Submitted:
10 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
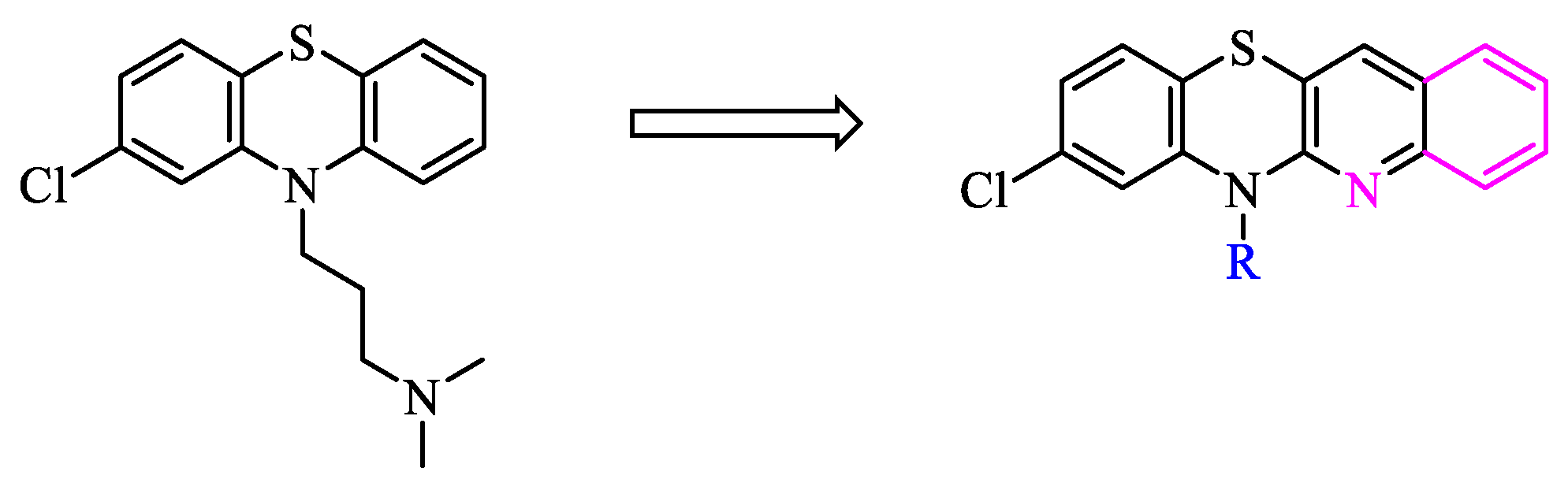
2. Results and discussion
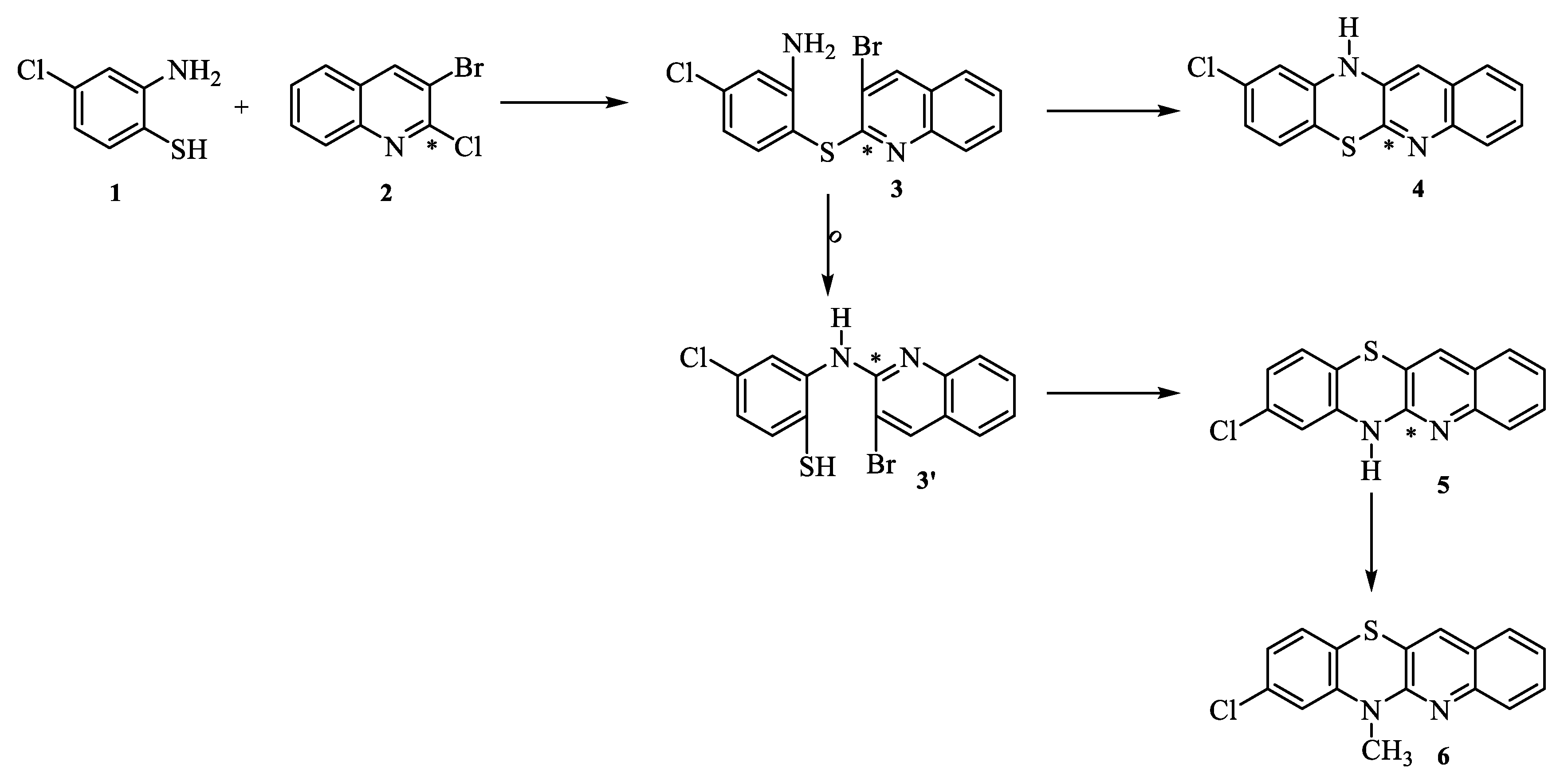
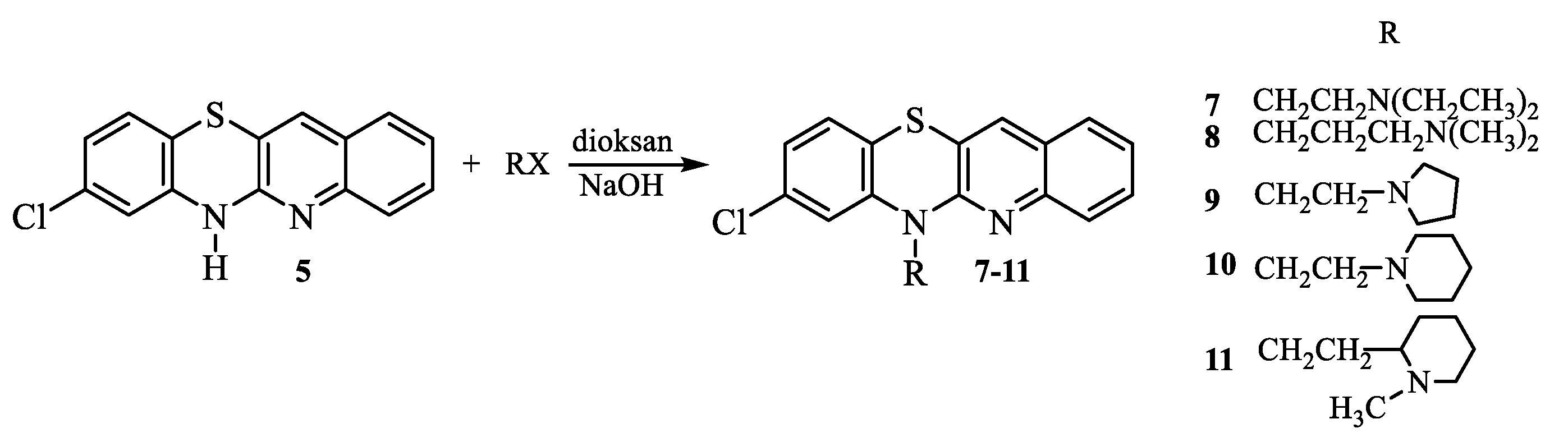
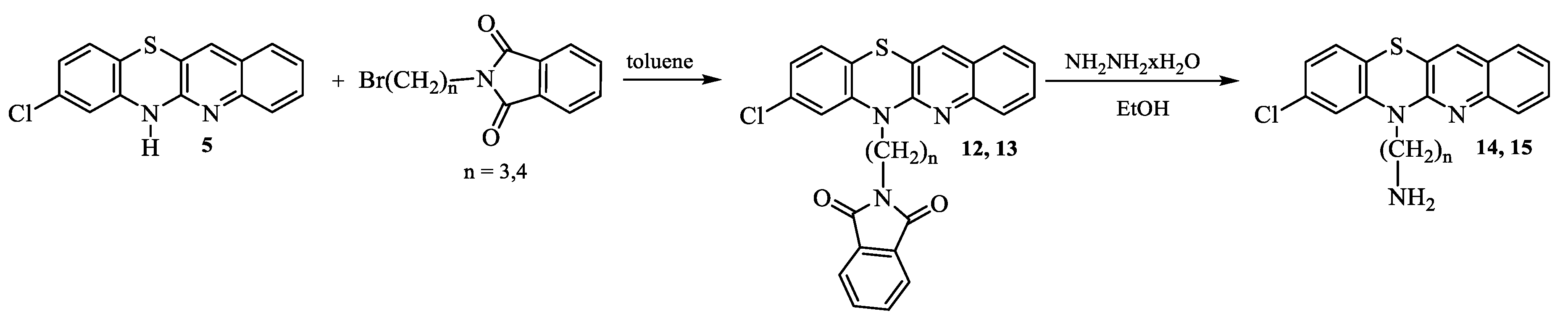
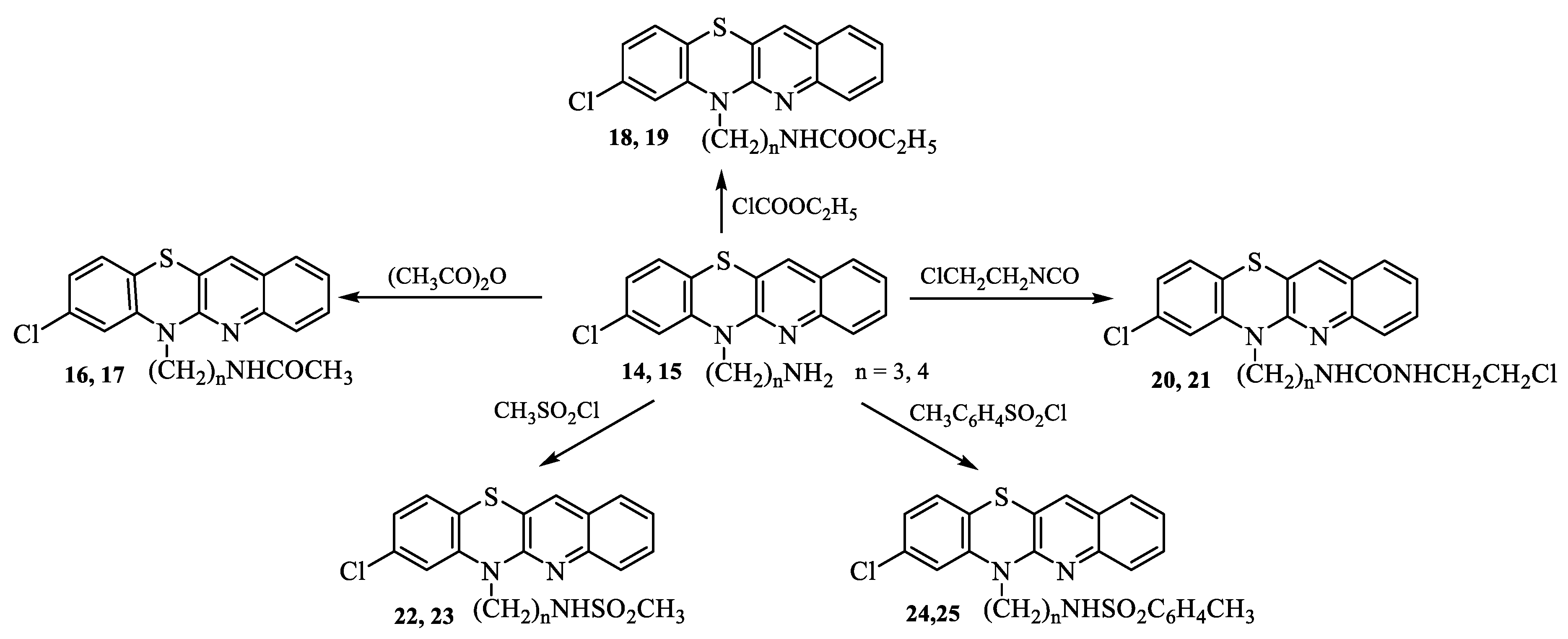
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Biological evaluation
2.2.1. Cytotoxic activity
2.2.2. In vitro antibacterial activity
2.2.3. Mechanism of cytotoxicity of newly derivatives
- Apoptotic activity:
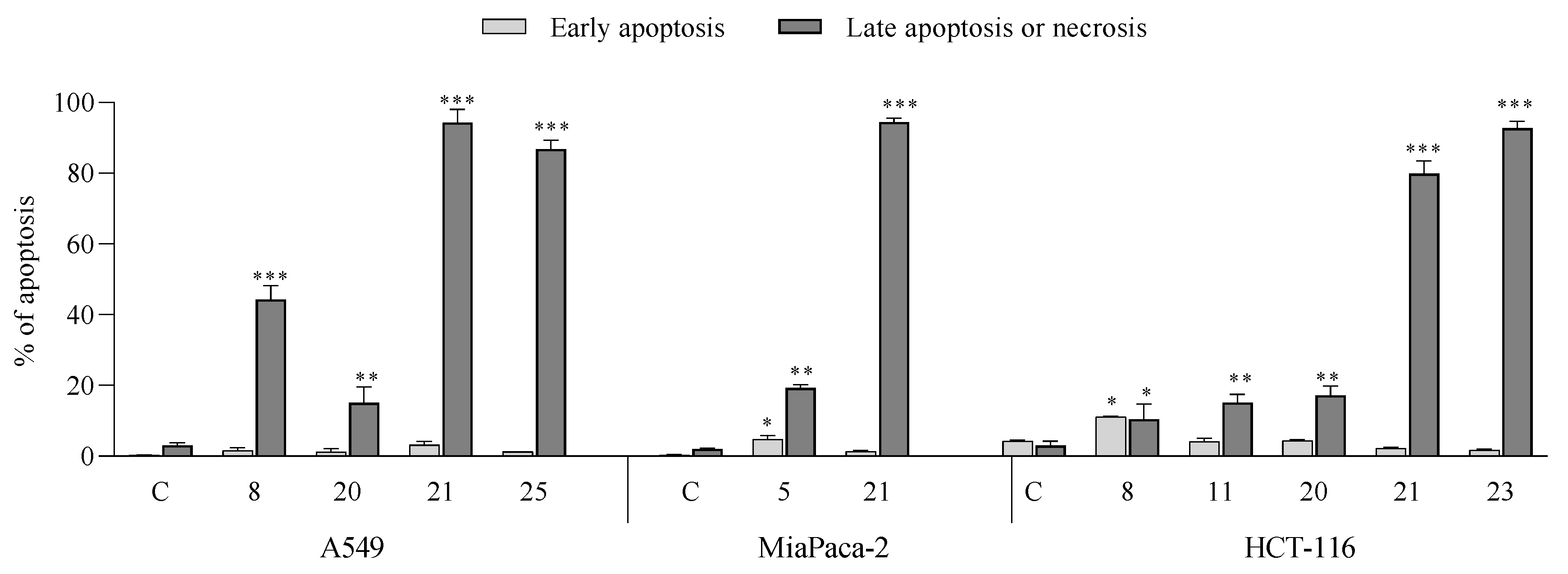
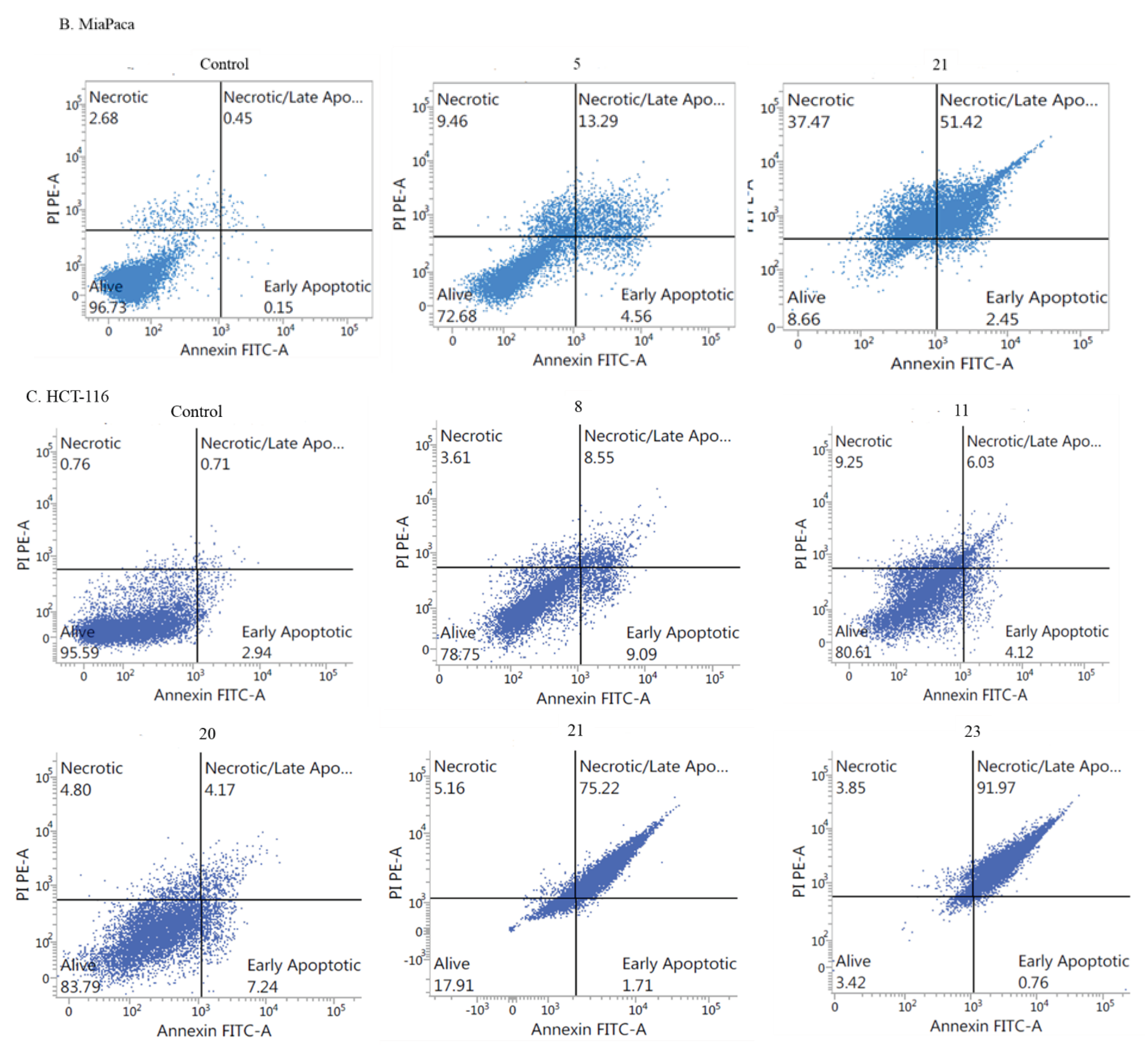
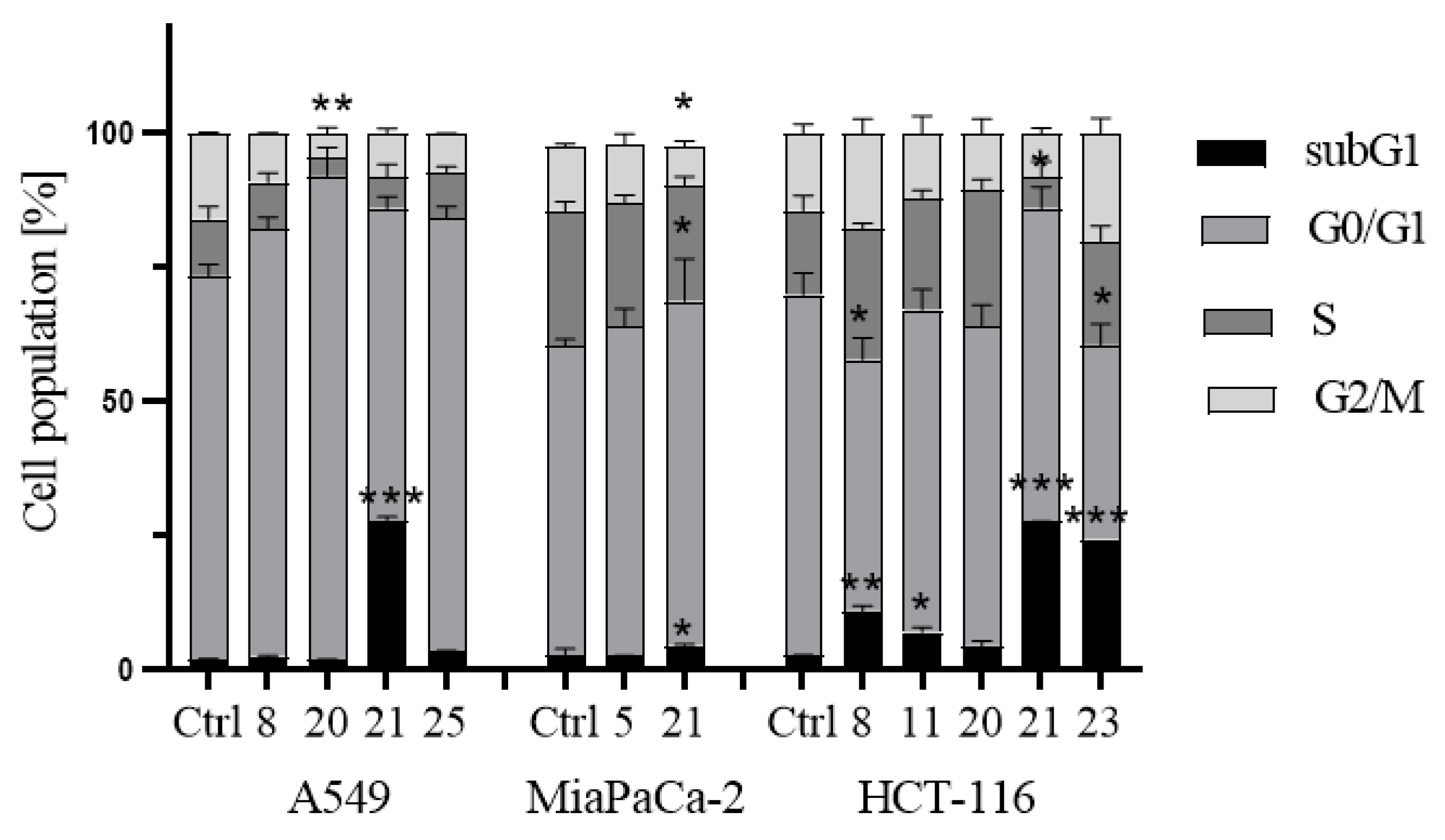
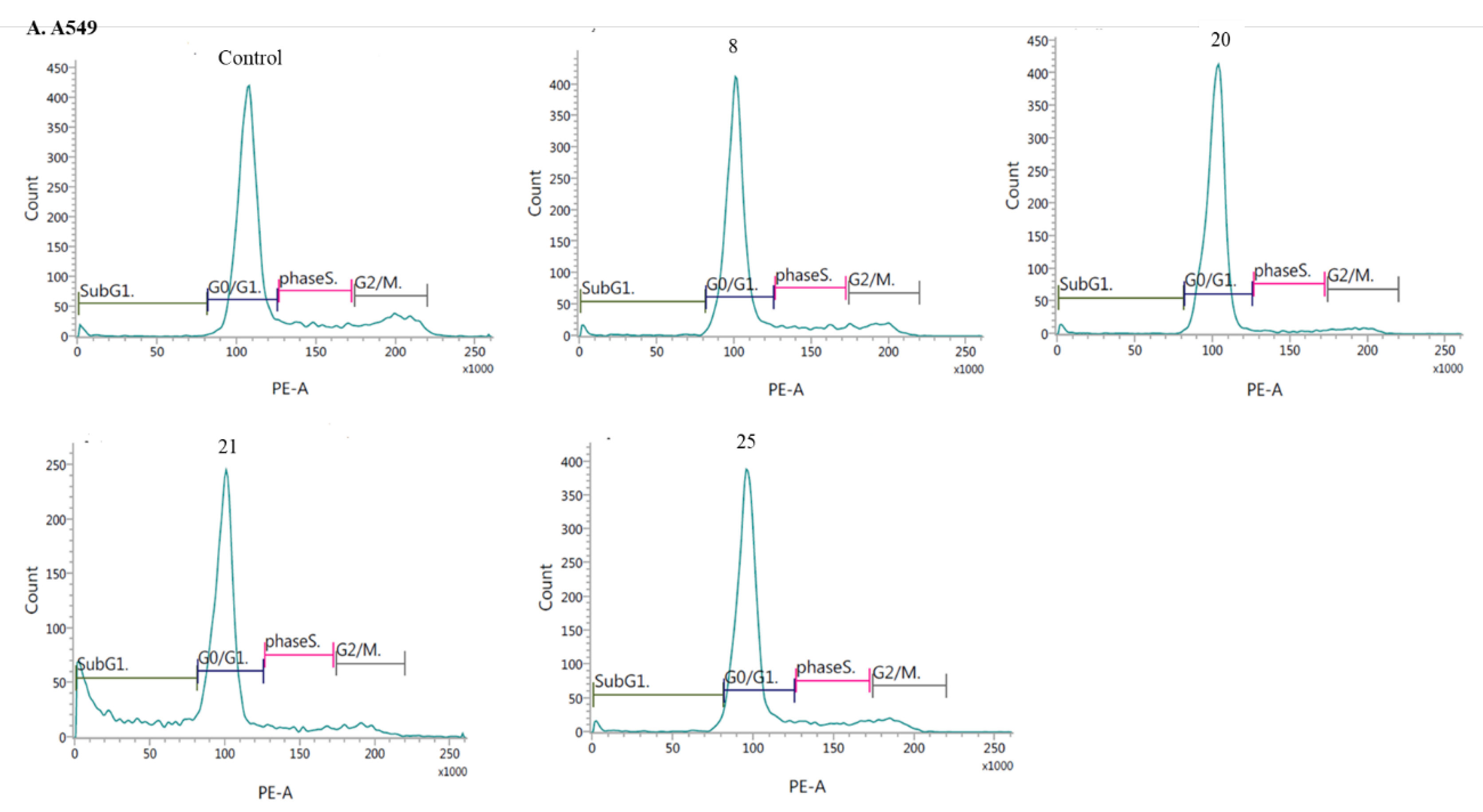
