Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
06 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Questionnaire Design
2.2. Questionnaire Validation
2.3. Questionnaire Application
2.4. Participants
2.5. Measuring Lifetime Physical Activity and Sedentary Patterns
2.6. Ethical Considerations
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Questionnaire Validation
3.2. Description of the Study Sample
3.2.1. Social and Demographic Characteristics
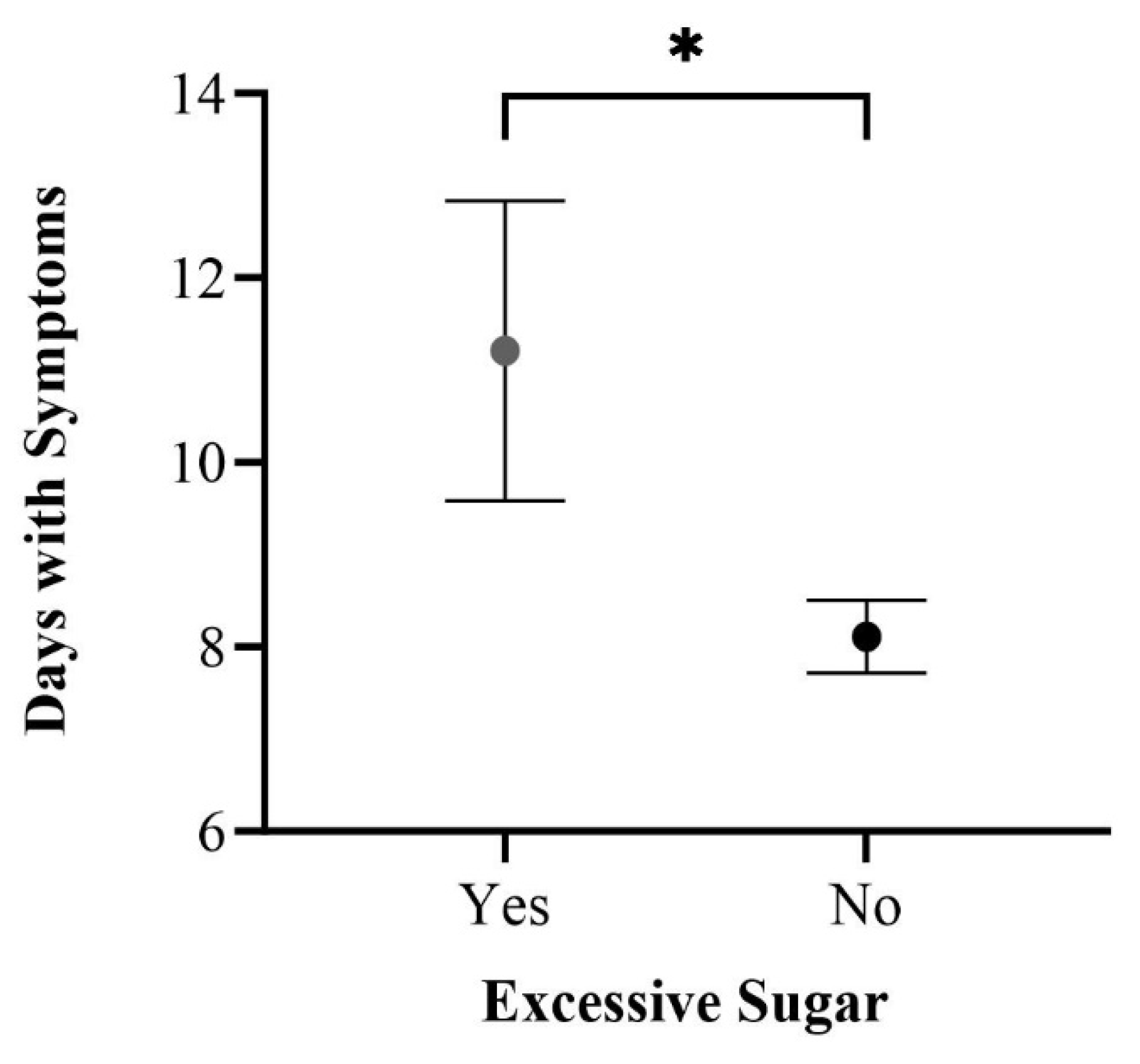
3.3. Significant Correlations among Study Participants
3.3.1. Social and Demographic Characteristics
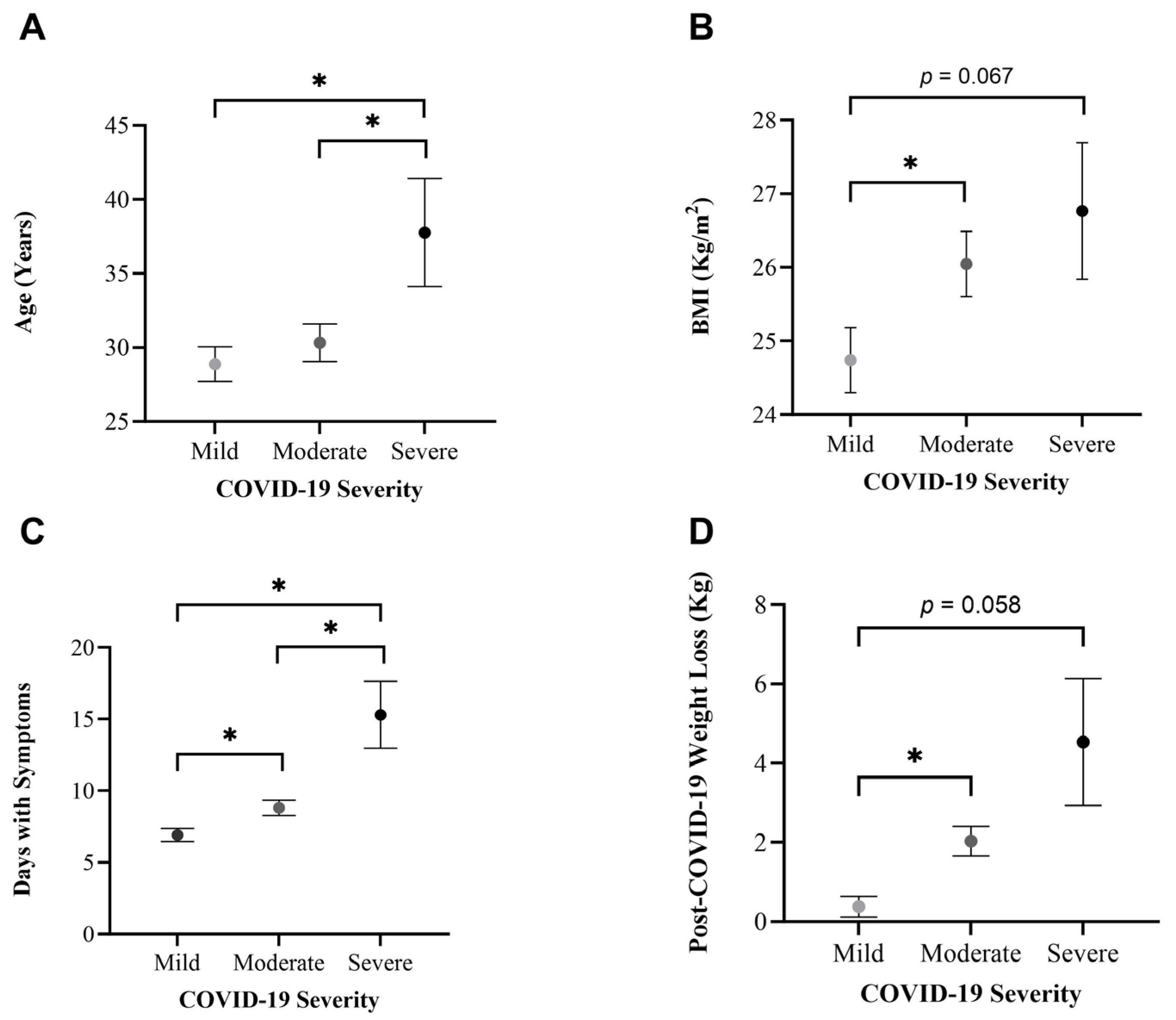
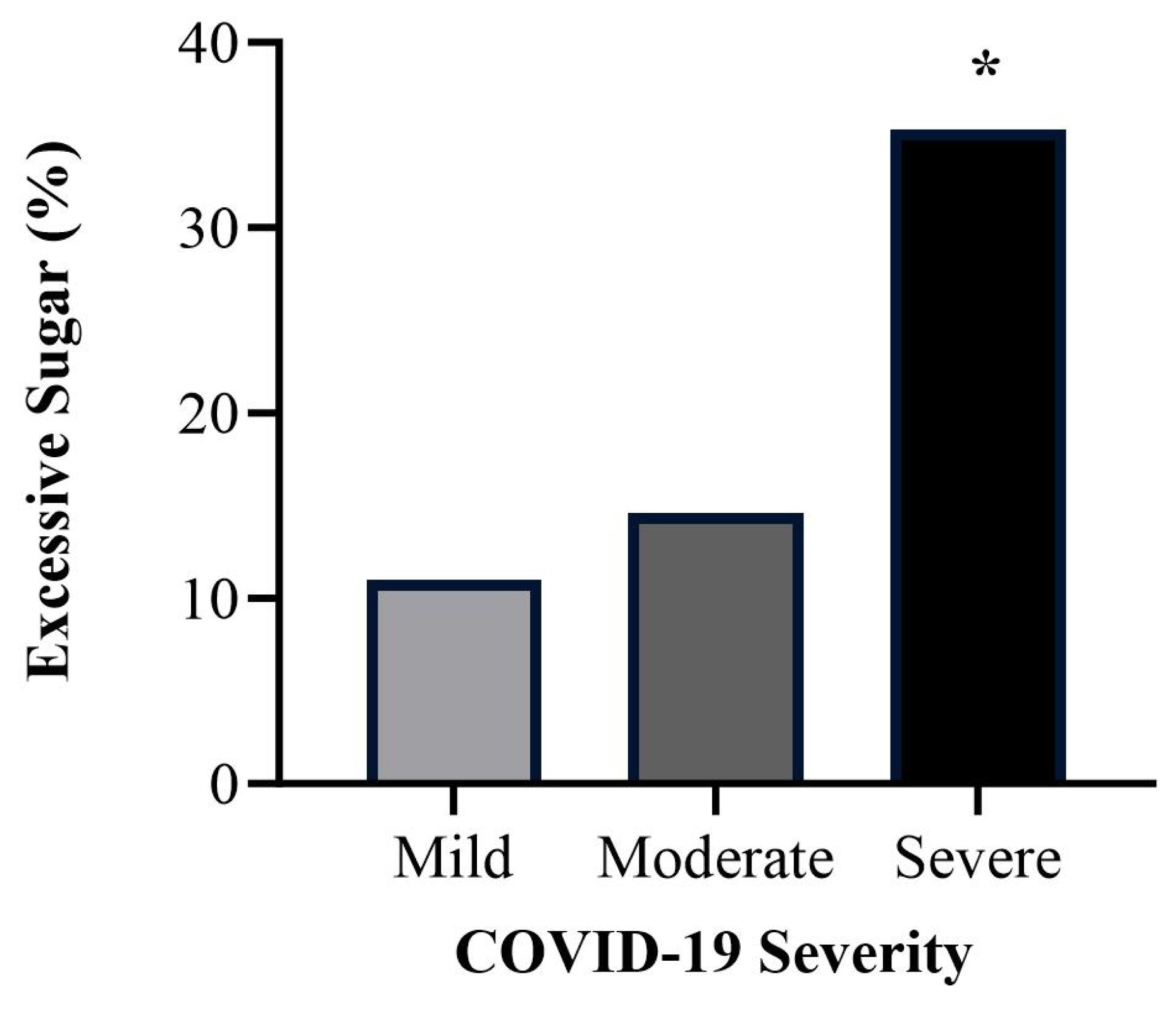
