Submitted:
15 March 2024
Posted:
18 March 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.2. Genomic DNA (gDNA) Extraction and Analysis
2.3. Search for Mango Simple Sequence Repeat Markers and Choice of PCR Primers
2.4. PCR Amplification and SSR Fragment Analysis
2.5. Denaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
2.6. Band Recording DATA Analysis for DNA Fingerprinting
2.7. Staistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Amplification of Mango Cultivars using SSR Markers
3.2. Distribution of Unique SSRs with Polymorphism
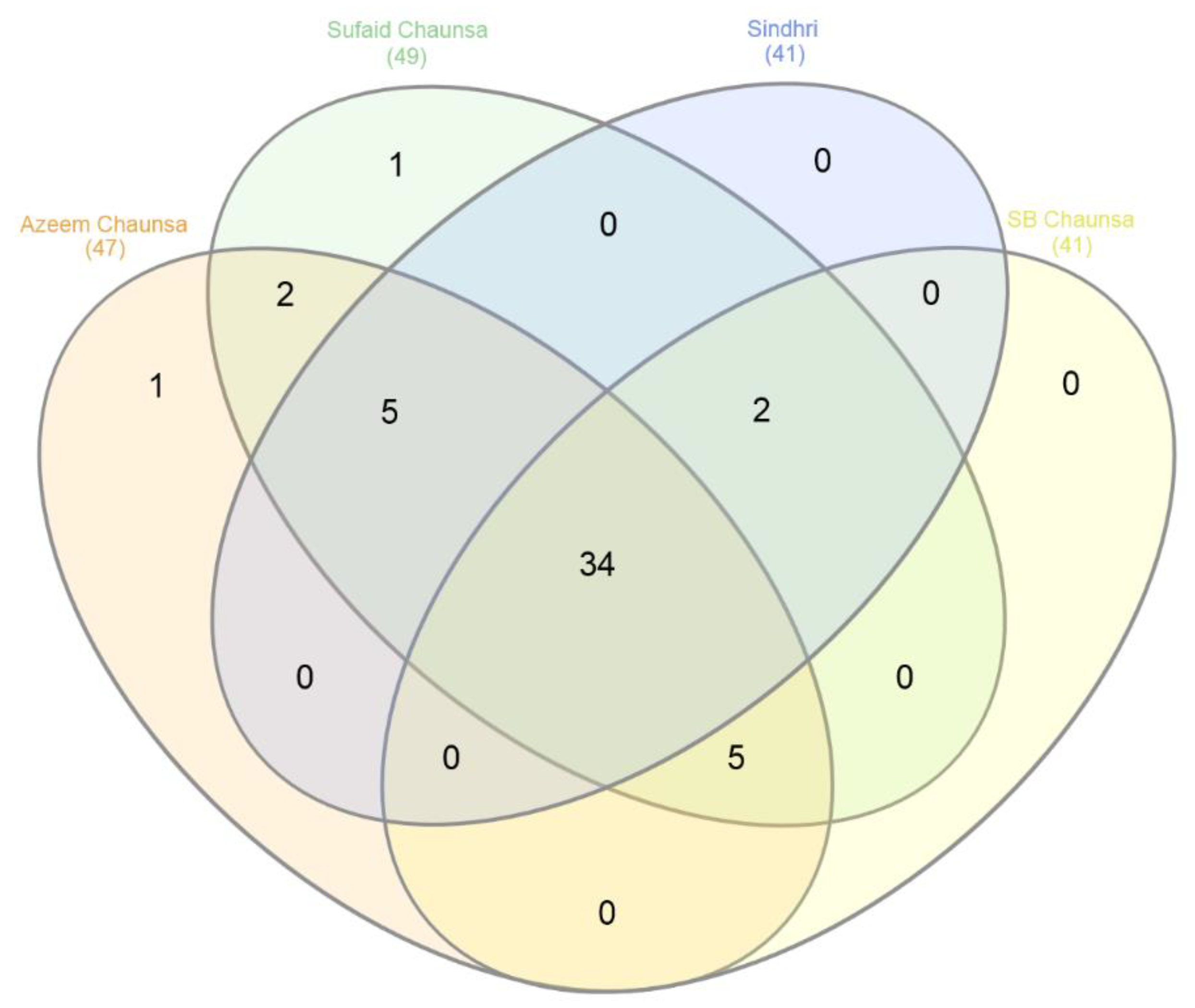
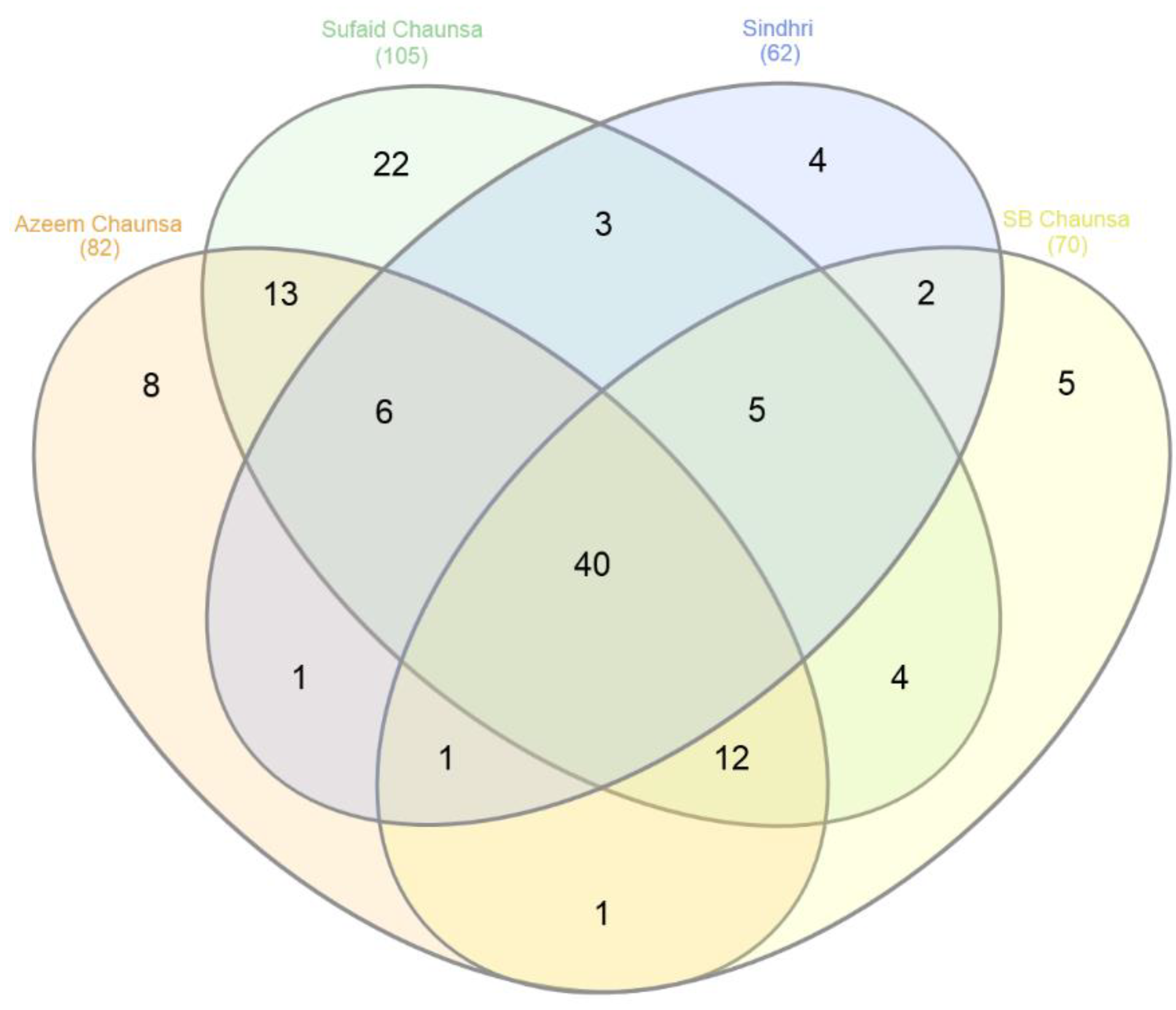
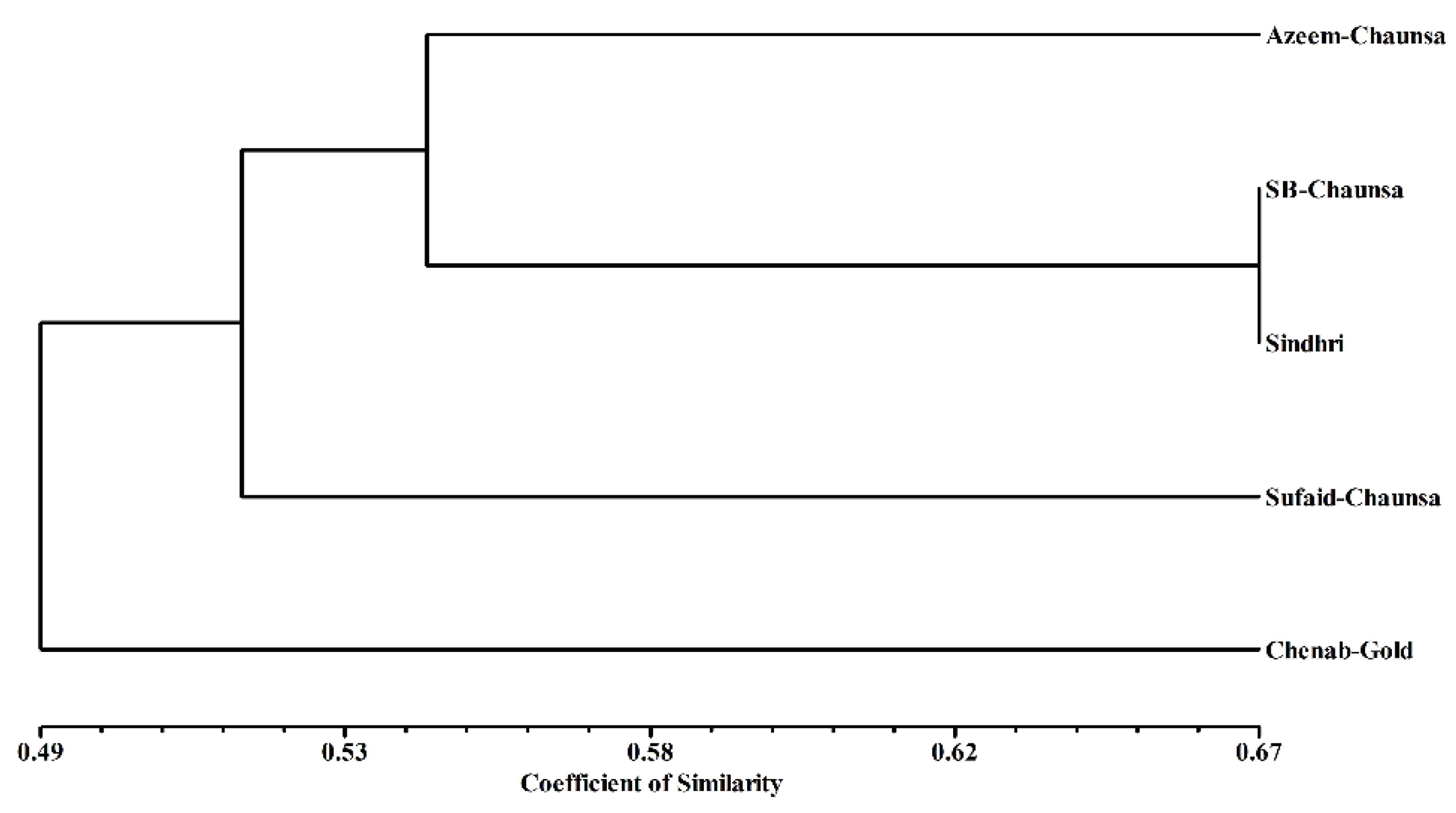
3.3. SSR Fingerprinting/ Allelic Diversity
3.5. DNA Fingerprinting Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Litz, R.E. The mango: botany, production and uses; Cabi, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khanum, Z.; Tiznado-Hernández, M.E.; Ali, A.; Musharraf, S.G.; Shakeel, M.; Khan, I.A. Adaptation mechanism of mango fruit (Mangifera indica L. cv. Chaunsa White) to heat suggest modulation in several metabolic pathways. RSC advances 2020, 10, 35531–35544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, G.; Aka Kaçar, Y.; Shimira, F.; Iftikhar, S.; Nadeem, M.A. Recent progress in omics and biotechnological approaches for improved mango cultivars in Pakistan. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 2022, 69, 2047–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, F.; Davenport, T.L. Mango (Mangifera indica L.) pollination: a review. Scientia Horticulturae 2016, 203, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.K. Mango: its allopolyploid nature. Nature 1950, 166, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Luo, Y.; Huang, J.; Gao, S.; Zhu, G.; Dang, Z.; Gai, J.; Yang, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H. The genome