Introduction:
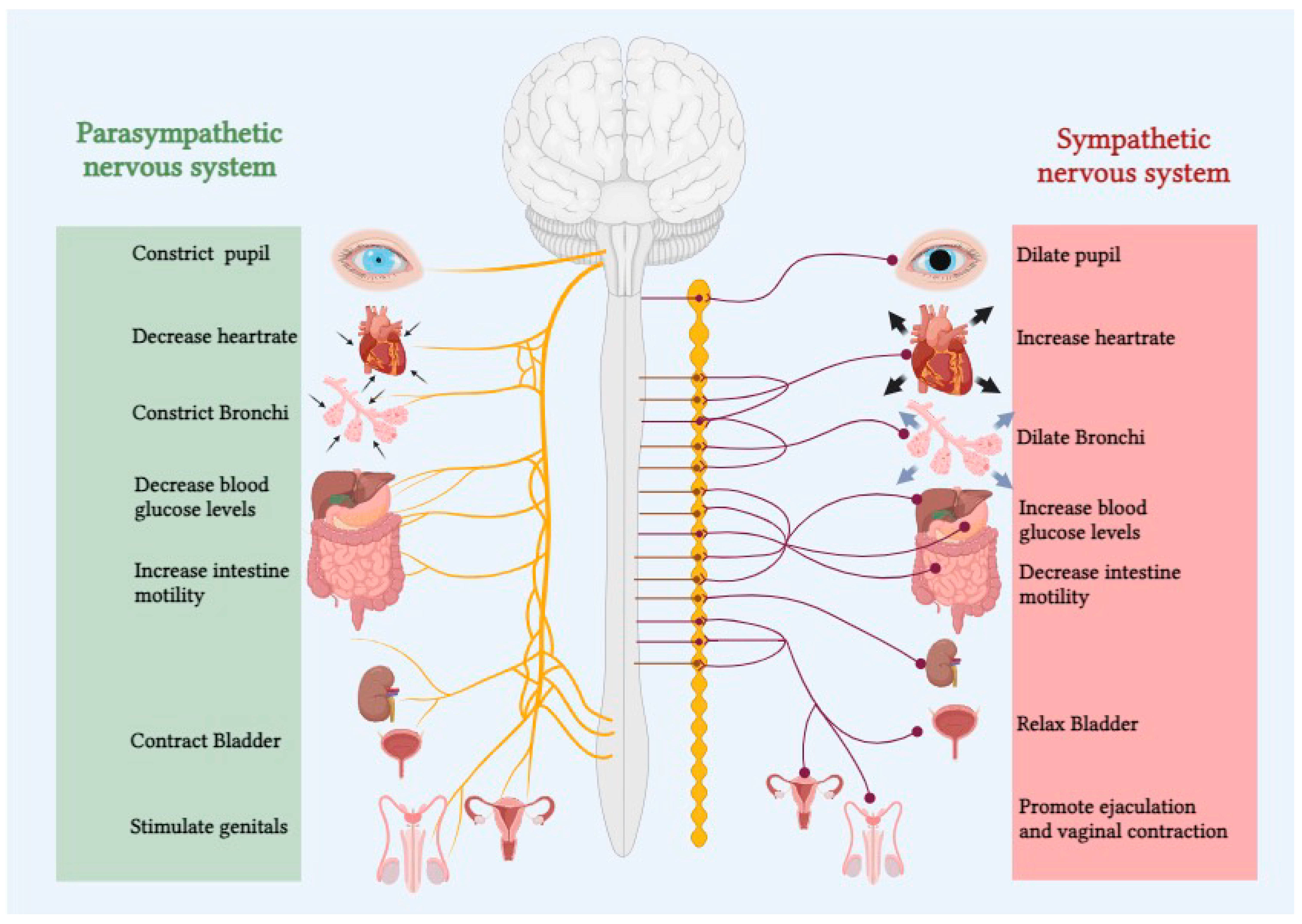
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a pivotal role in regulating various physiological functions essential for maintaining homeostasis within the human body. Comprising the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, the ANS dynamically modulates heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and other vital functions in response to internal and external stimuli (
Figure 1).[
1,
2] The delicate balance between these opposing branches is crucial for overall well-being. In recent years, the significance of quantifying autonomic system balance has gained prominence in both clinical and research settings.[
3,
4] Accurate measurement of ANS activity provides valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of numerous physiological and pathological processes, aiding in the assessment, diagnosis, and management of various health conditions. As a result, a myriad of methodologies and techniques have been developed to capture the intricate interplay between sympathetic and parasympathetic activities.