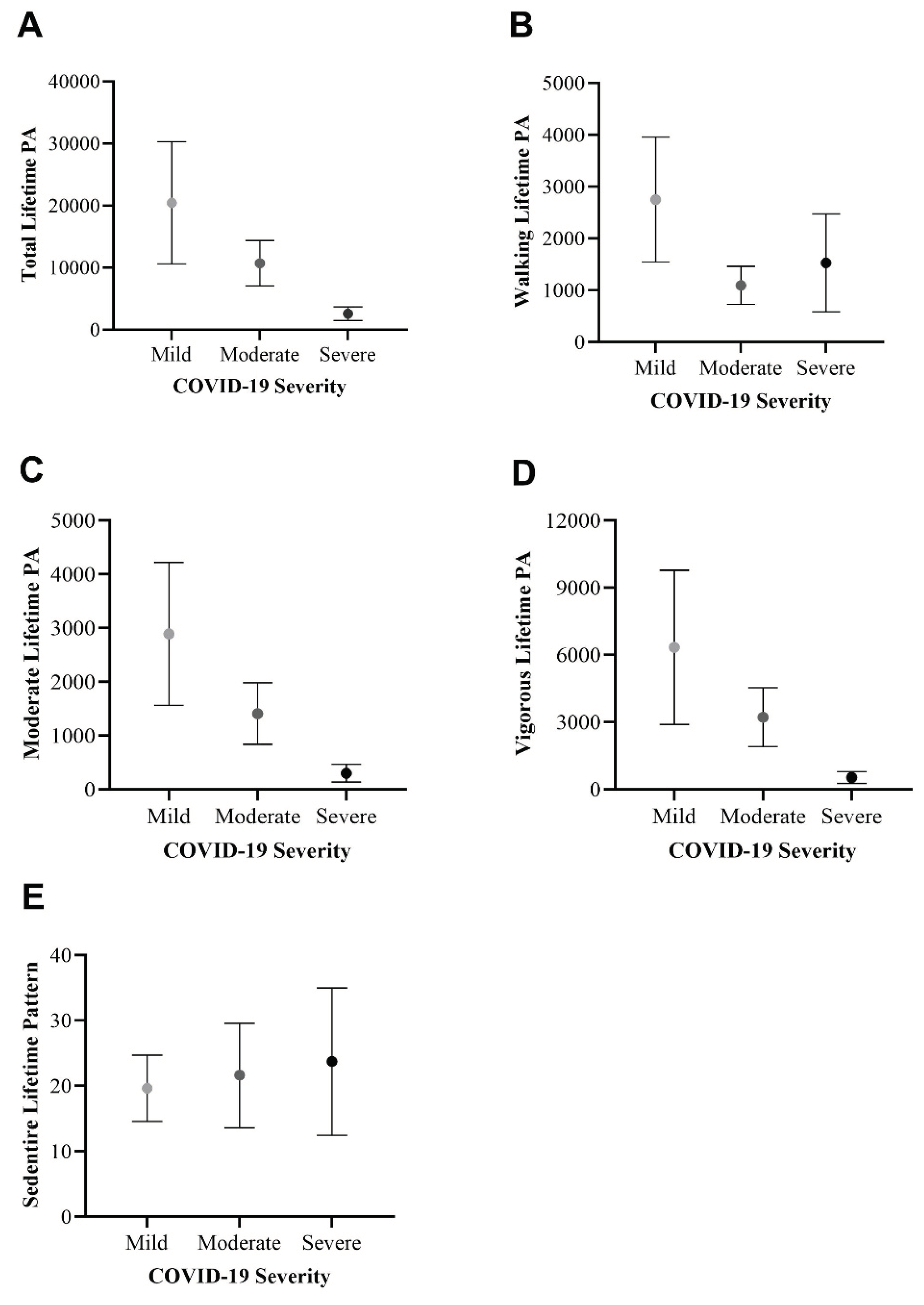
3.4. Differences per COVID-19 Severity
3.4.2. Dietary Patterns
3.4.3. Physical Activity Patterns
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Woods, J. A.; Hutchinson, N. T.; Powers, S. K.; Roberts, W. O.; Gomez-Cabrera, M. C.; Radak, Z.; Berkes, I.; Boros, A.; Boldogh, I.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Coelho-Júnior, H. J.; Marzetti, E.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Durstine, J. L.; Sun, J.; Ji, L. L. The COVID-19 Pandemic and Physical Activity. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2020, 2 (2), 55–64. [CrossRef]
- CDC. COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html (Accessed on 28 January 2024).
