1. Introduction
Nowadays, the scientific field of biomaterials gained great attention. Researchers are focused on the development of biomaterials compatible with the human body to preserve the physical integrity and life comfort of people with functional impairments or victims of injuries. Historically, several materials, such as metallic components, ceramics, polymers, and composite materials were widely used to assist in therapy. In recent decades, metallic materials have gained remarkable success due to their excellent mechanical properties [
1,
2,
3]. Stainless steels were the first metals to be used in orthopedics. The addition of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum improves corrosion resistance by forming a tough passive film. Cobalt-chromium alloys have been used in dental applications and recently in the manufacture of artificial joints [
4]. Titanium and its alloys, such as Ti
6Al
4V, are widely used as implant materials in orthopedic surgeries and have shown excellent performance in electrochemical corrosion properties and a favorable biological response [
4,
5]. Despite all the advantages of using these materials, there were also some dramatic failures. The placement implants (orthopedic, dental, etc.) can be excellent growth supports for pathogens, which, eventually, cause the appearance of biofilms. These biofilms can cause major complications since the antibiotic treatments become ineffective due to the difficulty for the antibiotic to reach the biofilm [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. The therapeutic responses currently used are therefore solutions for curative purposes, generally quite heavy, most often involving a second surgical operation. In this context, it is essential to develop preventive rather than curative solutions, to avoid bacterial colonization at the end of the surgical act. The choice of material and the antibacterial agent is crucial to guarantee both an effective action against microorganisms and harmlessness to the human body, in the best case a favorable biological activity (osteoconduction, osteointegration, etc.).
It has been reported that the use of bioactive glass can stimulate the good functioning of the implant due to its ability to increase tissue integration and enhance its regeneration [
11,
12,
13]. Based on the inorganic composition of natural bone, Hench stipulated that a biomaterial capable of forming hydroxyapatite in an
in vivo environment would be able to replace damaged bone tissue without being rejected by the human body [
11,
14]. Thus, the 45S5 bioglass® composed of 45% SiO
2, 24.5% Na
2O, 24.5% CaO, and 6% P
2O
5 (wt %) was produced. It represents one of the first examples of a bioactive glass capable of intimately and firmly bonding chemically to surrounding bone tissue without being rejected by the living environment and is considered to be the ancestor of the latest generation of bioactive materials. Indeed, when subjected to an
in vivo environment, the bioglass starts to release ions (Na
+, P
5+, Ca
2+) which leads to the formation of a silanols dioxide layer on the surface [
15,
16]. This layer attracts ions such as calcium and phosphate which at a high concentration entails the formation of a phosphocalcic layer on the surface of the glass, similar in composition to the mineral phase of bone [
17,
18,
19]. This apatite layer then allows the absorption of proteins and the adhesion of cells that proliferate, differentiate, and secrete collagen [
20]. The incorporation of collagen fibrils into the growing apatite layer results in a microstructure similar to that of the ligament-bone interface, which explains the important integration of bioglass within-host bone tissue [
21].
Recently, many efforts have been made to promote angiogenesis, regeneration, and the antibacterial potential of bioglass by the insertion of metal ions in the glass network [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. Copper is one of the necessary elements for the human body playing a critical role in angiogenesis and regeneration of hard and soft tissue [
29,
30]. Several studies performed on bioactive glass (BG), show that the incorporation of Cu enhances significantly angiogenesis by stabilizing the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) in human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSC) [
31,
32]. From the bioactivity point of view, the incorporation of copper into the BG network doesn’t provoke any adverse effect, i.e., the formation of hydroxyapatite precipitation on the bioglass surface is preserved after contact with the biological body [
31,
33]. Beyond being useful in stimulating tissue regeneration, copper is used with a potential antimicrobial effect against several pathogenic bacteria such as
Staphylococcus aureus,
Escherichia coli,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and,
Staphylococcus epidermis [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38]. All these promising properties make copper a promising ion to be inserted into bioglass to fabricate a multifunctional material for implant coating that combines osteoconduction, and osteogenesis with novel therapeutic functionalities.
This work aims to develop 45S5 bioglass modified by copper oxide insertion to be applied as a coating material for implants. The effect of copper doping on the structure and the morphology of the bioglasses prepared by melt-quenching were investigated in this study. The changes in the electrical properties were also verified due to the ability of these materials to electrically polarize, thus optimizing the osseointegration responses. The bioactivity of these glasses was also evaluated in vitro through an immersion test in simulated body fluid (SBF).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Glass Synthesis
Both base and modified bioglasses had been synthesized based on the composition of 45S5 (45% SiO
2, 24.5% Na
2O, 24.5% CaO, and 6% P
2O
5 (wt%)) proposed by Larry L. Hench [
8]. The bioactive glass composition 45S5 was studied by the introduction of various concentrations of copper, CuO, from 0 to 8 mol% (designed by BG0, BG0.5, …, BG8). In the synthesis of bioglasses, high-purity grade (>99%) SiO
2, P
2O
5, CaCO
3, Na
2CO
3, and CuO, supplied by Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany, were used as the starting compositions. These materials were mixed and homogenized in an agate vessel with milling agate balls, for 1 h at 300 rpm using a high-energy planetary ball milling system [
39]. The mixture was then calcinated for 8 h at 800 °C and, afterward, was melted in platinum crucibles that were placed in an electric furnace at 1300 °C for 1 h. The homogeneity was ensured by repeated hand mixing of the melt. Effective cooling was achieved by quenching the molten glasses after removal from the furnace in between casting plates to obtain bulk samples.
2.2. Thermal Analysis
Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) measurements were simultaneously used to examine the thermal characteristics of the glasses. An Hitachi STA 7300 system was used for those measurements, which were performed under Nitrogen N50 (99.999%) flowing at 200 mL/min with a heating rate of 10 °C/min.
2.3. Structural and Morphological Characterization
The X-ray diffraction, XRD, patterns were acquired at room temperature using a Malvern Panalytical Aeris powder diffractometer adopting CuKα radiation (λ = 1.54056 Å). The measurement parameters had a scan step of 0.02° in 1 s, in a 2θ angle range of 10-60°.
The Raman spectroscopy of the bulk glasses was performed on a Jobin Yvon HR 800 spectrometer with an Ar+ laser (λ = 532 nm), and the spectra were acquired in a back-scattering geometry between 200 and 1500 cm−1 using a 50X lens to focus the sample.
The morphologies of the samples were analyzed by TESCAN Vega 3 scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The bulk samples were coated with carbon before the microscopic observation. A Bruker EDS system was used in conjunction with a TESCAN Vega 3 microscope to perform a semiquantitative evaluation of the chemical elements on the surface of the samples. The measurements were taken at several surface sites using a 5 µm diameter electron beam spot.
2.4. Electrical Characterization
For the electrical analysis, the bulk glass samples were polished to obtain parallel surfaces with a thickness of around 1 mm. Silver conducting paste was applied to the opposite parallel sides of the samples. The AC electrical conductivity (σ
ac) was carried out by an Agilent 4294A precision impedance meter, measuring in the C
p–R
p configuration, in the temperature range from 200 K to 400 K with 5 K step and in a broad frequency window from 100 Hz to 1 MHz. The dielectric behaviour is investigated with the complex permittivity 𝜀* and the complex electric modulus M* formalisms, expressed by [
40,
41,
42,
43]:
where C
p and R
p are the measured capacitance and resistance, d is the sample thickness, A the electrode area, ω is the angular frequency, and ɛ
0 the permittivity of the free space (8.8542 × 10
−12 F/m).
The complex AC conductivity (σ
ac*) was determined using the following relation [
44,
45]:
The direct current (DC) conductivity measurements were carried out using a 617 Keithley electrometer. The measurement was performed in the temperature range between 200 and 400 K, where a DC voltage of 100 V was applied across the bulk glass.
