1. Introduction
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a multi-faceted, lethal condition characterized by increased pulmonary artery pressure, which may be attributed to a long list of conditions [
1,
2]. According to the most recent guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) PH is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) above 20 mmHg, using the right heart catheterization (RHC) at rest [
3]. Timely diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment are particularly important in patients with PH. RHC remains the gold standard technique for PH diagnosis, but due to its invasive modality it is difficult to perform or repeat in daily clinical practice. Alternatively, rest echocardiography is widely used for initial screening for PH, because it is an easy, repeatable, inexpensive technique and its measurements show high correlation with RHC and unravel progressive right ventricle (RV) dysfunction. Echocardiography mainly calculates pulmonary arterial systolic pressure (PASP) and draws the probability of PH presence [
4]. However, the diagnostic role remains challenging since its measurements are based on assumptions and altered hemodynamic conditions (e.g., severe tricuspid regurgitation; TR) may impair the accuracy of echocardiographic parameters. Regarding the impact of PH on right cavities and their function, additional classical echocardiographic parameters, like the right atrial area (RAA), tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) have been proposed to describe the severity of PH [
5].
Besides diagnosis, the prognostic value of several echocardiographic parameters is wondering. Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been conducted regarding the role of echocardiography in the severity and prognosis of PH [
6,
7]. Pericardial effusion (PE), RAA and TAPSE have been proposed as prognostic factors. Novel echocardiographic parameters like 3-dimension (3D) echocardiography, RV speckle tracking, right atrium (RA) strain have emerged as more accurate techniques with increasing prognostic power among patients with PH. Nevertheless, the echocardiographic assessment of PH and its consequences has to address important challenges due to required assumptions and inherent pitfalls. The operator should always be aware of them before getting firm conclusions on the prediction of PH progression.
The aim of this review is to describe the most important echocardiographic parameters proposed for the detection and prognosis of PH. A thorough analysis of the challenges which echocardiography faces in patients with suspected or established PH could assist its proper implementation.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted a literature search in the English language for publications in the MEDLINE and EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases from 1990 to February 2024. The following search terms, for titles and abstracts, including Medical Subject Headings (MeSH), were used: pulmonary hypertension; echocardiography; pulmonary arterial systolic pressure (PASP); diagnosis; prognosis; speckle tracking. Three investigators (EG, NV and EK) independently performed the literature search. We included experimental studies, in vitro and in vivo, and clinical studies as well. We further limited our literature search by setting the following exclusion criteria: studies with full text unavailable, published in languages other than English, and conference abstracts. The reference lists of the identified articles were checked for any additional relevant articles, especially among reviews.
3.2. Classic Echocardiographic Parameters: Diagnosis
3.1. Studies Comparing Echocardiography with Right Heart Catheterization (RHC)
The application of echocardiography in the diagnostic realm of PH has gained large recognition for the past decade. Echocardiography is an easy, cheap, easily available, uncomplicated, and repeatable technique compared to RHC. A variety of metrics have been proposed for this objective, adding to the ongoing debate on the agreement between non-invasive (echocardiography) and invasive assessment (RHC) of pulmonary pressure. The existing body of evidence reveals a high degree of agreement, but there is still a notable inconsistency in specific aspects of PH, underlining the need for a comprehensive review to address the discrepancies among various sources.
Forty years ago, the first published study indicated a high correlation between invasive and non-invasive methods [
8]. Regarding the RHC as the gold-standard technique for pulmonary artery pressure measurement and PH diagnosis, numerous studies have been conducted to validate the accuracy of echocardiography in pulmonary pressure estimation, presenting high correlation coefficients of 0.97, but with limited number of participants in each study [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. A retrospective analysis of 1695 individuals undergoing both RHC and echocardiography, with a maximum time interval of five days, aimed to investigate the correlation between invasive and echocardiographic measurements of PASP and mPAP [
14]. High Pearson’s correlation coefficients were identified between measurements from the two imaging modalities (r=0.87, r=0.82 respectively; p-value <0.001 for both coefficients), indicating high correlation between them [
14]. High correlation coefficients have been identified by other studies, using similar methodology but smaller number of participants [
15]. One of the largest and most recent studies also identified a high correlation between the invasive and non-invasive method for PASP in a population of 1400 individuals with severe aortic stenosis [
16]. On the other hand, there are studies exhibiting lower degree of correlation, especially when individuals with lung diseases are included [
17,
18,
19]. As a result, an overdiagnosis of PH through echocardiography is observed in populations with established lung disease, including chronic obstructive lung disease or pulmonary interstitial disease [
20]. Summarizing the above results, a recent systematic review investigated the accuracy of echocardiography in the detection of PH in comparison to RHC [
7]. Overall, 17 studies with over 3656 participants, 1342 of whom had a confirmed diagnosis of PH, were included in the analysis. All the included studies compared echocardiography versus RHC to test their sensitivity in PH diagnosis, setting the mean PAP> 25 mmHg as the diagnostic threshold. The time interval between RHC and echocardiography was less than seven days, to limit bias in the systematic review. There was great heterogeneity between studies regarding the PASP threshold used for the diagnosis of PH through echocardiography, which ranged from 30 to 47 mmHg. After analysis, the median value of sensitivity of echocardiography was 87% (range: 40% - 98%) and the median value of its specificity was 86% (range: 33% - 100%). A previous meta-analysis of 29 studies indicated a pooled correlation coefficient of 0.70 (95% CI: 0.67, 0.73), and again a high heterogeneity was observed between the included studies, making it challenging to draw definitive and reliable conclusions [
21].
Before examining the specific parameters of echocardiography, the level of operator’s experience may influence the correlation between those two modalities, since echocardiography is an operator-dependent technique [
15]. The implementation of semi-automated measurement of the RA pressure (RAP) may attenuate the impact of operator’s subjectivity [
22]. Various echocardiographic measurements are employed, each possessing its distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. They are depicted in
Table 1 and analyzed in the following sections:
3.2. Tricuspid Regurgitation Velocity Peak (TRVpeak) and PASP Calculation
The calculation of PASP through Doppler echocardiography is indirect and relies on the measurement of RV-RA pressure gradient and the assumption of RAP value. This is the most widely used approach for the quantification of PASP in echocardiography. In particular, the echocardiographer measures the peak velocity of TR (TRVpeak) and then using the Bernoulli equation can calculate the pressure gradient of RV-RA = 4Vpeak2. After adding an estimate of RAP, normally ranging 0-5mmHg, to RV-RA pressure gradient, the echocardiographer gets the estimated PASP. RAP assumption is based on the size of inferior vena cava (IVC) and its collapsibility during inspiration [
23]. The PASP estimation from echocardiography seems easy, repeatable, immediately available, and reproducible compared to the gold-standard measurements with RHC. Previous studies have supported the high accuracy of echocardiography in calculation of PASP compared to RHC. However, the required assumptions have raised concerns about the degree of agreement between those techniques in pulmonary pressures calculation in specific subpopulations.
In the 2022 guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of PH, the ESC and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) advise the use of TRVpeak as the main index of PH [
3]. According to these guidelines, TRVpeak above 2.8 m/s is suggestive of PH but the sole use of TRVpeak is insufficient for determining the true pressure gradients and possible the presence of PH. In severe TR, the peak velocity may underestimate pressure gradients, while in patients with high cardiac output due to liver disease or sickle cell disease or in case of artefacts, the pressure gradients may be overestimated [
24]. This is the reason why the current guidelines stress the importance of probability assignment based on a cluster of measurements during echocardiography and not the accurate diagnosis.