- Steenkamp, L.; Saggers, R. T.; Bandini, R.; Stranges, S.; Choi, Y.-H.; Thornton, J. S.; Hendrie, S.; Patel, D.; Rabinowitz, S.; Patricios, J. Small Steps, Strong Shield: Directly Measured, Moderate Physical Activity in 65 361 Adults Is Associated with Significant Protective Effects from Severe COVID-19 Outcomes. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56 (10), 568–577. [CrossRef]
- Sallis, R.; Young, D. R.; Tartof, S. Y.; Sallis, J. F.; Sall, J.; Li, Q.; Smith, G. N.; Cohen, D. A. Physical Inactivity Is Associated with a Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19 Outcomes: A Study in 48 440 Adult Patients. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55 (19), 1099–1105. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition., 2018. Available online: https://health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Bennett, D. A.; Du, H.; Clarke, R.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Millwood, I.; Yu, C.; He, P.; Zheng, X.; Collins, R.; Chen, J.; Peto, R.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; for the China Kadoorie Biobank Study Collaborative Group. Association of Physical Activity with Risk of Major Cardiovascular Diseases in Chinese Men and Women. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2 (12), 1349. [CrossRef]
- Uusitupa, M.; Khan, T. A.; Viguiliouk, E.; Kahleova, H.; Rivellese, A. A.; Hermansen, K.; Pfeiffer, A.; Thanopoulou, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Schwab, U.; Sievenpiper, J. L. Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes by Lifestyle Changes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2019, 11 (11), 2611. [CrossRef]
- Merino, J.; Joshi, A. D.; Nguyen, L. H.; Leeming, E. R.; Mazidi, M.; Drew, D. A.; Gibson, R.; Graham, M. S.; Lo, C.-H.; Capdevila, J.; Murray, B.; Hu, C.; Selvachandran, S.; Hammers, A.; Bhupathiraju, S. N.; Sharma, S. V.; Sudre, C.; Astley, C. M.; Chavarro, J. E.; Kwon, S.; Ma, W.; Menni, C.; Willett, W. C.; Ourselin, S.; Steves, C. J.; Wolf, J.; Franks, P. W.; Spector, T. D.; Berry, S.; Chan, A. T. Diet Quality and Risk and Severity of COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. Gut 2021, 70 (11), 2096–2104. [CrossRef]
- Gomide, E. B. G.; Abdalla, P. P.; Pisa, M. F.; Schneider, G.; Vieira, L. G.; Mazzonetto, L. F.; De Sousa Oliveira, A.; Sebastião, E.; Dos Santos, A. P. The Role of Physical Activity in the Clinical Outcomes of People Diagnosed with Covid-19: A Systematic Review. JSAMS Plus 2022, 1, 100007. [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Shamsi, M. M.; Khoramipour, K.; Malakoutinia, F.; Woo, W.; Park, S.; Yon, D. K.; Lee, S. W.; Shin, J. I.; Smith, L. Baseline Physical Activity Is Associated with Reduced Mortality and Disease Outcomes in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32 (5), e2349. [CrossRef]
- Ezzatvar, Y.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Izquierdo, M.; Garcia-Hermoso, A. Physical Activity and Risk of Infection, Severity and Mortality of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Non-Linear Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Data from 1 853 610 Adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56 (20), 1188–1193. [CrossRef]
- Hamer, M.; Kivimäki, M.; Gale, C. R.; Batty, G. D. Lifestyle Risk Factors, Inflammatory Mechanisms, and COVID-19 Hospitalization: A Community-Based Cohort Study of 387,109 Adults in UK. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 184–187. [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, J. P.; Lesser, I. A.; Thomson, C. J.; Giles, L. V. Does Higher Self-Reported Cardiorespiratory Fitness Reduce the Odds of Hospitalization From COVID-19? J. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 18 (7), 782–788. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. W.; Lee, J.; Moon, S. Y.; Jin, H. Y.; Yang, J. M.; Ogino, S.; Song, M.; Hong, S. H.; Ghayda, R. A.; Kronbichler, A.; Koyanagi, A.; Jacob, L.; Dragioti, E.; Smith, L.; Giovannucci, E.; Lee, I.-M.; Lee, D. H.; Lee, K. H.; Shin, Y. H.; Kim, S. Y.; Kim, M. S.; Won, H.-H.; Ekelund, U.; Shin, J. I.; Yon, D. K. Physical Activity and the Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Severe COVID-19 Illness and COVID-19 Related Mortality in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56 (16), 901–912. [CrossRef]
- Craig, C. L.; Marshall, A. L.; Sj??Str??M, M.; Bauman, A. E.; Booth, M. L.; Ainsworth, B. E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J. F.; Oja, P. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity: Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35 (8), 1381–1395. [CrossRef]
- Hernadnez-Nieto, R. A. Contributions to Statistical Analysis. 1992.