The activation energy (E
A) for the high-temperature range was determined in both AC and DC by fitting the data to the Arrhenius equation [
41,
44,
46]:
where σ
0 is a pre-exponential factor, E
A is the activation energy, k
B is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
2.5. In Vitro Bioactivity Evaluation
The bioactivity test was performed on 7 mm diameter pressed pellets. The assessment of bioactivity was conducted following the “ISO 23317—Implants for surgery—In vitro evaluation for the apatite-forming ability of implant materials” standard. After intervals of 24, 96 and 336 h of immersion in simulated bodily fluid (SBF) with stirring, the samples were withdrawn from the medium and rinsed with deionized water. To create an environment close to the biological one, the medium was changed every 48 h.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Analysis
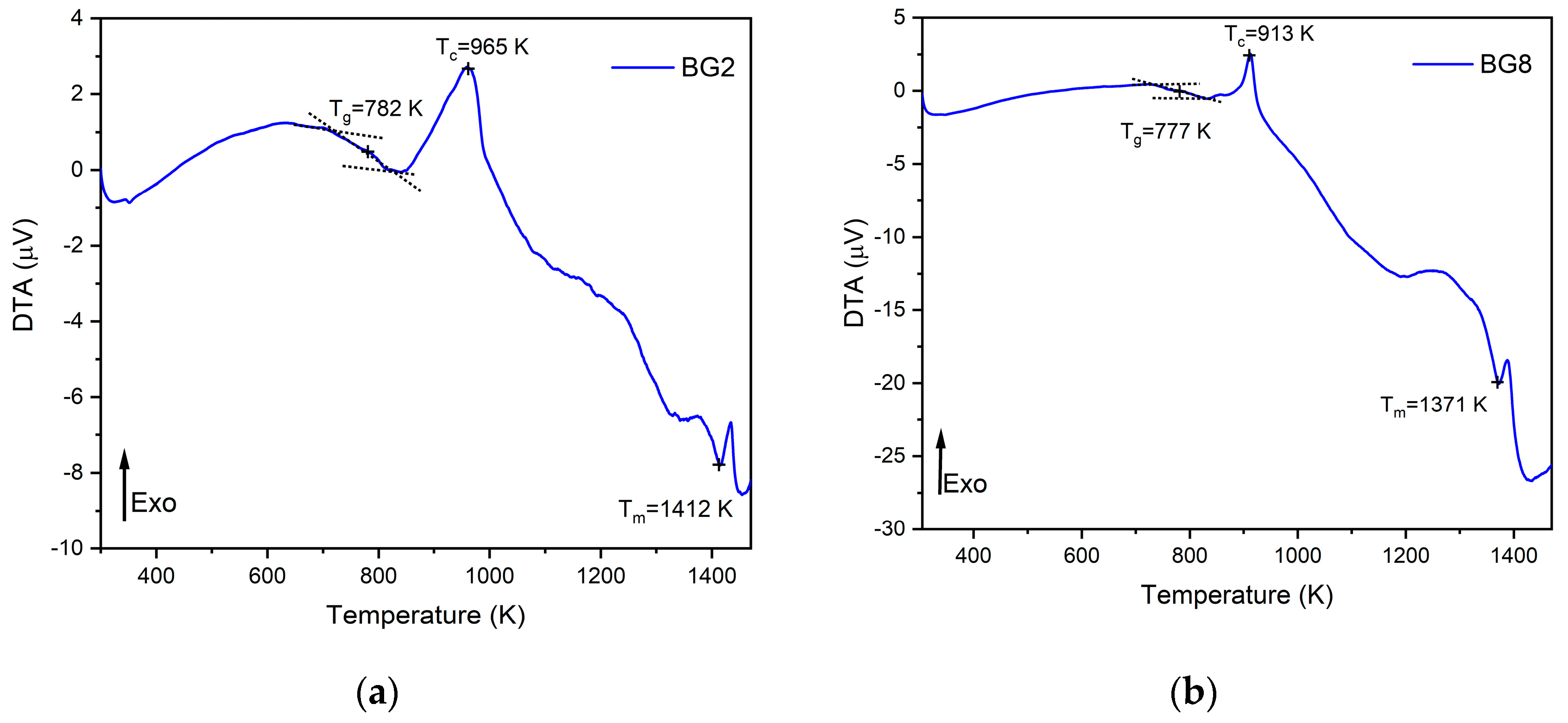
The thermal response of the bioglasses is illustrated in
Figure 1. The thermogram of BG2 and BG8 shows the existence of a glass transition temperature, T
g, followed by an exothermic peak, T
c, attributed to the structure modification related to the formation of crystalline phases, and at higher temperature an endothermic peak, T
m assigned to the melting point of bioglass.
In a previous study [
47], a thermal analysis of the 45S5 bioglass was conducted, revealing a thermal response similar to that of the modified bioglasses. The characteristic temperature values of modified glasses with the comparison of the 45S5 bioglass are shown in
Table 1. It can be noted that the characteristic temperatures decrease when the content of CuO introduced in the glass network increases. These results align with those reported in the literature [
48]. The changes in the glass temperature might be explained by the type of chemical bonds in the bioglass structure. Due to the stronger affinity of copper to phosphate than to silica groups, the P–O–P bonds were easily broken compared to Si–O–Si chemical bonds [
49]. Thus, Cu–O ionic bonds were created. These bonds have more covalent character (the ionicity iG of Cu–O bonds is equal to 0.617) and replace the more ionic bonds such as Ca–O (iG=0.707) [
50]. As a result, the thermal resistance of glasses is reduced, which could explain the decrease of T
g, T
c, and T
m.
3.2. Structural Characterization
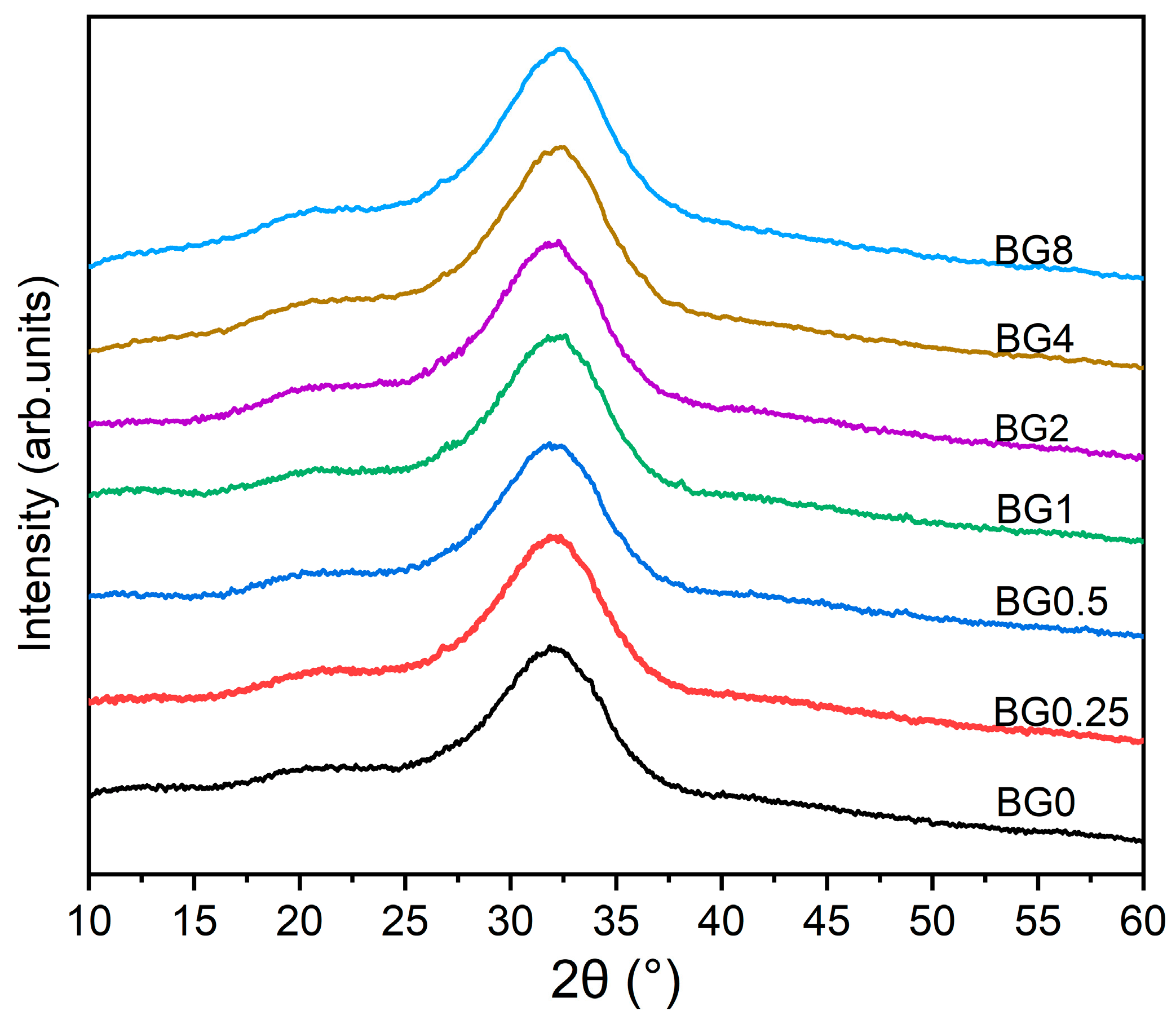
The XRD patterns of the prepared bioglasses, indicated in
Figure 2, show an amorphous hump arising from the glasses having no long-range atomic order in their molecular arrangement. The similarity in the XRD patterns of all samples demonstrates that the structure of the glass was not affected by the applied exchange conditions.
