1. Introduction
With the increasing prevalence of high-resolution remote sensing satellites in global Earth observation missions, high-resolution remote sensing data has become abundant and the primary source for Earth observation. Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5] plays a vital role in understanding the distribution of ground object features, enabling refined urban management, environmental monitoring, natural resource assessment, crop analysis, precise surveying, and mapping. High-resolution remote sensing images possess distinct characteristics, including complex background information, dense targets, and rich ground object features. Consequently, effectively leveraging global and local features of targets amidst complex backgrounds and bridging the differences between various features becomes crucial for enhancing the accuracy of semantic segmentation.
Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images [
6,
7,
8] can be broadly categorized into two types: single-branch segmentation networks and dual-branch networks.
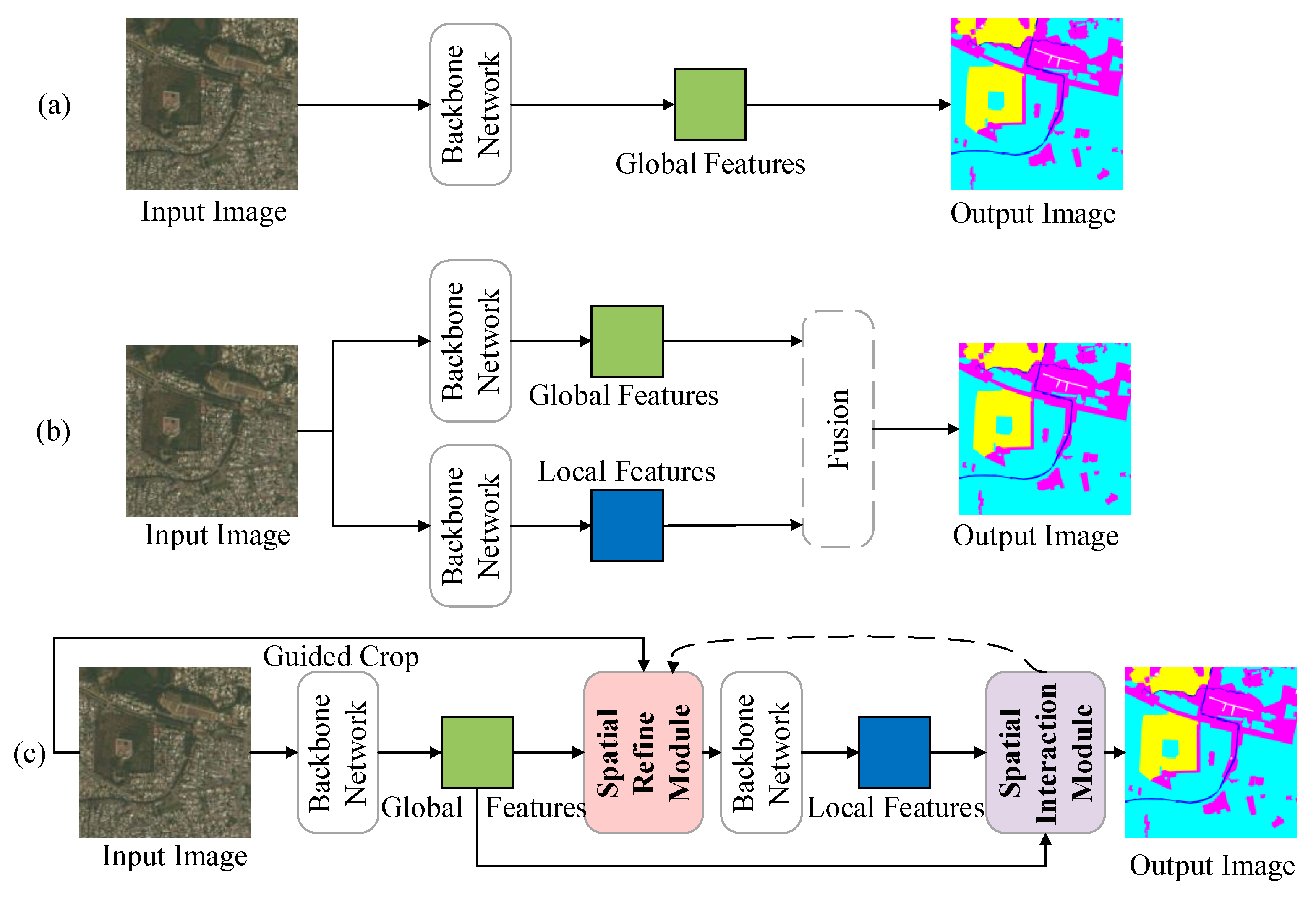
Figure 1a illustrates the single-branch segmentation networks [
9,
10,
11], which employ pure convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to enhance feature extraction capabilities. These single-branch architectures typically consist of well-known backbone networks such as FCN [
12], UNet [
13], DeepLabV3 [
14], and their combinations. However, these methods often overlook the effective interaction between global and local features of target objects within the complex backgrounds of high-resolution remote sensing images. Moreover, these approaches commonly involve downsampling the high-resolution remote sensing images before feature extraction, leading to the loss of either high-resolution details or spatial contextual information.
In recent years, the dual-branch structure has gained significant attention and achieved remarkable advancements in semantic segmentation.
Figure 1b illustrates these methods [
15,
16,
17,
18], which consist of two branches dedicated to extracting global and local features, respectively. The final segmentation is generated by aggregating high-level feature maps from both branches. This network architecture greatly enhances segmentation performance and effectively demonstrates the efficacy of extracting different features through separate branches. However, previous methods fused all the information from different branches without a mechanism for selectively incorporating spatial and positional features, treating each feature equally. Additionally, the fusion of global and local information was achieved through explicit interactions, such as simple concatenation or addition, lacking an adaptive mechanism.
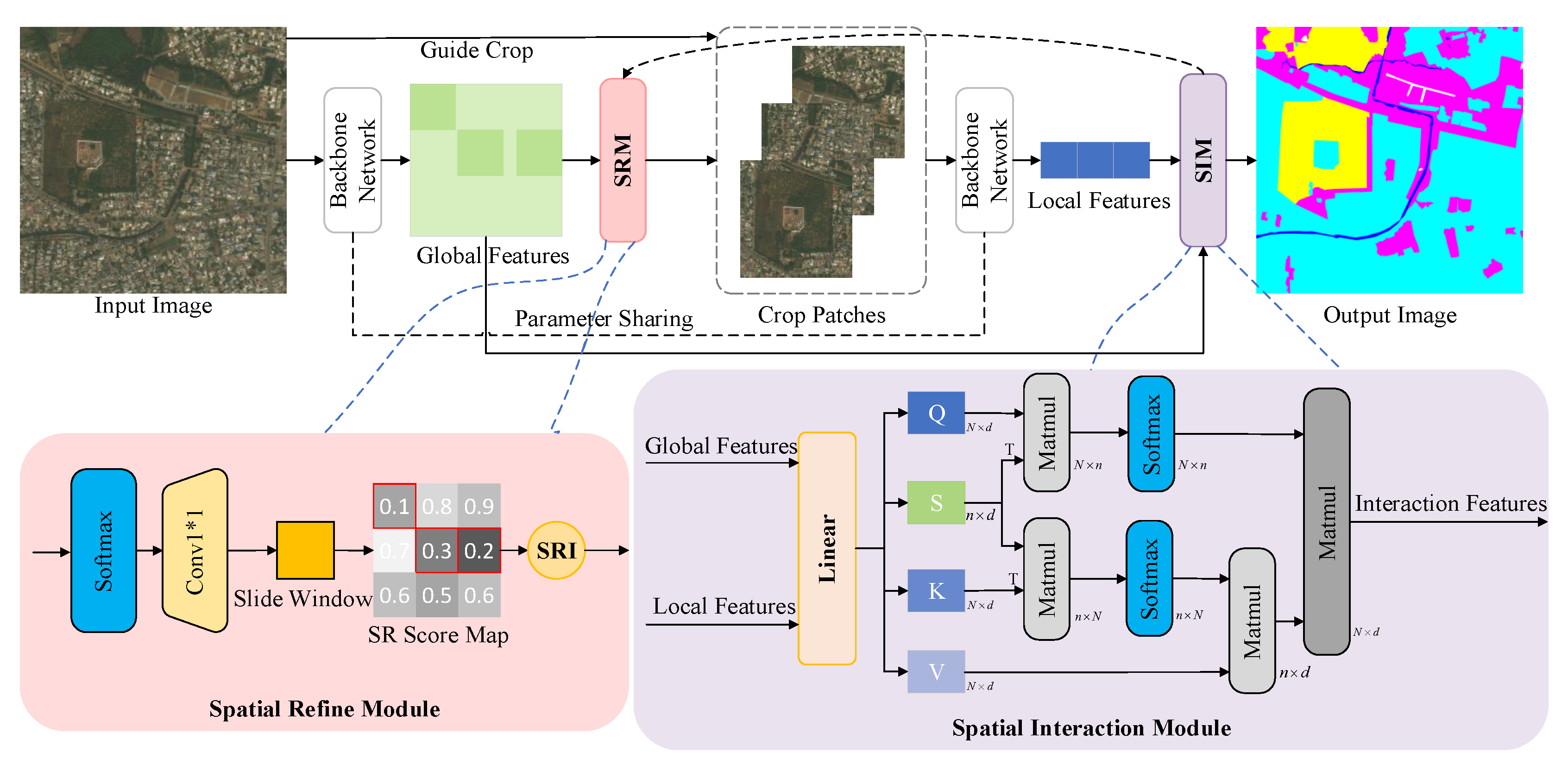
In this paper, we propose a novel spatially adaptive interaction network (SAINet) for the dynamic interaction of information across different features. As shown in
Figure 1c, SAINet concatenates the entire network through the spatial refined module (SRM) and spatial interaction module (SIM). To be specific, the whole image is first input to the backbone network to obtain coarse segmentation results. To ensure the coarse regions and enhance the segmentation accuracy, SRM is used to select local patches that are difficult to be segmented by the backbone network. Then crop the patches and they are input to the backbone network to obtain fine local features. To further enhance the segmentation accuracy, SIM is used to facilitate interaction between local salient areas and global information. As a result of integrating local and global information, it is possible to capture contextual information adaptively from multiple perspectives. To evaluate the effectiveness of the model, we conducted extensive experiments demonstrating that our proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the publicly available high-spatial-resolution image datasets DeepGlobe, Vaihingen, and Potsdam.