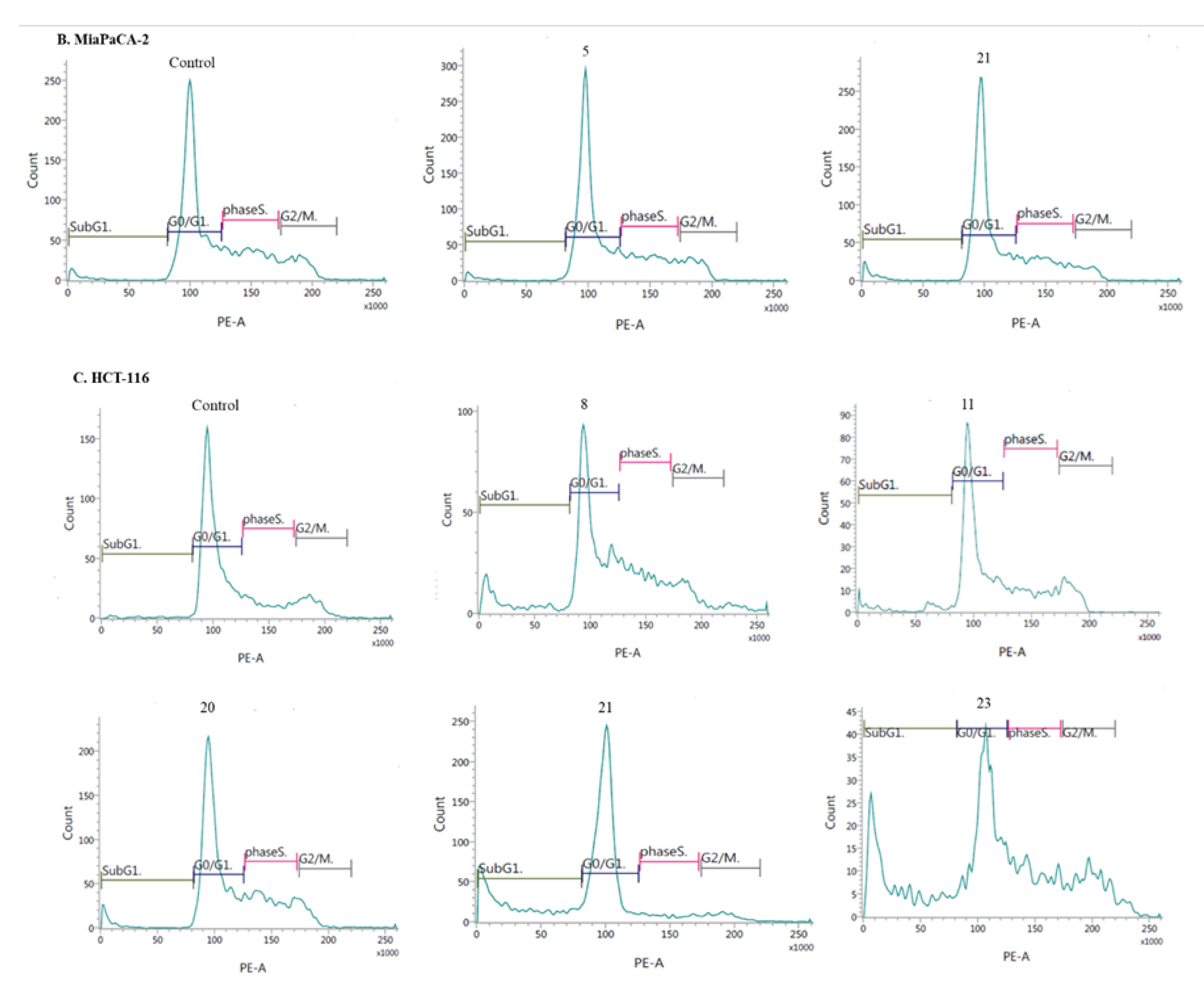
- Induction of cell cycle arrest
3. Methods and materials
3.1. Synthesis of compounds
3.1.1. General procedure for the synthesis of 8-chloroquinobenzothiazine derivatives:
- Synthesis of 6H-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine 5.
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-methylquinobenzothiazine 6.
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-dialkylaminoalkylquinobenzothiazines 7-11.
- 6-
- (2-Diethylaminoethyl)-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (7):
- 6-
- (3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (8):
- 6-