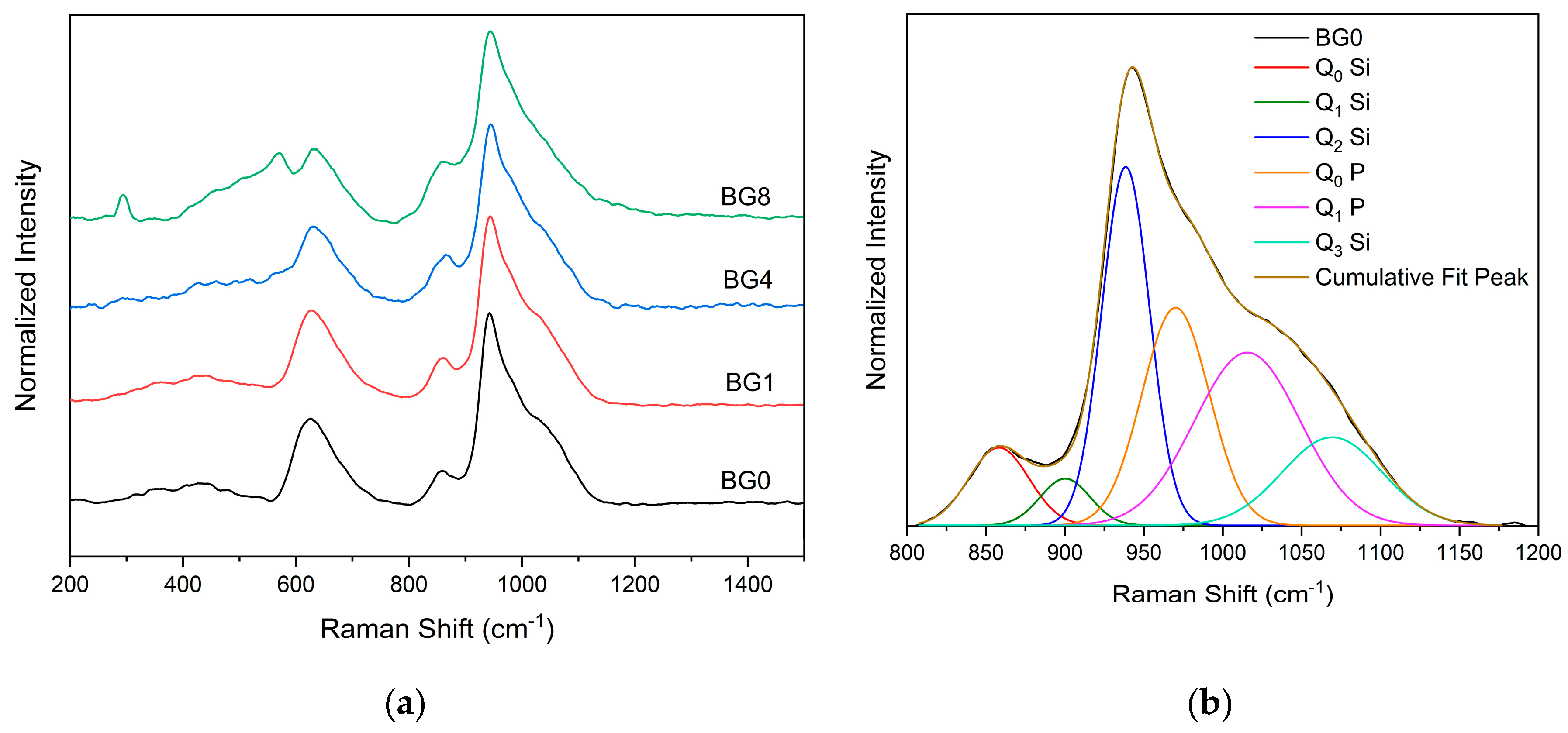
Figure 3a displays the Raman spectral measurement which clearly shows that the different bioglasses exhibit a very similar spectrum. However, at a high CuO content, two bands assigned to A
g and B
g modes of CuO appear at 292 and 568 cm
-1 respectively [
9,
51]. A Gaussian fitting was used to deconvolve the Raman spectra of the bioglass base for a more thorough investigation (
Figure 3b). In silicate glasses, vibrational modes at high wavenumbers (> 800 cm
-1) are considered relevant. Six vibrational modes located at around 855 cm
-1,903 cm
-1, 938 cm
-1, 967 cm
-1, 1018 cm
-1, and 1067 cm
-1 can be observed, which are attributed to symmetric stretching of Q
0 Si, Q
1 Si, Q
2 Si, Q
0 P, Q
1 P and Q
3 Si units, respectively [
52,
53,
54,
55].
Figure 4 depicts the sum of the area of Raman vibration bands associated with non-bridging oxygen ions (NBOs), i.e., the sum of Q
0, Q
1, Q
2, and Q
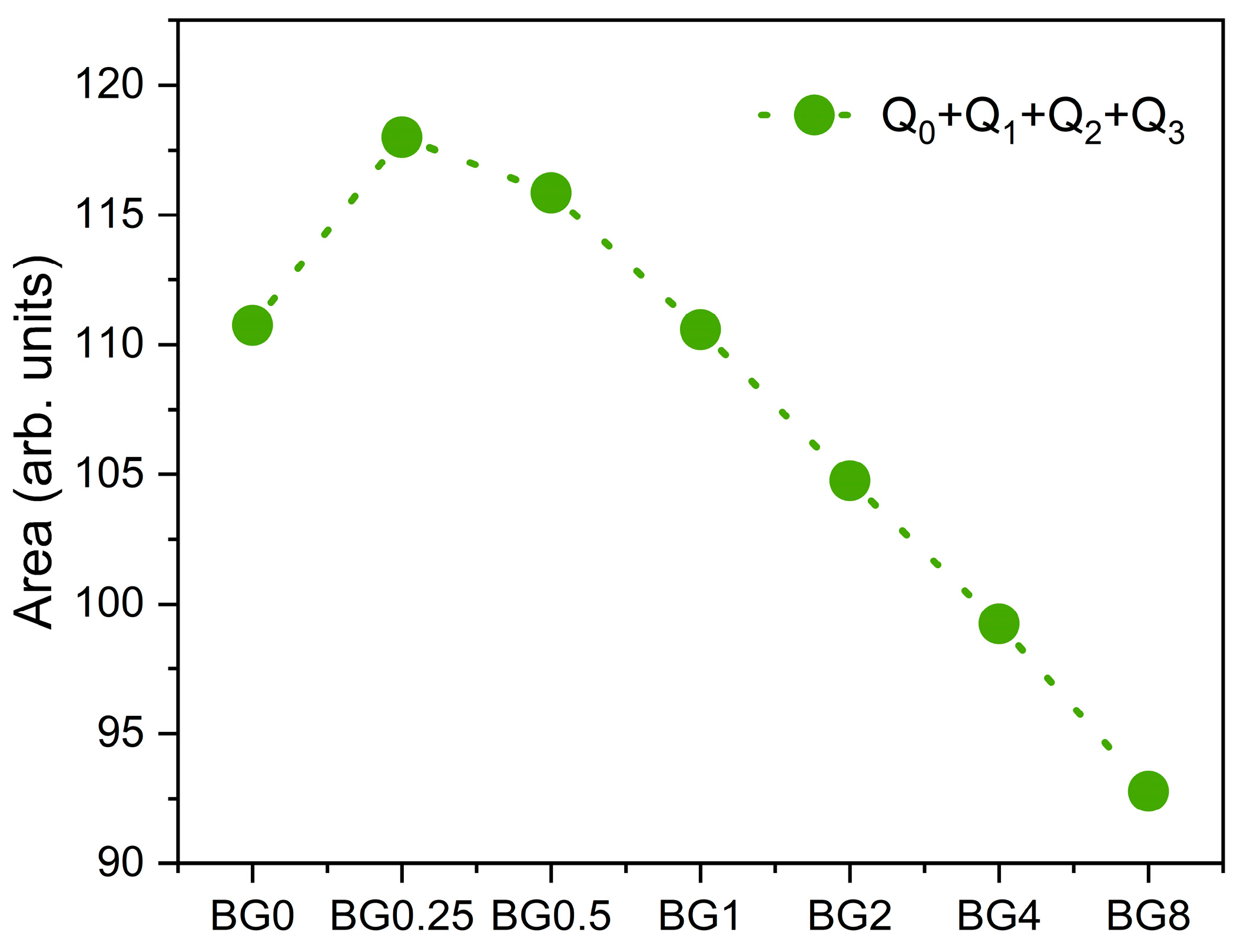
3 units, as a function of CuO content. It can be seen that compared to the bioglass base, the concentration of NBOs increases with increasing the CuO concentration up to 0.5%, then it decreases with further increases in CuO content.
