Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Harvest and Anatomical Dimensions
2.2. Collagen Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Histology
2.4. Collagen Crimp Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
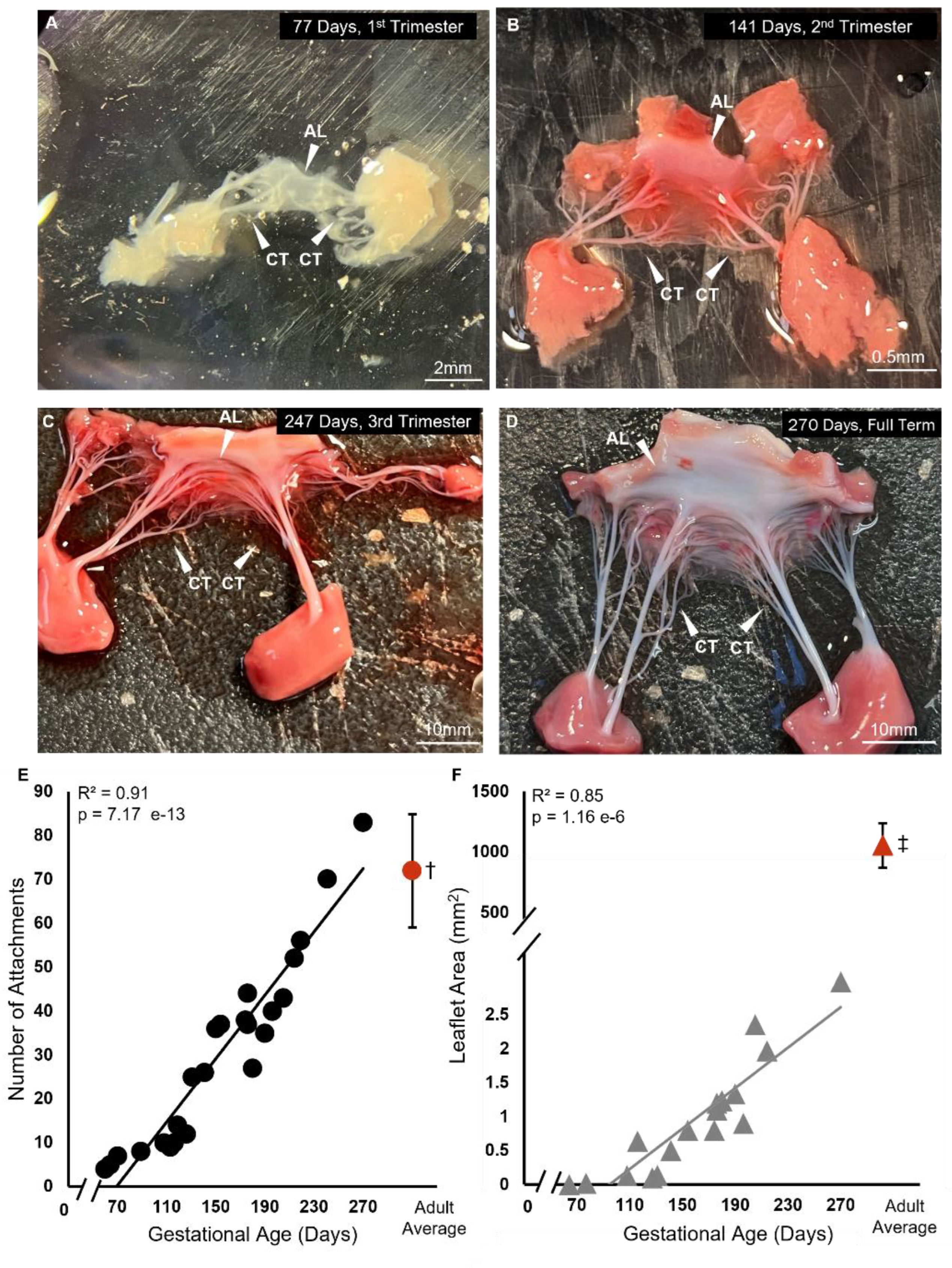
3.1. Chordae Division Occurs Only During Gestation Whereas Leaflet Area Continues to Increase Postnatally
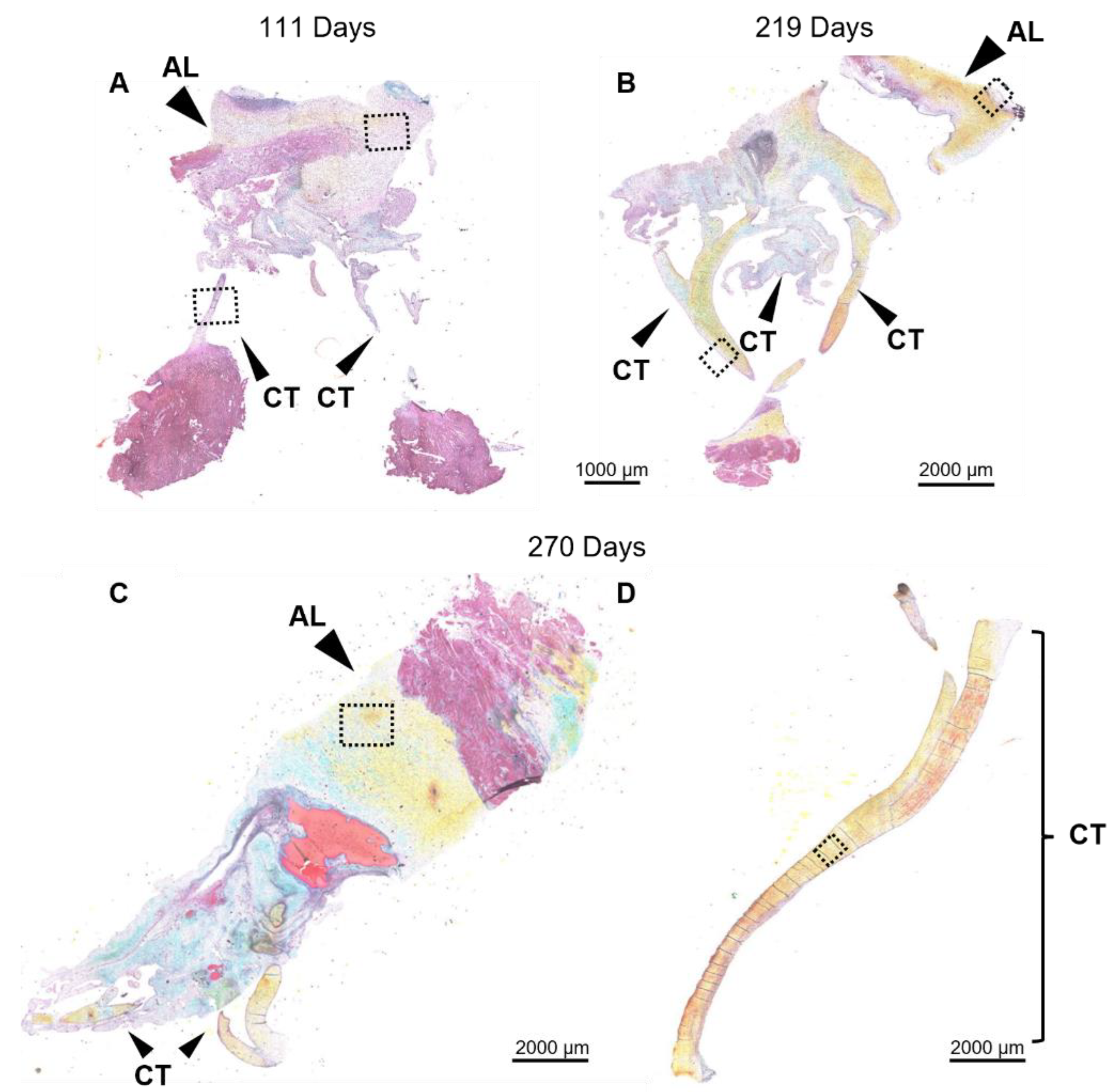
3.2. In Leaflet and Chordae, Mature Collagen Content Increases Over Gestation Despite Unchanged Levels of Newly Synthesized Collagen
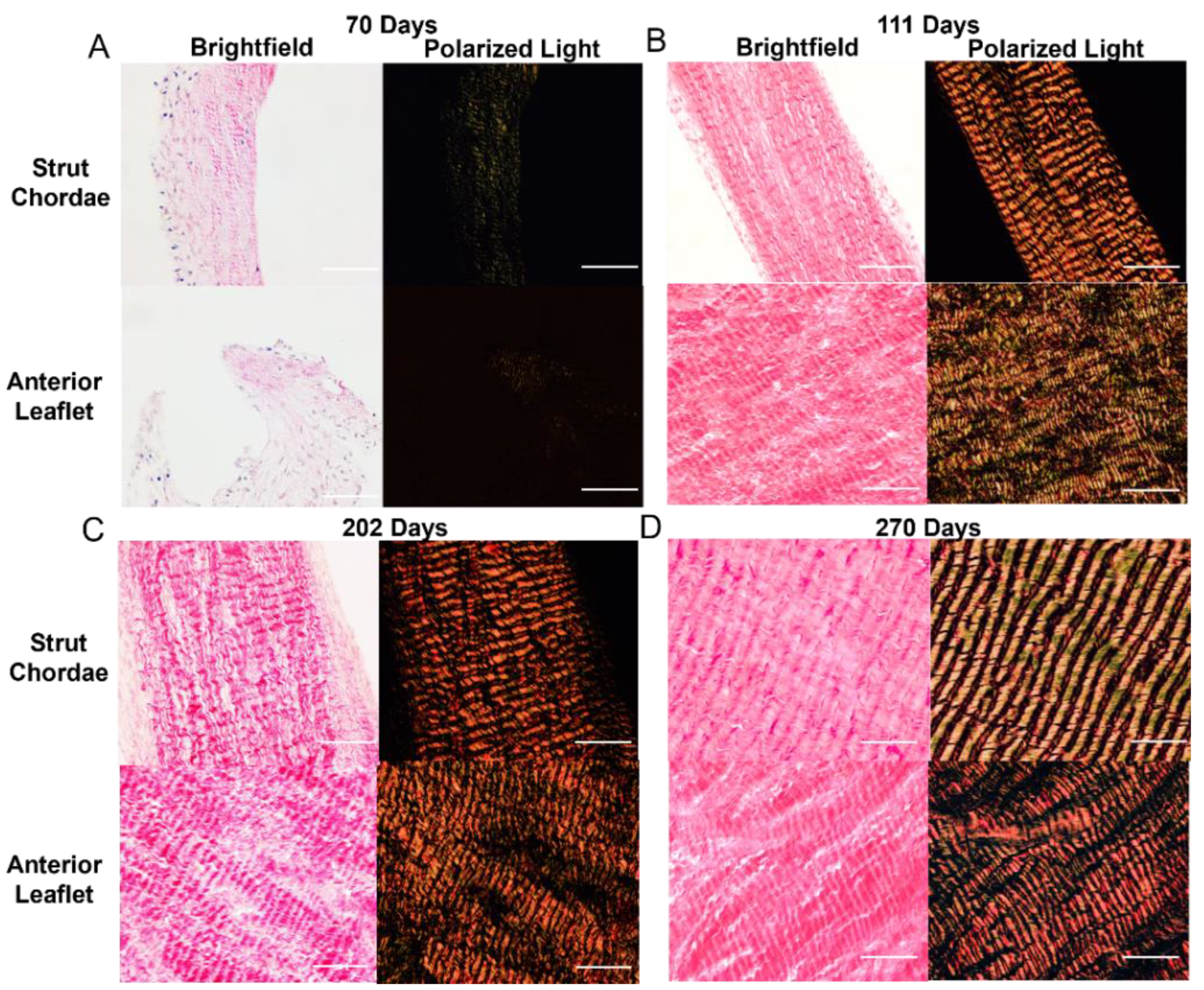
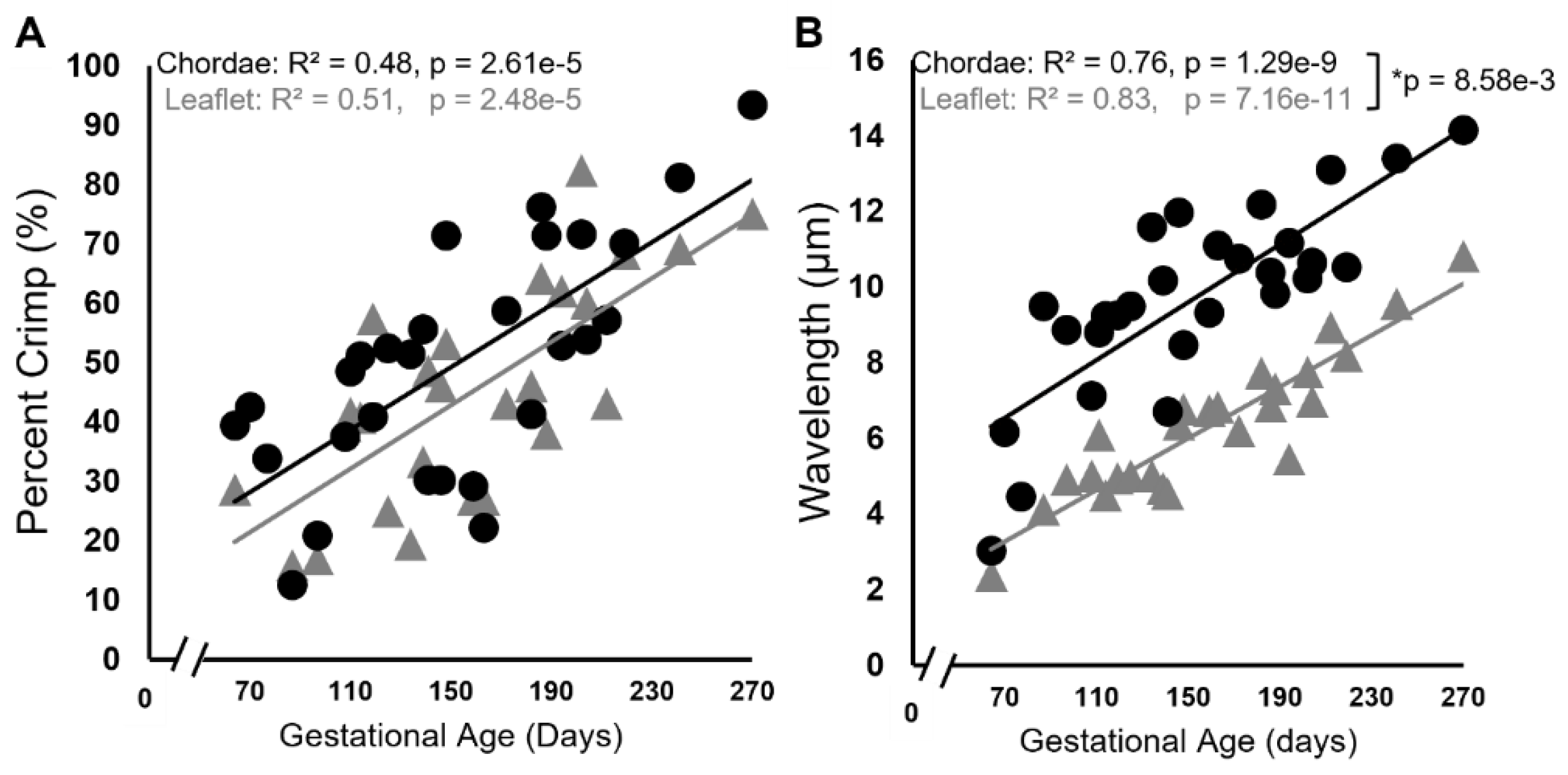
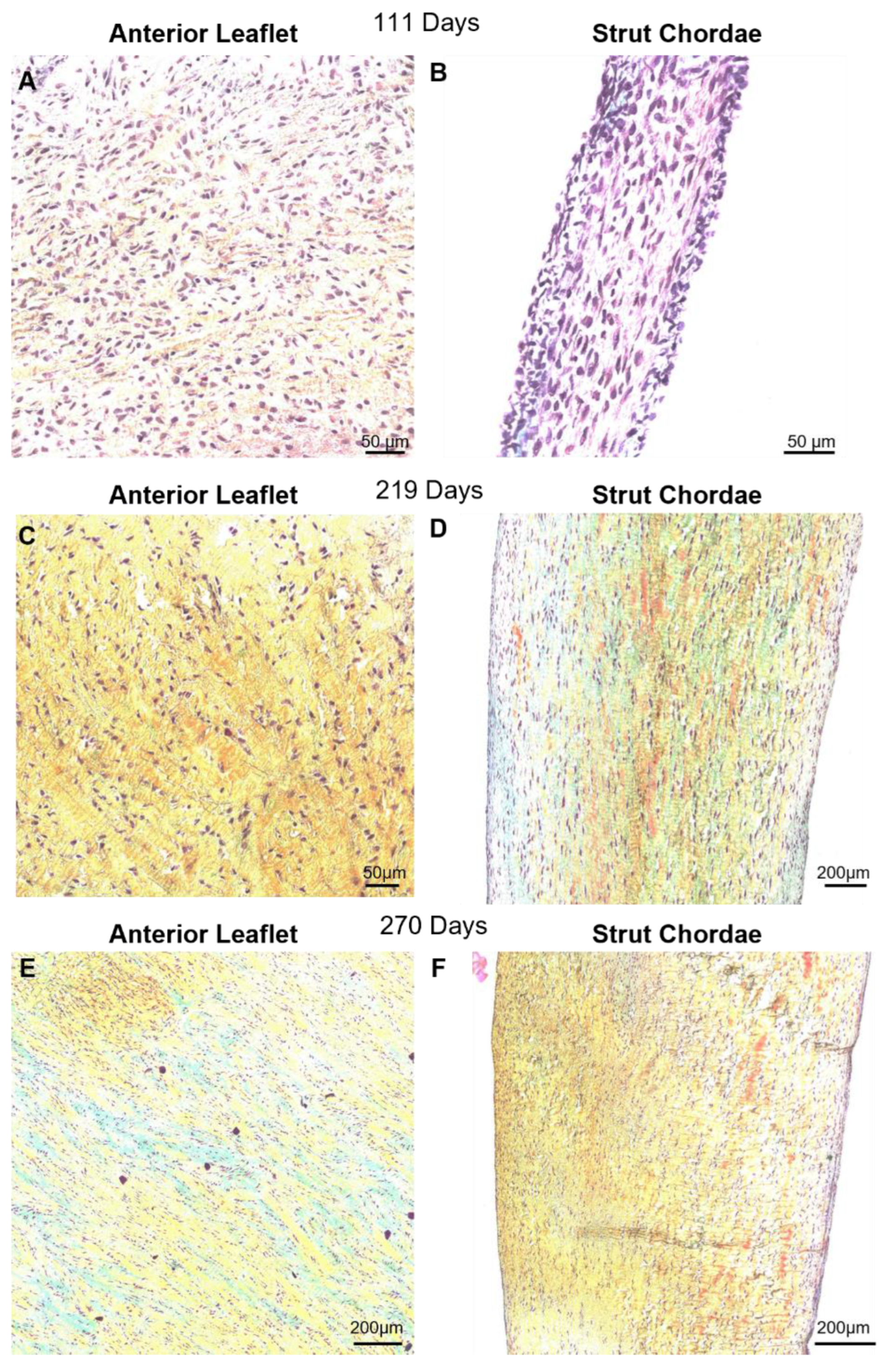
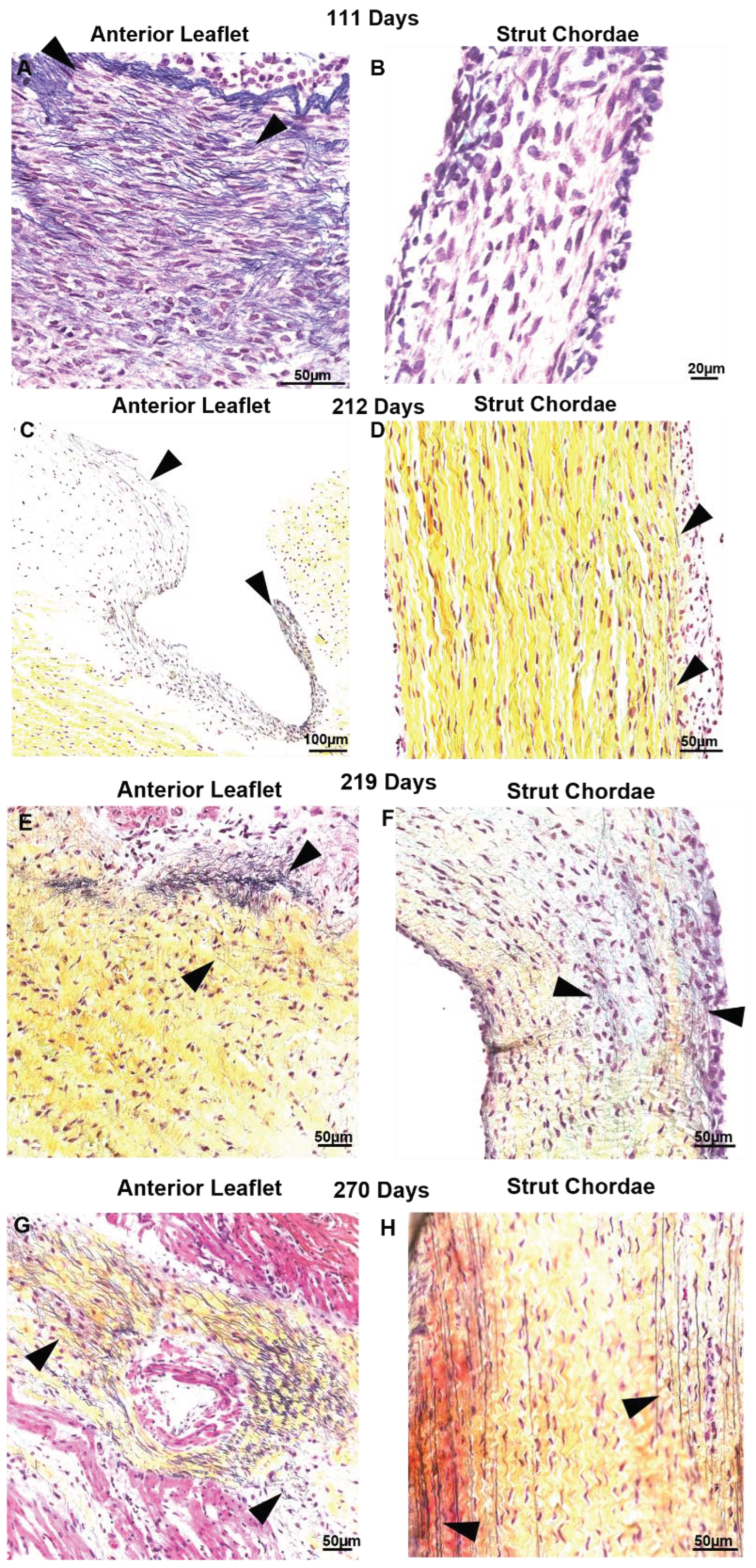
3.3. Collagen Crimp Develops Earlier in the Chordae Versus the Leaflet
3.4. Bovine Mitral Chordae and Leaflet Collagen Fibers Are Laid Down in Their Adult-Like Orientations
3.5. Contrary to Collagen Patterns, Elastic Fibers Appear in the Leaflet Ahead of the Chordae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coffey, S.; Roberts-Thomson, R.; Brown, A.; Carapetis, J.; Chen, M.; Enriquez-Sarano, M.; Zühlke, L.; Prendergast, B.D. Global Epidemiology of Valvular Heart Disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021, 18, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delling, F.N.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Adams, D.H.; Basso, C.; Borger, M.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Elmariah, S.; Evans, F.; Gerstenfeld, E.; Hung, J.; et al. Research Opportunities in the Treatment of Mitral Valve Prolapse. J Am Coll Cardiol 2022, 80, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.S.; Moore, R.; Fulmer, D.B.; Guo, L.; Gensemer, C.; Stairley, R.; Glover, J.; Beck, T.C.; Morningstar, J.E.; Biggs, R.; et al. DCHS1, Lix1L, and the Septin Cytoskeleton: Molecular and Developmental Etiology of Mitral Valve Prolapse. JCDD 