1. Introduction
Cyberspace, which incorporates the hardware infrastructures and devices, the connectivity among those devices, the software that runs on those devices, and the information maintained within those infrastructures, is growing exponentially in all aspects [
1]. This growth is redefining the world as traditional world activities such as communication, industrialization, social interaction, military, education, transportation and more are being enabled by cyber technologies. This makes cyberspace the new major element and focal point to the extent of being considered as the fifth domain [
2]. Currently, network connectivity, with the introduction of IoT devices, covers most of the world creating smart villages, smart cities, smart transportation, and smart homes. The software industry is also growing at an unprecedented rate, with AI replacing human intelligence in most expert systems. Social media platforms are also experiencing tremendous growth, with almost everyone is connected to one or more platforms [
1]. The world is enjoying the benefits of cyberspace and globalization more prevalent than ever before.
However, the growth of cyberspace has also redefined security perspectives for individuals, organizations, and countries alike [
2]. The attack surface has widened so much that cyberattacks are growing from year to year, becoming a major risk to the world. In fact, the Global Risk Report has labeled cyberattacks as the sixth most high-impact risk [
3]. As a result, digital crime investigation has become a major focus for countries and organizations, as cases that are facilitated or fully committed by computers increase exponentially.
1.1. Digital Forensics
Digital Forensics (DF) applies computer science for the investigation of digital crime by following proper investigation procedures such as chain of custody, validation, search authority, and reporting [
4]. The DF investigation process passes through four major stages, defined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The first stage is the Collection stage, which involves identifying and collecting digital pieces of evidence related to the crime. The second stage is Examination, which involves filtering the relevant information from the collected evidence. The third stage is Analysis, which involves analyzing the evidence and connecting the dots to reconstruct the crime scene. The final stage is Reporting, which involves presenting the case to the court [
4]. ISO has its own version of the DF investigation process [
5].
Many technical and governance challenges make winning a case very difficult. There are awareness challenges from the victim, to the police officers, the investigators, the judges, and the overall society that cases are lost because of the necessary precautions. Quick et. al [
6] discuss the challenge related to the volume of data collected for a crime case being too much that currently there is a huge backlog that continues to grow from time to time. S. Raghavan [
7] categorizes these challenges into five groups. First, complexity problem which arises from the huge and heterogeneous data volume problem that requires complex data mining solutions. Second, the diversity problem that arises from the solutions for different evidence sources being different and this created too many tools and techniques. Third, consistency and correlation problem which is the result of the diversity of the evidence sources and their solutions are expected to correlate, but there are challenges in correlating the solutions. Fourth, the volume problem that arises from the dynamic growth of cyberspace results in a dramatic increase in the number and size of storage devices. Fifth, the unified timeline problem that arises from the different timezone and timestamp interpretations makes investigation difficult.
Quick et. al [
6] summarize research on the challenges of DF in relation to the big volume data and the solutions proposed. The large volume of data is a result of the increase of cases with DF involved, the increase in the number of devices seized per case, and the big size of each individual device. This big data creates a huge backlog that even the big DF laboratories are challenged. They showed how the data volume is continuously increasing with a high slope linear scale by collecting data from 1997 to 2014. The backlog in turn creates problems including suspect suicide, suspect denied access to family, suspect denied working, and access to personal data. They also reviewed the solutions proposed by researchers for the backlog problem including Data mining which enables to extraction of useful information from big data, Data reduction and subset that helps to reduce the data to be analyzed, DF Triage which prioritizes the evidence according to their relevance, and using intelligence analysis such as profiling to filter data. Besides, other techniques such as distributed and parallel processing, visualization, DF as a service (DFaaS), and the use of AI techniques are also discussed.
1.2. Intention Recognition
The huge data generated by humans as well as devices become a huge problem for analysis by human beings and consequently, it is creating a delay not only in DF, but also in every sector. The paramount importance of owning machines that are capable of reasoning through a given data becomes clearer than ever.
Data mining is the process of discovering interesting patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data,Agarwal2014. However, it is very crucial to have a mechanism to add domain knowledge while mining data in order to get meaningful extraction [
9].
Intention Recognition is a process by which an agent (the observer / recognizing agent) becomes aware of the intentions of others (the observed/intending agent). In simple terms, the process of IR can be explained as: having an intention, the observed agent executes the action or sequences of actions to achieve his intent. Those actions will impact (change states) the environment. Based on those actions, or the state changes, an observer agent can predict the intent of the observed agent. Heinze [36] has modeled IR in three levels of intentional behavior of the intending agent and intention recognition of the observer agent: intentional level, activity level, and state level. However, in reality, the process becomes complicated as there are many other factors: there may be multiple cooperating observed agents, multiple intentions, multiple plans to achieve the intention, multiple hypotheses, different observability levels, different contexts, and many more.
Intent plays a crucial role in defining and understanding the context of the crime and it can serve as a clue to investigate the crime from different perspectives [
10,
11,
12]. Uncovering the criminals’ intent leads the investigation in the right direction and helps in uncovering the truth by clarifying which exhibit is more relevant and who else is involved in the crime. It also has paramount importance in reducing and sub-setting the data generated for the case by applying different filters, to facilitate for effective extraction and mining of court-admissible evidence. Efficient evidence extraction is mandatory especially for ongoing crimes, so that to prevent further damage with the help of the intelligence generated. In addition, IR is also important in the triage process for prioritizing the exhibits for further analysis.
1.3. Modeling
Different researchers employed different models for intent recognition in digital forensics and related domains. This paper provides an in-depth review of these works classified into three major categories, logic-based, classical machine learning, and deep learning-based approaches, adopted from [
13]. Logic-based approaches use logic-based formalisms to represent and reason about the actions, plans, and goals of the observed agent. They usually rely on predefined domain knowledge and rules to infer the most likely explanation for the observed behavior. Statistical methods and machine-learning techniques are employed by Classic Machine Learning approaches to learn patterns and models from data. These models can be used to recognize the actions and goals of the intending agent. Although these approaches do not require much domain knowledge or human intervention, they need a large amount of labeled data to train the models. Deep Learning approaches are the current state-of-the-art in the AI industry. They utilize deep neural networks to learn high-level features and representations from data, which can be used to recognize intents. However, these approaches lack explainability as they are considered a black box approach.
1.4. Paper Organization
This paper aims to systematically review the current status of Intention Recognition related to the DF domain. The remainder of this paper is structured as follows:
Section 2 provides an overview of previous reviews as related work.
Section 3 outlines the systematic literature review approach adopted in this study. In
Section 4, we analyze each study according to its methodological approach to IR, and the challenges are discussed in
Section 5.
Section 6 presents the findings and trends observed during the analysis. Finally,
Section 7 concludes the work and suggests possible avenues for future research.
2. Related Works
To the best of our knowledge, there is no systematic review study that focused on the contribution of intention recognition related to digital forensics or cybercrime. There are a few related studies and this section discusses them and the table below summarizes their contributions and limitations.
In 2017, A. Ahmed et al.[
14] conducted a review of research papers related to the different approaches to attack intention recognition. The authors categorized the approaches into four main categories, namely causal network, path analysis, graphical attacks, and dynamic Bayesian network. They discussed each approach in detail and pointed out the advantages and the limitations of the approaches. They also concluded that the causal network approach is more efficient in detecting attacks with similar intentions. However, their review included a small set of studies and they do not discuss how they selected the papers. Besides, the review is a bit old as it includes papers before 2017.
In 2021, F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13] is a comprehensive review of the problem of recognizing human actions, plans, and goals. The paper provides a general view of the problem, both from the human perspective and from the computational perspective, and proposes a classification of the main types of approaches that have been proposed to address it (logic-based, classical machine learning, deep learning, and brain-inspired), together with a description and comparison of the classes. They included papers from multiple disciplines and application areas. However, since their review is a general review of papers up to 2020 which tries to include all application areas, the attention given to digital forensics or cyber crime is much less. Besides it is not known how they selected the papers they reviewed and the number of digital forensics or cybersecurity-related papers is very few.
This study is meant to be a systematic review that focuses on intention recognition related to digital forensics and cybercrime. The study includes papers from 2018 to 2023. We adopted the approach categorization proposed by F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13], however, we eliminated the Brain-inspired category as we did not find a single paper that could be categorized under this category.
Table 1.
Summary of Research Reviews related to IR and DF.
Table 1.
