1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition that is initially characterized by memory impairment and cognitive decline, followed by behavior, speech, visuospatial orientation, and motor system alterations. It is a complex disorder, and its cause is multifactorial – both environmental and genetic factors are at its origin [
1,
2]. One of the most challenging tasks of research in genetics has been to uncover the genetic background of such diseases. Indeed, this is many times due to gene-gene and gene-environmental interactions that diminish and/or modulate the contribution of individual genes or variants for the phenotype. Since most of these diseases would benefit from early diagnosis so that progression can be delayed, it is important to be able to predict AD prior to the first symptoms, making genetic risk calculation a tempting hypothesis. Nevertheless, the genetic variants that were associated with AD until present have a very low predictability power, due to the above-mentioned limitations, and thus it is very important to find better statistics for this purpose.
In recent years, Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) have been conducted with genome-scale data sets of genetic variants (e.g. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms - SNPs). Most of these studies have relied on approaches that consist in univariate analysis of the association of each SNP with the phenotype. Consequently, the possibility of a correlational and interactional structure between SNPs is not taken into account [
3]. This type of approach is not well suited, especially in the detection of small effects [
4], that can become evident only in the presence of other causal effects. In univariate approaches, multiple tests are performed independently, so it is essential to correct the significance level to reduce the probability of type I errors (false positives). Frequently, however, the correction methods (e.g. Bonferroni) are too conservative and therefore it is not possible to detect any significant effect [
3], which leads to a paradoxical increase of type II errors (false negatives) [
5]. Another challenge in finding a plausible method to apply to genetic data is due to its high dimensionality: the number of variables (i.e. SNPs) is much higher than the number of individuals (
). Consequently, models that adjust data very well but with poor predictive ability when applied to new data are formed (overfitting and high variability). There are also correlational structures between the predictor variables, which lead to multicollinearity problems [
6]. Furthermore, traditional multivariate regression models were not designed to deal with these problems. Therefore, it is not suitable to apply them to high dimensionality genetic data.
Penalization techniques are one way to deal with the problems mentioned before and they have already been applied in the context of GWAS [
3,
7]. They combine traditional logistic regression with a penalty term to perform classification and gene selection simultaneously. They imply the choice of a penalty parameter (λ), usually through cross-validation procedures, which define the extent of the predictor coefficients shrinkage. The Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) was proposed by Tibshirani (1996) [
8] and it is a penalization technique that imposes a l1 - norm penalty. LASSO allows the explicit model simplification and consequently interpretability improvement of the model, once the predictor coefficients that are not important are forced to be equal to zero. For these reasons, LASSO has become very popular in high-dimensional data. However, it has some disadvantages. For example, it cannot select more variables than the sample size. In the context of GWAS, there are high correlations between variables due to linkage disequilibrium (LD) or putative group structures. This leads to an instability in the selection of highly correlated variables by LASSO, since it arbitrarily selects one or a few of the predictors and ignores the others [
5,
9]. Ridge, proposed by Hoerl and Kennard (1970) [
10], is a penalization technique that uses a l2 – norm penalty. In contrast with LASSO, Ridge does not have sparse properties on the coefficients estimates as none of them are equal to zero [
11]. However, Ridge deals better with higher correlations between predictors since it shrinks the coefficients of correlated predictors. To achieve a technique with better performance, [
12] proposed a novel tool that consists of a linear combination of l1 – norm penalty and l2 – norm penalty, which is known as Elastic-Net. Elastic-Net can achieve sparse coefficients estimates and can work appropriately with correlations between predictors [
11]. As mentioned before, penalized regression models imply the choice of a penalty parameter (λ), usually through cross-validation procedures, that establishes the estimation of predictors coefficients and, consequently, the selection of the most important predictor variables. The penalization parameter is sensitive to the data and in each iteration of cross-validation, a different parameter value can be chosen. As a result, in each iteration of cross-validation, the variable selection is not the same. In general, several runs of the same procedure led to different results, which means that the procedure is not stable.