- Arámburo-Gálvez, J.; Carvalho Gomes, I.; André, T.; Beltrán-Cárdenas, C.; Macêdo-Callou, M.; Braga Rocha, É.; Mye-Takamatu-Watanabe, E.; Rahmeier-Fietz, V.; Figueroa-Salcido, O.; Cárdenas-Torres, F.; Ontiveros, N.; Cabrera-Chávez, F. Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Evaluation of a Brazilian Portuguese Questionnaire to Estimate the Self-Reported Prevalence of Gluten-Related Disorders and Adherence to Gluten-Free Diet. Medicina (Mex.) 2019, 55 (9), 593. [CrossRef]
- Szigriszt-Pazos, F. Sistemas Predictivos de Legilibilidad Del Mensaje Escrito: Fórmula de Perspicuidad (PhD tesis). Universidad Complutense, Madrid. 2001.
- Barrio-Cantalejo, I. M.; Simón-Lorda, P.; Melguizo, M.; Escalona, I.; Marijuán, M. I.; Hernando, P. Validation of the INFLESZ Scale to Evaluate Readability of Texts Aimed at the Patient. An. Sist. Sanit. Navar. 2008, 31 (2), 132–152.
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J. M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323 (13), 1239. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648. (22) Ashok, P.; Kharche, J.; Raju, R.; Godbole, G. Metabolic Equivalent Task Assessment for Physical Activity in Medical Students. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 7 (2), 1. [CrossRef]
- Ashok, P.; Kharche, J.; Raju, R.; Godbole, G. Metabolic Equivalent Task Assessment for Physical Activity in Medical Students. Natl. J. Physiol. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 7 (2), 1. [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S. D.; Willis, E. A.; Ainsworth, B. E.; Barreira, T. V.; Hastert, M.; Kracht, C. L.; Schuna, J. M.; Cai, Z.; Quan, M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Whitt-Glover, M. C.; Jacobs, D. R. 2024 Adult Compendium of Physical Activities: A Third Update of the Energy Costs of Human Activities. J. Sport Health Sci. 2024, 13 (1), 6–12. [CrossRef]
- Chesnut, W. M.; MacDonald, S.; Wambier, C. G. Could Diet and Exercise Reduce Risk of COVID-19 Syndemic? Med. Hypotheses 2021, 148, 110502. [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, L.; Imamura, F.; Brage, S.; Griffin, S. J.; Wareham, N. J.; Forouhi, N. G. Intakes and Sources of Dietary Sugars and Their Association with Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37 (4), 1313–1322. [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D. W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G. W.; Miller, A. H.; Mantovani, A.; Weyand, C. M.; Barzilai, N.; Goronzy, J. J.; Rando, T. A.; Effros, R. B.; Lucia, A.; Kleinstreuer, N.; Slavich, G. M. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25 (12), 1822–1832. [CrossRef]
- Chastin, S. F. M.; Abaraogu, U.; Bourgois, J. G.; Dall, P. M.; Darnborough, J.; Duncan, E.; Dumortier, J.; Pavón, D. J.; McParland, J.; Roberts, N. J.; Hamer, M. Effects of Regular Physical Activity on the Immune System, Vaccination and Risk of Community-Acquired Infectious Disease in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2021, 51 (8), 1673–1686. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. P.; Turner, J. E. Debunking the Myth of Exercise-Induced Immune Suppression: Redefining the Impact of Exercise on Immunological Health Across the Lifespan. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 648. [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D. Exercise, Infection, and Immunity. Int. J. Sports Med. 1994, 15 (S 3), S131–S141. [CrossRef]
