Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Protocol and Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Joint Stiffness
3.2. Joint Mechanical Work
3.3. Joint Moment Angular Impulse
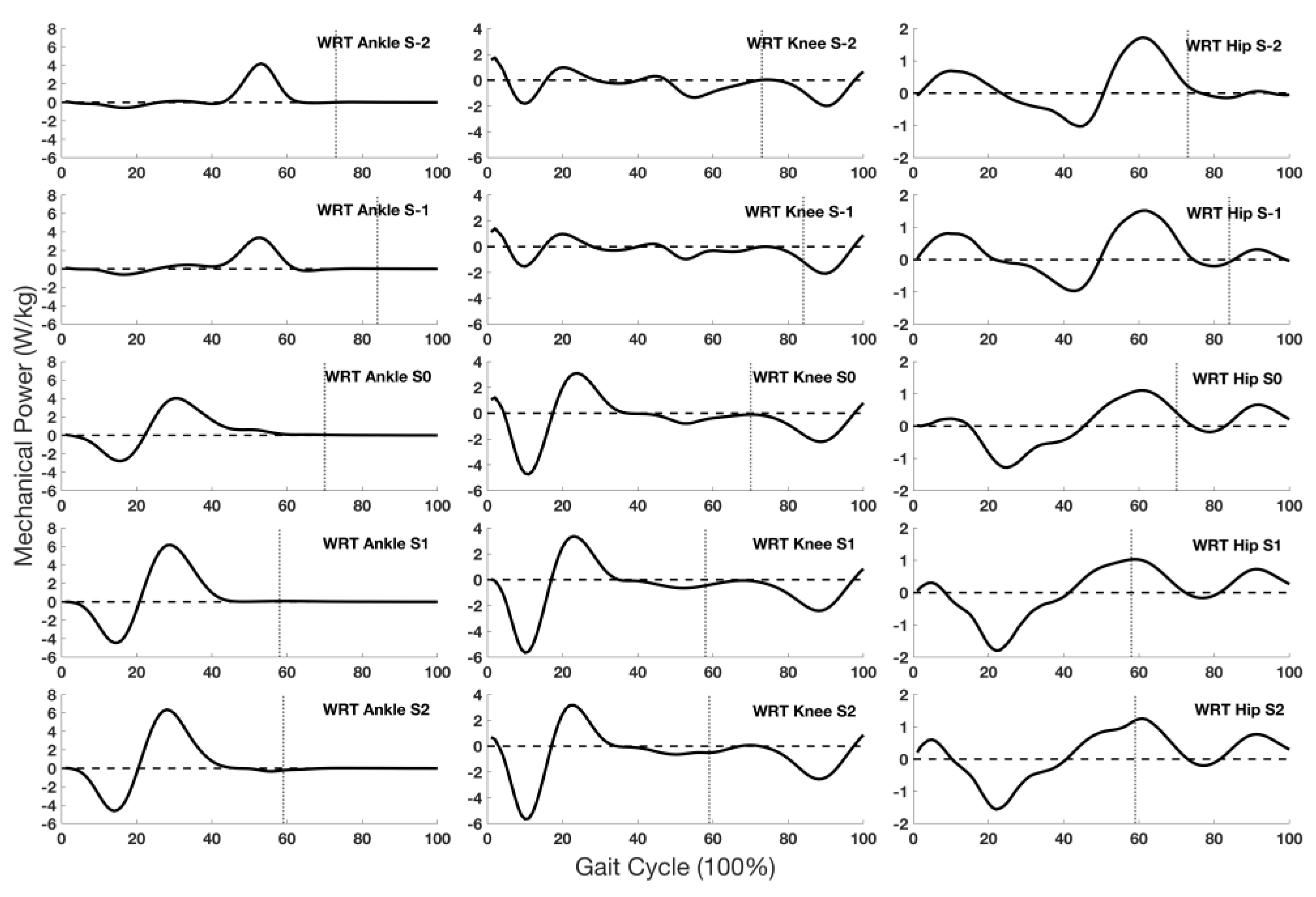
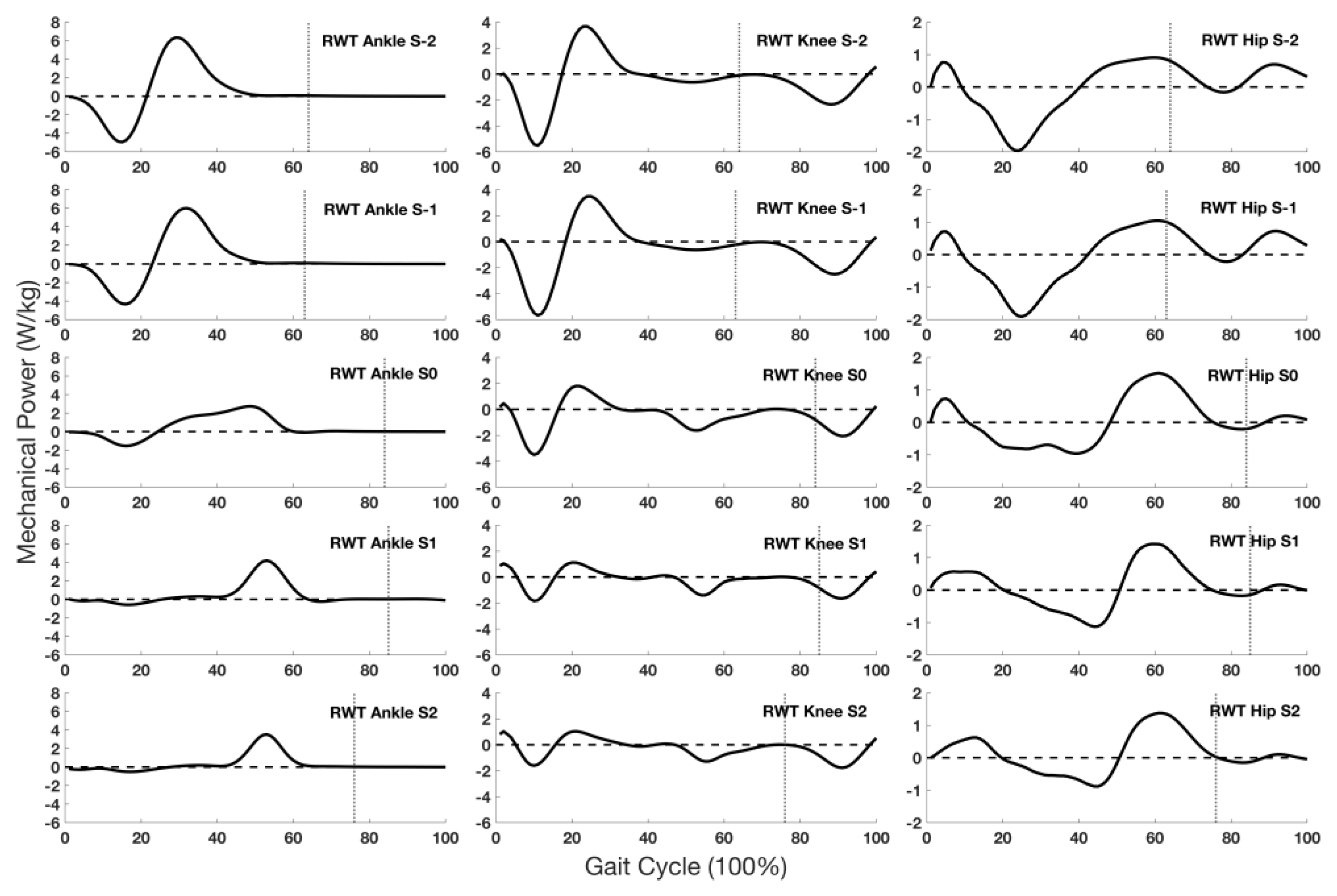
3.4. Joint Mechanical Power
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipfert, S.W.; Günther, M.; Renjewski, D.; Grimmer, S.; Seyfarth, A. A Model-Experiment Comparison of System Dynamics for Human Walking and Running. J Theor Biol 2011, 292C, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segers, V.; Aerts, P.; Lenoir, M.; De Clercq, D. Dynamics of the Body Centre of Mass during Actual Acceleration across Transition Speed. J Exp Biol 2007, 210, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, C.T.; Ferris, D.P. Biomechanics of Walking and Running: Center of Mass Movements to Muscle Action. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 1998, 26, 253–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipfert, S.W.; Günther, M.; Renjewski, D.; Grimmer, S.; Seyfarth, A. A Model-Experiment Comparison of System Dynamics for Human Walking and Running. J Theor Biol 2012, 292, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, F.; Minetti, A.E. Biomechanical and Physiological Aspects of Legged Locomotion in Humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 2003, 88, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, N.J.; Lay, B.S.; Rubenson, J. Joint-Level Mechanics of the Walk-to-Run Transition in Humans. Journal of Experimental Biology 2014, 217, 3519–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynor, A.J.; Yi, C.J.; Abernethy, B.; Jong, Q.J. Are Transitions in Human Gait Determined by Mechanical, Kinetic or Energetic Factors? Hum Mov Sci 2002, 21, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Stability Landscapes of Walking and Running near Gait Transition Speed. J Appl Biomech 2000, 16, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.M.; Fink, P.W.; Legg, S.J.; Ali, A.; Shultz, S.P. What Factors Determine the Preferred Gait Transition Speed in Humans? A Review of the Triggering Mechanisms. Hum Mov Sci 2018, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, D.J.; Sawicki, G.S. The Mechanics and Energetics of Human Walking and Running: A Joint Level Perspective. J R Soc Interface 2012, 9, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neptune, R.R.; Clark, D.J.; Kautz, S. a. Modular Control of Human Walking: A Simulation Study. J Biomech 2009, 42, 1282–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Neptune, R.R. Muscle Mechanical Work and Elastic Energy Utilization during Walking and Running near the Preferred Gait Transition Speed. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedrich, F.J.; Warren, W.H. Why Change Gaits? Dynamics of the Walk-Run Transition. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 1995, 21, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, A.E.; Ardigo, L.P.; Saibene, F. The Transition between Walking and Running in Humans: Metabolic and Mechanical Aspects at Different Gradients. Acta Physiol Scand 1994, 150, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farley, C.T.; Taylor, C.R. A Mechanical Trigger for the Trot-Gallop Transition in Horses. Science (1979) 1991, 253, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hreljac, A. Preferred and Energetically Optimal Gait Transition Speeds in Human Locomotion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1993, 25, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hreljac, A. Determinants of the Gait Transition Speed during Human Locomotion: Kinematic Factors. J Biomech 1995, 28, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreljac, A.; Imamura, R.T.; Escamilla, R.F.; Edwards, W.B.; MacLeod, T. The Relationship between Joint Kinetic Factors and the Walk-Run Gait Transition Speed during Human Locomotion. J Appl Biomech 2008, 24, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hamill, J. Characteristics of the Vertical Ground Reaction Force Component Prior to Gait Transition. Res Q Exerc Sport 2002, 73, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, J.; Li, L. Non-Linear Changes of Lower Extremity Kinetics Prior to Gait Transition. J Biomech 2018, 77, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ogden, L.L. Muscular Activity Characteristics Associated with Preparation for Gait Transition. J Sport Health Sci 2012, 1, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hahn, M.E. Modulation of Lower Extremity Joint Stiffness, Work and Power at Different Walking and Running Speeds. Hum Mov Sci 2018, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hahn, M.E. Comparison of Lower Extremity Joint Mechanics between Healthy Active Young and Middle Age People in Walking and Running Gait. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, V.; Aerts, P.; Lenoir, M.; De Clercq, D. External Forces during Actual Acceleration across Transition Speed. J Appl Biomech 2008, 24, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, V.; De Smet, K.; Van Caekenberghe, I.; Aerts, P.; De Clercq, D. Biomechanics of Spontaneous Overground Walk-to-Run Transition. Journal of Experimental Biology 2013, 216, 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segers, V.; Aerts, P.; Lenoir, M.; De Clercq, D. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Walk-to-Run and Run-to-Walk Transition When Gradually Changing Speed. Gait Posture 2006, 24, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schache, A.G.; Brown, N.A.T.; Pandy, M.G. Modulation of Work and Power by the Human Lower-Limb Joints with Increasing Steady-State Locomotion Speed. Journal of Experimental Biology 2015, 218, 2472–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuitunen, S.; Komi, P. v; Kyröläinen, H.; Kyrolainen, H. Knee and Ankle Joint Stiffness in Sprint Running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanyshyn, D.J.; Stergiou, P.; Lun, V.M.Y.; Meeuwisse, W.H.; Worobets, J.T. Knee Angular Impulse as a Predictor of Patellofemoral Pain in Runners. American Journal of Sports Medicine 2006, 34, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, D.J.; Sawicki, G.S. The Mechanics and Energetics of Human Walking and Running: A Joint Level Perspective. J R Soc Interface 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawers, A.; Hahn, M.E. Regulation of Whole-Body Frontal Plane Balance Varies within a Step during Unperturbed Walking. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell Esposito, E.; Blanck, R.V.; Harper, N.G.; Hsu, J.R.; Wilken, J.M. How Does Ankle-Foot Orthosis Stiffness Affect Gait in Patients with Lower Limb Salvage? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014, 472, 3026–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell Esposito, E.; Choi, H.S.; Owens, J.G.; Blanck, R.V.; Wilken, J.M. Biomechanical Response to Ankle-Foot Orthosis Stiffness during Running. Clinical Biomechanics 2015, 30, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell Esposito, E.; Ranz, E.C.; Schmidtbauer, K.A.; Neptune, R.R.; Wilken, J.M. Ankle-Foot Orthosis Bending Axis Influences Running Mechanics. Gait Posture 2017, 56, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobara, H.; Baum, B.S.; Kwon, H.J.; Miller, R.H.; Ogata, T.; Kim, Y.H.; Shim, J.K. Amputee Locomotion: Spring-like Leg Behavior and Stiffness Regulation Using Running-Specific Prostheses. J Biomech 2013, 46, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVita, P.; Hortobagyi, T. Age Causes a Redistribution of Joint Torques and Powers during Gait. J Appl Physiol 2000, 88, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E.; Frank, J.S.; Walt, S.E. Biomechanical Walking Pattern Changes in the Fit and Healthy