Autonomic balance measurement has an important role in the clinical assessment of several disorders which affect autonomic neurons, and these range from neurological, cardiovascular to gastrointestinal pathophysiologies.[
5] The assessment of autonomic balance involves measuring physiological parameters which are regulated by the two component of autonomic nervous system (ANS) namely; sympathetic and parasympathetic systems[
6,
7] or alternatively directly measuring the neurotransmitters of sympathetic (norepinephrine) and parasympathetic (acetylcholine) system. Autonomic function is influenced by multiple factors including circadian rhythm, medications, body position and emotional state therefore making most current approaches to measuring autonomic balance difficult in clinical settings where continuous or frequent monitoring is necessary.[
1,
8]
The two components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) operate in close proximity, demonstrating a somewhat antagonistic innervation pattern that enables precise regulation of bodily systems. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS), commonly referred to as the "fight or flight" system, responds to stressors primarily through adrenergic receptors.[
1,
2,
8] With exceptions such as the coronary arteries and vessels of skeletal muscles and external genitalia, heightened SNS tone generally leads to vasoconstriction.[
1,
2,
3,
8] Additional functions of the SNS include pupil dilation and adjustment of the eyes for distant vision, augmentation of cardiac output, bronchodilation in the lungs, relaxation of the detrusor muscle, contraction of the urinary sphincter, suppression of the immune system, and promotion of glycolysis and lipolysis.[
2,
9] Conversely, the Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), often referred to as “rest and digest”, acts on five muscarinic receptors allowing rest and preservation of energy.[
2,
8,
9] Increased PNS tone promotes blood vessels to dilate, and the alveoli in lungs to constrict. It also induces pupil constriction and adjusts the eyes for near vision, promotes gut motility, decreases cardiac output, aids urinary output by contraction of detrusor muscle and relaxation of urinary sphincter, and actively promotes energy conservation and increase glycogen synthesis.[
2,
8,
9]
In this review we aim to comprehensively examine the current state of literature on the measurement of autonomic system balance with a focus on different applications of autonomic balance measurement in various healthcare settings. By synthesizing and critically evaluating existing studies, we seek to elucidate the strengths, limitations, and advancements in methodologies employed for assessing autonomic function. Additionally, we will explore the diverse applications of these measures across different populations, from healthy individuals to those with specific medical conditions.
Methods
This review employed a systematic approach to identify relevant studies. We searched the Google Scholar database (
https://scholar.google.com), using a combination of keywords and Boolean operators tailored to our research question. The search was performed between 1
st July to 30
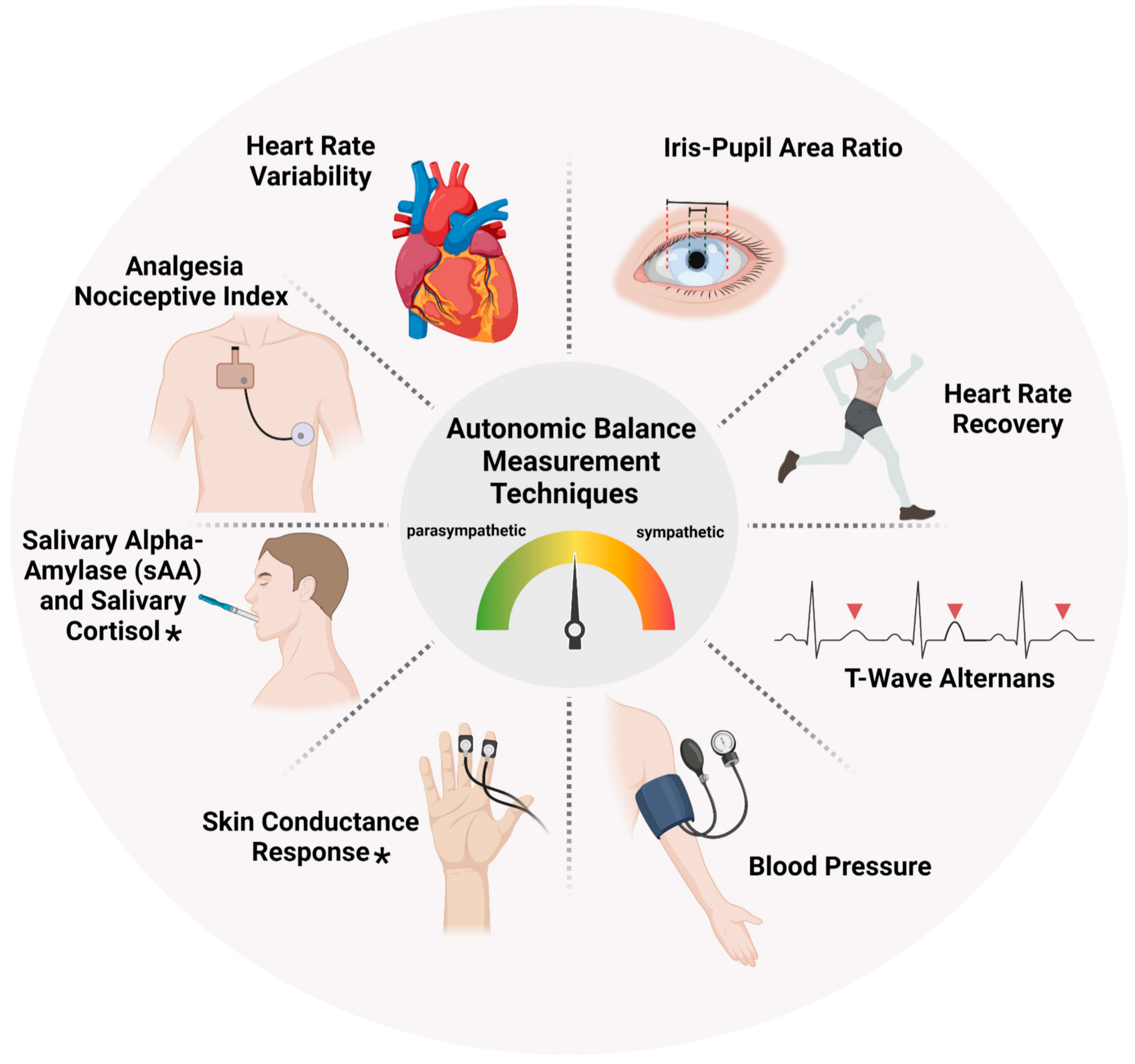
th November 2023. The search terms encompassed ‘autonomic balance’, ‘measurement’, ‘autonomic nervous system’, ‘sympathetic balance’, ‘parasympathetic balance’ and ‘clinical setting’. We limited the search to articles published from 2000 onwards and included only those written in English. Studies were then selected based on pre-defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Included studies were randomized controlled trials, observational/interventional and general investigational studies. To be eligible, studies had to focus on use of at least any one autonomic balance measurement tool highlighted in
Figure 2. Conversely, we excluded animal studies, case reports, studies with methodological limitations.