A recent clinical trial investigated among others the correlation between invasive and echocardiographic measurements of PASP in a population of 243 patients with severe TR [
25]. The threshold of 50 mmHg was used for both methods to classify an individual as PH positive. The time interval between the two methods varied from two to 17 days, with a median time the six days. This analysis indicated a moderate correlation between invasive and non-invasive PASP (r=0.47; p-value < 0.01). Simultaneously, the sensitivity and specificity of echocardiography for the RHC-diagnosed PH was 55% and 74% respectively. This is attributed partly to the rapid equalization of pressures between RA and RV, resulting in a practically low RV-RA pressure gradient, consequently to the underestimation of RAP [
23,
25]. Interestingly, in the aforementioned study, individuals with a false negative diagnosis of PH based on echocardiography had the more severe grades of TR [
25]. Those inconsistencies in results do not restrict the wide use of echocardiography in the diagnosis of PH but stress the importance of a more careful interpretation in patients with severe TR and the need for more studies to identify how echocardiographic measurements may apply.
An umbrella meta-analysis documented the high sensitivity of echocardiography-based PASP calculation to diagnose PH [
26]. However, the included studies showed a high heterogeneity, attributed mainly to the different ways of PASP calculation. Most of them used TRVpeak, while the rest used the jugular vein pressure. The discrepancy between echocardiography and RHC to calculate both mPAP and PASP was also outlined in a recent, small, comparative study, due to the overestimation of mPAP and PASP by echocardiography [
27]. Females, individuals with arrhythmias or patients under diuretic therapy are more susceptible to this overestimation. Another significant explanation for the discordance between echocardiography and RHC is the measurement of different parameters PASP and mPAP, respectively. The latter is not usually obtained in echocardiography and some studies have proposed the non-invasively measured PASP with a cut-off value > 40 mmHg showing the highest sensitivity and specificity for PH diagnosis [
14,
15,
16].
Although IVC dimensions can be accurately measured in most cases from the sub-costal view, it is not always a sensitive and representative index of RAP [
23]. For example, the IVC may be permanently distended in patients with heart or kidney failure due to chronic exposure to volume overload. Thereby, the IVC remains constantly enlarged, even in euvolemic patients, and it is dissociated from volume changes and RAP assumption. In healthy, young athletes, the IVC may be normally dilated and may not reflect an increased RAP [
23]. Additionally, in ventilator-dependent individuals, the reduced IVC collapse may reduce the accuracy of RAP estimation. In general, the reliability of IVC collapse is diminished in intermediate-to-high values of RAP. Alternative parameters can be considered, like a tricuspid E/E’ ratio >6 and diastolic flow predominance in the hepatic veins, when a restrictive right-sided diastolic filling pattern is recorded [
23]. The latter parameters require further investigation.
3.3. Right Ventricular Outflow Track Acceleration Time (RVOT-AT)
The right ventricular outflow track (RVOT) acceleration time (RVOT-AT) was firstly introduced 40 years ago and reflects the time between the start of right ventricular ejection and the peak flow velocity across the right ventricular outflow track, just below the pulmonary valve [
28]. According to this concept, the flow of blood in the RVOT accelerates more, in individuals with PH compared to those with normal pulmonary pressures. As a result, RVOT-AT shortens when pulmonary pressures increase. According to the latest guidelines, values under the cut-off of 105ms are suggestive of pre-capillary PH but this needs to be assessed in combination with other parameters [
3]. Previous studies have demonstrated the strong relationship of RVOT-AT with PASP, independent of TR severity [
29]. According to a recent meta-analysis RVOT-AT was highly correlated with PASP values [
26]. Another meta-analysis of 21 studies and 1280 patients showed adequately high pooled sensitivity [0.84 (95% CI: 0.75, 0.90)] and specificity [0.84 (95% CI: 0.78, 0.89)] of RVOT-AT to diagnose PH [
30]. The sensitivity of included studies showed high variability, while the heterogeneity for specificity was lower, indicating more consistent results. This can be partly explained by the different cut-off values used in the included studies, ranging from 90 to 104 ms, showing an inverse relationship between cut-off value and sensitivity at the expense of lower specificity.
Regarding co-founders, RVOT-AT can be easily obtained in most individuals, its accuracy seems not to be influenced by the etiology of PH, but the presence of arrythmias may affect its sensitivity. Moreover, the placement of sample volume at the RVOT may challenge the results. It seems that right measurement of pulmonary acceleration time below 100ms increases the probability of PH by nearly 5 times (OR: 4.8; 95% CI: 1.1, 20.4; p: 0.34) [
31]. Unlike to the aforementioned data from meta-analyses, an observational study with 236 participants admitted in the intensive care unit for acute cardiovascular or respiratory failure indicated a poor inverse correlation between PASP measurements through Doppler echocardiography and RVOT-AT [
32]. It seems that the impaired RV function significantly weakens the correlation of RVOT-AT with PASP in cardiothoracic critically ill patients, but this requires further validation.
3.4. Pulmonary Regurgitation
According to the recent guidelines, the early diastolic pulmonary regurgitation velocity is suggested as one of the parameters that needs to be considered when there is a suspicion of PH [
3]. More precisely, values over 2.2 m/s are among the factors that can help to define the probability of PH. More detailed data are required because it is an uncommon finding among patients with PH and therefore cannot be used as a screening parameter of PH.
4. Classic Echocardiographic Parameters: Prognosis
PH is linked to poor prognosis, with an estimated 1-year mortality rate exceeding 20%, when is accompanied by signs of RV failure, rapid symptom deterioration, recurrent syncope episodes, and elevated levels of B-type natriuretic peptide or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide surpassing 800 ng/L and 1100 ng/L, respectively [
3]. Irrespective of etiology, the survival rate of patients with PH exhibited a gradual decline over the years, reaching approximately 50% at the seven-year follow-up from the initial diagnosis [
33,
34]. A meta-analysis of 15 studies demonstrated that even mild PH was associated with 19% elevated risk of mortality over 5 years [
35]. The prognosis of PH is significantly influenced by the early diagnosis and prompt initiation of treatment [
33,
36]. Echocardiography in addition to its diagnostic value when PH is suspected, remains a crucial prognostic tool, by detecting preclinical stages of the disease, exploring treatment options, and monitoring the effectiveness of specific therapies [
37,
38].