evolution and domestication of tropical fruit mango. Genome biology 2020, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, A.; Rubinstein, M.; Eshed, R.; Benita, M.; Ish-Shalom, M.; Sharabi-Schwager, M.; Rozen, A.; Saada, D.; Cohen, Y.; Ophir, R. Mango (Mangifera indica L.) germplasm diversity based on single nucleotide polymorphisms derived from the transcriptome. BMC Plant Biology 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, A.K.; Sharma, N.; Singh, A.; Srivastav, M.; Jaiprakash; Singh, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Sharma, T.R.; Singh, N.K. Leaf transcriptome sequencing for identifying genic-SSR markers and SNP heterozygosity in crossbred mango variety ‘Amrapali’(Mangifera indica L.). PloS one 2016, 11, e0164325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Huang, H.; Ma, H. Advances in sequencing and key character analysis of mango (Mangifera indica L.). Horticulture Research 2023, 10, uhac259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carella, A.; Gianguzzi, G.; Scalisi, A.; Farina, V.; Inglese, P.; Bianco, R.L. Fruit growth stage transitions in two mango cultivars grown in a Mediterranean environment. Plants 2021, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samal, K.; Jena, R.; Swain, S.; Das, B.; Chand, P. Evaluation of genetic diversity among commercial cultivars, hybrids and local mango (Mangifera indica L.) genotypes of India using cumulative RAPD and ISSR markers. Euphytica 2012, 185, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Kiran, S.; Hussain, S.; Iqbal, R.K.; Ghafoor, U.; Younis, U.; Zarei, T.; Naz, M.; Germi, S.G.; Danish, S. Acidified biochar confers improvement in quality and yield attributes of sufaid chaunsa mango in saline soil. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Hosaka, F.; Matsumura, M.; Onoue-Makishi, Y.; Nashima, K.; Urasaki, N.; Ogata, T.; Shoda, M.; Yamamoto, T. Genetic diversity and relatedness of mango cultivars assessed by SSR markers. Breeding science 2019, 69, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, B.; Xu, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Qian, M.; Wu, H. Identification of F1 hybrid progenies in mango based on Fluorescent SSR markers. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.A.; Eid, M.; Rahimi, M.; Filimban, F.Z.; Abd El-Moneim, D. Comparative Assessment of SSR and RAPD markers for genetic diversity in some Mango cultivars. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.C.; Tsai, C.M.; Chen, Y.K.H.; Lee, S.R.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Tsai, C.C. Development and characterization of 20 new polymorphic microsatellite markers from Mangifera indica (Anacardiaceae). American journal of botany 2012, 99, e117–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, N.L.; Innes, D.J.; Bally, I.S.; Wright, C.L.; Devitt, L.C.; Dietzgen, R.G. Expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) marker resources for diversity analysis of mango (Mangifera indica L.). Diversity 2014, 6, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, K.V.; Mani, B.H.R.; Anand, L.; Dinesh, M.R. Development of new microsatellite markers from Mango (Mangifera indica) and cross-species amplification. American Journal of Botany 2011, 98, e96–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venison, E.P.; Litthauer, S.; Laws, P.; Denancé, C.; Fernández-Fernández, F.; Durel, C.-E.; Ordidge, M. Microsatellite markers as a tool for active germplasm management and bridging the gap between national and local collections of apple. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 2022, 69, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.T.; Qu, C.Q.; Cao, B.Y. An optimal method of DNA silver staining in polyacrylamide gels. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, X.; Li, R.; Xia, Y.; Bai, G.; Siddique, K.H.; Guo, P. A fast silver staining protocol enabling simple and efficient detection of SSR markers using a non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) 2018, e57192. [Google Scholar]
- Azmat, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Khan, I.A.; Rajwana, I.A.; Cheema, H.M.N.; Khan, A.S. Morphological characterization and SSR based DNA fingerprinting of elite commercial mango cultivars. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2016, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bally, I.S.; Dillon, N.L. Mango (Mangifera indica L.) breeding. Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Fruits: Volume 3 2018, 811–896. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, M.-F.; Bunel, J.; Sitbon, C.; Risterucci, A.-M. Development of microsatellite markers for mango (Mangifera indica L.). Molecular Ecology Notes 2005, 5, 824–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, R.; Olano, C.; Quintanilla, W.; Meerow, A. Isolation and characterization of 15 microsatellite loci from mango (Mangifera indica L.) and cross-species amplification in closely related taxa. Molecular Ecology Notes 2005, 5, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, K.V.; Dinesh, M.; Nischita, P.; Sandya, B. Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in mango (Mangifera indica) using next-generation sequencing technology and their transferability across species. Molecular Breeding 2015, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, P. Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Nat. 1908, 44, 223–270. [Google Scholar]
- FJ, R. NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.1; Exeter Software: New York, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gandrud, C. Reproducible research with R and RStudio; Chapman and Hall/CRC: 2018.