Following the initial search, reference management software (Endnote version 21) was used to screen titles, abstracts, and full texts based on the inclusion criteria mentioned above. This process ensured consistency and facilitated the identification of relevant articles. A final set of studies comprising of 50 articles were identified, and data extraction was conducted using a standardized form. This form captured key information such as study design, participant characteristics, interventions employed, and reported outcomes. The data analysis strategy was determined based on the nature of the included studies and the research question of assessing the utility of autonomic balance measurement in clinical practice. A narrative synthesis was employed to provide a comprehensive overview of the findings, identify key themes and patterns across studies. It is important to acknowledge both the strengths and limitations of our methodology. The use of a systematic search strategy and pre-defined criteria helped to minimize bias and ensure the transparency of the selection process. However, limitations include the potential for publication bias, which favours studies with statistically significant findings, and the exclusion of non-English language articles, which might limit the generalizability of our results.
Results
Cardiovascular System
Several tests have been implicated in the measurement of autonomic cardiovascular reflexes.[
2,
8,
9] The Valsalva manoeuvre, isometric handgrip test, active standing and head-up tilt test are all used to measure the efficiency of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) for the control of blood pressure.[
2,
8,
9] However, these tests may be affected by age, sex and medications taken. Heart rate variability (HRV)[
2,
8,
9] is one of the most popular non-invasive methods of ANS measurement, through 24-hour ECG recording or even at 5 minute intervals, to evaluate the influence of different factors on sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulations.[
2,
8,
9] This is done by using fluctuations in RR intervals to evaluate how heart rate is modulated by the ANS. Decreased RR variability could indicate a pathological process and may be useful in various clinical settings.[
8,
10] It has been established that HRV is an early predictor of brain death and that reduced HRV is associated with increased mortality and morbidity after trauma.[
8,
10] It is also related to increased intracranial pressure and decreased cerebral perfusion pressure. In the setting of trauma, HRV has been shown to have implications in pre-hospital and hospital settings. It was reported that HRV was a more accurate predictor of major injury and has applications for life-saving measures than heart rate, systolic blood pressure and Glasgow coma scale.[
9,
10] Also, a 2007 study by Proctor et al. showed that specific HRV patterns correlated with the presence of traumatic brain injury on CT as well as mortality.[
9,
11] Additionally, the HRV algorithm can be altered to take into account patient-specific factors to further refine its diagnostic and prognostic ability.[
9,
11] Furthermore, the diagnostic merit of HRV is supported by the use of its separate low frequency and high frequency components. Its low frequency component is predominantly determined by vagal activity which underlines the parasympathetic system’s importance in cardiac regulation.[
9,
12] The ratio between the low frequency and high frequency HRV can be used as a measure of autonomic balance in the context of cardiovascular regulation.[
9,
12] Despite these merits of HRV, one of the major limitations of relying on HRV for measuring autonomic balance is a large array of paracrine factors independent of ANS which can influence it.
Cardiac autonomic dysfunction is linked to several cardiovascular diseases and increased risk of mortality,[
4,
12] and this can be measured using heart rate decrement after exercise which can be quantified by heart rate recovery (HRR). HRR can be used to measure autonomic activity and could also predict mortality.[
4,
12] HRR is characterised by a fast phase which is mediated by a rapid decline in heart rate through vagal stimulation, whereas the slow phase causes a more gradual decline in heart rate and is mediated by vagal reactivation in addition to sympathetic withdrawal.[
1,
4] Sympathetic overactivation can damage cardiomyocytes through coronary constriction and malignant ventricular arrhythmias.[
1,
4] Population cohort studies have shown that HRR is an independent predictor of all-cause cardiovascular mortality. It was also found that an abnormally low HRR value was predictive of all-cause mortality regardless of age, gender, exercise capacity and other medical comorbidities.[
1,
4] Surprisingly, HRR was shown to be a better prognostic indicator than the 6-minute walk test.[
1,
4,
13] However, it is important to mention that exercise and recovery protocols employed by each study varies widely and similar to HRV several paracrine factors can also influence HRR.