Summary of Research Reviews related to IR and DF.
| Article |
Contributions |
Limitations |
| 2017, A. Ahmed et al.[14] Attack Intention Recognition: A Review |
They reviewed some papers related to attack intention recognition. They classified the approaches into four categories (causal networks, path analysis, graphical attacks, and dynamic Bayesian network) and discussed the papers under these approaches.
|
It is not known how the papers were selected, as the inclusion and exclusion criteria are not explained it doesn’t include many related studies The study is a bit old as it includes papers before 2017. |
| 2021, F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [13]
Activity, Plan, and Goal Recognition: A Review |
It is a comprehensive study in the sense that it includes papers from all disciplines that utilize activity, goal, and plan recognition. They categorize the papers into four according to the higher-level approaches (Logic-based, classical machine learning-based, deep learning-based, and Brain-inspired ) |
The study inclusion and exclusion criteria are not documented and it is not known how the reviewed papers are selected. The study included papers up to 2020, a bit older |
3. Method
There are many approaches to performing Systematic Literature Reviews [
15,
16,
17]. This research followed the six-phase systematic review approach prepared by Jesson et. al [
18]. The phases can be summarized as, first, Plan the systematic review by preparing the protocol, the questions, the keywords, the criteria, data extraction sheet. Second, Comprehensive search with the keywords, tune the keywords when necessary, screen using the title and the abstract, and document the results. Third, Quality Assessment by reading the paper and deciding whether to include or not, documenting the reason for exclusion, and maintaining the result. Fourth, Data Extraction, extract the relevant information by using the data extraction sheet. Fifth, Synthesize the data from each article. Six, Write up a balanced, impartial, and comprehensive report.
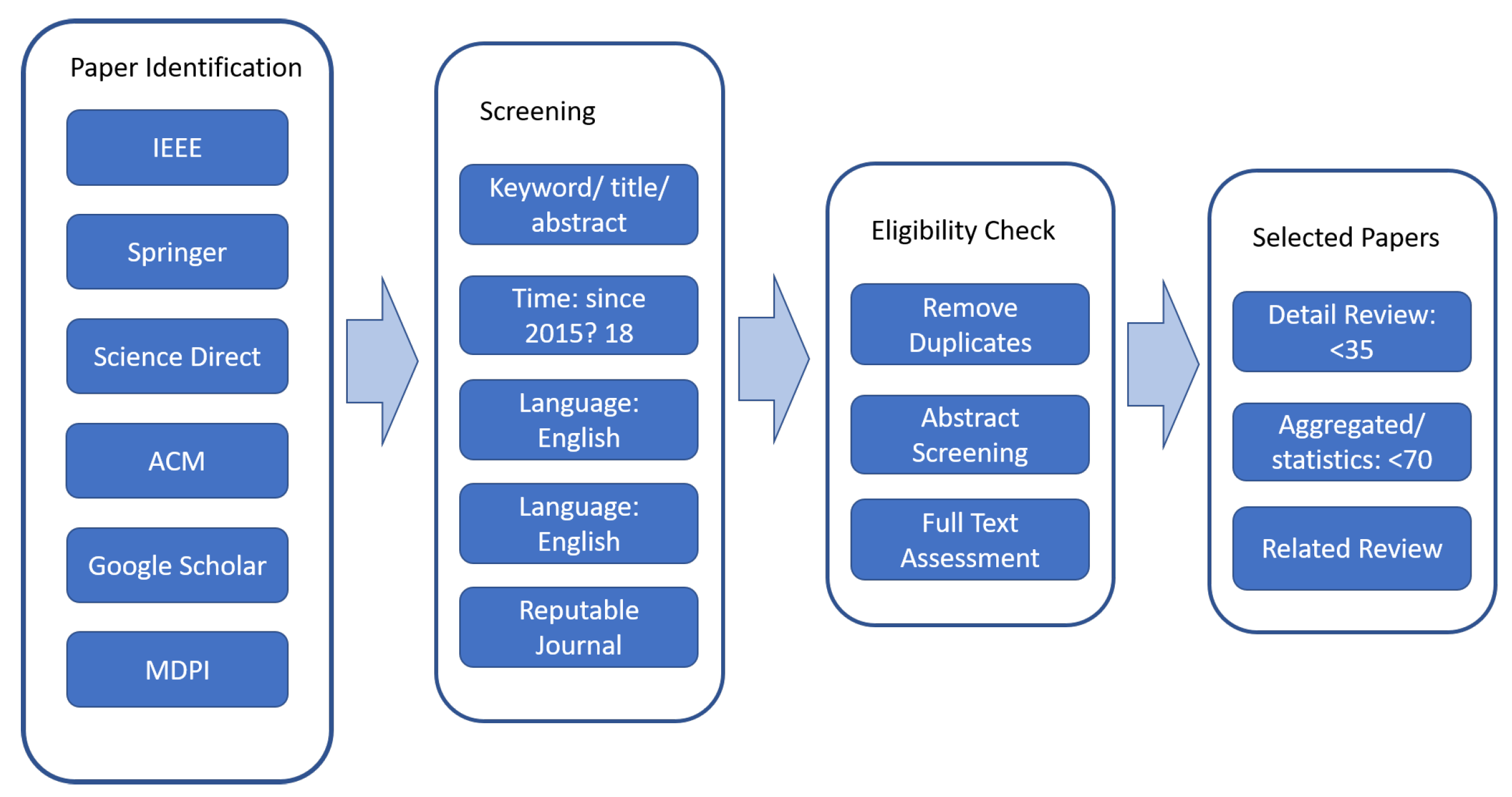
1. The review is focused on the solutions provided to solve the intention recognition problem in digital forensics and cybercrime. Thus the search keywords includes: synonyms to the word intention recognition: ("intent” OR “goal” OR “plan” OR “activity” OR “pattern”) AND (“recognition” OR “detection”); synonyms to the digital forensic investigation: (“attack” OR “cyberattack” OR “cybercrime” OR “digital forensics” OR “digital investigation” OR “DF”); and synonyms to model: (“model” OR “framework” OR “tool” OR "Algorithm"). The review includes research from 2018 to date which are written in English or have English versions. Besides Data extraction sheet is prepared.
2. Comprehensive searches are done with the known search engines, Google Scholar, IEEE Xplore, Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Digital Library, ScienceDirect, MDPI, and Springer are searched with the keywords combination. We included journal articles and conference proceedings from reputable journals with a high impact factor. Higher level filtering is done using the titles and to some extent by using the abstracts and 78 papers are selected.
3. Further filtering is done by reading the abstracts and to some extent by reading/skimming the full paper and 20 papers are selected for detailed systematic review. These papers are focused on providing solutions and contributing to the intention recognition problem in DF. They provide different solutions to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of DFI.
4. Data is extracted using the Data Extraction Sheet, as shown in Appendix A. The data extraction includes the sub-domain (such as Network Security, APT, Database, and Social media ) DF Categorization (Mobile Forensics, Computer, Network, IoT, Cloud, Memory, ...), approaches (such as Logic-based, Classical Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and also Similarity Based, attack graph-based, ...), Content Type (text, image, audio, video), intent level (activity, intent/goal, plan).
5. The Synthesis is discussed in each modeling approach and a combined synthesis together with findings is documented in the discussion section.
Figure 1.
Search and Filtering approaches.
Figure 1.
Search and Filtering approaches.
3.1. Analysis
The data collected is simple and small qualitative data, accordingly analyzing it doesn’t require sophisticated tools and techniques. However, the different data extracted from the papers are organized and analyzed by using Microsoft Excel software.
4. Review of Intention Recognition in DF
Intention Recognition has been applied in different stages of the DF process as well as in different DF categories. There are diversified techniques, tools, data sources, and devices involved in DF, this, in turn, creates complex and diversified solutions. This section reviews the papers selected through the systematic search categorized by three major modeling approaches: Logic Based, Classical Machine Learning, and Deep Learning based.
4.1. Logic Based
A logic-based, also symbolic AI, approach in AI is a methodology that uses formal languages like logic to represent knowledge and reasoning about problems and domains. They encode human knowledge in a compact and usable manner and can manipulate symbols to make deductions and inferences based on predefined rules. They can also learn new knowledge from examples and existing domain knowledge.
Abduction, hybrid logic-probabilistic, and causal reasoning approaches are some examples of logic-based approaches, which use formal languages like logic to represent knowledge and reasoning about problems and domains. Abduction is a form of logical reasoning that starts with single or multiple observations and then seeks to find the most likely explanation or conclusion for the observation. Abductive reasoning is useful for commonsense reasoning, diagnosis, planning, and natural language. Hybrid logic-probabilistic approaches are methods that combine logic and probability to handle uncertainty and complexity. Causal reasoning an approach that involves the use of causal relationships to infer the effects of actions, events, or interventions. It can also be used to explain why something happened or to predict what will happen under different scenarios. Causal reasoning is based on the assumption that there are causal mechanisms that govern the behavior of systems and that these mechanisms can be represented by causal models, such as causal graphs, causal networks, or structural causal models. In this section, we reviewed the following papers that employ logic-based approach for modeling IR in DF and related domains.
