values falling within the specified ranges, as outlined in Equations 1, 2, and 3, were utilized. This was done to reduce the impact of outliers in sensor readings on the resulting model.
where P = power consumed in kWh, T = dry bulb temperature in °C, and H = % relative humidity, and G = C0
2 level in parts per million (ppm).
Two (2) approaches to modeling of data are explored to derive a model that best fits the ACU power consumption of each room. The curve fitting [
27] and neural network fitting [
28] tools of MATLAB were used for this purpose. Curve fitting is a statistical technique that involves using regression analysis to identify the most appropriate mathematical function that accurately represents a set of observed data points and the relationship between two or more variables in a dataset. This approach develops a model that accurately represents the fundamental pattern or trend in the data. The model will enable predictions and insights that may be utilized to identify measures for operating cooling units with lower energy consumption. Curve-fitting involves selecting a mathematical function or model that precisely represents the relationship between the independent variable(s) (often denoted as x) and the dependent variable(s) (typically denoted as y). Model selection involves choosing between linear and non-linear fits to determine the appropriate relationship between power consumption and indoor temperature, humidity, and CO
2 levels. Adjustment of the model parameters minimizes the difference between the predicted values from the model and the actual values in the dataset. Optimization methods are commonly employed to iteratively augment parameter estimates to define the best fit with minimal prediction errors. This encompasses various techniques, such as data centering and scaling, degree modifications, utilization of a robust least-squares fitting approach, and the selection of algorithms like trust-region or Levenberg-Marquardt. The goodness-of-fit of a model can be assessed by various methods, such as R-squared, root mean square error (RMSE), or by visually examining the residuals (the differences between observed and predicted values). These statistical measurements are model’s parametric evaluation values to quantitatively describe the variances in the data.
The MATLAB Neural Network Toolbox has built-in and intuitive functionalities to train and simulate artificial neural networks (ANNs) prior to deployment. This requires data cleaning, annotation, normalization, and segmentation of the derived datasets into training, validation, and testing sets. Network design is often defined with single layers by default, where the number of neurons in each layer, activation functions, and connection weights are predetermined. Once target performance of the network is met, it undergoes training using Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. After completing the training phase, it is crucial to evaluate the performance of the trained network by using the validation dataset. This helps prevent overfitting and ensures that the model can generalize well. Occasionally, it is necessary to make modifications to hyperparameters such as learning rate, number of epochs, and regularization intensity based on the validation results to enhance the model's performance. After training and validating the model, its ability to generalize is assessed by making predictions on new, unseen data and evaluating its performance on the testing dataset.
3. Results
3.1. Polynomial Curve Fitting
Parametric fitting is the process of finding the coefficients, often known as parameters, for models that are used to fit data. The predictor variables utilized to build the power consumption model were the temperature, humidity, and CO
2 levels inside each room, with coefficients assigned to each variable. Both linear and nonlinear regression models were examined, and it was found that the polynomial regression model yielded the most accurate fit to the polynomial function based on the data. Equation 5 demonstrates the comprehensive correlation between power consumption (Pt) and drive bulb temperature (T). This correlation is established using the robust least-squares fitting approach and minimized least absolute residuals (LAR) at 95% confidence bounds.
where values of c
1, c
2, and c
3 varies according to room type.
Table 1 contains the summary of these coefficient values of Equation 5.
There are variations in the coefficient values of a first-degree polynomial equation for a computer room, laboratory room, and classroom. A second-degree polynomial was necessary to provide a suitable fit for power functions in shared office spaces and small enclosed cubicles with only one occupant. The predictor values for office spaces were normalized with a mean of 28.19 and a standard deviation of 1.421 for shared space, and with a mean of 28.07 and a standard deviation of 1.394 for cubicle space.
Equations 6 examined the impact of humidity (H) on power consumption (Ph) in various types of rooms, except for classrooms. In the case of classrooms, humidity needed to be normalized using a mean of 55.92 and a standard deviation of 9.765.
The values of c
1, c
2, c
3, and c
4 vary based on the room type, as seen in
Table 2.