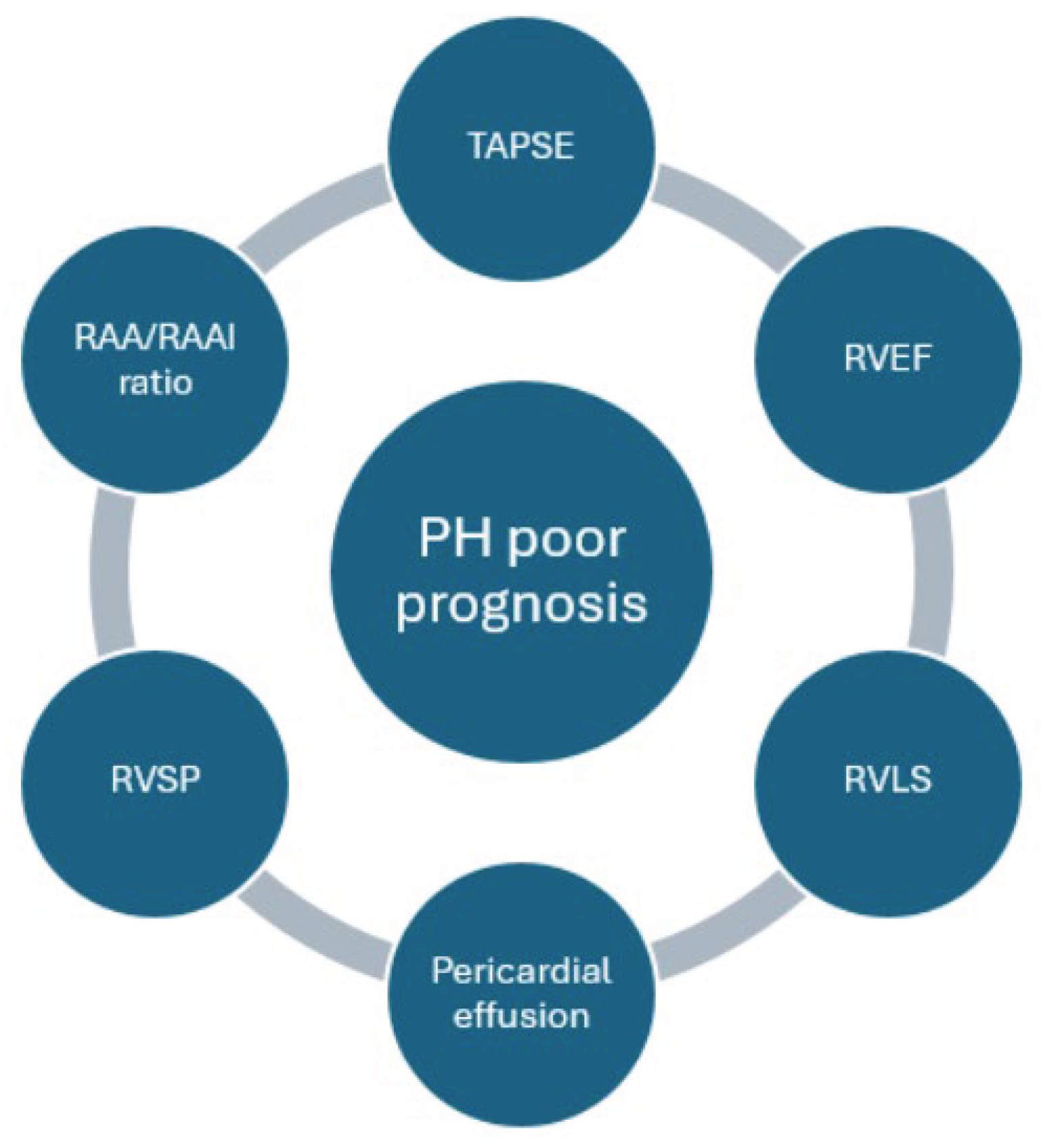
Figure 1 depicts the most important echocardiographic indices of PH prognosis.
4.1. Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion (TAPSE)
TAPSE has emerged as a crucial prognostic indicator in PH [
39,
40,
41,
42], particularly in patients with idiopathic PH, systemic sclerosis-associated PH, and Eisenmenger’s syndrome. Shukla M, et al., suggested that TAPSE plays a crucial role as a prognostic indicator in patients with PH, correlating with higher all-cause mortality [
43]. Nonetheless, it is worth noting that TAPSE is influenced by the angle of measurement and operator-dependent factors. Variations may occur based on heart motion, the severity of TR, and the dynamic interaction between the RV and RA [
44]. In a recent study involving children with PH, no significant correlation was observed between TAPSE and transplant-free survival. However, the combination of RA size and left ventricular (LV) eccentricity index emerged as a robust prognostic marker for transplant-free survival, potentially complemented by TAPSE [
42]. The combined assessment of TAPSE with other indices may overcome those shortcomings. TAPSE/PASP ratio serves as a non-invasive metric for assessing RV-arterial coupling and is influenced by RV diastolic stiffness, particularly in cases of severe PH [
45]. The TAPSE/PASP ratio is highlighted as a significant prognostic factor in the assessment of PH, with thresholds of 0.32mm/mmHg and 0.19mm/mmHg, distinguishing high, intermediate, and low mortality risk, respectively, as acknowledged in the 2022 ESC guidelines [
3,
26,
45]. Moreover, one of the biggest challenges in echocardiography is to predict the RV systolic reserve and its response to increase afterload. This is important in clinical decision making in patients with severe TR and concomitant PH, who are candidates for interventional TV correction [
46]. Moreover, the RAA exceeding 26cm² and the TAPSE/PASP ratio falling below 0.19mm/mmHg, are correlated with heightened mortality (>20% in one year) in patients with PH [
3].
The tricuspid annular systolic velocity (s′) has long been accompanied with TAPSE measurements. Many studies have supported it among others as a strong index of RV dysfunction with significant prognostic value [
47]. Patients planned to undergo surgery of left heart valvular disease and concomitant PH should be always evaluated for TV repair when severe TR is present [
47]. This is a great challenge in echocardiography because the assessment of RV systolic function and its response to altered volume and pressure load will influence the efficacy of interventional therapy of TR. The prognostic value of S’ is warrant in larger prospective studies to validate previous results.
4.2. Right Ventricular Size
In patients with PH, RV dilation is usually observed because of increased afterload and preload [
48]. After excluding transient volume overload, the RV dilatation combined with RV dysfunction can be an indirect poor prognostic factor in patients with PH and should always be considered in decision making. Basal and mid RV diameter as well as RV length can be measured. Basal RV diameter is calculated in the maximal transverse diameter in the basal one third of the RV while mid RV diameter in the level of LV papillary muscles [
48]. Values which are considered abnormal are above 41 and 35 mm, respectively [
49]. RV length corresponds to the distance between the tricuspid annulus until the RV apex during end diastole and the cut-off value is 83 mm [
49]. The cut-off values of RV size remained to be determined and clarify their relationship with prognosis [
50].
4.3. Right Ventricular Function
Impaired RV ejection fraction (RVEF) in RV failure is associated with adverse outcomes in PH, possibly through its connection with RA size and TR mechanism. Fractional area change (FAC), a widely used surrogate of RVEF with values <31-35% indicating RV dysfunction [
39,
51,
52] shows weak correlation with mortality in PH [
53]. RV dysfunction frequently dictates the severity of patients’ symptoms and stands as a primary contributor to PH mortality [
54,
55]. Moreover, the diastolic LV eccentricity index, a consequence of prolonged RV contraction in response to elevated PASP, is evident in severe PH and prognosticates adverse outcomes [
42]. Increased RAP, reflecting right heart failure, is a crucial prognostic indicator in PH [
54,
56], and the echocardiographic parameter A’ (a reflection of atrial contraction) is the most accurate surrogate of catheterization-based RAP [
57].
An alternative study proposed that apical traction, a distinct motion pattern of the heart characterized by the cardiac apex being pulled towards the LV, is linked to poorer outcomes in patients with PH [
58]. Additionally, a study led by Sano H et al. demonstrated that PH patients exhibiting a RV relative wall thickness <0.21 and lacking mid-term RV reverse remodeling (characterized by a relative decrease in the RV end-systole area of at least 15%) experienced poorer long-term outcomes following treatment [
59].
4.4. Right Atrium Size and Function
RA dilation and RAP elevation, resulting from RV dysfunction, TR and fluid overload are important prognostic factors in patients with PH [
42,
60]. RA size and RAP are indicative of RV overload in PH and are recognized as risk factors for adverse outcomes [
61]. RAP is merely essential for PASP quantification, however elevated levels have shown a correlation with increased mortality [
62]. A meta-analysis conducted by Liu K, et al. (2020) [
41] seeked the role of RAA and RAA index (RAAI). It demonstrated that RAA/RAAI ratio is related with increased risk of poor prognosis in this population, and the risk of all-cause mortality was increased by 50% for every 5 unit increase in RAA/RAAI ratio. Also, RAA increase is associated with mortality and transplantation [
53]. Furthermore, the novel RA function index (RAFI), calculated as: RAFI = RAEF × RVOT–VTI/RAESVI (RAEF: emptying fraction of right atrium, RVOT-VTI: right ventricular outflow tract velocity-time integral: RA end-systolic volume index), can be a robust predictor of clinical outcomes in individuals with precapillary PH [
55,
63].