Recently, Chinaka and Kumar[
6] reported the merit of Iris-pupil area ratio (IPR) as a predictor of myocardial infarction, supporting the role of non-invasive tools for the measurement of autonomic balance in relation to cardiovascular health. Thus, this could be a novel method for predicting myocardial infarctions. Moreover, unlike the influence of several paracrine factors on HRV and HRR, the IPR based assessment of autonomic balance is exclusively under the control of ANS under constant light intensity conditions. Hence under clinical setting where light intensity remains constant, the IPR based approach offers a specific and much sensitive system for the assessment of autonomic balance.
Neurovascular system
HRV has also been used to identify autonomic dysfunction after an acute stroke,[
3] specifically for cardiac complications such as arrhythmias and ischemic heart damage.[
3] This is specifically influenced by levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and adrenaline released by the ANS. Results by Esref et al,[
3] revealed that patients with right middle cerebral artery lesions had significant autonomic dysfunction, with increased HRV, suggesting cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction. These patients also had higher catecholamine levels, which implies that possibly HRV monitoring after acute stroke could help prevent cardiovascular complications. Interestingly, Colvicchi et al.,[
14] and Korpelainen et al.,[
15] have suggested that stimulation of the right insular cortex increases sympathetic cardiovascular activity, whereas left insular cortex stimulation influences parasympathetic tone. Thus, HRV monitoring could be a useful measure of predicting cardiovascular outcomes after ischemic stroke.
Patients with acute ischemic stroke often show impaired autonomic function, characterized by sympathetic activity predominance.[
16] Raedt et al.,[
16] correlated the right and left insular ischemia with ventricular arrhythmias and prolonged QT interval. Additionally, experimental and human studies have implied that coagulation and platelet activation may be influenced by sympathetic stimulation which increases the risk for further vascular events.[
17] Although studies investigating the role of the ANS in recurrent stroke or thrombotic events are lacking, Sander et al.,[
17] reported that recurrent stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA) and myocardial infarctions during 1 year follow-up only occurred in ischemic stroke patients who initially had increased serum norepinephrine levels. Aside from the acute phase after stroke, cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction may persist up to six months after stroke and parasympathetic dysfunction predominates.[
18] However, studies are conflicting over whether sympathetic or parasympathetic dysfunction predominates, hence more studies under randomised settings are necessary to validate the findings. Nevertheless, autonomic function after acute stroke could be considered for monitoring of therapeutic progress and as a prognostic indicator.
Furthermore, autonomic balance measurement has been implicated as an early marker of dementia. A study by Femminella et al.,[
19] revealed that autonomic dysfunction in common subtypes of dementia may be caused by generalized underactivity of the cholinergic system which is indirectly influenced by the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. There are six stages of Alzheimer's dementia (AD),[
20] on the basis of progressive involvement of the insular cortex and brainstem, which are major structures involved in autonomic control. Thus, neurodegeneration of these structures before other regions could mean that autonomic dysfunction may serve as the ‘early clinical’ stage of AD, making it a possible biomarker of neurodegeneration. Collins et al.,[
21] examined autonomic dysfunction in patients with mild cognitive impairment which represents the earliest stage of dementia and reported significant autonomic dysfunction (measured by Ewing battery of autonomic tests) in these patients compared to controls. Additionally, a predominance of parasympathetic dysfunction is also reported in patients with mild cognitive impairment, suggesting the pivotal role of cholinergic system in cognitive function.
Autonomic balance measurement has also been shown to be useful in patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. In these patients, Vagus nerve (Cranial nerve X) stimulation is thought to have cardioprotective effects against sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP).[
22] Markedly elevated levels of T-wave alternans and fluctuations in the morphology of the ST or T-wave segments is observed in these patients, which is a marker for sudden cardiac death and these levels are doubled during seizures, which increases the risk for life-threatening arrhythmias in those who have background cardiovascular disease.[
23,
24] It has also been suggested that the sympathetic tone of the heart is increased as measured by HRV, and this is an independent predictor of mortality in patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy.[
22] Schomer et al.,[
22] measured autonomic balance with T-wave alternans, HRV and KF/HF ratio in patients with drug resistant epilepsy and used vagal nerve stimulation to modulate them. In these patients, repeated seizures lead to hypoxemia and increased catecholamine levels which could be the basis for the pathologic cardiac changes, ultimately causing ischemia. In the interictal period, SNS dominance was confirmed at baseline, with decreased levels of Vagus nerve activity compared to healthy controls.[
22] Upon initiation of vagal nerve stimulation, Schomer et al report a reduced HRV and LF/HF ratio, making it plausible that autonomic balance was shifted in favour of increased PNS activity and decreased SNS activity which both contribute to a reduction in T-wave alternans and hence SUDEP by reducing cardiac electrical instability.[
22]-[
24] Therefore, autonomic balance measurement and modulation could be of merit in improving mortality and morbidity from cardiovascular effects of drug-resistant epilepsy.