Additional refinements were made to the process of fitting a power equation to the indoor CO
2 level data, specifically considering the slight fluctuations observed when the ACU is activated. Therefore, power measurement readings below 0.03Wh for instructional classes and 0.003Wh for offices were omitted from the analysis to get meaningful coefficients. However, it was observed that the laboratory room had an unusually high amount of CO
2, namely above 5,000ppm. This aspect was specifically excluded from the research as it pertains to exceptional activities (such as soldering and carpentry) that are not seen in the other rooms included in this study. Specifically, carbon dioxide (CO
2) levels were linked to the quality of ventilation and were not utilized to identify and quantify the existence of indoor contaminants. Equations 7 examined the impact of indoor CO
2 levels (G) on power consumption (Pc) in various types of rooms. The values of c1 and c2 vary per room type, as seen in
Table 2.
Table 3.
Coefficients of Polynomial Curve Fit for Power vs CO2 Levels.
Table 3.
Coefficients of Polynomial Curve Fit for Power vs CO2 Levels.
| Coefficients |
Classroom |
Computer Room |
Laboratory Room |
Office(shared) |
Office(solo) |
| Power vs CO2 Level |
c1
|
-0.0125 |
-0.0007 |
-0.0018 |
-0.0015 |
0.0002 |
| c2
|
0.1407 |
-0.1682 |
0.1548 |
-0.0220 |
-0.0548 |
The measured data displays variances that are regularly present due to several reasons. This includes variations in the occupancy level within the room, adjustments made to the setpoint or fan settings of the air conditioning units (ACUs), and the duration of operation. The analysis did not consider the immediate impacts of these factors. The fitted model may not precisely represent the data due to systematic variability. However,
Table 4 provides evidence that the model coefficients have physical significance, as indicated by the R-square values ranging from 0.9813 to 0.9998 for instructional rooms with different usage.
The variance proportions for office spaces with a relatively fixed number of inhabitants were measured and ranged from 0.9899 to 0.9944, as shown in
Table 5. These numbers indicate that the data fitting is satisfactory, as the uncertainties indicated by the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) are within an acceptable range. The absence of robustness or the utilization of Least Absolute Residuals (LAR) in regression modeling resulted in an unsatisfactory level of uncertainty, as provided in the
Supplemental Data (Supplemental Tables S1 to S6).
3.2. Neural Network Fitting
The objective of training a neural network on a dataset is to accurately capture the underlying correlation between the time series input and continuous-valued output variables. The training method for evaluating the neural fit using ten (10) layers yielded a moderate linear correlation, as evidenced by six (6) validation checks, between the anticipated power (P) and the actual dry bulb temperature (T) in classrooms and laboratory rooms. There is a higher correlation coefficient that indicates a strong linear association between these metrics in computer rooms and office areas. The model performance improved when power consumption was adjusted for indoor relative humidity (H) after a minimum of ten (10) iterations and six (6) validation checks. The correlation coefficients experienced an increase, reaching a minimum value of 0.5426 on the training set and 0.5395 on the testing set. Summary of the neural network fit results is presented in
Table 6.
The activation of ACUs in offices has a modest impact on the levels of CO
2, as indicated by the weak linear connection (R) observed during training and testing (0.0462 to 0.2151). This is ascribed to a finite number of individuals and a restricted range of human activities within the room, and demonstrated in the context of educational spaces, such as laboratory and computer rooms. The CO
2 levels at a training and testing correlation coefficients ranging from 0.4603 to 0.8370 have been significantly influenced by the presence of electrical appliances, varying occupancy rate, and human activities. The model performances were achieved after eight and ten iterations, respectively, during six validation checks. Details of the model’s hyperparameter, training, and validation performances are provided in the
Supplemental Data (Supplemental Tables S7 to S9).
