1. Introduction
Due to its high incidence and lethality, lung cancer (LC) imposes a significant burden on the healthcare system [
1,
2]. By the end of 2023, it is forecasted that there will be 609,820 cancer-related deaths in the United States, lung cancer remaining the leading cause of cancer mortality among them [
3]. Currently, clinical detection of lung cancer primarily relies on cellular or histopathology examinations, radiographic imaging such as X-rays and CT scans, and tumor marker assays in bodily fluids. But, these existing detection techniques have obvious drawbacks, including high cost and significant harm to the human body.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) containing in exhaled human breath are closely associated with various diseases. Breath analysis was as one solution to be put forward, which is a non-invasive early screening method that can be employed for the screening of various diseases, including lung cancer, diabetes, breast cancer and so on [
4,
5,
6] Research has indicated that lung cancer results in elevated levels of acetone and ethanol in exhaled breath. Both of these gases can serve as reliable exhalation biomarkers for early lung cancer [
7,
8]. In current clinical trials, spectroscopic methods, mass spectrometry, chromatography-related techniques, and electronic noses (e-nose) are considered as relatively viable and efficient standard technologies for detecting VOCs in human exhaled breath [
9,
10,
11]. However, techniques such as mass spectrometry, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods are constrained by their high equipment costs and technical operator requirements. In contrast, gas sensors array-based e-nose gas sensing technology holds greater cost advantage and development potential for applying in breath analysis [
12,
13,
14].
Through the analysis of the data collected by the sensor array by pattern recognition algorithm, the electronic nose can effectively identify complex gases. In pattern recognition task, feature selection and feature extraction directly affect the detection performance of electronic nose. Marzorati et al. [
15] extracted nine features from the response of each gas sensor to exhaled gas. Liu et al. [
16] used 19 sensors, selected 13 composite features from each sensor, and combined with classical classifiers to verify the feasibility of identifying LC patients through VOCs. In previous studies, it is found that the whole feature extraction process is particularly complex, and it is necessary to try the feature extraction method continuously to obtain better results. Gramian Angular Field (GAF) is a data visualization method proposed by Wang et al. which converts time series into two-dimensional color images [
17]. GAF encodes one-dimensional time series into two-dimensional color images with more prominent key features, so as to display the important information hidden in the sensor signal more clearly. By using the data visualization technology of GAF, the original data does not need to be processed, and is directly converted into two-dimensional color images, which can not only retain the deep features of the signal, but also avoid complex feature extraction engineering [
18].
Currently, pattern recognition algorithms employed in electronic noses are categorized into classical gas identification algorithms (machine learning), artificial neural networks (ANNs), and biologically-inspired pulse neural networks (SNNs) [
19,
20,
21]. To address complex gas recognition tasks, ANNs have been regarded as the current popular choice [
22,
23]. Compared with machine learning and SNNs, ANNs exhibit strong adaptability and do not require model redesign for different training tasks. Additionally, the Nets can automatically learn complex features from data without the need for manual feature extraction and they encompass various neural network architectures, such as Backpropagation Neural Networks (BPNNs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), etc. Avian et al [
24]. proposed a CNN architecture and built two models for analyzing VOCs in exhaled gas. The first model receives the signal processed by different feature extraction methods as input, while the second model directly processes the original signal. The results indicate that different classifiers demonstrate varying effects depending on the employed feature extraction methods, with Kernel PCA (KPCA) showing a positive impact on performance. Guo et al. [
25] introduced an innovative deep learning framework that combines an electronic nose to predict odor descriptor ratings, which was the first application of Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (ConvLSTM) on an electronic nose for olfaction prediction.
Although convolutional neural networks have been found extensive application in gas classification, they possess a substantial number of trainable parameters, high computational complexity, and slow inference speed and not to be hardware-friendly for devices, which hinder the transportability of pattern recognition algorithms into embedded systems. To address this problem, convolutional neural networks have progressively developed toward lightweight direction [