Pain and Inflammation Management
Autonomic cardiac control has also been implicated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.[
4,
13,
25] It was observed that not only was basal heart rate significantly higher in these patients, but there were also lower variations in parasympathetic activity. Compared to controls, rheumatoid arthritis patients also had less vagal withdrawal and lower sympathetic response compared to healthy controls. Thus, it was inferred that an inability of the ANS to efficiently compensate for internal and external environmental changes imply a decreased HRV and so put rheumatoid arthritis patients at a high risk of arrythmias.[
4,
13,
25] Hence, ANS evaluation and measurement could be useful in planning management of these patients and anticipation of cardiovascular complications.
The ANS and autonomic balance has been implicated in pain, with regards to nociceptive and anti-nociceptive balance. In pain monitoring for anaesthesia, assessment of analgesia is based on unspecific ‘clinical end points’ of movement, tachycardia or hypertension. In the current day, rapid detection of nociceptive input is performed through evaluation of autonomic balance, hence supporting its merit in pain measurement in those unable to verbalise.[
26] The analgesia nociceptive index (ANI) is based on HRV and has been proposed to be reflective of pain levels in the postoperative period.[
27] A small but significant correlation was found between ANI and higher states of sedation,[
27] but it cannot be used to differentiate between minor and severe pain. This is because anaesthetic agents may affect sympathetic function and act as confounding factors, thus, more research needs to be conducted in this area.[
27]
The ANS tone is strongly influenced by anaesthetic drugs, and various studies have supported the use of HRV for pain measurement.[
28] Novel measurement methods of ANI can be used to inform the anaesthetist of the pain/analgesia balance during general anaesthesia, in order to optimize drug delivery.[
28] Logier et al describe PhysioDoloris, a monitoring device for nociceptive balance in real-time using HRV during and after surgery to optimize pain management. However, it is important to note that ANI and influences on the ANS could be due to multiple factors.[
28] It is reported that ANI values of less than 50% mean sympathetic activation only which could often be related to insufficient analgesia/nociception balance.[
28] Therefore, although this is a new field with limited literature, the merit of ANS measurement and significance should not be underestimated because of its wide variety of applications in clinical medicine.
Interestingly, cardiovascular regulation through the ANS in fibromyalgia syndrome has been shown to be relevant in clinical pain reports. Through HRV measurement, del Reyes et al found that cardiovascular regulation is impaired in such patients due to reduced sympathetic and parasympathetic influences and baroreflex malfunctioning.[
29] This reduced baroreceptor sensitivity has an inverse relationship with pain severity, which reflects the pain inhibition functions of the baroreceptor system which has been well-documented.[
29] Hence, it could be inferred that deficient ascending pain inhibition due to ANS and baroreceptor malfunction may contribute to hyperalgesia and pain sensation.[
29]
Gastrointestinal System
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic and debilitating functional gastrointestinal disorder with recurrent abdominal discomfort and changes in bowel habits. It does not have a set of defining criteria.[
30] A meta-analysis by Liu et al.,[
30] aimed to investigate the links between ANS and the pathophysiology of IBS, through HRV analysis. Their results revealed that vagal activity was significantly lower in patients with IBS than in controls. They also suggested that IBS patients have abnormal sympatho-vagal balance, suggesting vagal dysfunction or excess sympathetic activity in these patients.[
30] Thus, ANS dysfunction may be a factor in IBS, but it cannot be determined whether it is a cause or consequence of this disease.
Additionally, the ANS function has been implicated in irritable bowel disease (IBD), specifically Crohn’s disease (CD), as well. Pellisier et al.,[
31,
32] aimed to study the association between vagal tone and inflammatory markers in patients with Crohn’s disease and IBS versus health controls. Their results showed that those who had low vagal tone as measured by HRV had higher salivary cortisol levels compared to healthy controls with high vagal tone. Also, there was an inverse association observed between vagal tone and TNF-alpha level in patients with Crohn’s disease exclusively and an inverse relationship between vagal tone and plasma epinephrine in IBS patients.[
31,
32] Accordingly, their data argues for vagal tone and the ANS having a role in IBD and IBS, suggesting a homeostatic link which highlights the relevance of autonomic balance measurement and its implications for designing novel disease interventions.
