Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Generalized Deepfake Detection
2.2. Contrastive Representation Learning in Deepfake Detection
2.3. Meta Pseudo Labels
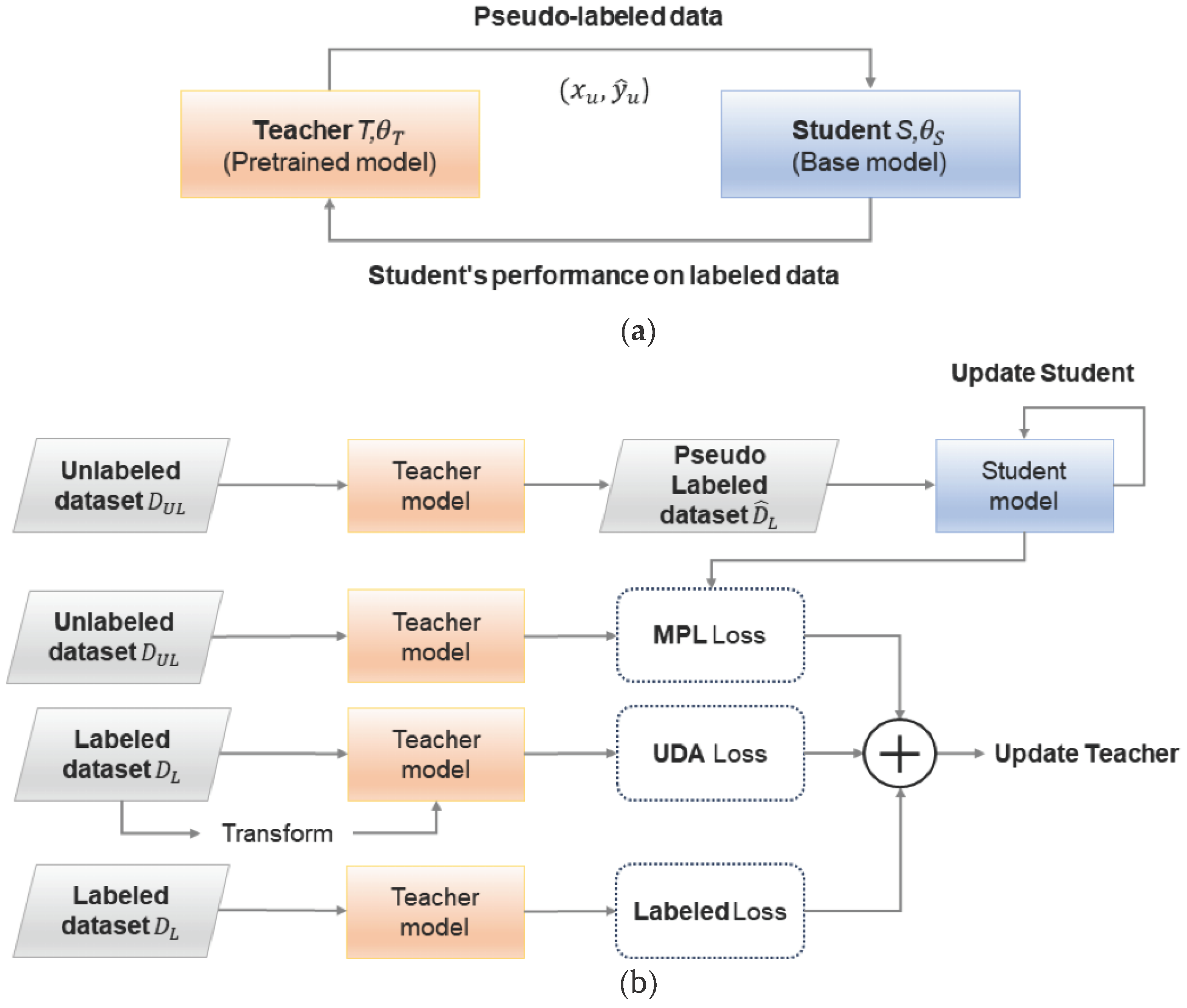
3. Proposed SupCon-MPL Based Deepfake Detection
3.1. Proposed Training Strategy
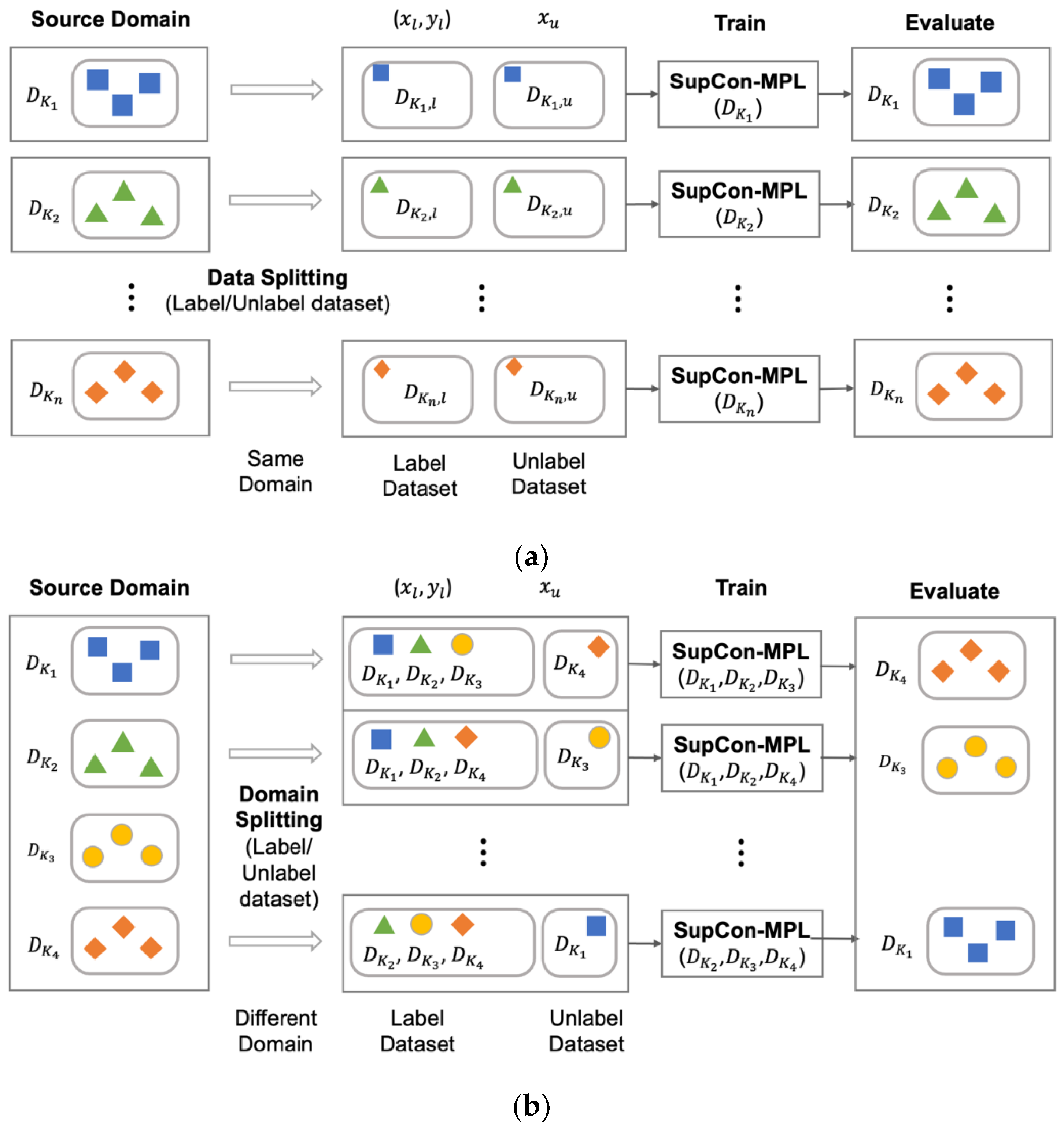
3.1.1. Known Domain and Unknown Domain in Deepfake
3.1.2. Training Strategy for Deepfake Unknown Domain Detection
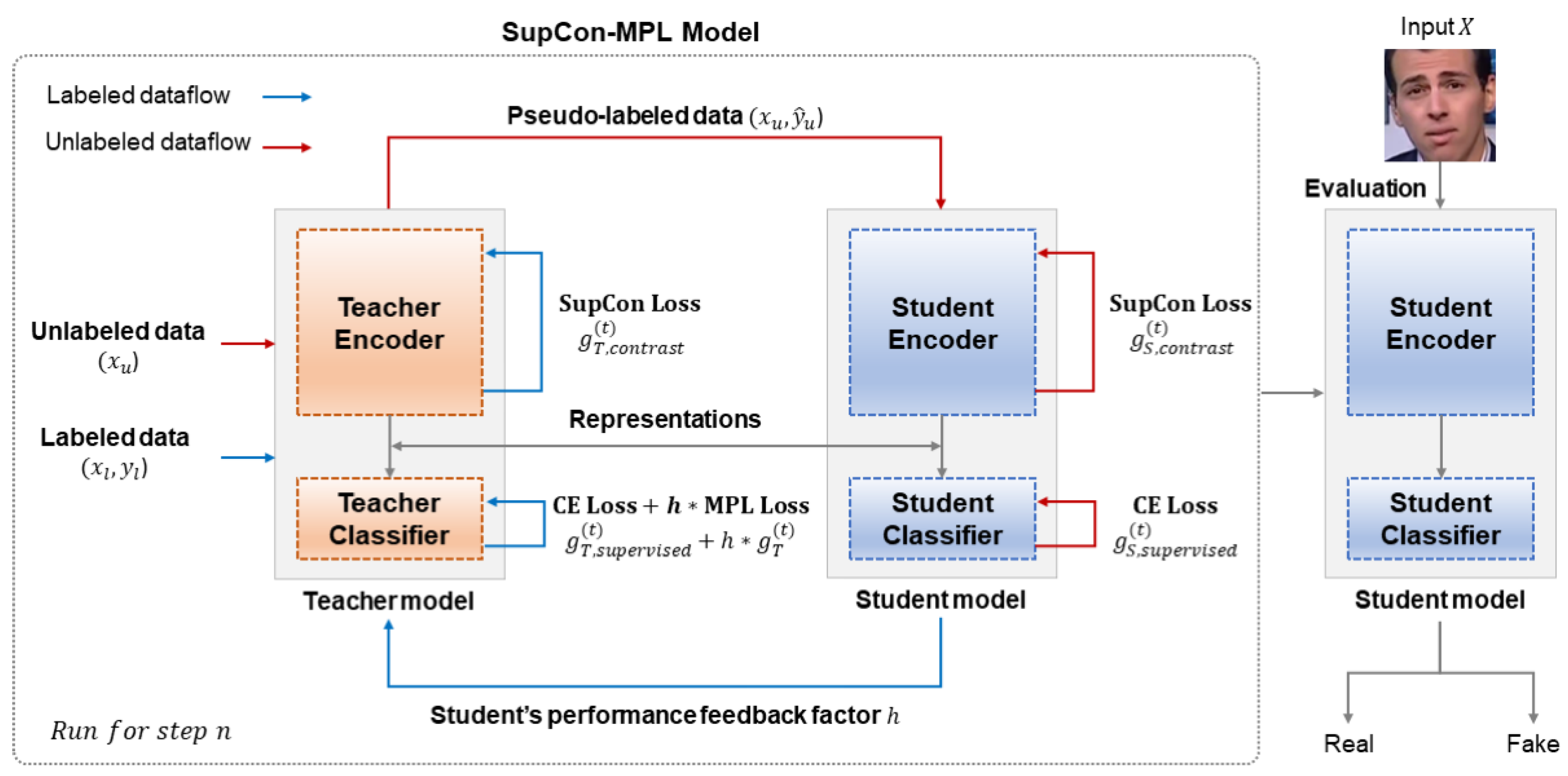
3.2. SupCon-MPL: Supervised Contrastive Learning with Meta-Pseudo Labels
3.3. SupCon-MPL Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.2. Single-domain Experiment
4.3. Multi-domain Experiment
4.4. SupCon-MPL Experiment
4.5. Deepfake Scenario Experiment
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusion
References
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems 2014, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv Preprint, 1411. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Ha, J. W.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. Stargan: Unified generative adversarial networks for multi-domain image-to-image translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 8789–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In International conference on machine learning, Sydney, Australia, 6-; pp. 214-223. 11 August.
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A. C. Improved training of wasserstein gans. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D. P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv Preprint 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, K.; Lee, H.; Yan, X. Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. Advances in neural information processing systems 2015, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aila, T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15-20 June 2019; pp. 4401–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Pavlov, M.; Goh, G.; Gray, S.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I. Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the ICML 2021 Workshop on Unsupervised Reinforcement Learning, Virtual, 18-24 July 2021; pp. 8821–8831. [Google Scholar]
- DeepFaceLab. Available online: https://github.com/iperov/DeepFaceLab (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Deepswap. Available online: https://www.deepswap.ai/ko (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- synthesia. Available online: https://www.synthesia.io (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18-24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Denton, E. L.; Norouzi, M. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, pp–36479. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Dhariwal, P.; Chen, M.; Sutskever, I. Consistency models. 2023.