- Campbell, R.; Zill, G. Mango selection and breeding for alternative markets and uses. In Proceedings of the VIII International Mango Symposium 820; 2006; pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, V.N.; Crane, J.; Freeman, B.; Kuhn, D.; Chambers, A.H. Mango seedling genotyping reveals potential self-incompatibility and pollinator behavior. Scientia Horticulturae 2023, 308, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, K.V.; Bommisetty, P.; Bajpai, A.; Srivastava, N.; Mani, B.H.; Vasugi, C.; Rajan, S.; Dinesh, M.R. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis of mango (Mangifera indica) cultivars assessed by microsatellite markers. Trees 2015, 29, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surapaneni, M.; Vemireddy, L.R.; Begum, H.; Purushotham Reddy, B.; Neetasri, C.; Nagaraju, J.; Anwar, S.; Siddiq, E. Population structure and genetic analysis of different utility types of mango (Mangifera indica L.) germplasm of Andhra Pradesh state of India using microsatellite markers. Plant Systematics and Evolution 2013, 299, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ying, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, R. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Fingerprint Construction of Major Mango Cultivars in China. Agricultural Science & Technology 2016, 17, 1289. [Google Scholar]
- Razak, S.A.; Azman, N.H.E.N.; Ismail, S.N.; Yusof, M.F.M.; Ariffin, M.A.T.; Sabdin, Z.H.M.; Hassan, M.H.M.; Nasir, K.H.; Sani, M.A.; Abdullah, N. Assessment of diversity and population structure of mango ('Mangifera indica'L.) germplasm based on microsatellite (SSR) markers. Australian Journal of Crop Science 2019, 13, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Ali, S.; Khan, I.A. Morphological and molecular characterization and evaluation of mango germplasm: An overview. Scientia Horticulturae 2015, 194, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez-López, D.; Hernández-Delgado, S.; González-Paz, M.; Becerra-Leor, E.N.; Salvador-Figueroa, M.; Mayek-Pérez, N. Genetic analysis of mango landraces from Mexico based on molecular markers. Plant Genetic Resources 2009, 7, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Alabart, N.; Serratosa, F.; Gómez, S.; Fernández, A. Nonunique UPGMA clusterings of microsatellite markers. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbac312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SSR Primer Pair ID | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| LMMA1F | ATGGAGACTAGAATGTACAGAG | ATTAAATCTCGTCCACAAGT |
| LMMA7F | ATTTAACTCTTCAACTTTCAAC | AGATTTAGTTTTGATTATGGAG |
| LMMA9F | TTGCAACTGATAACAAATATAG | TTCACATGACAGATATACACTT |
| mMiCIRO14 | GAGGA CATAAAGATGGTG | GACAAGATAAACAAC TGGAA |
| mMiCIRO18 | CCTCAATCTCACTCAACA | ACCCCACAATCAAACTAC |
| mMiCIRO32 | TCATTGCTGTCCCTTTTC | ATCGCTCAAACAATCC |
| MiSHRS-1 | TAACAGCTTTGCTTGCCTCC | TCCGCCGATAAACATCAGACA |
| MiSHRS-48 | TTTACCAAGCTAGGGTCA | CACTCTTAAACTATTCAACCA |
| MIAC-4 | CGTCATCCTTTACAGCGAACT | CATCTTTGATCATCCGAAAC |
| MIAC-6 | CGCTCTGTGAGAATCAAATGGT | GGACTCTTATTAGCCAATGGGAG |
| MGDSSR1 | CGAAATGAGACACCTGCAAA | TTTCCTCCATTGCTTTTTCG |
| MGDSSR2 | GGGAATGGTAGAGACGGACA | ATCCAAGCAGTCACCATCAA |
| MGDSSR5 | CGATAGTGCCAATCTGGTGA | TCATCTCACACACTCTCTCTCTCTC |
| MGDSSR11 | GGGAATGGTAGAGACGGACA | TTCATCATAGGTCCCACACG |
| MGDSSR14 | AATGCTGAGCCTGGTAAGGA | CAACATCCTCTTTCTTCCCTGT |
| MGDSSR34 | GAAAGTGAGACCTTCGGTTCC | AAGGCCCCTTCTTCACATTT |
| MillHR21 | TTTGGCTGGGTGATTTTAGC | TTAATTGCAGGACTGGAGCA |
| mMiCIR005 | GCCCTTGCATAAGTTG | TAAGTGATGCTGCTGGT |
| mMiCIR009 | AAAGATAAGATTGGGAAGAG | CGTAAGAAGAGCAAAGGT |
| mMiCIR013 | GCGTAAAGCTGTTGACTA | TCATCTCCCTCAGAACA |
| mMiCIR016 | TAGCTGTTTTGGCCTT | ATGTGGTTTGTTGCTTC |
| mMiCIR030 | GCTCTTTCCTTGACCTT | TCAAAATCGTGTCATTTC |
| MiSHRS-37 | CTCGCATTTCTCGCAGTC | TCCCTCCATTTAACCCTCC |
| MIAC-11 | GTGCGAGGAGATATCTGT | CTGGTTCTTCATTGTTGAGATG |