4. Discussion
The positioning of the sensors, both in terms of their distance from the ACU and the ceiling, influenced the regression analysis values for each parameter in each room. The generated model was based on the optimal test metrics obtained from both the curve fitting and neural network fitting procedure after numerous adjustments made to the parameters, datasets, and conditions. These adjustments were made to obtain the most accurate model for describing the relationship between cooling unit power consumption and indoor temperature, humidity, and CO
2 levels. The monitoring devices that yielded the most accurate model fit for dry bulb temperature were the ones placed near the entrance door, at 3m, and farther away from the ACU vent, at 5m. The monitoring sensors positioned near the cooling vent yielded more accurate results for humidity compared to those installed further away from the vent. The CO
2 levels measured near the door exhibited considerable variations, leading to the development of a model that accurately depicts the changes in CO
2 levels as the room cools down. The monitoring boxes are installed at 50cm below the ceiling. Adopting a more empirical method to determine the effects of sensor placements can enhance the accuracy of the model and provide valuable insights into the characteristics of data outliers. In the paper of [
29], the test setup includes 147 testing points for the temperature to calculate the thermal comfort level of the room.
Excluding the controllable parameters that influence data quality, the derived models were utilized to calculate the steady-state power consumption of each room under stable conditions (namely, dry bulb temperature, relative humidity, and CO
2 levels). This employs calculation of the average and standard deviation of predictor values (temperature, humidity, and CO
2 levels) and power data over a moving time window using statistical analysis. The MATLAB script systematically processes data points to calculate the average predictor values throughout a window size. Each window checks if the power data standard deviation, normalized by its mean, is below the stability threshold, as described in Equation 7 and Equation 8. When these ratio of standard deviation and mean is below the stabilization threshold, stabilization values of power and temperature (or humidity) are met, as defined in Equation 9 and Equation 10, respectively.
where
= standard deviation of power data,
= mean of power data, ,
= standard deviation of humidity or temperature,
= mean of humidity or temperature,
= stability threshold, S
P = steady-state values of power, S
T,H = settling values of temperature or humidity, i = iteration index, W = window size, P = set of power readings, H, set of humidity readings, and T = set of temperature readings.
The application calculates temperature data normalized standard deviation from the mean. After stabilizing within thresholds, the settling temperature (ST) and power (SP) are stored as the window's mean temperature and power. A percentage threshold is used to evaluate power stability. Consistent power ensures temperature stability. The loop ends at a stable place. Duration of operation time of ACU, number of occupants, and variety of physical activities effect data collection and stable point calculation.
The parametric conditions specified in Equations 2 to 4 were still considered, with measurements taken only when the power reached a minimum of 10Wh. This is to guarantee that the steady state situation is considered when the ACU condensing units are turned on. In addition to this, the presented resulting values on
Table 7 are products of simulation results and their corresponding bias factors. Bias factors are computed based on deviation between the real-time sensor’s measurement values and ACU setpoint and were compared to calibrated measuring test instruments.
It is important to mention that the levels of CO
2 in classroom and laboratory rooms exceed the typical levels found in indoor settings, indicating high levels of activity in these spaces [
30]. In the paper of [
31], a presentation was given on the worldwide requirements for sufficient indoor air quality, while [
32] defined conditions for indoor thermal comfort. Thermal comfort is person’s satisfaction and mind acceptability of warmness or coldness affecting productivity, health, and well-being [
33]. A control system to achieve this for a laboratory was developed by [
34] emphasizing on ANN-based demand prediction of fan-coil power. Several papers [
35,
36] identified thermal preference by the office occupants was ranging between 21.5°C to 24.5°.
Equation 7 describes how the power consumption, P(T,H), of an ACU is influenced by the levels of dry bulb temperature, T, and relative humidity, H. The polynomial curve fit coefficient values (k
1 to k
5) differ for instructional rooms and office spaces.
For instructional rooms: k1 = 2.9919, k2 = -0.0924, k3 = -0.0512, k4 = 0.0014, k5 = 0.0010.
For office spaces: k1 = 1.7940, k2 = -0.0442, k3 = -0.0463, k4 = 0.0009, k5 = 0.0002.