- Li, Y.; Lyu, S. Exposing deepfake videos by detecting face warping artifacts. arXiv Preprint 2018, arXiv:1811.00656. [Google Scholar]
- Matern, F.; Riess, C.; Stamminger, M. Exploiting visual artifacts to expose deepfakes and face manipulations. In 2019 IEEE Winter Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7-11 Jan. 2019; pp. 83-92; [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chang, M. C.; Lyu, S. In ictu oculi: Exposing ai generated fake face videos by detecting eye blinking. arXiv Preprint 2018, arXiv:1806.02877; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, U. A.; Demir, I.; Yin, L. Fakecatcher: Detection of synthetic portrait videos using biological signals. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccomini, D. A.; Messina, N.; Gennaro, C.; Falchi, F. Combining efficientnet and vision transformers for video deepfake detection. In International conference on image analysis and processing, Lecce, Italy, ; pp. 219-229; 23–27 May. [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In International conference on machine learning, Los Angeles County, California, United States, 9-15 Jan 2019; pp. 6105-6114.
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Houlsby, N. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv Preprint 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21-26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.-H.; Ok, S.-Y.; Seo, J.; Lee, S.-H. Meta Pseudo Labels Based Deepfake Video Detection. Journal of Korea Multimedia Society 2024, 27, pp–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. Improving generalization of deepfake detection by training for attribution. In 2021 IEEE 23rd International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, Tampere, Finland, 6-; pp. 1-6; 8 October. [CrossRef]
- Nadimpalli, A. V.; Rattani, A. On improving cross-dataset generalization of deepfake detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18-24 June 2022; pp. 91-99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C. C.; Lee, C. Y.; Zhuang, Y. X. Learning to detect fake face images in the wild. In 2018 international symposium on computer, consumer and control, Taichung, Taiwan, 6-; pp. 8 December. [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Contrastive learning-based general Deepfake detection with multi-scale RGB frequency clues. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiohara, K.; Yamasaki, T. Detecting deepfakes with self-blended images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18-24 June 2022; pp. 18720-18729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. Ost: Improving generalization of deepfake detection via one-shot test-time training. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 24597–24610. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, S.; Nießner, M. Generalized zero and few-shot transfer for facial forgery detection. arXiv Preprint 2020, arXiv:2006.11863. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Tariq, S.; Woo, S. S. Fretal: Generalizing deepfake detection using knowledge distillation and representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20-25 June 2021; pp. 1001-1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Guo, Q.; Juefei-Xu, F.; Xie, X.; Ma, L.; Feng, W.; Zhao, J. Deeprhythm: Exposing deepfakes with attentional visual heartbeat rhythms. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12-16 October 2020; pp. 4318-4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Tariq, S.; Kim, J.; Woo, S. S. Tar: Generalized forensic framework to detect deepfakes using weakly supervised learning. In IFIP International Conference on ICT Systems Security and Privacy Protection, Oslo, Norway, 22-; pp. 24 June. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Raja, K.; Pedersen, M. Supervised contrastive learning for generalizable and explainable deepfakes detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3-8 January 2022; pp. 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Fung, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.T. DeepfakeUCL: Deepfake Detection via Unsupervised Contrastive Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Dai, Z.; Xie, Q.; Le, Q. V. Meta pseudo labels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, pp. 11557-11568, 20-25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, pp–18661. [Google Scholar]