Thus, the main goal of this work is to provide a new shrinkage regression procedure with stable variable selection, for structures with a much higher number of variables than individuals, and to apply this procedure as a proof of concept to Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) public dataset to identify the SNPs that are associated with AD circumventing the above-mentioned limitations.
2. Materials and Methods
ADNI genotype data. The data used in this study was obtained from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) public dataset, more specifically from the ADNI-1 study (
https://adni.loni.usc.edu/about/adni1/). The individuals in this dataset underwent genotyping using Illumina Human610-Quad BeadChip. The dataset contains genotypic information of 599,011 SNPs from 757 individuals: 344 with Alzheimer's disease (IAD), 210 cognitively normal (ICN) and 203 with mild cognitive impairment (IMCI).
The data was submitted to a quality control and to a population stratification, which was carried out in accordance with a procedure described by Anderson and others (2010) [
13] and conducted using the PLINK software [
14] (version 1.9). To perform our study, we considered genotypic data from IAD and ICN individuals with ancestral relation with Western European Ancestry, and information regarding probes dedicated to copy number variation was excluded. During the quality control procedure, a total of 103 samples were excluded: 2 samples due to gender discrepancies; 96 samples due to divergent ancestry; 16 samples with a heterozygosity rate higher than expected; 2 samples due to non-reported relatedness to another participant of the study; and 4 samples with more than 5% missing genotypes. Additionally, for the initial 599,011 genotyped SNPs we used filters to allow for the exclusion of SNPs with missing rate higher than 5% (19,406), deviation from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (130) and for having a minor allele frequency lower than 5% (61,218). Also, the missing rate of genotyped SNPs was compared between cases (IAD) and controls (ICN) and no significant differences was detected [
13]. An imputation was made, to fill some missing genotypes using the
bigsnpr R package, namely the
snp_fastImpute method with default parameters. Therefore, the final database was composed of 451 individuals, with 163 ICN (36.1%) and 288 IAD (63.9%), and 518,257 SNPs.
Dataset handling. The data was divided into two datasets: training set and test set. The training set included 70% of the initial sample (116 ICN – 36.7%; 200 IAD – 63.3%) and was used to perform variable selection and to build the prediction models. The test set included the remaining 30% individuals (47 ICN – 34.8%; 88 IAD – 65.2%) and is used to assess the performance of the prediction models. This division was made randomly and stratified by the attributes of the dependent variable (IAD and ICN) to keep the proportion of cases and controls.
Stable variable selection method with shrinkage regression. The proposed method analyzes and combines the results of repeated applications of penalized regression models on the training dataset. First, the result of each repeated penalized regression model was associated with a relative goodness of fit weight. Second, a global weight was assigned to each variable, defined as the sum of the weights of all penalized models in which the variable was selected, assigning to each variable a relative importance. Then, if the variable' weight was greater than a defined threshold, the variable was selected for the final model and its coefficient estimate was defined as the average of the estimated coefficients in each penalized model, weighted by the relative goodness of fit weight of the model (see the graphical summary of the algorithm, in Supplementary Material). The procedure is detailed below:
Penalized regression models (Step 1). In this work, prediction models were constructed using the penalized regression techniques LASSO (α = 1) and Elastic-Net (0 < α < 1). The latter was studied for alpha values in the grid {0.75, 0.50, 0.25, 0.10, 0.05, 0.01}. Each model depends on a regularization parameter, λ, that controls the size of the selection set. For each case, the value of the penalization parameter λ was achieved through a 10-fold-cross-validation, chosen λ with the lowest validation error (deviance). The generalized linear models via penalized maximum likelihood were obtained using the cv.glmnet R function, available in the glmnet package.
Stable variable selection (Step 2). For each model, a different value of λ was proposed and consequently, different variables were selected. To reduce the impact of this variability we run the penalized regression model
times. Therefore, for each value of α, we obtained
models. The Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) was calculated for each model, and the difference between AIC and AIC of the best model was calculated (higher AIC means lower fitness):
These differences allowed us to obtain an Akaike’s weight for each model:
The next question was how to combine these weights to estimate the relative importance of each predictor. We defined the variable weight as the sum of the Akaike’s weight of all repeated penalized models in which the variable appears,
with
an indicator vector of non-null
th coefficient and
the number of variables. The criteria for classifying a variable as important was its weight,
, being at least 0.8. This importance threshold, in general, demonstrated good properties, allowing the minimization of the occurrence of type I and II errors [
15].