The optimal polynomial fit was obtained by using a power of one (1) for dry bulb temperature and a power of two (2) for humidity while applying the Least Absolute Residuals (LAR) method. For the given predictor values, the R-square values vary from 0.9874 to 0.9982. The root mean square error (RMSE) is 0.0048 for office spaces and 0.0026 for instructional spaces. These results are included in the
Supplementary Tables S10 and S11. Overall, the model derived from polynomial regression analysis shows better result than that of derived from neural network fitting – contrary to the results of [
37], which is limited to consumption submetering data in household, and [
38] that yielded best results in ANN than linear and polynomial regression from dataset of supermarket energy usage. It’s notable that [
38] emphasized on the time of the day and environmental conditions as primary predictors of energy consumption. The regression-based learning has exhibited faster processing in the energy consumption modeling patent of [
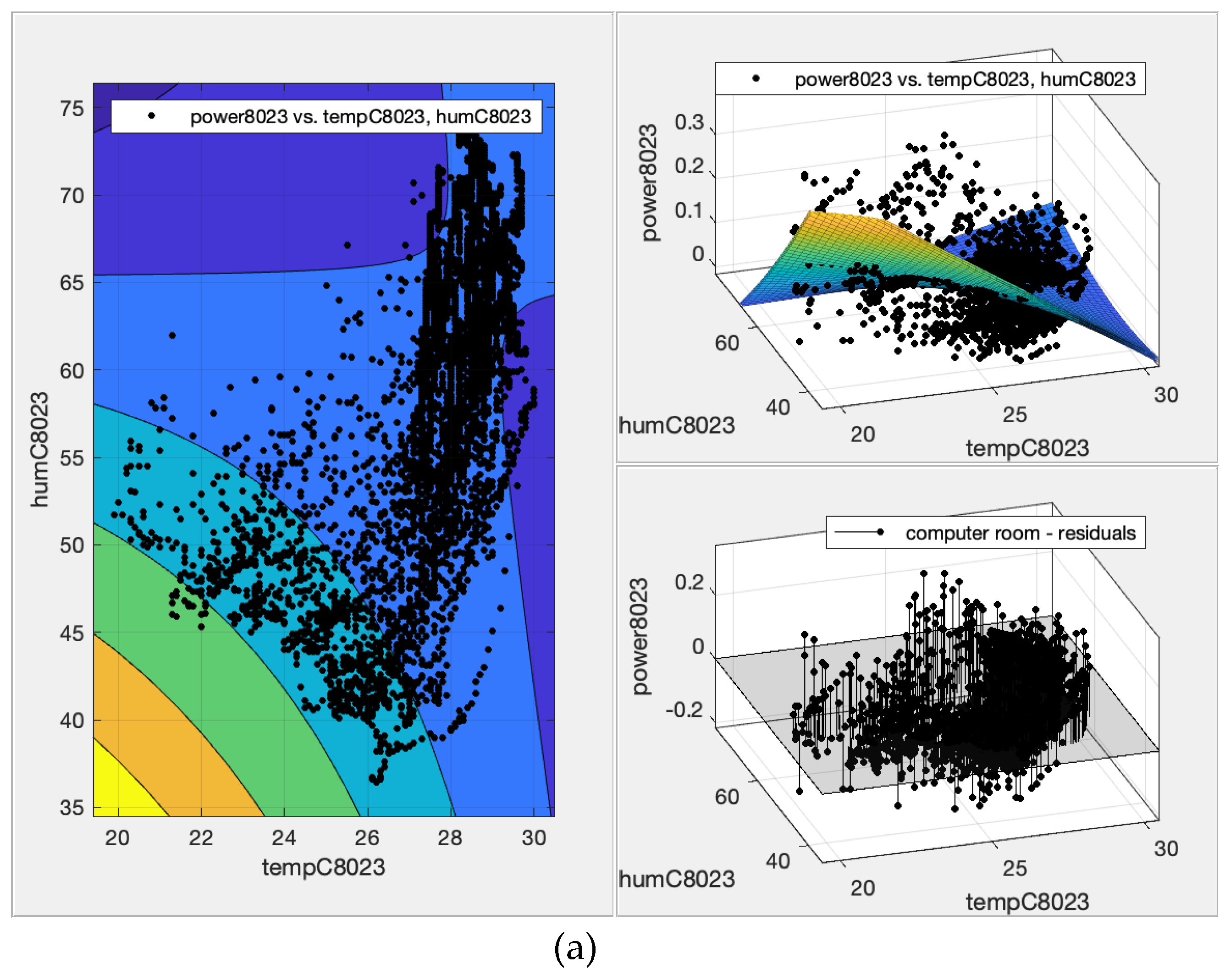
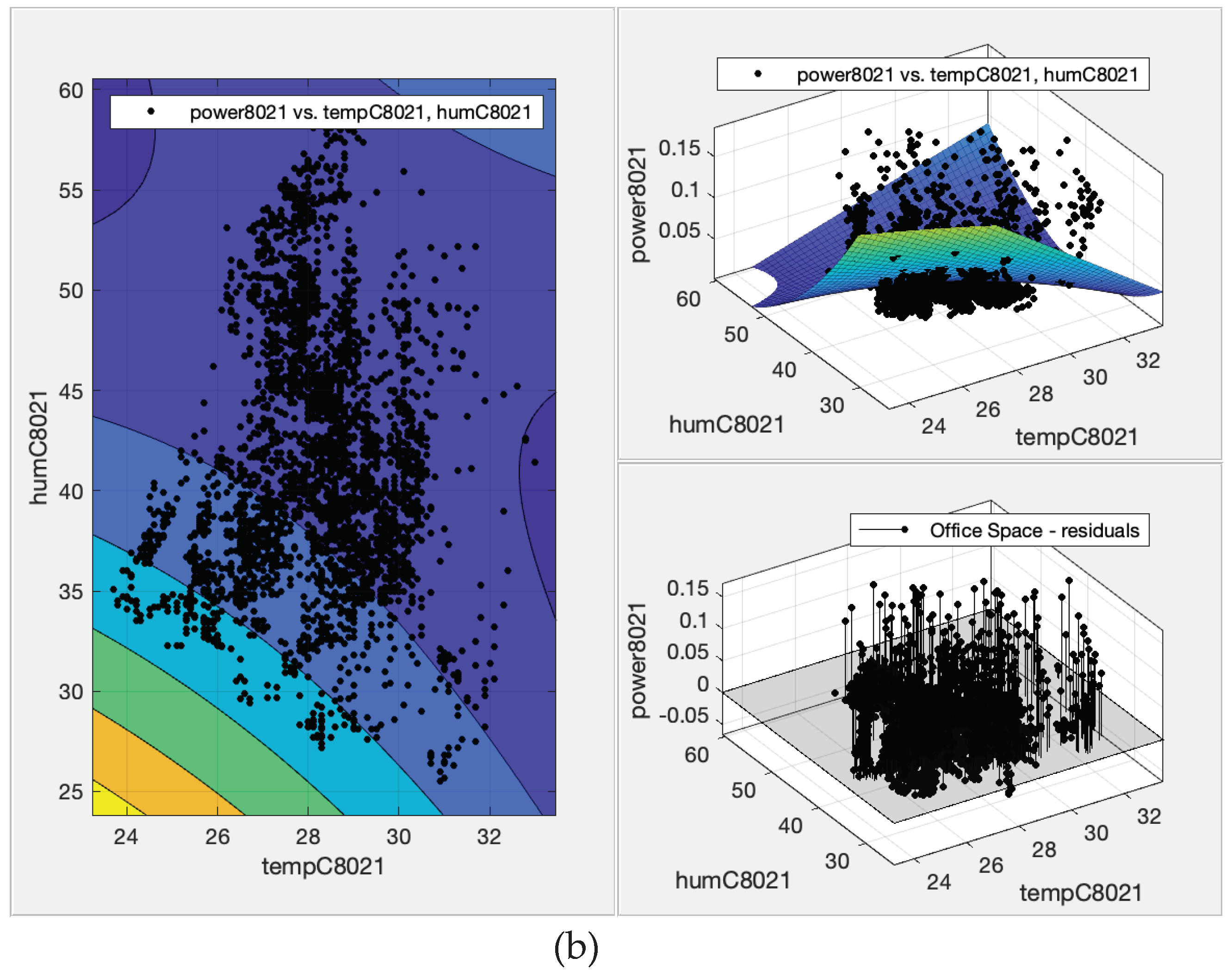
39] that employs demand response (DR) strategy. The comparison of contour, fit, and residual plots for the polynomial surface fit of the ACU power consumption based on dry bulb temperature and humidity are shown on Figure 4 for instructional room and
Figure 5 for office spaces.