Our main contributions are summarized as follows:
We propose a novel spatially adaptive interaction network (SAINet) for filtering and dynamic interaction among different spatial features in the remote sensing semantic segmentation task.
We present a new spatial refined module that uses local context information to filter spatial positions and extract salient regions.
We devise a spatial interaction model to adaptively modulate mechanisms to dynamically select and allocate spatial position weights to focus on target areas.
We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by achieving state-of-the-art semantic segmentation performance on three publicly available high-resolution remote sensing image datasets.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
The Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) [
12] pioneered the use of end-to-end convolutional networks for semantic segmentation, laying the foundation for this field. FCN eliminated connected layers, making it adaptable to inputs of any size. It utilized simple bilinear interpolation for initialization and employed deconvolution layers to upsample the feature maps from the final convolutional layer, preserving spatial positional information for pixel-wise predictions. Optional application of Conditional Random Fields (CRF) [
19] improved classification mapping and segmentation results. The encoder-decoder framework was subsequently introduced with influential models like UNet [
13] and SegNet [
20]. UNet, structured as a U-shape, employed deconvolutional upsampling and feature map concatenation from corresponding scales in preceding layers. It achieved high speed and became a baseline network for medical image segmentation tasks. SegNet, although not the first encoder-decoder structure, successfully generalized the architecture, balancing memory (parameters) and accuracy. It utilized unspooling for feature map upsampling, reducing parameters and preserving high-frequency information. The concept of dilated convolutions [
21] introduced background modules that used dilated convolutions for multi-scale aggregation, achieving dense prediction results without increasing parameters. Deeplabv2 [
22] proposed the pyramid-like atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) technique, employing multiple parallel atrous convolution layers with different sampling rates for effective multi-scale processing. EMRN [
23] proposes a multi-resolution features dimension uniform module to handle dimensional features from images of varying resolutions. PSPNet [
24] enhances the ResNet [
25] structure using atrous convolutions and incorporates a pyramid pooling module to capture contextual information at different scales. Deeplabv3 [
14] improves spatial ASPP by cascading multiple atrous convolution structures and introduces batch normalization after each parallel convolutional layer. In 2018 [
9], DeepLabv3 is adopted as an encoder architecture with an effective decoder module. It also explores the use of improved Xception and depth-wise separable convolutions to enhance the model’s performance in semantic segmentation tasks.
Recently, attention mechanism methods [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30] have been introduced to semantic segmentation. Transformer mechanisms and self-attention mechanisms [
31] were initially introduced in the field of natural language processing and later sparked widespread research interest in the field of computer vision [
32,
33,
34,
35]. The pioneering work, Vision Transformer (ViT) [
36], utilizes multiple Transformer blocks to process non-overlapping image patches, establishing a convolution-free image classification model. PVT (Pyramid Vision Transformer) [
37] draws inspiration from the pyramid structure of convolutional neural networks. It gradually reduces feature resolution by segmenting the input image into blocks of different scales. Transformer encoding blocks are then applied to each scale for feature extraction. This approach empowers PVT to handle features at various levels, resulting in remarkable performance across diverse image classification tasks. CFIL [
38] proposes a frequency-domain feature extraction module and feature interaction in the frequency domain to enhance salient features. MFC [
39] proposes a frequency-domain filtering module to achieve dense target feature enhancement. To avoid excessive attention computation, Swin Transformer [
40] employs window-based local attention to confine attention within local windows. To fully leverage the advantages of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in local feature extraction and the capabilities of Transformers in global relationship modeling, [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46] combining these two methods allows for the simultaneous capture of image details and overall context. This integration aims to enhance image analysis and understanding and has the potential to yield improved results across various computer vision tasks. In certain situations, different regions may possess varying degrees of importance. Deformable attention [
47] enables models to dynamically adjust their focus on different regions of an image based on object shapes and positions. This adaptive tuning allows the model to more accurately emphasize important object-related areas, thus enhancing its performance in image processing tasks. Recently, to reduce computational costs, researchers have introduced a coarse-fine-grained Visual Transformer (CF-ViT) [
48] to alleviate the computational burden while maintaining performance.
2.2. Dual-Branch Architecture
In visual tasks involving natural images [
49,
50,
51,
52], remote sensing images [
15,
17,
53,
54], and visible light images [
55,
56,
57,
58,
59], a substantial body of work has sought to address the subjectivity issue in balancing this trade-off by learning to integrate multi-scale information. Specifically, these approaches learn representations from multiple parallel networks and then aggregate information across different scales before making the final predictions. Taking the remote sensing domain as an example, GLNet [
15] consists of a global branch and a local branch, tailored to address both global downscaled images and localized cropped image blocks. GLNet achieves high-quality segmentation outcomes, effectively balancing precision and memory consumption. UHRSNet [
16] enhances and streamlines the local and global feature fusion approach of GLNet, enabling small blocks to gather information from surrounding ones. This effectively addresses the challenges posed by cropping and downsampling. HPGN [
60] proposes a novel pyramid graph network targeting features, which is closely connected behind the backbone network to explore multi-scale spatial structural features. To fully harness the potential of the multi-branch architecture, MBNet [
17] introduces a scaling module. The Zoom module relinquishes the prior L2 normalization before feature concatenation, instead exploiting the acquired attention to fuse distinct features. This approach maximizes the advantages of multi-resolution capabilities. The existing dual-branch architectures have shown promising results by seamlessly integrating patches and downsampled images during training. However, these approaches have primarily focused on merging information from different branches without considering the importance of spatial location features. They treat all extracted features uniformly, resulting in direct interactions (such as concatenation or addition) without an adaptive mechanism.
3. Method
We propose a spatially adaptive interaction network to utilize both global and local information better and achieve effective interaction between local saliency regions and global information: spatially adaptive interaction network, SAINet, a segmentation network based on high-resolution images. In
Section 3.1, we first give an overview of the network. From
Section 3.2 to
Section 3.3, we further introduce the composition of the network, including the backbone network, spatially refined module (SRM), and spatial interaction module (SIM).
3.1. Overview
SAINet network, as shown in
Figure 2, consists of the following parts: (1) Extracts global information from downsampled images; (2) Introduces a simple yet effective spatial refinement module, which utilizes local contextual information for spatial position filtering, extracting salient regions and their indices; (3) Extracts local detailed information; (4) Utilizes a spatial adaptive modulation mechanism for dynamically selecting and allocating spatial position weights, achieving the interaction of local salient regions and global information. The global feature extraction and local feature extraction are performed using the ResNet50-based FPN (Feature Pyramid Network), with the parameters of the two backbone networks shared.
Specifically, the proposed approach first uses the backbone network to extract features from the input image
X, generating the global feature map
. It then uses the spatial refine module to obtain the saliency regions and their indices
. Subsequently, SAINet uses
to crop the original image, obtain the cropped image block
, and apply the same backbone network to extract features from
, resulting in the local feature map
. To facilitate more effective interaction between the global feature
and the local feature
, we introduce the spatial interaction module (SIM), a novel attention mechanism that combines linear attention and softmax attention. Our network can be formulated as:
where the matrix
X represents the input image,
denotes the resize operation, and
is the backbone network, using the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) with ResNet50.
is the global feature map with coarse extraction results.
where
represents the saliency region index, and
denotes the spatial refine module, with details shown in sub
Section 3.2.
where
denotes the cropping operation with SRI. The matrix
represents the cropped image.
is the backbone network the same as formula 1.
denotes the local feature map with more detailed information.
where
signifies the newly obtained features through interaction, and
stands for the spatial interaction module, with operational details in sub
Section 3.3.
3.2. Spatial Refine Module
Not all the extracted global features from down-sampled images are inaccurate, meaning not every local area needs enhancement. Especially in high-resolution remote sensing images, some objects are often continuous and occupy a large proportion of the entire image. Therefore, we have introduced a spatial refinement module that utilizes local context information to screen spatial positions and extract salient regions.
As shown in
Figure 2, the global features
are first passed through the spatial refinement module, followed by a softmax operation, and then a 1x1 convolution is employed to obtain the saliency level on the channel dimension, denoted as
. Hence, the confidence level of the global image is noted as
, and Equation (
2) presents the calculation formulas.