Model coefficients estimation (Step 3). In the final model, only the important predictors were considered, that is the predictors with weight at least 0.8. For these, the estimated coefficient was defined by an overall weighted coefficient,
where
is the coefficient estimate of the predictor in the model obtained in run
, and
is the Akaike’s weight of that model. For each of the estimated parameter,
, a weighted variance was also calculated:
Therefore, it was possible to calculate an asymptotic Z confidence interval for each estimated parameter. The significance level used being 5%.
Models’ performance metrics and comparison. We analyzed the training dataset, consisting of 316 individuals (116 ICN; 200 IAD) and 518,257 SNPs. The proposed procedure was applied for two scenarios: one considering only the SNPs (scenario SNPs); and another with SNPs and adjusted to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (scenario SNPs + Cov). Therefore, for each value of the α parameter, two final models were proposed. The performance of the models was evaluated on the test dataset, using the Area Under the Curve (AUC), the Accuracy and the F1-measure.
To better understand the shrinkage impact on the coefficient’s estimation (effect sizes) and on the performance of the models, we compared each proposed model with the corresponding traditional logistic regression model, built based on the same set of selected variables. The above-mentioned performance metrics were used also for this purpose.
3. Results
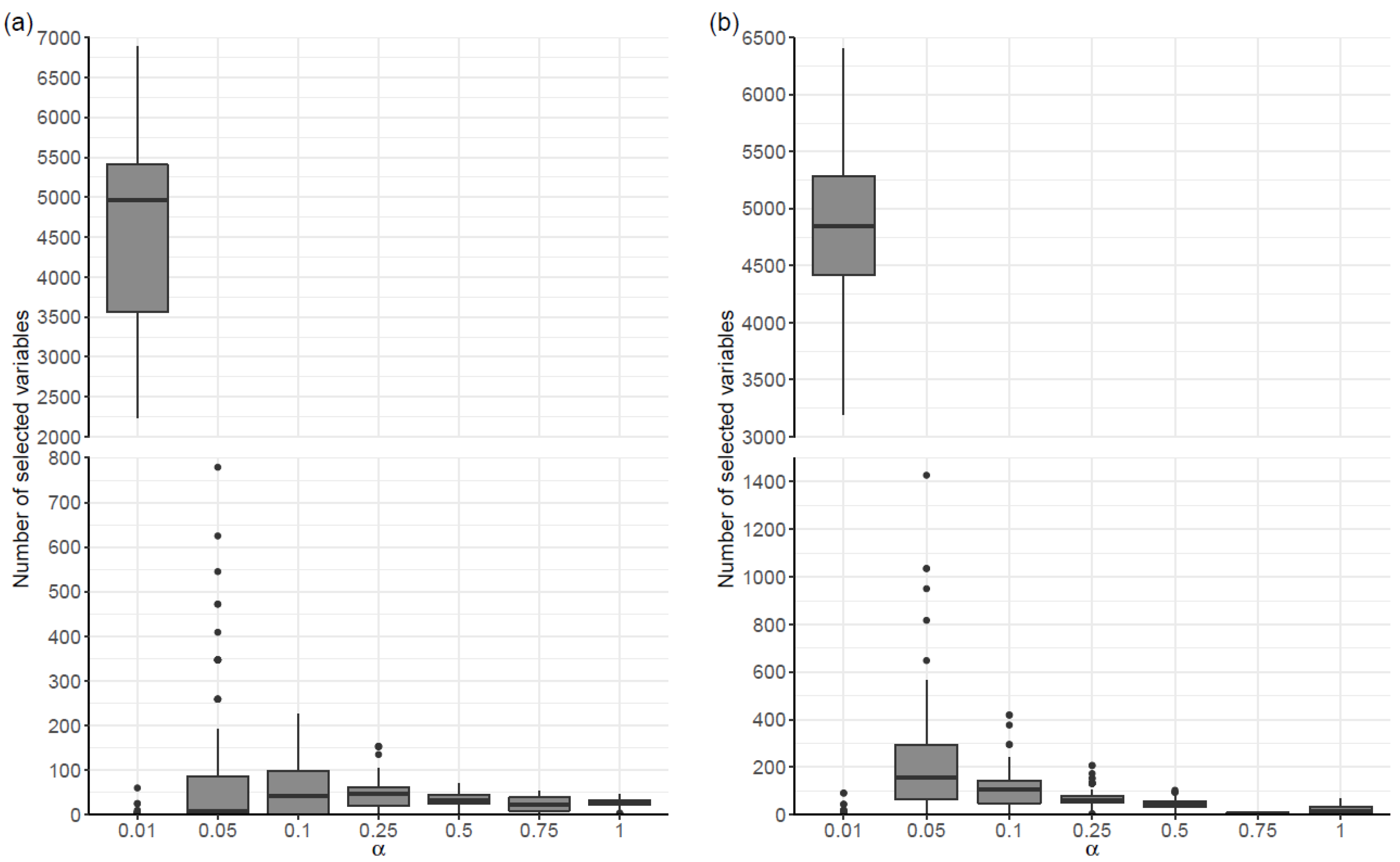
There was some variability in the number of selected variables in the penalized regression models, both in the case where models were fitted to covariates (Scenario SNPs+Cov) and in the case where they were not (Scenario SNPs). As shown in