2022, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, R.; Sauls, K.; Peal, D.S.; deVlaming, A.; Toomer, K.; Leyne, M.; Salani, M.; Talkowski, M.E.; Brand, H.; Perrocheau, M.; et al. Mutations in DCHS1 Cause Mitral Valve Prolapse. Nature 2015, 525, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauls, K.; de Vlaming, A.; Harris, B.S.; Williams, K.; Wessels, A.; Levine, R.A.; Slaugenhaupt, S.A.; Goodwin, R.L.; Pavone, L.M.; Merot, J.; et al. Developmental Basis for Filamin-A-Associated Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 96, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwarde, C.; Capoulade, R.; Mérot, J.; Le Scouarnec, S.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Yu, M.; Huttin, O.; Selton-Suty, C.; Sellal, J.-M.; Piriou, N.; et al. Genetics and Pathophysiology of Mitral Valve Prolapse. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1077788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemenceau, A.; Bérubé, J.; Bélanger, P.; Gaudreault, N.; Lamontagne, M.; Toubal, O.; Clavel, M.; Capoulade, R.; Mathieu, P.; Pibarot, P.; et al. Deleterious Variants in DCHS 1 Are Prevalent in Sporadic Cases of Mitral Valve Prolapse. Molec Gen & Gen Med 2018, 6, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.G.; Linneweh, M.; Liebscher, S.; Van Handel, B.; Layland, S.L.; Schenke-Layland, K. Endocardial-to-Mesenchymal Transformation and Mesenchymal Cell Colonization at the Onset of Human Cardiac Valve Development. Development 2016, 143, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenisch, T.D.; Schroeder, J.A.; Bradley, J.; Klewer, S.E.; McDonald, J.A. Heart-Valve Mesenchyme Formation Is Dependent on Hyaluronan-Augmented Activation of ErbB2–ErbB3 Receptors. Nat Med 2002, 8, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso, J.M.; Gratzinger, D.; Camenisch, T.D.; Canosa, S.; Pinter, E.; Madri, J.A. Elevated Glucose Inhibits VEGF-A–Mediated Endocardial Cushion Formation. J Cell Biol 2003, 160, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, D. ERBB3-Dependent AKT and ERK Pathways Are Essential for Atrioventricular Cushion Development in Mouse Embryos. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.T.; McQuinn, T.C.; Sedmera, D.; Turner, D.; Markwald, R.R. Transitions in Early Embryonic Atrioventricular Valvular Function Correspond With Changes in Cushion Biomechanics That Are Predictable by Tissue Composition. Circ Res 2007, 100, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskohl, P.R.; Gould, R.A.; Butcher, J.T. Quantification of Embryonic Atrioventricular Valve Biomechanics during Morphogenesis. J Biomech 2012, 45, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, E.; Boselli, F.; Roth, S.; Krudewig, A.; Belting, H.-G.; Charvin, G.; Vermot, J. Oscillatory Flow Modulates Mechanosensitive Klf2a Expression through Trpv4 and Trpp2 during Heart Valve Development. Curr Biol 2015, 25, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donat, S.; Lourenço, M.; Paolini, A.; Otten, C.; Renz, M.; Abdelilah-Seyfried, S. Heg1 and Ccm1/2 Proteins Control Endocardial Mechanosensitivity during Zebrafish Valvulogenesis. eLife 2018, 7, e28939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, F.; Gentile, A.; Gauvrit, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Bensimon-Brito, A. Nfatc1 Promotes Interstitial Cell Formation During Cardiac Valve Development in Zebrafish. Circ Res 2020, 126, 968–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassen, D.; Wang, M.; Pham, D.; Sun, S.; Rao, R.; Singh, R.; Butcher, J. Hydrostatic Mechanical Stress Regulates Growth and Maturation of the Atrioventricular Valve. Development 2021, 148, dev196519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, B.Y.; Sun, S.; Dai, C.; Long, F.; Butcher, J.T. Shear and Hydrostatic Stress Regulate Fetal Heart Valve Remodeling through YAP-Mediated Mechanotransduction. eLife 2023, 