5. Conclusions
The learning-based methodology incorporated actual data and utilized regression techniques, such as curve and neural network fitting, to determine the influence of indoor heat conditions and carbon dioxide levels on ACU power usage. The extensive data obtained during continuous ACU operation for at least four (4) hours greatly decreased measurement error when reanalyzing the model fit. The study obtained an optimal polynomial regression by using a first-order polynomial for dry bulb temperature and a second-order polynomial for humidity, utilizing the Least Absolute Residuals (LAR) approach. The R-square values, which range from 0.9874 to 0.9982, suggest a high level of correlation of power with indoor dry bulb temperature and humidity. The root mean square error (RMSE) is 0.0048 for office spaces and 0.0026 for instructional spaces. The neural model, assessed with ten layers, showed a modest linear relationship between predicted power (P) and measured dry bulb temperature (T) in classrooms and laboratory rooms. The model's performance increased after accounting for indoor relative humidity (H) in power consumption adjustments, with correlation values of 0.5426 on the training set and 0.5395 on the testing set. Furthermore, the influence of air conditioning units (ACUs) on CO2 levels was minimal, as it was mostly caused by the restricted human activity in educational areas. The most effective sensor placements for accurately capturing the correlation between power consumption of the cooling unit and inside temperature are in close proximity to the entrance door (at a distance of 3 meters) and at a greater distance from the ACU vent (5 meters away). Humidity measurements obtained from sensors located in close proximity to cooling vents are highly precise. Significantly, carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the vicinity of the door display fluctuations, providing data for a model that accurately represents changes due to cooling. In general, the polynomial regression model performs better than the neural network fitting strategy.
The point at which the temperature and power levels have reached a stable state within specified boundaries can be determined throughout the iterative process of analyzing data. Variables such as the duration of ACU operation, the number of people present, and the level of physical activity have an influence on the collecting of data and the determination of stable points. Determining the steady state of a system is crucial in control systems and experimental circumstances. The models and stable ACU power conditions can be used to create decision rules for controlling indoor temperature and humidity through the automated operation of cooling systems. The results of this work will be used in future research to create an optimized energy consumption model for a building. This will be accomplished by identifying the most efficient temperature setting and propert timing to operate the air conditioning unit (ACU) by considering parameters such as the surrounding temperature, humidity, time of day, and activities performed during specified hours.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Framework for Power Consumption Analysis Based on Indoor Thermal Condition and Air Quality.; Figure S2 Interconnectivity of Data Monitoring Modules and Devices, and Server.; Figure S3: Placement of Indoor Thermal and Air Quality Sensors (Room Size : 76 m2 for laboratory room, 61m2 for classroom and shared office space, 15m2 for solo office space); Figure S4a: Polynomial Surface Fit of Power, P(T,H)) vs Temperature, and Humidity for Instructional Room; Figure S4b: Polynomial Surface Fit of Power, P(T,H)) vs Temperature, and Humidity for Office Space; Table S1: Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Instructional Rooms (ACU Power vs Dry Bulb Temperature); Table S2: Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Office Spaces (ACU Power vs Dry Bulb Temperature); Table S3. Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Instructional Rooms (ACU Power vs Relative Humidity); Table S4. Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Office Spaces (ACU Power vs Relative Humidity); Table S5. Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Instructional Rooms (ACU Power vs CO2 level); Table S6. Polynomial Curve Fitting Performance for Office Spaces (ACU Power vs CO2 Level); Table S7. Neural Fit in ACU Power vs Dry bulb Temperature; Table S8. Neural Fit in ACU Power vs Relative Humidity; Table S9. Neural Fit in ACU Power vs Carbon Dioxide Level; Table S10. Coefficients of Polynomial Curve Fit for Power vs Temperature and Humidity; Table S11. Polynomial Curve of ACU Power using Least Absolute Residuals for Office Spaces.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G.B.; methodology, S.G.B. and R.F.A.; software, S.G.B..; validation, S.G.B and A.D.A.; formal analysis, S.G.B. and R.G.; investigation, S.G.B., A.D.A. and P.J.L.; resources, S.G.B.; data curation, S.G.B and A.A.I..; writing—original draft preparation, S.G.B. and A.D.A.; writing—review and editing, R.F.A., A.A.I, A.U., M.M.R., R.G. and P.J.L.; visualization, S.G.B and A.D.A.; supervision, A.D.A. and A.U.; project administration, A.D.A.; funding acquisition, A.U. and M.M.R.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has received financial assistance from De La Salle University Research and Grants Management Office (DLSU RGMO) on its pursuit for building energy optimization research agenda.