Table 1, for all values of α, there was a large dispersion in the amount of selected variables. For example, in scenario SNPs and α = 0.01, the number of selected variables ranged between 0 and 6886. In general, the range and the maximum number of selected variables increased as the α value decreased, in both scenarios. In relation to the median number of selected variables, a tendency to increase as the value of α decreased was also observed in Scenario SNPs+Cov. Although this trend was not observed in the SNPs scenario for alpha values ranging between 0.05 and 1, the median amount of selected variables increased substantially for the model with α = 0.01 (
Figure 1).
Regarding the final models, built based on the proposed procedure, the largest amount of selected variables occurred for α = 1 (with 11 variables), in the SNPs Scenario, and for α = 0.01 and α = 0.05 (with 9 variables), in the SNPs+Cov Scenario. In the latter scenario, the APOE genotype covariate was always selected. It should be noted that, in the SNPs scenario, there were several alpha values for which no variables were selected (
Table 2).
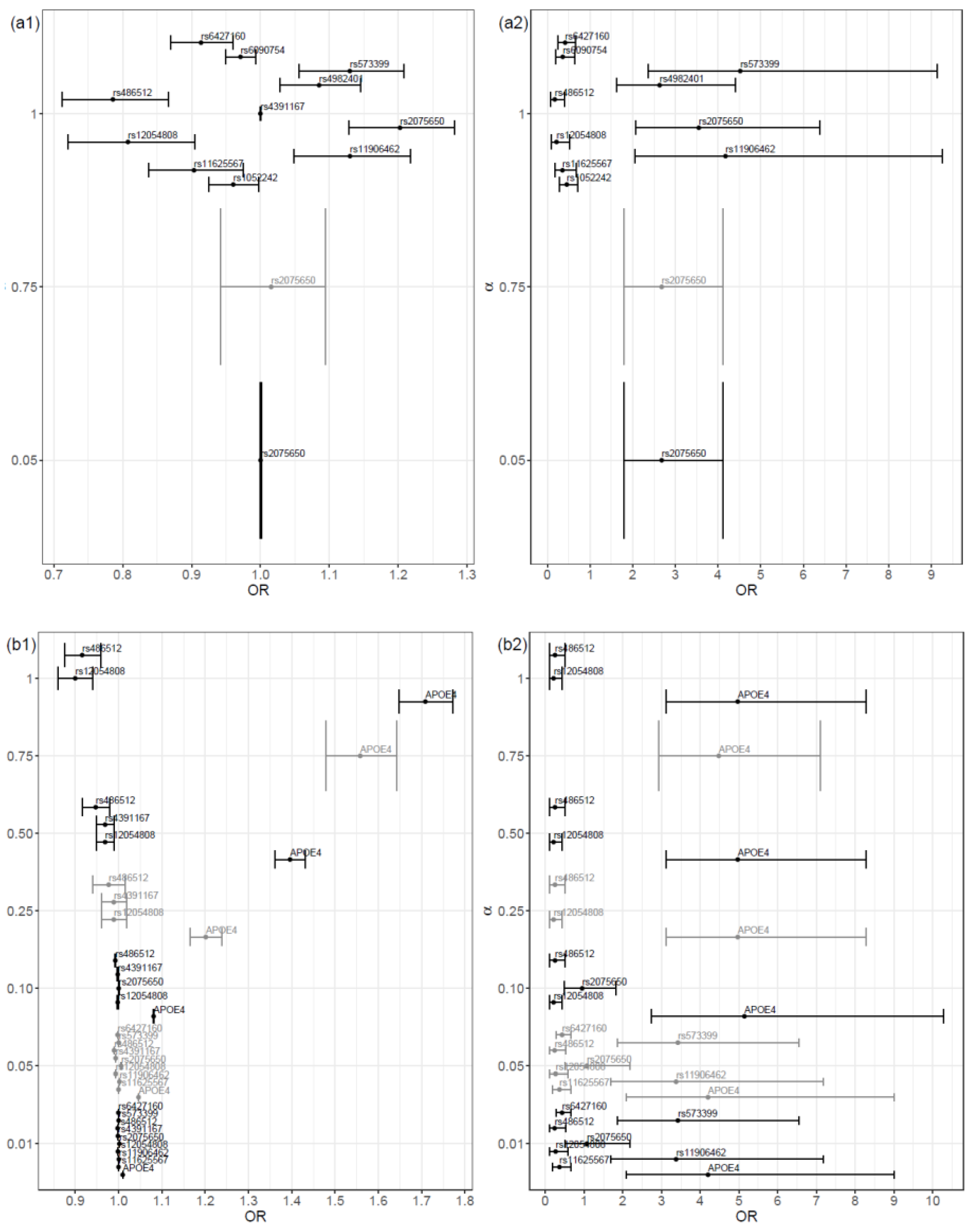
The magnitude of the coefficient estimates on the proposed models increased as the value of α increased. In general, as the alpha value increased, the odds ratio deviated further from the value 1 (
Figure 2, (a1) and (b1)). A high similarity existed between the selected variables, in both scenarios. The main difference was that the model fitted in Scenario SNPs+Cov contained the covariate APOE4 genotype, instead of the SNPs rs6090754, rs1052242 and rs4982401. Naturally, the magnitude of the coefficients estimates was higher in the model with α = 1 and, consequently, the risk and protection effects were increased.
As expected, the protective and risk effects were always lower in our approach when compared to traditional logistic regression due to the shrinkage (
Figure 2).
