1. Introduction
Reservoirs are essential for managing water resources, serving purposes such as agricultural watering, power generation, and ensuring water availabilityTraditionally, rivers were viewed as natural pathways for sediment transport, primarily toward coastal areas. Yet, the construction of dams has significantly altered the dynamics of sediment transportation (Kirwan and Megonigal, 2013). The International Commission on Large Dams (ICOLD, 2021) reports a global tally of approximately 58,713 expansive dams. These structures yield diverse advantages including water provision, power production, agricultural irrigation, flood mitigation, navigation facilitation, and various other benefits (Guo and Jin, 2002; Llamosas and Sovacool, 2021). Sedimentation had resulted in a 33% decrease in global storage capacity in 2018 (ICOLD, 2021). According to the World Commission on Dams study (2000), sedimentation has reduced global reservoir storage capacity by 0.5% to 1% each year. Sedimentation depletes reservoir storage volume by 33.5 km3 per year on average (Willis and Griggs, 2003) (White 2010). There is an anticipation that global reservoir capacity will be reduced by 50%, excluding new developments (Sumi and Hirose, 2009).
When rivers enter reservoirs and water velocity decreases, allowing for silt settling, the rate of sedimentation increases (Juracek, 2015; Kennedy, 1998). Previous research has shown that damming reduces flow velocity and causes sediment deposition by altering the longitudinal connectivity of rivers and raising reservoir water levels (Batalla et al., 2004; Moussa, 2013). Apart from influencing various functions like flood control, hydroelectric power generation, navigation, and fisheries, diminishing reservoir capacity poses an immediate threat to ensuring reliable water supplies for both agricultural and residential needs (Annandale et al., 2016). The accumulation of sediment in reservoirs affects downstream areas all the way to the coastline and upstream to other reservoirs. Rivers deprived of sediment, particularly larger particles crucial for maintaining reservoir structure, face significant degradation due to human activities along riverbanks, increased erosion, and habitat loss (Kondolf, 1997). Processes such as reservoir sediment trapping and in-channel mining (Torres et al., 2016) disrupt the natural balance of sediment flow, potentially exacerbating coastal erosion (Willis and Griggs, 2003).
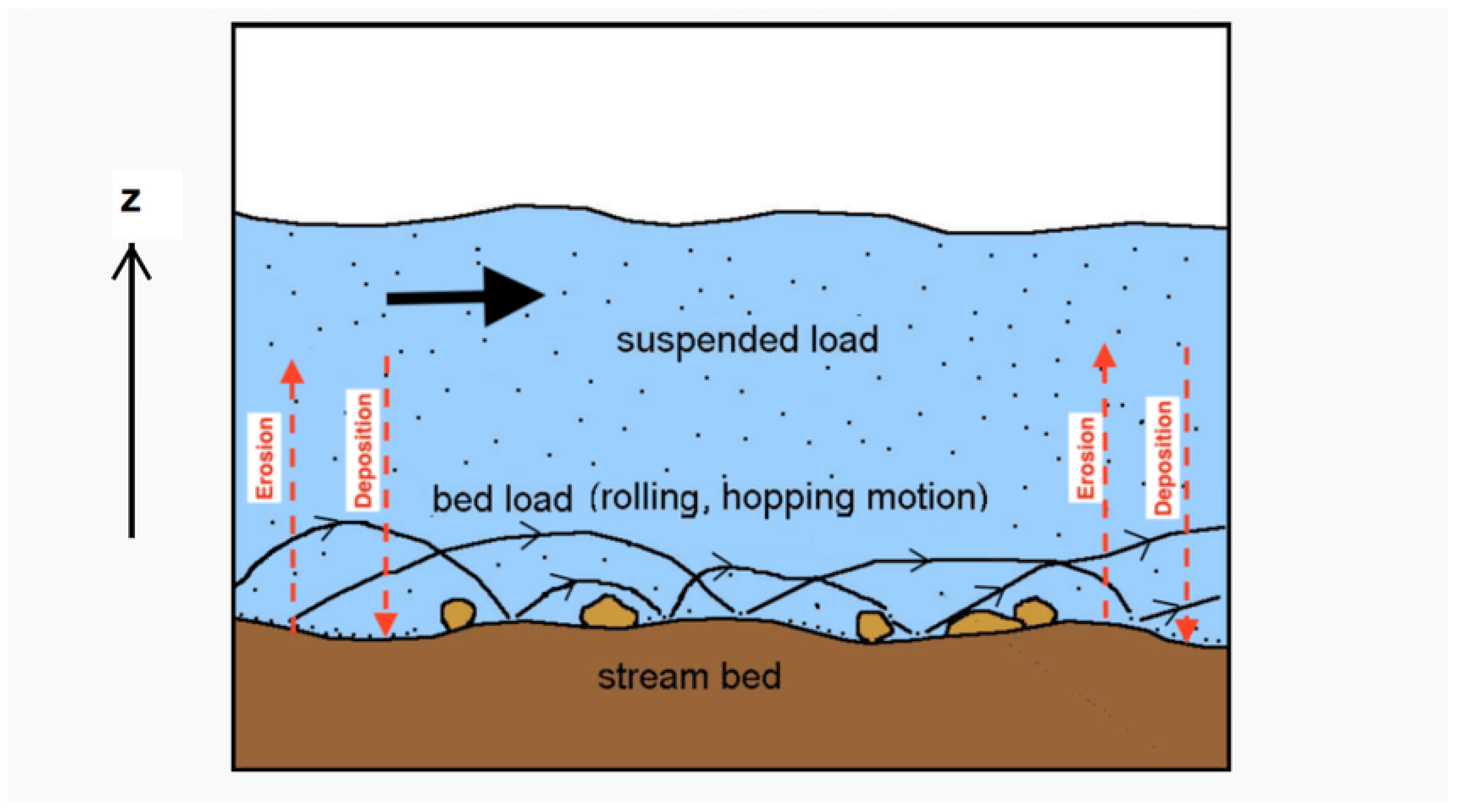
Sediments encompass a mixture of organic and inorganic materials, capable of being transported by various agents such as water, wind, or ice (Langland & Cronin, 2003). Sedimentation, on the other hand, refers to the erosion and conveyance of these materials by moving water or other carriers, leading to their deposition as solid accumulations in bodies of water like rivers and reservoirs (Tundu et al., 2018). Sediment transport involves the movement of both organic and inorganic particles through water bodies (Czuba et al., 2011). Within aquatic environments, sediment can exist either in a suspended state, floating within the water column, or bedded, settled on the water bottom. When both suspended and settled particles are considered, they are collectively referred to as SABS (suspended and bedded sediments). The total sediment load comprises all particles being transported, including those moving as bed load, suspended load, and wash load. Bed load denotes the sediment transported along the waterway bottom through rolling, sliding, or bouncing, while suspended load represents the sediment carried downstream within the water column by the flow of water (Southard, 2006), with wash load representing a subset of the suspended load, consisting of the finest suspended sediments. Mineral sediment primarily originates from erosion and weathering processes, while organic sediments predominantly consist of detritus and decomposing materials like algae (EPA, 2014).
The effects of sedimentation grow more severe and are recognized as reservoirs age, and the frequency and severity of sediment-related problems increase. Sedimentation, while essential to the growth of aquatic ecosystems in terms of nutrient replenishment and the construction of benthic habitats, can be harmful if it is excessive. Excessive reservoir sedimentation can diminish storage capacity by causing silt deposition, poor water quality, algae blooms, altering streams, and burying habitats. If a body of water is constantly subjected to considerable amounts of sediment movement, more sensitive species may leave, while silt-tolerant creatures move in (EPA, 2012). A considerable amount of silt in the reservoir diminishes its effective storage capacity and shortens its service life, affecting most of its operations, including flood control, electricity generation, and shipping (De Miranda and Mauad, 2015; Wang et al., 2018). Sedimentation also leads to the wear of hydraulic machinery and discharge facilities, accelerating the aging damage (Schleiss et al., 2016).
An overview of reservoir sedimentation processes, and models of reservoir and shallow water bodies is provided in this article.
2. Sediment Transport
The movement of sediments within river systems involves a complex interplay of various factors, including interactions between fluid and sediment. Both the dynamics of water flow and the behavior of sediment must be considered (Almousa et al., 2023; Afan et al., 2015). The combined influence of water flow and gravitational force drives the transport of sediment. Larger particles typically roll or bounce along the riverbed, while finer particles are carried in suspension by the flowing water, depending on factors such as sediment size, shape, and density. Sediment transport can occur in different forms: dissolved in the water (dissolved load), suspended in the water column (suspended load), or transported along the riverbed (bed load). The size distributions of sediment particles transported as bed load and suspended load vary, with suspended sediment particles generally being much smaller than bed load particles. Changes in land use, such as conversion from forest to agriculture or logging, can have a significant impact on sediment transport patterns and intensities in river systems by altering the supply of fine sediment (Turcotte and Morse, 2017).
There are numerous sediment transport equations, although some are for total load, some for suspended load, and others for bed load. No formula applies to all flow and sediment circumstances. Different formulae produce different answers, and so the accuracy of results is determined by how well the formula relates to the flow and sediment regime of a river.
In gravel-bed Rivers, bed load accounts for a significant fraction of the overall sediment load. The capacity for suspended sediment load can be determined based on factors such as the riverbed material and flow characteristics. In certain rivers, a portion of suspended sediment, such as clays, may consist of particles so fine that they are kept suspended due to thermal molecular agitation, rather than turbulence. These particles, known as wash load, are carried through the system by the flow of water (Hicklin, 2009). When sediment availability is constrained, the actual sediment loads transported by the stream will be less than the stream’s capacity for sediment transport. Typically, the concentration of suspended sediment is significantly lower than the channel’s capacity for sediment transport (Knighton, 1998). As a result, the supply rate is the most important determinant of suspended sediment concentrations. When the concentration of suspended silt is plotted against discharge, there is significant scatter. Temperature variations affect rivers with significant amounts of fine sediment, a characteristic often observed in many large rivers (Syvitski et al., 2019).
The flow of silt is influenced by the density and viscosity of the river’s fluids. Indicators of suspended sediment include turbidity and TSS. (Almousa et al., 2024) indicated that TSS is a direct indicator of the amount of organic and inorganic solids present in each volume of water. Although TSS and SSC are both measurements of the solid-phase material inside a water column, their results can vary because of different laboratory techniques that were utilized to make them.
Figure 1 above provides a visual representation of the transportation of sediments, illustrating how the water flow carries the suspended load within the water column and how the bed load rolls and hops down the stream bed of the waterway.
