Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Alzheimer’s Disease
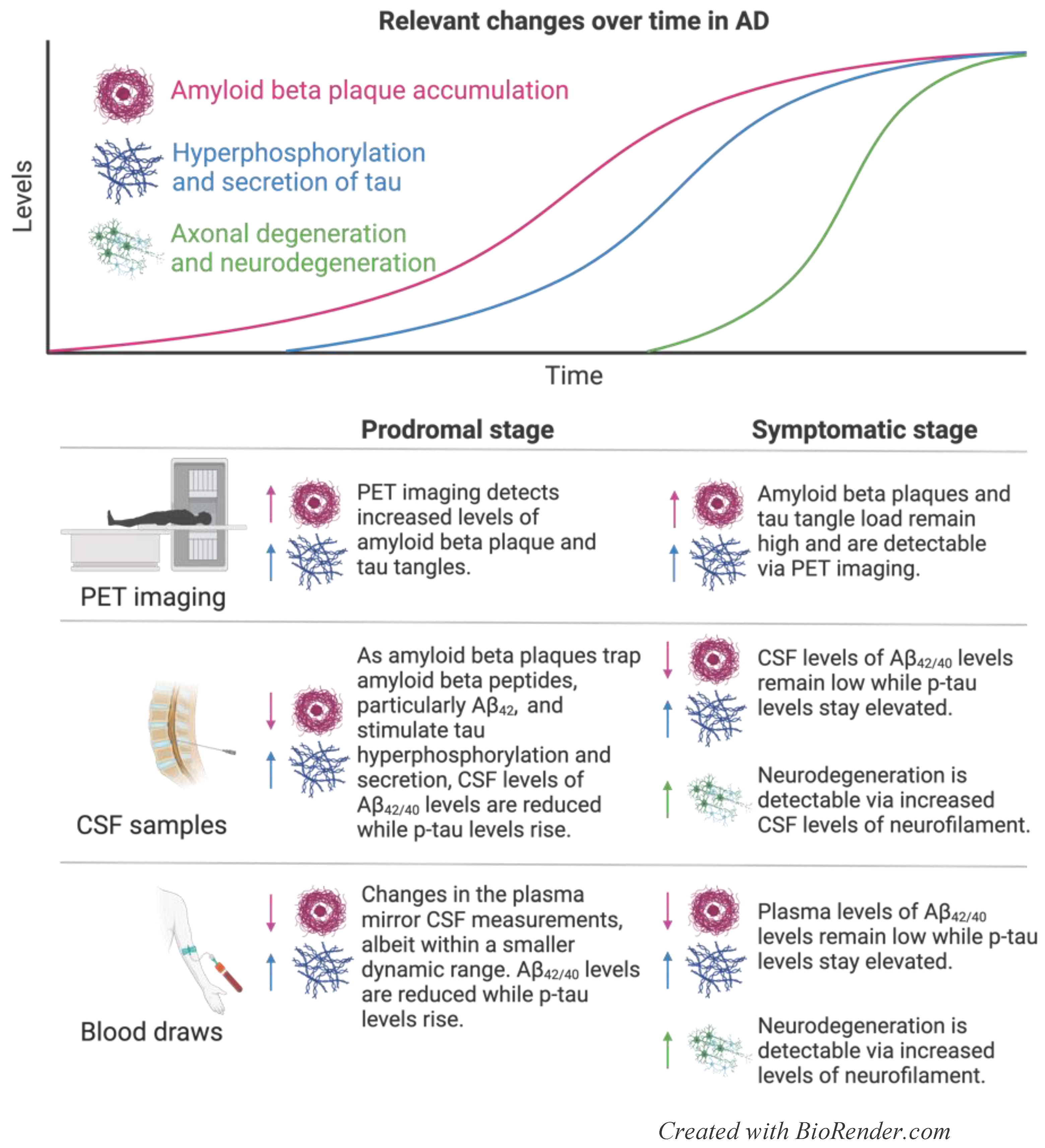
2.1. Current Prognostic and Diagnostic Indicators for AD
2.1.1. PET Scans
2.1.2. Aβ42/Aβ40
2.1.3. Phosphorylated Tau
2.1.4. Neurofilament Light
2.2. Biomarker Use and Misuse in AD Therapies and Clinical Trials
3. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
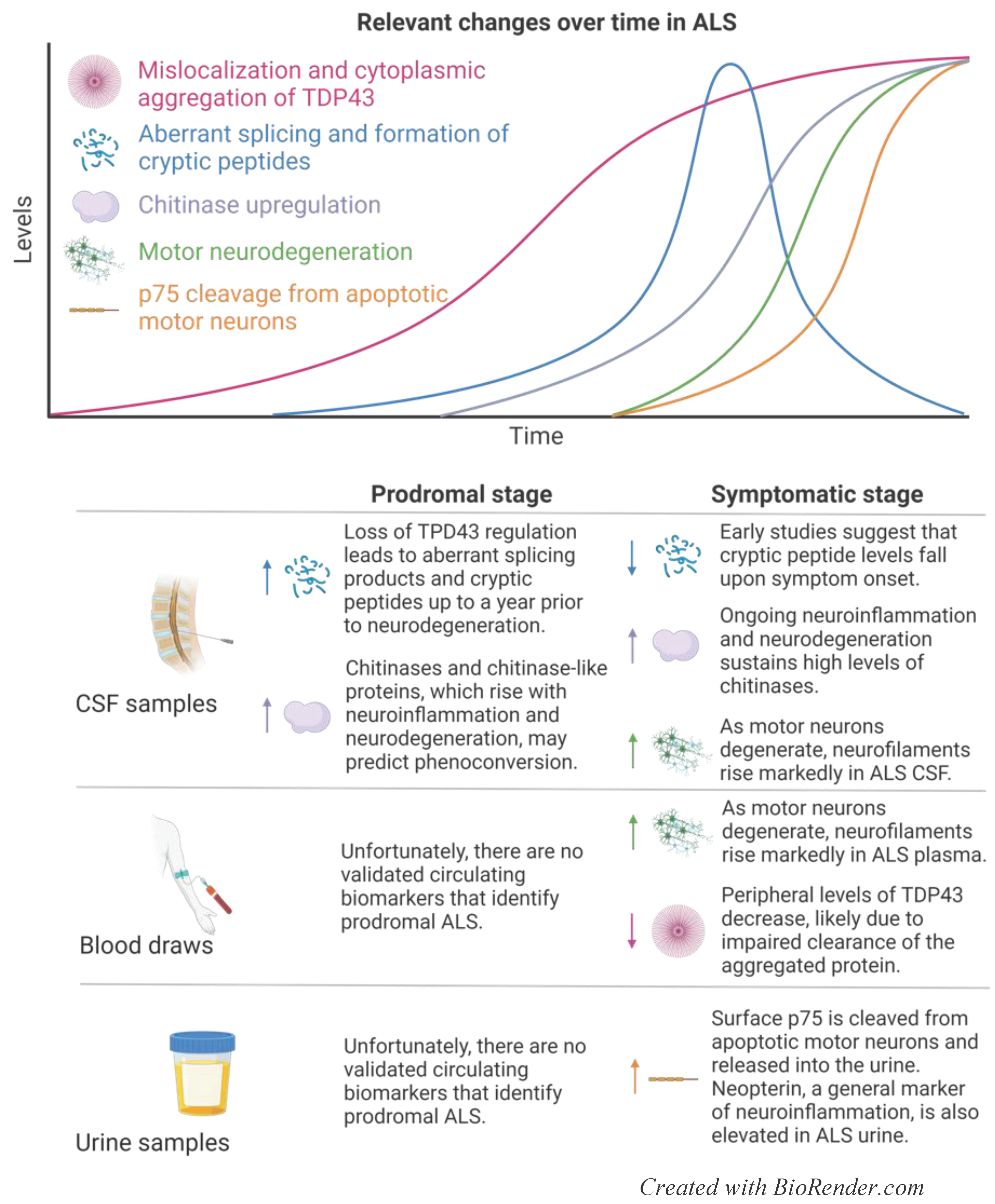
3.1. Current Prognostic and Diagnostic Indicators for ALS
3.1.1. Neurofilaments
3.1.2. TDP43
2.1.3. Chitinases
2.1.4. Urinary Markers: p75ECD and Neopterin
3.2. Biomarker Use in ALS Therapies and Clinical Trials
4. Parkinson’s Disease
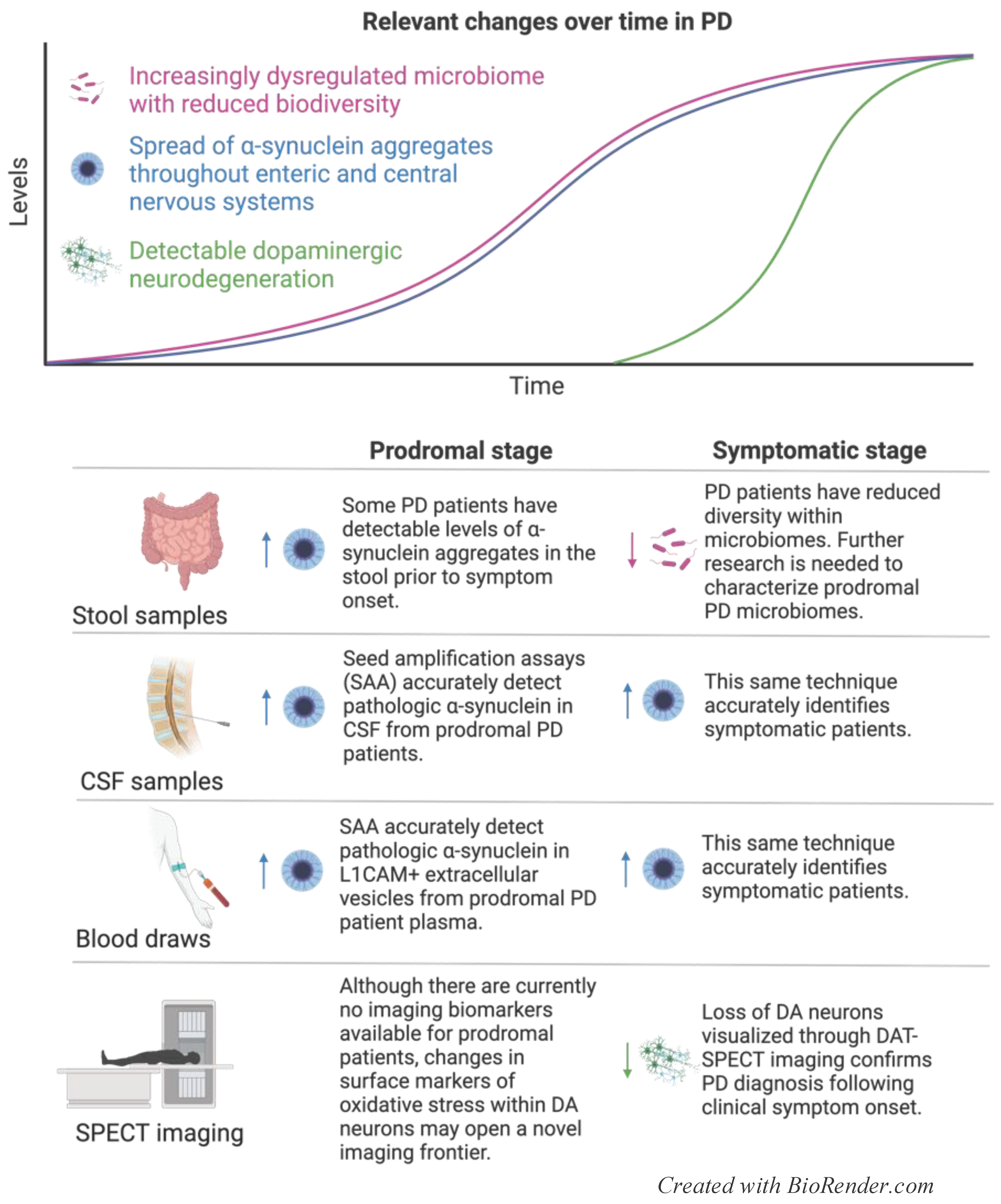
4.1. Current Prognostic and Diagnostic Indicators for PD
4.1.1. Imaging
4.1.2. Alpha-Synuclein
4.1.3. MIRO1
4.1.4. Glucocerebrosidase Activity
4.1.5. Microbiome
4.2. Biomarker Use in PD Therapies and Clinical Trials
4.2.1. Anti-α-Synuclein
4.2.2. GBA-Related Targets
4.2.3. Microbiome Restoration
5. Conclusions
6. Hopeful Directions on the Horizon
- Reduced CSF and plasma levels of Aβ42/Aβ40 and p-tau are strongly correlated to different stages of AD development. They are effective in identifying prodromal patients, offering therapeutic targets, and monitoring response to disease-modifying therapy, and will likely pave the way in validating future therapies.
- Although NfL has not been definitively linked to current disease-modifying therapies for treating ALS, this lack of association must be considered in the context of the short treatment window that patients typically have from diagnosis until death. More research is necessary to determine whether currently available ALS treatments slow the rate of neurodegeneration, and whether this correlates with NfL levels over time.