26,
27].
The contributions of this article are summarized as follows:
- (1)
A hardware-friendly lightweight neural network model (LTNet) using depth-separable convolution structure for gas classification is constructed.
- (2)
To settle the decrease in classification accuracy caused by depthwise separable convolutions, we proposed to add Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) attention mechanisms and residual connections in the model.
- (3)
The convolutional and batch normalization (BN) layers are combined together so as to reduce the model parameters, speed up the inference speed and improve the stability of the model.
2. Experimental Section
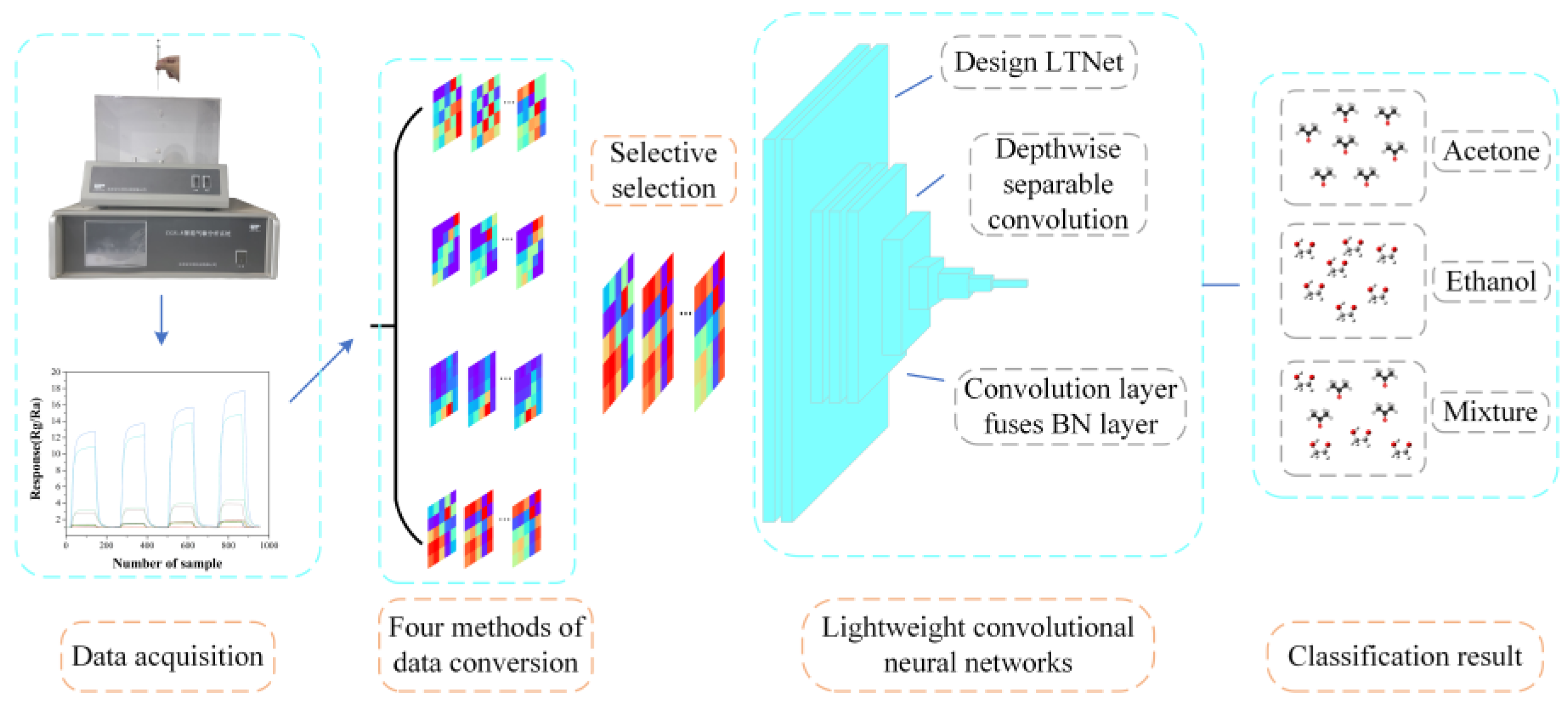
Data collection was performed using the CGS-8 intelligent gas sensor analysis system provided by Beijing Ailite Technology Co., Ltd. And the collected data was transformed into images using the Gramian Angular Field (GAF) which were as classification input for LTNet. Two different datasets were employed to assess the performance of the model, and the overall process is illustrated in
Figure 1.
2.1. Data Sources I: Gas Mixture Data Set
Exhaled breath from lung cancer patients contains biomarkers including numerous species, such as acetone, ethanol, isoprene and etc. To validate LTNet's classification capabilities, this work utilized acetone and ethanol gases as target gases. In the experiment, a sensor array composed of 16 commercial semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors manufactured by FIGARO was used, which matched the sensor model in Data Sources II (UCI database).
n Data Sources II (UCI database).
The experiment employed a static gas volumetric method using 98% AR acetone and 98% anhydrous ethanol with a microsyringe capable of handling a range of 10
for liquid extraction. As indicated by Equation (1), it can be observed that conducting experiments directly with high-concentration test liquids would result in a very small volume of extracted liquid, making it difficult to inject into the gas chamber. To address this issue, the concentration of the test liquid was chosen to dilute to 10% in the experiment.
where Q is the volume of the test liquid (mL), V denotes the volume of the gas chamber (mL), C stands for the desired gas concentration to be prepared (ppm), M is the molecular weight of the substance, d is the concentration of the test liquid, r signifies the liquid density(), represents the laboratory ambient temperature (℃), and is the gas chamber temperature (℃).
Following the specifications in the sensor manual, the working voltage of all 16 sensors was set to 5V. The sensor operating current was adjusted on the CGS-8 smart gas sensing analysis system through multiple experiments to identify the optimal operating current for each sensor. The sensor models and their optimal operating currents are presented in
Table 1, respectively.
After setting the optimal operating current, it is necessary to preheat the sensor for two hours and wait for the baseline to stabilize. Then, activate the evaporation and heating functions of the experimental apparatus. Using a microsyringe to extract a certain amount of liquid from the test liquid prepared according to formula (1) and vertically drops the liquid into the evaporation dish. Expose the sensor array to acetone, ethanol, or a binary mixture of these two VOC gases. The concentration indices for the two gas mixtures are detailed in
Table 2. The experimental response time is set approximately 120 seconds, and the recovery time is also about 120 seconds.
2.2. Data Sources II: UCI Database
This work also used a public database from the University of California (UCI) to complement and validate Data sources I. This dataset is a collection of gas sensor drift datasets at different concentrations collected by the Chemical Signaling Research Laboratory at the UCI BioCircuits Institute in San Diego [
28,
29]. The acetone concentrations in the dataset range from 12-500 ppm and ethanol concentrations range from 10-500 ppm. A total of 4650 data from UCI dataset were used for classification with LTNet.
2.3. Experimental Environment and Hardware Configuration
The algorithmic programming environment for this study is Python 3.10, running on a computer with an RTX 3060 graphics card. The LTNet network, as well as the comparison network, uses the Adam optimizer with a cross-entropy loss function. The model usually converges after about ten rounds of training, so Epoch was set to 30. Conventional convolutional neural networks take up a lot of graphics card memory during training, and for comparison purposes, the Batch size was set to 16. For the own mixed gas dataset, the learning rate was set to 0.0006, while for the UCI database, the learning rate was set to 0.0004.