To further enhance the expressiveness of salient regions, a sliding window is used to calculate the local region scores, resulting in the ScoreMap. In this paper, the appropriate sliding window size of 3x3 was determined through subsequent ablation experiments. The final window size s is set to 3x3. The threshold for determining salient regions denoted as T, is determined using the formula:
In this study, the values of t and
are set to 0.08 and 7, respectively. Areas of the ScoreMap with scores below the threshold T are considered salient regions (SR) along with their corresponding index (SRI), where
Subsequently, the original image is cropped using the SRI to determine local crop patches. The weight matrix of the salient region
is learned by the spatial interactive module, for details see
Section 3.3.
3.3. Spatial Interaction Module
Traditional feature fusion involves merging global and local features entirely, and the fusion method is merely a simple addition or concatenation. This is not only inefficient but also results in insufficient fusion. We all know that the large and sometimes even global, receptive field of the Transformer model gives it superior representational abilities compared to its CNN counterparts, especially in terms of understanding global context. Therefore, this paper presents a fusion method based on Transformer. However, simply enlarging the receptive field can also lead to some issues. On the one hand, using dense attention in ViT can result in excessive memory and computational costs, and the features may be affected by irrelevant parts beyond the region of interest. On the other hand, the sparse attention adopted in PVT or Swin Transformer is data-agnostic and may limit the ability to model distant relationships. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel interactive attention mechanism, where the interactive positions are selected in a data-dependent manner. This flexible attention mechanism can focus on relevant areas and integrate more informative features.
As shown in
Figure 2, our spatial interaction module (SIM) is an innovative mode of attention that integrates the powerful Softmax attention with the efficient linear attention, represented as a quadruple (Q, S, K, V). With two inputs of N tokens represented as
,
and
are obtained from Eq.(1) and Eq.(3) respectively. So self-attention can be formulated as follows in each head:
where
denote projection matrices,
C and
d are the channel dimension of the module and each head, and
represents the similarity function. When using
in Eq.(8), it becomes Softmax attention [
31]. So Softmax attention can be abbreviated as:
Where
denote query, key, and value matrices and
represents Softmax function. When similarity is measured as
in Eq.(8), it becomes Linear attention [
61]. So linear attention can be abbreviated as:
Softmax and linear attention suffer from either excessive computation complexity or insufficient model expressiveness. So this paper introduces a set of additional saliency region tokens
into the traditional attention module. As shown in
Figure 2, our interaction module consists of two Softmax attention operations. We initially treat tokens
S as queries and perform attention calculations between
S,
K and
V to aggregate local salient features
:
The saliency region tokens S first act as intermediaries for the query tokens Q, aggregating information from K and V, and then broadcasting the information back to Q. The number of saliency region tokens is determined by the RM module and is far less than the number of query tokens. The saliency region attention is notably more efficient than the widely used Softmax attention, while still preserving the global context modeling capability.
Subsequently, we utilize S as keys and
as values in the second attention calculation with the query matrix
Q, interactions the global information and local salient information to obtain the final output
:
Then our attention used in the interaction module can be written as:
3.4. Loss
In the first training phase, we employ cross-entropy loss as a loss function to measure the difference between the prediction results of the backbone network and the ground truth data.
where
p is the prediction result, and
y is the ground truth data.
In the second training phase, We use the Focal Loss [
62] with
as the optimization target.
where
represents the probability that the second backbone network predicts for a certain category;
is used to balance the number of positive and negative samples, with a smaller
value assigned to categories with more samples and a larger
value to those with fewer samples;
is used to adjust the imbalance between hard-to-separate and easy-to-separate samples. In this paper, we take
to reduce the loss of easy-to-separate samples with a power function.
4. Experiment
We conduct experiments on three datasets to verify the effectiveness of our proposed method. DeepGlobe dataset, which primarily focuses on rural areas, and the Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets, which emphasize urban regions.
4.1. Datasets
Table 1.
Three public semantic segmentation datasets of ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing images are used in this paper.
Table 1.
Three public semantic segmentation datasets of ultra-high-resolution (UHR) remote sensing images are used in this paper.
| Dataset |
Max Size |
Number of Classes |
%of 4K UHR Image |
#Image |
| DeepGlobe [63] |
6M pixels (2448×2448) |
7 |
100% |
803 |
| Vaihingen * |
28M pixels (2494×2064) |
6 |
100% |
33 |
| Potsdam * |
103M pixels (6000×6000) |
6 |
100% |
38 |
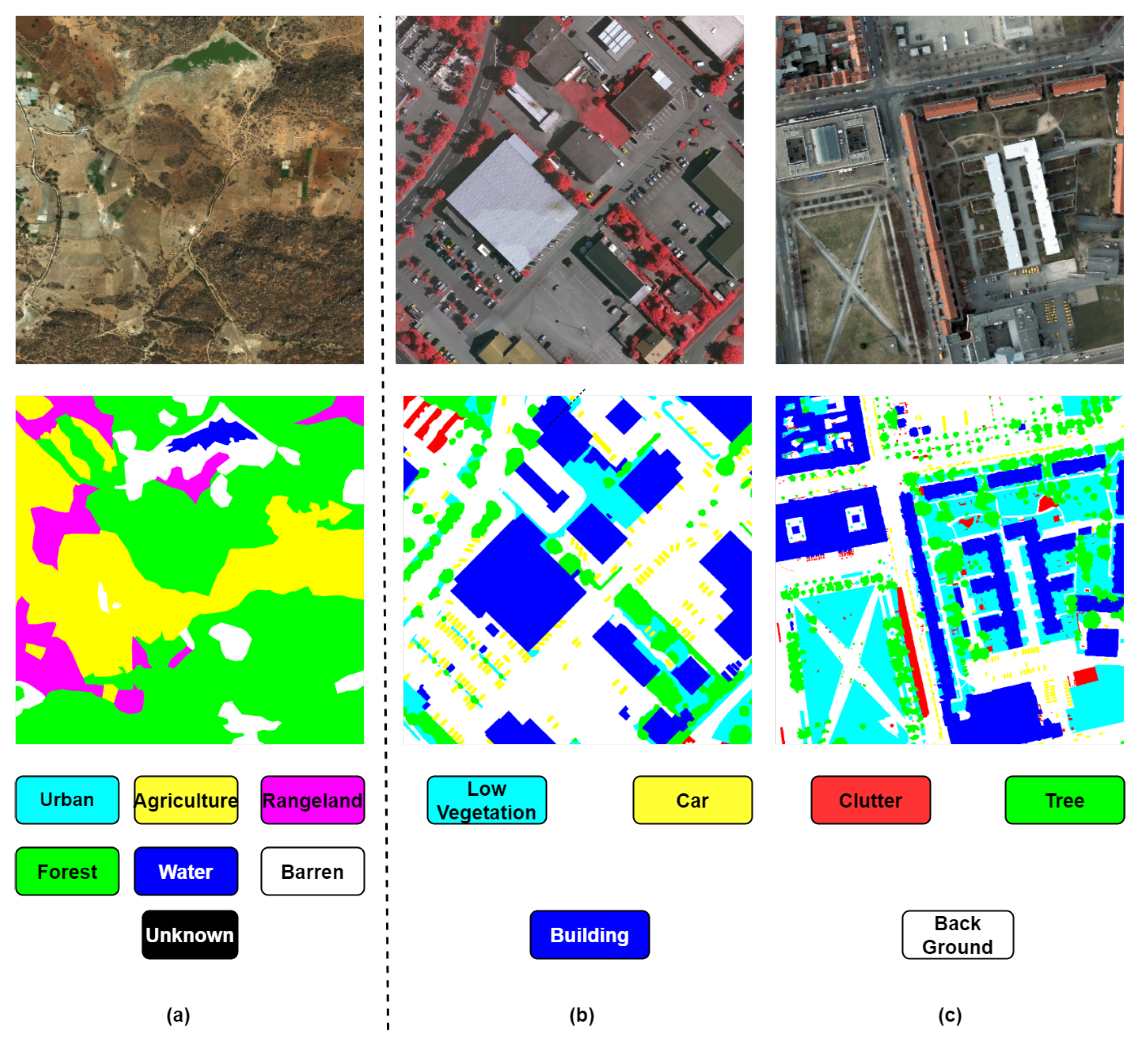
Figure 3.
Image sample and corresponding ground truth of(
a) DeepGlobe and (
b) Vaihingen and (
c) Potsdam. The mask of DeepGlobe is an RGB image with seven classes following the Anderson Classification. Label colors are given at the bottom left of
Figure 3. The labels of Vaihingen and Potsdam challenges include six categories; they are given at the bottom right of
Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Image sample and corresponding ground truth of(
a) DeepGlobe and (
b) Vaihingen and (
c) Potsdam. The mask of DeepGlobe is an RGB image with seven classes following the Anderson Classification. Label colors are given at the bottom left of
Figure 3. The labels of Vaihingen and Potsdam challenges include six categories; they are given at the bottom right of
Figure 3.