The ANS by its contribution to psychological factors could also influence the pathogenesis and symptomatology of IBS and IBD. Compared to healthy controls, CD patients with positive affectivity had an adapted high sympathetic activity, whereas in ulcerative colitis negative affectivity blunted parasympathetic activity.[
31,
32] However, in IBS, dysautonomia with high sympathetic and low parasympathetic tone persisted with both affectivity states of the patients.[
31,
32] Hence, ANS activity adapts according to the disease with regards to its pathogenesis as well as psychological adjustment. Hence ANS function and its measurement is important for understanding disease and treatment pathways, which merits its integration into routine clinical practice. Although, more research is needed in this area, especially with regards to understanding the mechanisms associated around the gastrointestinal disorders.
Acute and Critical Care
ANS dysfunction may complicate the course of critically ill patients and may adversely affect the outcome of those in intensive care units (ICU) with cardiovascular, septic and neurologic complications. Mazzeo et al.,[
33] have suggested that due to its role in systemic homeostasis, ANS measurement and assessment of its function may be useful for stratifying patients according to risk, pathophysiology and prognosis. As a bedside test, HRV is a non-invasive tool for ANS balance measurement by detecting ANS dysfunction in various diseases. Episodes of increased intracranial pressure have been associated with low HRV, leading to increased mortality and disability[
33] after traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, changes in HRV may present changes in intracranial pressure and low HRV independently predicts mortality.[
34] Thus, this would be extremely useful in unconscious patients in neurosurgical ICU, as it would help assess their prognosis and initiate early interventions. This also includes patients with spinal cord infarction, as they have profound alterations in cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and thermoregulatory and urinary systems. A decreased HRV in these patients suggests reduced sympathetic cardiac control and parasympathetic predominance.[
35] Therefore, monitoring HRV for these patients in critical care can help physicians foresee a prognosis and decide for appropriate early treatment options.
A recent study has suggested a possible association between HRV indices and inflammatory biomarkers in septic patients.[
36] A decrease in HRV and sympatho-vagal balance is associated with increased hyperinflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses during septic shock.[
36] An explanation for this could be decreased reflex responses of the end target organs and central nervous system, in turn affecting autonomic balance.[
36] To characterize autonomic dysfunction then, HRV measurement can be used to characterize autonomic function and prognosticate patients at risk of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.[
36] Furthermore, Mazzeo et al.,[
33] also found that altered sympathetic modulation of cardiac activity and HRV suppression could be an early marker for impending septic shock which could be useful in the emergency department.
It is important however, to recognize that various factors may interfere with the ANS and its measurement in the ICU, such as sedation, nursing manoeuvres and ambient noise in the environment. Concomitant diseases also play a role, as do the multiple drugs used in ICU, hence many times it can be hard to determine the cause of autonomic dysfunction and the merit of its measurement for prognostic and therapeutic purposes.[