- New biomarkers that reflect TDP43 pathology offer fresh hope in identifying early disease and using gene therapy to restore healthy splicing regulation. Research into the potential of TDP43 gene therapy should investigate the ability to delay or prevent neurodegeneration, as determined through motor scores, cryptic peptide levels, and NfL levels.
- Alpha-synuclein is a well-established biomarker for predicting, diagnosing, and tracking the progression of PD severity. However, the lack of disease-modifying therapies available to PD patients precludes the ability to use biomarkers to monitor response to treatment. Further research is necessary to characterize early changes in mitophagy and the microbiome in prodromal patients to help identify potential therapeutic targets and establish additional readouts of pathology and response to treatment.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Schependom, J.; D’Haeseleer, M. Advances in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J Clin Med. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, H.; Bendlin, B.B. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease-preparing for a new era of disease-modifying therapies. Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordower, J.H.; Olanow, C.W.; Dodiya, H.B.; Chu, Y.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Halliday, G.M.; Bartus, R.T. Disease duration and the integrity of the nigrostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2013, 136, 2419–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelborghs, S.; Niemantsverdriet, E.; Struyfs, H.; Blennow, K.; Brouns, R.; Comabella, M.; Dujmovic, I.; van der Flier, W.; Frolich, L.; Galimberti, D.; Gnanapavan, S.; Hemmer, B.; Hoff, E.; Hort, J.; Iacobaeus, E.; Ingelsson, M.; Jan de Jong, F.; Jonsson, M.; Khalil, M.; Kuhle, J.; Lleo, A.; de Mendonca, A.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Nagels, G.; Paquet, C.; Parnetti, L.; Roks, G.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Scheltens, P.; Skarsgard, C.; Stomrud, E.; Tumani, H.; Visser, P.J.; Wallin, A.; Winblad, B.; Zetterberg, H.; Duits, F.; Teunissen, C.E. Consensus guidelines for lumbar puncture in patients with neurological diseases. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2017, 8, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Batrla, R.; El-Agnaf, O.; Galasko, D.R.; Lashuel, H.A.; Merchant, K.M.; Shaw, L.M.; Selkoe, D.J.; Umek, R.; Vanderstichele, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Zhang, J.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Coffey, C.; Hutten, S.J.; Frasier, M.; Taylor, P.; Investigating Synuclein Consortium of the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. A user’s guide for alpha-synuclein biomarker studies in biological fluids: Perianalytical considerations. Mov Disord. 2017, 32, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.J.; Janssen, O.; et al. Prevalence Estimates of Amyloid Abnormality Across the Alzheimer Disease Clinical Spectrum. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chetelat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, H.; Mutlu, S.A.; Bowser, D.A.; Moore, M.J.; Wang, M.C.; Zheng, H. The Amyloid Precursor Protein Is a Conserved Receptor for Slit to Mediate Axon Guidance. eNeuro. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Binette, A.P.; Groot, C.; Smith, R.; Strandberg, O.; Palmqvist, S.; Stomrud, E.; Tideman, P.; Ohlsson, T.; Jogi, J.; Johnson, K.; Sperling, R.; Dore, V.; Masters, C.L.; Rowe, C.; Visser, D.; van Berckel, B.N.M.; van der Flier, W.M.; Baker, S.; Jagust, W.J.; Wiste, H.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Hansson, O. Amyloid and tau PET-positive cognitively unimpaired individuals are at high risk for future cognitive decline. Nat Med. 2022, 28, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Mattsson, N.; Johansson, P.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K.; Olsson, M.; Hansson, O.; Swedish BioFINDER study group. Detailed comparison of amyloid PET and CSF biomarkers for identifying early Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2015, 85, 1240–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDade, E.; Wang, G.; Gordon, B.A.; Hassenstab, J.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Buckles, V.; Fagan, A.M.; Holtzman, D.M.; Cairns, N.J.; Goate, A.M.; Marcus, D.S.; Morris, J.C.; Paumier, K.; Xiong, C.; Allegri, R.; Berman, S.B.; Klunk, W.; Noble, J.; Ringman, J.; Ghetti, B.; Farlow, M.; Sperling, R.A.; Chhatwal, J.; Salloway, S.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Schofield, P.R.; Masters, C.; Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C.; Levin, J.; Jucker, M.; Bateman, R.J.; the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer. Longitudinal cognitive and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2018, 91, e1295–e1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Thijssen, E.H.; Vermunt, L.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Del Campo, M. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: towards clinical implementation. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovod, V.; Ramsey, K.N.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; Bollinger, J.G.; Hicks, T.; Schneider, T.; Sullivan, M.; Paumier, K.; Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.; Fagan, A.M.; Patterson, B.W.; Bateman, R.J. Amyloid beta concentrations and stable isotope labeling kinetics of human plasma specific to central nervous system amyloidosis. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, S.E.; Bollinger, J.G.; Ovod, V.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; Li, Y.; Gordon, B.A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Xiong, C.; Fagan, A.M.; Bateman, R.J. High-precision plasma beta-amyloid 42/40 predicts current and future brain amyloidosis. Neurology. 2019, 93, e1647–e1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavan, A.; Pannee, J.; Karikari, T.K.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Ashton, N.J.; Nicholas, J.M.; Cash, D.M.; Coath, W.; Lane, C.A.; Parker, T.D.; Lu, K.; Buchanan, S.M.; Keuss, S.E.; James, S.N.; Murray-Smith, H.; Wong, A.; Barnes, A.; Dickson, J.C.; Heslegrave, A.; Portelius, E.; Richards, M.; Fox, N.C.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Schott, J.M. Population-based blood screening for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease in a British birth cohort at age 70. Brain. 2021, 144, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Insel, P.S.; Stomrud, E.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Brix, B.; Eichenlaub, U.; Dage, J.L.; Chai, X.; Blennow, K.; Mattsson, N.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarker trajectories with increasing amyloid deposition in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med. 2019, 11, e11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, E.H.; La Joie, R.; Wolf, A.; Strom, A.; Wang, P.; Iaccarino, L.; Bourakova, V.; Cobigo, Y.; Heuer, H.; Spina, S.; VandeVrede, L.