The DeepGlobe Land Cover Classification dataset is the first publicly available benchmark that offers high-resolution sub-meter satellite imagery with a focus on rural regions. DeepGlobe provides real pixel masks for seven classes: urban in blue, agriculture in yellow, rangeland in purple, forest in green, water in blue, barren in white, and unknown. It consists of 1146 annotated satellite images, all sized at 2448×2448 pixels. Compared to previous land cover classification datasets, DeepGlobe has a much higher resolution and is more challenging.
The Vaihingen dataset comprises thirty-three images with a spatial resolution of 9 cm and an average image size of 2494 × 2064 pixels. Each image consists of three channels: red, green, near-infrared (NIR), and their corresponding digital surface model. The Vaihingen dataset contains six classes: impervious surfaces, buildings, low vegetation, trees, cars, and background. Sixteen images with ground truth are used for network training and validation, while the remaining seventeen images are reserved for testing. It’s worth noting that the digital surface model was not utilized in our experiments.
The Potsdam dataset consists of twenty-eight images, all of which have the same dimensions of 6000×6000 pixels, with a spatial resolution of 5cm for both the top-level imagery and DSM. Similar to the Vaihingen region, this dataset includes remote sensing TIFF files with three bands and a single-band DSM. Each remote sensing image covers the same geographic area, ensuring that both the images and DSM are defined within the same reference system (UTM WGS84). Additionally, each image is accompanied by an affine transformation file, enabling the decomposition of the image into smaller sections as needed. All images are densely labeled with the same six classes as the Vaihingen dataset. Twenty-four images, each containing ground truth data, are utilized for network training and validation, while the remaining fourteen images are reserved for testing purposes. To streamline computation, we chose not to utilize the DSM in our experiments. It is noteworthy that only the red, green, and blue channels were employed in our experiments.
4.2. Experimental Settings
To validate the performance of the proposed method, we compared SAINet with widely used single-branch networks and GLNet-based segmentation networks on the DeepGlobe, Vaihingen, and Potsdam datasets. In all the experiments, none of the networks utilized pre-trained weights. To demonstrate that our fusion method is more effective than GLNet’s fusion approach, both the downsampled global image and the cropped local patches share the same size as GLNet, 500×500 pixels. Neighboring patches have a 50-pixel overlap to avoid boundary vanishing for all the convolutional layers.
The experiments were implemented under the Pytorch framework, with Python version 3.8, and using an NVIDIA Geforce RTX2080Ti 11-GB GPU. To accelerate convergence during model training, we use the Adam optimizer and set the momentum to 0.9 and weight decay to for training the global branch, and for the local branch. The number of training epochs was set to 150, and a minibatch size of 6 for all training. We used an early stopping mechanism in the training process to terminate the training when the performance of the test dataset did not increase in 10 epochs.
4.3. Evaluation Matrix
To evaluate the performance of the algorithm in this paper, four evaluation common metrics are used: the overall accuracy (OA), the F
1 score, the mean of classwise intersection over union (mIoU), and the accuracy of foreground categories (Acc). The OA is used to assess the proportion of correctly classified pixels to the total pixels. (OA) is defined as:
where
TP(True Positive): the prediction result is a positive example, and the actual value is also a positive example, the prediction is correct, it is true;
TN(True Negative): the prediction result is negative, the actual value is positive, and the prediction error is false.
For each category, the F
1 score can be computed by:
where
is the equivalent factor of the precision rate and recall rate and is set to one.
We use the pixel-wise Intersection over Union (IoU) score as our evaluation metric. It was defined slightly differently for each class, as there are multiple categories. Assuming there are n images, the formulation is defined as:
where
TPij is the number of pixels in image i that are correctly predicted as class
j,
FPij is the number of pixels in image
i that are wrongly predicted as class
j, and
FNij is the number of pixels in image
FPij that are wrongly predicted as any class other than class
j. Note that we have an unknown class that is not active in our evaluation (i.e., the predictions on such pixels will not be added to the calculation and thus do not affect the final score). Assuming there are k land cover classes, the final score is defined as the average IoU among all classes as in Eqn. (18).
4.4. Results
To demonstrate the superiority of our proposed algorithm, we compared it with traditional semantic segmentation algorithms and the dual-branch GLNet network. Our network, as well as the single-branch networks, can only produce prediction results for patches. Therefore, we combine these patches to obtain the overall prediction result for the entire image. GLNet offers two methods to obtain predictions for the entire image, and we have chosen the combination method, which yields better results.
4.4.1. Results on DeepGlobe
To verify the performance of SAINet, we compare the model with other CNN-based and GLNet-based semantic segmentation networks on the DeepGlobe dataset. GLNet only computed the mIoU, so we are consistent with it here. The specific results are shown in
Table 2. The results show that double-branch GLNet-based methods outperform single-branch CNN-based methods on the DeepGlobe dataset. SAINet has a significant performance improvement compared to other networks. Compared to GLNet [
15] and MBNet [
17], the mIoU of SAINet is improved by 6.2% and 5.2%, respectively. Compared to DeepLabv3+ [
9], the top-performing single-branch network, the mIoU of SAINet is improved by 20.7%. Hence, our network achieves optimal results in all classes and the mIoU matrix, indicating that our model outperforms GLNet, UHRSNet [
16], and MBNet. As UHRSNet and MBNet are based on improvements to GLNet, our experiments on the DeepGlobe dataset include an extended range of experiments incorporating UHRSNet and MBNet.
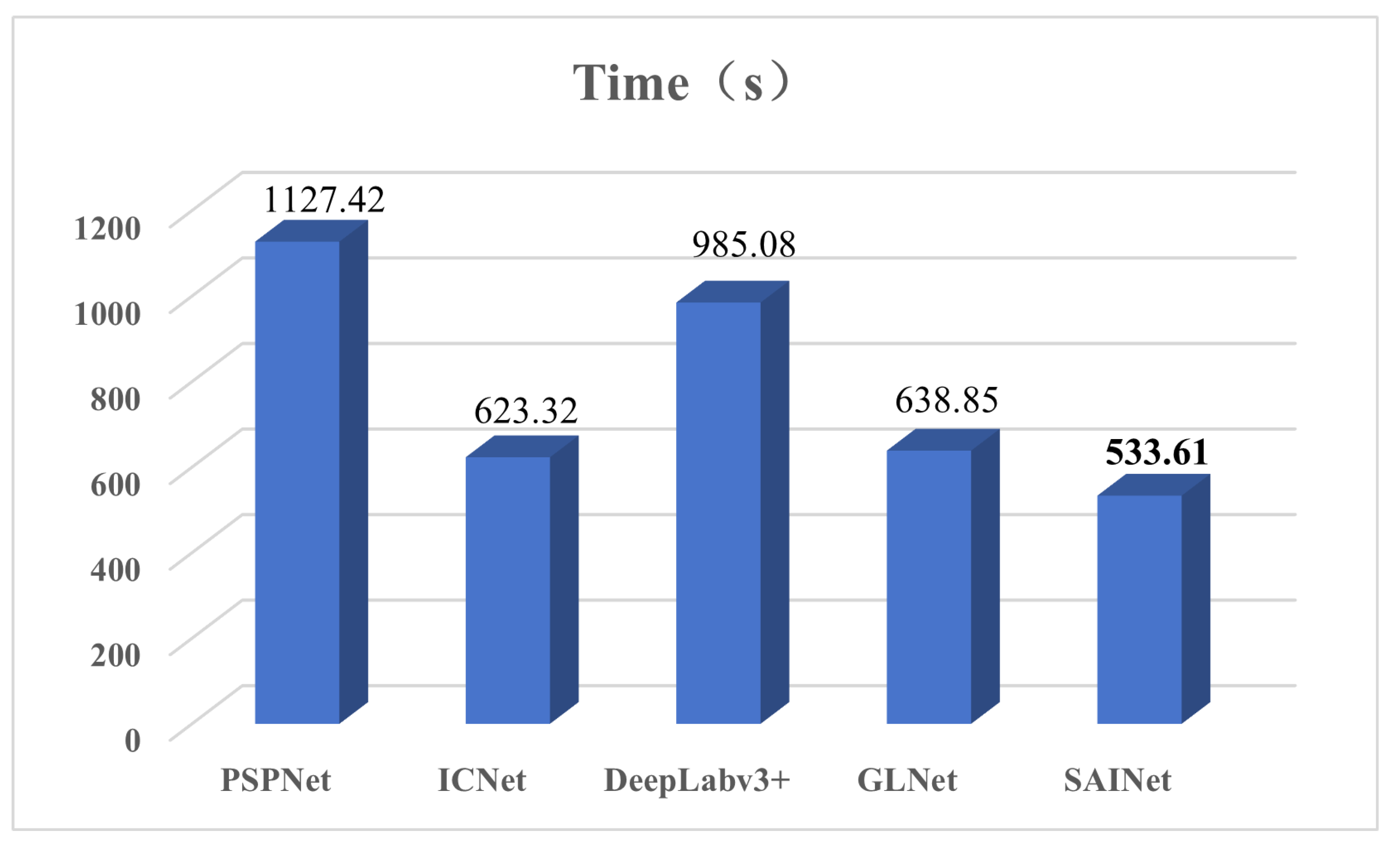
We also compared the inference speed of the networks. For SAINet and GLNet, the prediction time is for the entire original image. However, for single-branch networks like DeepLabv3+, ICNet [
64], and PSPNet [
24], the prediction time is the sum of the prediction time for all the smaller patches obtained by cropping the original image. As shown in
Figure 5, our method and GLNet demonstrate superior inference speed compared to single-branch networks. Thanks to the design of the spatial refine module and spatial interaction module, our network achieves faster inference for the entire original image while maintaining accuracy, outperforming GLNet by 105.24 seconds. While DeepLabv3+ achieves high accuracy, its inference efficiency is compromised. Although ICNet improves inference efficiency, it struggles to maintain high accuracy. PSPNet, on the other hand, increases accuracy but at the cost of significantly longer inference time.