- Rossler, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Verdoliva, L.; Riess, C.; Thies, J.; Niessner, M. Faceforensics++: Learning to Detect Manipulated Facial Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October-2 November 2019; pp. 1-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhansky, B.; Bitton, J.; Pflaum, B.; Lu, J.; Howes, R.; Wang, M.; Ferrer, C. C. The deepfake detection challenge (dfdc) dataset. arXiv Preprint 2020, arXiv:2006.07397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Yang, X.; Sun, P.; Qi, H.G.; Lyu, S. Celeb-DF: A Large-scale Challenging Dataset for DeepFake Forensics. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14-19 June 2020; pp. 3207-3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, P.; Marcel, S. Deepfakes: a new threat to face recognition? assessment and detection. arXiv Preprint 2018, arXiv:1812.08685. [Google Scholar]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17-, 2; pp. 2, 22 June. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20-25 June 2009; pp. 248-255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv Preprint 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Luong, M.T.; Hovy, E.; Le, Q.V. Self-training with noisy student improves imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13-19 June 2020; pp. 10687–10698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Dai, Z.; Hovy, E.; Luong, T.; Le, Q. Unsupervised data augmentation for consistency training. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6-12 December 2020; pp. 6256–6268. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3730–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint Face Detection and Alignment Using Multitask Cascaded Convolutional Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, pp–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference On Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Wide residual networks. arXiv Preprint 2016, arXiv:1605.07146. [Google Scholar]

| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| EfficientNetb5[21] | DF | DF | 89.35 | 89.35 | 90.08 | 90.08 |
| F2F | F2F | 77.21 | 77.21 | 80.35 | 80.35 | |
| FS | FS | 84.52 | 84.31 | 87.90 | 87.43 | |
| NT | NT | 64.13 | 63.33 | 74.79 | 74.47 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| EfficientNetb5[21] | DF | F2F | 51.59 | 51.60 | 51.70 | 51.70 |
| FS | 55.97 | 52.06 | 56.45 | 52.65 | ||
| NT | 55.37 | 51.26 | 55.41 | 51.37 | ||
| F2F | DF | 57.56 | 57.55 | 53.87 | 53.84 | |
| FS | 56.47 | 54.05 | 55.48 | 51.92 | ||
| NT | 54.63 | 51.91 | 54.76 | 50.99 | ||
| FS | DF | 57.25 | 57.22 | 57.61 | 57.88 | |
| F2F | 51.76 | 51.77 | 51.98 | 51.99 | ||
| NT | 53.79 | 49.89 | 54.32 | 49.80 | ||
| NT | DF | 58.72 | 58.71 | 61.03 | 61.00 | |
| F2F | 54.52 | 54.53 | 55.88 | 55.89 | ||
| FS | 51.65 | 49.42 | 53.29 | 49.34 | ||
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNet50[50] | DF | DF | 91.16 | 91.16 | 91.29 | 91.30 |
| F2F | F2F | 82.47 | 82.48 | 83.98 | 83.97 | |
| FS | FS | 87.55 | 87.21 | 88.31 | 88.09 | |
| NT | NT | 74.96 | 74.28 | 76.22 | 75.84 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNet50[50] | DF | F2F | 52.91 | 52.89 | 51.92 | 51.86 |
| FS | 56.80 | 52.68 | 57.02 | 53.00 | ||
| NT | 55.91 | 51.77 | 55.45 | 51.33 | ||
| F2F | DF | 53.94 | 53.90 | 53.79 | 53.75 | |
| FS | 54.62 | 50.97 | 55.32 | 51.35 | ||
| NT | 54.76 | 51.20 | 54.96 | 51.04 | ||