3. Data Processing
3.1. Image Conversion Methods
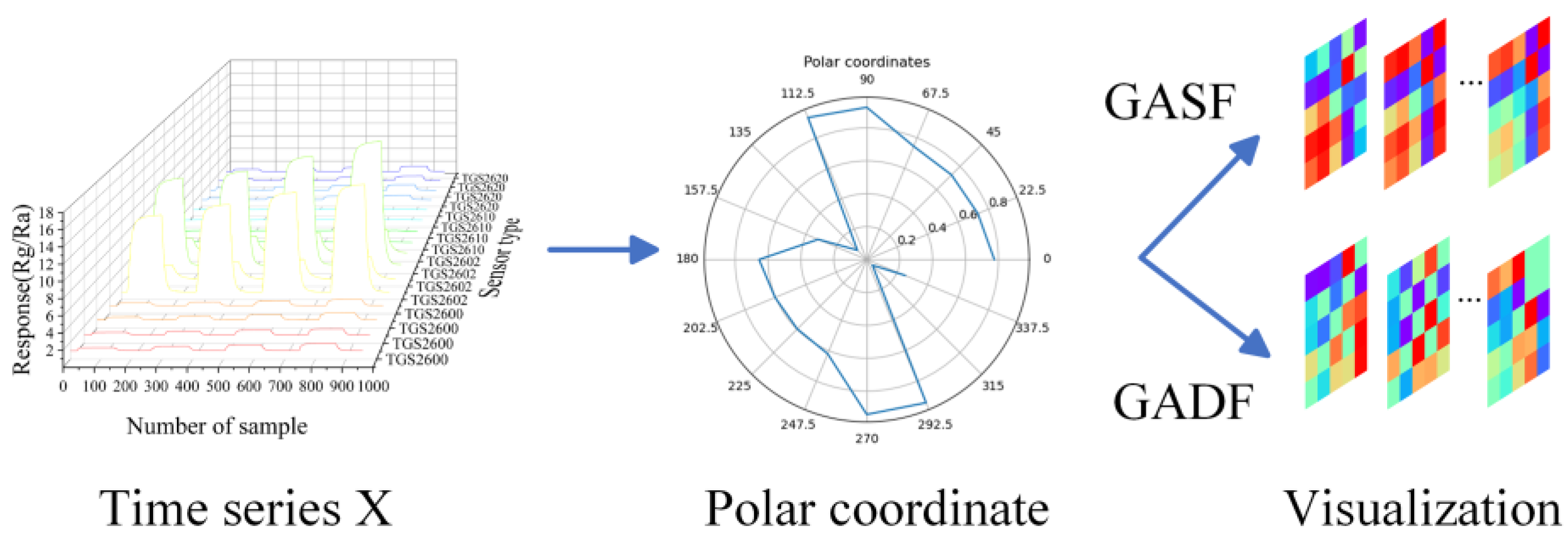
CNNs are typically used for processing two-dimension image data. However, the raw data collected from each channel of the sensor array were one-dimensional results and not suitable for processing by the CNNs directly. To figure out this issue, an image transformation model based on Gramian Angular Field (GAF) was utilized [
30], transforming one-dimensional time series data into two-dimensional images which would become effective input for the LTNet. The coding diagram based on GAF is shown in
Figure 2. The response data of 16 sensors is selected at a certain sampling point, and the response data were denoted as
,then normalizing the response data
to the range of
were carried out using the min-max normalization with formula (2).
Where represents the response data of the sampling points, and is the response data of the ith sensor, this step constrains the angular range between 0 and π, facilitating the acquisition of more detailed GAF information.
The selected data for this study consists of the response data from 16 sensors at a specific sampling point, and it does not involve time series. Therefore, there is no need to encode the timestamps as radii. Formula (3) is used to calculate the arccosine values of the response data for the sensors at this sampling point.
After transforming the scaled
into polar coordinates, Capturing the Correlation Between Response Data of Different Sensors Through the Summation of Triangular Relationships Among Each Point. Therefore, GASF and GADF are defined by the following equations, respectively.
In which, and represent the normalized and inverse cosine-transformed response data of the first and nth sensors, respectively, in the sensor array.
3.2. Lightweight Neural Network Model
The high complexity, a large number of parameters, and relatively slow inference speed of neural networks could potentially impede the feasibility of porting pattern recognition algorithms to embedded systems. Therefore, a lightweight neural network model (LTNet) is proposed to figure out this problem. It includes a backbone network based on depthwise separable convolutions, and the complete network architecture is illustrated in
Figure 3.
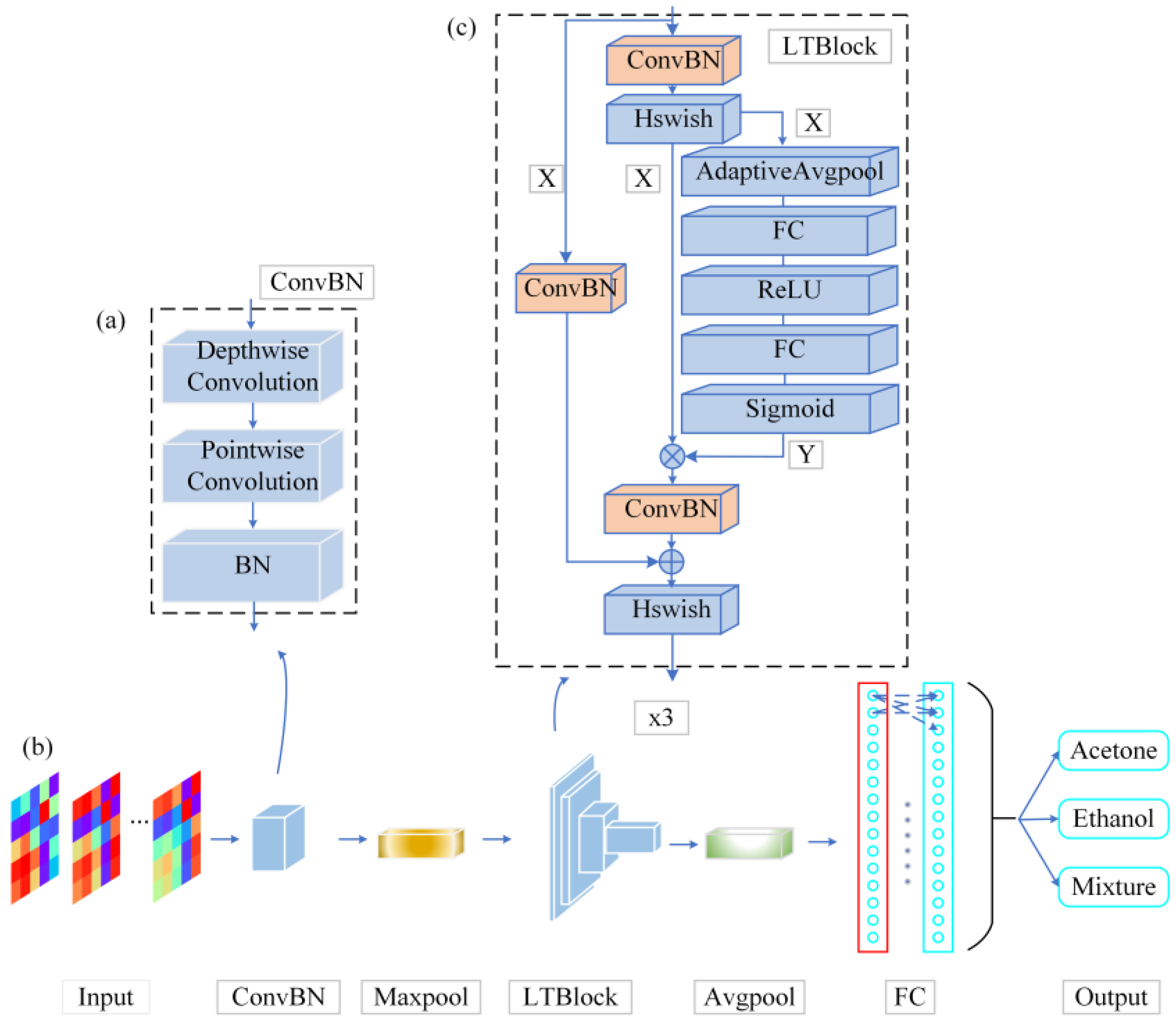
As shown in
Figure 3, the architecture of the LTNet is mainly composed of the ConvBN layer and the LTBlock module. The convolutional layer is fused with the BN layer into a new ConvBN layer and the weights and biases of the ConvBN layer are reinitialized. The aim of this design is to reduce the parameter size of the network and improve the inference speed of the network in the validation procedure.