3. Process of Reservoir Sedimentation
Engineers prioritize three key physical aspects of reservoir sedimentation: the total volume of sediment trapped, the spatial arrangement of deposited sediment, and the sediment load carried by released flows, which includes the distribution of particle sizes (Mahmood, 1987). The volume of sediment entering a reservoir dictates its rate of capacity loss relative to its size. A small reservoir on a very muddy river will lose capacity quickly, whereas a large reservoir on a clear river may take centuries to lose an appreciable amount of storage. During floods, the amount of silt delivered into a reservoir is at its peak. In other situations, only 5 to 10 days of flood flow can transport half of a river’s yearly sediment load (Mbajiorgu, 2018). Several criteria influence dam sedimentation, and thus the total volume and internal structure of sedimentary formations. The topography of the pre-reservoir flood plain is an essential feature that governs sediment dispersion following dam construction (Venteris and May 2014). Knowledge of pre-reservoir morphology aids in the identification of historical and current sediment accumulation sites, as well as the calculation of sediment thickness and architecture (Viseras et al., 2009; Moorman et al., 2001).
The geometry of a dam reservoir influences sediment transport and distribution. Reservoir sedimentation is primarily governed by hyperpycnal flows (Balacco et al., 2004; Lai and Capond, 2009), but it is also influenced by human-induced changes in water levels (Lopez et al., 2016), wind-driven sediment transformation (Teeter et al., 2001.) and underwater currents and slides (Shotbolt et al., 2005).
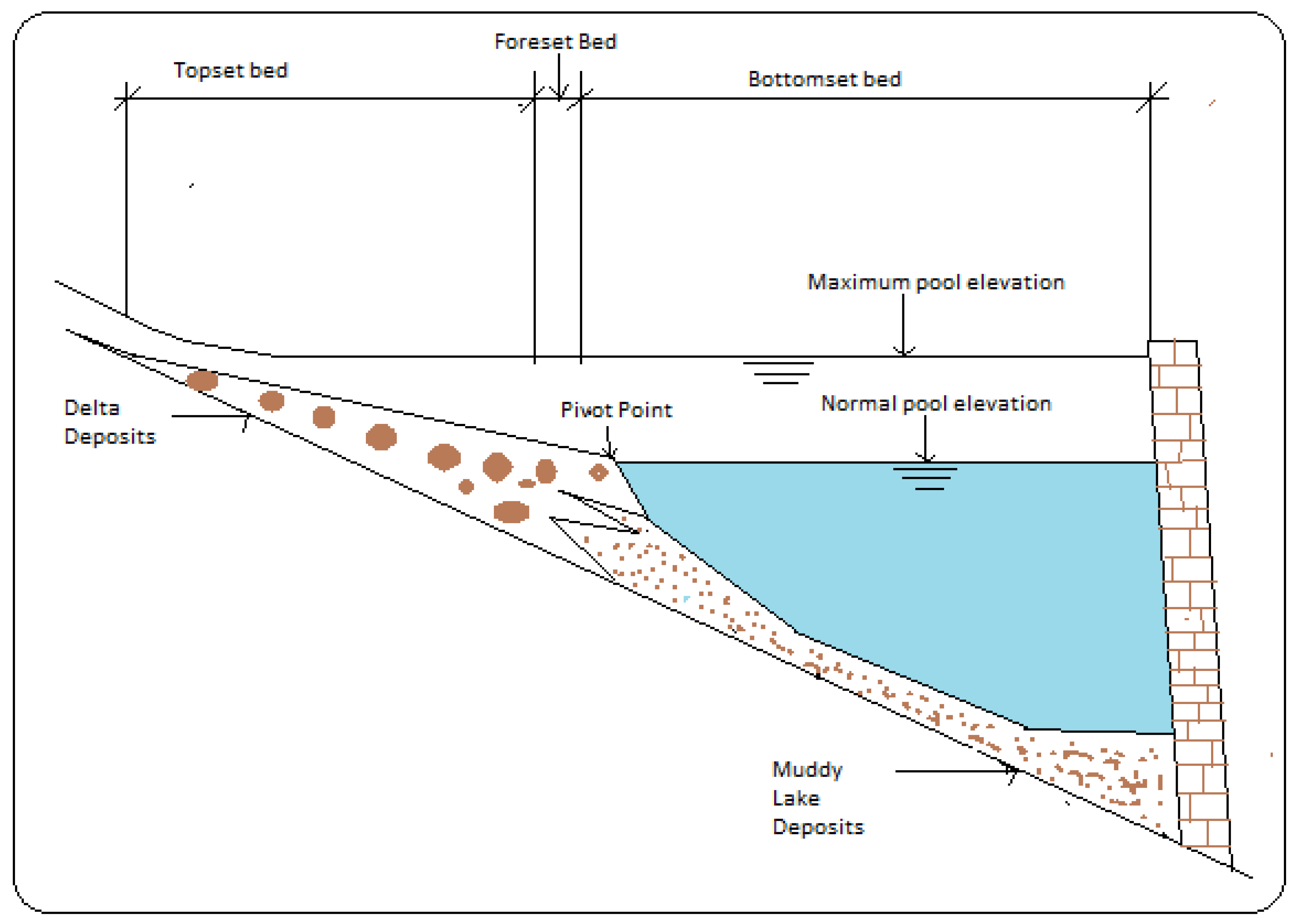
Figure 2.
Illustrates sediment deposit zones in reservoirs, as outlined by Morris and Fan (1998).
Figure 2.
Illustrates sediment deposit zones in reservoirs, as outlined by Morris and Fan (1998).
The diagram provides a simplified depiction of these sedimentation areas
4. Approaches in Sedimentation Studies
4.1. Modeling of Sediment Transport and Deposition in Reservoirs
A model that forecasts future behavior and response to disturbance is necessary to manage any system. All models begin as mental pictures, but they can develop in sophistication over time to incorporate visuals, desktop computations, numerical simulations, and physical scale modeling, depending on the circumstance (Morris and Fan, 1998).The primary sediment modeling challenges examined in reservoirs can be categorized into four main areas:
Estimating water and sediment yield from the watershed.
Analyzing the rate and pattern of sediment transport, deposition, or scour upstream of the dam under various operational conditions.
Investigating localized patterns of deposition and scour near hydraulic structures.
Assessing sediment scour, transport, and deposition downstream of the dam. These sediment yield assessments often involve employing sediment rating curves, erosion modeling, or similar techniques.
The presence of sediments, which are transported by water from the main channel and deposited along the floodplains, can have an impact on even the modeling of a single flooding that occurs at the local level. Sediments alter channel capacity, posing an elevated risk of food contamination and potentially prolonging water retention on floodplains (Nones, 2019).
4.2. Models for Sediment Transportation
To utilize sediment transport models and hydrodynamic models, solving one or more governing differential equations of fluid continuity, momentum, and energy, as well as numerically solving the sediment continuity equation, is necessary (Zang, 2014). These models encompass a wide range of applications, including distinctions between suspended load and bed load, physical and chemical transport, and their formulation across spatial and temporal continua, such as one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D), or three-dimensional (3D) models, as well as steady-state versus unsteady conditions. The selection of a specific model for a given problem hinges on factors such as the problem’s nature and complexity, the model’s accuracy in simulating the problem, data availability for model calibration and verification, as well as time and budget constraints. Numerical sediment transport models enable the simulation of flows in one, two, and three dimensions. These models prove invaluable for scenario assessments and optimizing sediment Best Management Practices (BMPs), as they require extensive simulation techniques. Coupled models have shown promise as a valuable tool for integrated sediment modeling and management planning in such scenarios (Shin et al., 2019). Computational models offer a distinct advantage over physical models in their adaptability to multiple physical domains, a feature particularly useful for representing a variety of site-specific conditions
4.2.1. One Dimensional (1D) Models
Since the early 1980s, one-dimensional (1D) models have been effectively employed in both research and engineering applications. Typically utilizing a rectilinear coordinate system, these models employ finite-difference techniques to solve the differential conservation equations governing mass and momentum of flow (St. Venant flow equations) as well as the sediment mass continuity equation (Exner equation). Primarily used for long-term simulation of extensive river reaches, 1D models often require minimal field data for calibration and testing. Their numerical solutions are particularly suited for narrow reservoirs, prolonged simulations, and diverse analytical approaches due to their stability and lower computational demands (Anari et al., 2020; Garcia, 2008). These models can accurately predict essential channel characteristics such as bulk velocity, water surface elevation, bed-elevation changes, and sediment transport loads (Delaney and Adhikari, 2020; Martínez-Salvador and Conesa-García, 2020). Employed across vast river expanses or reservoirs, 1D mathematical models facilitate sediment transport analysis, effectively replicating significant transport processes within a one-dimensional flow field. These models are commonly utilized to address various sediment-related issues, including sediment pass-through, dam scour, and sediment accumulation in reservoirs (HEC-RAS, 2016; Shin et al., 2019)
4.2.2. Two Dimensional (2D) Models
There has been a movement in computational research toward 2D models since the early 1990s. The majority of the 2D models are now available to the hydraulic engineering community as interface-based software, allowing for simple data input and visualization of results.
2D models give depth-averaged information regarding water depth and bed elevation within rivers, lakes, and estuaries, as well as the amplitude of depth-averaged streamwise and transverse velocity components. Both suspended load and bedload can be individually modeled (Nones, 2019). Most 2-D models use finite difference, finite element, or finite volume methods to solve the depth-averaged continuity and Navier-Stokes equations, as well as the sediment mass balance equation.
4.2.3. Three Dimensional (3D) Models
When two-dimensional (2D) models prove insufficient to capture certain hydrodynamic and sediment transport phenomena, the utilization of three-dimensional (3D) models becomes necessary in hydraulic engineering applications. Instances where 3D flow structures are prevalent, and 2D models fail to accurately represent physics, include flows near piers and hydraulic systems (Bhattacharjee and Akter, 2018).Recent advancements in computing technology, such as increased processing speed, parallel computing capabilities, and improved data storage, have made 3D hydrodynamic and sediment transport models more attractive to use (Chao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2018). The majority of 3D models employ finite difference, finite element, or finite volume methods to solve the continuity, Navier-Stokes, and sediment mass balance equations. These governing equations are typically solved using the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) method (Burkow and Griebel, 2016; Lai and Wu, 2019; Paik et al., 2009).
Table 1.
Summary of selected sediment transport models.
Table 1.