X. Cheng et al. [
19] address the problem of cyber situation comprehension for Internet of Things (IoT) systems, which are vulnerable to advanced persistent threat (APT) attacks, by utilizing the concepts of intention recognition. They argue that existing methods for cyber situation awareness are not suitable for IoT systems, as they do not consider the semantic and logical relationships among different types of data. Therefore, they propose a similarity-based method for the comprehension of APT attacks in IoT environments. In order to do this, they built a framework called APTALCM, which consists of an ontology of the APT potential attacks and two modules for alert and log correlation. The ontology models the concepts and properties to formalize APT attack activities in IoT systems. It depicts the attacks using the classes (alerts and logs), attributes, domain, relationships among instances, and similarity of instances. They use an alert class with seven attributes and six log classes with 19 attributes to calculate the similarity within each class. The alert and log correlation modules use a similarity-based method based on SimRank to recognize the APT attack intentions and scenarios. SimRank is a general similarity measure that exploits the object-to-object relationships in graphs, based on the idea that “two nodes are similar if they are pointed to (have incoming edges) from similar nodes”. The alert correlation module uses SimRank to reconstruct APT attack scenarios by measuring the similarity between alert instances. In contrast, the log correlation module uses SimRank to detect log instance communities by measuring the similarity between log instances. As a result, APTALCM can accomplish the cyber situation comprehension effectively by recognizing the APT attack intentions in the IoT systems. The exhaustive experimental results demonstrate that the two kernel modules, i.e., Alert Instance Correlation Module (AICM) and Log Instance Correlation Module (LICM) in APTALCM achieve a low false positive rate of 4.2% and a high true positive rate of 83.7%.
R. Mirsky et al. [
20] proposed two new metric-based algorithms for goal recognition in network security by adapting previously proposed planner-based algorithms. The first algorithm is Plan Edit Distance (PED), which calculates the distance metric between the optimal plan and the observation sequence without requiring online planner execution. The second algorithm is Alternative Plan Cost (APC), which finds the minimal mapping from the states visited by the attacker to the states in the optimal plan. They experimented on a network of 60 hosts and compared five algorithms, including PED, APC, and two planner-based algorithms proposed by previous researchers, and one planner-based algorithm which is modified to run offline. The experiments confirmed that PED and APC outperformed the planner-based algorithms in terms of Prediction Quality, Noisy Observations, and running times. However, in terms of Missing Observations, the planner-based algorithms were shown to be more robust.
B. Chen et al. [
21] propose an attack graph-based method to recognize the intention of attackers in network security, especially for complex and multi-step attacks. In the first step of their method, they identify the key assets in the network by calculating the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA) triads for each asset and ranking them according to their security importance. Then, they generate hypothetical attack intents based on the security requirements of the key asset and the network topology. An attack intent is defined as a specific goal that an attacker wants to achieve by exploiting the vulnerabilities in the network. Next, they adopt an attack path graph generation algorithm based on vulnerability attributes, network accessibility, and causality model. An attack path graph is a directed graph that represents the possible attack paths from the attacker’s entry point to the target asset. Finally, they identify the network attack intent by employing qualitative and quantitative attack intent analysis. The qualitative analysis matches the attack path information to a corresponding attack intent, while the quantitative analysis quantifies the degree of concealment of vulnerabilities, the probability of successful utilization, and the similarity between the attack path and the hypothetical attack intent. They also conduct an experiment involving three network domains and eight hosts and show that their method can successfully identify the intents of attackers.
A. Shinde et al. [
22] proposed a model for cyberattack intent recognition using the interactive partially observable Markov decision process (I-POMDP), a framework for modeling strategic interactions under uncertainty. They applied their model to a cyber deception domain, where the defender and the attacker interact on a single honeypot host system. They considered three types of attackers with different objectives and preferences: the data exfil attacker, who aims to steal sensitive data; the data manipulator, who aims to modify critical data; and the persistent threat, who aims to maintain a strong presence for future attacks. Their model actively deceives the attacker by providing fake data and observes the attacker’s reactions to infer their behavior and intent. Their model also estimates the attacker’s beliefs, capabilities, and preferences, and uses them to calculate how the deception affects the attacker’s mental state. They conducted simulation-based and agent-based experiments to compare their model with other strategies for intent recognition. They showed that their model can effectively recognize the attacker’s type and intent, and provide appropriate deception strategies. They claim their model achieved significantly higher accuracy and robustness in predicting the attacker’s actions and goals than the other commonly known strategies.
D. Kim et al. [
23] proposed an attack detection application for the Android OS to protect users’ personal information from theft. The application uses an attack tree approach to detect the intention of the attacks. The algorithm has two phases: pre-phase and post-phase. The pre-phase consists of four steps: collect, normalize, create a tree, and apply levels. In phase one, the attack intents are categorized into three: interception, modification, and system damage. Interception attacks aim to steal personal information from the user’s device, such as passwords, credit card details, or other sensitive data. Modification attacks aim to alter the user’s data or settings, such as changing the user’s password or modifying the user’s contacts. System damage attacks aim to damage the user’s device or the system, such as deleting files or rendering the device unusable. The post-phase also consists of four steps: log collect, compare & analyze, visualize, and warn or block. The system was tested using two attacks, smishing (which is SMS phishing) and backdoor, and successfully detected them.
The work by X. Zhang et al. [
24] introduces an innovative approach for recognizing attack intentions in network security. Their research centers around the premise that the dynamics of attack-defense interactions resemble a strategic game, characterized by opposition, non-cooperation, and strategy-dependent decision-making. To unravel the true intents behind network attacks, the authors propose a framework grounded in signaling game theory. They identified key assets and categorized the possible attacks on each key asset. They also map attackers’ intent to security requirements (CIA) and generate possible hypotheses of attack intentions. In their methodology, they generate attack intention hypotheses, leveraging the signaling game model. They then compute the probabilities associated with each attack intention by solving game equilibria. To validate their approach, they employ NetLogo simulations, providing empirical evidence of its effectiveness. The authors claim that the method effectively improves the accuracy of attack intention recognition.
Table 2.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: using Logic Based Method.
Table 2.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: using Logic Based Method.
| Article |
Sub-Domain |
Approach |
Intent Level |
Accuracy |
| 2019, R. Mirsky et al. [20] New Goal Recognition Algorithms Using Attack Graphs |
Network Security |
Attack graph, metric based algorithm |
Plan |
Online Test in seconds:
R&G+SC: 0.6578, PED: 0.0002, AED: 0.3246
|
| 2019, X. Cheng et al. [19] Cyber Situation Comprehension for IoT Systems based on APT Alerts and Logs Correlation |
APT on IoT |
Similarity Based |
Intent |
True Positive: 83.7 False Negative: 4.2 |
| 2019, D. Kim et al. [23] Attach detection application with attack tree for mobile phone using log analysis. |
Mobile forensics |
attack tree |
Intent |
- |
| 2020, B. Chen et al. [21] Attack Intent Analysis Method Based on Attack Path Graph |
Network Security |
Attack Path Graph |
Intent |
- |
| 2021, A. Shinde et al. [22] Cyber-attack intent recognition and active deception using Factored Interactive POMDPs |
Network Security |
Partially observable Markov decision process |
Intent |
- |
| 2021, X. Zhang et al. [24] Network Attack Intention Recognition Based on Signaling Game Model and Netlogo Simulation |
Network Security |
Signal Gaming Model |
Intent |
- |
4.1.1. Summary
The logic-based approach remains the prevailing method in addressing the challenge of intention recognition within digital forensics and related domains. This preference may stem from the domain’s inherent need for explainability, as Digital forensics investigators are tasked with elucidating the rationale behind a suspect’s culpability, and this approach provides a structured framework for explaining both why and how conclusions are derived. Over the past years, this approach has consistently dominated the field, as highlighted by F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13]
An analysis of the available literature (as listed in the table) reveals that the majority of research efforts in IR in DF center around the sub-domain of network security. These studies primarily delve into the analysis of various alerts and network traffic data. Notably, the work by X. Cheng et al. [
19] focuses on intention recognition in the Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) on IoT subdomain, while D. Kim et al. [
23] contribute to the role of intent in mobile security. These show there exist notable gaps in the application of the IR technology across different categories within DF. Furthermore, most works focus on the intention recognition level, while the work by R. Mirsky et al. [
20] operates at a higher level of plan recognition. In contrast, there is no study that focus on malicious activity detection, operating at a granular level.
The logic-based approach, while valuable for intention recognition, faces several challenges and limitations. First, scalability remains an issue; these AI systems can be computationally expensive and struggle to handle large and complex domains, especially when dealing with uncertainty, inconsistency, or incomplete information. Second, integration poses difficulties; logic-based methods may not seamlessly combine with other AI techniques, such as sub-symbolic approaches (e.g., neural networks) or hybrid models that leverage the strengths of both paradigms. Third, while logic-based systems are generally more interpretable than sub-symbolic counterparts, they can still be too abstract or complex for human understanding. Unfamiliar symbols, technical jargon, or lengthy proofs may hinder trust in their results. Fourth, the inherent rigidity of rule-based systems demands that cases neatly fit predefined rules for accurate identification. Finally, the manual introduction of new knowledge by experts is a necessity. However, in extensive and intricate domains, this reliance on human expertise introduces the risk of errors and limitations in keeping up with evolving scenarios.