4.5. Pericardial Effusion
Additionally, the presence of moderate or large PE is also associated with high mortality rate in this population, while minimal PE is related with an intermediate risk (estimated 1-year mortality rate between 5-20%) [
3]. PE is considered a manifestation of RV failure, where fluid accumulation occurs due to elevated RAP, resulting in compromised venous and lymphatic drainage [
51]. Moreover, a meta-analysis showed the presence of PE to be independently associated with mortality, transplantation, and clinical deterioration in patients with PH [
64].
4.6. Right Ventricular Systolic Pressure (RVSP)
RVSP is usually mentioned in published studies as a substitute of PASP. The prognostic significance of estimated RVSP at rest is negligible, showing no correlation with disease progression and exerting no influence on treatment strategies. An increase in RVSP does not necessarily reflects disease deterioration and a decrease in RVSP does not reflect improvement in prognosis [
3]. A large retrospective cohort study used echocardiographic data from 47000 participants, dividing them according to their RVSP values [
65]. Participants with mild PH, defined by RVSP 33-39 mmHg, compared to those with RVSP lower than 33 mmHg, had higher mean TAPSE values (2.7 m/s vs 2.2 m/s respectively), indicating a compensatory increase of RV function. Simultaneously, a higher occurrence of RV dilation and mean RV end diastolic diameter (EDV) was observed in the group of mild PH in comparison to no PH. Another point of consideration is the impaired RV-PA (right ventricle-pulmonary artery) coupling, as expressed by the ratio of TAPSE/RVSP. Furthermore, worse RV function and RV-PA coupling were observed in the PH group, defined by RVSP values above 40 mmHg, compared to both no PH and mild PH group. These results indicate that RSVP values between 33 and 39 mmHg, although considered normal, may be associated with RV dysfunction and dilatation.
4.7. Other Echocardiographic Parameters
Another study investigated the predictive value of pulmonary arterial capacitance (PAC) using echocardiographic parameters. The study employed the ratio RVOT-VTI/ PASP and demonstrated its association with mortality in patients with PH [
66]. Similarly, reduced RV systolic function, as assessed by TAPSE, accompanied with elevated RV thickness were correlated with increased mortality. In contrast, LV systolic function, LV diastolic parameters, PASP, or echocardiography-derived pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) did not exhibit a significant association with heightened mortality in patients with cardiopulmonary co-morbidities [
67].
Another interesting index is the Tei myocardial performance index (MPI), which was studied in patients with chronic thromboembolic PH in comparison to healthy individuals [
68]. Right ventricular Tei index is defined as (A – B)/B, where A (IVCT+SC+IVRT) is the period including the isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT), systolic contraction (S), and the isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT). B is defined as the time of systolic contraction. MPI is calculated from Doppler recordings from the lateral tricuspid annular velocity and represents the RV myocardial function. Individuals with PH had statistically higher values of MPI compared to healthy controls (0.52 vs 0.27) and exhibit a strong correlation between MPI and PVR. This association is preserved, even after pulmonary thromboendoarterectomy, although slightly attenuated and may assist to predict the progression.
Figure 2.
Classical echocardiographic indices of pulmonary hypertension diagnosis and prognosis: (a) TRVpeak doppler; (b) TR color doppler; (c) RVOT-AT; (d) TAPSE; (e) Pericardial effusion and RA enlargement.
Figure 2.
Classical echocardiographic indices of pulmonary hypertension diagnosis and prognosis: (a) TRVpeak doppler; (b) TR color doppler; (c) RVOT-AT; (d) TAPSE; (e) Pericardial effusion and RA enlargement.
5. Novel Echocardiographic Techniques for Diagnosis and Prognosis
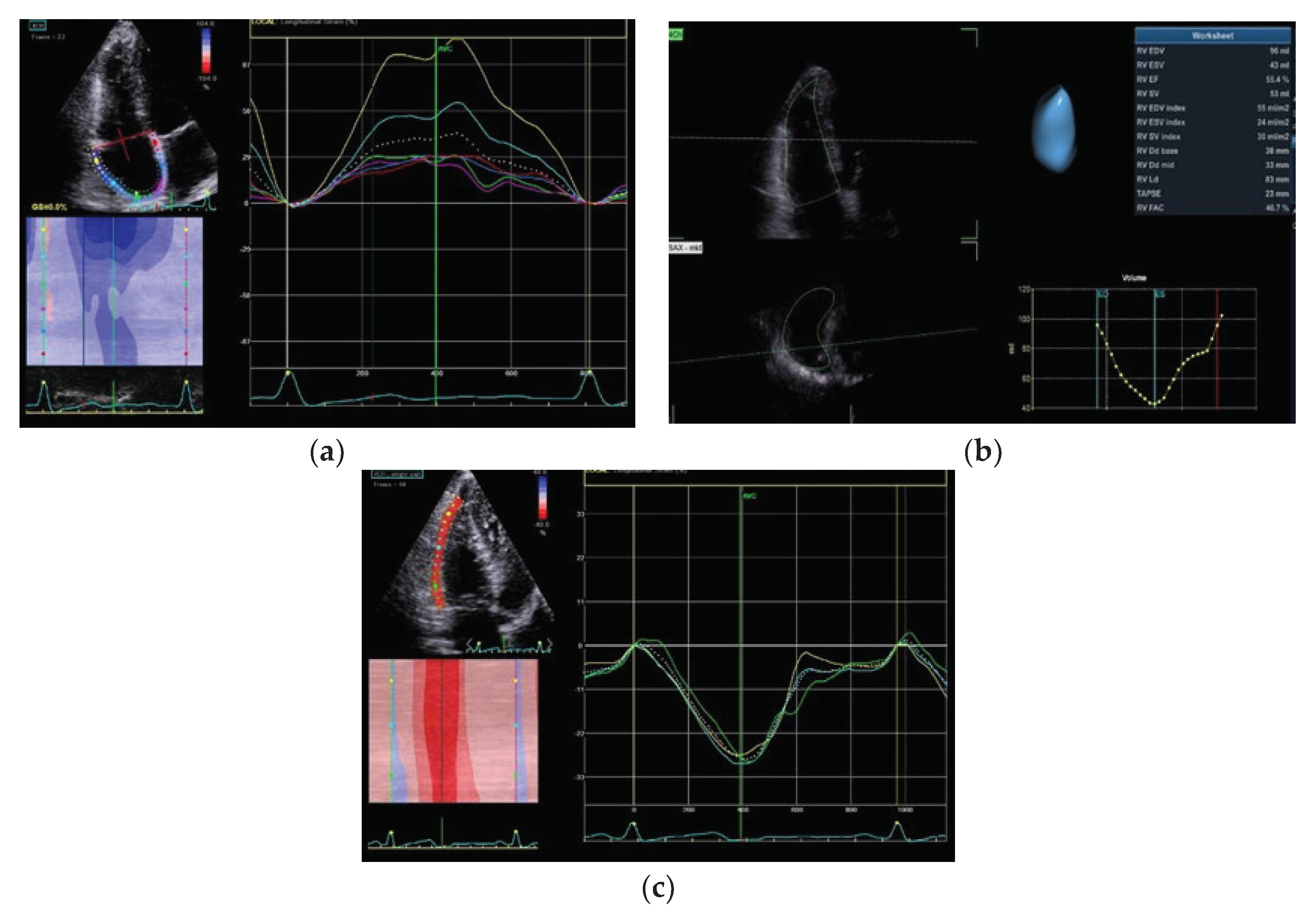
5.1. RV Function Assessment with 3D Echocardiography
There are specific conditions that are associated with inaccurate measurements of RV dimensions and volumes. For example, PVR can increase when cardiac output cannot be maintained and so RVSP may be constant or even decrease. Similarly, when TR increases, RVSP values may decrease [
69]. A way to address this problem is probably through 3D-echoardiography. In a recent study encompassing 96 pediatric patients with PH, noteworthy distinctions emerged in RV EDV index (RV EDVi), RVEF, and free wall RVLS among those with and without clinical adverse events. The findings underscored the prognostic relevance of 3D RV functional indices and volumes in pediatric PH patients [
70]. An additional study revealed that 3D echocardiography exhibited substantial agreement with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, considered the gold standard for the evaluation of RV volumes and function in patients with PH [
71]. This encompassed assessments such as EDV, end-systolic volume (ESV), stroke volume (SV), and RVEF. The measurements from both techniques demonstrated a comparable correlation with other clinical prognostic parameters in these patients. Consequently, the utilization of 3D echocardiography holds significance in the clinical evaluation of individuals with PH [
71]. Data from PVR seems to positively correlate with RVESV index and negatively correlate with LVEDV) index in small scale study. Additionally, mPAP had a positive correlation with both RVEDV index and RVESV index. Two further indices were calculated as the ratios of RVEDV /LVEDV index and RVESV/ LVESV index, which represent the characteristic pattern of enlarged RV and compressed LV in PH. Both indices had positive linear associations with PVR (r=0.67; r=0.55) and may weakly support the PH diagnosis prognosis.