Data Availability Statement
Restrictions apply to the availability of these data. Data were obtained from Asia Pacific College’s Artificial Intelligence and Robotics Hub and Energy and Indoor Air Quality Monitoring System and are available from the corresponding author with the permission of Asia Pacific College (
www.apc.edu.ph).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the contribution to Asia Pacific College’s Building Maintenance Office headed by Engr. Marr Lauriel B. Bringas, and Engr. Leonardo A. Samaniego Jr., Executive Director of the School of Engineering, for sharing the electrical layout drawings of the building, permission to install the energy monitoring devices to selected distribution panels and allowing the researcher to conduct periodic random testing. Special thanks to Engr. Luigi Carlo M. de Jesus, Head of Engineering and Sciences Laboratory Office, and Engr. Ireneo P. Quinto, Registered Electrical Engineer, who helped in the technical aspects of the IoT devices and safe installation of the sensors. .
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Seyedzadeh:, S.; Rahimian, F.P.; Glesk, I.; Roper, M. Machine Learning for Estimation of Building Energy Consumption and Performance: A Review. Vis. Eng. 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Han, N.; Li, D.; Tian, S. Trend Analysis of Building Power Consumption Based on Prophet Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 Asia Energy and Electrical Engineering Symposium (AEEES); IEEE: Chengdu, China, May, 2020; pp. 1002–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, R.; Yang, Q.; Xing, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, L.; Chen, W. Predicting the Electric Power Consumption of Office Buildings Based on Dynamic and Static Hybrid Data Analysis. Energy 2024, 290, 130149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Yi, X.; Kong, J.; Wang, X. Analysis of User’s Power Consumption Behavior Based on K-Means. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence (MLBDBI); IEEE: Shanghai, China, October 2022; pp. 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Q. Analysis of User Power Consumption Characteristics and Behavior Portrait Based on KS-RF Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/IAS Industrial and Commercial Power System Asia (I&CPS Asia); IEEE: Chengdu, China, July 18, 2021; pp. 1586–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjaji, I.; Alami, H.E.; Alami, R.E.; Dahmouni, H. Energy Consumption Characterization in University Campus Microgrid Based on Power Data Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud); IEEE: Rome, Italy, August, 2022; pp. 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlov, I.; Zatsepina, V. Power Consumption Analysis with Independent Component Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Control Systems, Mathematical Modeling, Automation and Energy Efficiency (SUMMA), 9 November 2022; IEEE: Lipetsk, Russian Federation, 2022; pp. 804–807. [Google Scholar]
- Borowski, M.; Zwolińska, K. Prediction of Cooling Energy Consumption in Hotel Building Using Machine Learning Techniques. Energies 2020, 13, 6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Wei, D. Building Cooling Load Prediction Based on Time Series Method and Neural Networks. Int. J. Grid Distrib. Comput. 2015, 8, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaowen, H.; Dong, W. Prediction on Hourly Cooling Load of Buildings Based on Neural Networks. Int. J. Smart Home 2015, 9, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Y. Application of Machine Learning and Its Improvement Technology in Modeling of Total Energy Consumption of Air Conditioning Water System. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 4841–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Research on Energy Consumption Prediction Based on Machine Learning. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 791, 012100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakır, M.; Akbulut, A.; Hatay Önen, Y. Analysis of the Use of Computational Intelligence Techniques for Air-Conditioning Systems: A Systematic Mapping Study. Meas. Control 2019, 52, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines For Energy Conserving Design of Buildings and Utility Systems | Department of Energy Philippines. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.ph/guidelines-energy-conserving-design-buildings-and-utility-systems# (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Ylaya, V.J.V.; Malicay, L.G. Assessment of Energy Savings Potentials at University in Lanao Del Norte, Philippines. 7.