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Airey, D.C.; Shcherbinin, S.; Evans, C.D.; Sims, J.R.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Karydas, A.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Kramer, J.H.; Grinberg, L.T.; Seeley, W.W.; Rosen, H.; Boeve, B.F.; Miller, B.L.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Dage, J.L.; Rojas, J.C.; Boxer, A.L.; Advancing Research and Treatment for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (ARTFL) investigators. Diagnostic value of plasma phosphorylated tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat Med. 2020, 26, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, M.; Galimberti, D.; Elias, N.; Boonkamp, L.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; van Swieten, J.C.; Watts, K.; Paciotti, S.; Beccari, T.; Hu, W.; Teunissen, C.E. Novel CSF biomarkers to discriminate FTLD and its pathological subtypes. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018, 5, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Hagen, C.E.; Xu, J.; Chai, X.; Vemuri, P.; Lowe, V.J.; Airey, D.C.; Knopman, D.S.; Roberts, R.O.; Machulda, M.M.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Petersen, R.C.; Dage, J.L. Plasma phospho-tau181 increases with Alzheimer’s disease clinical severity and is associated with tau- and amyloid-positron emission tomography. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Suarez-Calvet, M.; Troakes, C.; King, A.; Emersic, A.; Aarsland, D.; Hye, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Ashton, N.J. Plasma p-tau181 accurately predicts Alzheimer’s disease pathology at least 8 years prior to post-mortem and improves the clinical characterisation of cognitive decline. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karikari, T.K.; Pascoal, T.A.; Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Rodriguez, J.L.; Chamoun, M.; Savard, M.; Kang, M.S.; Therriault, J.; Scholl, M.; Massarweh, G.; Soucy, J.P.; Hoglund, K.; Brinkmalm, G.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Gauthier, S.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Blennow, K. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: a diagnostic performance and prediction modelling study using data from four prospective cohorts. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, N.R.; Horie, K.; Sato, C.; Bateman, R.J. Blood plasma phosphorylated-tau isoforms track CNS change in Alzheimer’s disease. J Exp Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, N.R.; Bateman, R.J.; Hirtz, C.; Marin, P.; Becher, F.; Sato, C.; Gabelle, A.; Lehmann, S. Cerebrospinal fluid phospho-tau T217 outperforms T181 as a biomarker for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and PET amyloid-positive patient identification. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2020, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Smith, R.; Palmqvist, S.; Mattsson, N.; Airey, D.C.; Proctor, N.K.; Chai, X.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sims, J.R.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; Theunis, C.; Slemmon, R.; Mercken, M.; Kolb, H.; Dage, J.L.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau217 performs better than p-tau181 as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2020, 11, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Strandberg, O.; Smith, R.; Villegas, A.; Sepulveda-Falla, D.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Beach, T.G.; Blennow, K.; Dage, J.L.; Reiman, E.M.; Hansson, O. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA. 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Berron, D.; Smith, R.; Strandberg, O.; Proctor, N.K.; Dage, J.L.; Stomrud, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O. Associations of Plasma Phospho-Tau217 Levels With Tau Positron Emission Tomography in Early Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mila-Aloma, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvado, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; Day, T.A.; Gonzalez-Escalante, A.; Sanchez-Benavides, G.; Minguillon, C.; Fauria, K.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Dage, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Gispert, J.D.; Suarez-Calvet, M.; Blennow, K. Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-beta pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therriault, J.; Vermeiren, M.; Servaes, S.; Tissot, C.; Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Brum, W.S.; Lussier, F.Z.; Bezgin, G.; Stevenson, J.; Rahmouni, N.; Kunach, P.; Wang, Y.T.; Fernandez-Arias, J.; Socualaya, K.Q.; Macedo, A.C.; Ferrari-Souza, J.P.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; Bellaver, B.; Leffa, D.T.; Zimmer, E.R.; Vitali, P.; Soucy, J.P.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; Kolb, H.C.; Pascoal, T.A.; Saha-Chaudhuri, P.; Gauthier, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Rosa-Neto, P. Association of Phosphorylated Tau Biomarkers With Amyloid Positron Emission Tomography vs Tau Positron Emission Tomography. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Shanker, A.; Khera, T.; Subramaniam, B. Neurofilament light: a narrative review on biomarker utility. Fac Rev. 2021, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberlein, S.B.; Aisen, P.S.; Barkhof, F.; Chalkias, S.; Chen, T.; Cohen, S.; Dent, G.; Hansson, O.; Harrison, K.; von Hehn, C.; Iwatsubo, T.; Mallinckrodt, C.; Mummery, C.J.; Muralidharan, K.K.; Nestorov, I.; Nisenbaum, L.; Rajagovindan, R.; Skordos, L.; Tian, Y.; van Dyck, C.H.; Vellas, B.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Sandrock, A. Two Randomized Phase 3 Studies of Aducanumab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 9, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Chu, F.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, J. Impact of Anti-amyloid-beta Monoclonal Antibodies on the Pathology and Clinical Profile of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Focus on Aducanumab and Lecanemab. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 870517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, S. FDA approves Alzheimer’s drug lecanemab amid safety concerns. Nature. 2023, 613, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, O. Aduhelm: Biogen abandons Alzheimer’s drug after controversial approval left it unfunded by Medicare. BMJ. 2024, 384, q281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Jones, D.T.; Greicius, M.D. Failure to demonstrate efficacy of aducanumab: An analysis of the EMERGE and ENGAGE trials as reported by Biogen, December 2019. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, R.J.; Shan, N.; Reiser, H.J.; Marshall, F.; Shaw, P.