Summary of selected sediment transport models.
| Model Acronym |
Model Name |
Type |
Reference |
HEC-RAS
HEC-HMS
HEC-6 |
HydraulicEngineering Center
HydraulicEngineering Center
HydraulicEngineering Center |
1D
1D
1D |
Thomas and Prashum,(1977)
Sathya et al., (2023)
Joshi et al., (2019) |
S.WAT Model |
Soil & Water Assessment Tool |
Model spanning from small watershed to river basin scale |
MRC, (2010) |
SEDNET |
European Sediment Network |
1D |
Brils, (2020) |
MOBED |
MObile BED;
|
1D |
Krishnappan, (1981) |
| MAST-1D |
|
1D |
Lauer, (2016) |
GSTARS
|
Generalized sediment
transport models for alluvial River
simulation |
1D |
Molinas and Yang, (1986) |
SEDICOUP
|
S.EDIment COUPled |
1D |
Holly &Rahuel, (1990) |
3STD1
|
steep stream sediment
Transport 1D model |
1D |
Papanicolaou et al. (2004) |
OTIS
HEC-RAS |
One--dimensional transport and inflow and storage
Hydraulic Engineering Center |
1D
2D |
Runkel and Broshears, (1991)
Shabani et al. (2021) |
MIKE 21 |
Danish acronym of the word microcomputer |
2D |
Danish Hydraulic Institute, (1993) |
SEDIMORPH
CCHE2D
|
Sediment Morphology
The National Center for Computational Hydroscience and
Engineering |
2D
2D |
Gundlach et al., (2023)
Jia and Wang, (1999) |
FAST2D:
|
Flow Analysis Simulation Tool |
2D |
Minh Duc et al. (1998) |
UNI.BEST-- TC
|
UNI.form BEach
Sediment Transport-Transport Cross-shore; |
2D |
Bosboom et al. (1997) |
USTARS
|
Unsteady Sediment
Transport Models for Alluvial Rivers Simulations |
2D |
Lee et al. (1997) |
| Telemac-2D |
|
2D |
Hervouet, (2007) |
D.elft -2D
|
|
2D |
Walstra et al. (1998) |
CST-3D
SCHISM |
Wave average area morphologic change numerical modeling system
Semi-implicit Cross-Scale |
3D
3D |
Specht et al., (2021)
Yoo et al., (2021) |
ECOMSED |
Estuarine, Coastal, and
Ocean Model-SEDiment transport |
3D |
Blumberg and Mellor, (1987) |
CH.3D-SED |
Computational
Hydraulics 3D-SEDiment;
|
3D |
Spasojevic and Holly, (1994) |
| FAST3D |
Flow Analysis
Simulation Tool
|
3D |
Landsberg et al. (1998) |
| TEL.EMAC; |
|
3D |
Hervouet and Bates _2000 |
SSIIM
|
Sediment Simulation In
Intakes with Multiblock options |
3D |
Olsen, (1994) |
In comparison to physical models, numerical models have several significant advantages, including lower cost, the ability to be easily rerun to simulate a variety of different conditions, the ability to numerically simulate some types of problems that are inappropriate for physical modeling due to the scaling laws involved (e.g., sediment cohesion), portability, and reproducibility.
A physical model is a scaled physical depiction of the prototype system that simulates prototype behavior using fluid and sediment. Water is typically utilized as a fluid, while air models have been employed in rare cases to analyze difficulties such as groyne positions for river training. Natural grains or manufactured materials such as plastics or walnut shells can be used to create model sediment. Physical models are broadly categorized into four types: undistorted fixed-bed model in which both vertical and horizontal scales are equal, distorted fixed-bed model with a larger vertical than horizontal scale, undistorted movable-bed model, and distorted movable-bed model.
4.3. Field Application of Models
4.3.1. Sediment Transport Models
Numerous mathematical models have been developed by researchers to forecast reservoir sedimentation. Many of these models utilize one-dimensional (1D) software tools, such as Hec-Ras (Kim and Shin 2013; Mohammad et al. 2016; Ghimire and DeVantier 2016) and Gstars (Yang et al. 1989; Yang and Simões 2002). Conversely, some models employ two-dimensional (2D) approaches, such as Mike21 (DHI 1993; de Villiers and Basson 2007) and CCHE2D (Zhang 2005; Moussa 2013). While most 1D models are based on the equilibrium concept for sediment entrainment (Papanicolaou et al. 2008), 2D sediment transport models typically consider the logarithmic distribution of sediment across depth rather than assuming uniformity. Moreover, these models address the impact of sediment concentration towards the top of the bed load-layer on the net deposition rate (van Rijn 1987; Wu et al. 2000).
Three-dimensional (3D) models are rarely employed in dam reservoir sediment investigations due to their substantial computational requirements, particularly for long-term sediment studies. To ensure model stability, a minimal computational time step must be selected, and a large number of cells are essential due to the domain’s size and the complexity of various processes involved, including flow dynamics, bed load transport, suspended load concentrations, sediment deposition, and soil erosion (Omer et al., 2015). In numerical models, sediment transport can be simulated using one of two methods: the “Non-Equilibrium Capacity” concept, which considers suspended load and incorporates time lag and adjustment length effects on sediment adaptation with flow, or the “Equilibrium Capacity” concept, which accounts for bed material (Juez et al., 2016; Langendoen et al., 2016). Khorrami and Banihashemi (2020) devised a non-coupled algorithm for long-term simulation of dam reservoir sedimentation in 2D/3D. Over a span of 30 years, the model was utilized to simulate sedimentation in the Zonouz dam reservoir in Iran. The non-coupled algorithm integrates the flow, sediment transport, and bed modules by solving the depth-averaged Navier-Stokes equations for the flow module, the 3D equation of sediment mass conservation for the sediment module, and the Exner equation for bed deformations. This approach reduced simulation time and demonstrated the feasibility of using a 3D sediment model for long-term modeling
The numerical model comprised flow, sediment, and bed modules. Below are the Governing Equations:
2D Shallow water flow equations
where η = h + zb, and Zb is the bed level; η and h are water surface elevation and the water depth, respectively; ρ is fluid density; U and V refer to depth-averaged velocity components in the x and y directions, respectively; g is the gravitational acceleration; ε is the depth-averaged turbulent eddy viscosity; τbx and τby refer to the bed shear stresses in the x and y directions, respectively, which are calculated as follows:
3D sediment transport equationswhere C is the suspended sediment concentration; ws is the fall velocity of the sediment particles; u and v are the local fluid velocities at elevation z. ε
i is the turbulent diffusivity in direction i (where i = x, y, z).
Bed evolution equation (van Rijn 1987)
Bilal et al. (2017) employed a 1D numerical model (HEC-RAS) to conduct a sediment dynamics investigation of the Tenryu River stretch upstream of Sakuma Dam in Japan, aiming to forecast future bathymetric alterations. Their simulations also aimed to anticipate potential changes in the riverbed profile and estimate the point at which Sakuma Dam might no longer fulfill all its intended purposes. The study showcased the feasibility of conducting sediment dynamic analyses even with limited data, albeit such inquiries may only provide qualitative insights into sediment movements.
In another study, Yao Li (2020) devised a series of methodologies for generating high-resolution 3-D bathymetry maps and long-term storage records on a global scale, applicable for diverse purposes including global hydrological modeling and local water resource assessments. The initial research effort involved creating a 3D reservoir bathymetry by integrating elevations obtained from the Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite (ICESat-2) airborne prototype with area data derived from Landsat-based water classifications spanning from 1982 to 2017. Subsequently, the bathymetry generating algorithm was employed to construct a global dataset encompassing 347 reservoirs worldwide using satellite altimetry and imaging observations. In the latter study, a combination of multi-source remote sensing data and an enhanced area-depth-storage database were utilized to estimate monthly storage fluctuations for 7245 reservoirs globally from 1999 to 2018.Olsson et al. (2011) introduced an integrated modeling strategy that merges a basic water budget model (THC-model) with a 3D reservoir sedimentation model (MOHIDWater) to adjust reservoir operations and showcase their impacts on sediment deposition. The results from the modeled scenarios affirm the efficacy of the revised operation rules for THC reservoirs and highlight the potential for altering the operation of significant dams to facilitate integrated sediment-water management.
Governing equation (Sorokin and Ikramova 2005):where,
ΔV Change in water storage volume (m3)
QS Reservoir inflow (m3)
QG Groundwater inflow (m3)
QSO Reservoir release (m3)
QGE Ground-water exchange (m3)
B Run-off of reservoir catchment (m3)
E Evaporation (m3)
P Precipitation (m3)
t Time step
r Modelled reservoir or lake
Faghihirad et al., (2015) created a revised numerical model of a three-dimensional layer-integrated turbulence model and applied it to a scaled physical model of Iran’s Hamidieh Reservoir. The study utilized a numerical model to analyze the flow dynamics and sediment transport mechanisms in an Iranian reservoir featuring a dam, water intakes, and sluice gates, particularly focusing on the vicinity of hydraulic structures. By employing the numerical model, various scenarios were simulated, offering insights into conditions that would pose challenges for physical experimentation.
Governing Equations (Lin and Falconer, 1997):
Qiu and Li (2021) devised a method to calculate the rate of suspended sediment transport within reservoirs, which formed the basis for developing a multi-objective model. This model aimed to optimize both sediment transportation efficiency and power production efficiency simultaneously. The Pareto front of the model was identified employing the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) and principles of Pareto optimality. The study applied this approach to the Three Gorges project in China, revealing not only the Pareto front of the reservoir operation scheme but also indicating a 6% increase in maximum annual sediment runoff at the expense of a 9% reduction in annual power generation.