4.2. Classical Machine Learning
Classic Machine Learning approaches use statistical methods and machine-learning techniques to learn patterns and models from data that can be used to recognize the actions, and intents of the observed agent. They usually do not require much domain knowledge or human intervention, but they need a large amount of labeled data to train the models. They can handle uncertainty and noise in the data, but they may not capture the underlying structure and semantics of the problem domain. They also may not generalize well to new or unseen situations. These algorithms can be further divided into two categories: supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
In supervised learning, the algorithm is trained on labeled data, where the correct answer is provided to the algorithm. Some widely used supervised learning algorithms include k-Nearest Neighbor, Support Vector Machines, Decision Tree, and Logistic Regression. The first three algorithms are used for both classification and regression tasks, while logistic regression is used for regression only. k-Nearest Neighbor works by finding the k-nearest data points to the input data point and then classifying the input data point based on the majority class of the k-nearest neighbors. Support Vector Machines (SVM) work by finding the hyperplane that best separates the data points into different classes. The hyperplane is chosen such that the margin between the hyperplane and the closest data points from each class is maximized. Decision Tree works by recursively splitting the data into subsets based on the values of the input features until a stopping criterion is met. The stopping criterion can be a maximum depth, a minimum number of samples per leaf, or a minimum reduction in impurity. Logistic Regression works by modeling the probability of the input data point belonging to a certain class using a logistic function that maps any real-valued input to a value between 0 and 1, which can be interpreted as a probability.
On the other hand, unsupervised learning algorithms are used to find patterns in data without any prior knowledge of the data’s structure. Some widely used supervised learning algorithms include: K-Means Clustering that works by partitioning the data into k clusters based on the similarity of the data points. The algorithm starts by randomly selecting k centroids and then iteratively assigns each data point to the nearest centroid. The centroids are then updated based on the mean of the data points assigned to them, and the process is repeated until convergence. Hierarchical Clustering works by creating a hierarchy of clusters by recursively merging the most similar clusters. The algorithm starts by treating each data point as a separate cluster and then iteratively merges the two closest clusters until all the data points belong to a single cluster. These two algorithms are used for clustering tasks. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) works by finding the principal components of the data, which are the directions in which the data varies the most. The algorithm then projects the data onto these principal components, reducing the dimensionality of the data while retaining most of the information. The t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) works by mapping high-dimensional data to a low-dimensional space while preserving the pairwise distances between the data points. The algorithm is particularly useful for visualizing complex, nonlinear structures in the data. We reviewed studies that utilize the classical machine learning approach in this section.
A. Ahmed et al. [
10] proposed a method for recognizing the intentions of cyber attackers based on similarity analysis. They defined two types of attack intentions: General and Specific. The general intentions correspond to the security objectives of availability, confidentiality, and integrity, while the specific intentions refer to the actual attacks or violations such as DDoS. The main contribution of their paper is the creation of attack patterns, which are the key to intention recognition. The attack patterns are constructed by extracting the features of the main attributes of the known attacks and formulating them as evidence. The second contribution is the improvement in the process of investigating the similarity between the created patterns and the new attacks, which is the core of their method. They devised a similarity metric-based algorithm using the fuzzy min-max (FMM) neural network technique. The algorithm compares a new attack with the existing attack patterns and evaluates the level of similarity between them to identify the attacker’s intentions. Their method is able to create a new class of signature or pattern if the new attack is not similar to any of the existing patterns. The authors claimed that their method provides useful information and increases the possibility of recognizing attack intentions in advance by eliminating similar cases using the FMM neural network model. They tested their method on a subset of the page block dataset and demonstrated its high accuracy and efficiency.
Considering the fact that, criminals often use slang expressions to communicate, plan, and execute their illicit activities online, to capture the hidden meanings and intention behind these expressions, Ricardo R. de Mendonça et al. [
25] proposed a novel framework to detect and classify criminal intentions in social media texts ciphered with slangs. The framework, called Ontology-Based Framework for Criminal Intention Classification (OFCIC), combines Semantic Web, Semiotics, Speech Act Theory, and Machine Learning techniques to select, decipher, and classify posts with criminal slang expressions according to their illocutionary classes, which are the types of speech acts that convey the speaker’s intention. The framework consists of four main steps: (1) data collection and preprocessing, (2) ontology-based post-selection, (3) ontology-based post deciphering, and (4) intention classification. The framework utilizes machine learning models such as SVM, Neural Networks, and Random Fields to classify the texts according to their criminal intent. They show that their framework can effectively identify posts with criminal slang expressions, translate them into standard language, and classify them into eight illocutionary classes: Proposal, Inducement, Forecast, Wish, Assertion, Valuation, Palinode, or Contrition. The authors evaluated the framework on a dataset of 8.8 million tweets and demonstrated its effectiveness in automatically classifying criminal intentions from social media texts with slangs. The paper contributes to the field of cybercrime prevention by providing a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach to analyze social media slang-ciphered texts in Portuguese.
The article by S. Abarna et al. [
26] presents an algorithm for detecting cyber harassment and intention from text on social media platforms, using Instagram comments as a case study. The paper utilizes a conventional scheme that analyzes the lexical meaning of the text using natural language processing techniques, and a Fast Text model that captures the word order of the text. The authors perform various preprocessing steps to normalize and contextualize the text, and then employ a Bag of Words (BOW) model and a Word2Vec technique to transform the words into vectors. To identify the intention of the comments, such as bullying, threatening, or trolling, they use a probabilistic similarity technique that compares the vector representations of the words. The authors also devise a score for intention detection that incorporates the frequency of words and the bully-victim participation score, which quantifies the degree of engagement of the users in the cyber harassment scenario. They evaluate the effectiveness of their algorithm using various metrics and benchmark it against seven existing methods, including RF, SVM, and Bi-LSTM. They demonstrate that their algorithm outperforms all the other methods in terms of precision, recall, and F1-score. The authors conclude that their algorithm achieves superior accuracy and lower error rate than the state-of-the-art methods and that it can robustly detect cyber harassment and its intention on social media platforms.
T. Li et al. [
27] proposed a novel approach to recognize multi-step attacks by employing a hidden Markov model with probabilistic reasoning. As multi-step attacks have interrelated attack steps, to accurately obtain the internal relationship between different attacks they employed the concept of temporal relationship. Considering the dynamic characteristics of the network, they employed runtime rule updating. Furthermore, rather than analyzing the intents of each attack, they consider higher-level Intrusion Intent Recognition and apply probabilistic reasoning. They built three algorithms: The parameter Estimation Algorithm to estimate the parameters of the HMM model for alerts correlation; the Attack intent Inference Algorithm to infer the attack intent based on the observation sequence for possible attack intent recognition; and the Attack Prediction Algorithm to analyze the possible attack sequence for possible attack prediction. They built three models based on the Hidden Markov Model (HMM), HMM with Probabilistic inference (HMM-PI), and HMM-PI with Updated Conditional Probability Table (CPT) Model (HMM-PI-UCM), and experimented with the LLDOS1.0 dataset from MIT, compared the three models, and HMM-PI-UCM model performed better.
Table 3.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: Using Classical Machine Learning Method.
Table 3.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: Using Classical Machine Learning Method.
| Article |
Sub-Domain |
Approach |
Intent Level |
Accuracy |
| 2018, A. Ahmed et al. [10] SAIRF: A similarity approach for attack intention recognition using fuzzy min-max neural network |
General Attack |
Fuzzy min-max neural network |
Intent |
94.74% |
| 2020, R. de Mendonça et al. [25] A framework for detecting intentions of criminal acts in social media: A case study on Twitter |
Social Media |
Similarity Based |
Intent |
True Positive: 83.7 False Negative: 4.2 |
| 2020, T. Li et al. [27] Attack plan recognition using hidden Markov and probabilistic inference |
General Attack |
Hidden Markov |
Plan |
- |
| 2022, S. Abarna et al. [26] Identification of cyber harassment and intention of target users on social media platforms |
Social Media |
Similarity |
Intent |
Precision: 91.45% |
4.2.1. Summary
The Classical machine learning-based approach is employed by researchers to address the limitations of logic-based methods, particularly those related to rigidity and manual knowledge encoding. Additionally, this approach is well-suited for handling uncertainties, as it leverages probability. The introduction of probability also proves valuable in managing partial observability and handling various data noises.
The landscape within the subdomain has undergone a significant shift, transitioning from a focus primarily on network security (in the case of logic-based approaches) to encompassing a broader range of cases [
10,
27]. Additionally, researchers have delved into identifying intents related to social media utilization, as explored by [
25,
26]. Notably, the work by T. Li et al. [
27] stands out as it operates at a higher level of plan recognition, while the remaining studies primarily address intent or goal recognition.
However, this method also faces several limitations. Some of these are akin to logic-based approaches, including scalability issues due to the challenges posed by scaling probabilities. Additionally, as the number of parameters increases, manual input becomes necessary. Furthermore, the approach has specific limitations, notably a lack of applicability as understanding how conclusions are inferred can be challenging. This becomes particularly critical in applications related to digital forensics, where explainability is a mandatory requirement.
4.3. Deep Learning
Deep Learning approaches use deep neural networks to learn high-level features and representations from data that can be used to recognize the actions, plans, and goals of the observed agent. They usually do not require any domain knowledge or feature engineering, but they need a huge amount of labeled data to train the networks. They can handle complex and multimodal data, but they may not be interpretable or explainable. They also may overfit the data or suffer from catastrophic forgetting.