12, e83209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, R.A.; Yalcin, H.C.; MacKay, J.L.; Sauls, K.; Norris, R.; Kumar, S.; Butcher, J.T. Cyclic Mechanical Loading Is Essential for Rac1-Mediated Elongation and Remodeling of the Embryonic Mitral Valve. Curr Biol 2016, 26, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermot, J.; Forouhar, A.S.; Liebling, M.; Wu, D.; Plummer, D.; Gharib, M.; Fraser, S.E. Reversing Blood Flows Act through Klf2a to Ensure Normal Valvulogenesis in the Developing Heart. PLoS Biol 2009, 7, e1000246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, L.M.; Duchemin, A.-L.; Ramalingan, H.; Wu, B.; Chen, M.; Bamezai, S.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Morley, M.P.; Wang, T.; et al. Hemodynamic Forces Sculpt Developing Heart Valves through a KLF2-WNT9B Paracrine Signaling Axis. Dev Cell 2017, 43, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignes, H.; Vagena-Pantoula, C.; Prakash, M.; Fukui, H.; Norden, C.; Mochizuki, N.; Jug, F.; Vermot, J. Extracellular Mechanical Forces Drive Endocardial Cell Volume Decrease during Zebrafish Cardiac Valve Morphogenesis. Dev Cell 2022, 57, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthoek, P.W.; Wenink, A.C.G.; Vrolijk, B.C.M.; Wisse, L.J.; DeRuiter, M.C.; Poelmann, R.E.; Gittenberger-de Groot, A.C. Development of the Atrioventricular Valve Tension Apparatus in the Human Heart. Anat Embryol 1998, 198, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruithof, B.P.T.; Krawitz, S.A.; Gaussin, V. Atrioventricular Valve Development during Late Embryonic and Postnatal Stages Involves Condensation and Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Dev Biol 2007, 302, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, J.D.; Lu, Y.; Koch, M.; Kadler, K.E.; Lincoln, J. Temporal and Spatial Expression of Collagens during Murine Atrioventricular Heart Valve Development and Maintenance. Dev. Dyn. 2008, 237, 