1. Introduction
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to proliferate, ensuring the security of interconnected devices and networks becomes increasingly crucial. A complete IoT system includes devices, sensors, networks, software, and other essential components necessary for operation and interconnection. Devices and sensors of this nature often have low resource requirements and multiple security vulnerabilities from manufacturers [
1]. It is forecasted that by 2030, there will be approximately 500 billion IoT devices connected to the internet [
2]. Edge devices, gateways, cloud servers, data-analysis tools, and user interfaces represent the main components of an IoT system. In addition to having sensors and controllers, edge devices can also perform initial data reviews before transmitting it to the cloud.
Cybersecurity is a critical concern in today’s digital age due to the increasing number of cyber-attacks and the growing sophistication of cybercriminals. Ensuring the security of computer systems, networks, and data is of utmost importance, particularly for IoT devices. IoT environments are vulnerable to various cyber threats and attacks, making intrusion detection a fundamental aspect of IoT security. There are many security flaws in IoT devices, often originating from the manufacturer, along with insufficient defense against cyberattacks in the edge network areas. Additionally, the importance of the data collected by IoT devices contributes to the increase in cyberattacks in IoT systems.
Traditional rule-based IDS have limitations in detecting emerging and unknown attacks. This has led to the integration of machine learning techniques into IDS, enabling them to adapt and evolve to ever-changing security threats. The complexity of high-dimensional features poses challenges for the speed and performance of intrusion detection classification [
3]. An Intrusion Detection System is a security mechanism designed to monitor network traffic, detect suspicious activities, and alert system administrators of potential intrusions or security breaches. Analyzing data traffic patterns within a network enables intrusion detection systems (IDS) to detect potential attacks. Feature extraction becomes essential to reduce the computational burden associated with processing raw data in IDS.
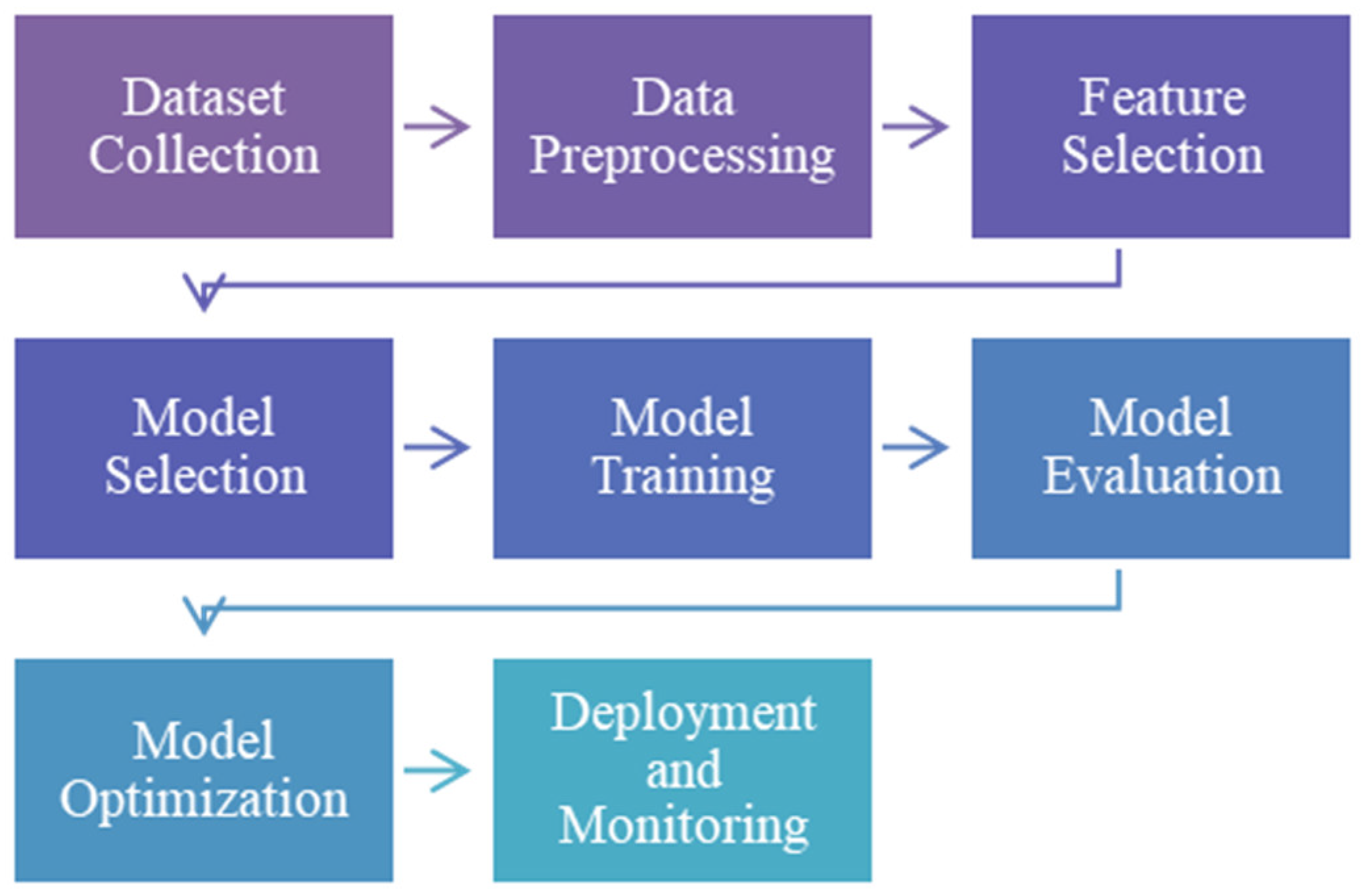
Figure 1.