Some widely used deep learning algorithms include Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These are deep learning networks that are commonly used for image recognition tasks. They work by applying convolutional filters to the input image to extract features and then passing these features through a series of fully connected layers to make a prediction. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): These are deep learning networks that are commonly used for sequence prediction tasks such as speech recognition and natural language processing. They work by processing the input sequence one element at a time and maintaining an internal state that captures the context of the sequence. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): These are deep learning networks that are used for generating new data that is similar to the training data. They work by training two networks: a generator network that generates new data and a discriminator network that tries to distinguish between the generated data and the real data. The two networks are trained together in a process called adversarial training. Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTMs): These are deep learning networks that are commonly used for sequence prediction tasks such as speech recognition and natural language processing. They work by maintaining an internal state that captures the context of the sequence and using this state to make predictions. Different researchers applied these algorithms to solve IR challenges related to DF domain, and we dedicate this section to review them.
U. Navalgund et al. [
28] proposed a deep learning-based system that can detect criminal intentions in real-time videos and images captured by CCTV cameras in various locations. The system aims to enhance the crime control and prevention capabilities of the existing surveillance infrastructure. The system employs and evaluates different pre-trained models, such as VGGNet-19 and GoogleNet InceptionV3, to identify and localize objects of violence, such as guns and knives, in the input data. The experimental results show that VGGNet-19 outperforms GoogleNet InceptionV3 in terms of accuracy and efficiency in detecting crime objects and inferring criminal intents. They also use Faster RCNN to draw bounding boxes over the detects guns and knives. Furthermore, the system incorporates an SMS alert mechanism that notifies the relevant authorities when potential crimes are detected.
R. Pandey et al. [
11] proposed a distributional semantic approach to detect malicious intent in Twitter conversations related to sexual assault. The authors aimed to detect the intention by building a typology for malicious intent using social construction theory. The typology includes three categories of intent: accusational, validational, and sensational. The accusational category refers to messages that accuse someone of sexual assault or harassment. The validational category refers to messages that validate the experience of sexual assault or harassment. The sensational category refers to messages that focus more on politics or provocation than on the issue of rape or sexual assault. The authors adopted a convolutional neural network to model the system and tested their model using Twitter messages collected over four months. They compared their model against several baseline models and found that their system performed better.
In order to detect query-based adversarial black-box attacks on deep neural networks (DNNs) at an early stage, R. Pang et al. [
29] introduce a model called AdviMind. The model has three variants: Naive Intent Estimator which only serves as a passive observer of the adversaries’ queries. It provides a baseline understanding of intent but lacks robustness and proactive features. Robust Intent Estimator which is built upon the naive model, and capable of identifying fake queries even in the presence of adversarial noise. It maintains reliability while estimating intent. Proactive Intent Solicitation which is the most advanced model, not only estimates intent robustly but also actively prompts adversaries to reveal their true intent. By synthesizing query results, it deters successful attacks and achieves early-stage detection. Empirical evaluation of the models on different datasets demonstrates that these models can detect attack intents with an accuracy of over 75% after observing fewer than 3 query batches. Additionally, they increase the query cost of adaptive attacks by more than 60%.
The paper by J. Zhao et al. [
30] aims to demystify cyber attack intent by analyzing the preference of intruders using a novel framework called HinAp. The framework uses attributed heterogeneous attention networks and transductive learning to analyze the attack preferences of intruders. They first build an attributed heterogeneous information network (AHIN) of attack events to model attackers, vulnerabilities, exploited scripts, compromised devices, and 20 types of meta-paths describing interdependent relationships among them, in which attribute information of vulnerabilities and exploited scripts are embedded. Then, they propose the attack preference prediction model based on attention mechanism and transductive learning. They collected social data to train and test their model. Finally, an automated model for predicting cyber attack preferences is constructed by stacking these two basic prediction models, which are capable of integrating more comprehensive and complex semantic information from meta-paths and meta-graphs to characterize the attack preference of intruders. They compared their model with six other models and their model outperformed all
T. Hsu et al. [
31] proposed an approach to detect malicious activity in physical environments. The proposed method is aimed at reducing the risk of malicious activities by combining three fundamental defense systems, namely access control, surveillance, and host defense systems. Firstly, they employed a multilayer perceptron (MLP) model to identify anomalies in access control systems. By analyzing login attempts and the duration of successful logins, the MLP effectively pinpointed suspicious behavior. Secondly, the researchers harnessed the power of natural language processing (NLP), specifically leveraging techniques like Word2Vec and deep learning, to detect anomalies arising from executed commands. This linguistic analysis provided valuable insights into potentially harmful actions. Thirdly, the team utilized the YOLOv5 object detection model to identify unauthorized entry points. By monitoring physical spaces, they could swiftly detect any breaches. To assess the proximity of individuals to restricted areas, they employed distance measurement methods such as Intersection Over Union (IOU) and Intersection Over Area (IOA). These metrics helped determine whether people were accessing unauthorized zones. Finally, the researchers integrated the results from all three anomaly detection components, aggregating threat scores to generate a comprehensive malicious activity alarm. The authors executed experiments on their model and claimed that their method successfully detected malicious activity.
J. Kang et al. [
32] proposed a framework called ActDetector that detects attack activities automatically from the raw Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS) alerts, which will greatly reduce the workload of security analysts. The framework consists of three components: an extractor, an embedder, and a classifier. The extractor extracts attack phase descriptions by using a knowledge base of adversary tactics and techniques. The embedder uses doc2vec embedding to get the numerical representation of the attack phase descriptions. Finally, the classifier employs a temporal-sequence-based LSTM model to detect the attack activity type from the attack activity description. The authors evaluate ActDetector with three datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that ActDetector can detect attack activities from the raw NIDS alerts with an average of 94.8% Precision, 95.0% Recall, and 94.6% F1-score.
The paper by N. Tsinganos et al. [
33] proposes CSE-PersistenceBERT, a transfer learning-based model that can detect the persistence of chat-based social engineering (CSE) attacks, which are malicious attempts to manipulate the behavior of online users by exploiting their psychological vulnerabilities. The paper argues that persistent CSE attackers use different chat texts to achieve the same malicious goal, such as phishing, fraud, or malware installation, and that recognizing the persistence of CSE attacks is an important step to prevent them from succeeding. The paper adapts BERT-base, a pre-trained language model that has shown impressive results in various natural language processing tasks, and fine-tunes it on a small size corpus that they create, called CSE-Persistence, which contains more than 16 thousand pairs of chat texts, annotated as similar, identical, or different in terms of their intentions. The paper evaluates CSE-PersistenceBERT on a test set of CSE-Persistence and compares it with BERT-base. The paper reports that CSE-PersistenceBERT outperforms the BERT-base in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, demonstrating its effectiveness and robustness in detecting the persistence of CSE attacks. The CSE-PersistenceBERT model can be used as a specific part of a general CSE attack detection system, which can alert the users or the administrators of potential threats and prevent them from falling victim to the CSE attacks.
To add more to the chat-based social engineering (CSE) attack detection system, N. Tsinganos et al. [
34] proposed a deep learning-based model for recognizing the intentions of CSE attacks using dialogue state tracking. They created ontology and a small corpus called SG-CSE and adopted from BERT-based they built a model called SG-CSE BERT. They tested their model by using the dataset to evaluate their approach and achieved promising results.
Q. Tang et al. [
35] present a method for detecting the attack intentions of malicious actors in power systems using graph convolutional networks (GCNs). Their proposed model, called Attack Intention Detection for Power System Using Graph Convolutional Networks (AIGCN), consists of two main steps. First, they identify the abnormal IPs based on their log execution behaviors, using four tuples: destination IP, destination port, event time, and protocol. This step aims to filter out the normal IPs and reduce the noise in the data. Second, they model a graph from the interactive relationship among abnormal IPs, construct an attack graph, and apply a GCN model to learn the patterns and classify the attack intentions. This step leverages the graph structure and the node features to capture the complex and dynamic behaviors of the attackers. They evaluate their model on two datasets that they prepared from real-world network logs and compare it with five baseline methods, such as LSTM and BERT. The results show that AIGCN achieves a high precision of 97.34% and 98.25% for both datasets, outperforming the baseline methods which demonstrates the effectiveness and robustness of the AIGCN model for detecting the attack intentions in power systems.
A. Bhugul et al. [
36] proposed a deep learning model for detecting suspicious activities in private settings such as bank robbery. While security cameras are already commonplace, real-time reaction and 24/7 monitoring are essential for automated detection techniques. This study addresses the critical need for preventive measures against gunshots and terrorist attacks in public areas with heavy foot traffic. The focus of their study is on identifying suspicious human activity related to weapons. Specifically, they consider two parameters, a person with a weapon (gun) and a person wearing a helmet with a weapon. They introduce an algorithm for multiple gun detection using a modified dense deep learning neural network (CNN) model to detect guns from video frames. The temporal complexity of the model across various hardware platforms is also explored, and the proposed system is able to detect all types of guns with an impressive 99.3% accuracy, outperforming existing methods, such as YOLO v3, v4, v5 and SVM.
Table 4.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: using Deep Learning Method.
Table 4.