3.3. Morphological Characterization
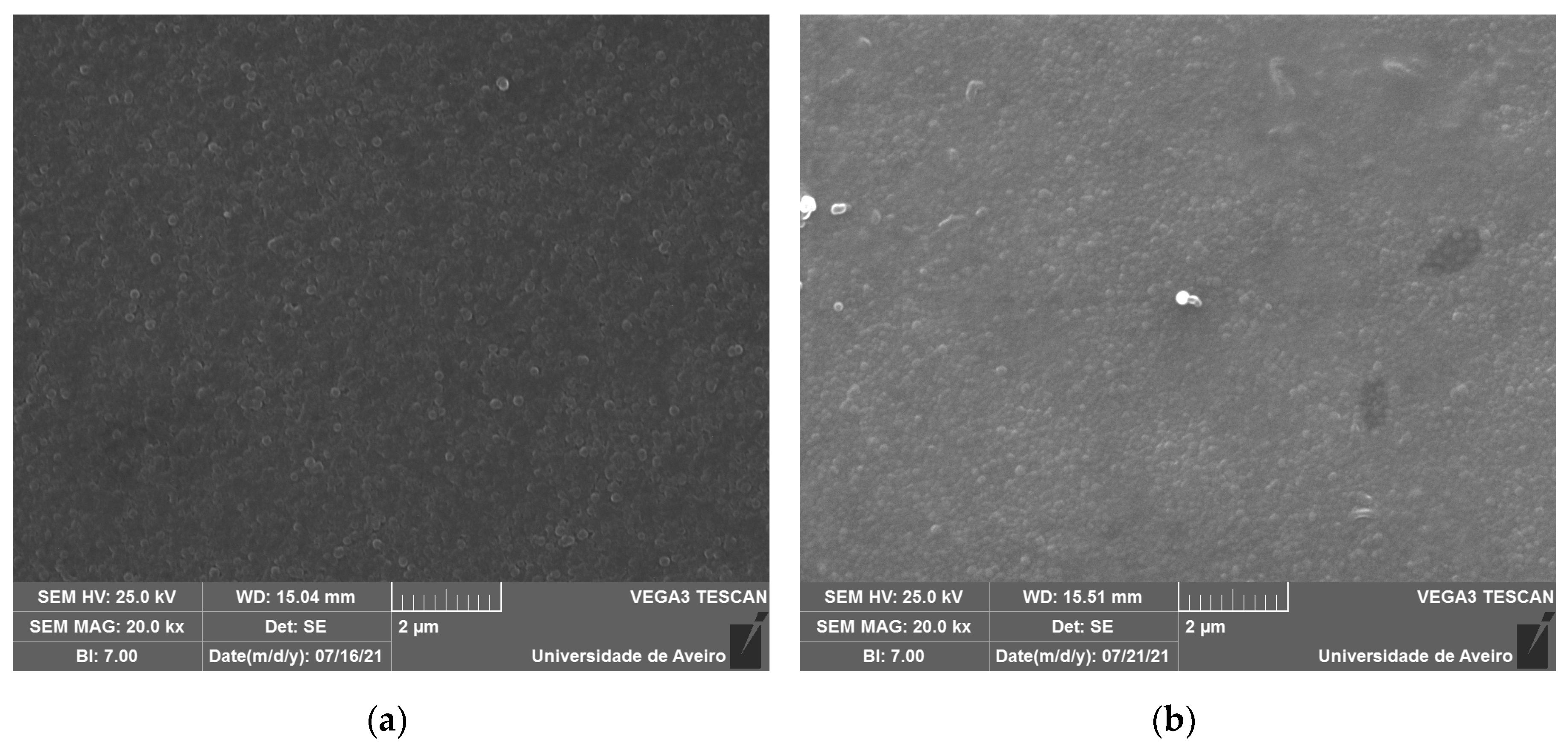
The SEM micrographs, represented in
Figure 5, revealed spherical inclusions in the amorphous matrix in both free and fracture surfaces. The morphology confirms its glassy structure.
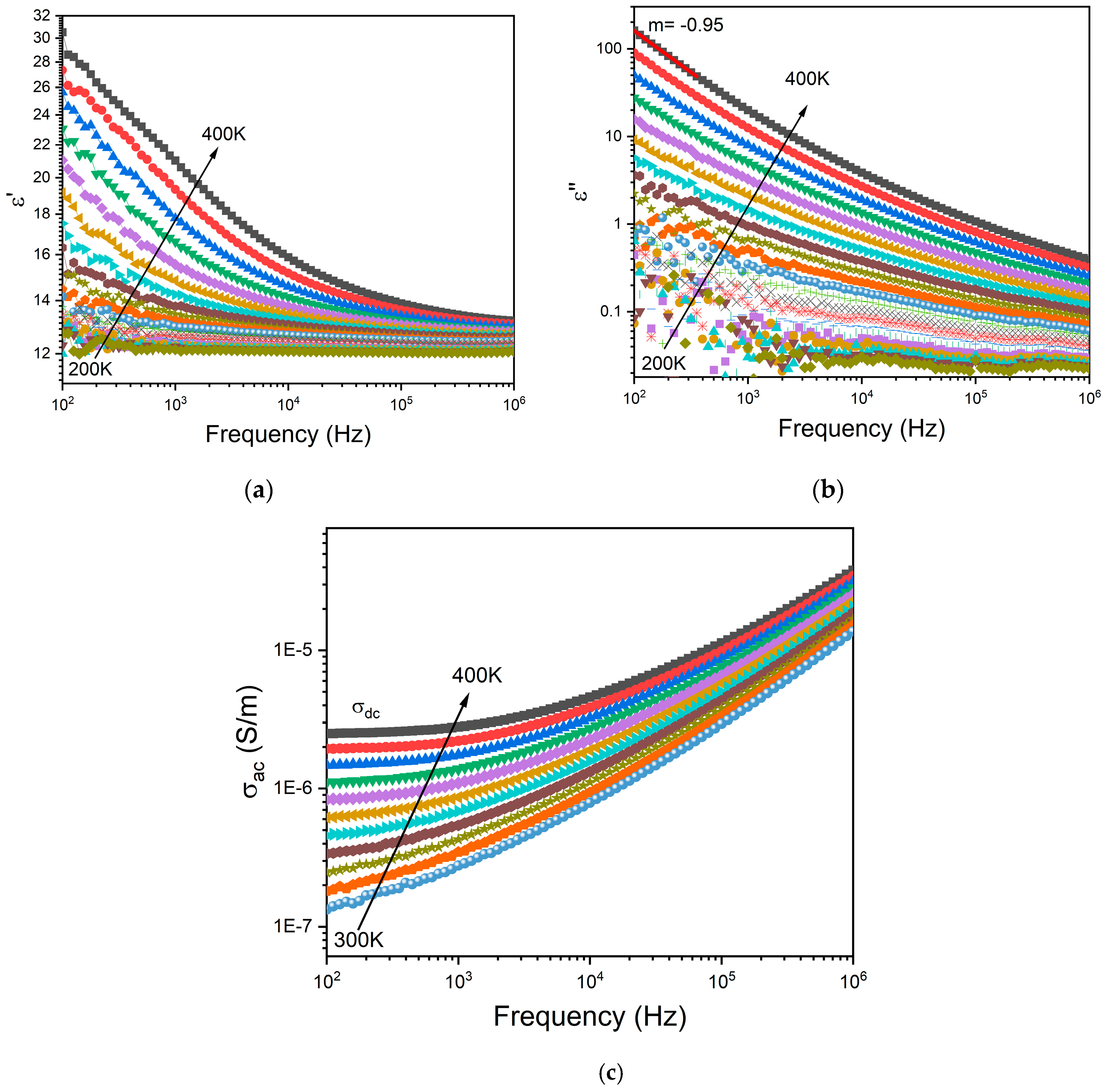
3.4. Electrical Properties
Figure 6a,b depict the frequency dependence of the dielectric permittivity ε′ and the loss factor ε″, respectively, for the BG2 glass. In this representation, the presence of dielectric relaxation behavior was not observed. At the high temperatures and low frequencies region, those variations show a linear increase with a slope of ε ‘‘ close to −1 (m= -0.95 at 400 K –
Figure 5b), indicating thus the existence of the DC conductivity effect [
56]. The frequency dependency of AC conductivity may be used to detect this effect. The appearance of a horizontal plateau at low frequencies correlates to the DC conductivity effect, as seen in
Figure 6c.
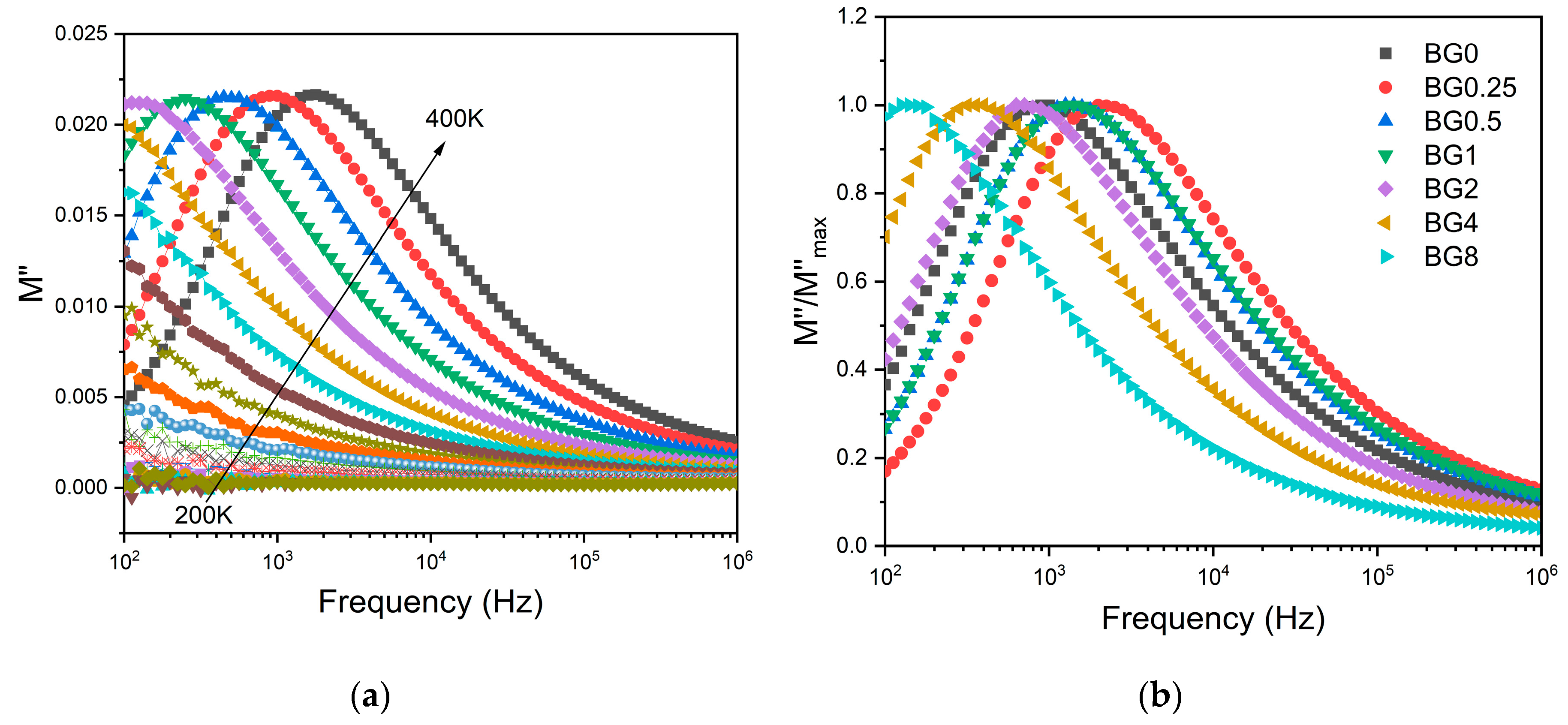
To minimize the electrode polarization and conductivity effects, the electric modulus (M*=1/ ε*) was used [
57]. The presence of a dielectric relaxation was observed, whose maximum shifts to higher frequencies with increasing temperature (
Figure 7a). Thus, the relaxation behavior should be associated with the electrical dipole form between the network modifier ions and the NBOs ions.