| MITGI75 | TGCGTCTTGTGTGTGTGTGT | GGAATGCTGTGTGTGTGTG |
| MITGg62 | TGTTCGATTTGCAAACTTTTT | GGCCTAATGTGTGTGTGTG |
| MICA231-1 | TGGAAGGACCATGCTTGAAT | GGTCACACACACACACACA |
| MICA235 | TGTCACACACACACACACA | AATGGAAGGACCATGCTTGA |
| MIGA2O3 | TGAAGGATAGGTGTGGTG | CATGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGA |
| MIGA224 | CACGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGA | GGGTCTCAGAGGGAGGATTT |
| MIAC251-1 | CCTTGGGTTCATTCGCTAAA | GGACGCCACACACACACAC |
| MIAC251-2 | TGGCGCTACACACACACAC | CACACACACACACACACACG |
| LMMA8 | CATGGAGTTGTGATACCTAC | CAGAGTTAGCCATATAGAGTG |
| MillHR04c | CGTTTTTGACCCTCTTGAGC | CCGCATACTTCCCTTCACAT |
| MillHR06 | CGCCGAGCCTATAACCTCTA | ATCATGCCCTAAACGACGAC |
| MillHR07a | GCCACTCAGCTAAATAGCCTCT | TGCAGTCGGTAAAGTGATGG |
| MillHR11a | CAGTGAAACCACCAGGTCAA | TGGCCAGCTGATACCTTCTT |
| MillHR20a | CCTAACGCGCAAGAAACATA | ACCCACCTTCCCAATCTTTT |
| AJ635164 | AAACAAAGAATGGAGCA | TGGACTGAATGTGGATAG |
| AY942826 | TGTGAAATGGAAGGTTGAG | ACAGCAATCGTTGCATTC |
| AJ635178 | GTATAAATCGCGTGCAT | AGTTTCCCTCCTTGTATCT |
| AJ635187 | ATCCCCAGTAGCTTTGT | TGAGAGTTGGCAGTGTT |
| AY942817 | TAACAGCTTTGCTTGCCTCC | TCCGCCGATAAACATCAGAC |
| AY942825 | CGAGGAAGAGGAAGATTATGAC | CGAATACCATCCAGCAAAATAC |
| AJ635166 | CTTGAAAGAGATTGAGATTG | AGAAGGCAGAAGGTTTAG |
| AJ635184 | TGTCTACCATCAAGTTCG | GCTGTTGTTGCTTTACTG |
| AY942820 | AGGTCTTTTATCTTCGGCCC | AAACGAAAAAGCAGCCCA |
| AB190349 | AATTATCCTATCCCTCGTATC | AGAAACATGATGTGAACC |
| AY942828 | CTCGCATTTCTCGCAGTC | TCCCTCCATTTAACCCTCC |
| AJ635189 | ACGGTTTGAAGGTTTTAC | ATCCAAGTTTCCTACTCCT |
| SSR Marker ID | Sufaid Chaunsa | Sindhri | SB Chaunsa | Azeem Chaunsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMA1F | 290, 295 | 310 | 290, 295, 310 | 295 |
| LMMA7F | 260 | 205, 220, 260, 340 | 220, 340 | 220, 340 |
| LMMA9F | 205 | 0 | 200, 205 | 200 |
| mMiCIRO14 | 210 | 205 | 0 | 160, 200, 210 |
| mMiCIRO18 | 195, 240, 250, 350 | 380 | 250 | 250, 280 |
| mMiCIRO32 | 190, 200 | 200 | 190, 200 | 190, 200 |
| MiSHRS-1 | 180 | 175, 180 | 175, 240 | 210 |
| MiSHRS-48 | 180, 190, 200 | 180 | 180, 210, 220 | 180, 200, 280 |
| MIAC-4 | 90, 125 | 90, 125 | 90 | 90, 100, 125 |
| MIAC-6 | 250 | 0 | 250 | 390 |
| MGDSSR1 | 205 | 205 | 205 | 205 |
| MGDSSR2 | 260, 270 | 260 | 150, 260 | 0 |
| MGDSSR5 | 155, 295 | 155, 190, 300 | 160, 300 | 300 |
| MGDSSR11 | 190, 240, 390 | 190, 240, 390 | 200, 240 | 190, 240 |
| MGDSSR14 | 150, 200, 225, 250 | 150 | 150, 225 | 200 |
| MGDSSR34 | 150, 190 | 150, 190 | 150, 190 | 100, 150, 175, 180 |
| MillHR21 | 140, 310, 400, 425 | 400 | 140, 400, 425 | 140, 310, 400, 425 |
| mMiCIR005 | 210, 240, 250 | 210, 240 | 250 | 230 |
| mMiCIR009 | 175, 240 | 175, 220, 240 | 220 | 220 |
| mMiCIR013 | 160, 220 | 160, 220 | 160, 220 | 160, 220 |
| mMiCIR016 | 250, 260, 280, 360 | 260 | 250, 260, 280 | 250 |
| mMiCIR030 | 230, 245, 250 | 245, 250, 295 | 180, 245, 290, 295 | 180, 290 |
| MiSHRS-37 | 200, 220 | 200 | 140, 245 | 140, 200 |
| MIAC-11 | 145, 150 | 145, 150 | 145, 150 | 145 |
| MITGI75 | 110, 150, 175 | 175 | 0 | 100, 110 |
| MITGg62 | 450 | 175, 200 | 200 | 170, 200, 450 |
| MICA231-1 | 300 | 600 | 195, 300, 620 | 320, 600 |
| MICA235 | 120, 200, 400 | 0 | 400 | 200 |
| MIGA2O3 | 155, 275 | 155 | 155 | 155, 275, 380 |
| MIGA224 | 250, 300 | 250 | 300 | 250, 300 |
| MIAC251-1 | 350, 600, 700 | 350, 600 | 350, 600 | 350, 600, 700 |
| MIAC251-2 | 200 | 175, 200 | 175, 200 | 200 |
| LMMA8 | 480 | 430 | 0 | 430 |
| MillHR04c | 160, 250 | 160 | 0 | 160 |
| MillHR06 | 105 | 0 | 120 | 105 |
| MillHR07a | 160 | 0 | 160 | 160 |
| MillHR11a | 190, 220, 290 | 220 | 220 | 190, 220 |
| MillHR20a | 0 | 0 | 0 | 190 |
| AJ635164 | 240, 380 | 240 | 240 | 240, 380 |
| AY942826 | 225 | 0 | 0 | 225 |
| AJ635178 | 240 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AJ635187 | 240, 250 | 290 | 290 | 240 |
| AY942817 | 200, 210, 250 | 200 | 190, 200 | 210, 250 |
| AY942825 | 230, 260, 280 | 260 | 0 | 260 |