- Lopez, N.S.; Gonzaga, J.; Lim, L.A.G. Energy Audit and Analysis of the Electricity Consumption of an Educational Building in the Philippines for Smart Consumption. In Proceedings of the 2017IEEE 9th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (HNICEM), December 2017; IEEE: Manila, Philippines, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Metallidou, C.K.; Psannis, K.E.; Egyptiadou, E.A. Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings: IoT Approaches. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 63679–63699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halhoul Merabet, G.; Essaaidi, M.; Ben Haddou, M.; Qolomany, B.; Qadir, J.; Anan, M.; Al-Fuqaha, A.; Abid, M.R.; Benhaddou, D. Intelligent Building Control Systems for Thermal Comfort and Energy-Efficiency: A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ding, Y. Cooling Load Prediction and Optimal Operation of HVAC Systems Using a Multiple Nonlinear Regression Model. Energy Build. 2019, 197, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, J.; Bonnema, E. Regression-Based Approach to Modeling Emerging HVAC Technologies in EnergyPlus: A Case Study Using a Vuilleumier-Cycle Heat Pump. Energy Build. 2019, 186, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study on Simplified Energy-efficient Control Methods of HVAC Cooling Water System from the Global Online Optimization Perspective - Zhao - 2021 - Energy Science & Engineering - Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ese3.861 (accessed on 14 March 2024).
- Asvadi-Kermani, O.; Momeni, H.; Justo, A.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Rodriguez, J.; Khan, B. Energy Optimization of Air Handling Units Using Constrained Predictive Controllers Based on Dynamic Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 56578–56590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffal, I.; Inard, C. A Metamodeling Method to Study the Nonlinearity of Building Thermal Behavior. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 28, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurov, V.; Duganov, M. Study on Power Consumption Modes and Power Quality According to IEEE1459 Standard in the Electric Power Supply Systems Of Public Buildings. In Proceedings of the 2023 18th Conference on Electrical Machines, Drives and Power Systems (ELMA), 29 June 2023; IEEE: Varna, Bulgaria, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mega 2560 Rev3 | Arduino Documentation. Available online: https://docs.arduino.cc/hardware/mega-2560/ (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Weather in February 2024 in Makati, Philippines. Available online: https://www.timeanddate.com/weather/philippines/makati/historic?month=2&year=2024 (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Parametric Fitting - MATLAB & Simulink. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/curvefit/parametric-fitting.html?searchHighlight=parametric%20fitting&s_tid=srchtitle_support_results_1_parametric%20fitting (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Solve Fitting Problem Using Two-Layer Feed-Forward Networks - MATLAB. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/ref/neuralnetfitting-app.html (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Zhao, S.; He, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, G.; Xie, J.; Cai, S. Evaluation of Thermal Comfort in Air-Conditioned Rooms Based on Structure/Control-Related Parameters and Data-Mining Method. Int. J. Air-Cond. Refrig. 2023, 31, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TC-04.03-FAQ-35.Pdf.
-
Weltgesundheitsorganisation WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants; WHO: Copenhagen, 2010; ISBN 978-92-890-0213-4.
- ASHRAE - iWrapper. Available online: https://ashrae.iwrapper.com/ASHRAE_PREVIEW_ONLY_STANDARDS/STD_55_2023 (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Chow, D.H.C. Indoor Environmental Quality: Thermal Comfort. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier, 2022; p. B9780323903868000061 ISBN 978-0-12-409548-9.
- Alamin, Y.; Álvarez, J.; Castilla, M. del M.; Ruano, A. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model to Predict the Electric Load Profile for an HVAC System ⁎. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andamon, M.M. Thermal Comfort Standards and Building Energy Use in Philippine Office Environments.
- Aniag, B.A.; Avenilla, A.; Collas, J.J.; Regner, P.A.; Cruz, E.G.D. A Study on Thermal Comfort of Office Employees in the Philippines. 2017.
- Qin, J. Experimental and Analysis on Household Electronic Power Consumption. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D.; Tassou, S.A.; Marriott, D. Application of Neural Networks for the Prediction of the Energy Consumption in a Supermarket.
- US20150248118A1 - Systems and Methods for Modeling Energy Consumption and Creating Demand Response Strategies Using Learning-Based Approaches - Google Patents. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20150248118A1/en (accessed on 14 March 2024).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).