Figure 7b shows a comparison of normalized imaginary parts of the electric modulus M″/M″
max as a function of frequency for the different CuO contents introduced into the Bioglass network.
The results presented in
Figure 7b reveal that increasing the CuO concentration to 0.25 mol% causes a shift in the peak of the electrical modulus to a higher frequency, implying a reduction in the relaxation time. With a further increase in CuO concentration, the dielectric relaxation peak shifts towards a lower frequency range, indicating an increase in the relaxation time. The increase in the relaxation time with the insertion of more CuO suggests a decrease of freedom for dipoles in the glass network to orient with the direction of the applied electric field. These findings indicate that the network of the glass containing a concentration of CuO above 0.25 mol% is more “polymerized”. This change in the glass structure is mainly due to a change in NBOs content as depicted in
Figure 4.
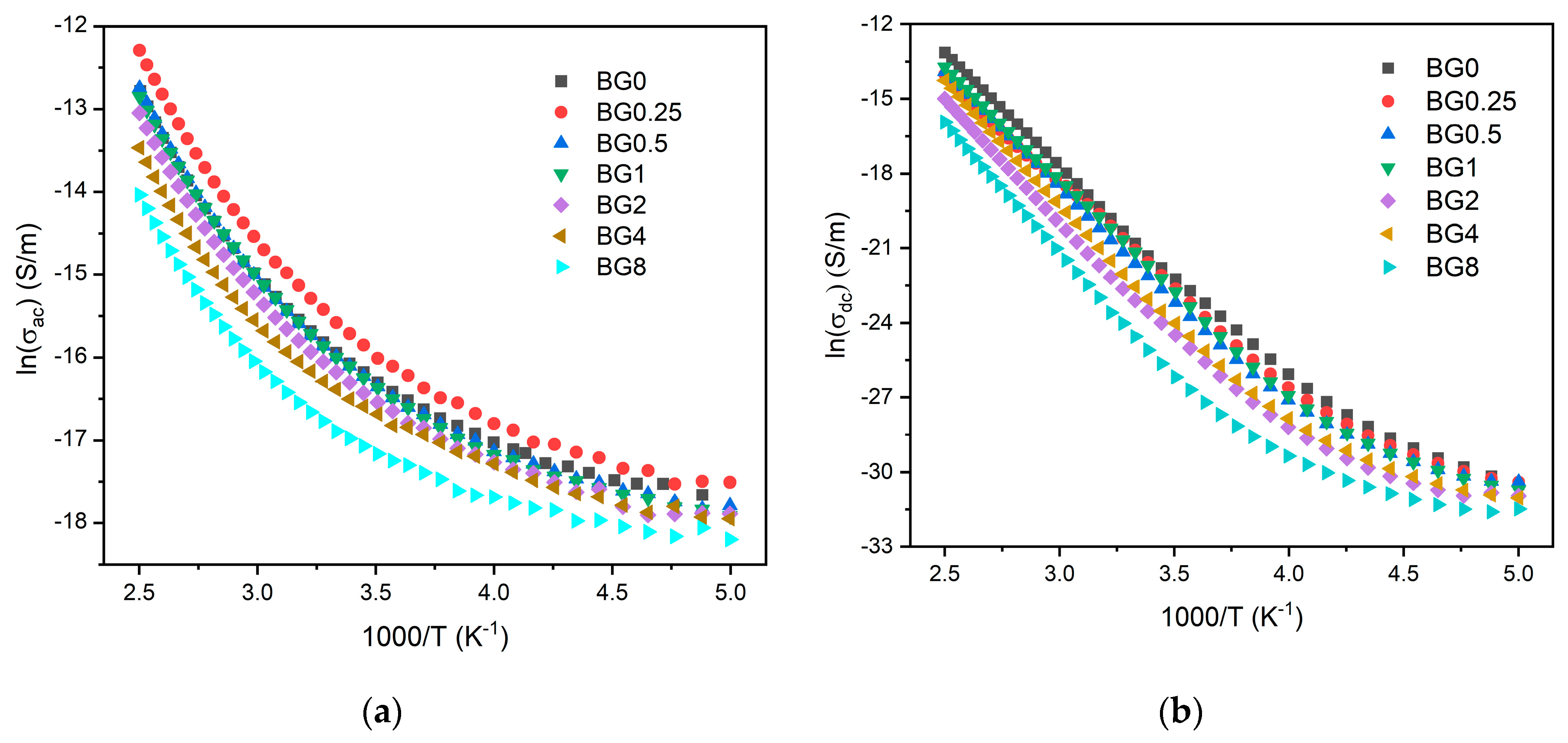
Figure 8a,b display the AC and DC conductivity, in logarithmic scale, versus 1000/T, respectively. For all the samples, an increase in temperature is related to the increase in the charge carriers’ mobility, and at the high-temperature range this variation becomes linear. This behavior shows that the conductivity is a thermal-activated process and can be analyzed using the Arrhenius formalism (eq.4). Thus, the calculated activation energies for both AC and DC conductivity are presented in
Table 2.
The activation energy for DC conductivity is higher compared to AC conductivity. This difference arises from the fact that AC conduction is attributed to ion motion over limited distances, while DC conduction entails motion across longer distances. Consequently, AC conduction involves lower barriers compared to DC conduction and therefore it requires less energy [
45]. The results illustrated in
Table 2 show an increase of the AC and DC conductivity for the sample modified with 0.25% CuO compared to the bioglass base, then it decreases with the insertion of a higher concentration of CuO. It is known that the conductivity in the bioglass system is mostly correlated with the energy carried by the network modifier, NaO and CaO, whose mobility increases with rising the amount of NBOs present in the glass network [
58,
59]. As depicted in
Figure 4, the NBOs amount increases with the introduction of 0.25% CuO into the bioglass, therefore contributing to elevated AC and DC conductivity. However, as the concentration of CuO is further increased beyond 0.25%, the NBOs amount decreases, leading to a decrease in the AC and DC conductivities.