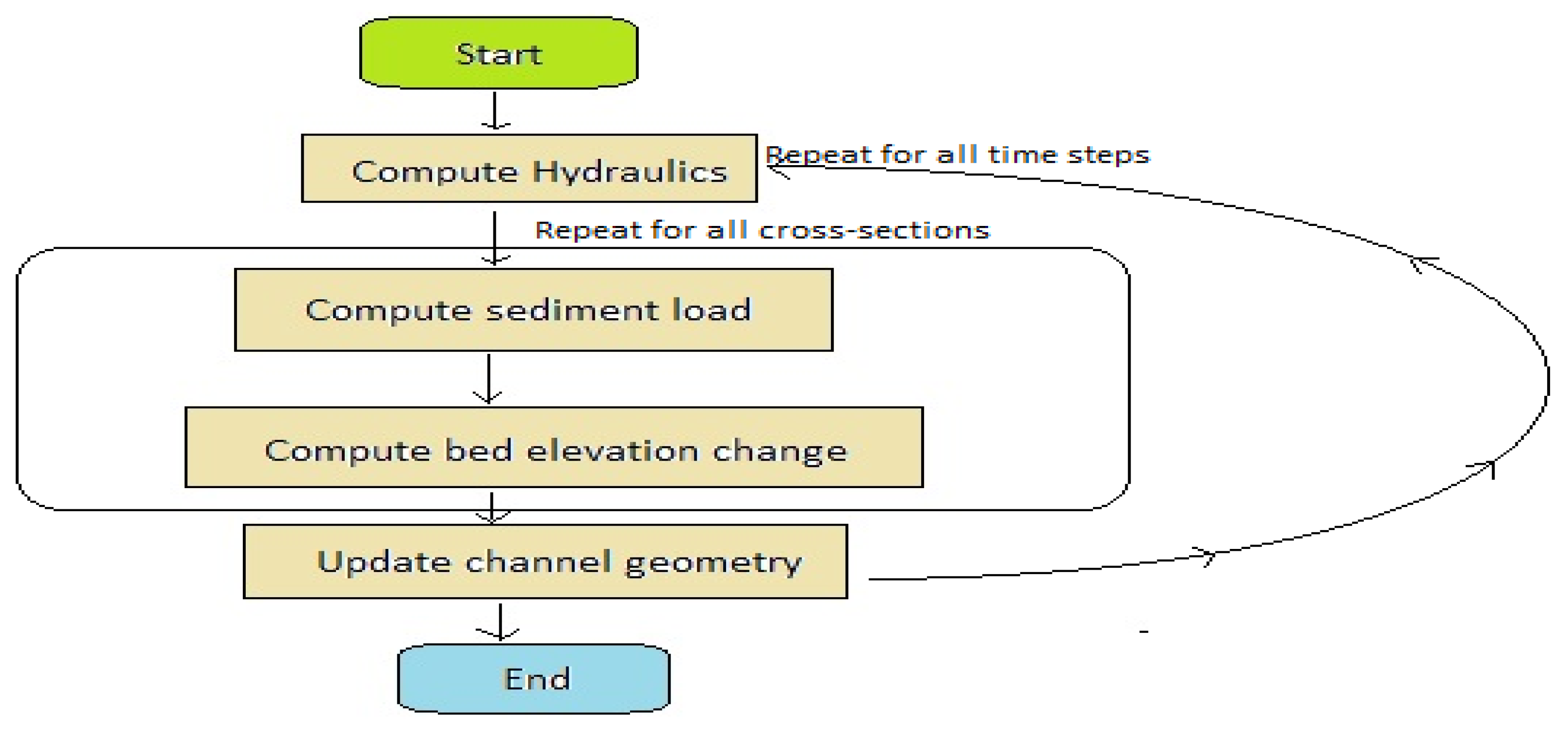
Wang et al. (2020) developed a numerical model in three dimensions (3D) to investigate both the thermodynamic dynamics and sediment processes occurring within a subtropical drinking water reservoir. Data-driven models were established to generate inflow conditions. The modeling results illustrated that climatic factors such as storms and winds significantly influence the stratification and mixing processes within the lake. Storm events drive sediment transport, and amorphous flux dominates sediment delivery to the reservoir.
Figure 3 illustrates the flow-chart used in the development of their 3D Numerical Model.
Zeleke et al. (2013) employed the River Hydraulics and Sedimentation one-dimensional model (SRH-1D), version 2.6, to simulate and forecast the sedimentation pattern in the Angereb Reservoir, Ethiopia, up to the year 2015. The observed trends were effectively replicated, demonstrating satisfactory alignment between measurements and model predictions. However, the model tended to overestimate sediment deposition volumes in certain upstream areas of the reservoir, except for one instance.
Governing equations (U.S. Department of Interior User’s Manual SRH-1D, 2010):
In their study, Bai et al. (2019) employed a multi-objective model alongside two single-objective models to optimize water-sediment regulation in the Longyangxia and Liujiaxia cascade reservoirs. They introduced a novel approach, FSS-MOPSO, which combines the Feasible Search Space (FSS) with the Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) algorithm to seek optimal solutions for the joint operation of cascade reservoirs. By investigating various optimization strategies for five objectives—hydropower generation, sediment transport, water supply, flood control, and ice control—the study uncovered a significant trade-off between hydropower generation and sediment transport objectives. Bronstert et al. (2014) developed a modeling framework to quantify water and sediment fluxes in catchments, river systems, and reservoirs. Their system included hydrological components adapted to dryland characteristics, hill slope erosion, sediment transport, and reservoir deposition processes. They employed a hierarchical spatial discretization using a multi-scale concept to account for specific process scales, improving understanding of hydro-sedimentological systems characterized by flashy runoff generation and erosion pulses.
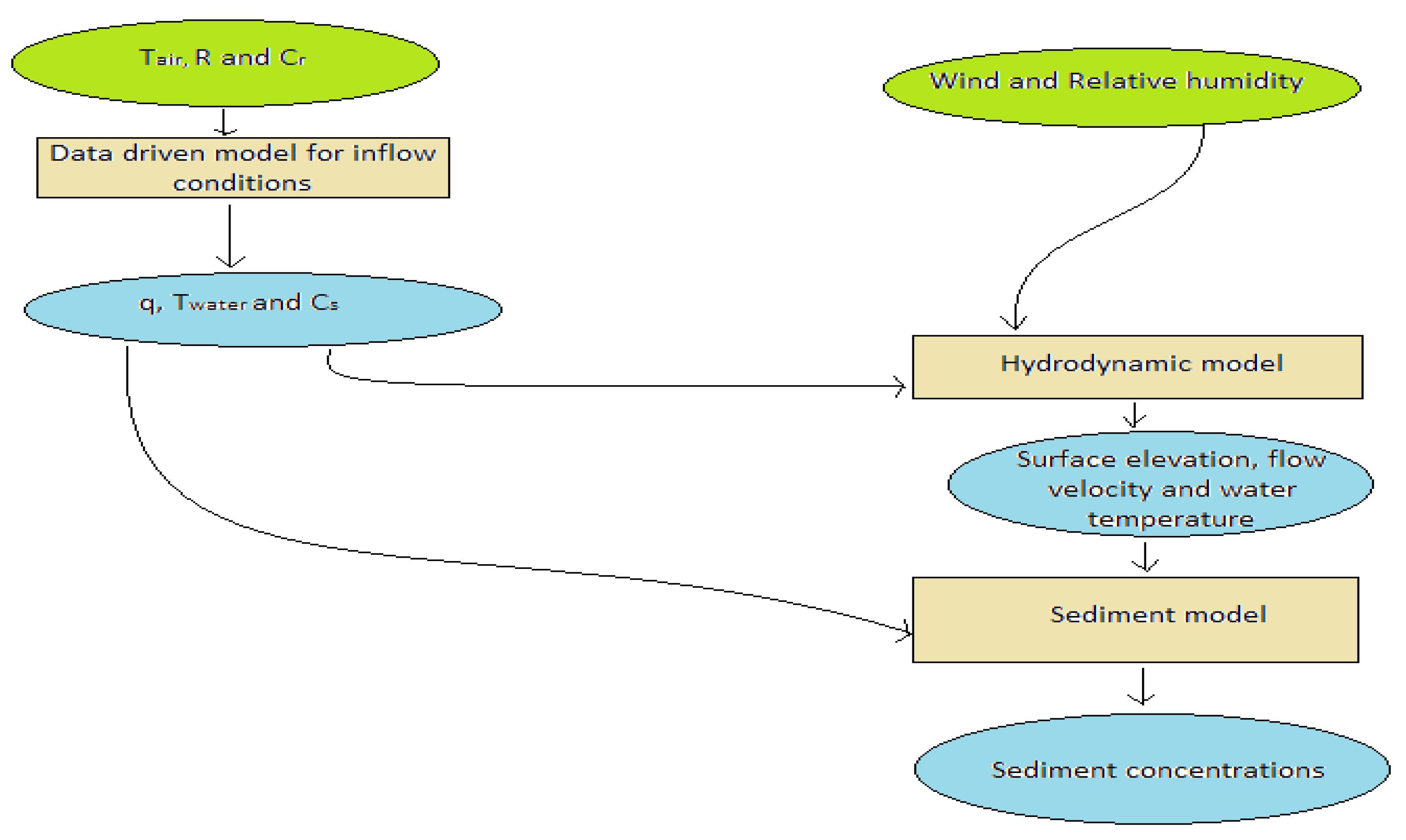
Ahn and Yen (2015) developed numerical modeling approaches for long-term reservoir sedimentation using the Generalized Stream Tube computer models for Alluvial River Simulation version 3.0 (GSTARS3). They demonstrated that semi-two-dimensional modeling incorporating non-equilibrium sediment transport equations and the theory of minimum stream power could predict reservoir sedimentation over time.
Figure 4.
Flow Chart of Conventional One-Dimensional Sediment Transport Model (Ahn and Yen, 2015).
Figure 4.
Flow Chart of Conventional One-Dimensional Sediment Transport Model (Ahn and Yen, 2015).
In their study, Sukhinov et al. (2014) utilized a non-stationary spatial two-dimensional model to examine sediment transport in water reservoir coastal zones. They considered various physical parameters and processes, including soil porosity, critical shear stress for sediment movement, turbulent exchange, changing bottom elevation levels, and factors like wind currents and bottom friction. The study also incorporated a hydrodynamic spatial two-dimensional model to analyze sediment transport in reservoir coastal zones.
On the other hand, Li et al. (2019) investigated waves and sediment transport resulting from landslides impacting reservoirs using a two-dimensional coupled double-layer averaged shallow water hydro-sediment-morphodynamic model. Unlike previous models, this model represents a significant advancement by fully addressing sediment transport. It was validated against laboratory studies of landslide-induced waves and compared favorably. The model’s ability to simulate sediment transport in terms of concentration and bed deformation was also demonstrated. The findings suggest that sediment transport speed influences wave characteristics and landslide-to-wave momentum transfer, affecting landslide efficiency, defined as the ratio of horizontal runout distance to vertical fall height.
Tarar et al. (2019) utilized sediment rating curves (SRC) alongside wavelet artificial neural networks (WA-ANNs) to establish sediment load boundary conditions for the HEC-RAS 1D numerical model, This initiative was directed towards replicating sediment transportation dynamics within Tarbela Reservoir. The model underwent morphodynamic calibration by incorporating more precisely reconstructed sediment load boundary conditions in HEC-RAS, resulting in significant enhancements, with R2 = 0.980 and NSE = 0.979. Given that the WA-ANN-based sediment load boundary conditions effectively captured the intricacies of sediment transport, this modeling approach presents a promising avenue for exploring variations in bed levels across reservoirs and rivers globally. I mean try to paraphrase this inside the text.
4.3.2. Bathymetric Surveys
Bathymetric surveying is a direct approach for assessing sedimentation distribution and bed profile in dam reservoirs. The bathymetric survey is a significant method for gaining an understanding of sediment storage in reservoirs. The fieldwork needs a relatively short time investment and does not entail continuous monitoring and/or maintenance of sediment yield/runoff equipment.
Bathymetric data for three reservoirs along the lower Susquehanna River were acquired using HYPACK software, incorporating a 210 kHz echo sounder, single beam transducer, and DGPS unit. This technological setup facilitated an estimation of the remaining sediment-storage capacity (Langland, 2015). Earlier studies indicated that the upper two reservoirs had reached a state of equilibrium concerning long-term sediment storage, while the downstream reservoir retained the capacity for sediment trapping. Depth data were systematically recorded through transects within HYPACK at predefined intervals for each reservoir and overlaid on geo-referenced aerial photographs. To ensure data accuracy, post-processing of raw data sets was conducted to eliminate any erroneous spikes identified from analog data recorded on thermal paper. Notably, diagonal transects were employed to validate depth observations. The analysis revealed a total deposition of approximately 14,700,000 tons of silt across the three reservoirs between 1996 and 2008, with the majority, around 12,000,000 tons, accumulated in Conowingo Reservoir.