5.2. Right Ventricle Speckle Tracking
Another imaging technique that is investigated for its possible use in PH diagnosis is 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography (2D-STE) [
72]. Through 2D-STE several measurements regarding RV function can be made including peak systolic strain (PSS) and post-systolic index (PSI) of the RV free wall. Results from a small observational study indicated the cut-off value of -20.75% for PSS with high sensitivity and specificity for detecting mPAP above 35 mmHg (87.5%, 87.5% respectively). The same cut-off value offers even higher sensitivity and specificity for a detection of PVR above 5 Wood units. Furthermore, PSS seems to be the only independent factor for elevated PVR and mPAP. Another measurement that can be extracted through 2D-STE is RV peak strain (RV-PS). Its absolute value seems to be lower in PH patients in comparison to those without PH and having a high correlation with mPAP [
73]. It needs to be stressed that this study was conducted on a population with chronic thromboembolic PH, perhaps limiting the generalizability of the results.
Indicators of RV myocardial deformation, such as RV strain and strain rate index, are pivotal in gauging the severity of PH, but also for prognosis. Based on accumulated evidence, a RVLS evaluation (≥-19%) stands out as a crucial predictor of all-cause mortality [
33,
56,
74,
75] and its prognostic significance has been extensively highlighted [
26]. Even more, RV strain above -15% (both global and free wall in absolute values) serves as an indicator of the poorer survival [
54]. A recent umbrella review of 13 meta-analyses evaluated the prognostic role of echocardiographic parameters in PH. RVLS in addition to another 4 parameters (PE, RAA, RAA index, TAPSE) correlated with PH prognosis [
26]. In two meta-analyses assessing the prognostic implications of RVLS in PH patients, the results demonstrated that patients with a 22% reduction in RVLS exhibited a markedly elevated risk of all-cause mortality. Also, RVLS proved to be superior index of mortality than TAPSE [
43,
76]. RVLS has proven to be a reliable predictor of both outcome and responsiveness to medical therapy in PH [
53]. However, in patients with PH and Eisenmenger syndrome RV transverse strain has a higher predictive value than RVLS [
77].
5.3. Right Atrium Volume and Strain
Another study illustrated that 3D echocardiography enables the measurement of RA volume and phasic function, highlighting its feasibility and consistency throughout the cardiac cycle [
78]. In patients with PH, the volumetric assessment of the RA and the modifications in passive and active emptying fractions, particularly when precedes RV dilation, can become meaningful prognostic markers. These observations underscore the potential of 3D RA assessments in anticipating cardiovascular morbidity and mortality among individuals with PH [
78].
Notably, various aspects of RA phasic function, including reservoir, passive, and active strain, along with RAP, showed correlations with disease severity and overall outcomes [
79]. A recent study involving 54 PH patients highlighted the prognostic relevance of RA strain, outlining the significance of RA reservoir function [
79]. In a pediatric PH population there was a significant association between RA reservoir function and PASP, PVR, and other systolic parameters (TAPSE, FAC, RV strain), highlighting its prognostic value [
80]. Despite those associations, the impact of changes in RA phasic function requires further investigation. Conversely, previous research indicated that impaired RA reservoir function (longitudinal strain) lacks correlation with PASP and PVR [
79]. A prospective study of 104 patients with idiopathic PH demonstrated that several factors of RA function, including peak longitudinal strain rate were found to be independently and significantly associated with events and prognosis [
61]. Impaired RA reservoir function, as assessed by speckle tracking longitudinal strain, signifies an unfavorable outcome [
54]. A prerequisite for 3D echocardiography and strain analysis is the good images quality, which is not always present in patients with PH.
Figure 3 provides some representative examples of novel echocardiographic indices for diagnosis and prognosis of PH.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion echocardiography remains a reliable, non-invasive, cheap, convenient, and easily reproducible modality not only for the preliminary screening of PH but also for PH prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic indices, some of them classical (e.g., TRVpeak and PASP) and some other novel (e.g., RVLS, RA strain) have been proposed for PH diagnosis and prognosis. Their implementation in clinical practice faces significant challenges and the clinicians should be aware of them before echocardiography interpretation. Future studies are required to validate their usage in patients with suspected or established PH.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K.; methodology, N.K.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K., and N.V.; writing—review and editing, E.G., M.M., E.K., and N.V.; visualization, N.K..; supervision, N.K., and M.M.; project administration, N.K.; funding acquisition, N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS, Internal research project (128-IAT-2021).