- (1-Pyrrolidylethyl)-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (9):
- 6-
- (1-Piperidylethyl)-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (10):
- 6-
- (1-Methyl-2-piperidylethyl)-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (11):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-phthalimidoalkylquinobenzothiazines 12 and 13.
- 8-Chloro-6-phthalimidopropylquinobenzothiazine (12):
- 8-Chloro-6-phthalimidobutylquinobenzothiazine (13):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-aminoalkylquinobenzothiazines 14 and 15.
- 6-Aminopropyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (14):
- 6-Aminobutyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (15):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-acetylaminoalkylquinobenzothiazines 16-25.
- 6-Acetylaminopropyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (16):
- 6-Acetylaminobutyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (17):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-etoxycarbonylaminoalkylquinobenzothiazines 18 and 19.
- 6-Ethoxycarbonylaminopropyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (18):
- 8-Chloro-6-ethoxycarbonylaminobutylquinobenzothiazine (19):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-chloroethylureidoalkylquinobenzothiazines 20 and 21.
- 6-Chloroethylureidopropyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (20):
- 6-Chloroethylureidobutyl-8-chloroquinobenzothiazine (21):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro 6-methanesulfonylaminoalkylquinobenzothiazines 22 and 23.
- 8-Chloro-6-methanesulfonylaminopropylquinobenzothiazine (22):
- 8-Chloro-6-methanesulfonylaminobutylquinobenzothiazine (23):
- Synthesis of 8-chloro-6-p-toluenesulfonylaminolkylquinobenzothiazines 24 and 25.
- 8-Chloro-6-p-toluenesulfonylaminopropylquinobenzothiazine (24):
- 8-Chloro-6-p-toluenesulfonylaminobutylquinobenzothiazine (25):
- Synthesis of 8-chloroquinobenzothiazines with triazole substituents 27-33.