USGS in partnership with the city of Santa Cruz, assessed Loch Lomond Reservoir to evaluate its current storage capacity and sedimentation rates (Whealdon-Haught et al., 2019). This assessment integrated various survey techniques, including sonar soundings for bathymetric analysis, lidar scans with GPS data for near-shore topography assessment, and sediment bed sampling to analyze reservoir bed-material size. The collected data facilitated the creation of a bare-earth digital elevation model (DEM) with a resolution of 1 square meter or better up to the spillway elevation, enabling accurate estimation of storage capacity.
In another collaboration with the San Francisco Public Utilities Commission (SFPUC), the US Geological Survey conducted a similar evaluation of San Antonio Reservoir in 2018 to assess its storage capacity and sedimentation characteristics (Marineau et al., 2018). The bathymetric survey employed depth soundings obtained through a multi-beam echo sounder mounted on a boat. Findings from the reservoir capacity study revealed a storage capacity of 53,266 (plus or minus 140) acre-ft, representing a 2,766 acre-ft (or 5.5 percent) increase from the original 1965 estimate, attributed to enhanced survey methodologies.
For Morse and Geist Reservoirs, bathymetric data were collected using a high-resolution multibeam echosounder, supplemented by acoustic Doppler current profiler data for shallow areas (Boldt and Martin, 2020). These surveys aimed to update bathymetric maps, determine storage capacities at specified water-surface elevations, and compare current conditions with historical surveys.
Iradukunda and Bwambale (2021) conducted a study on the Murera reservoir dam, focusing on assessing reservoir sedimentation and its impact on storage loss. They utilized the Bathymetric Survey System (BSS), which employed a navigation twin boat system equipped with a built-in Global Positioning System (GPS). By employing a multi-frequency acoustic system, they determined the reservoir bed level, identified sediment layers, and evaluated deposited sediments relative to pre-impoundment levels. Data processing and analysis were conducted using Depthpic 5.0.2, Surfer 15.5, and ArcGIS 10.3 applications. The findings revealed a depth increase from north to south within the reservoir, with the southern half exhibiting more sediment deposition.
Additionally, in collaboration with the City of Santa Cruz, the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) conducted a bathymetric and topographic survey to assess water storage capacity and quantify capacity loss due to sedimentation. Utilizing bathymetric scanning with multibeam-sidescan sonar and topographic surveying with laser scanning (LiDAR), the USGS determined the reservoir’s maximum storage capacity as of March 2009 to be 8,646.85 acre-ft at the spillway altitude of 577.5 ft, with a 99 percent confidence level.
Foxgrover et. al., (2014) reported that bathymetry surveys were conducted on Coyote Creek and Alviso Slough, South San Francisco Bay, California using the state-of-the-art research vessel R/V Parke Snavely outfitted with an interferometric side scan sonar for swath mapping in extremely shallow water. We provide high-resolution bathymetric data collected by the USGS. For the 2010 baseline survey we have merged the bathymetry with aerial lidar data that were collected for the USGS during the same time period to create a seamless, high-resolution digital elevation model (DEM) of the study area. The series of bathymetry datasets are provided at 1 m resolution and the 2010 bathymetric/topographic DEM at 2 m resolution. The data are formatted as both X, Y, and Z text files and ESRI Arc ASCII files that are accompanied by FGDC-compliant metadata.
The US Geological Study conducted a bathymetric study of the lower Sixmile Creek reservoir in Tompkins County, New York, in collaboration with the City of Ithaca, New York, and the New York State Department of State, in November 2015. The reservoir’s useful storage capacity was evaluated using the data gathered (Wernly et al., 2016). This assessment could assist municipal management in making decisions about the disposition of the reservoir’s 30-foot (ft) dam and the reservoir’s potential usage as a flood control structure. The US Geological Survey used an acoustic Doppler current profiler to acquire bathymetric data. Depths were manually measured in areas where aquatic vegetation interfered with the acoustic Doppler current profiler signal. The reservoir’s maximum depth of 16.6 feet was determined 130 feet upstream from the dam. A lot shallower than the original 30-ft depth, the depths closest to the dam were just about 13.5 feet.
Bathymetric data for Loch Raven and Prettyboy reservoirs were acquired during the fall of 1998 and early summer of 1998, respectively. This data collection involved the use of a differential global positioning system (DGPS) and digital echo-sounding technology. More than 32,000 individual soundings were compiled to develop the present bathymetric model of L-och-Raven Reservoir (Ortt et al., 2000).A bathymetry model of Prettyboy Reservoir was created using over 48,000 discrete soundings gathered. The bathymetric models reveal that Loch Raven and Prettyboy reservoirs presently possess storage capacities of 19.1 billion gallons equivalent to 72.3 MCM and 18.4 billion gallons equivalent to 69.7 Mcm, respectively.
4.3.3. Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System (GIS)
Liu et al., (2020) carried out a remote sensing-based modeling of the bathymetry and water storage for channel-type reservoirs worldwide. The study proposed a novel approach for determining the bathymetry and water storage of channel-type Reservoirs, referred to as ADBAR, for which only an open-access digital elevation model (DEM) and satellite images are required.
Al-Mamari et al., (2023) applied the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) along with remote sensing information to estimate the annual soil erosion within the upstream catchment area of a reservoir. They conducted UAV surveys combined with photogrammetry analysis to assess the sediment buildup in the Assarin Dam reservoir in Oman, aiming to measure siltation levels. Data from seven previous sediment trapping events were collected to investigate the relationship between soil erosion at the catchment scale and sediment deposition volumes in the reservoir. By considering factors such as rainfall erosivity, soil erodibility, topography, land cover management, and conservation practices, the RUSLE method was utilized to estimate soil erosion rates. The study utilized remote sensing data and GIS platforms to analyze the quantitative and spatial distribution patterns of the RUSLE parameters.
4.3.4. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) in Sediment Modeling
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are data processing and modeling tools that are frequently used in estimation, forecasting, pattern recognition, optimization, and the establishment of links between intricately detailed variablesHaykin and Lippmann (1994) discuss an artificial neural network (ANN), which is characterized as a highly parallelized and distributed information processing system as having some performance traits in common with biological neural networks found in the human brain.
Many tasks in hydrology, hydraulics, and water resources management have effectively used ANN models, including forecasting floods, groundwater levels, and rainfall-runoff ( Noori and Kalin, 2016; Yaseen et al., 2016).
The utilization of artificial neural networks (ANN) has expanded to include the estimation of suspended sediment, leading to numerous studies focusing on sediment transport. Several investigations have applied ANN in this context (Afan et al., 2015; Jain, 2001; Mustafa et al., 2012; Rai and Mathur, 2008; Singh et al., 2013; Van Maanen et al., 2010). Generally, these AI models exhibit satisfactory performance, accurately predicting suspended discharge concentrations with an accuracy of up to 90% (Afan et al., 2015).
5.0. Strategies for Reservoir Sedimentation Management
The reduction in reservoir capacity poses an immediate challenge to ensuring sustainable water for agricultural sectors and urban needs. Additionally, it disrupts other essential functions such as flood control, hydropower generation, navigation, and fisheries (Annandale et al., 2015). Reservoir function cannot be maintained in the absence of a sediment control plan. Sustainable sediment management strives for a balance of sediment intake and outflow, restoring sediment delivery to the downstream channel, optimizing long-term storage, hydropower, and other advantages, and avoiding environmental impact.
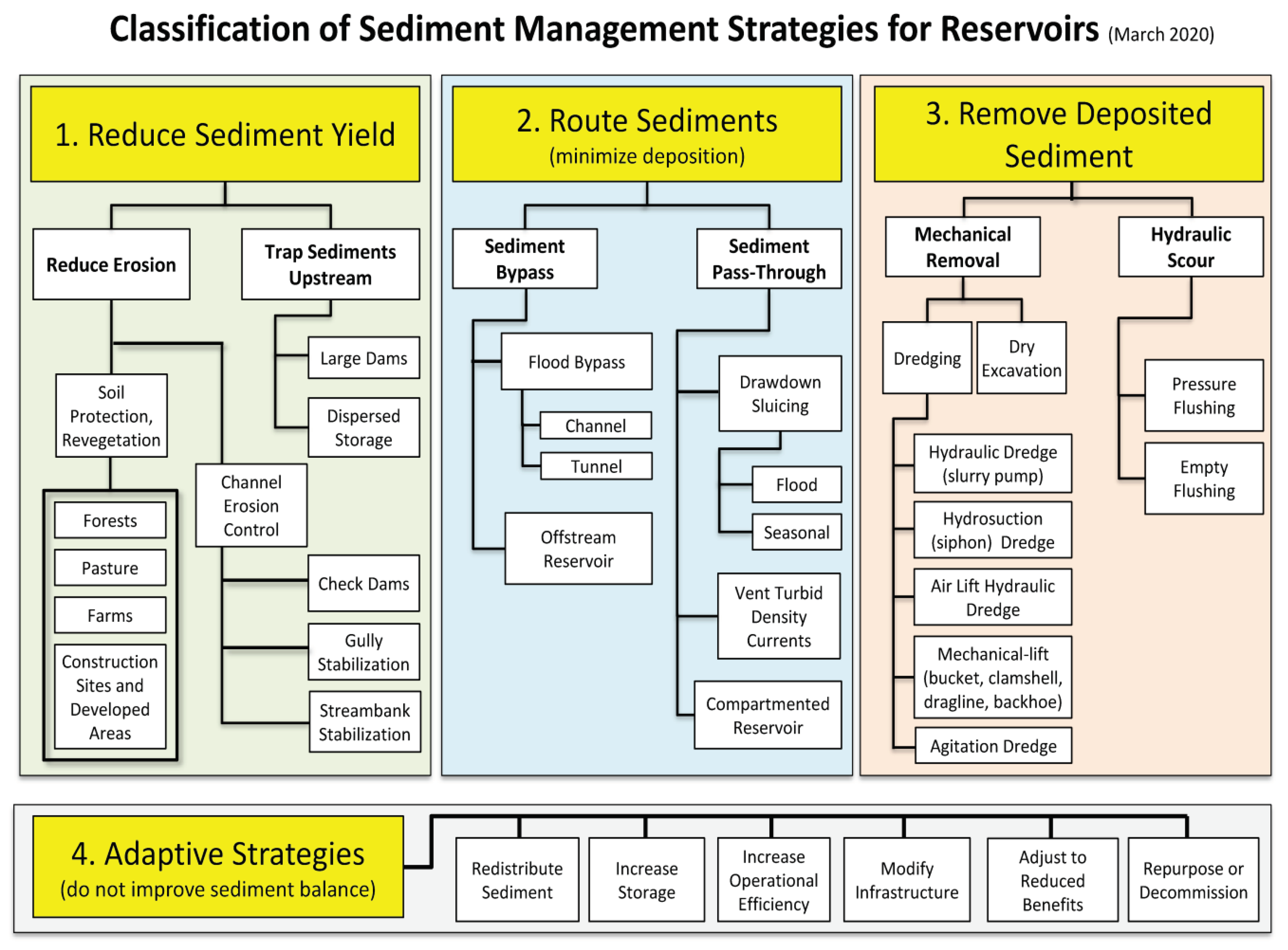
Management strategies can be divided into four types. Three classifications prioritize enhancing sediment equilibrium throughout reservoirs by diminishing sediment yield from the watershed, diverting sediment-laden flows around or through the storage pool, and extracting sediment post-deposition. The fourth group comprises adaptive tactics that react to capacity depletion but do not tackle the sediment equilibrium (Morris, 2014).