To extract features from the input image, the network uses a 3x3 deep convolution to learn the feature maps of the input channels when the input image passes through the ConvBN layer, in order to preserve the correlation between different channels. Subsequently, the feature maps produced by deep convolution are mapped by a 1x1 point-by-point convolutional layer to improve the ability of capturing local information of the models. In order to avoid increasing the depth of the network, the LTBlock module uses the ConvBN layer for feature extraction several times, and introduces the SE attention mechanism and residual connectivity in order to enhance the feature interactions between channels, maintaining the integrity of the original input information. The LTBlock module employs the Hard Swish as activation function (Hswish) in order to introduce the nonlinear nature of the output of the network neurons, and finally obtains the classification results through the Fully Connected Layer (FC layer).
3.3. Calculation of Depthwise Separable Convolutions Parameters
To enhance the efficiency of standard convolutions while maintaining network performance and generalization capability, LTNet introduced depthwise separable convolutions. Depthwise separable convolutions decompose standard convolutions into two steps: first, a depthwise convolution with a K×K kernel, followed by a pointwise convolution with a 1×1 kernel. In the depthwise convolution stage, independent convolution filters are applied to each input channel, making the convolution operation independent in the channel dimension and effectively capturing spatial features within each channel [
31]. The role of pointwise convolution is to construct new features by computing a linear combination of input channels. The parameters and floating-point operations (FLOPs) for standard convolution and depthwise separable convolution are as follows:
Where and represent the parameters and floating-point operations (FLOPs) of standard convolution, and and represent the parameters and FLOPs of depthwise separable convolution. The convolution kernel size is
.
and
represent the dimensions of the output feature map.
is the number of input feature map channels, and
is the number of output feature map channels. The comparison of parameters and FLOPs between standard convolution and depthwise separable convolution is as follows:
From equations (10) and (11), it can be observed that depthwise separable convolution involves fewer parameters and floating-point operations, making the model more lightweight.
This study integrates deep convolution with the BN layer, further reducing the number of parameters in the LTNet model and accelerating the model's inference speed. The parameter calculations before and after fusion are shown in equations (12) and (13).
where
is the number of parameters before fusion and
is the number of parameters after fusion. The parameters of BN layer are mainly determined by four parameters which are scale parameter, offset parameter, mean and variance of BN layer. The purpose of BN layer is to normalize the data on each channel, so the number of parameters of BN layer corresponds to the output channel
. From Equation (12) and (13), fusing the depth-separable convolution with the BN layer only reduces the parameters of
with a factor of three. But, the fused weights and biases can be directly used in the testing and validation phases of LTNet, which can speed up the inference of LTNet and reduce the computation and memory consumption. The merged ConvBN layer obtained after fusion needs to be computed according to the relevant parameters of the convolutional and BN layers to generate new weights and biases, which are described by the following formula:
where
represents the output of the merged ConvBN layer,
is the output of the pre-merged convolutional layer,
and
denote the weights and biases of the BN layer,
represents the variance, and
is a constant which is to prevent division by zero.
represents the input of the pre-merged convolutional layer, while
and
are the weights and biases of the convolutional layer, respectively. Formula (14) can be simplified as follows:
where the weights
and biases
of the ConvBN layer are calculated as follows:
4. Results and Discussion
The dataset was divided into training, testing, and validation sets in a 6:3:1 ratio. For the own mixed gas dataset, the numbers of images in the training, testing, and validation sets are 4,474, 2,234, and 744, respectively. For the UCI database, the training, testing, and validation sets consist of 2,791, 1,395, and 464 images, respectively. In this study, validation set accuracy and six evaluation metrics were adopted as criteria for assessing both the lightweight of the model and its classification performance. These criteria include the model's total accuracy on the validation set (Accuracy) (ethanol, acetone and the mixture), the time required for the model to complete thirty training epochs (Training time), the GPU memory usage under the same conditions when different models are trained with a cleared background (GPU RAM), the inference time on the validation set (Inference time), the model's parameters (Params), and the size of the best-preserved weights on the test set (Weight size).