3051–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, F.J.; Moorman, A.F.M.; Anderson, R.H.; Männer, J.; Soufan, A.T.; Vries, C. de G.; Schneider, M.D.; Webb, S.; van den Hoff, M.J.B.; Christoffels, V.M. Lineage and Morphogenetic Analysis of the Cardiac Valves. Circ Res 2004, 95, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, J.; Alfieri, C.M.; Yutzey, K.E. Development of Heart Valve Leaflets and Supporting Apparatus in Chicken and Mouse Embryos. Dev. Dyn. 2004, 230, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.A.; Kern, C.B.; Wessels, A.; Moralez, E.I.; Markwald, R.R.; Mjaatvedt, C.H. Identification and Detection of the Periostin Gene in Cardiac Development. Anat. Rec. 2004, 281A, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, D.E.; Hamlett, W.C.; Noble, C.W. Morphogenesis of Chordae Tendineae. I: Scanning Electron Microscopy. Anat. Rec. 1984, 210, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Junor, L.; Price, R.L.; Norris, R.A.; Potts, J.D.; Goodwin, R.L. Expression and Deposition of Fibrous Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Cardiac Valves during Chick Development. Microsc Microanal 2011, 17, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, E.H.; Grande-Allen, K.J. Age-Related Changes in Collagen Synthesis and Turnover in Porcine Heart Valves. J Heart Valve Dis 2007, 16, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Kasyanov, V.; Moreno-Rodriguez, R.A.; Kalejs, M.; Ozolanta, I.; Stradins, P.; Wen, X.; Yao, H.; Mironov, V. Age-Related Analysis of Structural, Biochemical and Mechanical Properties of the Porcine Mitral Heart Valve Leaflets. Connec Tissue Res 2013, 54, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, E.H.; Post, A.D.; Laucirica, D.R.; Grande-Allen, K.J. Perinatal Changes in Mitral and Aortic Valve Structure and Composition. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2010, 13, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Wirrig, E.E.; Hinton, R.B.; Merrill, W.H.; Spicer, D.B.; Yutzey, K.E. Twist1 Promotes Heart Valve Cell Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Gene Expression during Development in Vivo and Is Expressed in Human Diseased Aortic Valves. Dev Biol 2010, 347, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, R.A.; Moreno-Rodriguez, R.A.; Sugi, Y.; Hoffman, S.; Amos, J.; Hart, M.M.; Potts, J.D.; Goodwin, R.L.; Markwald, R.R. Periostin Regulates Atrioventricular Valve Maturation. Dev Biol 2008, 316, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikawa, E.; Whittaker, P.; Farber, M.; Mendelson, K.; Padera, R.F.; Aikawa, M.; Schoen, F.J. Human Semilunar Cardiac Valve Remodeling by Activated Cells From Fetus to Adult: Implications for Postnatal Adaptation, Pathology, and Tissue Engineering. Circulation 2006, 113, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Votteler, M.; Berrio, D.A.C.; Horke, A.; Sabatier, L.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Nsair, A.; Aikawa, E.; Schenke-Layland, K. Elastogenesis at the Onset of Human Cardiac Valve Development. Development 2013, 140, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaussin, V.; Morley, G.E.; Cox, L.; Zwijsen, A.; Vance, K.M.; Emile, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, C.; Myers, D.; et al. Alk3/Bmpr1a Receptor Is Required for Development of the Atrioventricular Canal Into Valves and Annulus Fibrosus. Circ Res 2005, 97, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.G.; Vesely, I. Structural Changes of Rat Mitral Valve Chordae Tendineae During Postnatal Development. J Heart Valve Dis 2012, 21, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Aldous, I.G.; Lee, J.M.; Wells, S.M. Differential Changes in the Molecular Stability of Collagen from the Pulmonary and Aortic Valves During the Fetal-to-Neonatal Transition. Ann Biomed Eng 2010, 38, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, W.D.; Youn, I.; Lukoff, H.D.; Krueger, P.M.; Guilak, F.; Hopkins, R.A.; Sacks, M.S. Correlation