Data Availability Statement
The literature cited in this review article was sourced from MEDLINE and EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane and Google Scholar databases. All referenced publications are publicly available through these databases, ensuring accessibility and transparency in data availability.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Poch, D.; Mandel, J. Pulmonary Hypertension. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, ITC49–ITC64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadoglou, N. P. E.; Papadopoulos, C. H.; Krommydas, A. The prognostic value of exercise-induced pulmonary hypertension in asymptomatic patients with primary mitral regurgitation. J. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M. M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R. M. F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A. J. S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; Ferreira, D. S.; Ghofrani, H. A.; Giannakoulas, G.; Kiely, D. G.; Mayer, E.; Meszaros, G.; Nagavci, B.; Olsson, K. M.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Quint, J. K.; Rådegran, G.; Simonneau, G.; Sitbon, O.; Tonia, T.; Toshner, M.; Vachiery, J. L.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Delcroix, M.; Rosenkranz, S. ESC/ERS Scientific Document Group. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velidakis, N.; Khattab, E.; Gkougkoudi, E.; Kadoglou, N. P. E. Pulmonary Hypertension in Left Ventricular Valvular Diseases: A Comprehensive Review on Pathophysiology and Prognostic Value. Life (Basel). 2023, 13(9), 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parperis, K.; Velidakis, N.; Khattab, E.; Gkougkoudi, E.; Kadoglou, N. P. E. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(6), 5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Minalyan, A.; Saleem, S.; Nadeem, N.; Abdullah, H. M.; Abdalla, A.; Chan, V.; Saeed, R.; Khan, M.; Collins, S.; Mukhtar, M.; Grover, H.; Sattar, Y.; Panchal, A.; Narayana Gowda, S.; Khwaja, U.; Lashari, B.; Fischman, D. L. Comparative accuracy of non-invasive imaging versus right heart catheterization for the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2020, 29, 100568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimoto, Y.; Kumasawa, J.; Shimizu, S.; Nakano, Y.; Kataoka, Y.; Tsujimoto, H.; Kono, M.; Okabayashi, S.; Imura, H.; Mizuta, T. Doppler trans-thoracic echocardiography for detection of pulmonary hypertension in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 5(5), CD012809. [Google Scholar]
- Yock, P. G.; Popp, R. L. Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation 1984, 70, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Haimowitz, A.; Van Tosh, A.; Berdoff, R. L.; Goldberg, E. Quantitative assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with tricuspid regurgitation using continuous wave Doppler ultrasound. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 6, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, P. J.; Seward, J. B.; Chan, K. L.; Fyfe, D. A.; Hagler, D. J.; Mair, D. D.; Reeder, G. S.; Nishimura, R. A.; Tajik, A. J. Continuous wave Doppler determination of right ventricular pressure: a simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study in 127 patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 6, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez de Prada, J. A.; Ruano, J.; Martin-Duran, R.; Larman, M.; Zueco, J.; Ortiz de Murua, J. A.; Torres, A.; Figueroa, A. Noninvasive determination of pulmonary arterial systolic pressure by continuous wave Doppler. Int. J. Cardiol. 1987, 16, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S. M.; Oudiz, R. J.; Cao, T.; Romano, M. A.; Beckmann, X. J.; Georgiou, D.; Mandayam, S.; Ginzton, L. E.; Brundage, B. H. Primary Pulmonary Hypertension: Improved Long-Term Effects and Survival with Continuous Intravenous Epoprostenol Infusion. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1997, 30, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, F.; Zamanian, R.; Beraud, A.-S.; Schnittger, I.; Feinstein, J.; Peterson, T.; Yang, P.; Doyle, R.; Rosenthal, D. A Novel Non-Invasive Method of Estimating Pulmonary Vascular Resistance in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2009, 22, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, S.; Jud, A.; Aurich, M.; Hess, A.; Hilbel, T.; Hardt, S.; Katus, H. A.; Mereles, D. Reliability of noninvasive assessment of systolic pulmonary artery pressure by Doppler echocardiography compared to right heart catheterization: analysis in a large patient population. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e001103; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsallem, M.; Sternbach, J. M.; Adigopula, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Vu, T. A.; Zamanian, R.; Liang, D.; Dhillon, G.; Schnittger, I.; McConnell, M. V.; Haddad, F. Addressing the Controversy of Estimating Pulmonary Arterial Pressure by Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schewel, J.; Schlüter, M.; Schmidt, T.; Kuck, K.; Frerker, C.; Schewel, D. Correlation between Doppler Echocardiography and Right Heart Catheterization Assessment of Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis. Echocardiography 2020, 37, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaban, J.-P.; Diebold, B.; Zelinski, R.; Lafay, M.; Raffoul, H.; Rochemaure, J. Noninvasive Estimation of Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure Using Doppler Echocardiography in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chest 1989, 96, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramarin, R.; Torbicki, A.; Marchandise, B.; Laaban, J. P.; Morpurgo, M. Tramarin, R.; Torbicki, A.; Marchandise, B.; Laaban, J. P.; Morpurgo, M. Doppler Echocardiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. A European Multicentre Study. Working Group on Noninvasive Evaluation of Pulmonary Artery Pressure. European Office of the World Health Organization, Copenhagen. Eur. Heart J. 1991, 12, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecker, S. J.; Gibbs, J. S.; Fox, K. M.; Yacoub, M. H.; Gibson, D. G. Comparison of Doppler Derived Haemodynamic Variables and Simultaneous High Fidelity Pressure Measurements in Severe Pulmonary Hypertension. Br. Heart J. 1994, 72, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcasoy, S. M.; Christie, J. D.; Ferrari, V. A.; Sutton, M. St.; Zisman, D. A.; Blumenthal, N. P.; Pochettino, A.; Kotloff, R. M. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, S.; Shahidi, N.; Gin, K.; Swiston, J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Echocardiography for Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heart 2011, 97, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albani, S.; Pinamonti, B.; Giovinazzo, T.; de Scordilli, M.; Fabris, E.; Stolfo, D.; Perkan, A.; Gregorio, C.; Barbati, G.; Geri, P.; et al. Accuracy of Right Atrial Pressure Estimation Using a Multi-Parameter Approach Derived from Inferior Vena Cava Semi-Automated Edge-Tracking Echocardiography: A Pilot Study in Patients with Cardiovascular Disorders. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 36(7), 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudski, L. G.; Lai, W. W.; Afilalo, J.; Hua, L.; Handschumacher, M. D.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Solomon, S. D.; Louie, E. K.; Schiller, N. B. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of the right heart in adults: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography endorsed by the European Association of Echocardiography, a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology, and the Canadian Society of Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2010, 23, 685–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortmeier, V.; Lachmann, M.; Körber, M. I.; Unterhuber, M.; von Scheidt, M.; Rippen, E.; Harmsen, G.; Gerçek, M.; Friedrichs, K. P.; Roder, F.; Rudolph, T. K.; Yuasa, S.; Joner, M.; Laugwitz, K.-L.; Baldus, S.; Pfister, R.; Lurz, P.; Rudolph, V. Solving the Pulmonary Hypertension Paradox in Patients With Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation by Employing Artificial Intelligence. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2022, 15, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurz, P.; Orban, M.; Besler, C.; Braun, D.; Schlotter, F.; Noack, T.; Desch, S.; Karam, N.; Kresoja, K.-P.; Hagl, C.; Borger, M.; Nabauer, M.; Massberg, S.; Thiele, H.; Hausleiter, J.; Rommel, K.-P. Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis, and Risk Stratification of Pulmonary Hypertension in Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation and Implications for Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Repair. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.-X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, S.-T.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, G.-Y.; Kong, F.-X.; Ma, C.-Y. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Echocardiography in Pulmonary Hypertension: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaglioni, A.; Cassandro, R.; Luisi, F.; Ferrante, D.; Nicolosi, G. L.; Lombardo, M.; Anzà, C.; Harari, S. Correlation Between Doppler Echocardiography and Right Heart Catheterisation-Derived Systolic and Mean Pulmonary Artery Pressures: Determinants of Discrepancies Between the Two Methods. Heart Lung Circ 2021, 30, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabatake, A.; Inoue, M.; Asao, M.; Masuyama, T.; Tanouchi, J.; Morita, T.; Mishima, M.; Uematsu, M.; Shimazu, T.; Hori, M.; et al. Noninvasive Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension by a Pulsed Doppler Technique. Circulation 1983, 68, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yared, K.; Noseworthy, P.; Weyman, A. E.; McCabe, E.; Picard, M. H.; Baggish, A. L. Pulmonary Artery Acceleration Time Provides an Accurate Estimate of Systolic Pulmonary Arterial Pressure during Transthoracic Echocardiography. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2011, 24, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Tu, Y.-K. Pulmonary Hypertension and Pulmonary Artery Acceleration Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2018, 31, 201–210e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenkamp, K.; Unsöld, B.; Mushemi-Blake, S.; Shah, A. M.; Friede, T.; Hasenfuß, G.; Seidler, T. Echocardiographic Estimation of Mean Pulmonary Artery Pressure: A Comparison of Different Approaches to Assign the Likelihood of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2018, 31(1), 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammassa, V.; Corradi, F.; Colombo, C. N.; Mojoli, F.; Price, S.; Tavazzi, G. Pulmonary Artery Acceleration Time Accuracy for Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure Estimation in Critically Ill Patients. Ultrasound J 2022, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengier, F.; Melzig, C.; Derlin, T.; Marra, A. M.; Vogel-Claussen, J. Advanced Imaging in Pulmonary Hypertension: Emerging Techniques and Applications. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 35(8), 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandras, S. A.; Mehta, H. S.; Vaidya, A. Pulmonary Hypertension: A Brief Guide for Clinicians. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95(9), 1978–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolte, D.; Lakshmanan, S.; Jankowich, M. D.; Brittain, E. L.; Maron, B. A.; Choudhary, G. Mild Pulmonary Hypertension Is Associated With Increased Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7(18), e009729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virsinskaite, R.; Karia, N.; Kotecha, T.; Schreiber, B. E.; Coghlan, J. G.; Knight, D. S. Pulmonary Hypertension - The Latest Updates for Physicians. Clin. Med. (Lond). 2023, 23(5), 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alto, M.; Romeo, E.; Argiento, P.; Di Salvo, G.; Badagliacca, R.; Cirillo, A. P.; Kaemmerer, H.; Bossone, E.; Naeije, R. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: The Key Role of Echocardiography. Echocardiography 2015, 32 (Suppl 1), S23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, E.; Velidakis, N.; Gkougkoudi, E.; Kadoglou, N. P. E. Exercise-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension: A Valid Entity or Another Factor of Confusion? Life (Basel) 2023, 13(1), 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoette, S.; Creuzé, N.; Günther, S.; Montani, D.; Savale, L.; Jaïs, X.; Parent, F.; Sitbon, O.; Rochitte, C. E.; Simonneau, G.; Humbert, M.; Souza, R.; Chemla, D. RV Fractional Area Change and TAPSE as Predictors of Severe Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Pulmonary Hypertension: A CMR Study. Lung 2018, 196(2), 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyńska-Kopczyńska, K.; Krentowska, A.; Sawicka, E.; Skoneczny, A.; Jasiewicz, M.; Knapp, M.; Musiał, W. J.; Sobkowicz, B.; Kamiński, K. A. The strengths and weaknesses of non-invasive parameters obtained by echocardiography and cardiopulmonary exercise testing in comparison with the hemodynamic assessment by the right heart catheterization in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62(1), 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, P. Association between right atrial area measured by echocardiography and prognosis among pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10(9), e031316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, A. E.; Marek, J.; Diller, G. P.; Haworth, S. G.; Moledina, S. Prognostic Value of Transthoracic Echocardiography in Children With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12(6), e023118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Park, J. H.; Thomas, J. D.; Delgado, V.; Bax, J. J.; Kane, G. C.; et al. Prognostic Value of Right Ventricular Strain Using Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Cardiol. 2018, 34(8), 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moceri, P.; Baudouy, D.; Chiche, O.; Cerboni, P.; Bouvier, P.; Chaussade, C.; Ferrari, E. Imaging in Pulmonary Hypertension: Focus on the Role of Echocardiography. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 107(4), 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, K.; Wan, J.; Dalmer, A.; Vanderpool, R.; Ghofrani, H. A.; Naeije, R.; Roller, F.; Mohajerani, E.; Seeger, W.; Herberg, U.; Sommer, N.; Gall, H.; Richter, M. J. Validation of the Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion/Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure Ratio for the Assessment of Right Ventricular-Arterial Coupling in Severe Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2019, 12(9), e009047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brener, M. I.; Lurz, P.; Hausleiter, J.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Fam, N.; Kodali, S. K.; Rommel, K. P.; Muntané-Carol, G.; Gavazzoni, M.; Nazif, T. M.; Pozzoli, A.; Alessandrini, H.; Latib, A.; Biasco, L.; Braun, D.; Brochet, E.; Denti, P.; Lubos, E.; Ludwig, S.; Kalbacher, D.; Estevez-Loureiro, R.; Connelly, K. A.; Frerker, C.; Ho, E. C.; Juliard, J. M.; Harr, C.; Monivas, V.; Nickenig, G.; Pedrazzini, G.; Philippon, F.; Praz, F.; Puri, R.; Schofer, J.; Sievert, H.; Tang, G. H. L.; Andreas, M.; Thiele, H.; Unterhuber, M.; Himbert, D.; Alcázar, M. U.; Von Bardeleben, R. S.; Windecker, S.; Wild, M. G.; Maisano, F.; Leon, M. B.; Taramasso, M.; Hahn, R. T. Right Ventricular-Pulmonary Arterial Coupling and Afterload Reserve in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Repair. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79(5), 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, E. P.; Caruso, V.; Grapsa, J.; Bosco, P.; Lucchese, G. Predictors of Outcome in Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Undergoing Mitral and Tricuspid Valve Surgery. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59(6), 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, D. X.; Coates-Bradshaw, L. D.; Willis, J.; Harkness, A.; Ring, L.; Grapsa, J.; Coghlan, G.; Kaye, N.; Oxborough, D.; Robinson, S.; Sandoval, J.; Rana, B. S.; Siva, A.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.; Howard, L. S.; Fox, K.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Sharma, V.; Steeds, R. P.; Mathew, T. Echocardiographic Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension: A Guideline Protocol from the British Society of Echocardiography. Echo Res Pract 2018, 5, G11–G24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R. M.; Badano, L. P.; Mor-Avi, V.; Afilalo, J.; Armstrong, A.; Ernande, L.; Flachskampf, F. A.; Foster, E.; Goldstein, S. A.; Kuznetsova, T.; Lancellotti, P.; Muraru, D.; Picard, M. H.; Rietzschel, E. R.; Rudski, L.; Spencer, K. T.; Tsang, W.; Voigt, J.-U. Recommendations for Cardiac Chamber Quantification by Echocardiography in Adults: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 16, 233–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeißer, A.; Rauwolf, T.; Groscheck, T.; Fischbach, K.; Kropf, S.; Luani, B.; Tanev, I.; Hansen, M.; Meißler, S.; Schäfer, K.; Steendijk, P.; Braun-Dullaeus, R. C. Predictors and prognosis of right ventricular function in pulmonary hypertension due to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8(4), 2968–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawade, T.; Holloway, B.; Bradlow, W.; Steeds, R. P. Noninvasive imaging for the diagnosis and prognosis of pulmonary hypertension. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2014, 12(1), 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabysa, R.; Wańkowicz, Z. Can Echocardiography, Especially Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion Measurement, Predict Pulmonary Hypertension and Improve Prognosis in Patients on Long-Term Dialysis? Med Sci Monit 2015, 21, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L. M.; Dwyer, N.; Celermajer, D.; Kritharides, L.; Marwick, T. H. Follow-Up of Pulmonary Hypertension With Echocardiography. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2016, 9(6), 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselberg, N. E.; Kagiyama, N.; Soyama, Y.; Sugahara, M.; Goda, A.; Ryo-Koriyama, K.; Batel, O.; Chakinala, M.; Simon, M. A.; Gorcsan, J. 3rd. The Prognostic Value of Right Atrial Strain Imaging in Patients with Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2021, 34(8), 851-861.e1. [CrossRef]