Combinations of methods may be used to effectively manage sedimentation, and these strategies may evolve as sedimentation progresses.
Figure 5 displays the classification of reservoir sedimentation management systems and their consequences.
There exist numerous approaches to enhance the equilibrium of sediment in reservoirs and adapt to the consequences of sediment intrusion and storage loss. Typically, a variety of methods are deployed at each specific reservoir. Adaptive strategies are particularly crucial as restoring and maintaining original reservoir capacities is seldom feasible. Different tactics may be implemented sequentially over time or simultaneously. They can also be employed in interconnected reservoirs along a river. Interventions may be phased as sedimentation progresses and more aggressive methods become necessary. While techniques like sluicing, flushing, and dredging are often more applicable as sedimentation reduces reservoir volume, alternative solutions such as turbidity current venting may be more appropriate in newly formed storage reservoirs.
When formulating sustainable sediment management blueprints for reservoirs, it’s crucial to incorporate both short-term and enduring strategies. The initial step in executing sediment management initiatives involves pinpointing and ranking locations with notable issues and considerable impacts. Application across further reservoirs will be made easier based on the knowledge gathered from the initial implementation sites, which will unavoidably be needed. Whatever technique is adopted, sediment control in reservoirs is an intricate and costly operation. There is no perfect sustainable answer for every circumstance, but efforts can be tailored to the specifics of each reservoir. Methods for preventing sediment deposition, including as sediment bypass structures, sluicing, and density current venting, can be most effective in areas where heavy sediment loads occur frequently and predictably. Methods for removing sediment deposits, like as flushing or dredging, are frequently used to reclaim lost storage as a result of non-sustainable reservoir design.
6.0. Challenges and Prospects
Sediment movement is an ongoing, dynamic process influenced by air or water movements within the Earth. The utilization of sediment transport modeling has become widespread in addressing various environmental and engineering challenges, driven by advancements in computational capabilities. Despite significant progress in numerical modeling of waves and currents, our comprehension of sediment transport mechanisms remains incomplete (Zhang, 2014). The intricate nature of sediment particle mobility, affected by diverse environmental factors and processes across different temporal and spatial scales, complicates the alignment of theoretical predictions with real-world observations. Currently, there is no mathematical formula capable of accurately predicting the movement of numerous sediment particles in natural environments. Existing formulas are largely empirical and are applicable only within specific environmental contexts.
The genetic diversity of sediment particles presents a notable challenge to the precise modeling of sediment transport in marine environments. Their varied physical and biological characteristics produce a range of dynamic responses to surrounding water dynamics. For instance, the sand and gravel grains that make up granular, non-cohesive material often travel as separate particles, perhaps interacting directly through collisions that transfer momentum and energy (Zhang, 2014). Due to the presence of a cohesive force, fine sediment particles with a diameter of less than 0.063 mm exhibit significantly diverse behavior. Rarely do they exist as solitary particles; instead, they frequently group to form considerably larger formations, some of which may have tens of thousands of particles. According to several factors (such as turbulence strength, particle concentration, ion concentration, temperature, and organic matter) in the surrounding water, these flocculated structures may further attract more fine particles or disintegrate into smaller ones during the transport process. These dynamics still require more research.
The random nature of sediment particle movement in fluids is another important barrier. The randomness of particle movements is mostly caused by turbulence, which is still one of the hardest problems in fluid dynamics. The fundamental vagueness of the method used to gather particles from the seafloor is a substantial additional source of uncertainty. It is generally agreed upon that sediment particles only start to move when the driving forces—applied by ambient water motion outweigh the stabilizing forces. The mathematical formulation of the pickup threshold is still unknown, although the physics of this event are well understood.
There has been a growth in the amount of data accessible on coastal systems over the years, ranging from bathymetric and topographic data to sediment transport and physical forcing data (Garel and Ferreira, 2015; Bolanos and Souza, 2010). The generation of vast spatial and temporal extent, high resolution, and swift turnaround from acquisition to availability indicate that coastal morphodynamic research will be expanded.
A renewed focus is being placed on research driven by data. This approach holds promise as a research strategy (Hey et al., 2009). Coastal researchers now have access to techniques from the field of computer science, specifically machine learning (ML), to derive inductive statements and optimized predictions directly from datasets, owing to advancements in computational capacity and the increasing volume of data. Unlike statistical learning, machine learning does not make assumptions or hypotheses about the nature of relationships within the data; instead, it autonomously searches for rules and relationships. Moreover, machine learning does not impose restrictive assumptions on the data. The absence of data restrictions and assumptions is cited as a key reason why machine learning predictors often outperform statistical learning methods.
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is one of the machine learning techniques used in coastal sediment transport and morphodynamics. (Olden et al. 2004; LeCun et al. 2015). Others include Regression Trees (RT) by De’ath and Fabricus, (2000); Hastie et al. (2009), and General Algorithms (GA) by Holland, (1975)
ML offers more practical, ideal sediment transport equations to address the need to produce a predictor that is either more generally valid or more specifically valid. ML methods frequently outperform the established method by utilizing the error measure. Furthermore, greater study in the burgeoning domains of RS and GIS is recommended for ongoing studies on reservoir sedimentation caused by climate change impacts.
7.0. Conclusion
Accumulation of sediment presents a significant peril to river ecosystems globally. All rivers transport both silt and water; dam construction affects both, though with considerable differences. This is because rivers convey far more water than sediment, filling a reservoir with sediment takes much longer than with water, so much longer that the gradual accumulation of silt is often overlooked. One of the key concerns affecting reservoir storage capacity is reservoir sedimentation. Furthermore, sediment-related issues tend to have a variety of negative hydrological, morphological, and environmental repercussions in both upstream and downstream portions of river systems where such interventions are installed.
The detrimental impacts of the sedimentation and erosion processes in controlled rivers and reservoirs include a reduction in storage space in reservoirs due to silt deposits, an increase in flood levels upstream, erosion and bank shifting in downstream areas, bed incision, and coastal erosion as a result of a lack of sediment supply, negative effects on agricultural activities in downstream areas as a result of a lack of fertile silt supply, and more. Random desiltation with high turbidity, on the other hand, may have an impact on water quality and the aquatic ecosystem in the downstream area.
In general, models rooted in physical principles tend to yield results that are more visually intuitive compared to alternative approaches. Additionally, these physically-based models are often utilized to capture intricate flow dynamics and sediment transport patterns around complex structures (Morris and Fan, 1997). However, physical models are subject to the unavoidable scale effect. Conversely, numerically-based models solve governing equations such as those governing mass, momentum, and energy conservation. One significant advantage of numerical models is their versatility, allowing them to be applied to various scenarios more readily than physically-based models, which are typically tailored to specific site conditions (Papanicolaou et al., 2008). Numerically-based models are particularly well-suited for predicting long-term reservoir capacity reduction resulting from sedimentation, as they can simulate changes over decades along the reservoir’s reach. The expanding frontiers of reservoir sediment modeling research are further propelled by advancements in remote sensing, geographic information systems, and artificial intelligence.
Statements and Declarations
The author declares that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Competing Interest
The author has no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
References
- Afan, H.A.; El-Shafie, A.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Hameed, M.M.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Hussain, A. ANN-Based Sediment Prediction Model Utilizing Different Input Scenarios. Water Resour Manag. 2015, 29, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yen, H. Semi-two dimensional numerical prediction of non-equilibrium sediment transport in reservoir using stream tubes and theory of minimum stream power. KSCE J Civ Eng 2015, 19, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajao, A. and Lim, Y.H.; 2023. Sustainable Management of Dams and Reservoirs in North Dakota: Sediment Transport Characterization.
- Almousa, M.; Olusegun, T.; Lim, Y.; Al-Zboon, K.; Khraisat, I.; Alshami, A.; Ammary, B. 2024. Chemical recovery of magnesium from the Dead Sea and its use in wastewater treatment. Journal of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene for Development, p. washdev2024267.
- Almousa, M.; Tomomewo, O.S. and Lim, Y.H.; 2023. Salts Removal as an Effective and Economical Method of Bakken Formation Treatment.
- Almousa, M.; Olusegun, T.S.; Lim, Y.H.; Khraisat, I. and Ajao, A.; 2023, October. Groundwater Management Strategies for Handling Produced Water Generated Prior Injection Operations in the Bakken Oilfield. In ARMA/DGS/SEG International Geomechanics Symposium (pp. ARMA-IGS). ARMA.
- Al-Mamari, M.M.; Kantoush, S.A.; Al-Harrasi, T.M.; Al-Maktoumi, A.; Abdrabo, K.I.; Saber, M.; Sumi, T. Assessment of sediment yield and deposition in a dry reservoir using field observations, RUSLE and remote sensing: Wadi Assarin, Oman. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anari, R.; Hotchkiss, R.H.; Langendoen, E. Elements for the Successful Computer Simulation of Sediment Management Strategies for Reservoirs. Water 2020, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Karki, P. n.d. Extending the Life of Reservoirs.
- Bai, T.; Wei, J.; Chang, F.J.; Yang, W.; Huang, Q. Optimize multi-objective transformation rules of water-sediment regulation for cascade reservoirs in the Upper Yellow River of China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 123987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balacco, G.; Castorani, A.; Di Santo, A. (2004). Role of turbidity currents in the siltation process of an artificial lake. In: Hu, C.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, X.; Liu, C. (Eds.), Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on River Sedimentation. Tsinghua University Press, Yichang, pp. 987–996.
- Batalla, R.J.; Gómez, C.M.; Kondolf, G.M. Reservoir-induced hydrological changes in the Ebro River basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, L.; Akter, A. 2018. A REVIEW ON SEDIMENT TRANSPORT MODELS OF TIDAL RIVERS.