3.5. In Vitro Bioactivity Evaluation
An
in vitro experiment was conducted to evaluate the capacity of bioactive glasses to facilitate the integration with the host bone and stimulate new bone formation. The test involved observing the development of an apatite layer on the material surface after immersion in simulated body fluid (SBF). This technique offers valuable information regarding the physicochemical processes taking place at the interface of the bioactive glass within a biological medium, a crucial factor influencing the adhesion and proliferation of osteoblast cells [
60]. The SEM micrographs, illustrated in
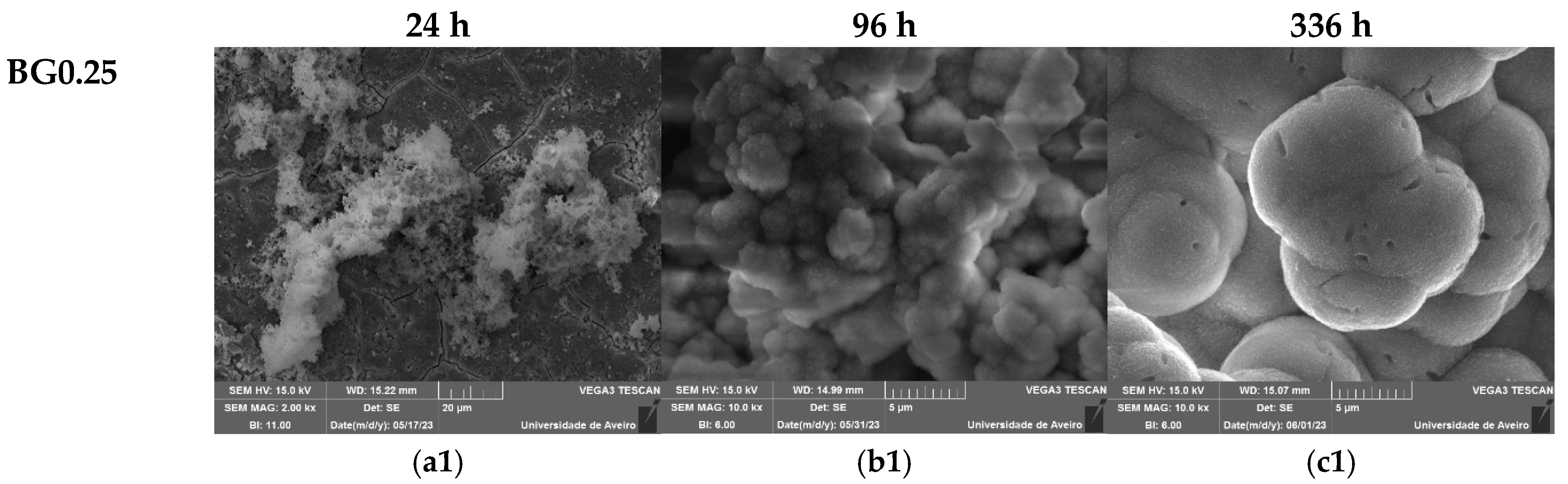
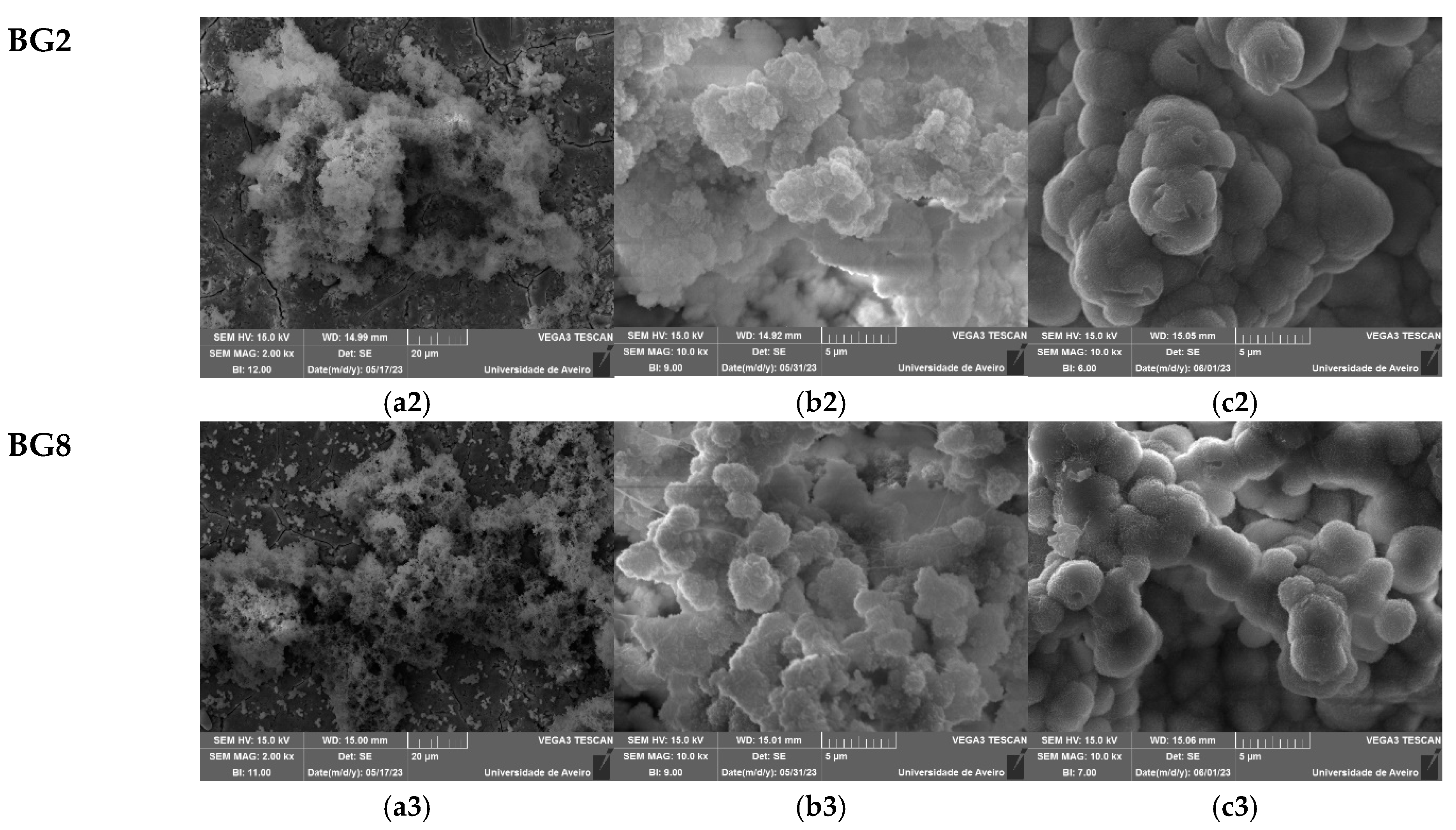
Figure 9, show the surface of the samples after 24 h, 96 h, and 336 h of SBF immersion. It is visible for all samples, a formation of spherical particles on the surface, with the size increasing with immersion time. The surface of the pellet becomes fully covered by the precipitated apatite layer with a cauliflower shape. The results suggest that the bioglass modified with copper shows promise as an osteoconductive material.
The atomic elements presented on the surface of the prepared glasses were examined using SEM-EDS. The obtained results, illustrated in
Table 3, show a decrease in Si and Na concentration with increasing immersion time, associated with the dissolution of these elements into the medium. Within the first days of SBF immersion, the Ca/P ratio approaches a value close t to the Ca/P ratio of hydroxyapatite in normal bone (Ca/P ≈ 1.67), confirming the formation of the apatite layer [
61,
62].
4. Conclusions
The present investigation discloses the synthesis of 45S5 bioactive glasses modified by the insertion of CuO using the melt quenching technique. The structural characterization shows that the glass matrix was not altered by the addition of copper. The deconvolution of Raman spectra showed an increase in the NBOs amount with the insertion of CuO. Nevertheless, increasing the concentration of this oxide inserted into the glass network decreases the NBOs levels. This change in NBOs amount impacts the network modifier mobility, resulting in an increased conductivity for the sample with 0.25% CuO. Bioactivity assessment confirms the glasses’ ability to form an apatite layer on the surface, ensuring a strong connection with bone when applied in regenerative medicine.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.H., and M.P.F.G.; methodology, I.H., S.R.G., L.C.C., and M.P.F.G.; software, I.H. and M.P.F.G.; validation, I.H., J.C.S., J.P.B., I.C.C., and M.P.F.G.; formal analysis, I.H.; investigation, I.H., S.R.G., S.K.J., and M.P.F.G.; resources, J.C.S., J.P.B., L.C.C., and M.P.F.G.; data curation, I.H.; writing—original draft preparation, I.H.; writing—review and editing, M.P.F.G., I.C.C., J.C.S., and J.P.B.; visualization, I.H.; supervision, M.P.F.G., J.C.S., and J.P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FEDER funds through the COMPETE 2020 Program and National Funds through the FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology under the projects LISBOA-01-0247-FEDER-039985/POCI-01-0247-FEDER-039985, LA/P/0037/2020, UIDP/50025/2020, and UIDB/50025/2020 of the Associate Laboratory Institute of Nanostructures, Nanomodelling and Nanofabrication—i3N, UIDP/04378/2020 and UIDB/04378/2020 of the Research Unit on Applied Molecular Biosciences—UCIBIO, and LA/P/0140/2020 of the Associate Laboratory Institute for Health and Bioeconomy—i4HB. S.R. Gavinho acknowledge the FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology for the Ph.D. grant (SFRH/BD/148233/2019). S.K. Jakka acknowledges FCT—Fundaçao para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, Portugal, I.P., in the scope of the framework contract foreseen in the numbers 4, 5, and 6 of article 23 of the Decree Law 57/2016 of 29 August, changed by Law 57/2017 of 19 July.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Civantos, A.; Martínez-Campos, E.; Ramos, V.; Elvira, C.; Gallardo, A.; Abarrategi, A. Titanium Coatings and Surface Modifications: Toward Clinically Useful Bioactive Implants. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerikli, M.; Jaurich, H.; Wallner, C.; Wagner, J.M.; Dadras, M.; Jettkant, B.; Pöhl, F.; Seifert, M.; Jung, O.; Mitevski, B. P2000-A High-Nitrogen Austenitic Steel for Application in Bone Surgery. Plos one 2019, 14, e0214384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C. Titanium Implant Osseointegration Problems with Alternate Solutions Using Epoxy/Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Composite. Metals 2014, 4, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Ramalingam, M.; Kumar, T.S.; Soboyejo, W.O. Biomaterials: A Nano Approach, CRC press, 2016.