4.4.2. The Result on the Vaihingen Dataset
Table 2.
Comparison on the DeepGlobe Dataset.
Table 2.
Comparison on the DeepGlobe Dataset.
| Method |
Barren |
Rangeland |
Forest |
Water |
Urban |
Agriculture |
mIoU (%) |
| ICNet[64] |
35.2 |
31.3 |
24.2 |
42.1 |
24.3 |
69.2 |
37.7 |
| FCN[12] |
36.1 |
36.4 |
35.5 |
38.9 |
26.2 |
72.3 |
40.9 |
| U-Net[13] |
34.1 |
33.5 |
28.2 |
45.1 |
26.1 |
71.7 |
39.8 |
| PSPNet[24] |
39.3 |
36.9 |
53.6 |
64.2 |
48.2 |
74.7 |
52.8 |
| SegNet[65] |
43.1 |
38.2 |
54.8 |
67.8 |
53.1 |
75.2 |
55.4 |
| DeepLabv3+[9] |
44.1 |
42.2 |
56.3 |
68.4 |
54.1 |
77.3 |
57.1 |
| UHRSNet[16] |
81.2 |
61.3 |
72.3 |
70.1 |
78.9 |
68.4 |
72.0 |
| MBNet[17] |
64.1 |
87.3 |
41.5 |
80.6 |
83.1 |
78.9 |
72.6 |
| Baseline[15] |
63.6 |
38.6 |
79.8 |
82.6 |
78.1 |
86.8 |
71.6 |
| SAINet |
86.5 |
46.1 |
83.1 |
84.4 |
79.2 |
87.3 |
77.8 |
Figure 4.
Inference time on the DeepGlobe dataset.
Figure 4.
Inference time on the DeepGlobe dataset.
To verify the robustness of SAINet, we conducted comparative experiments on the Vaihingen dataset. The results are shown in
Table 3 where SAINet yields mean F1 of 90.7%, OA 91.9%, mIoU 82.5% respectively and is quantitively superior to other methods. Specifically, compared with the second method, the proposed SAINet improvement in mean F1 is 0.9%, OA 1.3%, and mIoU% respectively. The "Building" class gains the highest classification accuracy of 96.5%. Especially in high-resolution remote sensing images, the Car, as a relatively small object, is difficult to identify in the Vaihingen dataset. Even so, the proposed SAINet reached 89.4% of the F1 score, significantly exceeding the secondary method. The experimental results show that SAINet maintains stable performance on the Vaihingen dataset, which indicates that SAINet has a better practical generalization ability.
4.4.3. Results on Potsdam
From the
Table 4, it can be seen that the SAINet proposed in this paper also outperforms previous segmentation methods on the Postdam dataset. In detail, compared with BGFNet, SAINet obtains increments of 0.4% and 0.3% in mean F1 and OA, respectively. Notably, our method scored 96.2% on F1 in the “Car” category, outperforming other networks by more than 0.65%. Compared to the DeepGlobe dataset, our algorithm exhibits a slightly smaller improvement in the Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets. This is primarily because the Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets are already mature and well-established. As shown in
Figure 3, relative to the DeepGlobe dataset, the Vaihingen and Potsdam datasets primarily focus on urban areas, characterized by well-defined boundaries and intricate details.
4.5. Ablation Studies and Analysis
In the previous subsection, we have shown the superiority of SAINet by comparing it to state-of-the-art methods. In what follows, we comprehensively analyze intrinsic factors that lead to SAINet’s superiority in the dataset, including: (1) The role of SRM and SIM. (2) The effectiveness of variant SRM. (3) The impact of variant SIM. (4) Compared with different attention modules.
The role of SRM and SIM. It can be observed from
Table 5 that the two modules significantly influence the performance of the algorithm, and their effects on different datasets are consistent: the effect of using SIM alone is better than using SRM alone, while the best performance is achieved when both are used simultaneously. When SRM is used alone, the algorithm adopts the simplest addition operation to interact with the global and local features, which leads to less improvement compared to GLNet, as GLNet performs more complex interactions between all global and local features. However, there is still an improvement in mIoU compared to using a single-branch network. When SIM is used alone, it interacts with all features, resulting in some improvement, although not significant, as not all features require interaction, and excessive interaction may have a detrimental effect. Only when both SAM and SIM are used together, the network in this paper can achieve the best performance.
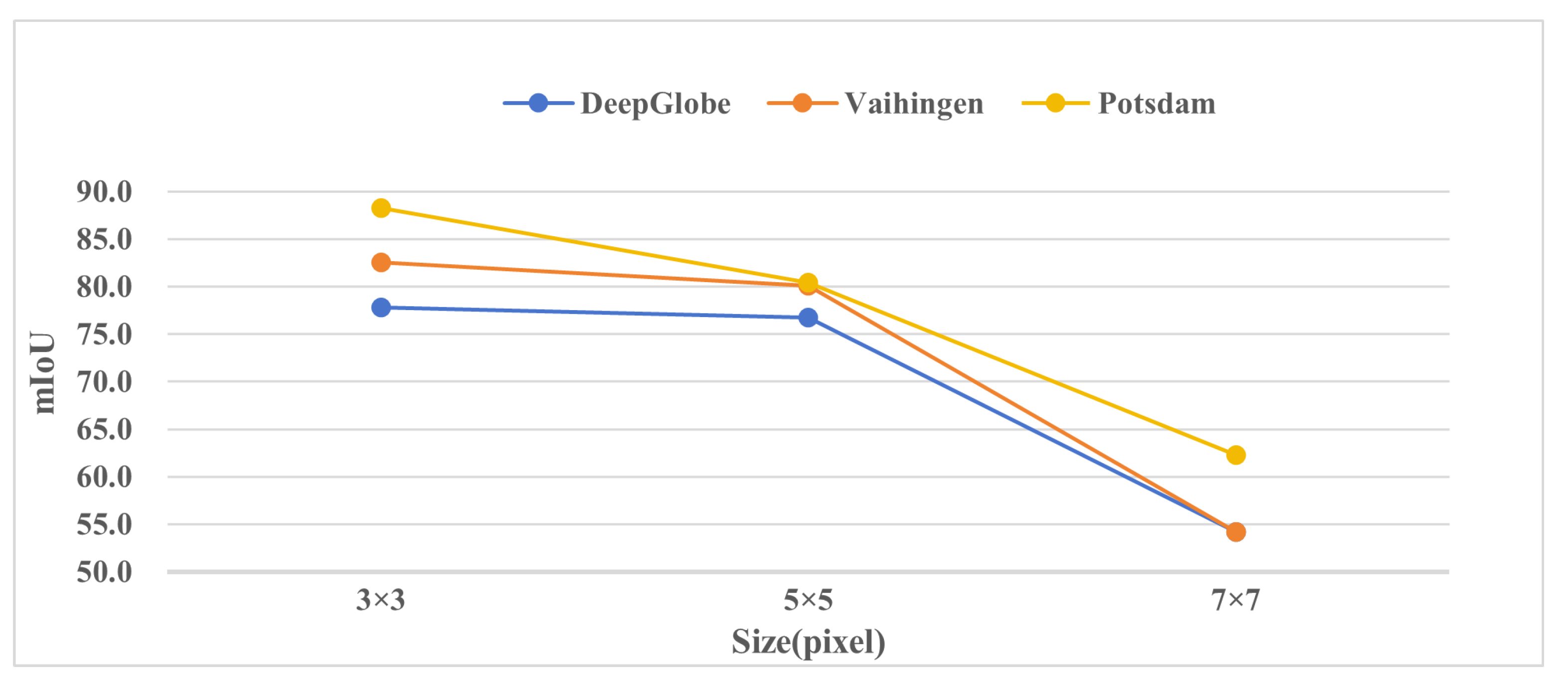
Figure 5.
The effectiveness of variant window size of SRM.
Figure 5.
The effectiveness of variant window size of SRM.
The effectiveness of variant window size of SRM. To explore which window size of SRM gives the best performance boost, we set the window size to
respectively, and select mIoU as the evaluation metric. As shown in
Figure 5, when the window size is
, the segmentation results are the best. With a window size of
, the segmentation results are slightly worse, and with a window size of
, the segmentation results are inferior. The size of the window of SRM is an important parameter when filtering spatial locations and extracting salient regions. According to the results, the segmentation results are best when the window size is
. This is because global features have already been extracted before the first backbone network. Therefore, a
window is already quite large, and increasing the window size further would only introduce unnecessary interference or noise without improving the results. Hence, choosing a
window size is wise in this scenario, as it provides the best segmentation results.