4.1. Data Conversion Comparison Test and Results Discussion
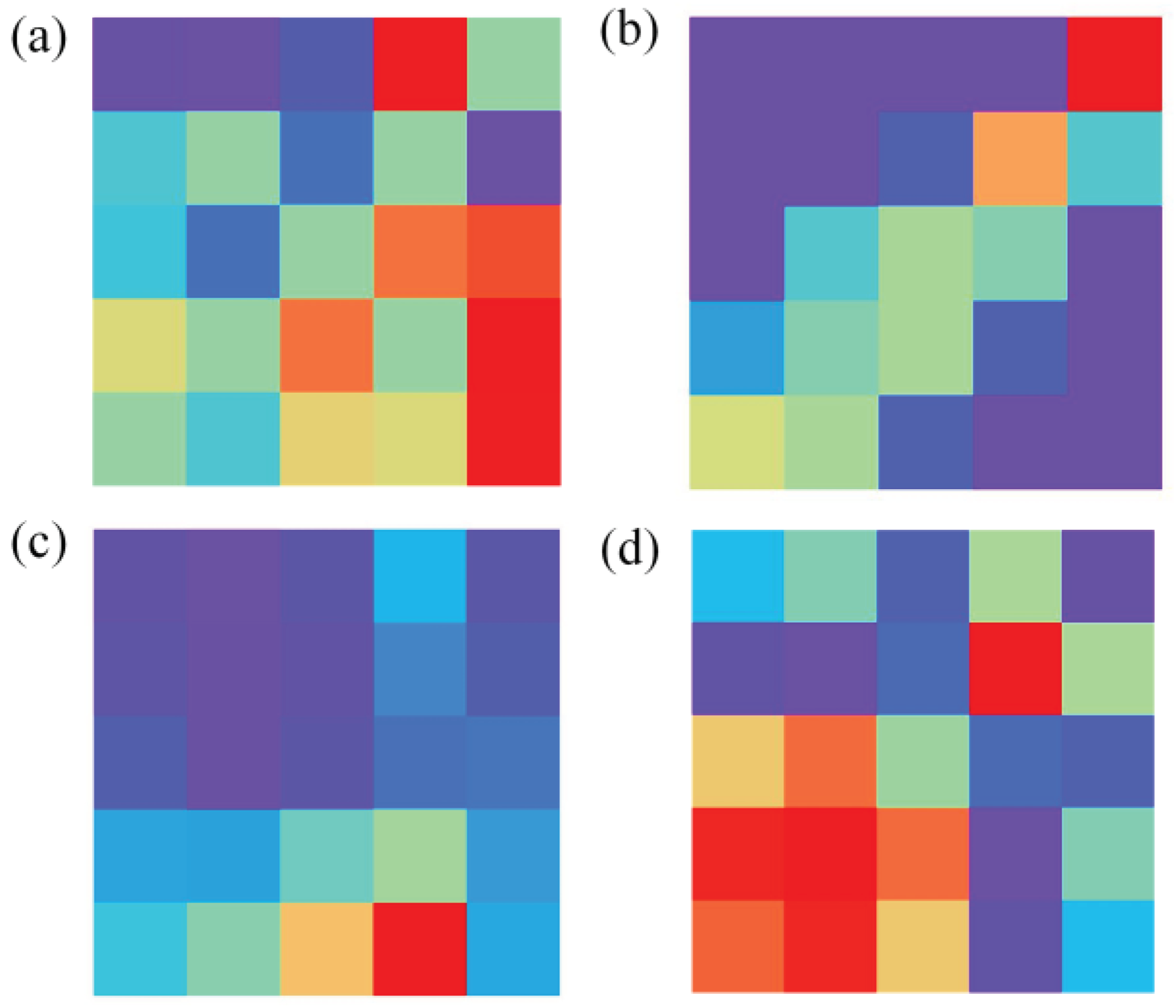
In the data preprocessing, GASF is compared with Gramian Angular Difference Field (GADF), Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT), and Markov Transition Field (MTF).
Figure 4 illustrates the images transformed by these four data transformation methods.
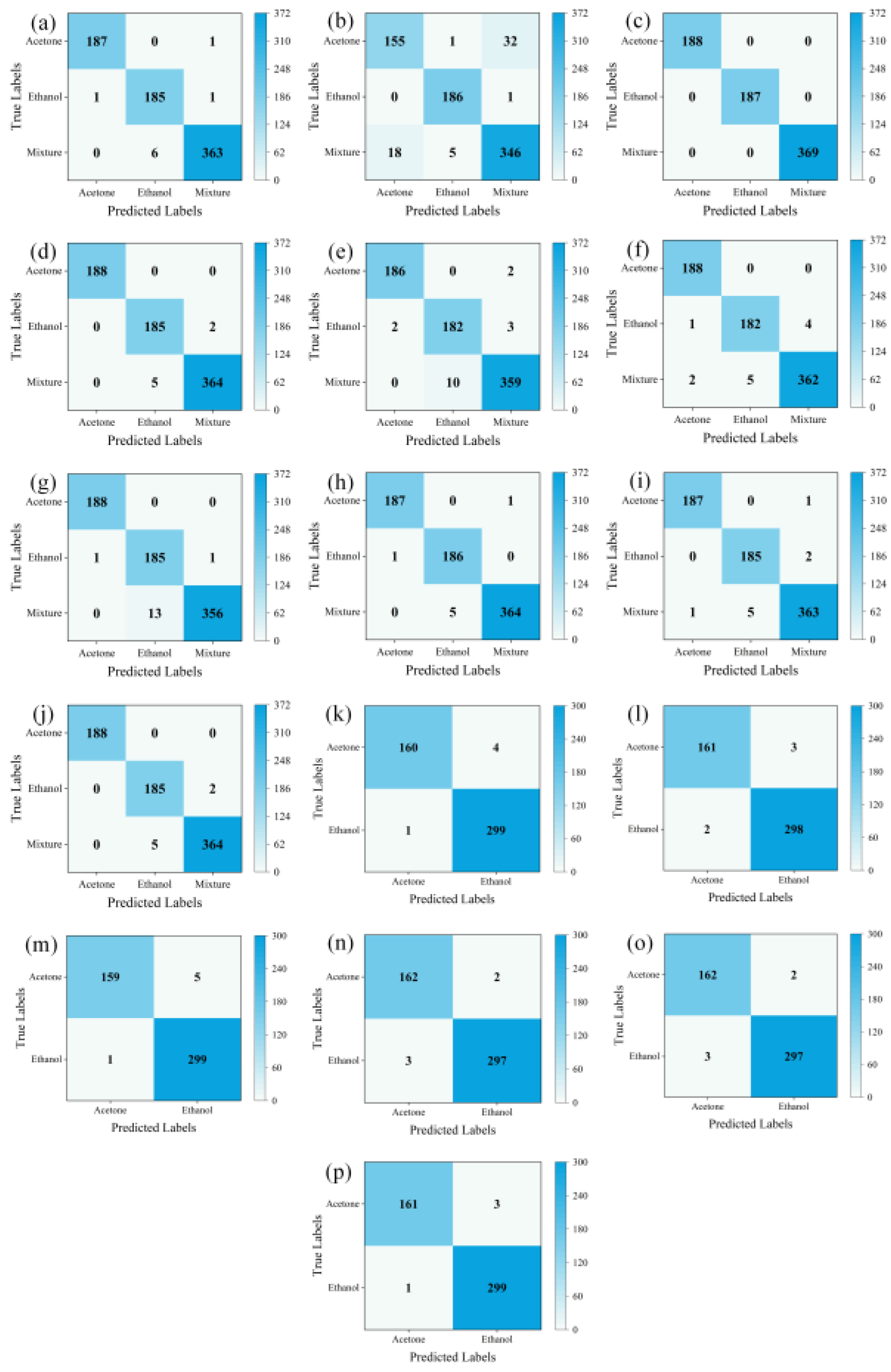
LTNet was employed to evaluate four different methods for transforming one-dimensional time series into two-dimensional images. The confusion matrices which can display the classification of each sample intuitively, and is an important index used to measure the classification performance are depicted in
Figure 5 (a), (b), (c), and (d), while
Table 3 presents a comparative analysis of the results obtained using these four methods.