The best performance for Scenario SNPs+Cov was achieved with α = 0.01. In the case of Scenario SNPs, an overall better result was achieved with α = 1, than for lower values of α. Models for Scenario SNPs+Cov had a better performance than models for scenario SNPs (
Figure 3).
When comparing the proposed model with the corresponding traditional logistic regression, the performances were similar. In truth, the proposed models show a slightly better performance with higher values of AUC and F1-measure (
Figure 3). It should be noted that the traditional logistic regression model was obtained due to the prior selection of variables, achieved with the proposed approach.
4. Discussion
In this work a stable variable selection method with shrinkage regression is proposed and applied to the ADNI public dataset. For each value of α we observed differences between the set of variables selected for each model. Notably, in step 2, where the important variables are identified, it is observed that the order of variables is the same for the different alpha values. However, due to the cutoff value for the variable weight (defined as 0.8), some variables were not flagged as important and, therefore, were not integrated into the final model. The lack of consistency between models could be overcome by adjusting the threshold value to the α values. As expected, for each fixed α, there were differences between models with and without adjusting to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (Scenario SNPs and Scenario SNPs+Cov, respectively).
In general, the results were consistent for the common SNPs of the two models proposed: the significance of the coefficients and the effect of the variables (risk or protection) remained the same (
Figure 2 (a1) and (b1)). The same was verified in relation to the correspondent traditional logistic regression models.