Summary of Research on IR in DF and Cybercrime: using Deep Learning Method.
| Article |
Sub-Domain |
Approach |
Intent Level |
Accuracy |
| 2018, U. Navalgund et al. [28] Crime Intention Detection System Using Deep Learning |
CCTV |
transfer learning |
intent |
92% |
| 2018, R. Pandey et al. [11] Distributional Semantics Approach to Detect Intent in Twitter Conversations on Sexual Assaults |
social media |
distributional semantic and CNN |
intent |
- |
| 2020, R. Pang et al. [29] AdvMind: Inferring Adversary Intent of Black-Box Attacks |
Black-box attack |
DL |
intent |
75% |
| 2021, J. Zhao et al. [30] Automatically predicting cyber attack preference with attributed heterogeneous attention networks and transductive learning |
social attack |
attention mechanism and transductive learning |
intent |
- |
| 2022, Q. Tang et al. [35] AIGCN: Attack Intention Detection for Power System Using Graph Convolutional Networks |
Network Security |
Graph Convolutional Networks |
Intent |
97.34 % |
| 2022, T. Hsu et al. [31] Detection of Malicious Activities Using Machine Learning in Physical Environment |
access control, surveillance, and host defense systems |
YOLOv5 object detection model |
Intent |
- |
| 2022, J. Kang et al. [32] ActDetector: A Sequence-based Framework for Network Attack Activity Detection |
Network Security |
temporal-sequence-based LSTM |
Activity |
Precision: 94.8% |
| 2022, N. Tsinganos et al. [33] Applying BERT for Early-Stage Recognition of Persistence in Chat-Based Social Engineering Attacks |
Social Engineering Attack |
transfer learning |
Intent |
78.03% |
| 2023, A. Bhugul et al. [36] Novel Deep Neural Network for Suspicious Activity Detection and Classification |
CCTV |
CNN |
Intent |
99.3% |
| 2023, N. Tsinganos et al. [34] Leveraging Dialogue State Tracking for Zero-Shot Chat-Based Social Engineering Attack Recognition |
Social Engineering Attack |
transfer learning |
Intent |
78.03% |
4.3.1. Summary
The deep Learning approach overcomes some of the limitations of the logic-based and classical machine learning approaches. One of the main advantages of the approach is that it can automatically learn features from the data, which means that it doesn’t require the features to be hand-engineered. Because of that they can learn different patterns and uncover non-linear relationships in data that would be difficult to detect through traditional methods. This makes it a useful tool for extracting insights from big data. The approach has paramount importance particularly for tasks where the features are difficult to define, such as image recognition. Deep learning algorithms can handle large and complex datasets that would be difficult for classical machine learning and/or logic-based algorithms to process. Deep learning algorithms are also good at dealing with uncertainty, partial observability, and noise, which makes them a useful tool for intention recognition.
The literature reviewed on deep learning for intention recognition, as shown in the table, reveals that the subdomains have shifted from network security to social media (4 out of 10 articles) and physical security (3 out of 10 articles), while only two article focuses on network security. This shift in focus from network security to social media and physical security suggests that intention recognition is becoming more relevant in these domains. Additionally, a new subdomain related to AI security has emerged. The emergence of this new subdomain highlights the need for intention recognition-based models in the context of securing AI itself. Transfer learning is employed in many cases to improve the performance of deep learning models. This also indicates that deep learning models can benefit from pre-trained models to improve their performance.
However, Deep learning approaches also have several disadvantages. Firstly, they require a large amount of training data to achieve high accuracy, similar to classical machine learning approaches. Secondly, they are not explicable, to the extent that even the designers don’t know how the conclusions are inferred from the input evidence. This lack of transparency can also make it difficult to debug and improve the model. Thirdly, most deep learning models cannot learn new classes from live/online data. This means that if the model encounters a new class of data that it has not seen before, it will not be able to recognize it. Finally, deep learning models require high computational power to train and run, which can be a significant barrier to entry for many researchers and organizations. These limitations can make it challenging to use deep learning approaches for intention recognition in practice.
5. Challenges
IR models face various challenges, as identified by F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13]. While most of these challenges are inherited in the context of digital forensics (DF) and related domains, the magnitude and characteristics of the challenges differ. Our review identified the following challenges, though this is not an exhaustive list:
Contextualization: The need to recognize the context in which an action is performed, as it can affect the interpretation of the action. In digital forensics, the cybercrime context can provide valuable information about the intent of the actor [
19,
21,
23,
25,
26,
28,
35].
Missed activities, partial observability, or handling noise: The difficulty of recognizing an activity, and consequently intent, when only a part of it is observed or when some of the actions are totally missed. It is common to encounter incomplete or partial data about cybercrime. This can make it difficult to recognize an attack or to determine the intent behind it [
20,
22,
35].
Predictive capabilities: The ability to predict future actions based on current observations. Such capabilities can be useful in digital forensics to reconstruct the crime scene and identify potential future attacks, in order to predict the behavior of an attacker [
20,
22,
27].
Handling uncertainty: The need to handle uncertainty in the observations and the predictions. Logic-based systems generally lack such capability, while classical machine learning and deep learning handle it by using probabilistic and statistical approaches. In digital forensics, there is often a high degree of uncertainty as the observed agents try to hide themselves and usually take high precautions. This can make it difficult to determine the intent behind an action or to make accurate predictions [
21,
29].
Managing multiple hypotheses: Different IR models generate multiple hypotheses about the intent of the agent based on the observed activities. It is important to manage these hypotheses and select the most plausible one by evaluating them based on the available evidence [
21,
35].
Multi-step attack: nowadays, attackers instead of attacking immediately, build their attack through time by advancing step by step. Identifying such a situation from network traffic is difficult, and consequently recognizing the intent is challenging [
21,
27].
Scalability: Digital forensics generates a huge volume of heterogeneous data that IR models are expected to scale in the sense of size and type of data as well as the complexity of the environment [
20].
Cooperating agents: The need to recognize the intentions of multiple agents that are cooperating to achieve a common goal. Identifying cooperating agents can help identify the scope and nature of an attack [
10].
Adversarial agents: Such agents can intentionally try to mislead the recognition system by performing actions that are inconsistent with their true intentions [
10,
11,
21,
22,
23,
27,
29].
Understanding the attacker’s ability and belief: This can help in predicting their future actions and identifying potential vulnerabilities [
22,
30,
35].
Lack of standard intent classification: This makes it difficult to compare and evaluate different intent recognition systems [
10,
11,
21,
22,
23].
As most of the works we reviewed are inclined toward detecting active attacks and aiming to prevent them, DF investigation faces additional challenges such as interpretability/ explicability. Interpretability is the ability to explain the reasoning behind the recognition of an action, intent, or plan. It is not only important but also a mandatory requirement in digital forensics, as courts require an explanation as well as supporting evidence to criminalize or free a suspect.
6. Discussion
In this comprehensive review, we delve into the intricate world of intention recognition within the realms of digital forensics and cybercrime. Our investigation involves a meticulous review of existing literature, drawing from reputable journals. Our primary objective is to understand how intention recognition models operate and to identify gaps in the current landscape. Following the categorization proposed by F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13], we categorized the collected papers based on their modeling approaches. This systematic grouping allowed us to discern patterns and variations across different studies.
During our analysis, we see that Researchers often resort to creating their own intent categories or borrowing from prior studies because there are no predefined and specific intention classes. This lack of standardized classes underscores the need for a more comprehensive taxonomy. B. Chen et al. [
21] took a commendable step by attempting to generalize technical intents into security triads (CIA: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability). This broader perspective opens up new avenues for understanding intentions beyond traditional boundaries. Intentions can even be categorized at higher levels such as management level and for digital forensics the legal definitions of intentions can also be considered.
While most works concentrate on cyber attack detection and prevention, there remains a dearth of studies that fully integrate the concept of digital forensics. Bridging this gap is crucial for advancing our understanding of cybercriminal intent.
In the synthesis of findings across the three tables (Tables 2, 3, and 4), a discernible thematic concentration emerges: intent recognition. The majority of scholarly endeavors within this domain are dedicated to unraveling the intricacies of attackers’ intentions. Notably, two studies delve into the realm of plan recognition. The first, conducted by R. Mirsky et al. [
20], adopts a logic-based approach, while the second, authored by T. Li et al. [
27], harnesses classical machine learning paradigms. However, there is only one study for activity recognition by J. Kang et al. [
32], their work employs a sequence-based LSTM framework to detect network attack activities. In practical terms, the pursuit of intent recognition necessitates not only the identification of discrete actions (commonly referred to as activity detection) but also the consideration of state transitions. Consequently, activity recognition becomes an indispensable facet woven into the fabric of each intention recognition study.