- Singh, N.; Hameed, P.; Ummethala, R.; Manivasagam, G.; Prashanth, K.G.; Eckert, J. Selective Laser Manufacturing of Ti-Based Alloys and Composites: Impact of Process Parameters, Application Trends, and Future Prospects. Materials Today Advances 2020, 8, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; Lovering, A.M.; Webb, J.C. The Role of Microbial Biofilms in Prosthetic Joint Infections. Acta Orthopaedica 2015, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, S.; J, J.; X, G.; Y, Z.; D, C.; Y, G.; X, Z. Reduced Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilm Formation in the Presence of Chitosan-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2016, Volume 11, 6499–6506. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, D.J.; Spratt, D.; Liddle, A.D. Implant Materials and Prosthetic Joint Infection: The Battle with the Biofilm. EFORT Open Reviews 2019, 4, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriyutha Murthy, P.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Das; Arunya, D.; Dhara, S.; Pandiyan, R.; Tyagi, A.K. Antibiofilm Activity of Nano Sized CuO. Proceedings of the International Conference on Nanoscience, Engineering and Technology, ICONSET 2011 2011, 580–583. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Haapasalo, M. Dental Materials with Antibiofilm Properties. Dental Materials 2014, 30, e1–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. The Story of Bioglass®. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. An Introduction to Bioceramics, Second edition.; Imperial College Press: London, 2013; ISBN 978-1-908977-15-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hench, L.L.; Greenspan, D. Interactions between Bioactive Glass and Collagen: A Review and New Perspectives. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society 2013, 49, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. An Introduction to Bioceramics, Second Edition. An Introduction to Bioceramics, Second Edition 2013, 1–600. [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, D.; Sola, A.; Anesi, A.; Salvatori, R.; Chiarini, L.; Cannillo, V. Bioactive Glass/Hydroxyapatite Composites: Mechanical Properties and Biological Evaluation. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2015, 51, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, L.-C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive Glass and Glass-Ceramic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2010, 3, 3867–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, A.; Balossier, G.; Laurent-Maquin, D.; Pina, S.; Rebelo, A.H.S.; Faure, J.; Ferreira, J.M.F. An in Vitro Biological and Anti-Bacterial Study on a Sol-Gel Derived Silver-Incorporated Bioglass System. undefined 2008, 24, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.S.; Farooq, I.; Awais, M.; Najeeb, S.; Khurshid, Z.; Zohaib, S. Chapter 11 - Bioactive Surface Coatings for Enhancing Osseointegration of Dental Implants. In Biomedical, Therapeutic and Clinical Applications of Bioactive Glasses; Kaur, G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing, 2019; pp. 313–329 ISBN 978-0-08-102196-5.
- Guglielmotti, M.B.; Olmedo, D.G.; Cabrini, R.L. Research on Implants and Osseointegration. Periodontology 2000 2019, 79, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ghannam, A.; Ducheyne, P.; Shapiro, I.M. Effect of Serum Proteins on Osteoblast Adhesion to Surface-Modified Bioactive Glass and Hydroxyapatite. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 1999, 17, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücheler, M.; Haisch, A. Tissue Engineering in Otorhinolaryngology. DNA and Cell Biology 2003, 22, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.H.; Ng, A.M.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z.; Gethings, L.A.; Wong, M.T.; Chan, C.M.; Guo, M.Y.; Ng, Y.H.; Djurišić, A.B. Mechanisms of Antibacterial Activity of MgO: Non-ROS Mediated Toxicity of MgO Nanoparticles towards Escherichia Coli. Small 2014, 10, 1171–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Wu, C.; Chang, J. Preparation and in Vitro Osteogenic, Angiogenic and Antibacterial Properties of Cuprorivaite (CaCuSi 4 O 10, Cup) Bioceramics. RSC advances 2016, 6, 45840–45849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, I.; Gavinho, S.R.; Pádua, A.S.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Silva, J.C.; Borges, J.P.; Valente, M.A.; Graça, M.P.F. Bioactive Glass Modified with Zirconium Incorporation for Dental Implant Applications: Fabrication, Structural, Electrical, and Biological Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, F.; Hoomehr, B.; Saidi, R.; Raeissi, K. Synthesis and Electrophoretic Deposition of Zinc Oxide and Zinc Oxide-Bioactive Glass Composite Nanoparticles on AZ31 Mg Alloy for Biomedical Applications. Ceramics International 2022, 48, 34013–34024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabia, Z.; Mabrouk, K.E.; Bricha, M.; Nouneh, K. Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Doped with Magnesium: Drug Delivery and Acellular in Vitro Bioactivity. RSC Advances 2019, 9, 12232–12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammami, I.; Gavinho, S.R.; Pádua, A.S.; Graça, M.P.F.; Silva, J.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Iron Containing Bioactive Glass for Implants. In Proceedings of the 2022 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB); IEEE, 2022; pp. 1–4.
- Fernandes, G.V.; de, O.; Alves, G.; Linhares, A.B.R.; Prado da Silva, M.H.; Granjeiro, J.M. Evaluation of Cytocompatibility of Bioglass-Niobium Granules with Human Primary Osteoblasts: A Multiparametric Approach. In Proceedings of the Key engineering materials; Trans Tech Publ, 2012; Vol. 493, pp. 37–42.
- Chitra, S.; Bargavi, P.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Chandran, R.R.; Balakumar, S. Impact of Copper on In-Vitro Biomineralization, Drug Release Efficacy and Antimicrobial Properties of Bioactive Glasses. Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications 2020, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, I.; Gavinho, S.R.; Jakka, S.K.; Valente, M.A.; Graça, M.P.F.; Pádua, A.S.; Silva, J.C.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Borges, J.P. Antibacterial Biomaterial Based on Bioglass Modified with Copper for Implants Coating. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2023, 14, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; Bloise, N.; Fiorilli, S.; Novajra, G.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Bruni, G.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Visai, L.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Copper-Containing Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles as Multifunctional Agent for Bone Regeneration. Acta Biomaterialia 2017, 55, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Sriranganathan, N.; Waldrop, S.G.; Sharma, P.; Chudasama, B.N. Effect of Copper on the Up-Regulation/down-Regulation of Genes, Cytotoxicity and Ion Dissolution for Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses. Biomedical Materials 2017, 12, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, M.; Verné, E.; Ciraldo, F.E.; Cordero-Arias, L.; Boccaccini, A.R. Electrophoretic Deposition of Chitosan/45S5 Bioactive Glass Composite Coatings Doped with Zn and Sr. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 2015, 3, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Santhiya, D.; Murugavel, S.; Kumar, A.; Aditya, A.; Ganguli, M.; Gupta, S. Effects of Transition Metal Ion Dopants (Ag, Cu and Fe) on the Structural, Mechanical and Antibacterial Properties of Bioactive Glass. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2018, 538, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtach, S.; Tabia, Z.; El Mabrouk, K.; Bricha, M.; Belkhou, R. A Comprehensive Study on Copper Incorporated Bio-Glass Matrix for Its Potential Antimicrobial Applications. Ceramics International 2021, 47, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solioz, M. Copper Oxidation State and Mycobacterial Infection. Mycobact Dis 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.; Duval, R. e.; Hartemann, P.; Engels-Deutsch, M. Contact Killing and Antimicrobial Properties of Copper. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2018, 124, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, S.; Kumar, R.; Solioz, M. Copper Reduction and Contact Killing of Bacteria by Iron Surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 2015, 81, 6399–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.C.; Valente, M.A.; Graça, M.P.F.; Sombra, A.S.B. Preparation and Optical Characterization of Hydroxyapatite and Ceramic Systems with Titanium and Zirconium Formed by Dry High-Energy Mechanical Alloying. Solid State Sciences 2004, 6, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, M.P.F.; Prezas, P.R.; Costa, M.M.; Valente, M.A. Structural and Dielectric Characterization of LiNbO3 Nano-Size Powders Obtained by Pechini Method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 2012, 64, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mallawany, R.A. Tellurite Glasses Handbook: Physical Properties and Data, CRC press, 2014.