Both the SNP rs2075650 and the
APOE4 genotype were already referenced in the literature as risk factors for AD [
16,
17]. The first factor was indeed selected in both models (Scenario SNPs and Scenario SNPs+Cov). The OR estimates obtained by the proposed procedure were, as expected, lower than those obtained with a traditional regression procedure (without shrinkage) in this work and in the literature (e.g., in reference [
16] OR = 4.178 and 95% CI 1.891–9.228). The second risk factor,
APOE4 genotype, was selected in the model for the Scenario SNPs+Cov only.
In addition, the SNPs rs573399 and rs11906462, despite not being found in the literature as risk factors for AD, were selected in the two proposed models. Also, rs12054808 and rs486512 were selected consistently with an odds ratio less than one, which points to an antecipated protective effect for AD. Since the proposed variable selection procedure was more restrictive than the correspondent usual penalized regression approach, we believe that the selected variables have potential to be tested as genetic predictors of AD.
The proposed procedure for feature selection can thus be advantageously applied to other contexts where a very high amount of predictors exist in relation to the number of individuals under study. It is well known that, in such contexts, the usual feature selection methods are unstable, i.e., same dataset yielding distinct results. Our results demonstrate the potential of the new procedure to overcome this issue and out-perform other methods with respect to stability of variable selection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Graphical summary algorithm of the proposed; Table S1: Models coefficients and performance measures for each model (Supplementary_table.xlsx).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, AHT, LR, VA and VE; methodology, AHT, LR, VA and VE; software, LR, MP, VE.; validation, AHT, VA and VE; formal analysis, AHT, LR, VA and VE; investigation, AHT, GM, LR, MP, VA and VE; data curation, MP; writing—review and editing, AHT, GM, LR, MP, VA and VE; supervision, AHT, GM, MP, VA. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Center for Research and Development in Mathematics and Applications (CIDMA) through the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, references UIDB/04106/2020 and UIDP/04106/2020 (
https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/04106/2020 and
https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDP/04106/2020) and by the Institute for Biomedicine (iBiMED) of the University of Aveiro (UID/BIM/04501/2013) and GenomePT (Portugal 2020: POCI/01/0145/FEDER/022184).
Acknowledgments
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (adni.loni.usc.edu). As such, the investigators within the ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report. A complete listing of ADNI investigators can be found at:
http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ridge, P.G.; Mukherjee, S.; Crane, P.K.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease: Analyzing the missing heritability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeTure, M.; Dickson, D. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Joint Identification of Multiple Genetic Variants via Elastic-Net Variable Selection in a Genome-Wide Association Analysis. Annals of Human Genetics 2010, 74, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridley, B.; Biernacka, J. Gene set analysis of SNP data: benefits, challenges, and future directions. European Journal of Human Genetics 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, P.; Gredler, G.M.B.; Fürst, C.; et al. Evaluation of the lasso and the elastic net in genome-wide association studies. Frontiers in Genetics 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algamal, Z.; Ali, H. An efficient gene selection method for high-dimensional microarray data based on sparse logistic regression. Electronic Journal of Applied Statistical Analysis 2017, 10, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherlin, S.; Howey, R.; Cordell, H. Using penalized regression to predict phenotype from SNP data. BMC Proceedings 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the LASSO. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society - Series B (Methodological) 1996, 58, 267–288. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2346178. [CrossRef]
- Algamal, Z.; Lee, M. A two-stage sparse logistic regression for optimal gene selection in high-dimensional microarray data classification. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification 2019, 13, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerl, A.; Kennard, R. Ridge regression: Biased estimation for nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 1970, 12, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Wang, K. Genome-wide association studies using a penalized moving-window regression. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3887–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society - Series B (Statistical Methodology) 2005, 67, 301–320. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3647580. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.; Pettersson, F.; Clarke, G.; et al. Data quality control in genetic case-control association studies. Nature Protocols 2010, 5, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; et al. Plink: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagno, V.; Mazancourt, C. glmulti: An R package for easy automated model selection with (generalized) linear models. Journal of Statistical Software 2019, 34, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, J.; Xu, B.; et al. The tomm40 gene rs2075650 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease in caucasian, and asian populations. Neuroscience letters 2016, 628, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, H.; Mollers, T.; Perna, L.; et al. The genetic risk of Alzheimer’s disease beyond APOE 4: systematic review of Alzheimer’s genetic risk scores. Translational Psychiatry 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Distribution of the number of selected variables in 100 penalized regression models, organized by alpha value (α), for each scenario: (a) models constructed considering only the SNPs; and (b) models adjusted to the covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype.