- Bilal, A.; Dai, W.; Larson, M.; Beebo, Q.N.; Xie, Q. Qualitative simulation of bathymetric changes due to reservoir sedimentation: A Japanese case study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolanos, R.; and Souza, A. (2010). Measuring hydrodynamics and sediment transport processes in the Dee Estuary, Earth Syst. Sci, Data,2, 157-165. [CrossRef]
- Boldt, J. A.; and Martin, Z. W. (2020) Bathymetric surveys of Morse and Geist Reservoirs in central Indiana made with a multibeam echosounder, 2016, and comparison with previous surveys: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2020–5067, 39 p. [CrossRef]
- Bosboom, J.; Aarninkhof, S. G.; Reniers, J. M.; Roelvink, J. A.; and Walstra, D. J. (1997). “UNIBEST TC-2.0 model: Overview of formulations.”Rep. H2305-42, Delft Hydraulics, The Netherlands.
- Brils, J. Including sediment in European River Basin Management Plans: twenty years of work by SedNet. Journal of Soils and Sediments 2020, 20, 4229–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstert, A.; De Araújo, J.-C.; Batalla, R.J.; Costa, A.C.; Delgado, J.M.; Francke, T.; Foerster, S.; Guentner, A.; López-Tarazón, J.A.; Mamede, G.L.; Medeiros, P.H.; Mueller, E.; Vericat, D. Process-based modelling of erosion, sediment transport and reservoir siltation in mesoscale semi-arid catchments. J Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 2001–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkow, M.; Griebel, M. A full three dimensional numerical simulation of the sediment transport and the scouring at a rectangular obstacle. Comput. Fluids 2016, 125, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-J.; Chen, P.-A.; Lu, Y.-R.; Huang, E.; Chang, K.-Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Hossain, A.K.M.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Jia, Y.; Cizdziel, J.V. Three-Dimensional Numerical Modeling of Flow Hydrodynamics and Cohesive Sediment Transport in Enid Lake, Mississippi. Geosciences 2022, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI) (1993). MIKE 21. Coastal hydraulics and oceanography, Hydrodynamic module. release 2.7. User guide and reference manual. Hoersholm, Denmark.
- De’Ath, G. and Fabricuis, K. E.; (2000). Classification and regression trees: a powerful yet simple technique for ecological data analysis. Ecology 81(11), 3178–3192.
- De Miranda, R.B.; Mauad, F.F. Influence of Sedimentation on Hydroelectric Power Generation: Case Study of a Brazilian Reservoir. J. Energy Eng. 2015, 141, 04014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, J.W.L.; and Basson, G. R. (2007) Modeling of long-term sedimentation at Welbedacht Reservoir. J South Africa 49:10–18.
- Delaney, I.; Adhikari, S. Increased Subglacial Sediment Discharge in a Warming Climate: Consideration of Ice Dynamics, Glacial Erosion, and Fluvial Sediment Transport. Geophysical Research Letters 2020, 47, e2019GL085672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihirad, S.; Lin, B.; Falconer, R. Application of a 3D Layer Integrated Numerical Model of Flow and Sediment Transport Processes to a Reservoir. Water 2015, 7, 5239–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxgrover, A.C.; Finlayson, D.P.; Jaffe, B.E.; and Fregoso, T.A. (2014). Bathymetry and Digital Elevation Models of Coyote Creek and Alviso Slough, South San Francisco Bay, California (ver. 2, March, 2014): U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2011-1315, 20 p. 10.3133/ofr20111315. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M. (Ed.) , 2008. Sedimentation Engineering: Processes, Measurements, Modeling, and Practice, 110th ed. American Society of Civil Engineers, Reston, VA. [CrossRef]
- Garel, E.; and Ferreira, O. Multiyear high frequency physical and environmental observations at the Guardian estuary. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2015, 7, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, G.R. and DeVantier, B.A.; 2016. Sediment modeling to develop a deposition prediction model at the olmsted locks and dam area. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2016 (pp. 410-420).
- Guo, Q.-C.; Jin, Y.-C. Modeling Nonuniform Suspended Sediment Transport in Alluvial Rivers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T Tibshirani, R.; and Friedmann, J. (2000). The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference and prediction. (springer series in statistics).
- Haykin, S.; and Lippmann, R. (1994). Neural networks, a comprehensive foundation. Int. J. Neural Sysyt 1994, 5, 363–364. [Google Scholar]
- HEC-RAS Hydraulic Reference Manual.pdf, (2015).
- Hey, T.; Tansley, S.; and Tolle, K. M. (2009). The fourth paradigm: data-intensive-scientific discovery. Microsoft research, Redmond, W.A.
- Hicklin, E.J. Chapter 4: Sediment transport. In Rivers. Course Notes for an Undergraduate Course in Fluvial Geomorphology; Department of Geography, Simon Fraser University: Burnaby, BC, Canada, 2009; Available online: http://www.sfu.ca/~{}hickin/RIVERS/Rivers4%28Sediment%20transport%29.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2021). [Google Scholar]
- Holland, J. H. (1975). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. An introductory analysis with application to biology, control, and artificial intelligence. Ann Arbor; MI university of Michigan Press.
- Holly, F. M.; and Rahuel, J. L. (1990). “New numerical/physical framework for mobile-bed modeling. Part 1: Numerical and physical principles.”Journal of. Hydraul. Res.; 28(4), 401–416.
- Iradukunda, P.; Bwambale, E. Reservoir sedimentation and its effect on storage capacity – A case study of Murera reservoir, Kenya. Cogent Eng. 2021, 8, 1917329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K. Development of Integrated Sediment Rating Curves Using ANNs. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; and Wang, S. S. (1999). “Numerical model for channel flow and morphological change studies.” Journal. Hydraul. Eng.; 125 (9), 924–933.
- Joshi, N.; Lamichhane, G.R.; Rahaman, M.M.; Kalra, A. and Ahmad, S.; 2019, May. Application of HEC-RAS to study the sediment transport characteristics of Maumee River in Ohio. In World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2019 (pp. 257-267). Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers.
- Juez, C.; Ferrer-Boix, C.; Murillo, J.; Hassan, M.A.; García-Navarro, P. A model based on Hirano-Exner equations for two-dimensional transient flows over heterogeneous erodible beds. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juracek, K.E. (2015). The aging of America’s reservoirs: in-reservoir and downstream physical changes and habitat implications. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 51, 168–184. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, R.H. (1998). Basinwide Considerations for Water Quality Management: Importance of Phosphorus Retention by Reservoirs (No. WES-MS-03). Vicksburg Ms,.
- Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station.
- Khorrami1, Z.; Banihashemi1, M. Development of a non-coupled algorithm for simulating long-term sedimentation in the Zonouz dam reservoir, Iran. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2021; 21, 545–560. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.G.; Shin, K.G. Long-term simulation of reservoir sedimentation considering particle-size distributions of suspended sediment and bed materials. Journal of Korea Water Resources Association, 2013; 46, 87–97. [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Megonigal, J.P. Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knighton, D. (1998). Fluvial Forms and Processes: A New Perspective; Arnold: London, UK, 1998; 383p. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M. PROFILE: Hungry Water: Effects of Dams and Gravel Mining on River Channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnappan, B. G. (1985). “Comparison of MOBED and HEC-6 river flow models.” Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 12, 464–471.
- Lai, S.Y.J.; Capart, H. (2009). Reservoir infill by hyperpycnical deltas over bedrock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L08402.
- Lai, Y.; Wu, K. A Three-Dimensional Flow and Sediment Transport Model for Free-Surface Open Channel Flows on Unstructured Flexible Meshes. Fluids 2019, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langland, M.; and Cronin, T. (2003). A summary report of sediment processes in Chesapeake Bay and Watershed. In water- resources investigations report 03-4123. New Cumberland PA: US Geological Survey retrieved from http://pa.water.usgs.gov/reports/wnr03-4123.pdf.
- Langland, M. J. (2015). Sediment transport and capacity change in three reservoirs, Lower Susquehanna River Basin, Pennsylvania and Maryland, 1900–2012: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2014–1235, 18 p. [CrossRef]
- Langendoen, E.J.; Mendoza, A.; Abad, J.D.; Tassi, P.; Wang, D.; Ata, R.; El Kadi Abderrezzak, K.; Hervouet, J.-M. Improved numerical modeling of morphodynamics of rivers with steep banks. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hilton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. Y.; Hsieh, H. M.; Yang, J. C.; and Yang, C. T. _1997_. “Quasi– two-dimensional simulation of scour and deposition in alluvial chan nels.” J. Hydraul. Eng.; 123_7_, 600–609.
- Li, Y. (2020). A Global Reservoir Database For High-Resolution Bathymetry And Long-Term Storage Variations. A PhD Dissertation Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University.
- Liu, K.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Ke, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ma, R.; Luo, Z. Remote Sensing-Based Modeling of the Bathymetry and Water Storage for Channel-Type Reservoirs Worldwide. Water Resources Research 2020, 56, e2020WR027147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamosas, C.; Sovacool, B.K. The future of hydropower? A systematic review of the drivers, benefits and governance dynamics of transboundary dams. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’opez, P.; L´opez-Taraz´on, J.A.; Casas-Ruiz, J.P.; Pompeo, M.; Ordo˜nez, J.; Mu˜noz, I. (2016). Sediment size distribution and composition in a reservoir affected by severe water level fluctuations. Sci. Total Environ. 540, 158–167.
- Marineau, M.D.; Wright, S. A, and Lopez, J.V.; (2020). Storage capacity and sedimentation characteristics of the San Antonio Reservoir, California, 2018: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2019–5151, 34 p. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Salvador, A.; Conesa-García, C. Suitability of the SWAT Model for Simulating Water Discharge and Sediment Load in a Karst Watershed of the Semiarid Mediterranean Basin. Water Resour Manag. 2020, 34, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, K. (1987). Reservoir Sedimentation: Impact, Extent and Mitigation. World Bank Technical paper number 71.Library International Reference Centre For Community Water Supply and Sanitation (IRC).
- Mbajiorgu, C.C. Reservoir Sedimentation Modelling and Prediction of Project Lifetime. Journal of the Nigerian Academy of Engineering, 2018; 1, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, K.R.; Freeman, L.A.; and Flint, L.E. (2011), Analysis of Methods to Determine Storage Capacity of, and Sedimentation in, Loch Lomond Reservoir, Santa Cruz County, California, 2009: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2011–5141, 88 p.
- Minh Duc, B.; Wenka, T.; and Rodi, W. (1998). “Depth-average numerical modeling of flow and sediment transport in the Elbe River.” Proc.; 3rd Int. Conf. on Hydroscience and Eng., Berlin.