33] HRV has also been shown to be useful in monitoring of critically injured patients and trauma triage.[
10] A systematic review by Ryan et al.,[
10] showed that HRV decrease in trauma patients, which accurately predicted mortality and morbidity and indicated significant injury. However, a major issue for its use is the lack of normal values and treatment thresholds, as well as lack of appropriate guidelines for its use in clinical practice.[
10]
Conclusion
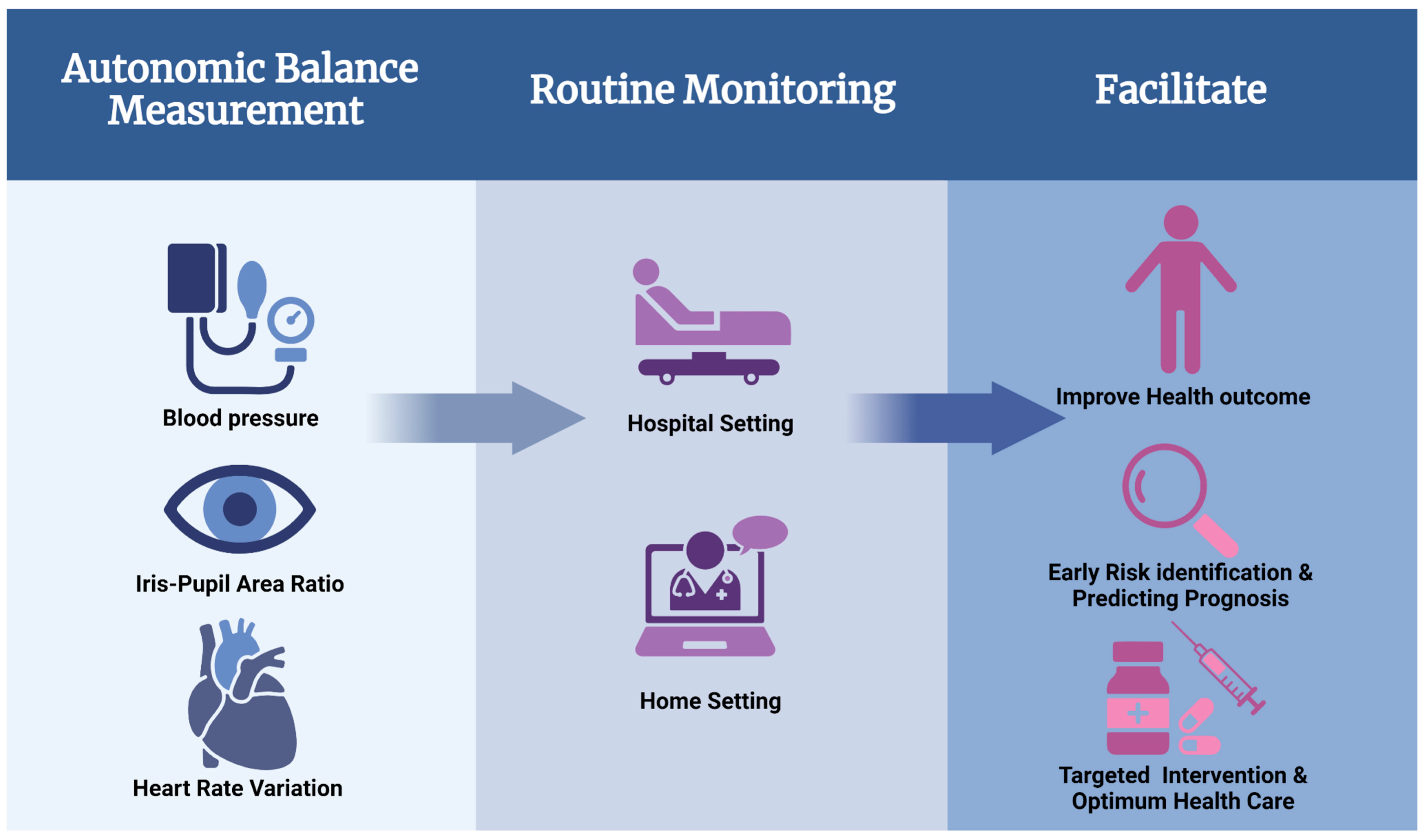
Overall, our review highlights that autonomic balance measurement is a novel approach to clinical management of various diseases (
Figure 3). The role of the ANS is evident and significant in all organ systems of the body, and its measurement can help with the understanding of various pathophysiological mechanisms and even the physiological effects of drugs (
Figure 4). Although the lack of standardized tools or therapeutic protocols has limited its wider use in routine clinical practice. Nevertheless, our review illustrates the merits and limitations of ANS balance measurement, which should encourage targeted clinical research to address the current gaps. Clinical benefit will become more apparent once more research is done in this area, including robust clinical trials that help with the development of standardized protocols.
Acknowledgements
Research support from University College Dublin-Seed funding/Output Based Research Support Scheme (R19862, 2019), Royal Society-UK (IES\R2\181067, 2018) and Stemcology (STGY2917, 2022) is acknowledged.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Tindle J, Tadi P. Neuroanatomy, parasympathetic nervous system. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Karemaker, JM. An introduction into autonomic nervous function. Physiological measurement. 2017, 38, R89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eşref A, Tamam Y, Akil MA, Kaplan İ, Bilik MZ, Acar A, Tamam B. Identifying autonomic nervous system dysfunction in acute cerebrovascular attack by assessments of heart rate variability and catecholamine levels. Journal of neurosciences in rural practice. 2015, 6, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peçanha T, Silva-Júnior ND, Forjaz CLdM. Heart rate recovery: autonomic determinants, methods of assessment and association with mortality and cardiovascular diseases. Clinical physiology and functional imaging. 2014, 34, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman R, Chapleau MW. Testing the autonomic nervous system. Hand Clinic. 2013, 115, 115–136. [Google Scholar]
- Chinaka I, Kumar AH. A Retrospective Analysis of the Merit of Iris-pupil Area Ratio as a Predictor of Risk of Myocardial Infarction. BEMS Reports. 2019, 5, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lin A, Maguire L, Kilroy D, Kumar AH. The Utility of Iris-pupillary Area Ratio as a Non-invasive Index of Stress in Primates. BEMS Reports. 2018, 4, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zygmunt A, Stanczyk J. Methods of evaluation of autonomic nervous system function. Archives of Medical Science. 2010, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- King DR, Ogilvie MP, Pereira BM, Chang Y, Manning RJ, Conner JA, Schulman CI, McKenney MG, Proctor KG. Heart rate variability as a triage tool in patients with trauma during prehospital helicopter transport. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 2009, 67, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan ML, Thorson CM, Otero CA, Vu T, Proctor KG. Clinical applications of heart rate variability in the triage and assessment of traumatically injured patients. Anesthesiology research and practice 2011, 2011.