- Yogeswaran, A.; Rako, Z. A.; Yildiz, S.; Ghofrani, H. A.; Seeger, W.; Brito da Rocha, B.; Gall, H.; Kremer, N. C.; Douschan, P.; Papa, S.; Vizza, C. D.; Filomena, D.; Tedford, R. J.; Naeije, R.; Richter, M. J.; Badagliacca, R.; Tello, K. Echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular diastolic function in pulmonary hypertension. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9(5), 00226–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querejeta Roca, G.; Campbell, P.; Claggett, B.; Solomon, S. D.; Shah, A. M. Right Atrial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8(11), e003521; discussion e003521. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Amano, H.; Saito, F.; Toyoda, S.; Sakuma, M.; Abe, S.; Nakajima, T.; Inoue, T. Echocardiographic surrogates of right atrial pressure in pulmonary hypertension. Heart Vessels 2019, 34(3), 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlu, S.; Farsalinos, K.; Ameloot, K.; Daraban, A. M.; Ciarka, A.; Delcroix, M.; Voigt, J. U. Apical traction: a novel visual echocardiographic parameter to predict survival in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 17(2), 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Tanaka, H.; Motoji, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hatani, Y.; Matsuzoe, H.; Hatazawa, K.; Shimoura, H.; Ooka, J.; Ryo-Koriyama, K.; Nakayama, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Emoto, N.; Hirata, K. I. Right ventricular relative wall thickness as a predictor of outcomes and of right ventricular reverse remodeling for patients with pulmonary hypertension. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 33(3), 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M. J.; Zedler, D.; Berliner, D.; Douschan, P.; Gall, H.; Ghofrani, H. A.; Kimmig, L.; Kremer, N.; Olsson, K. M.; Brita da Rocha, B.; Rosenkranz, S.; Seeger, W.; Yogeswaran, A.; Rako, Z.; Tello, K. Clinical Relevance of Right Atrial Functional Response to Treatment in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 775039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alto, M.; D’Andrea, A.; Di Salvo, G.; Scognamiglio, G.; Argiento, P.; Romeo, E.; Di Marco, G. M.; Mattera Iacono, A.; Bossone, E.; Sarubbi, B.; Russo, M. G. Right atrial function and prognosis in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 248, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doutreleau, S.; Canuet, M.; Enache, I.; Di Marco, P.; Lonsdorfer, E.; Oswald-Mammoser, M.; Charloux, A. Right Heart Hemodynamics in Pulmonary Hypertension - An Echocardiography and Catheterization Study. Circ. J. 2016, 80(9), 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratoglou, S. A.; Dimopoulos, K.; Kamperidis, V.; Feloukidis, C.; Kallifatidis, A.; Pitsiou, G.; Stanopoulos, I.; Grosomanidis, V.; Hadjimiltiades, S.; Karvounis, H.; Giannakoulas, G. Right Atrial Function Predicts Clinical Outcome in Patients with Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2018, 31(10), 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggen, V. J. M.; Driessen, M. M. P.; Post, M. C.; van Dijk, A. P.; Roos-Hesselink, J. W.; van den Bosch, A. E.; et al. Echocardiographic findings associated with mortality or transplant in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neth. Heart J. 2016, 24(6), 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, J. H.; Maron, B. A.; French, J.; Huang, S.; Thayer, T.; Farber-Eger, E. H.; Wells, Q. S.; Choudhary, G.; Hemnes, A. R.; Brittain, E. L. Association of Mild Echocardiographic Pulmonary Hypertension With Mortality and Right Ventricular Function. JAMA Cardiol 2019, 4, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papolos, A.; Tison, G. H.; Mayfield, J.; Vasti, E.; DeMarco, T. Echocardiographic assessment of pulmonary arterial capacitance predicts mortality in pulmonary hypertension. J. Cardiol. 2021, 77(3), 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Wu, W. C.; Jankowich, M.; Maron, B. A.; Sharma, S.; Choudhary, G. Echocardiographic predictors of mortality in patients with pulmonary hypertension and cardiopulmonary comorbidities. PLoS One 2015, 10(3), e0119277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, D. G.; Malouf, P. J.; Gurudevan, S. V.; Auger, W. R.; Madani, M. M.; Thistlethwaite, P.; Waltman, T. J.; Daniels, L. B.; Raisinghani, A. B.; DeMaria, A. N. Utility of Right Ventricular Tei Index in the Noninvasive Evaluation of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension before and after Pulmonary Thromboendarterectomy. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2009, 2, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Yao, A.; Nakao, T.; Hatano, M.; Maki, H.; Imamura, T.; Shiga, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Sonoda, M.; Kinugawa, K.; Shiota, T.; Suzuki, J.; Takenaka, K.; Hirata, Y.; Nagai, R. Volumetric and Functional Assessment of Ventricles in Pulmonary Hypertension on 3-Dimensional Echocardiography. Circ J 2013, 77, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jone, P. N.; Schäfer, M.; Pan, Z.; Bremen, C.; Ivy, D. D. 3D echocardiographic evaluation of right ventricular function and strain: a prognostic study in paediatric pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2018, 19(9), 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzio, M.; Scelsi, L.; Golino, M.; Lattuada, M.; Raineri, C.; Turco, A.; Giuntini, C.; Ceriani, F.; Curti, M.; Bonelli, A.; Piacentino, F.; Venturini, M.; Ghiringhelli, S.; Morandi, F.; De Ponti, R.; Ghio, S. Assessment of right ventricle in pulmonary arterial hypertension with three-dimensional echocardiography and cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2021, 22(12), 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Tsuneto, A.; Kojima, S.; Koga, S.; Nakata, T.; Yoshida, T.; Eto, M.; Minami, T.; Yanagihara, K.; Maemura, K. Longitudinal Strain of Right Ventricular Free Wall by 2-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography Is Useful for Detecting Pulmonary Hypertension. Life Sci 2014, 111, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiino, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Yamada, A.; Takada, K.; Kawai, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Takahashi, H.; Takagi, Y.; Iwase, M.; Ozaki, Y. Usefulness of Right Ventricular Basal Free Wall Strain by Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Int Heart J 2015, 56, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeck, M. L.; Scherptong, R. W.; Marsan, N. A.; Holman, E. R.; Schalij, M. J.; Bax, J. J.; Vliegen, H. W.; Delgado, V. Prognostic value of right ventricular longitudinal peak systolic strain in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2012, 5(5), 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoji, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Ryo, K.; Emoto, N.; Kawai, H.; Hirata, K. Efficacy of right ventricular free-wall longitudinal speckle-tracking strain for predicting long-term outcome in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Circ J 2013, 77(3), 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulshof, H. G.; Eijsvogels, T. M. H.; Kleinnibbelink, G.; van Dijk, A. P.; George, K. P.; Oxborough, D. L.; Thijssen, D. H. J.; Opondo, M. A. Prognostic value of right ventricular longitudinal strain in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2019, 20(4), 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moceri, P.; Bouvier, P.; Baudouy, D.; Dimopoulos, K.; Cerboni, P.; Wort, S. J.; Gatzoulis, M. A. Cardiac remodelling amongst adults with various aetiologies of pulmonary arterial hypertension including Eisenmenger syndrome-implications on survival and the role of right ventricular transverse strain. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017, 18(11), 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng Y, Guo SL, Wu WF, Wang Q, Su HY, Tan Z, Wang F, He QY. Right Atrial Evaluation in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension: A Real-time 3-Dimensional Transthoracic Echocardiographic Study. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35(1), 49-61. [CrossRef]
- Tello K, Dalmer A, Vanderpool R, Ghofrani HA, Naeije R, Roller F, Seeger W, Wiegand M, Gall H, Richter MJ. Right ventricular function correlates of right atrial strain in pulmonary hypertension: a combined cardiac magnetic resonance and conductance catheter study. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020, 318(1), H156-H164. [CrossRef]
- Jone PN, Schäfer M, Li L, Craft M, Ivy DD, Kutty S. Right Atrial Deformation in Predicting Outcomes in Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017, 10(12), e006250. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).