- Feroci, M. Investigation of the Role of Electrogenerated N-Heterocyclic Carbene in the Staudinger Synthesis in Ionic Liquid. International Journal of Organic Chemistry 2011, 1, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoukov, E.; Macdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
- Graça, M.P.F.; da Silva, M.F.; Sombra, A.S.B.; Valente, M.A. Electric and Dielectric Properties of a SiO2–Na2O–Nb2O5 Glass Subject to a Controlled Heat-Treatment Process. Physica B: Condensed Matter 2007, 396, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, I.; Sales, A.M.J.; Benhamou, K.; Arous, M.; Costa, L.C.; da Cruz, J.A.; Kaddami, H. Dielectric Response and Molecular Dynamics of Nanocomposites Based on TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils and Polyvinyl Acetate. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress 2022, 34, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, Jr. Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems. Impedance Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gavinho, S.R.; Graça, M.P.F.; Prezas, P.R.; Kumar, J.S.; Melo, B.M.G.; Sales, A.J.M.; Almeida, A.F.; Valente, M.A. Structural, Thermal, Morphological and Dielectric Investigations on 45S5 Glass and Glass-Ceramics. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2021, 562, 120780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wers, E.; Oudadesse, H.; Lefeuvre, B.; Lucas-Girot, A.; Rocherullé, J.; Lebullenger, R. Excess Entropy and Thermal Behavior of Cu- and Ti-Doped Bioactive Glasses. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2014, 117, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, S.; Wren, A.W.; Kazuo, S.M. Copper Containing Glass-Based Bone Adhesives for Orthopaedic Applications: Glass Characterization and Advanced Mechanical Evaluation. bioRxiv, 2020; 2020.11.19.390138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlich, E. The Effective Nuclear Charges and Their Relation to the Pauling’s Electronegativity Scale. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 1989, 270O, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.F.; Haleem, Y.A.; Sun, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, D. Surface-Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering in Partially Oxidized Thin Copper Film. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 2020, 51, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadek, M.; Zagrajczuk, B.; Jelen, P.; Olejniczak, Z.; Cholewa-Kowalska, K. Structural Variations of Bioactive Glasses Obtained by Different Synthesis Routes. Ceramics international 2016, 42, 14700–14709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, H.; Serra, J.; González, P.; León, B. Structural Study of Sol–Gel Silicate Glasses by IR and Raman Spectroscopies. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2009, 355, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.S.; Silva, A.C.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Mello-Castanho, S. Structural and Thermal Behavior of 45S5 Bioglass®-Based Compositions Containing Alumina and Strontium. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2020, 103, 3620–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, H.; Solla, E.L.; Serra, J.; González, P.; León, B.; Almeida, N.; Cachinho, S.; Davim, E.J.C.; Correia, R.; Oliveira, J.M. Orthophosphate Nanostructures in SiO2–P2O5–CaO–Na2O–MgO Bioactive Glasses. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids 2008, 354, 4075–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.F.; Talib, Z.A.; Daud, W.M.; Sidek, H.A.A.; Ng, B.H. Effects of MgO on Dielectric Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Ternary Zinc Magnesium Phosphate Glasses. Journal of non-crystalline solids 2009, 355, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Prasad, A.; Kumari, K.; Prasad, K. Dielectric, Impedance/Modulus and Conductivity Studies on [Bi 0.5 (Na 1-x K x ) 0.5 ] 0.94 Ba 0.06 TiO 3, (0.16 ≤ x ≤0.20) Lead-Free Ceramics. American Journal of Materials Science 2016, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, A.; Nakamura, S.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Yamashita, K. Electrical Polarization of Bioactive Glass and Assessment of Their in Vitro Apatite Deposition. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A: An Official Journal of The Society for Biomaterials, The Japanese Society for Biomaterials, and The Australian Society for Biomaterials and the Korean Society for Biomaterials 2003, 67, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, I.; Gavinho, S.R.; Pádua, A.S.; Lança, M. do C.; Borges, J.P.; Silva, J.C.; Sá-Nogueira, I.; Jakka, S.K.; Graça, M.P.F. Extensive Investigation on the Effect of Niobium Insertion on the Physical and Biological Properties of 45S5 Bioactive Glass for Dental Implant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V.; Epple, M. Biological and Medical Significance of Calcium Phosphates. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2002, 41, 3130–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukha, Z.; Yeste, M.P.; Cauqui, M.Á.; González-Velasco, J.R. Influence of Ca/P Ratio on the Catalytic Performance of Ni/Hydroxyapatite Samples in Dry Reforming of Methane. Applied Catalysis A: General 2019, 580, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaufils, S.; Rouillon, T.; Millet, P.; Le Bideau, J.; Weiss, P.; Chopart, J.-P.; Daltin, A.-L. Synthesis of Calcium-Deficient Hydroxyapatite Nanowires and Nanotubes Performed by Template-Assisted Electrodeposition. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2019, 98, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
DTA spectra of (a) BG2 and (b) BG8 samples.
Figure 1.
DTA spectra of (a) BG2 and (b) BG8 samples.
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of bioglasses modified with CuO.
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of bioglasses modified with CuO.
Figure 3.
(a) Raman spectra of bioglass samples and (b) Deconvoluted Raman spectra of BG0 sample.
Figure 3.
(a) Raman spectra of bioglass samples and (b) Deconvoluted Raman spectra of BG0 sample.
Figure 4.
The sum of the areas of the bands associated with NBOs vibrations.
Figure 4.
The sum of the areas of the bands associated with NBOs vibrations.
Figure 5.
SEM micrograph of (a) BG0, and (b) BG2.
Figure 5.
SEM micrograph of (a) BG0, and (b) BG2.
Figure 6.
Frequency dependence of (a) real part ε’, (b) imaginary part ε”, of the dielectric permittivity and (c) AC conductivity for BG2.
Figure 6.
Frequency dependence of (a) real part ε’, (b) imaginary part ε”, of the dielectric permittivity and (c) AC conductivity for BG2.
Figure 7.
(a) The imaginary part of the dielectric modulus M″ versus frequency for BG2 sample, (b) The normalized imaginary part of the modulus M″/M″max versus the frequency at 390 K for all bioglass samples.
Figure 7.
(a) The imaginary part of the dielectric modulus M″ versus frequency for BG2 sample, (b) The normalized imaginary part of the modulus M″/M″max versus the frequency at 390 K for all bioglass samples.
Figure 8.
(a) AC conductivity versus 1000/T at 10 kHz and (b) DC conductivity versus 1000/T.
Figure 8.
(a) AC conductivity versus 1000/T at 10 kHz and (b) DC conductivity versus 1000/T.
Figure 9.
SEM micrographs of the surface of the bioglasses after immersion in SBF for (a1–a3) 24 h; (b1–b3) 96 h; (c1–c3) 336 h. (The magnification of SEM images is 10 kX).
Figure 9.
SEM micrographs of the surface of the bioglasses after immersion in SBF for (a1–a3) 24 h; (b1–b3) 96 h; (c1–c3) 336 h. (The magnification of SEM images is 10 kX).
Table 1.
The characteristic temperatures for BG0, BG2, and BG8.
Table 1.
The characteristic temperatures for BG0, BG2, and BG8.
| Samples |
Tg (K) |
Tc (K) |
Tm (K) |
| BG0 [47] |
825 |
1001 |
1448 |
| BG2 |
782 |
965 |
1412 |
| BG8 |
777 |
913 |
1371 |
Table 2.
The dielectric constant (ε’), dielectric loss (tan δ), AC conductivity (σac), AC activation energy Ea (AC), DC conductivity (σdc), and DC activation energy Ea (DC), for all bioglass samples.
Table 2.
The dielectric constant (ε’), dielectric loss (tan δ), AC conductivity (σac), AC activation energy Ea (AC), DC conductivity (σdc), and DC activation energy Ea (DC), for all bioglass samples.
| Sample |
ε’ |
tan δ (10−2) |
σac (10−6)
[S/m] |
Ea (AC)
[kJ/mol] |
σdc (10−9)
[S/m] |
Ea (DC)
[kJ/mol] |
| (300 K; 10 kHz) |
(10 kHz) |
(300 K) |
|
| BG0 |
13.59±0.72 |
1.58±0.02 |
11.92±0.01 |
37.95±0.98 |
0.91±0.08 |
75.82±0.79 |
| BG0.25 |
13.75±1.42 |
2.21±0.01 |
17.12±0.03 |
38.89±0.73 |
1.27±0.11 |
74.27±0.77 |
| BG0.5 |
11.12±1.24 |
1.81±0.06 |
11.37±0.04 |
38.05±0.79 |
1.02±0.13 |
77.24±0.11 |
| BG1 |
10.14±0.98 |
2.01±0.03 |
11.23±0.02 |
37.37±0.70 |
1.07±0.15 |
77.12±0.38 |
| BG2 |
12.66±1.32 |
1.32±0.05 |
9.46±0.08 |
37.32±0.85 |
0.23±0.05 |
83.51±0.12 |
| BG4 |
12.26±0.83 |
1.14±0.07 |
7.66±0.05 |
37.81±0.86 |
0.28±0.09 |
84.00±0.19 |
| BG8 |
12.34±1.12 |
0.64±0.02 |
4.61±0.09 |
34.53±0.88 |
0.06±0.001 |
87.47 ±0.26 |
Table 3.
The atomic percentage of Si and Na elements and the Ca/P ratio measured using SEM-EDS, on the surface of the samples before and after immersion in SBF for 96 h and 336 h.
Table 3.
The atomic percentage of Si and Na elements and the Ca/P ratio measured using SEM-EDS, on the surface of the samples before and after immersion in SBF for 96 h and 336 h.
| Samples |
Si (at. %) |
Na (at. %) |
Ca/P |
| |
0 h |
96 h |
336 h |
0 h |
96 h |
336 h |
0 h |
96 h |
336 h |
| BG0 |
11.62±1.1 |
1.12±0.5 |
0.11±0.01 |
15.43±1.1 |
3.53±0.8 |
1.31±0.1 |
7.02±0.9 |
2.05±0.3 |
1.78±0.7 |
| BG0.25 |
11.60±0.9 |
1.43±0.3 |
0.52±0.08 |
15.17±1.3 |
3.73±0.7 |
1.27±0.5 |
5.94±0.7 |
1.77±0.5 |
1.71±0.8 |
| BG0.5 |
11.58±0.7 |
1.14±0.7 |
0.14±0.03 |
15.14±0.9 |
3.13±0.4 |
1.26±0.7 |
5.84±0.7 |
1.71±0.8 |
1.70±0.3 |
| BG1 |
10.23±1.3 |
1.29±0.1 |
0.06±0.01 |
14.91±1.5 |
4.07±0.3 |
1.49±0.3 |
6.66±0.5 |
1.80±0.7 |
1.75±0.4 |
| BG2 |
9.25±0.8 |
1.47±0.2 |
0.1±0.04 |
15.42±1.7 |
3.76±0.1 |
1.22±0.2 |
6.87±0.3 |
1.74±0.4 |
1.73±0.5 |
| BG4 |
10.27±0.6 |
1.03±0.7 |
0.08±0.01 |
13.97±1.2 |
3.97±0.9 |
1.18±0.8 |
6.81±0.9 |
1.81±0.6 |
1.78±0.9 |
| BG8 |
9.34±1.2 |
1.09±0.3 |
0.07±0.02 |
14.84±1.3 |
4.32±0.2 |
1.68±0.9 |
6.71±0.4 |
1.83±0.5 |
1.79±0.2 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).