Compared with different attention modules. To further demonstrate the capability of our proposed spatial interaction module in understanding spatial relationships in data, we replaced the spatial interaction module with another attention mechanism and calculated the mIoU on three datasets. From
Table 6, it can be seen that replacing our spatial interaction module with the convolutional block attention module results in a better mIoU on all three datasets compared to replacing it with the channel attention module and spatial attention module. The best results obtained after replacing with the channel attention module and spatial attention module are close, with differences of 0.4%, 0.3%, and 0.1% on the DeepGlobe dataset, Vaihingen dataset, and Potsdam dataset, respectively, indicating that the channel attention module and spatial attention module focus on important features to a similar extent. The convolutional block attention module, which concatenates the channel attention module and spatial attention module, further enhances the capability to focus on local information. The results of the proposed spatial interaction module on the three datasets are respectively 5.5%, 3.4%, and 8.6% better than the results of the convolutional block attention module on the three datasets. This is because our designed spatial interaction module is more compatible with the proposed spatial refine module, and it better achieves the interaction between global and local information.
The correlation between segmentation accuracy and patch size. As can be seen from
Table 7, our network’s segmentation accuracy remains relatively stable despite variations in patch size. The highest and lowest segmentation accuracies of GLNe across different patch sizes differ by 7%, whereas the difference between the highest and lowest segmentation accuracies of our network across different patch sizes is only 3.5%. This is attributed to our proposed Spatial Refine Module and Spatial Interaction Module, which adapt better to features of different sizes. This stability allows the network to be trained with smaller patches, consequently reducing the hardware requirements.
4.6. Visual Results and Analysis
To further evaluate the performance of our algorithm on different datasets and highlight its advantages, we selected five representative image samples from both the Vaihingen dataset and the Postdam dataset. We analyzed and compared the prediction results using visualizations. For the single-branch network, we chose Deeplabv3+ as the representative, and for the multi-branch network, we selected GLNet.
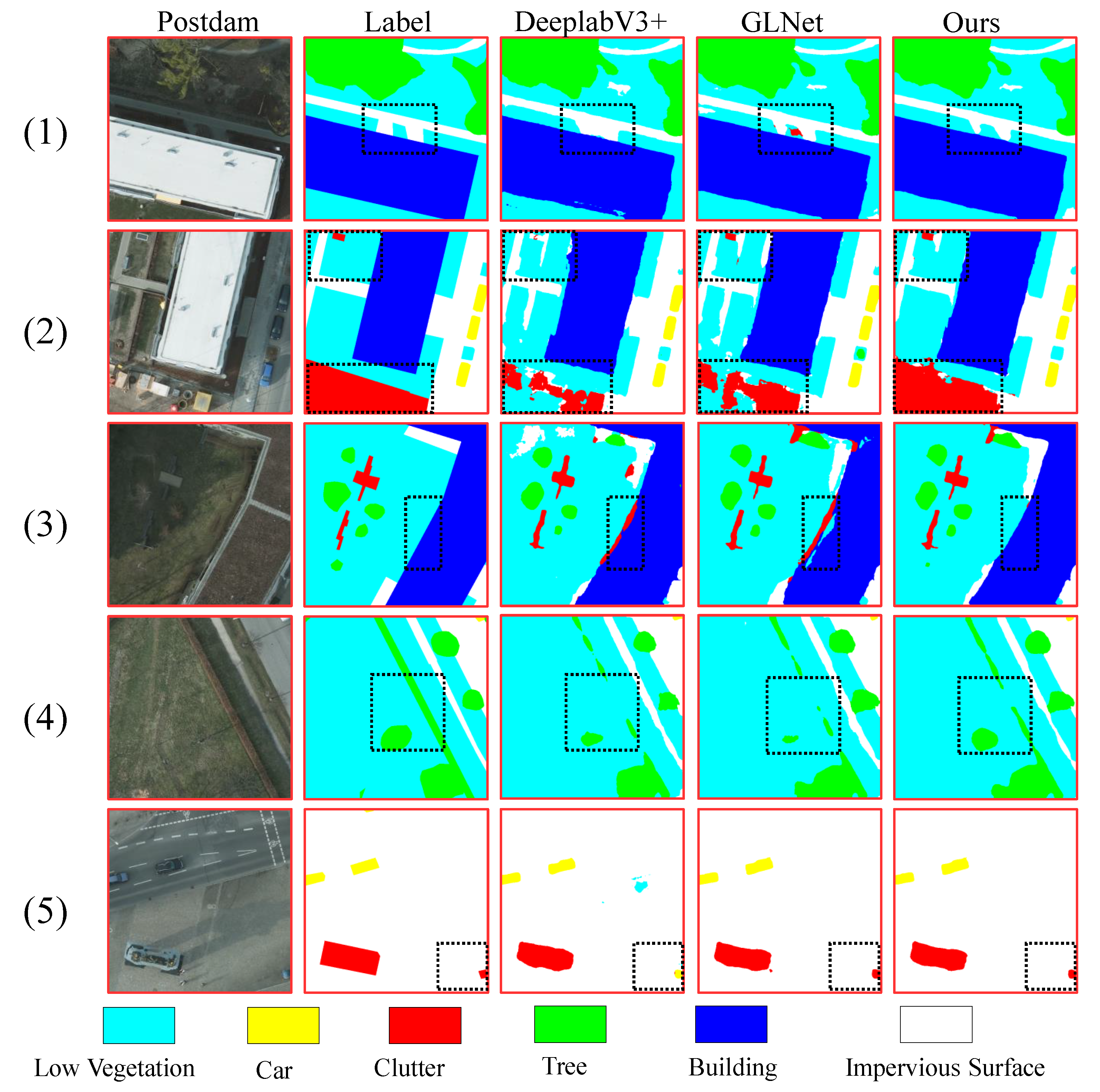
From the visualization results in
Figure 6, it can be seen that our algorithm shows a remarkable improvement on the Postdam dataset. Compared to the prediction results of other algorithms, our algorithm outperforms in predicting buildings, clutter, and low vegetation. In
Figure 6-(1), the area of low vegetation within the black dashed box is small. Deeplabv3+ fails to segment it accurately, and although GLNet identifies low vegetation, it is not very precise and falsely classifies a small portion as clutter. In contrast, our algorithm yields the correct segmentation result, resembling the true label. In
Figure 6-(2) and
Figure 6-(3), it is evident that Deeplabv3+ and GLNet easily confuse clutter and low vegetation, whereas our algorithm in this paper can better discriminate between these two categories. For simple scenes like
Figure 6-(4) and (5), while other algorithms can correctly segment it, our algorithm can extract more detailed segmentation. In
Figure 6-(5), the small red clutter within the black dashed box is incorrectly classified as a car by Deeplabv3+. However, GLNet and our algorithm can accurately segment it, highlighting the advantage of the dual-branch network. The global branch in the dual-branch network takes the entire original image as input, enabling correct segmentation of clutter.