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
- 8-Chloro-6-
3.2. Biological assays
3.2.1. Cell line and culture
3.2.2. MTT assay
3.2.3. Apoptosis and cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry (FCM)
- Cell cycle analysis:
3.2.4. In vitro antibacterial studies
3.2.5. Statistical analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, S.C. Phenothiazine: the parent molecule. Curr. Drug. Targets. 2006, 7, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristiansen, J.E.; Dastidar, S.G.; Palchoudhuri, S.; Roy, D.S.; Das, S.; Hendricks, O.; Christensen, J.B. Phenothiazines as a solution for multidrug resistant tuberculosis: from the origin to the present. Int. Microbiol. 2015, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, G.; Hahn, M.K.; Agarwal, S.M.; Chintoh, A.; Agid, O. Schizophrenia: antipsychotics and drug development. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 414, 113507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.E.; Awad, G.A.; Rathbone, J.; Thornley, B.; Soares-Weiser, K. Chlorpromazine versus placebo for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 1, CD00028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd-Kimball, D.; Gonczy, K.; Lewis, B.; Mason, T.; Siliko, N.; Wolfe, J. Classics in chemical neuroscience: chlorpromazine. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, M.; Espinoza, J.L.; Kumode, T.; Tanimura, A.; Yokota, T.; Oritani, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kanakura, Y.; Matsumura, I. Chlorpromazine eliminates acute myeloid leukemia cells by altering the subcellular localisation of FLT3-ITD and KIT-D816V. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lidsky, T.; Yablonsky-Alter, E.; Zuck, L.; Banerjee, S. Antipsychotic drug effects on glutamatergic activity. Brain Res. 1997, 764, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Muñoz, F.; Alamo, C.; Cuenca, E.; Shen, W.; Clervoy, P.; Rubio, G. History of the discovery and clinical introduction of chlorpromazine. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry. 2005, 17, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otręba, M.; Kośmider, L. In vitro anticancer activity of fluphenazine, perphenazine and prochlorperazine. A review. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamgar-Dayhoff, P.; Brelidze, T.I. Multifaceted effect of chlorpromazine in cancer: implications for cancer treatment. Oncotarget. 2021, 12, 1406–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendouei, N.; Saghafi, F.; Shadfar, F.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Molecular mechanisms of antipsychotic drugs for improvement of cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csatary, L.K. Chlorpromazines and cancer. The Lancet. 1972, 300, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, P.B. Neuroleptic treatment and other factors modifying cancer risk in schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1987, 75, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yde, C.W.; Clausen, M.P.; Bennetzen, M.V.; Lykkesfeldt, A.E.; Mouritsen, O.G.; Guerra, B. The antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine enhances the cytotoxic effect of tamoxifen in tamoxifen-sensitive and tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2009, 20, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.E.; Lee, W.Y.; Cheng, H.W.; Chung, C.H.; Mi, F.L.; Lin, C.W. The antipsychotic chlorpromazine suppresses YAP signaling, stemness properties, and drug resistance in breast cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 302, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.Y.; Lee, W.T.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, K.C.; Chou, C.M.; Chung, C.H.; Sun, M.S.; Cheng, H.W.; Ho, M.N.; Lin, C.W. Repositioning antipsychotic chlorpromazine for treating colorectal cancer by inhibiting sirtuin 1. Oncotarget. 2015, 6, 27580–27595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Johansen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wilson, A.; Keegan, M.; Avery, W.; Elliott, P.; Borisy, A.A.; Keith, C.T. The novel combination of chlorpromazine and pentamidine exerts synergistic antiproliferative effects through dual mitotic action. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11359–11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, J.; Hirao, Y.; Nakano, H.; Fukunishi, Y.; Nishimura, Y. Sertraline, chlorprothixene and chlorpromazine characteristically interact with the REST-binding site of the corepressor mSin3, showing inhibitory activities of medulloblastoma cell growth. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, C.R.; Zhang, W.; Langford, C.; Suto, M.J.; Griguer, C.E. Repositioning chlorpromazine for treating chemoresistant glioma through the inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase bearing the COX4-1 regulatory subunit. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 37568–37583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. H.; Kim, Y. S.; Lim, Y.; Lee, Y.H. Chlorpromazine activates p21Waf1/Cip1 gene transcription via early growth response-1 (Egr-1) in C6 glioma cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Choi, Y.K.; Lim, H.J.; Lee, H.G.; Lim, Y.; Lee, Y.H. The antipsychotic agent chlorpromazine induces autophagic cell death by inhibiting the Akt/mTOR pathway in human U-87MG glioma cells. Carcinogenesis. 2013, 34, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Ad, I.; Shtaif, B.; Levkovitz, Y.; Nordenberg, J.; Taler, M.; Korov, I.; Weizman, A. Phenothiazines induce apoptosis in a B16 mouse melanoma cell line and attenuate in vivo melanoma tumor growth. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, Z.; Ohba, H.; Bakalova, R.; Hadjimitova, V.; Ishikawa, M.; Shinohara, Y.; Baba, Y. Phenothiazines suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis in cultured leukemic cells without any influence on the viability of normal lymphocytes. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2004, 53, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, D.; Zielinska-Chomej, K.; Juntti, T.; Mörk, B.; Lewensohn, R.; Hååg, P.; Viktorsson, K. Harnessing the lysosome-dependent antitumor activity of phenothiazines in human small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, S.; Giehl, K.; Henis, Y.I.; Ehrlich, M. Differential interference of chlorpromazine with the membrane interactions of oncogenic K-Ras and its effects on cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27279–27288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, A.J.; Chang, H.C.; Hung, C.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Liu, W.; Lee, C.H. Chlorpromazine, an antipsychotic agent, induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis via regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy pathways in human oral cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 184, 114403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbruzzese, C.; Matteoni, S.; Persico, M.; Villani, V.; Paggi, M.G. Repurposing chlorpromazine in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: analysis of literature and forthcoming steps. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Xi, H.; Liao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wu, M.; Xue, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y. Repurposed antipsychotic chlorpromazine inhibits colorectal cancer and pulmonary metastasis by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamgar-Dayhoff, P.; Brelidze, T.I. Multifaceted effect of chlorpromazine in cancer: implications for cancer treatment. Oncotarget. 2021, 12, 1406–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, N.C.; Ekins, S.; Williams, A.J.; Tropsha, A. A bibliometric review of drug repurposing. Drug Discovery Today. 2018, 23, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, B.; Csonka, Á.; Csonka, A.; Molnár, J.; Amaral, L.; Spengler, G. Possible biological and clinical applications of phenothiazines. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 5983–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, K.Y.; Tay, W.L.; Chui, W.K.; Chan, A. Clinically relevant drug interactions between anticancer drugs and psychotropic agents. Eur. J. Cancer Care. 2011, 20, 6–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendouei, N.; Saghafi, F.; Shadfar, F.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Molecular mechanisms of anti-psychotic drugs for improvement of cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 5, 856:172402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, K.; Jeleń, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Zimecki, M.; Artym, J.; Kocięba, M.; Zaczyńska, E. Azaphenothiazines - promising phenothiazine derivatives. An insight into nomenclature, synthesis, structure elucidation and biological properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 774–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, K.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Jeleń, M. Synthesis and properties of diaza-, triaza- and tetraazaphenothiazines. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009, 46, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morak-Młodawska, B.; Jeleń, M.; Pluta, K. Phenothiazines modified with the pyridine ring as promising anticancer agents. Life (Basel). 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeleń, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Korlacki, R. Anticancer activities of tetra-, penta-, and hexacyclic phenothiazines modified with quinoline moiety. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1287, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Vigato, C.; Boschi, D.; Lolli, M.L.; Kumar, D. Phenothiazines as anti-cancer agents: SAR overview and synthetic strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 254, 115337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posso, M.C.; Domingues, F.C.; Ferreira, S.; Silvestre, S. Development of phenothiazine hybrids with potential medicinal interest: A review. Molecules. 2022, 27, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, M.; Pluta, K.; Latocha, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Suwińska, K.; Kuśmierz, D. Evaluation of angularly condensed diquinothiazines as potential anticancer agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, M.; Pluta, K.; Szmielew, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Herman, K.; Giercuszkiewicz, K.; Kasprzycka, A.; Skonieczna, M. 14-Substituted diquinothiazines as a new group of anticancer agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, M.; Ying, P.; Ting, C.; Hao, Y. J.; Balachandran, A.; Anamalay, K.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Gaurav, A.; Lavilla, C.A.; Uy, M.M.; Billacura, M.P.; Okechukwu Nwabueze, P. In vitro study of antioxidant, antigylycation, sugar hydrolysis enzyme inhibitory effect and molecular in silico docking study of angularly condensed diquinothiazines. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1296, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artym, J.; Kocięba, M.; Zaczyńska, E.; Zimecki, M.; Kałas, W.; Strządała, L.; Pawlak, A.; Jeleń, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Pluta, K.; Kaleta-Kuratewicz, K.; Madej, J.P.; Kuropka, P.; Kuryszko, J. Therapeutic effects of an azaphenothiazine derivative in mouse experimental colitis. Histol. Histopathol. 2020, 35, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artym, J.; Kocięba, M.; Zaczyńska, E.; Kochanowska, I.; Zimecki, M.; Kałas, W.; Strządała, L.; Zioło, E.; Jeleń, M.; Morak-Młodawska, B.; Pluta, K. Prolongation of skin graft survival in mice by an azaphenothiazine derivative. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 208, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, M.; Pluta, K. Synthesis of quinobenzo-1,4-thiazines from diquino-1,4-dithiin and 2,2'-dichloro-3,3'-diquinolinyl disulfide. Heterocycles. 2009, 78, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.M.; Matin, P.; Rahman, M.R.; Hadda, T. B.; Almalki, F.A.; Mahmud, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alruwaily, M.; Alshehri, S. Triazoles and their derivatives: chemistry, synthesis, and therapeutic applications. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 864286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J.; Cao, S.; Long, S. Recent advances in 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-triazole hybrids as antimicrobials and their SAR: A critical review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 259, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z. Recent updates on 1,2,3-triazole-containing hybrids with in vivo therapeutic potential against cancers: A mini-review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 251, 115254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. Comprehensive review on the anti-bacterial activity of 1,2,3-triazole hybrids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 168, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorov, K.; Zhao, J.; Aisa, H.A. 1,2,3-Triazole-containing hybrids as leads in medicinal chemistry: A recent overview. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3511–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M. 1,2,3-Triazole hybrids as anticancer agents: A review. Arch. Pharm. 2022, 355, 2100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddyrajula, R.; Dalimba, U.; Kumar, S. Molecular hybridization approach for phenothiazine incorporated 1,2,3-triazole hybrids as promising antimicrobial agents: Design, synthesis, molecular docking and in silico ADME studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 168, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Guo, J.M.; Zhang, T.T.; Lin, H.J.; Qi, N.S.; Li, Z.G.; Zhou, J.C.; Zhang, Z.Z. Antiproliferative phenothiazine hybrids as novel apoptosis inducers against MCF-7 breast cancer. Molecules. 2018, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, J. Antitumor evaluation of novel phenothiazine derivatives that inhibit migration and tubulin polymerization against gastric cancer MGC-803 cells. Invest. New Drugs. 2019, 37, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvester, P.W. Optimization of the tetrazolium dye (MTT) colorimetric assay for cellular growth and viability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 716, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. CLSI; Wayne, PA, USA: 2006.