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcimen, F.; Lopez, E.R.; Landers, J.E.; Nath, A.; Chio, A.; Chia, R.; Traynor, B.J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: translating genetic discoveries into therapies. Nat Rev Genet. 2023, 24, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturmey, E.; Malaspina, A. Blood biomarkers in ALS: challenges, applications and novel frontiers. Acta Neurol Scand. 2022, 146, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Wilkins, O.G.; Keuss, M.J.; Hill, S.E.; Zanovello, M.; Lee, W.C.; Bampton, A.; Lee, F.C.Y.; Masino, L.; Qi, Y.A.; Bryce-Smith, S.; Gatt, A.; Hallegger, M.; Fagegaltier, D.; Phatnani, H.; Consortium, N.A.; Newcombe, J.; Gustavsson, E.K.; Seddighi, S.; Reyes, J.F.; Coon, S.L.; Ramos, D.; Schiavo, G.; Fisher, E.M.C.; Raj, T.; Secrier, M.; Lashley, T.; Ule, J.; Buratti, E.; Humphrey, J.; Ward, M.E.; Fratta, P. TDP-43 loss and ALS-risk SNPs drive mis-splicing and depletion of UNC13A. Nature. 2022, 603, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.R.; Prudencio, M.; Koike, Y.; Vatsavayai, S.C.; Kim, G.; Harbinski, F.; Briner, A.; Rodriguez, C.M.; Guo, C.; Akiyama, T.; Schmidt, H.B.; Cummings, B.B.; Wyatt, D.W.; Kurylo, K.; Miller, G.; Mekhoubad, S.; Sallee, N.; Mekonnen, G.; Ganser, L.; Rubien, J.D.; Jansen-West, K.; Cook, C.N.; Pickles, S.; Oskarsson, B.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Shorter, J.; Myong, S.; Green, E.M.; Seeley, W.W.; Petrucelli, L.; Gitler, A.D. TDP-43 represses cryptic exon inclusion in the FTD-ALS gene UNC13A. Nature. 2022, 603, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guise, A.J.; Misal, S.A.; Carson, R.; Boekweg, H.; Watt, D.V.; Truong, T.; Liang, Y.; Chu, J.H.; Welsh, N.C.; Gagnon, J.; Payne, S.H.; Plowey, E.D.; Kelly, R.T. TDP-43-stratified single-cell proteomic profiling of postmortem human spinal motor neurons reveals protein dynamics in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. bioRxiv. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, J.H.; Santosa, M.M.; Lim, V.J.W.; Ho, B.X.; Taylor, A.; Khong, Z.J.; Ravits, J.; Fan, Y.; Liou, Y.C.; Soh, B.S.; Ng, S.Y. ALS motor neurons exhibit hallmark metabolic defects that are rescued by SIRT3 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1379–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMackin, R.; Bede, P.; Ingre, C.; Malaspina, A.; Hardiman, O. Biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: current status and future prospects. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023, 19, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaby, C.; Alcolea, D.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Illan-Gala, I.; Morenas-Rodriguez, E.; Barroeta, I.; Altuna, M.; Estelles, T.; Santos-Santos, M.; Turon-Sans, J.; Munoz, L.; Ribosa-Nogue, R.; Sala-Matavera, I.; Sanchez-Saudinos, B.; Subirana, A.; Videla, L.; Benejam, B.; Sirisi, S.; Lehmann, S.; Belbin, O.; Clarimon, J.; Blesa, R.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Rojas-Garcia, R.; Fortea, J.; Lleo, A. Differential levels of Neurofilament Light protein in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with a wide range of neurodegenerative disorders. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, A.; Pujol-Calderon, F.; Tjust, A.E.; Wuolikainen, A.; Hoglund, K.; Forsberg, K.; Portelius, E.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Andersen, P.M. Neurofilaments can differentiate ALS subgroups and ALS from common diagnostic mimics. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 22128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Gromicho, M.; Pronto-Laborinho, A.; Almeida, C.; Gomes, R.A.; Guerreiro, A.C.L.; Oliva, A.; Pinto, S.; de Carvalho, M. Cerebrospinal Fluid Chitinases as Biomarkers for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Dong, S.Q.; Yang, W.B.; Qian, T.; Liu, X.N.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, J.C.; Chen, X.J. Role of Blood Neurofilaments in the Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis. Front Neurol. 2021, 12, 712245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatar, M.; Wuu, J.; Andersen, P.M.; Lombardi, V.; Malaspina, A. Neurofilament light: A candidate biomarker of presymptomatic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and phenoconversion. Ann Neurol. 2018, 84, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Kasai, T.; Noto, Y.I.; Ohmichi, T.; Tatebe, H.; Kitaoji, T.; Tsuji, Y.; Kitani-Morii, F.; Shinomoto, M.; Allsop, D.; Teramukai, S.; Mizuno, T.; Tokuda, T. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Correlations between fluid biomarkers of NfL, TDP-43, and tau, and clinical characteristics. PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0260323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziff, O.J.; Neeves, J.; Mitchell, J.; Tyzack, G.; Martinez-Ruiz, C.; Luisier, R.; Chakrabarti, A.M.; McGranahan, N.; Litchfield, K.; Boulton, S.J.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Kelly, G.; Humphrey, J.; Patani, R. Integrated transcriptome landscape of ALS identifies genome instability linked to TDP-43 pathology. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, Z.; Lopez-Erauskin, J.; Baughn, M.W.; Zhang, O.; Drenner, K.; Sun, Y.; Freyermuth, F.; McMahon, M.A.; Beccari, M.S.; Artates, J.W.; Ohkubo, T.; Rodriguez, M.; Lin, N.; Wu, D.; Bennett, C.F.; Rigo, F.; Da Cruz, S.; Ravits, J.; Lagier-Tourenne, C.; Cleveland, D.W. Premature polyadenylation-mediated loss of stathmin-2 is a hallmark of TDP-43-dependent neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klim, J.R.; Williams, L.A.; Limone, F.; Juan, I.G.S.; Davis-Dusenbery, B.N.; Mordes, D.A.; Burberry, A.; Steinbaugh, M.J.; Gamage, K.K.; Kirchner, R.; Moccia, R.; Cassel, S.H.; Chen, K.; Wainger, B.J.; Woolf, C.J.; Eggan, K. ALS-implicated protein TDP-43 sustains levels of STMN2, a mediator of motor neuron growth and repair. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, K.E.; Jasin, P.; Braunstein, K.E.; Sinha, I.; Bowden, K.D.; Moghekar, A.; Oh, E.S.; Raitcheva, D.; Bartlett, D.; Berry, J.D.; Traynor, B.; Ling, J.P.; Wong, P.C. A fluid biomarker reveals loss of TDP-43 splicing repression in pre-symptomatic ALS. bioRxiv. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddighi, S.; Qi, Y.A.; Brown, A.L.; Wilkins, O.G.; Bereda, C.; Belair, C.; Zhang, Y.; Prudencio, M.; Keuss, M.J.; Khandeshi, A.; Pickles, S.; Hill, S.E.; Hawrot, J.; Ramos, D.M.; Yuan, H.; Roberts, J.; Sacramento, E.K.; Shah, S.I.; Nalls, M.A.; Colon-Mercado, J.; Reyes, J.F.; Ryan, V.H.; Nelson, M.P.; Cook, C.; Li, Z.; Screven, L.; Kwan, J.Y.; Shantaraman, A.; Ping, L.; Koike, Y.; Oskarsson, B.; Staff, N.; Duong, D.M.; Ahmed, A.; Secrier, M.; Ule, J.; Jacobson, S.; Rohrer, J.; Malaspina, A.; Glass, J.D.; Ori, A.; Seyfried, N.T.; Maragkakis, M.; Petrucelli, L.; Fratta, P.; Ward, M.E. Mis-spliced transcripts generate de novo proteins in TDP-43-related ALS/FTD. bioRxiv. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Luo, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, F.; Gao, X.; Qiao, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J. Chitinases as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinteac, R.; Montalban, X.; Comabella, M. Chitinases and chitinase-like proteins as biomarkers in neurologic disorders. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, N.; Steinbach, R.; Plaas, M.; Witte, O.W.; Brill, M.S.; Grosskreutz, J. Chitinase dysregulation predicts disease aggressiveness in ALS: Insights from the D50 progression model. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023, 94, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.; An, J.; Kovalik, T.; Gendron, T.; Petrucelli, L.; Bowser, R. Cross-sectional and longitudinal measures of chitinase proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and expression of CHI3L1 in activated astrocytes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020, 91, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, E.; Thompson, A.G.; Wuu, J.; Pelt, J.; Talbot, K.; Benatar, M.; Turner, M.R. CSF chitinases before and after symptom onset in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2020, 7, 1296–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.L.; Schultz, D.W.; Karnaros, V.; Shepheard, S.R. Urinary biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: candidates, opportunities and considerations. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepheard, S.R.; Wuu, J.; Cardoso, M.; Wiklendt, L.; Dinning, P.G.; Chataway, T.; Schultz, D.; Benatar, M.; Rogers, M.L. Urinary p75(ECD): A prognostic, disease progression, and pharmacodynamic biomarker in ALS. Neurology. 2017, 88, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunetta, C.; Lizio, A.; Gerardi, F.; Tarlarini, C.; Filippi, M.; Riva, N.; Tremolizzo, L.; Diamanti, S.; Dellanoce, C.C.; Mosca, L.; Sansone, V.A.; Campolo, J. Urinary neopterin, a new marker of the neuroinflammatory status in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol. 2020, 267, 3609–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepheard, S.R.; Karnaros, V.; Benyamin, B.; Schultz, D.W.; Dubowsky, M.; Wuu, J.; Chataway, T.; Malaspina, A.; Benatar, M.; Rogers, M.L. Urinary neopterin: A novel biomarker of disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol. 2022, 29, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esselin, F.; De la Cruz, E.; Hirtz, C.; Tiers, L.; Alphandery, S.; Baudesson, L.; Taieb, G.; Camu, W.; Lehmann, S. Repeated neurofilament light chain measurements did not capture Riluzole therapeutic effect in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022, 28, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Writing Group; the Edaravone (MCI-186) ALS 19 Study Group. Safety and efficacy of edaravone in well defined patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattee, G.L.; Genge, A.; Couratier, P.; Lunetta, C.; Sobue, G.; Aoki, M.; Yoshino, H.; Jackson, C.E.; Wymer, J.; Salah, A.; Nelson, S. Oral Edaravone - Introducing a Flexible Treatment Option for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother. 2023, 23, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, S.; Hendrix, S.; Dickson, S.P.; Knowlton, N.; Macklin, E.A.; Berry, J.D.; Elliott, M.A.; Maiser, S.; Karam, C.; Caress, J.B.; Owegi, M.A.; Quick, A.; Wymer, J.; Goutman, S.A.; Heitzman, D.; Heiman-Patterson, T.D.; Jackson, C.E.; Quinn, C.; Rothstein, J.D.; Kasarskis, E.J.; Katz, J.; Jenkins, L.; Ladha, S.; Miller, T.M.; Scelsa, S.N.; Vu, T.H.; Fournier, C.N.; Glass, J.D.; Johnson, K.M.; Swenson, A.; Goyal, N.A.; Pattee, G.L.; Andres, P.L.; Babu, S.; Chase, M.; Dagostino, D.; Hall, M.; Kittle, G.; Eydinov, M.; McGovern, M.; Ostrow, J.; Pothier, L.; Randall, R.; Shefner, J.M.; Sherman, A.V.; Pierre, M.E.S.; Tustison, E.; Vigneswaran, P.; Walker, J.; Yu, H.; Chan, J.; Wittes, J.; Yu, Z.F.; Cohen, J.; Klee, J.; Leslie, K.; Tanzi, R.E.; Gilbert, W.; Yeramian, P.D.; Schoenfeld, D.; Cudkowicz, M.E. Long-term survival of participants in the CENTAUR trial of sodium phenylbutyrate-taurursodiol in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve. 2021, 63, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganoni, S.; Macklin, E.A.; Hendrix, S.; Berry, J.D.; Elliott, M.A.; Maiser, S.; Karam, C.; Caress, J.B.; Owegi, M.A.; Quick, A.; Wymer, J.; Goutman, S.A.; Heitzman, D.; Heiman-Patterson, T.; Jackson, C.E.; Quinn, C.; Rothstein, J.D.; Kasarskis, E.J.; Katz, J.; Jenkins, L.; Ladha, S.; Miller, T.M.; Scelsa, S.N.; Vu, T.H.; Fournier, C.N.; Glass, J.D.; Johnson, K.M.; Swenson, A.; Goyal, N.A.; Pattee, G.L.; Andres, P.L.; Babu, S.; Chase, M.; Dagostino, D.; Dickson, S.P.; Ellison, N.; Hall, M.; Hendrix, K.; Kittle, G.; McGovern, M.; Ostrow, J.; Pothier, L.; Randall, R.; Shefner, J.M.; Sherman, A.V.; Tustison, E.; Vigneswaran, P.; Walker, J.; Yu, H.; Chan, J.; Wittes, J.; Cohen, J.; Klee, J.; Leslie, K.; Tanzi, R.E.; Gilbert, W.; Yeramian, P.D.; Schoenfeld, D.; Cudkowicz, M.E. Trial of Sodium Phenylbutyrate-Taurursodiol for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2020, 383, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatar, M.; Wuu, J.; Turner, M.R. Neurofilament light chain in drug development for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a critical appraisal. Brain. 2023, 146, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudkowicz, M.E.; Shefner, J.M. Regulatory Approval in ALS; When Is a Single Study Enough? Ann Neurol. 2022, 91, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.M.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Genge, A.; Shaw, P.J.; Sobue, G.; Bucelli, R.C.; Chio, A.; Van Damme, P.; Ludolph, A.C.; Glass, J.D.; Andrews, J.A.; Babu, S.; Benatar, M.; McDermott, C.J.; Cochrane, T.; Chary, S.; Chew, S.; Zhu, H.; Wu, F.; Nestorov, I.; Graham, D.; Sun, P.; McNeill, M.; Fanning, L.; Ferguson, T.A.; Fradette, S.; VALOR and OLE Working Group. Trial of Antisense Oligonucleotide Tofersen for SOD1 ALS. N Engl J Med. 2022, 387, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. NfL makes regulatory debut as neurodegenerative disease biomarker. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funayama, M.; Nishioka, K.; Li, Y.; Hattori, N. Molecular genetics of Parkinson’s disease: Contributions and global trends. J Hum Genet. 2023, 68, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Robak, L.A.; Yu, M.; Cykowski, M.; Shulman, J.M. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Syndrome. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023, 18, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellingiri, B.; Suriyanarayanan, A.; Abraham, K.S.; Venkatesan, D.; Iyer, M.; Raj, N.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Influence of heavy metals in Parkinson’s disease: an overview. J Neurol. 