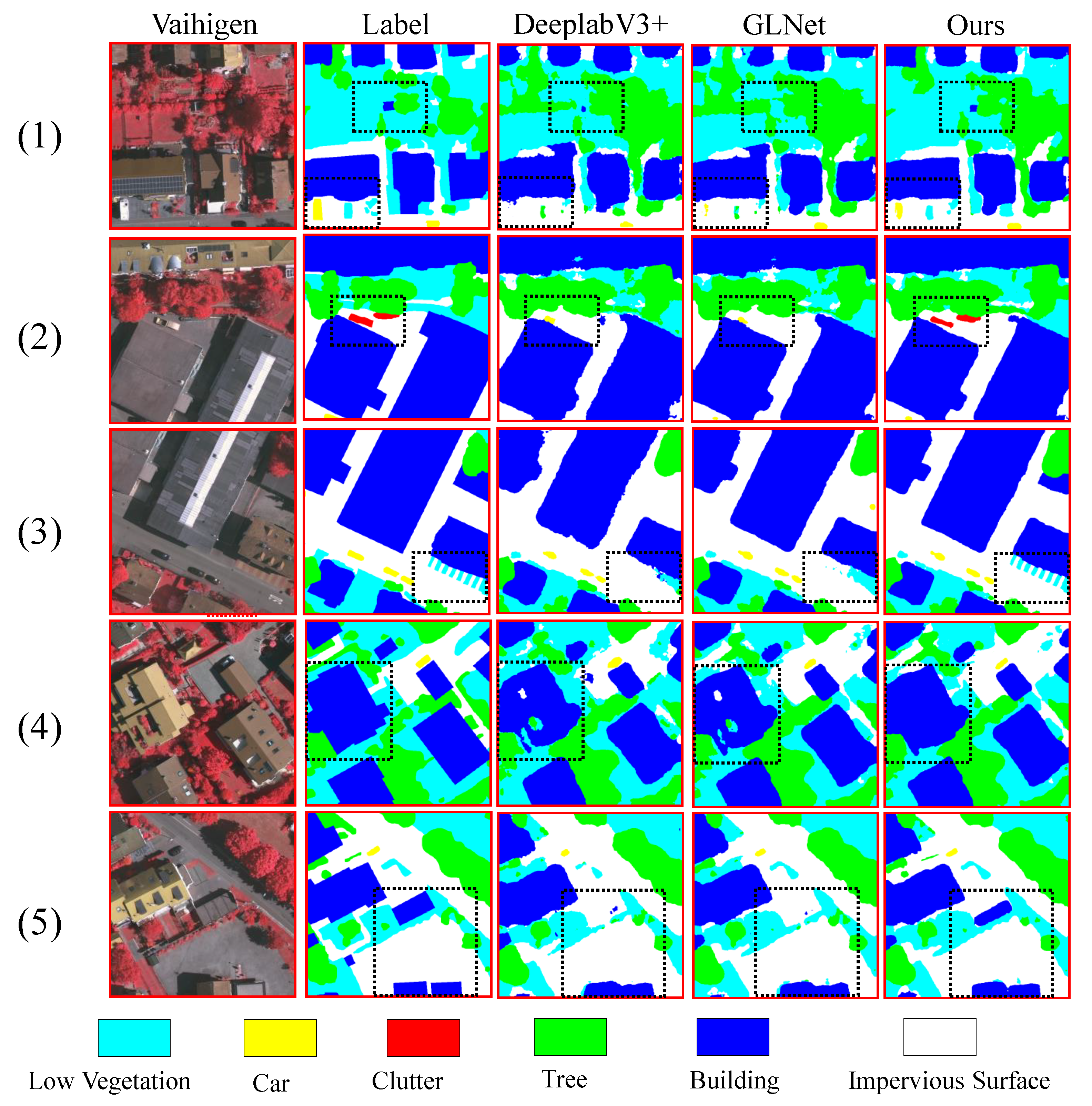
Figure 7 compares segmentation results using different algorithms on the Vaihingen dataset. It can be seen that our algorithm overall performs better, especially in building segmentation, where it produces more complete results with more accurate edges. This indicates that our algorithm can accurately separate buildings from other areas and produce clearer outlines. Additionally, our algorithm exhibits greater accuracy in segmenting smaller objects. Our algorithm can effectively identify and segment smaller targets, leading to more precise segmentation results.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a novel spatially adaptive interaction network (SAINet). By addressing the limitations of the previous methods from focus salient regions and spatial adaptive interaction, our module achieves an impressive result. Incorporating this adaptable method empowers the dual-branch network to prioritize pertinent regions, enhancing the network’s capacity to encompass richer informative features. Consequently, this refinement contributes to heightened segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model over competitive baselines. Although a complete analysis model has been established, there are still several limitations: first, in the comparative experiments on the Vaihingen dataset, our method achieves slightly lower segmentation F1 scores for the categories "Impervious Surface" and "Tree" compared to the best-performing algorithm. Second, We only conducted comparative experiments on high-resolution remote sensing images and lacked comparative experiments on high-resolution images in other scenarios. In future work, we aim to further improve segmentation accuracy while also conducting comparative experiments on high-resolution images in other scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S., and H.H.; methodology, W.S., and H.H.; software, H.H.; validation, H.H., G.J., and J.F.; data curation, J.D.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.; writing—review and editing, W.S., G.J.and H.H..; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.42071343), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.42071428), and the Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (No. LJKZ1070).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers and the editor for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kussul, N.; Lavreniuk, M.; Skakun, S.; Shelestov, A. Deep learning classification of land cover and crop types using remote sensing data. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2017, 14, 778–782. [CrossRef]
- Milioto, A.; Lottes, P.; Stachniss, C. Real-time semantic segmentation of crop and weed for precision agriculture robots leveraging background knowledge in CNNs. 2018 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2018, pp. 2229–2235.
- Malambo, L.; Popescu, S.; Ku, N.W.; Rooney, W.; Zhou, T.; Moore, S. A deep learning semantic segmentation-based approach for field-level sorghum panicle counting. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 2939. [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.A.C.; Oliveira, H.; dos Santos, J.A.; Feitosa, R.Q. Open set semantic segmentation for multitemporal crop recognition. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2021, 19, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Tarasiou, M.; Güler, R.A.; Zafeiriou, S. Context-self contrastive pretraining for crop type semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2022, 60, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Paisitkriangkrai, S.; Sherrah, J.; Janney, P.; Hengel, V.D.; others. Effective semantic pixel labelling with convolutional networks and conditional random fields. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2015, pp. 36–43.
- Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Shen, F.; He, D.; Xian, Q. A Bag of Tricks for Fine-Grained roof Extraction. IGARSS 2023-2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, 2023.
- Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Zhou, R.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q. Classification for high resolution remote sensing imagery using a fully convolutional network. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 498. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 801–818.
- Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Z. Building extraction in very high resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning and guided filters. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 144. [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2020, 162, 94–114.
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2015, pp. 3431–3440.
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer, 2015, pp. 234–241.
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.05587 2017.
- Chen, W.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cui, K.; Qian, X. Collaborative global-local networks for memory-efficient segmentation of ultra-high resolution images. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 8924–8933.
- Shan, L.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Lv, K.; Luo, B.; Chen, S.B.; Wang, W. Uhrsnet: A semantic segmentation network specifically for ultra-high-resolution images. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1460–1466.
- Shan, L.; Wang, W. MBNet: A Multi-Resolution Branch Network for Semantic Segmentation Of Ultra-High Resolution Images. ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2022, pp. 2589–2593.
- Du, X.; He, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, C. Multi-Field Context Fusion Network for Semantic Segmentation of High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 5830. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.7062 2014.
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; SegNet, R.C. A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.00561 2015, 5. [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.07122 2015.
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2017, 40, 834–848.
- Shen, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, J.; Zeng, H.; Lei, Z.; Cai, C. An Efficient Multiresolution Network for Vehicle Reidentification. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 9, 9049–9059. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 2881–2890.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016.
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 3146–3154.
- Shen, F.; Wei, M.; Ren, J. HSGNet: Object Re-identification with Hierarchical Similarity Graph Network. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.05486 2022.
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.C.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H.; Hua, W.; Yuille, A.L.; Fei-Fei, L. Auto-deeplab: Hierarchical neural architecture search for semantic image segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 82–92.
- Shen, F.; Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Shu, M.; Wang, Y. HSGM: A Hierarchical Similarity Graph Module for Object Re-identification. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–6.
- Li, M.; Wei, M.; He, X.; Shen, F. Enhancing Part Features via Contrastive Attention Module for Vehicle Re-identification. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1816–1820.
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, .; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30.
- Xu, R.; Shen, F.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H. Dual modal meta metric learning for attribute-image person re-identification. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC). IEEE, 2021, Vol. 1, pp. 1–6.
- Shen, F.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, H. Git: Graph interactive transformer for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2023. [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 12077–12090.
- Fu, X.; Shen, F.; Du, X.; Li, Z. Bag of Tricks for “Vision Meet Alage” Object Detection Challenge. 2022 6th International Conference on Universal Village (UV). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–4.
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; others. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 2020.
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2021, pp. 568–578. [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Ling, W.; Lin, F.; Ren, J.; Shen, F. A Novel Cross Frequency-domain Interaction Learning for Aerial Oriented Object Detection. Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV). Springer, 2023.
- Qiao, C.; Shen, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Cao, F.; Zhao, S.; Li, C. A Novel Multi-Frequency Coordinated Module for SAR Ship Detection. 2022 IEEE 34th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI). IEEE, 2022, pp. 804–811.
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2021, pp. 10012–10022.
- Wang, Z.; Cun, X.; Bao, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Uformer: A general u-shaped transformer for image restoration. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022, pp. 17683–17693.
- Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tay, F.E.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Tokens-to-token vit: Training vision transformers from scratch on imagenet. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2021, pp. 558–567.
- Shen, F.; Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J. Triplet Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Vehicle Re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.09498 2023.
- Xiao, T.; Singh, M.; Mintun, E.; Darrell, T.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Early convolutions help transformers see better. Advances in neural information processing systems 2021, 34, 30392–30400.
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Mobile-former: Bridging mobilenet and transformer. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 5270–5279.
- Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Pan, Y.; Mei, T. Contextual transformer networks for visual recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2022, 45, 1489–1500.
- Xia, Z.; Pan, X.; Song, S.; Li, L.E.; Huang, G. Vision transformer with deformable attention. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022, pp. 4794–4803.
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022, pp. 11976–11986.
- Jin, C.; Tanno, R.; Xu, M.; Mertzanidou, T.; Alexander, D.C. Foveation for segmentation of ultra-high resolution images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.15124 2020.
- Shen, F.; Shu, X.; Du, X.; Tang, J. Pedestrian-specific Bipartite-aware Similarity Learning for Text-based Person Retrieval. Proceedings of the 31th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2023.
- Shan, L.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Decouple the high-frequency and low-frequency information of images for semantic segmentation. ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1805–1809.
- Huynh, C.; Tran, A.T.; Luu, K.; Hoai, M. Progressive semantic segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021, pp. 16755–16764.
- Hou, J.; Guo, Z.; Wu, Y.; Diao, W.; Xu, T. BSNet: Dynamic hybrid gradient convolution based boundary-sensitive network for remote sensing image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2022, 60, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, L.; Gan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yi, R.; Ma, L.; others. Isdnet: Integrating shallow and deep networks for efficient ultra-high resolution segmentation. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 4361–4370.
- Liu, J.; Shen, F.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhu, J.; Cai, C. A Large-Scale Benchmark for Vehicle Logo Recognition. 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC). IEEE, 2019, pp. 479–483.
- Kamnitsas, K.; Ledig, C.; Newcombe, V.F.; Simpson, J.P.; Kane, A.D.; Menon, D.K.; Rueckert, D.; Glocker, B. Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Medical image analysis 2017, 36, 61–78.