| Number of Experts | Relevance Mean ± SD | Clarity Mean ± SD | Writing and terminology Mean ± SD | Format Mean ± SD | CVCt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 4.53 ± 0.67 | 4.47 ± 0.77 | 4.44 ± 0.78 | 4.45 ± 0.82 | 0.90 |
| Variable | |
|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 30.30 ± 12.05 |
| Sex n (%) | |
| Female | 130 (66.0) |
| Male | 67 (34.0) |
| BMI kg/m2 (mean ± SD) | 25.50 ± 4.21 |
| Ethnicity n (%) | |
| Mexican Mestizo | 197 (100) |
| Marital Status n (%) | |
| Single | 123 (62.4) |
| Married | 63 (32.0) |
| Consensual Union | 7 (3.6) |
| Other | 4 (2.0) |
| Education n (%) | |
| Postsecondary Education | 137 (69.5) |
| Elementary and Secondary Education | 60 (30.5) |
| Occupation n (%) | |
| Student | 75 (38.1) |
| Employee | 64 (32.5) |
| Self-Employed | 43 (21.8) |
| Unemployed | 5 (2.5) |
| Other | 10 (5.1) |
| Total sample = 197. Quantitative variables are represented as “Mean (± SD)” and qualitative variables as “n (%)”. | |
| Variable | Variable | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Tool n (%) | Days with Symptoms (mean ± SD) | 8.57 ± 5.72 | |
| PCR | 76 (38.6) | Hospitalized n (%) | |
| Antigen Test | 59 (29.9) | No | 185 (98.4) |
| Antibody Test | 22 (11.2) | Yes | 3 (1.6) |
| Antigen Test + Clinical | 4 (2.0) | ICU | 1 (33.3) |
| Antibody Test + Clinical | 7 (3.6) | Oxygen Need n (%) | |
| Clinical | 29 (14.7) | No | 181 (96.3) |
| Year of Diagnosis n (%) | Yes | 7 (3.7) | |
| 2022 | 56 (28.6) | Severity n (%) | |
| 2021 | 81 (41.3) | Mild | 91 (46.2) |
| 2020 | 55 (28.1) | Moderate | 89 (45.2) |
| 2019 | 4 (2.0) | Severe | 17 (8.6) |
| Symptoms n (%) | Post COVID-19 Weight Loss (Kg) (mean ± SD) | 1.48 ± 3.67 | |
| Present | 188 (95.4) | Comorbidities n (%) | |
| Headache | 149 (75.6) | No | 162 (82.2) |
| Fatigue | 137 (69.5) | Yes | 35 (17.8) |
| Fever | 119 (60.4) | Vaccination n (%) | |
| Sore Throat | 111 (56.3) | Yes | 187 (96.4) |
| Anosmia | 107 (54.3) | No | 7 (3.6) |
| Cough | 91 (46.2) | Initial Vaccine Type | |
| Joint Pain | 89 (45.2) | AstraZeneca | 70 (37.4) |
| Eye Pain | 73 (37.1) | Sinovac | 69 (37.0) |
| Nasal Congestion | 69 (35.0) | Pfizer | 23 (12.3) |
| Runny Nose | 66 (33.5) | CanSino | 15 (8.0) |
| Shortness of Breath | 60 (30.5) | Other | 10 (5.3) |
| Diarrhea | 26 (13.2) | COVID-19 Post Vaccine n (%) | |
| Vomit | 11 (5.6) | Yes | 62 (35.0) |
| Absent | 9 (4.6) | No | 115 (65.0) |
| Items totaling less than 197 (total sample) are attributed to instances where participants left items in blank. Quantitative variables are represented as “Mean (± SD)” and qualitative variables as “n (%)”. | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