2022, 269, 5798–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouchieu, C.; Piel, C.; Carles, C.; Gruber, A.; Helmer, C.; Tual, S.; Marcotullio, E.; Lebailly, P.; Baldi, I. Pesticide use in agriculture and Parkinson’s disease in the AGRICAN cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Boltz, D.A.; Webster, R.G.; Smeyne, R.J. Viral parkinsonism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009, 1792, 714–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Le, W. New Understanding on the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Constipation in Parkinson’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 917499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.; Fedorova, T.D.; Bekker, A.C.; Iversen, P.; Ostergaard, K.; Krogh, K.; Borghammer, P. Objective Colonic Dysfunction is Far more Prevalent than Subjective Constipation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Colon Transit and Volume Study. J Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Taliyan, R.; Dubey, S.K. Comprehensive Review on Potential Signaling Pathways Involving the Transfer of alpha-Synuclein from the Gut to the Brain That Leads to Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023, 14, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Meng, H. The involvement of alpha-synucleinopathy in the disruption of microglial homeostasis contributes to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Commun Signal. 2024, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Rub, U.; Gai, W.P.; Del Tredici, K. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2003, 110, 517–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Derkinderen, P.; Kordower, J.H.; Freeman, R.; Munoz, D.G.; Kremer, T.; Zago, W.; Hutten, S.J.; Adler, C.H.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G. The Search for a Peripheral Biopsy Indicator of alpha-Synuclein Pathology for Parkinson Disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2017, 76, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, N.J.; Tumbarello, D.A. The relationship of alpha-synuclein to mitochondrial dynamics and quality control. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022, 15, 947191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiser, J.; Weindl, D.; Hiller, K. Complexity of dopamine metabolism. Cell Commun Signal. 2013, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, W.; Furuta, T.; Nakamura, K.C.; Hioki, H.; Fujiyama, F.; Arai, R.; Kaneko, T. Single nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons form widely spread and highly dense axonal arborizations in the neostriatum. J Neurosci. 2009, 29, 444–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacelli, C.; Giguere, N.; Bourque, M.J.; Levesque, M.; Slack, R.S.; Trudeau, L.E. Elevated mitochondrial bioenergetics and axonal arborization size are key contributors to the vulnerability of dopamine neurons. Curr Biol. 2015, 25, 2349–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostuk, E.W.; Cai, J.; Iacovitti, L. Subregional differences in astrocytes underlie selective neurodegeneration or protection in Parkinson’s disease models in culture. Glia. 2019, 67, 1542–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Ravindranath, V. Ca(V)1.3 L-Type Calcium Channels Increase the Vulnerability of Substantia Nigra Dopaminergic Neurons in MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheslow, L.; Byrne, M.; Kopenhaver, J.S.; Iacovitti, L.; Smeyne, R.J.; Snook, A.E.; Waldman, S.A. GUCY2C signaling limits dopaminergic neuron vulnerability to toxic insults. Res Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Conde, L.D.; Ramos-Acevedo, R.; Reyes-Hernandez, M.A.; Balbuena-Olvera, A.J.; Morales-Moreno, I.D.; Arguero-Sanchez, R.; Schule, B.; Guerra-Crespo, M. Alpha-Synuclein Physiology and Pathology: A Perspective on Cellular Structures and Organelles. Front Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Outeiro, T.F. Aggregation and beyond: alpha-synuclein-based biomarkers in synucleinopathies. Brain. 2024, 147, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderowf, A.; Concha-Marambio, L.; Lafontant, D.E.; Farris, C.M.; Ma, Y.; Urenia, P.A.; Nguyen, H.; Alcalay, R.N.; Chahine, L.M.; Foroud, T.; Galasko, D.; Kieburtz, K.; Merchant, K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Poston, K.L.; Seibyl, J.; Simuni, T.; Tanner, C.M.; Weintraub, D.; Videnovic, A.; Choi, S.H.; Kurth, R.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Coffey, C.S.; Frasier, M.; Oliveira, L.M.A.; Hutten, S.J.; Sherer, T.; Marek, K.; Soto, C.; arkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative. Assessment of heterogeneity among participants in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative cohort using alpha-synuclein seed amplification: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majbour, N.; Aasly, J.; Abdi, I.; Ghanem, S.; Erskine, D.; van de Berg, W.; El-Agnaf, O. Disease-Associated alpha-Synuclein Aggregates as Biomarkers of Parkinson Disease Clinical Stage. Neurology. 2022, 99, e2417–e2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Jiang, C.; Janzen, A.; Barber, T.R.; Seger, A.; Sommerauer, M.; Davis, J.J.; Marek, K.; Hu, M.T.; Oertel, W.H.; Tofaris, G.K. Neuronally Derived Extracellular Vesicle alpha-Synuclein as a Serum Biomarker for Individuals at Risk of Developing Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Hopfner, F.; Berg, D.; Hu, M.T.; Pilotto, A.; Borroni, B.; Davis, J.J.; Tofaris, G.K. Validation of alpha-Synuclein in L1CAM-Immunocaptured Exosomes as a Biomarker for the Stratification of Parkinsonian Syndromes. Mov Disord. 2021, 36, 2663–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Luo, N.; Yao, M.; Kang, W.; Liu, J. A longitudinal study on alpha-synuclein in plasma neuronal exosomes as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease development and progression. Eur J Neurol. 2020, 27, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, A.; Bunk, J.; Schaeffer, E.; Drobny, A.; Xiang, W.; Knacke, H.; Bub, S.; Luckstadt, W.; Arnold, P.; Lucius, R.; Berg, D.; Zunke, F. Detection of neuron-derived pathological α-synuclein in blood. Brain. 2022, 145, 3058–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Feng, T. alpha-Synuclein in salivary extracellular vesicles as a potential biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett. 2019, 696, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Becker, K.; Donadio, V.; Siedlak, S.; Yuan, J.; Rezaee, M.; Incensi, A.; Kuzkina, A.; Orru, C.D.; Tatsuoka, C.; Liguori, R.; Gunzler, S.A.; Caughey, B.; Jimenez-Capdeville, M.E.; Zhu, X.; Doppler, K.; Cui, L.; Chen, S.G.; Ma, J.; Zou, W.Q. Skin alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Seeding Activity as a Novel Biomarker for Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 78, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzkina, A.; Rossle, J.; Seger, A.; Panzer, C.; Kohl, A.; Maltese, V.; Musacchio, T.; Blaschke, S.J.; Tamguney, G.; Kaulitz, S.; Rak, K.; Scherzad, A.; Zimmermann, P.H.; Klussmann, J.P.; Hackenberg, S.; Volkmann, J.; Sommer, C.; Sommerauer, M.; Doppler, K. Combining skin and olfactory alpha-synuclein seed amplification assays (SAA)-towards biomarker-driven phenotyping in synucleinopathies. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffrath, A.; Schleyken, S.; Seger, A.; Jergas, H.; Ozduzenciler, P.; Pils, M.; Blomeke, L.; Cousin, A.; Willbold, J.; Bujnicki, T.; Bannach, O.; Fink, G.R.; Willbold, D.; Sommerauer, M.; Barbe, M.T.; Tamguney, G. Patients with isolated REM-sleep behavior disorder have elevated levels of alpha-synuclein aggregates in stool. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Miraglia, F.; Rota, L.; Benvenuti, L.; Di Salvo, C.; Testa, G.; Capsoni, S.; Carta, G.; Antonioli, L.; Cattaneo, A.; Blandizzi, C.; Colla, E.; Fornai, M. Enteric alpha-synuclein impairs intestinal epithelial barrier through caspase-1-inflammasome signaling in Parkinson’s disease before brain pathology. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Domenech, G.; Howden, J.H.; Covill-Cooke, C.; Morfill, C.; Patel, J.V.; Burli, R.; Crowther, D.; Birsa, N.; Brandon, N.J.; Kittler, J.T. Loss of neuronal Miro1 disrupts mitophagy and induces hyperactivation of the integrated stress response. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Li, L.; Vanhauwaert, R.; Nguyen, K.T.; Davis, M.D.; Bu, G.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Wang, X. Miro1 Marks Parkinson’s Disease Subset and Miro1 Reducer Rescues Neuron Loss in Parkinson’s Models. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1131–1140.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Bharat, V.; Conradson, D.M.; Nandakishore, P.; Wang, X. Miro1 Impairment in a Parkinson’s At-Risk Cohort. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021, 14, 734273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Schapira, A.H.V. GBA Variants and Parkinson Disease: Mechanisms and Treatments. Cells. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.E.; Park, H.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Tuncali, I.; Liu, G.; Locascio, J.J.; Shirvan, J.; Hutten, S.J.; Rotunno, M.S.; Viel, C.; Shihabuddin, L.S.; Wang, B.; Sardi, S.P.; Scherzer, C.R. Glucosylceramide in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with GBA-associated and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease enrolled in PPMI. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, S.; Schulte, C.; Wurster, I.; Machetanz, G.; Roeben, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Deuschle, C.; Hauser, A.K.; Bohringer, J.; Krageloh-Mann, I.; Waniek, K.; Lachmann, I.; Petterson, X.T.; Chiang, R.; Park, H.; Wang, B.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Maetzler, W.; Galasko, D.; Scherzer, C.R.; Gasser, T.; Mielke, M.M.; Hutten, S.J.; Mollenhauer, B.; Sardi, S.P.; Berg, D.; Brockmann, K. The Mutation Matters: CSF Profiles of GCase, Sphingolipids, alpha-Synuclein in PD(GBA). Mov Disord. 2021, 36, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Heijer, J.M.; Cullen, V.C.; Pereira, D.R.; Yavuz, Y.; de Kam, M.L.; Grievink, H.W.; Moerland, M.; Leymarie, N.; Khatri, K.; Sollomoni, I.; Spitalny, L.; Dungeon, L.; Hilt, D.C.; Justman, C.; Lansbury, P.; Groeneveld, G.J. A Biomarker Study in Patients with GBA1-Parkinson’s Disease and Healthy Controls. Mov Disord. 2023, 38, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.E.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Locascio, J.J.; Liao, Z.; Liu, G.; Choudhury, K.; Kuras, Y.I.; Tuncali, I.; Videnovic, A.; Hunt, A.L.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Hung, A.Y.; Herrington, T.M.; Hayes, M.T.; Hyman, B.T.; Wills, A.M.; Gomperts, S.N.; Growdon, J.H.; Sardi, S.P.; Scherzer, C.R. beta-Glucocerebrosidase activity in GBA-linked Parkinson disease: The type of mutation matters. Neurology. 2020, 95, e685–e696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Chen, W.; Gao, H.; Che, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, M. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Exerts a Protective Role in MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease via the TLR4/PI3K/AKT/NF-kappaB Pathway Stimulated by alpha-Synuclein. Neurochem Res. 2021, 46, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.; Meisner, A.; Schwiertz, A.; Unger, M.M.; Becker, A.; Fassbender, K.; Schnell, S.; Schafer, K.H.; Egert, M. Association between Parkinson’s disease and the faecal eukaryotic microbiota. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios, N.; Wilkinson, J.; Bjornevik, K.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; McIver, L.; Ascherio, A.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomics of the Gut Microbiome in Parkinson’s Disease: Prodromal Changes. Ann Neurol. 2023, 94, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bie, R.M.A.; Clarke, C.E.; Espay, A.J.; Fox, S.H.; Lang, A.E. Initiation of pharmacological therapy in Parkinson’s disease: when, why, and how. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okun, M.S. Diagnosis and Treatment of Parkinson Disease: A Review. JAMA. 2020, 323, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s disease: etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, G.; Taylor, K.I.; Anzures-Cabrera, J.; Marchesi, M.; Simuni, T.; Marek, K.; Postuma, R.B.; Pavese, N.; Stocchi, F.; Azulay, J.P.; Mollenhauer, B.; Lopez-Manzanares, L.; Russell, D.S.; Boyd, J.T.; Nicholas, A.P.; Luquin, M.R.; Hauser, R.A.; Gasser, T.; Poewe, W.; Ricci, B.; Boulay, A.; Vogt, A.; Boess, F.G.; Dukart, J.; D’Urso, G.; Finch, R.; Zanigni, S.; Monnet, A.; Pross, N.; Hahn, A.; Svoboda, H.; Britschgi, M.; Lipsmeier, F.; Volkova-Volkmar, E.; Lindemann, M.; Dziadek, S.; Holiga, S.; Rukina, D.; Kustermann, T.; Kerchner, G.A.; Fontoura, P.; Umbricht, D.; Doody, R.; Nikolcheva, T.; Bonni, A.; PASADENA Investigators and Prasinezumab Study Group. Trial of Prasinezumab in Early-Stage Parkinson’s Disease. N Engl J Med. 2022, 387, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.H.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Stefanis, L. Who Ever Said It Would Be Easy? Reflecting on Two Clinical Trials Targeting alpha-Synuclein. Mov Disord. 2023, 38, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Hernandez, P.; Liow, K.; Damiano, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Feng, D.; Chen, M.; Maccecchini, M. Buntanetap, a Novel Translational Inhibitor of Multiple Neurotoxic Proteins, Proves to Be Safe and Promising in Both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Patients. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 10, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, X.Y.; Yao, X.H.; Xu, L.J.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.P.; Liu, Y.; Pei, S.F.; Zhou, C.L. Evaluation of fecal microbiota transplantation in Parkinson’s disease patients with constipation. Microb Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