- Shen, F.; Lin, L.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H.; Cai, C.; Zheng, L. A large benchmark for fabric image retrieval. 2019 IEEE 4th International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC). IEEE, 2019, pp. 247–251.
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, Q. Classification of breast cancer histology images using multi-size and discriminative patches based on deep learning. Ieee Access 2019, 7, 21400–21408.
- Xie, Y.; Shen, F.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H. Viewpoint robust knowledge distillation for accelerating vehicle re-identification. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2021, 2021, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, J. Exploring spatial significance via hybrid pyramidal graph network for vehicle re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2021, 23, 8793–8804. [CrossRef]
- Katharopoulos, A.; Vyas, A.; Pappas, N.; Fleuret, F. Transformers are rnns: Fast autoregressive transformers with linear attention. International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2020, pp. 5156–5165.
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017, pp. 2980–2988.
- Demir, I.; Koperski, K.; Lindenbaum, D.; Pang, G.; Huang, J.; Basu, S.; Hughes, F.; Tuia, D.; Raskar, R. Deepglobe 2018: A challenge to parse the earth through satellite images. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2018, pp. 172–181.
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 405–420.
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Pan, C.; He, L.; Xu, Z. A Full-Scale Feature Extraction Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. 2022 4th International Conference on Intelligent Control, Measurement and Signal Processing (ICMSP). IEEE, 2022, pp. 725–728.
- Chen, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, G. CLANET: a cross-linear attention network for semantic segmentation of urban scenes remote sensing images. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2023, 44, 7321–7337. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, P.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W. CTFNet: CNN-Transformer Fusion Network for Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X. Multilevel feature fusion and attention network for high-resolution remote sensing image semantic labeling. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2022, 19, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qian, Y.; Cao, R.; Tuerxun, P.; Hu, Z. BGFNet: Semantic Segmentation Network Based on Boundary Guidance. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018, pp. 7132–7141.
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; others. Spatial transformer networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2015, 28.
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 3–19.
Figure 1.
Comparison of SAINet with other networks in semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images: (a) Single-branch networks, typically train on downsampled images, resulting in insufficient capability to extract local detailed information. (b) Dual-branch networks, train with both global and local branches, fuse all the information from different branches, and treat each feature equally. (c) Our proposed SAINet, dynamic interaction of information across different features
Figure 1.
Comparison of SAINet with other networks in semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images: (a) Single-branch networks, typically train on downsampled images, resulting in insufficient capability to extract local detailed information. (b) Dual-branch networks, train with both global and local branches, fuse all the information from different branches, and treat each feature equally. (c) Our proposed SAINet, dynamic interaction of information across different features
Figure 2.
An overview of the proposed SAINet. SAINet first downsamples the input image and then puts it into the backbone network extracting global features. The spatial refined module (SRM) extracts salient regions within the global features and obtains the salient regions index (SRI). The local features are extracted from crop patches. The spatial interaction module (SIM) performs the spatially adaptive interaction between global features and local features.
Figure 2.
An overview of the proposed SAINet. SAINet first downsamples the input image and then puts it into the backbone network extracting global features. The spatial refined module (SRM) extracts salient regions within the global features and obtains the salient regions index (SRI). The local features are extracted from crop patches. The spatial interaction module (SIM) performs the spatially adaptive interaction between global features and local features.
Figure 6.
Visualization results on the Postdam dataset. In each column from left to right, the original image, label, prediction result from Deeplabv3+, prediction result from GLNet, and prediction result from SAINet are displayed, respectively. The first three rows represent complex scenes, while the fourth and fifth rows depict simple scenes.
Figure 6.
Visualization results on the Postdam dataset. In each column from left to right, the original image, label, prediction result from Deeplabv3+, prediction result from GLNet, and prediction result from SAINet are displayed, respectively. The first three rows represent complex scenes, while the fourth and fifth rows depict simple scenes.
Figure 7.
Visualization results on the Vaihigen dataset. In each column from left to right, the original image, label, prediction result from Deeplabv3+, prediction result from GLNet, and prediction result from SAINet are displayed, respectively.
Figure 7.
Visualization results on the Vaihigen dataset. In each column from left to right, the original image, label, prediction result from Deeplabv3+, prediction result from GLNet, and prediction result from SAINet are displayed, respectively.
Table 3.
Quantitative comparison results on the Vaihingen Dataset with state-of-the-art methods. Best results are in bold.
Table 3.
Quantitative comparison results on the Vaihingen Dataset with state-of-the-art methods. Best results are in bold.
| Method |
Impervious
Surface |
Building |
Low
Vegetation |
Tree |
Car |
mean F1
|
OA |
mIoU |
| DeepLabv3+[9] |
91.4 |
94.7 |
79.6 |
87.6 |
85.8 |
87.8 |
89.9 |
79.0 |
| PSPNet[24] |
90.6 |
94.3 |
79.0 |
87.0 |
70.7 |
84.3 |
89.1 |
74.1 |
| FSFNet [66] |
91.9 |
94.8 |
82.5 |
89.0 |
85.4 |
88.7 |
89.8 |
- |
| CLANet [67] |
91.5 |
94.6 |
82.9 |
89.5 |
87.3 |
89.2 |
89.8 |
80.7 |
| CTFNet [68] |
90.7 |
94.4 |
81.7 |
87.3 |
82.7 |
87.4 |
88.6 |
77.8 |
| MFANet [69] |
92.7 |
95.8 |
84.2 |
89.3 |
84.7 |
89.3 |
90.6 |
81.6 |
| BGFNet [70] |
92.9 |
95.5 |
84.4 |
89.6 |
86.7 |
89.8 |
90.6 |
81.7 |
| Basaeline[15] |
88.3 |
93.0 |
79.7 |
87.1 |
83.3 |
89.0 |
86.3 |
78.7 |
| SAINet |
92.5 |
96.5 |
85.9 |
89.3 |
89.4 |
90.7 |
91.9 |
82.5 |
Table 4.
Quantitative comparison results on the Potsdam Dataset with state-of-the-art methods. Best results are in bold.
Table 4.
Quantitative comparison results on the Potsdam Dataset with state-of-the-art methods. Best results are in bold.
| Method |
Impervious
Surface |
Building |
Low
Vegetation |
Tree |
Car |
mean F1
|
OA |
mIoU |
| DeepLabv3+[9] |
91.3 |
94.8 |
84.2 |
86.6 |
93.8 |
90.1 |
89.2 |
73.8 |
| PSPNet[24] |
90.7 |
94.8 |
84.1 |
85.9 |
90.5 |
89.2 |
88.7 |
71.7 |
| FSFNet [66] |
92.2 |
95.0 |
85.2 |
87.2 |
95.5 |
91.0 |
89.3 |
- |
| CLANet [67] |
92.1 |
96.3 |
86.8 |
88.4 |
95.4 |
91.8 |
90.3 |
85.1 |
| CTFNet [68] |
91.5 |
96.3 |
86.0 |
87.2 |
92.5 |
90.7 |
89.4 |
83.2 |
| MFANet [69] |
93.1 |
96.6 |
87.0 |
88.0 |
94.9 |
91.9 |
90.9 |
88.3 |
| BGFNet [70] |
95.3 |
96.3 |
88.8 |
88.6 |
95.6 |
92.9 |
92.2 |
86.9 |
| Basaeline[15] |
90.3 |
94.5 |
79.4 |
87.2 |
84.4 |
89.5 |
87.6 |
79.3 |
| SAINet |
95.4 |
96.7 |
89.5 |
88.6 |
96.2 |
93.3 |
92.5 |
88.3 |
Table 5.
The role of SRM and SIM of our method on the results.
Table 5.
The role of SRM and SIM of our method on the results.
| border-bottom:solid thin">Dataset |
Model |
Spatial Refine Module |
Spatial Interation Module |
mIoU |
| DeepGlobe |
Baseline |
× |
× |
71.6 |
| Ours |
✓ |
× |
65.7 |
| × |
✓ |
72.4 |
| ✓ |
✓ |
77.8 |
| Vaihingen |
Baseline |
×
|
×
|
78.7 |
| Ours |
✓ |
× |
75.6 |
| × |
✓ |
78.9 |
| ✓ |
✓ |
82.5 |
| Postdam |
Baseline |
×
|
×
|
79.3 |
| Ours |
✓ |
× |
70.3 |
| × |
✓ |
79.6 |
| ✓ |
✓ |
88.3 |
Table 6.
Compared with different attention modules.
Table 6.
Compared with different attention modules.
| Method |
Dataset |
| DeepGlobe |
Vaihingen |
Potsdam |
| CAM [71] |
71.9 |
78.6 |
79.0 |
| SAM [72] |
71.5 |
78.3 |
78.9 |
| CBAM [73] |
72.3 |
79.1 |
79.7 |
| Ours |
77.8 |
82.5 |
88.3 |
Table 7.
Results with different patch sizes on DeepGlobe.
Table 7.
Results with different patch sizes on DeepGlobe.
| Method |
PatchSize |
| 500×500 |
400×400 |
256×256 |
128×128 |
| GLNet |
71.6 |
70.6 |
66.4 |
64.6 |
| Ours |
77.8 |
77.1 |
75.7 |
74.3 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).