between Heart Valve Interstitial Cell Stiffness and Transvalvular Pressure: Implications for Collagen Biosynthesis. Am J Physiol-Heart C 2006, 290, H224–H231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, R.B.; Alfieri, C.M.; Witt, S.A.; Glascock, B.J.; Khoury, P.R.; Benson, D.W.; Yutzey, K.E. Mouse Heart Valve Structure and Function: Echocardiographic and Morphometric Analyses from the Fetus through the Aged Adult. Am J Physiol-Heart C 2008, 294, H2480–H2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipoiu, F.M. Chapter 2: The Specific Development Period. In Atlas of Heart Anatomy and Development, 1st ed.; Springer London: London, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4471-5381-8. [Google Scholar]
- Aldous, I.G.; Veres, S.P.; Jahangir, A.; Lee, J.M. Differences in Collagen Cross-Linking between the Four Valves of the Bovine Heart: A Possible Role in Adaptation to Mechanical Fatigue. Am J Physiol-Heart C 2009, 296, H1898–H1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, H.E.; Sack, W.O. Prenatal Development of Domestic and Laboratory Mammals: Growth Curves, External Features and Selected References. Anatom Histol Embryol 1973, 2, 11–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierlot, C.M.; Moeller, A.D.; Lee, J.M.; Wells, S.M. Biaxial Creep Resistance and Structural Remodeling of the Aortic and Mitral Valves in Pregnancy. Ann Biomed Eng 2015, 43, 1772–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierlot, C.M.; Lee, J.M.; Amini, R.; Sacks, M.S.; Wells, S.M. Pregnancy-Induced Remodeling of Collagen Architecture and Content in the Mitral Valve. Ann Biomed Eng 2014, 42, 2058–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierlot, C.M.; Moeller, A.D.; Lee, J.M.; Wells, S.M. Pregnancy-Induced Remodeling of Heart Valves. Am J Physiol-Heart C 2015, 309, H1565–H1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing 2021.