Figure 1.
Distribution of the number of selected variables in 100 penalized regression models, organized by alpha value (α), for each scenario: (a) models constructed considering only the SNPs; and (b) models adjusted to the covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype.
Figure 2.
Odd Ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval of the variables selected in each final model, organized by alpha value, for the two scenarios: (a1) scenario SNPs and (b1) scenario SNPs+Cov; and for the corresponding traditional logistic regression model: (a2) scenario SNPs and (b2) scenario SNPs+Cov. The grid of α values was {0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1}.
Figure 2.
Odd Ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval of the variables selected in each final model, organized by alpha value, for the two scenarios: (a1) scenario SNPs and (b1) scenario SNPs+Cov; and for the corresponding traditional logistic regression model: (a2) scenario SNPs and (b2) scenario SNPs+Cov. The grid of α values was {0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1}.
Figure 3.
AUC and corresponding , Accuracy and corresponding , and F1-measure (from left to right) for each final model (black) and for the corresponding logistic regression model (gray) for two scenarios: (a) scenario SNPs; (b) scenario SNPs+Cov. Results are organized by alpha values in grid {0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1}.
Figure 3.
AUC and corresponding , Accuracy and corresponding , and F1-measure (from left to right) for each final model (black) and for the corresponding logistic regression model (gray) for two scenarios: (a) scenario SNPs; (b) scenario SNPs+Cov. Results are organized by alpha values in grid {0.01, 0.05, 0.10, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, 1}.
Table 1.
Minimum, maximum and median number of selected variables in 100 penalized regression models, organized by alpha value, for each scenario: models considering only SNPs (at left); and models adjusted to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (at right). Results are shown as: median (minimum – maximum).
Table 1.
Minimum, maximum and median number of selected variables in 100 penalized regression models, organized by alpha value, for each scenario: models considering only SNPs (at left); and models adjusted to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (at right). Results are shown as: median (minimum – maximum).
| alpha parameter |
Number of selected variables |
| Scenario SNPs |
Scenario SNPs+Cov |
| 0.01 |
4958 (0 - 6886) |
4843 (9 - 6399) |
| 0.05 |
9 (1 - 779) |
156 (9 - 1427) |
| 0.10 |
41 (0 - 225) |
107 (5 - 419) |
| 0.25 |
48 (0 - 153) |
61 (4 - 207) |
| 0.50 |
33 (0 - 70) |
49 (4 - 103) |
| 0.75 |
22 (1 - 52) |
6 (1 - 14) |
| 1 |
27 (0 - 45) |
16 (1 - 66) |
Table 2.
Number of selected variables for each final model, organized by alpha parameter, for the two scenarios: model considering only SNPs (left); and model adjusted to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (right). SNPs+Cov Scenario results are shows as: number of SNPs + number of covariates.
Table 2.
Number of selected variables for each final model, organized by alpha parameter, for the two scenarios: model considering only SNPs (left); and model adjusted to covariates age, sex, educational level and APOE4 genotype (right). SNPs+Cov Scenario results are shows as: number of SNPs + number of covariates.
| alpha parameter |
Number of selected variables |
| Scenario SNPs |
Scenario SNPs+Cov |
| 0.01 |
0 |
8 + 1 |
| 0.05 |
1 |
8 + 1 |
| 0.10 |
0 |
4 + 1 |
| 0.25 |
0 |
3 + 1 |
| 0.50 |
0 |
3 + 1 |
| 0.75 |
1 |
0 + 1 |
| 1 |
11 |
2 + 1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).