From
Table 3 and the results of confusion matrices, it is evident that STFT exhibits the highest total classification accuracy, reaching 100%. The majority of errors for GADF and GASF are concentrated in the mixed gas class, with total classification accuracies of 98.79% and 99.06%, respectively. MTF, on the other hand, experiences more classification errors in the mixed gas and ethanol classes, resulting in the total accuracy of only 92.34%. However, training with images transformed using STFT takes the longest training time, reaching 1630.92 seconds, and it also requires the highest GPU RAM usage. Conversely, training with images transformed using GASF for the same thirty epochs only takes 844.38 seconds and occupies a mere 2.1GB of GPU RAM while achieving similar accuracy to STFT. Therefore, GASF was chosen as the data transformation method in this work.
4.2. Model Evaluation and Comparison Experiment
LTNet is compared with a total of five different networks, including three traditional convolutional neural networks (AlexNet, ResNet50, VGG16) and two lightweight convolutional neural networks (EfficientNet, MobileNetV3_large). AlexNet is a relatively deep neural network, which facilitates the model in learning more complex features. ResNet50 implements classification using skip-connected residual blocks, VGG16 employs deep convolutional networks for feature extraction from raw samples, followed by classification using fully connected layers. EfficientNet achieves high performance in resource-constrained environments through strategies like Compound Scaling and Width Multiplier. MobileNetV3_large classifies raw samples using depthwise separable convolution.
Before conducting the classification task, we compared the model parameters and the size of the best saved weights during training of LTNet with the other five networks, as shown in
Table 4. Among these six models, LTNet has only 32,614 parameters, which is equivalent to just 0.139% of the traditional convolutional neural network ResNet50, less than 0.1% of AlexNet and VGG16, and even less than 1% of the popular lightweight convolutional neural networks, EfficientNet and MobileNetV3_large. The optimal training weight size of LTNet is 0.155MB, demonstrating a more efficient memory utilization compared to MobileNetV3_large, EfficientNet, and AlexNet. This indicates that relative to the existing lightweight convolutional neural networks and traditional convolutional neural networks, LTNet is better suited for use in resource-constrained environments.
4.3. Classification Results of Own Mixed Gas Dataset
From (e), (f), (g), (h), (i), and (j) in
Figure 5 and
Table 5, it can be observed that for the own mixed gas dataset, LTNet had five errors in the mixed gas category and only two errors in the ethanol gas category, achieving the highest classification accuracy of 99.06%. Additionally, it's worth noting that LTNet's GPU RAM usage during training was significantly lower than that of traditional convolutional networks such as VGG16 and lightweight networks like EfficientNet. It completed thirty rounds of training in only 844.38 seconds, making it the fastest among all compared networks, far surpassing ResNet50, VGG16, and EfficientNet. LTNet only takes 23 seconds to complete inference on 744 validation set images, making it the fastest among these six networks. It significantly outperforms traditional convolutional neural networks, with the required inference time being only a quarter of that of the lightweight network MobileNetV3_large.
4.4. UCI Database Classification Results
From
Figure 5 (k), (l), (m), (n), (o), (p), and the
Table 6, it can be observed that for the UCI database, LTNet achieved similar results as on the own mixed gas dataset. LTNet still maintains the highest classification accuracy while significantly outperforming the traditional convolutional neural network models and lightweight convolutional neural network models in terms of GPU RAM, training time, and inference time.
Results from the own mixed gas dataset and the UCI database demonstrate that LTNet can achieve high accuracy in gas classification tasks while maintaining low computational resource requirements, further validating the lightweight nature of LTNet.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed a lightweight and efficient LTNet network model combined with GASF to convert one-dimensional time series into two-dimensional images for high-precision classification of acetone and ethanol gases, which are respiratory markers for lung cancer patients. The 6-evaluation metrics verified that LTNet outperforms classical convolutional neural network models such as VGG16 and ResNet50, as well as lightweight neural network models such as MobileNetV3_large. Validation with the own mixed gas dataset and the UCI database shows that comparing with the other five models, LTNet has higher classification accuracy, superior generalization performance, and fewer number of parameters. And by fusing the convolutional layer with the BN layer, the inference speed of LTNet in the validation set is much faster than that of ResNet50, MobileNetV3_large and so on. In addition, it required less graphic card resources during the training process and the model weights took up less memory. This indicated that the LTNet network requires less computational resources and is suitable for less configured hardware. The lightweight network model lays the foundation for subsequent algorithm transplant. In future, Artificial intelligence and novel biomarkers play a key role in the entire lung cancer screening process, promising to transform lung cancer screening [
32].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Z., L.L, F.Z and Y.Z.; methodology, C.Z. and L.L.; software, C.Z.; validation, C.Z.; formal analysis, L.L.; investigation, C.Z., L.L, F.Z and Y.Z.; resources, C.Z. and L.L.; data curation, C.Z. and L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, L.L.; visualization, C.Z.; supervision, L.L and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21605006), Science and Technology Development Program of Jilin Province (20170520160JH) and the Education Department of Scientific Research Project of Jilin Province, China (No. JJKH20230758KJ, JJKH20191291KJ, JJKH20170567KJ, and 201592). (Corresponding author: Lei Li).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, Z. P.; Cheng, H. L.; Loh, S. Y.; Cheng, K. K. F., Functional Status, Supportive Care Needs, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Advanced Lung Cancer Patients Aged 50 and Older. Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing 2020, 7, (2), 151-160. [CrossRef]
- Vranas, K. C.; Lapidus, J. A.; Ganzini, L.; Slatore, C. G.; Sullivan, D. R., Association of Palliative Care Use and Setting With Health-care Utilization and Quality of Care at the End of Life Among Patients With Advanced Lung Cancer. Chest 2020, 158, (6), 2667-2674. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R. L.; Miller, K. D.; Wagle, N. S.; Jemal, A., Cancer statistics, 2023. Ca-a Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2023, 73, (1), 17-48.