| FS | DF | 56.34 | 56.30 | 59.57 | 59.53 | |
| F2F | 51.16 | 51.10 | 51.57 | 51.52 | ||
| NT | 53.67 | 49.44 | 53.81 | 49.61 | ||
| NT | DF | 60.45 | 60.43 | 60.17 | 60.15 | |
| F2F | 54.74 | 54.70 | 53.56 | 53.51 | ||
| FS | 51.59 | 48.15 | 51.84 | 48.51 | ||
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNet101[50] | DF | DF | 91.16 | 91.16 | 91.13 | 91.13 |
| F2F | F2F | 81.41 | 81.41 | 83.50 | 83.49 | |
| FS | FS | 87.59 | 87.37 | 87.75 | 87.66 | |
| NT | NT | 74.17 | 74.56 | 76.03 | 75.53 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNet101[50] | DF | F2F | 52.69 | 52.63 | 51.26 | 51.20 |
| FS | 56.90 | 52.73 | 56.02 | 51.84 | ||
| NT | 55.93 | 51.74 | 54.93 | 50.73 | ||
| F2F | DF | 53.63 | 53.59 | 53.50 | 53.46 | |
| FS | 54.33 | 50.08 | 54.86 | 50.85 | ||
| NT | 54.62 | 51.01 | 55.17 | 51.28 | ||
| FS | DF | 57.04 | 57.70 | 59.55 | 59.51 | |
| F2F | 51.43 | 51.37 | 51.84 | 51.79 | ||
| NT | 53.66 | 49.55 | 53.61 | 49.59 | ||
| NT | DF | 62.66 | 62.65 | 60.16 | 60.14 | |
| F2F | 52.69 | 52.63 | 51.26 | 51.20 | ||
| FS | 56.90 | 52.73 | 56.02 | 51.84 | ||
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNext50[51] | DF | DF | 90.29 | 90.29 | 91.14 | 91.14 |
| F2F | F2F | 81.19 | 81.17 | 82.87 | 82.85 | |
| FS | FS | 87.04 | 86.77 | 87.36 | 87.36 | |
| NT | NT | 74.26 | 74.43 | 76.32 | 75.78 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Test Dataset | Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNext50[51] | DF | F2F | 51.83 | 51.73 | 51.66 | 51.56 |
| FS | 56.57 | 52.53 | 57.24 | 53.21 | ||
| NT | 55.25 | 51.57 | 54.72 | 50.50 | ||
| F2F | DF | 54.57 | 54.58 | 54.46 | 54.47 | |
| FS | 54.31 | 50.38 | 55.28 | 51.45 | ||
| NT | 54.67 | 50.89 | 54.80 | 51.02 | ||
| FS | DF | 59.23 | 59.23 | 60.33 | 60.33 | |
| F2F | 52.02 | 51.93 | 52.98 | 52.89 | ||
| NT | 53.31 | 49.22 | 53.41 | 49.55 | ||
| NT | DF | 60.58 | 60.58 | 58.50 | 58.51 | |
| F2F | 54.16 | 54.11 | 52.46 | 52.38 | ||
| FS | 49.17 | 46.78 | 51.26 | 47.80 | ||
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Unlabeled Dataset |
Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNext50[51] | F2F, FS, NT | DF | 63.33 | 63.32 | 66.23 | 66.22 |
| DF, FS, NT | F2F | 57.35 | 57.39 | 58.04 | 58.08 | |
| DF, F2F, NT | FS | 50.69 | 50.53 | 51.81 | 51.54 | |
| DF, F2F, FS | NT | 53.63 | 53.05 | 53.89 | 53.06 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset | Unlabeled Dataset |
Pretrained model | MPL model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| WideResNet50[52] | F2F, FS, NT | DF | 63.17 | 63.14 | 66.03 | 66.00 |
| DF, FS, NT | F2F | 56.86 | 56.87 | 57.60 | 57.60 | |
| DF, F2F, NT | FS | 48.37 | 47.74 | 52.86 | 51.13 | |
| DF, F2F, FS | NT | 54.22 | 53.43 | 53.92 | 51.96 | |
| Baseline model | Train Dataset |
Unlabeled Dataset |
Pretrained model |
SupCon model [35] |
SupCon-MPL(ours) model |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | ACC | AUC | |||
| ResNet50 [50] | FF (without DF) | DF (unknown) | 64.24 | 64.27 | 62.88 | 62.84 | 64.60 | 64.55 |
| F2F+FS+NT (known) | 70.56 | 71.36 | 75.44 | 75.52 | 75.84 | 76.00 | ||
| FF (without F2F) | F2F (unknown) | 55.76 | 55.64 | 56.61 | 56.64 | 58.74 | 58.77 | |
| DF+FS+NT (known) | 77.26 | 76.89 | 75.54 | 75.54 | 78.11 | 78.28 | ||
| FF (without FS) | FS (unknown) | 54.47 | 52.07 | 55.75 | 53.68 | 55.72 | 53.41 | |
| DF+F2F+NT (known) | 75.99 | 75.87 | 76.02 | 75.88 | 77.22 | 77.12 | ||
| FF (without NT) | NT (unknown) | 56.71 | 54.95 | 56.58 | 54.31 | 56.76 | 54.02 | |
| DF+F2F+FS (known) | 77.39 | 77.41 | 79.09 | 79.26 | 81.22 | 81.32 | ||
| Model |
Scenario Deepfakes (Known) |
Current-Generation Deepfakes (Unknown) |
Post-Generation Deepfakes (Unknown) |
| Tar [34] | 52.40 | 44.62 | 49.96 |
| DDT [31] | 80.41 | 44.62 | 49.49 |
| MPL [24] | 79.82 | 56.53 | 43.16 |
| SupCon [35] | 79.01 | 56.66 | 47.77 |
| SupCon-MPL(ours) | 81.40 | 57.85 | 51.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