- Bonelli, M.; La Monica, S.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R. Multiple effects of CDK4/6 inhibition in cancer: from cell cycle arrest to immunomodulation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 170, 113676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Downregulation of NIMA-related kinase-7 inhibits cell proliferation by inducing cell cycle arrest in human retinoblastoma cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1360–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plati, J.; Bucur, O.; Khosravi-Far, R. Dysregulation of apoptotic signaling in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 1124–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Mielczarek-Puta, M.; Graboń, W. The real cytotoxic effect of artemisinins on colon cancer cells in a physiological cell culture setting. How composition of the culture medium biases experimental findings. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoszczak, M.; Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Kordylas, M.; Struga, M.; Huczyński, A. Synthesis of lasalocid-based bioconjugates and evaluation of their anticancer activity. ACS Omega. 2022, 7, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struga, M.; Roszkowski, P.; Bielenica, A.; Otto-Ślusarczyk, D.; Stępień, K.; Stefańska, J.; Zabost, A.; Augustynowicz-Kopeć, E.; Koliński, M.; Kmiecik, S.; Myslovska, A.; Wrzosek, M. N-Acylated ciprofloxacin derivatives: synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation as antibacterial and anticancer agents. ACS Omega. 2023, 8, 18663–18684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
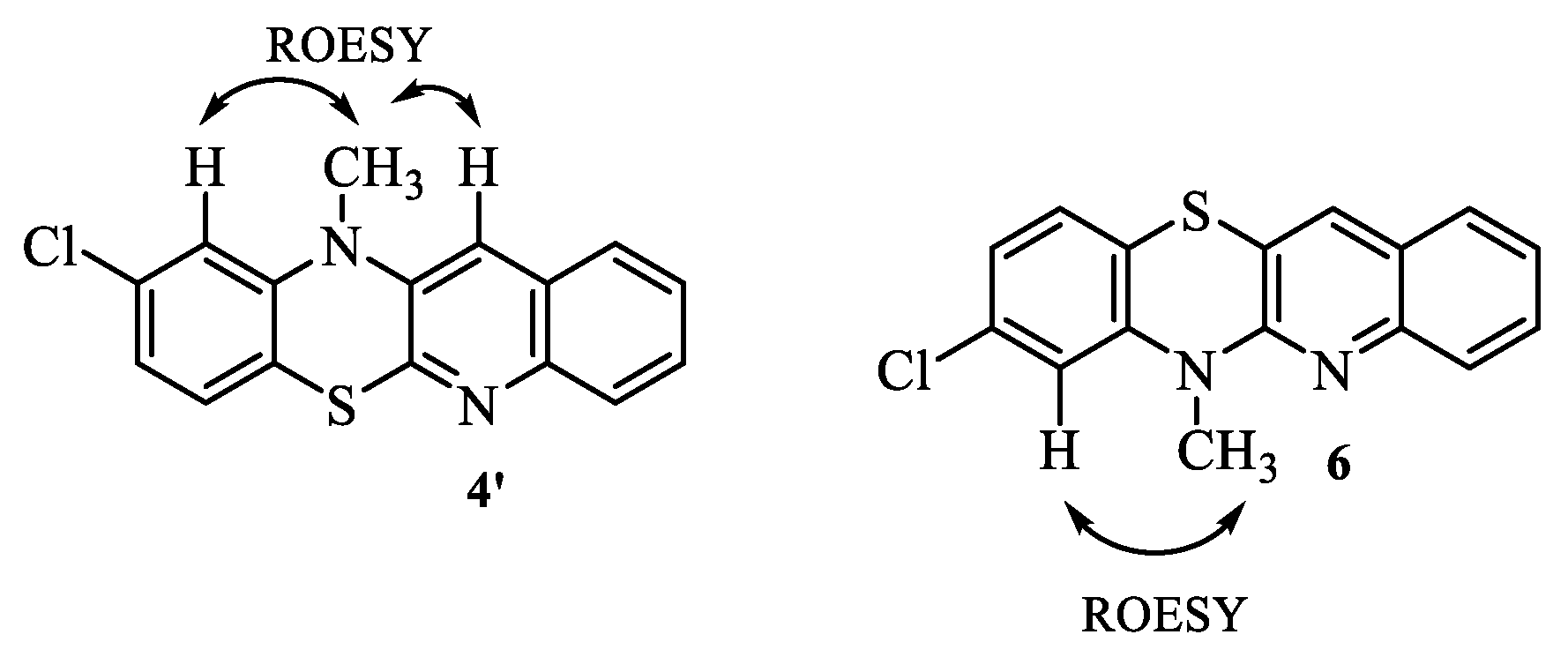
| 1H NMR (ppm) | ROESY | COSY |
|---|---|---|
| 3.61 CH3 | 6.94 | |
| 6.94 H7 | 3.61 | |
| 6.96 H9 | 7.05 | |
| 7.05 H10 | 6.96 | |
| 7.32 H2 | 7.54-7.57 | |
| 7.54-7.57 H1 and H3 | 7.32 | |
| 7.70 H12 | ||
| 7.79 H4 | 7.54-7.57 |
| 13C NMR | HSQC | HMBC |
|---|---|---|
| 29.73 | 3.61 | |
| 115.70 | 3.61 and 6.94 C7 | 6.96 |
| 118.19 | 6.96 and 6.94 C8 | |
| 118.95 | 6.94 C4a | |
| 122.48 | 6.96 C9 | |
| 124.53 | 7.32 C2 | |
| 125.99 | 7.32 C11a | |
| 126.30 | 7.54-7.57 C1 | |
| 127.23 | 7.79 C4 | |
| 127.47 | 7.05 C10 | |
| 129.33 | 7.54-7.57 C3 | 7.54-7.57 |
| 132.21 | 7.70 C12 | |
| 133.60 | 6.94 and 7.05 C10a | |
| 144.17 | 7.05 and 3.61 C6a | |
| 145.74 | 7.70 and 7.54-7.57 C12a | |
| 152.77 | 7.70 and 3.61 C5a |
| Compound | Cancer cells | Normal cells | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549d | MDAe | HaCaTf | |||||||
| IC50b | SIc | IC50 | SI | IC50 | |||||
| 5 | 14.9 ± 2.7 | 3.8 | 76.5 ± 0.8 | 0.7 | 56.5 ± 4.5 | ||||
| 7 | 27.2 ± 8.4 | 3.7 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 8 | 8.2 ± 3.6 | 7.6 | 52.1 ± 2.7 | 1.2 | 62.3 ± 2.5 | ||||
| 9 | 17.4 ± 4.1 | 5.7 | 77.1 ± 1.6 | 1.3 | < 100 | ||||
| 10 | 63.8 ± 8.5 | 1.6 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 11 | 16.0 ± 4.2 | 1 | 16.7 ± 1.1 | 0.9 | 12.7 ± 1.9 | ||||
| 16 | 24.6 ± 6.1 | 4.1 | 76.6 ± 8.9 | 1.3 | < 100 | ||||
| 17 | 82.3 ± 6.2 | 1.2 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 18 | 86.6 ± 0.8 | 1.1 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 19 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 20 | 9.3 ± 1.2 | 10.7 | 48.6 ± 7.3 | 2.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 21 | 6.98 ± 1.2 | 0.1 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | ||||
| 22 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 23 | 30.5 ± 8.3 | 3.3 | < 100 | 0.2 | < 100 | ||||
| 24 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 25 | 9.45 ± 1.3 | 10.5 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 26 | <100 | 1.0 | 95.8 ± 9.2 | 0.7 | 71.7 ± 5.7 | ||||
| 27 | 27.5 ± 6.2 | 2.5 | < 100 | 0.7 | 70.2 ± 10.4 | ||||
| 28 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 29 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 30 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 31 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 32 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| 33 | <100 | 1.0 | <100 | 1.0 | < 100 | ||||
| DXg | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.14 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | ||||
| Compound | Cancer cells | Normal cells | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MiaPaCa-2d | PC3e | HCT116f | HaCaTg | ||||
| IC50b | SIc | IC50 | SI | IC50 | SI | IC50 | |
| 5 | 11.1 ± 0.4 | 5.0 | 76.5 ± 8.1 | 0.7 | 33.5 ± 6.8 | 1.7 | 56.5 ± 6.4 |
| 8 | 40.2 ± 0.7 | 1.6 | 52.1 ± 7.1 | 1.2 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 39 | 62.3 ± 3.5 |
| 9 | 57.4 ± 9.6 | 1.7 | 77.1 ± 9.4 | 1.3 | 17.5 ± 1.4 | 5.7 | < 100 |
| 11 | 24.3 ± 3.5 | 0.5 | 16.7 ± 1.8 | 0.7 | 7.7 ± 1.2 | 1.6 | 12.7 ± 2.1 |
| 20 | 23.2 ± 2.7 | 4.3 | 34.8 ± 9.8 | 2.8 | 10.4 ± 1.6 | 8.8 | < 100 |
| 21 | 6.4 ± 2.4 | 0.2 | 76.6 ± 9.8 | 0.1 | 11.3 ± 2.2 | 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| 23 | 98.4 ± 5.6 | 1.0 | < 100 | 1.0 | 0.7 ± 0.08 | 143 | < 100 |
| 25 | < 100 | 1.0 | 48.6 ± 4.7 | 2.0 | < 100 | 1.0 | < 100 |
| 27 | 37.4 ± 5.6 | 1.9 | < 100 | 1.0 | 49.6 ± 4.7 | 1.4 | 71.7 ± 7.5 |
| DXh | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.14 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| Compound | Bacterial strains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus NCTC 4163 | S. aureus ATCC 25923 | S. aureus ATCC 6538 | S. aureus ATCC 29213 | S. epidermidis ATCC 12228 | S. epidermidis ATCC 35984 | E. coli ATCC 25922 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 15442 | |
| 5 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 256 | 256 |
| 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | >256 | >256 |
| 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 64 | 256 |
| 9 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | >256 | >256 |
| 10 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 11 | 8 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 256 | 256 | >256 | >256 |
| 16 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 17 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 18 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 19 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 20 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | >256 | >256 |
| 21 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | >256 |
| 22 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 23 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 24 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 25 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 26 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 27 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 28 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 29 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 30 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 31 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 32 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| 33 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| control - ciprofloxacin | 0,125 | 0,25 | 0,125 | 0,25 | 0,125 | 0,125 | 0,0075 | 0,125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