- Marzorati, D.; Mainardi, L.; Sedda, G.; Gasparri, R.; Spaggiari, L.; Cerveri, P., A review of exhaled breath: a key role in lung cancer diagnosis. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, (3), 20. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. H.; Shao, K.; Wang, T., Detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from exhaled breath as noninvasive methods for cancer diagnosis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, (11), 2759-2780. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, L., A Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithm for Detection of Simulated Expiratory Markers of Diabetic Patients Based on Gas Sensor Array. Ieee Sensors Journal 2023, 23, (3), 2940-2947. [CrossRef]
- Buszewski, B.; Ulanowska, A.; Kowalkowski, T.; Cieslinski, K., Investigation of lung cancer biomarkers by hyphenated separation techniques and chemometrics. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2012, 50, (3), 573-581. [CrossRef]
- Ulanowska, A.; Kowalkowski, T.; Trawinska, E.; Buszewski, B., The application of statistical methods using VOCs to identify patients with lung cancer. J. Breath Res. 2011, 5, (4). [CrossRef]
- Apolonski, A.; Maiti, K. S., Towards a standard operating procedure for revealing hidden volatile organic compounds in breath: the Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy case. Appl. Optics 2021, 60, (14), 4217-4224. [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Woollam, M.; Grocki, P.; Davis, M. D.; Agarwal, M., Methods to Detect Volatile Organic Compounds for Breath Biopsy Using Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2023, 28, (11). [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z. Y.; Wang, J.; Hua, H.; Zhou, X. D.; Li, Q. L., Precise Detection and Quantitative Prediction of Blood Glucose Level With an Electronic Nose System. Ieee Sensors Journal 2022, 22, (13), 12452-12459. [CrossRef]
- Baldini, C.; Billeci, L.; Sansone, F.; Conte, R.; Domenici, C.; Tonacci, A., Electronic Nose as a Novel Method for Diagnosing Cancer: A Systematic Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, (8). [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Annema, J. T.; Schot, R.; van der Schee, M. P. C.; Spanevello, A.; Carratú, P.; Resta, O.; Rabe, K. F.; Sterk, P. J., An electronic nose in the discrimination of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and COPD. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, (2), 166-170. [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Pennazza, G.; Carratu, P.; Resta, O., Electronic Nose Technology in Respiratory Diseases. Lung 2017, 195, (2), 157-165. [CrossRef]
- Marzorati, D.; Mainardi, L.; Sedda, G.; Gasparri, R.; Spaggiari, L.; Cerveri, P., MOS Sensors Array for the Discrimination of Lung Cancer and At-Risk Subjects with Exhaled Breath Analysis. Chemosensors 2021, 9, (8). [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, D.; Gong, J.; Tian, L.; Qian, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, R., Lung cancer detection via breath by electronic nose enhanced with a sparse group feature selection approach. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2021, 339. [CrossRef]
- Zhiguang Wang, T. O, Imaging Time-Series to Improve Classification and Imputation. presented at the Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Buenos Aires, 2015.
- Wang, X.; Qian, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Jiao, M., A Novel Gas Recognition Algorithm for Gas Sensor Array Combining Savitzky–Golay Smooth and Image Conversion Route. Chemosensors 2023, 11, (2). [CrossRef]
- Binson, V. A.; Subramoniam, M.; Sunny, Y.; Mathew, L., Prediction of Pulmonary Diseases With Electronic Nose Using SVM and XGBoost. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, (18), 20886-20895. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Nie, B.; Lu, B.; Fu, L.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Pi, X.; Liu, H., Recognizing lung cancer and stages using a self-developed electronic nose system. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 131. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zheng, Y., Robust gas recognition with mixed interference using a spiking neural network. Measurement Science and Technology 2021, 33, (1). [CrossRef]
- Lekha, S.; M, S., Real-Time Non-Invasive Detection and Classification of Diabetes Using Modified Convolution Neural Network. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2018, 22, (5), 1630-1636. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H. X.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, W. K.; Chen, X. W.; Zeng, M.; Yang, J. H.; Su, Y. J.; Hu, N. T.; Yang, Z., Target discrimination, concentration prediction, and status judgment of electronic nose system based on large-scale measurement and multi-task deep learning. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 351, 12. [CrossRef]
- Avian, C.; Mahali, M. I.; Putro, N. A. S.; Prakosa, S. W.; Leu, J.-S., Fx-Net and PureNet: Convolutional Neural Network architecture for discrimination of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease from smokers and healthy subjects through electronic nose signals. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 148. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, D. H.; Wong, K. Y.; Hung, K.; Li, X., ODRP: A Deep Learning Framework for Odor Descriptor Rating Prediction Using Electronic Nose. Ieee Sensors Journal 2021, 21, (13), 15012-15021. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, S.; Feng, N.; Yin, C.; Shi, Y., PSCFormer: A lightweight hybrid network for gas identification in electronic nose system. Pattern Recognition 2024, 145. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, B.; Yin, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y., Performance improvement: A lightweight gas information classification method combined with an electronic nose system. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2023, 396. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Lujan, I.; Fonollosa, J.; Vergara, A.; Homer, M.; Huerta, R., On the calibration of sensor arrays for pattern recognition using the minimal number of experiments. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2014, 130, 123-134. [CrossRef]
- Vergara, A.; Vembu, S.; Ayhan, T.; Ryan, M. A.; Homer, M. L.; Huerta, R., Chemical gas sensor drift compensation using classifier ensembles. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2012, 166, 320-329. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L. J.; He, M.; Hu, C.; Hou, Y. X.; Han, S. Y.; Tang, X. Y., Image presentation and effective classification of odor intensity levels using multi-channel electronic nose technology combined with GASF and CNN. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2023, 395. [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, Y. M.; Huang, X. M., A CNN Accelerator on FPGA Using Depthwise Separable Convolution. Ieee Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ii-Express Briefs 2018, 65, (10), 1415-1419.
- Adams, S. J.; Stone, E.; Baldwin, D. R.; Vliegenthart, R.; Lee, P.; Fintelmann, F. J., Lung cancer screening. The Lancet 2023, 401, (10374), 390-408.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the overall process of this work.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the overall process of this work.
Figure 2.
The diagram of GAF coding. X represents the response data of 16 sensors at a certain sampling point. After scaling, X is converted to the polar coordinate system, and finally the GASF/GADF image is generated.
Figure 2.
The diagram of GAF coding. X represents the response data of 16 sensors at a certain sampling point. After scaling, X is converted to the polar coordinate system, and finally the GASF/GADF image is generated.