- Proctor KG, Atapattu SA, Duncan RC. Heart rate variability index in trauma patients. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 2007, 63, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes del Paso GA, Langewitz W, Mulder LJ, Van Roon A, Duschek S. The utility of low frequency heart rate variability as an index of sympathetic cardiac tone: a review with emphasis on a reanalysis of previous studies. Psychophysiology. 2013, 50, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahalin LP, Arena R, Labate V, Bandera F, Lavie CJ, Guazzi M. Heart rate recovery after the 6 min walk test rather than distance ambulated is a powerful prognostic indicator in heart failure with reduced and preserved ejection fraction: a comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. European journal of heart failure. 2013, 15, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colivicchi F, Bassi A, Santini M, Caltagirone C. Prognostic implications of right-sided insular damage, cardiac autonomic derangement, and arrhythmias after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2005, 36, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpelainen JT, Sotaniemi KsA, Mäkikallio A, Huikuri HV, Myllylä VV. Dynamic behavior of heart rate in ischemic stroke. Stroke. 1999, 30, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Raedt S, De Vos A, De Keyser J. Autonomic dysfunction in acute ischemic stroke: an underexplored therapeutic area? Journal of the neurological sciences. 2015, 348, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander D, Winbeck K, Klingelhofer J, Etgen T, Conrad B. Prognostic relevance of pathological sympathetic activation after acute thromboembolic stroke. Neurology. 2001, 57, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong L, Leung HH, Chen XY, Han JH, Leung TW, Soo YO, Chan AY, Lau AY, Wong LK. Comprehensive assessment for autonomic dysfunction in different phases after ischemic stroke. International Journal of Stroke. 2013, 8, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femminella GD, Rengo G, Komici K, Iacotucci P, Petraglia L, Pagano G, De Lucia C, Canonico V, Bonaduce D, Leosco D. Autonomic dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: tools for assessment and review of the literature. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2014, 42, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbă D, Cozma L, Popescu BO, Davidescu EI. Dysautonomia in Alzheimer's disease. Medicina. 2020, 56, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins O, Dillon S, Finucane C, Lawlor B, Kenny RA. Parasympathetic autonomic dysfunction is common in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of aging. 2012, 33, 2324–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomer AC, Nearing BD, Schachter SC, Verrier RL. Vagus nerve stimulation reduces cardiac electrical instability assessed by quantitative T-wave alternans analysis in patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014, 55, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, RL. Microvolt T-Wave Alternans: Pathophysiology and Clinical Aspects. Cardiac Repolarization: Basic Science and Clinical Management 2020, 313–331. [Google Scholar]
- Verrier RL, Klingenheben T, Malik M, El-Sherif N, Exner DV, Hohnloser SH, Ikeda T, Martínez JP, Narayan SM, Nieminen T. Microvolt T-wave alternans: physiological basis, methods of measurement, and clinical utility—consensus guideline by International Society for Holter and Noninvasive Electrocardiology. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2011, 58, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellens HJ, Schwartz PJ, Lindemans FW, Buxton AE, Goldberger JJ, Hohnloser SH, Huikuri HV, Kääb S, La Rovere MT, Malik M. Risk stratification for sudden cardiac death: current status and challenges for the future. European heart journal. 2014, 35, 1642–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenewald M, Ilies C. Monitoring the nociception–anti-nociception balance. Best Practice & Research Clinical Anaesthesiology. 2013, 27, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ledowski T, Tiong W, Lee C, Wong B, Fiori T, Parker N. Analgesia nociception index: evaluation as a new parameter for acute postoperative pain. British journal of anaesthesia. 2013, 111, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logier R, Jeanne M, Dassonneville A, Delecroix M, Tavernier B. PhysioDoloris: a monitoring device for analgesia/nociception balance evaluation using heart rate variability analysis. Paper/Poster presented at: 2010 annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology. 2010.
- Del Paso GAR, Garrido S, Pulgar A, Martín-Vázquez M, Duschek S. Aberrances in autonomic cardiovascular regulation in fibromyalgia syndrome and their relevance for clinical pain reports. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2010, 72, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Q, Wang EM, Yan XJ, Chen SL. Autonomic functioning in irritable bowel syndrome measured by heart rate variability: A meta-analysis. In: Wiley Online Library; 2013:638-646.
- Pellissier S, Dantzer C, Mondillon L, Trocme C, Gauchez A-S, Ducros V, Mathieu N, Toussaint B, Fournier A, Canini F. Relationship between vagal tone, cortisol, TNF-alpha, epinephrine and negative affects in Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome. PloS one. 2014, 9, e105328. [Google Scholar]
- Pellissier S, Dantzer C, Canini F, Mathieu N, Bonaz B. Psychological adjustment and autonomic disturbances in inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010, 35, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo AT, La Monaca E, Di Leo R, Vita G, Santamaria L. Heart rate variability: a diagnostic and prognostic tool in anesthesia and intensive care. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 2011, 55, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowery NT, Norris PR, Riordan W, Jenkins JM, Williams AE, Morris Jr JA. Cardiac uncoupling and heart rate variability are associated with intracranial hypertension and mortality: a study of 145 trauma patients with continuous monitoring. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery. 2008, 65, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claydon VE, Krassioukov AV. Clinical correlates of frequency analyses of cardiovascular control after spinal cord injury. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2008, 294, H668–H678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaioannou VE, Dragoumanis C, Theodorou V, Gargaretas C, Pneumatikos I. Relation of heart rate variability to serum levels of C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and 10 in patients with sepsis and septic shock. Journal of critical care. 2009, 24, 625–e621. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).