| AJ635166 | 225, 250, 290 | 225 | 225 | 225, 290 |
| AJ635184 | 160, 165, 190 | 175 | 165 | 165, 175 |
| AY942820 | 200, 205, 250 | 205, 250 | 200, 250 | 205, 250 |
| AB190349 | 130 | 130 | 130 | 0 |
| AY942828 | 130, 135, 160 | 0 | 0 | 135 |
| AJ635189 | 145, 155 | 145 | 145 | 145, 155 |
| SSR Primer Pair ID | Tm °C | Allele Size (bp) | No. of Loci | No. of Polymorphic loci | Polymorphic loci % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMA1F | 59 | 290-310 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| LMMA7F | 55 | 205-340 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| LMMA9F | 56 | 200-205 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| mMiCIRO14 | 57 | 160-210 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| mMiCIRO18 | 59 | 195-380 | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| mMiCIRO32 | 57 | 190-200 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| MiSHRS-1 | 65 | 175-240 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| MiSHRS-48 | 57 | 180-280 | 6 | 5 | 83.33 |
| MIAC-4 | 59 | 90-125 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| MIAC-6 | 65 | 250-390 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| MGDSSR1 | 62 | 205 | 1 | 0 | - |
| MGDSSR2 | 65 | 150-270 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| MGDSSR5 | 65 | 155-300 | 5 | 5 | 100 |
| MGDSSR11 | 65 | 190-390 | 4 | 3 | 75 |
| MGDSSR14 | 65 | 150-250 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| MGDSSR34 | 65 | 100-190 | 5 | 4 | 80 |
| MillHR21 | 64 | 140-425 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| mMiCIR005 | 58 | 210-250 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| mMiCIR009 | 57 | 175-240 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| mMiCIR013 | 60 | 160-220 | 2 | 0 | - |
| mMiCIR016 | 58 | 250-360 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| mMiCIR030 | 55 | 180-295 | 6 | 6 | 100 |
| MiSHRS-37 | 65 | 140-245 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| MIAC-11 | 61 | 145-150 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| MITGI75 | 65 | 100-175 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| MITGg62 | 59 | 170-450 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| MICA231-1 | 65 | 195-600 | 5 | 5 | 100 |
| MICA235 | 65 | 120-400 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| MIGA2O3 | 60 | 155-380 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| MIGA224 | 63 | 250-300 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| MIAC251-1 | 64 | 350-700 | 3 | 1 | 33.33 |
| MIAC251-2 | 65 | 175-200 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| LMMA8 | 60 | 430-480 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| MillHR04c | 65 | 160-250 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| MillHR06 | 65 | 105-120 | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| MillHR07a | 65 | 160 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MillHR11a | 65 | 190-290 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| MillHR20a | 64 | 190 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| AJ635164 | 56 | 240-380 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| AY942826 | 60 | 225 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| AJ635178 | 57 | 240 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| AJ635187 | 61 | 240-290 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| AY942817 | 65 | 190-250 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| AY942825 | 62 | 230-280 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| AJ635166 | 56 | 225-290 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| AJ635184 | 59 | 160-190 | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| AY942820 | 64 | 200-250 | 3 | 2 | 66.66 |
| AB190349 | 57 | 130 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| AY942828 | 65 | 130-160 | 3 | 3 | 100 |
| AJ635189 | 58 | 145-155 | 2 | 1 | 50 |