Figure 3.
Block diagrams of LTNet network structure. (a) the ConvBN module is presented, which results from the fusion of depthwise separable convolution and Batch Normalization (BN) layers, (b) the backbone network, and (c) the LTBlock module, constructed by integrating the ConvBN module, residual connections, and the Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) attention mechanism.
Figure 3.
Block diagrams of LTNet network structure. (a) the ConvBN module is presented, which results from the fusion of depthwise separable convolution and Batch Normalization (BN) layers, (b) the backbone network, and (c) the LTBlock module, constructed by integrating the ConvBN module, residual connections, and the Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) attention mechanism.
Figure 4.
Image generated after data conversion. (a), (b), (c) and (d) are images converted by GADF, MTF, SFTF and GASF, respectively.
Figure 4.
Image generated after data conversion. (a), (b), (c) and (d) are images converted by GADF, MTF, SFTF and GASF, respectively.
Figure 5.
shows the confusion matrices. (a), (b), (c), and (d) represent the evaluation results of LTNet on the GADF, MTF, SFTF, and GASF image transformation methods, respectively. (e), (f), (g), (h), (i), and (j) show the evaluation results of AlexNet, ResNet50, VGG16, EfficientNet, MobileNetV3_large, and LTNet on the mixed gas dataset. (k), (l), (m), (n), (o), and (p) display the evaluation results of AlexNet, ResNet50, VGG16, EfficientNet, MobileNetV3_large, and LTNet on the UCI database.
Figure 5.
shows the confusion matrices. (a), (b), (c), and (d) represent the evaluation results of LTNet on the GADF, MTF, SFTF, and GASF image transformation methods, respectively. (e), (f), (g), (h), (i), and (j) show the evaluation results of AlexNet, ResNet50, VGG16, EfficientNet, MobileNetV3_large, and LTNet on the mixed gas dataset. (k), (l), (m), (n), (o), and (p) display the evaluation results of AlexNet, ResNet50, VGG16, EfficientNet, MobileNetV3_large, and LTNet on the UCI database.
Table 1.
Sensor models and optimal operating currents.
Table 1.
Sensor models and optimal operating currents.
| NO. |
Models |
Target gases |
Detection ranges (ppm) |
Optimal operating currents (mA) |
| 1 |
TGS2600 |
Ethanol、Hydrogen |
1-30 |
45 |
| 2 |
TGS2602 |
Ammonia、Ethanol |
Ethanol 1-30 |
50 |
| 3 |
TGS2610 |
Organic compounds |
500-10000 |
55 |
| 4 |
TGS2620 |
Ethanol、Organic compounds |
Ethanol 50-5000 |
43 |
Table 2.
Details of concentration indicators in the acetone ethanol experimental dataset.
Table 2.
Details of concentration indicators in the acetone ethanol experimental dataset.
| NO. |
Ethanol (ppm) |
Acetone (ppm) |
Mixed gas (ppm) |
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| 2 |
0 |
3 |
3 |
| 3 |
0 |
5 |
5 |
| 4 |
0 |
7 |
7 |
| 5 |
0 |
9 |
9 |
| 6 |
0 |
11 |
11 |
| 7 |
0 |
13 |
13 |
| 8 |
0 |
15 |
15 |
| 9 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| 10 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
| 11 |
5 |
0 |
5 |
| 12 |
7 |
0 |
7 |
| 13 |
9 |
0 |
9 |
| 14 |
11 |
0 |
11 |
| 15 |
13 |
0 |
13 |
| 16 |
15 |
0 |
15 |
| 17 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
| 18 |
1 |
5 |
6 |
| 19 |
1 |
10 |
11 |
| 20 |
1 |
15 |
16 |
| 21 |
5 |
1 |
6 |
| 22 |
5 |
5 |
10 |
| 23 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
| 24 |
5 |
15 |
20 |
| 25 |
10 |
1 |
11 |
| 26 |
10 |
5 |
15 |
| 27 |
10 |
10 |
20 |
| 28 |
10 |
15 |
25 |
| 29 |
15 |
1 |
16 |
| 30 |
15 |
5 |
20 |
| 31 |
15 |
10 |
25 |
| 32 |
15 |
15 |
30 |
Table 3.
Comparison of results of four data conversion methods.
Table 3.
Comparison of results of four data conversion methods.
| Models |
Accuracy |
Training time (S) |
GPU RAM (G) |
| GADF |
98.79% |
863.49 |
2.3 |
| MTF |
92.34% |
929.08 |
2.6 |
| STFT |
100% |
1630.92 |
2.6 |
| GASF |
99.06% |
844.38 |
2.1 |
Table 4.
Model parameters and weights.
Table 4.
Model parameters and weights.
| Models |
Params. |
Weight size (MB) |
| AlexNet |
57012034 |
217 |
| ResNet50 |
23514179 |
89.9 |
| VGG16 |
134268738 |
512 |
| EfficientNet |
4586092 |
17.8 |
| MobileNetV3_large |
4208443 |
16.2 |
| LTNet (This work) |
32614 |
0.155 |
Table 5.
Classification results of mixed gas data sets.
Table 5.
Classification results of mixed gas data sets.
| Models |
Accuracy |
GPU RAM (G) |
Training time (S) |
Inference time (S) |
| AlexNet |
97.71% |
3.1 |
853.27 |
283 |
| ResNet50 |
98.39% |
3.8 |
1234.34 |
284 |
| VGG16 |
97.98% |
6.9 |
2249.56 |
592 |
| EfficientNet |
99.06% |
5.4 |
1373.48 |
170 |
| MobileNetV3_large |
98.79% |
3.3 |
877.53 |
91 |
| LTNet (This work) |
99.06% |
2.1 |
844.38 |
23 |
Table 6.
Classification accuracy and model parameters of UCI database.
Table 6.
Classification accuracy and model parameters of UCI database.
| Models |
Accuracy |
GPU RAM (G) |
Training time (S) |
Inference time (S) |
| AlexNet |
98.92% |
3.2 |
613.50 |
187 |
| ResNet50 |
98.92% |
3.7 |
841.81 |
178 |
| VGG16 |
98.71% |
7.1 |
1477.44 |
377 |
| EfficientNet |
98.92% |
5.3 |
933.21 |
109 |
| MobileNetV3_large |
98.92% |
3.3 |
606.20 |
60 |
| LTNet (this work) |
99.14% |
2.1 |
584.67 |
14 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).