Elderly. Phys Ther 1990, 70, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Neptune, R.R. Differences in Muscle Function during Walking and Running at the Same Speed. J Biomech 2006, 39, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crenna, P.; Frigo, C. Dynamics of the Ankle Joint Analyzed through Moment-Angle Loops during Human Walking: Gender and Age Effects. Hum Mov Sci 2011, 30, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, R.C.; Abrantes, J.; Granata, K.; Bulas-Cruz, J.; Melo-Pinto, P.; Filipe, V. Dynamic Joint Stiffness of the Ankle during Walking: Gender-Related Differences. Physical Therapy in Sport 2008, 9, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Joint Stiffness (Nm/kg/deg) | Steps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S−2 | S−1 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| WRT | |||||
| Ankle | 0.13 (0.05) c | 0.12 (0.04) c | 0.16 (0.09) c | 0.23 (0.11) b | 0.24 (0.10) b,c |
| Knee | 0.11 (0.05) | 0.10 (0.03) | 0.11 (0.06) | 0.11 (0.05) a,b | 0.11 (0.06) b |
| Hip | 0.08 (0.03) d | 0.08 (0.02) d | 0.17 (0.09) | 0.20 (0.06) a,d | 0.24 (0.12) |
| RWT | |||||
| Ankle | 0.21 (0.09) e,g | 0.18 (0.07) e,g | 0.19 (0.10) | 0.15 (0.06) | 0.13 (0.06) g |
| Knee | 0.12 (0.08) e,f | 0.11 (0.07) e,f | 0.12 (0.07) | 0.12 (0.07) | 0.09 (0.04) |
| Hip | 0.21 (0.12) f | 0.18 (0.07) f,h | 0.12 (0.05) | 0.11 (0.05) h | 0.08 (0.05) h |
| Joint Work (J/kg) | Steps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S−2 | S−1 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| Stance Phase Positive Work | |||||
| Ankle | 0.40 (0.16) a | 0.39 (0.13) a | 0.55 (0.25) | 0.63 (0.29) b | 0.61 (0.23) a,b |
| Knee | 0.21 (0.08) a | 0.20 (0.08) a | 0.37 (0.19) | 0.31 (0.15) c | 0.28 (0.14) a,c |
| Hip | 0.20 (0.07) d | 0.24 (0.08) e | 0.09 (0.09) e | 0.05 (0.05) b,c,d,e | 0.06 (0.03) b,c,d,e |
| Stance Phase Negative Work | |||||
| Ankle | −0.10 (0.04) h | −0.11 (0.06) f,i | −0.28 (0.13) | −0.36 (0.12) h,i | −0.36 (0.08) h,i |
| Knee | −0.30 (0.21) | −0.24 (0.06) f | −0.41 (0.32) | −0.43 (0.18) g | −0.41 (0.21) g |
| Hip | −0.17 (0.12) | −0.15 (0.08) | −0.22 (0.18) | −0.24 (0.19) g | −0.19 (0.19) g |
| Swing Phase Positive Work | |||||
| Ankle j | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.00) |
| Knee k | 0.02 (0.02) | 0.02 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.03 (0.04) |
| Hip j,k | 0.14 (0.03) l | 0.13 (0.06) | 0.21 (0.07) | 0.23 (0.07) l | 0.26 (0.11) |
| Swing Phase Negative Work | |||||
| Ankle m | −0.01 (0.03) | <−0.01 (0.00) o | <−0.01 (0.00) o | <−0.01 (0.00) o | −0.03 (0.10) |