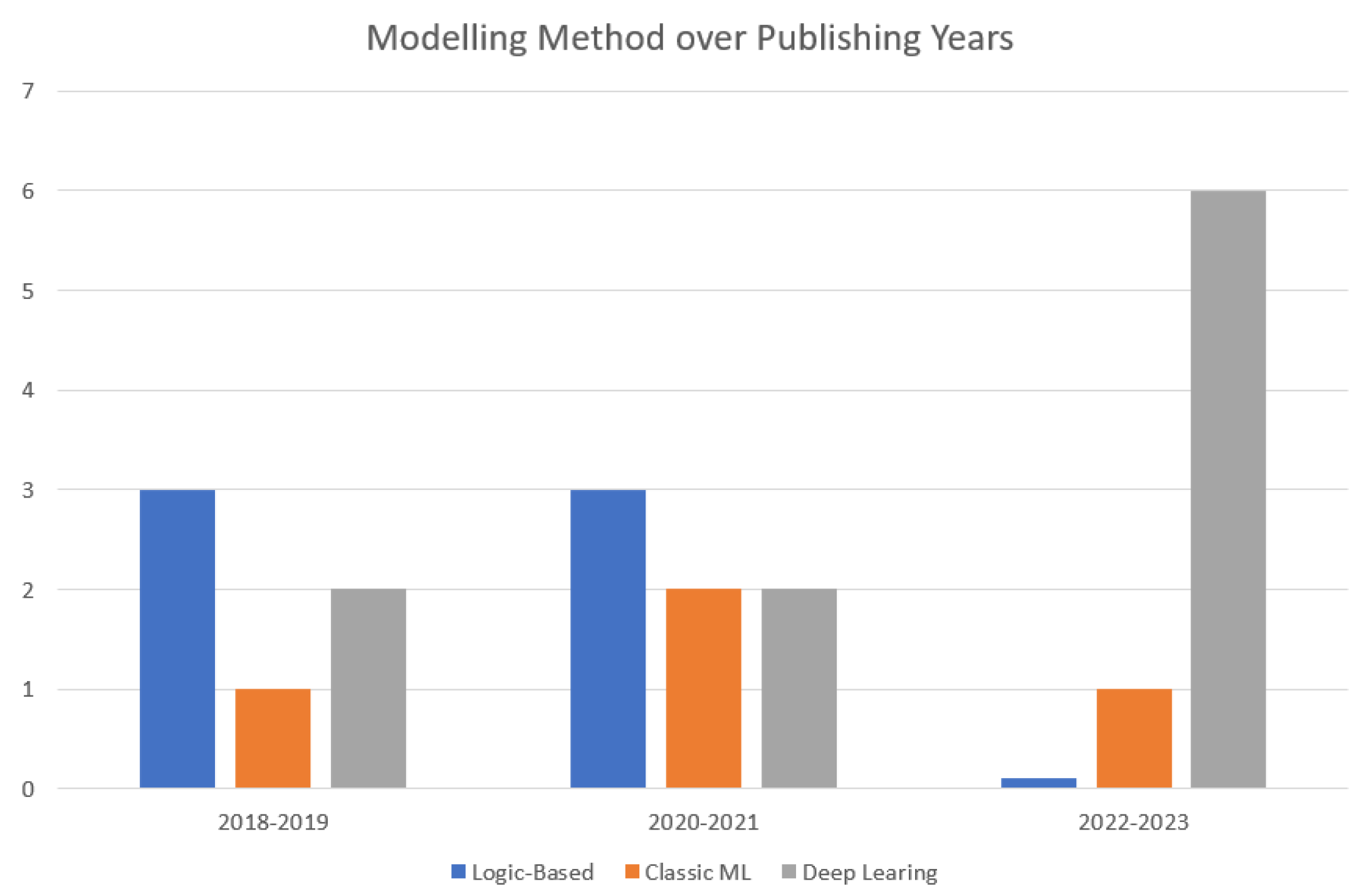
Figure 2.
Transitions of IR Modelling approaches in DF over the years.
Figure 2.
Transitions of IR Modelling approaches in DF over the years.
As shown in the chart, in recent years, the field of modeling intention recognition has undergone a significant transformation. Traditionally, logic-based methods held sway, but now we observe a transition towards machine learning, particularly deep learning. This evolution reflects the dynamic landscape of research and its practical applications. F. Van-Horenbeke et al. [
13] highlight the historical dominance of logic-based approaches in recognizing activity, intent, and planning. However, contemporary trends reveal a surge in the adoption of deep learning techniques. Most current research, as shown on the chart, endeavors to identify malicious intents to prevent cyber attacks. Deep learning models, with their ability to discern intricate patterns from vast data, excel in this domain. However, when dealing with already committed cyber crimes, the explainability requirement becomes paramount. Logic-based approaches, rooted in formal reasoning and rule-based systems, offer a structured framework for post-incident analysis. Their deterministic nature ensures rigorous adherence to predefined rules, making them indispensable in solving complex cases. While Classical machine learning and deep learning models thrive in proactive cybersecurity, they fall short in fulfilling the stringent explainability criteria. So in the context of digital forensic investigation logic-based reasoning and data-driven techniques become essential.
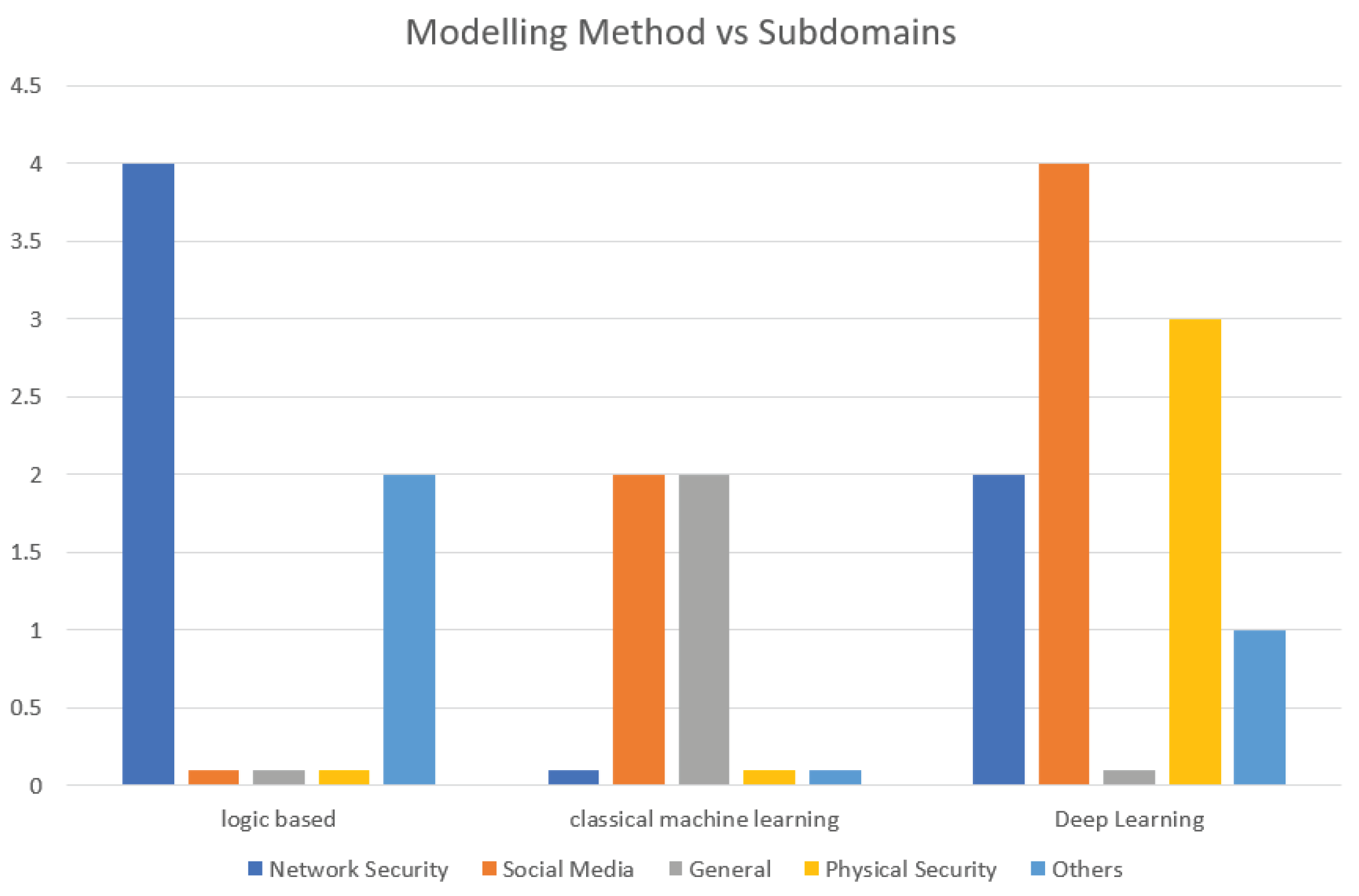
Figure 3.
IR Modelling approaches in DF per Subdomains.
Figure 3.
IR Modelling approaches in DF per Subdomains.
The landscape of intention recognition has expanded beyond its traditional stronghold in network security. While the protection of network infrastructure once dominated this field, recent developments reveal intriguing diversification. Historically, intent recognition found its primary application in safeguarding network boundaries C. Geib [
37]. However, a notable shift has occurred towards Social engineering attacks, which driven by human psychology and manipulation, now prominently employ intent recognition. Classical machine learning and Deep learning techniques are utilized in deciphering the intricate motives of cybercriminals in social engineering attacks. Beyond external threats, intention recognition has turned inward. Researchers explore its application in securing artificial intelligence (AI) systems themselves. As AI algorithms proliferate across domains, safeguarding their integrity and decision-making processes becomes paramount. Intent recognition aids in identifying anomalies, unauthorized access attempts, and adversarial inputs. By scrutinizing AI behavior, we fortify the very systems that drive technological advancements.