| SSR Loci ID | Nature | Polymorphic type | Polymorphic alleles (N.) | Allele size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMA1F | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 295 |
| LMMA7F | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 220, 340 |
| LMMA9F | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 200 |
| mMiCIRO14 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 3 | 160, 200, 210 |
| mMiCIRO18 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 250, 280 |
| mMiCIRO32 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 190, 200 |
| MiSHRS-1 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 210 |
| MiSHRS-48 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 180, 200, 280 |
| MIAC-4 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 90, 100, 125 |
| MIAC-6 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 390 |
| MGDSSR1 | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | 205 |
| MGDSSR2 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 0 | 0 |
| MGDSSR5 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 300 |
| MGDSSR11 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 190, 240 |
| MGDSSR14 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 200 |
| MGDSSR34 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 3 | 100, 150, 175, 180 |
| MillHR21 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 3 | 140, 310, 400, 425 |
| mMiCIR005 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 230 |
| mMiCIR009 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 220 |
| mMiCIR013 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 0 | 160, 220 |
| mMiCIR016 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 250 |
| mMiCIR030 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 180, 290 |
| MiSHRS-37 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 140, 200 |
| MIAC-11 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 0 | 145 |
| MITGI75 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 100, 110 |
| MITGg62 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 3 | 170, 200, 450 |
| MICA231-1 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 320, 600 |
| MICA235 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 200 |
| MIGA2O3 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 155, 275, 380 |
| MIGA224 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 250, 300 |
| MIAC251-1 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 350, 600, 700 |
| MIAC251-2 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 0 | 200 |
| LMMA8 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 430 |
| MillHR04c | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 160 |
| MillHR06 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 105 |
| MillHR07a | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | 160 |
| MillHR11a | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 190, 220 |
| MillHR20a | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | 190 |
| AJ635164 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 240, 380 |
| AY942826 | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | 225 |
| AJ635178 | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | 0 |
| AJ635187 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 240 |
| AY942817 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 210, 250 |
| AY942825 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 260 |
| AJ635166 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 225, 290 |
| AJ635184 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 2 | 165, 175 |
| AY942820 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 205, 250 |
| AB190349 | monomorphic | dominant | 0 | - |
| AY942828 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 135 |
| AJ635189 | polymorphic | co-dominate | 1 | 145, 155 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