| Knee m,n | −0.23 (0.03) p | −0.24 (0.04) q | −0.31 (0.05) p,q | –0.34 (0.06) p,q | −0.35 (0.06) p,q |
| Hip n | −0.03 (0.02) | −0.02 (0.01) o | −0.02 (0.01) o | –0.02 (0.01) o | −0.02 (0.01) |
| Joint Work (J/kg) | Steps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S−2 | S−1 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| Stance Phase Positive Work | |||||
| Ankle | 0.67 (0.31) a,b,d | 0.66 (0.33) a,b | 0.50 (0.21) a,b | 0.48 (0.34) | 0.37 (0.20) d |
| Knee | 0.33 (0.16) a,c | 0.32 (0.15) a,c,e | 0.21 (0.14) a | 0.23 (0.17) e | 0.19 (0.11) |
| Hip | 0.06 (0.04) b,c,f | 0.07 (0.05) b,c,g | 0.16 (0.08) b | 0.20 (0.06) f,g | 0.18 (0.04) f,g |
| Stance Phase Negative Work | |||||
| Ankle | −0.41 (0.19) i | −0.38 (0.18) j | −0.17 (0.12) i,j | −0.12 (0.08) h,i,j | −0.10 (0.05) h,i,j |
| Knee | −0.41 (0.21) | −0.45 (0.24) | −0.42 (0.22) | −0.28 (0.10) h | −0.26 (0.06) h |
| Hip | −0.25 (0.22) | −0.26 (0.18) | −0.23 (0.18) | −0.22 (0.15) | −0.18 (0.11) |
| Swing Phase Positive Work | |||||
| Ankle l | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.00) m | 0.01 (0.00) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.00) |
| Knee k | 0.01 (0.01) | <0.01 (0.00) m | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.04) | 0.01 (0.01) |
| Hip k,l | 0.22 (0.09) | 0.22 (0.09) | 0.13 (0.04) | 0.12 (0.06) | 0.12 (0.03) |
| Swing Phase Negative Work | |||||
| Ankle n | <−0.01 (0.00) | <−0.01 (0.00) p | <−0.01 (0.00) p | <−0.01 (0.00) p | <−0.01 (0.00) p |
| Knee n,o | −0.33 (0.09) q | −0.34 (0.08) q,r | −0.23 (0.05) r | −0.21 (0.08) | −0.21 (0.04) q |
| Hip o | −0.01 (0.01) | −0.02 (0.01) p | −0.02 (0.01) p | −0.02 (0.01) p | −0.02 (0.01) p |
| s/kg) | Steps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S−2 | S−1 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| WRT | |||||
| Ankle a | 0.40 (0.12) b | 0.36 (0.07) b | 0.38 (0.12) | 0.41 (0.15) | 0.40 (0.11) |
| Knee | 0.16 (0.12) b,d | 0.14 (0.08) b,e | 0.29 (0.19) | 0.30 (0.14) c,d,e | 0.26 (0.15) d |
| Hip a | 0.12 (0.03) f | 0.12 (0.02) g | 0.10 (0.04) h | 0.05 (0.03) c,f,g,h | 0.07 (0.02) f,g |
| Total | 0.68 (0.23) | 0.62 (0.12) | 0.77 (0.28) | 0.76 (0.28) | 0.73 (0.24) |
| RWT | |||||
| Ankle i | 0.46 (0.22) | 0.44 (0.21) | 0.41 (0.19) | 0.44 (0.24) | 0.37 (0.15) |
| Knee | 0.30 (0.15) j,k | 0.32 (0.15) j,k | 0.25 (0.13) | 0.18 (0.10) k | 0.16 (0.08) |
| Hip i | 0.06 (0.03) j,l | 0.06 (0.04) j,m | 0.08 (0.05) | 0.12 (0.04) l | 0.11 (0.04) l,m |
| Total | 0.82 (0.36) | 0.82 (0.36) | 0.73 (0.33) | 0.75 (0.37) | 0.65 (0.24) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