- Mohammad, M.E.; Al-Ansari, N.; Issa, I.E.; Knutsson, S. Sediment in Mosul Dam reservoir using the HEC-RAS model. Lakes & Reservoirs: Research & Management, 2016; 21, 235–244. [Google Scholar]
- Molinas, A.; and Yang, J. C. (1986). Computer program user’s manual for GSTARS, U.S. Department of Interior, Bureau of Reclamation, Engineering Research Center, Washington, D.C.
- Moorman, B. J. (2001). Ground penetrating radar applications in paleolimnology. In: Last WM, Smol JP (Eds.), Tracking environmental chase using lake sediments - Volume 1: Basin Analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques (Developments in Paleoenvironmental Research). Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, pp. 23–47.
- Morris, Gregory L. and Fan, Jiahua. (1998). Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook, McGraw-Hill Book Co.; New York.
- Morris, G.L. (2014). Sediment management and sustainable use of reservoirs. In Modern Water Resources Engineering;Wang, L.K., Yang, C.T., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 279–337. ISBN 978-1-62703-594-1.
- Moussa, A.M.A. Predicting the deposition in the Aswan High Dam Reservoir using a 2-D model. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2013, 4, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRC. (2010). The MRC modeling toolbox. Retrieved from https://portal.mrcmekong.org/toolbox/mrctoolbox.
- Mustafa, M.R.; Rezaur, R.B.; Saiedi, S.; Isa, M.H. River Suspended Sediment Prediction Using Various Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network Training Algorithms—A Case Study in Malaysia. Water Resour Manag. 2012, 26, 1879–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nones, M. Dealing with sediment transport in flood risk management. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, N.; Kalin, L. Coupling SWAT and ANN models for enhanced daily streamflow prediction. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olden, J. D.; Joy, M. K.; Death, R. G (2004). An accurate comparison of methods for quantifying variable importance in artificial neural networks using simulated data. Ecol. Model. 178, 389-3897.
- Olsson, O.; Sorokin, A.; Ikramova, M. Modelling scenarios to identify a combined sediment-water management strategy for the large reservoirs of the Tuyamuyun hydro-complex. Irrig Drainage Syst 2011, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.Y.A.; Ali, Y.S.A.; Roelvink, J.A.; Dastgheib, A.; Paron, P.; Crosato, A. Modelling of sedimentation processes inside Roseires Reservoir (Sudan). Earth Surf. Dynam. 2015, 3, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortt, R.A.; Kerhin, R.T.; Wells, D.; Cornwell, J. n.d. BATHYMETRIC SURVEY AND SEDIMENTATION ANALYSIS OF LOCH RAVEN AND PRETTYBOY RESERVOIRS.
- Paik, J.; Eghbalzadeh, A.; Sotiropoulos, F. Three-Dimensional Unsteady RANS Modeling of Discontinuous Gravity Currents in Rectangular Domains. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 135, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-Y.; Yang, Y.-T.; Kuo, H.-C.; Tan, Y.-C.; Lai, J.-S.; Chang, T.-J.; Lee, C.-S.; Hsu, K.H. Improvement of watershed flood forecasting by typhoon rainfall climate model with an ANN-based southwest monsoon rainfall enhancement. J. Hydrol. 2013, 506, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Li, F.-F. Multiobjective Reservoir Optimization Considering Sedimentation Applied to the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manage. 2021, 147, 05021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanicolaou, A.; Bdour, A.; and Wicklein, E. (2004). “A numerical model for the study of sediment transport in steep mountain streams.”Journal. Hydraul. Res.; 42_4_, 357–366.
- Papanicolaou, A. N.; Elhakeem, M.; Krallis, G.; Prakash, S. (2008). Sediment transport modeling review—current and future developments. J Hydraul Eng 134:1.
- Rai, R.K.; Mathur, B.S. Event-based Sediment Yield Modeling using Artificial Neural Network. Water Resour Manag. 2008, 22, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runkel, R. L.; and Broshears, R. E. (1991). “OTIS: One-dimensional transport with inflow and storage: A solute transport model for small streams.” CADSWES Technical Rep. 91-01, Univ. of Colorado, Boulder,
Colo.
- Sathya, A.; Thampi, S.G.; Chithra, N.R. Development of a framework for sand auditing of the Chaliyar River basin, Kerala, India using HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS model coupling. International Journal of River Basin Management 2023, 21, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J.; Juez, C.; De Cesare, G. Reservoir sedimentation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2016, 54, 595–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Woznicki, S.A.; Mehaffey, M.; Butcher, J.; Wool, T.A.; Whung, P.Y. A coupled hydrodynamic (HEC-RAS 2D) and water quality model (WASP) for simulating flood-induced soil, sediment, and contaminant transport. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.; Song, J.-H.; Kang, M.-S. Integrated sediment transport process modeling by coupling Soil and Water Assessment Tool and Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 116, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotbolt, L.A.; Thomas, A.D.; Hutchinson, S.M. The use of reservoir sediments as environmental archives of catchment inputs and atmospheric pollution. Prog. Phys. Geogr. : Earth Environ. 2005, 29, 337–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Imtiyaz, M.; Isaac, R.K.; Denis, D.M. Comparison of Artificial Neural Network Models for Sediment Yield Prediction at Single Gauging Station of Watershed in Eastern India. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A. and Ikramova, M.; 2005. Modelling studies Tuyamuyun Hydro Complex model. IWMT ‘Development of integrated water management tools for the Tuyamuyun reservoir complex—Improvement of drinking water supply and public health in the disaster zone of lower Amu Darya’, Final Report EU-INTAS 1043. DFG 1607/FR1-1.
- Southard, J. n.d. Introduction to Fluid Motions and Sediment Transport.
- Sukhinov, A.I.; Chistyakov, A.E.; Protsenko, E.A. Mathematical modeling of sediment transport in the coastal zone of shallow reservoirs. Math Models Comput Simul 2014, 6, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, T.; Hirose, T. n.d. Accumulation of Sediment in Reservoirs.
- Syvitski, J.; Cohen, S.; Miara, A.; Best, J. River temperature and the thermal-dynamic transport of sediment. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 178, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarar, Z.R.; Ahmad, S.R.; Ahmad, I.; Hasson, S.U.; Khan, Z.M.; Washakh, R.M.A.; Ateeq-Ur-Rehman, S.; Bui, M.D. Effect of Sediment Load Boundary Conditions in Predicting Sediment Delta of Tarbela Reservoir in Pakistan. Water 2019, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeter, A.M.; Johnson, B.H.; Berger, C.; Stelling, G.; Scheffner, N.W.; Garcia, M.H.; Parchure, T.M. n.d. Hydrodynamic and sediment transport modeling with emphasis on shallow-water, vegetated areas (lakes, reservoirs, estuaries and lagoons).
- Thomas, W. A.; and Prashum, A. I. (1977). “Mathematical model of scour and deposition.” Journal of Hydr. Div.; 110(11), 1613–1641.
- Torres, A.; Brandt, J.; Lear, K.; Liu, J. A looming tragedy of the sand commons. Science 2017, 357, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundu, C.; Tumbare, M.J.; Kileshye Onema, J.-M. Sedimentation and Its Impacts/Effects on River System and Reservoir Water Quality: case Study of Mazowe Catchment, Zimbabwe. Proc. IAHS 2018, 377, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, B.; Morse, B. The Winter Environmental Continuum of Two Watersheds. Water 2017, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Interior User’s Manual SRH-1D, 2010.
- Van Maanen, B.; Coco, G.; Bryan, K.R.; Ruessink, B.G. The use of artificial neural networks to analyze and predict alongshore sediment transport. Nonlin. Process. Geophys. 2010, 17, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, L. C. (1987). Mathematical modelling of morphological processes in the case of suspended sediment transport (Ph.D. dissertation), Civil Engineering and Geosciences Faculty. Delft Technical University, Delft.
- Venteris, E.R.; May, C.J. Cost-Effective Mapping of Benthic Habitats in Inland Reservoirs through Split-Beam Sonar, Indicator Kriging, and Historical Geologic Data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viseras, C.; Fern´andez, J.; García-García, F.; Soria, J.M.; Calvache, M.L.; J´auregui, P. (2009). Dynamics of sedimentary environments in the accelerated siltation of a reservoir: the case of Alhama de Granada, southern Spain. Environ. Geol. 56 (7), 1353–1369.
- Wang, D.; Cao, A.; Zhang, J.; Fan, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A three-dimensional cohesive sediment transport model with data assimilation: Model development, sensitivity analysis and parameter estimation. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2018, 206, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R.A.; O’Halloran, K. Numerical Study of the Hydrodynamic and Sediment Transport Process in a Subtropical Water Reservoir: the Impacts of Storms and Winds. Env. Model Assess 2020, 25, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernly, J.F.; Zajd, H.J., Jr.; Coon, W.F. (2016). Bathymetric survey and estimation of storage capacity of lower Sixmile Creek reservoir, Ithaca, New York: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2016–1157, 13 p. [CrossRef]
- Whealdon-Haught, D.R.; Wright, S.A.; Marineau, M.D. 2021. Storage capacity and sedimentation characteristics of Loch Lomond Reservoir, California, 2019 (No. 2021-5081). US Geological Survey.
- White, W. R. (2010). World water: resources, usage and the role of manmade reservoirs. Foundation for
Water Research, Marlow.
- Willis, C.M.; Griggs, G.B. Reductions in Fluvial Sediment Discharge by Coastal Dams in California and Implications for Beach Sustainability. J. Geol. 2003, 111, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu W, Rodi W, Wenka T (2000). 3D numerical modeling of flow and sediment transport in open channels. J Hydraul Eng 126:4–15.
- Yang, C. T.; Molinas, A.; Song, C. C. S. (1989). GSTARS–generalized stream tube model for alluvial river simulation, twelve selected computer stream sedimentation models developed in the United States, U. S. Interagency Subcommittee Report on Sedimentation, 10 edited by S. S. Fan, Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 148–178.
- Yang, C. T. and Simões, F. J. M.; 2002, User’s Manual for GSTARS3 (Generalized Sediment Transport model for Alluvial River Simulation version 3.0), U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Technical Service Center, Denver, Colorado.
- Yaseen, Z.M.; El-Shafie, A.; Afan, H.A.; Hameed, M.; Mohtar, W.H.M.W.; Hussain, A. RBFNN versus FFNN for daily river flow forecasting at Johor River, Malaysia. Neural Comput Applic 2016, 27, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. (2005). CCHE2D-GUI – graphical user interface for the CCHE2D model, User’s manual– version 2.2, Technical report No. NCCHE-TR-2005-03, The University of Mississippi, USA.
- Zhang, W. (2014). Sediment transport models. Encyclopedia of Marine Geosciences. [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, T.; Moussa, A.M.; El-Manadely, M.S. Prediction of sediment inflows to Angereb dam reservoir using the SRH -1D sediment transport model. Lakes Reserv. 2013, 18, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).