This multifaceted journey—spanning network security, social engineering, physical security, database security, AI self-defense, and general security represents a divergence. It serves as a springboard for interdisciplinary exploration. As researchers delve into novel crime types, the intention recognition paradigm adapts. Its fusion with cognitive science, linguistics, and behavioral analysis opens doors to innovative solutions. Whether combating cyber threats or enhancing AI resilience, intention recognition remains a powerful tool.
Finally, Deep learning has emerged as a potent technique for modeling intent recognition, yet it faces limitations in meeting the stringent requirements of digital forensic investigations, particularly with regard to explainability. Courts demand conclusions grounded in robust logical foundations, and mere predictive power is insufficient. Conversely, logic-based approaches, while inherently interpretable, suffer from inefficiencies and inaccuracies due to their susceptibility to human error. To address these challenges, future research endeavors should explore hybrid solutions that synergistically combine the strengths of both deep learning and logic-based methodologies. By leveraging the interpretability of logic-based reasoning alongside the predictive capabilities of deep learning, such hybrid models can mitigate their respective weaknesses. This interdisciplinary approach holds promise for advancing the field of digital forensics, ensuring both rigorous analysis and transparency in decision-making processes.
7. Conclusion and Future Work
In this systematic literature review, we meticulously examined the contributions of intention recognition within the digital forensics and cybercrime domain. Our study followed a rigorous six-step approach, including protocol development and adherence. The following can be considered as the key takeaways: First, Categorization of Research: We meticulously curated research articles from reputable journals. These studies were classified into three distinct modeling approaches: logic-based, classical machine learning-based, and deep learning-based. Second, Expanding Beyond Network Security: Our analysis revealed a significant shift in the application of intention recognition. While it was predominantly utilized for network security in the past, we now observe its adoption across various cyber security subdomains. Notably, intention recognition plays a pivotal role in addressing challenges related to social engineering attacks, AI black box vulnerabilities, and physical security. Third, Deep Learning Dominance: Among the modeling approaches, deep learning (DL) has emerged as the de facto choice. Its ability to overcome limitations associated with other methods has positioned DL at the forefront. However, a critical consideration arises in the context of digital forensics: the need for explainability.
Fourth, The Explainability Conundrum: In the digital forensics domain, explainability is not merely desirable; it is mandatory. DL models, while powerful, often lack transparency. Therefore, researchers should seize this opportunity to explore hybrid solutions. Combining the strengths of DL with interpretable techniques such as a logic-based approach could yield more robust and accountable intention recognition systems. Fifth, Taxonomy Development: we emphasize the importance of defining intention recognition more precisely, especially within the context of digital forensics. To address this, we propose the creation of a comprehensive taxonomy and formal definition. Such a framework would provide clarity, and standardization, and facilitate further advancements in this critical field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, Y.K., and supervision, writing—review and editing, J.J.; and supervision, writing—review and editing, E.B.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DF |
Digital Forensics |
| DFI |
Digital Forensics Investigation |
| IR |
Intention Recognition |
| DL |
Deep Learning |
Appendix A
The following Data extraction sheet is used to extract the data from each article reviewed.
Table A1.
Data Extraction Sheet.
Table A1.
Data Extraction Sheet.
| Article |
DF Category |
Content Type |
Modeling Approach |
Sub-domain |
Level of IR |
Targeted Problem |
| - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
References
- Malik, J.K.; Choudhury, S. Cyber Space - Evolution and Growth. East African Scholars Journal of Education, Humanities and Literature 2019, 2, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanaso, U.M.; Dandaura, E.S. The Cyberspace: Redefining A New World. IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering 2015, 17, 2278–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados Franco, E. Global Risks 2020: An Unsettled World. The Global Risks Report 2020, pp. 8–17.
- Kent, K.; Chevalier, S.; Grance, T.; Dang, H. Guide to Integrating Forensic Techniques into Incident Response. The National Institute of Standards and Technology 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO/IEC 27037:2012 Information technology — Security techniques — Guidelines for identification, collection, acquisition and preservation of digital evidence. ISO 2012, p. 38.
- Quick, D.; Choo, K.K.R. Impacts of increasing volume of digital forensic data: A survey and future research challenges. Digital Investigation 2014, 11, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S. Digital forensic research: current state of the art. CSI Transactions on ICT 2013, 1, 91–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S. Data mining: Data mining concepts and techniques; 2014; pp. 203–207. [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, U.; Piatetsky-Shapiro, G.; Smyth, P. From data mining to knowledge discovery in databases. AI Magazine 1996, 17, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Mohammed, M.F. SAIRF: A similarity approach for attack intention recognition using fuzzy min-max neural network. Journal of Computational Science 2018, 25, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Purohit, H.; Stabile, B.; Grant, A. Distributional Semantics Approach to Detect Intent in Twitter Conversations on Sexual Assaults. 2018 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI), 2018, pp. 270–277. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Gan, Y. Intrusion intention recognition and response based on weighed plan knowledge graph. COMPUTER MODELLING & NEW TECHNOLOGIES 2014, 18, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Van-Horenbeke, F.A.; Peer, A. Activity, Plan, and Goal Recognition: A Review. Frontiers in Robotics and AI 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Ahlami, N.; Zaman, K. Attack Intention Recognition : A Review 2017. 19, 244–250. [CrossRef]
- Jesson, J.; Matheson, L.; Lacey, F.M. Doing your literature review: Traditional and systematic techniques 2011.
- Okoli, C.; Schabram, K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research 2010.
- Caulley, D.N. Conducting research literature reviews: From the internet to paper. Qualitative Research Journal 2007, 7, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jill K. Jesson, L.M.; Lacey, F.M. Doing your Literature Review; 2016; pp. 57–67. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B. Cyber Situation Comprehension for IoT Systems based on APT Alerts and Logs Correlation. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsky, R.; Shalom, Y.; Majadly, A.; Gal, K.; Puzis, R.; Felner, A. New Goal Recognition Algorithms Using Attack Graphs. Cyber Security Cryptography and Machine Learning; Dolev, S., Hendler, D., Lodha, S., Yung, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 260–278. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Gao, X. Attack Intent Analysis Method Based on Attack Path Graph. Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Communication and Network Security; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.; Doshi, P.; Setayeshfar, O. Cyber Attack Intent Recognition and Active Deception Using Factored Interactive POMDPs. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems; International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems: Richland, SC, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Shin, D.; Shin, D.; Kim, Y.H. Attack Detection Application with Attack Tree for Mobile System using Log Analysis. Mobile Networks and Applications 2019, 24, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Sun, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Network Attack Intention Recognition Based on Signaling Game Model and Netlogo Simulation. 2021 International Conference on Digital Society and Intelligent Systems (DSInS), 2021, pp. 162–166. [CrossRef]
- de Mendonça, R.R.; de Brito, D.F.; de Franco Rosa, F.; dos Reis, J.C.; Bonacin, R. A framework for detecting intentions of criminal acts in social media: A case study on twitter. Information (Switzerland) 2020, 11, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarna, S.; Sheeba, J.I.; Jayasrilakshmi, S.; Devaneyan, S.P. Identification of cyber harassment and intention of target users on social media platforms. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2022, 115, 105283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Nguyen, N.A. Attack plan recognition using hidden Markov and probabilistic inference. Computers and Security 2020, 97, 101974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navalgund, U.V.; K., P. Crime Intention Detection System Using Deep Learning. 2018 International Conference on Circuits and Systems in Digital Enterprise Technology (ICCSDET), 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ji, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, T. AdvMind: Inferring Adversary Intent of Black-Box Attacks. Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Yan, Q.; Li, B.; Shao, M.; Peng, H.; Sun, L. Automatically predicting cyber attack preference with attributed heterogeneous attention networks and transductive learning. Computers and Security 2021, 102, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.; Tang, C. Detection of Malicious Activities Using Machine Learning in Physical Environments. 2022 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI); IEEE Computer Society: Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 2022; pp. 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhan, M.; Wang, W. ActDetector: A Sequence-based Framework for Network Attack Activity Detection. 2022 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), 2022, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Tsinganos, N.; Fouliras, P.; Mavridis, I. Applying BERT for Early-Stage Recognition of Persistence in Chat-Based Social Engineering Attacks. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinganos, N.; Fouliras, P. Leveraging Dialogue State Tracking for Zero-Shot Chat-Based Social Engineering Attack Recognition 2023.
- Tang, Q.; Chen, H.; Ge, B.; Wang, H. AIGCN: Attack Intention Detection for Power System Using Graph Convolutional Networks. Journal of Signal Processing Systems 2022, 94, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhugul, A.M.; Gulhane, V.S. Novel Deep Neural Network for Suspicious Activity Detection and Classification. 2023 IEEE International Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science (SCEECS), 2023, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Geib, C.W.; Goldman, R.P. Plan recognition in intrusion detection systems. Proceedings DARPA Information Survivability Conference and Exposition II. DISCEX’01, 2001, Vol. 1, pp. 46–55 vol.1. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).