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An {R} Companion to Applied Regression 2019.
- Jarek, S. Mvnormtest: Normality Test for Multivariate Variables 2012.
- Signorell, A. DescTools: Tools for Descriptive Statistics. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Hester, J.; Chang, W.; Bryan, J. Devtools: Tools to Make Developing R Packages Easier 2022.
- Scott, B.P. Physiological Remodelling of Mitral Valve Chordae Tendineae In The Maternal Bovine Heart. Masters, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, S.M.; Pierlot, C.M.; Moeller, A.D. Physiological Remodeling of the Mitral Valve during Pregnancy. Am J Physiol-Heart C 2012, 303, H878–H892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodigepalli, K.M.; Thatcher, K.; West, T.; Howsmon, D.P.; Schoen, F.J.; Sacks, M.S.; Breuer, C.K.; Lincoln, J. Biology and Biomechanics of the Heart Valve Extracellular Matrix. JCDD 2020, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington-Sanders, C.; Meir, A.; Lawrence, L.; Stolinski, C. Structure of Chordae Tendineae in the Left Ventricle of the Human Heart. J Anatomy 1998, 192, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, E.H.; de Jonge, N.; McNeill, M.P.; Durst, C.A.; Grande-Allen, K.J. Age-Related Changes in Material Behavior of Porcine Mitral and Aortic Valves and Correlation to Matrix Composition. Tissue Eng Pt A 2010, 16, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.A.; Potts, J.D.; Yost, M.J.; Junor, L.; Brooks, T.; Tan, H.; Hoffman, S.; Hart, M.M.; Kern, M.J.; Damon, B.; et al. Periostin Promotes a Fibroblastic Lineage Pathway in Atrioventricular Valve Progenitor Cells. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Cheek, J.; Sakthivel, B.; Aronow, B.J.; Yutzey, K.E. Shared Gene Expression Profiles in Developing Heart Valves and Osteoblast Progenitor Cells. Physiol Genomics 2008, 35, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratzl, P. Chapter 2: Collagen Diversity, Synthesis and Assembly. In Collagen: Structure and Mechanics; Springer: New York, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-73905-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kalson, N.S.; Lu, Y.; Taylor, S.H.; Starborg, T.; Holmes, D.F.; Kadler, K.E. A Structure-Based Extracellular Matrix Expansion Mechanism of Fibrous Tissue Growth. eLife 2015, 4, e05958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herchenhan, A.; Kalson, N.S.; Holmes, D.F.; Hill, P.; Kadler, K.E.; Margetts, L. Tenocyte Contraction Induces Crimp Formation in Tendon-like Tissue. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2012, 11, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legerlotz, K.; Dorn, J.; Richter, J.; Rausch, M.; Leupin, O. Age-Dependent Regulation of Tendon Crimp Structure, Cell Length and Gap Width with Strain. Acta Biomater 2014, 10, 4447–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryan, A.; Shoushtari, A.H. Histology and Ultrastructure of the Developing Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon in Rabbits. Anatom Histol Embryol 2008, 37, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz-Timme, S.; Laumeier, I.; Collins, M.J. Aspartic Acid Racemization: Evidence for Marked Longevity of Elastin in Human Skin. Br J Dermatol 2003, 149, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.J.; Robson, P.; Hew, Y.; Keeley, F.W. Decreased Elastin Synthesis in Normal Development and in Long-Term Aortic Organ and Cell Cultures Is Related to Rapid and Selective Destabilization of mRNA for Elastin. Circ Res 1995, 77, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, J.; Alfieri, C.M.; Yutzey, K.E. BMP and FGF Regulatory Pathways Control Cell Lineage Diversification of Heart Valve Precursor Cells. Dev Biol 2006, 292, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, R.B.; Lincoln, J.; Deutsch, G.H.; Osinska, H.; Manning, P.B.; Benson, D.W.; Yutzey, K.E. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Organization in Developing and Diseased Aortic Valves. Circ Res 2006, 98, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettell, L.M.; McGowan, S.E. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Decreases Elastin Production by Neonatal Rat Lung Fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1994, 10, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, C.B.; Fontanilla, M.R.; Nugent, M.; Foster, J.A. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Decreases Elastin Gene Transcription through an AP1/cAMP-Response Element Hybrid Site in the Distal Promoter. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 33433–33439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowden, A.L.; Li, J.; Forhead, A.J. Glucocorticoids and the Preparation for Life after Birth: Are There Long-Term Consequences of the Life Insurance? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1998, 57, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, C.B.; Goud, H.D.; Bashir, M.; Rosenbloom, J.; Foster, J.A. Developmental Regulation of Aortic Elastin Gene Expression Involves Disruption of an IGF-I Sensitive Repressor Complex. Biochem Bioph Res Co 1993, 196, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, R.A.; Mariencheck, W.I.; Sandefur, S.; Crouch, E.C.; Parks, W.C. Glucocorticoids Upregulate Tropoelastin Expression during Late Stages of Fetal Lung Development. Am J Physiol-Lung C 1995, 268, L491–L500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