Intrusion Detection Steps Using Machine Learning.
Figure 1.
Intrusion Detection Steps Using Machine Learning.
It becomes imperative to identify and select the most relevant data features to enhance the performance of a machine learning model, particularly for IDS systems in IoT devices where securing these environments with conventional algorithms and techniques poses a challenge. IoT devices often have limitations such as low computing capabilities, limited power sources, restricted storage, or memory capacity. Traditional feature selection methods face optimization difficulties and have high computational complexity [
2]. The limitations of IoT devices lead to a higher likelihood of attacks or flaws in their security protocols [
4]. These limitations and challenges of IoT encompass various categories including hardware constraints, software issues, network concerns, and security vulnerabilities. It is crucial to thoroughly consider all these limitations and challenges before embarking on the development of any systems and security solutions.
Feature selection involves searching within the training data to enhance the classification accuracy of a machine learning classifier. It is crucial to identify and select the most relevant features in the data to improve the performance of the ML model, particularly in anomaly-based IDS [
5]. This process entails selecting a subset of input features from the original set of features in the training data. Feature selection holds significant importance, especially as data scale increases, to improve the accuracy and efficiency of machine learning models and prevent overfitting [
6]. One of the main challenges in ML is to identify the group of relevant features that strike a balance between high accuracy and low time complexity [
7].
The contributions of this work are as follows:
Innovative Approach to Feature Selection: Introduced novel feature selection techniques specifically tailored for Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) in IoT environments. This approach not only significantly reduces the dimensionality of the dataset but also ensures the selection of the most relevant features, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of intrusion detection.
Enhanced Intrusion Detection Performance: Demonstrated through rigorous experiments that our methodology outperforms existing methods in extracting optimal feature subsets. It achieves superior classification accuracy with fewer features, significantly reducing computational time and power consumption, thereby addressing the critical constraints of IoT-based IDS.
Benchmarking Against Outdated Practices: Highlighted the limitations of using non-compatible and outdated datasets, like the KDD’99, in current IDS research. Our results underscore the importance of updated and relevant datasets for developing more accurate and efficient IDS solutions tailored to modern IoT ecosystems.
In this study, the latest InSDN dataset published in 2020 is used. The rest of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 reviews related research on enhancing feature selection.
Section 3 provides an overview of the proposed method, the dataset used, and the four stages for enhancing feature selection.
Section 4 presents the experimental results and discussion, followed by section 5 which discusses future work and challenges. Finally,
Section 6 concludes this paper.
2. Related Work
Many researchers are interested in securing IoT and wireless networks, and in this section, the focus is on the research that uses the InSDN dataset, and it compares their results with the results of this study. Numerous published studies rely on datasets that are either incompatible or outdated. For example, the KDDCup99 dataset, which was published in 1999, has been used in recent research [
9,
10]. Additionally, the Nsl-KDD dataset, published in 2009, has been used in research such as [
3,
5,
11,
12,
13,
14]. However, using outdated datasets in an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) for machine learning may not accurately reflect the current threat landscape. New types of attacks and vulnerabilities may have emerged since the dataset was created, making the model less effective in identifying contemporary threats. Outdated datasets can also introduce disadvantages such as limited relevance to current threats, obsolete features, lack of diversity, mismatch with real-world scenarios, and reduced model performance, which can lead to a false sense of security. Therefore, in this section, we discuss several methodologies proposed in recent research that utilize the InSDN dataset, which was published in 2020, such as [
8,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20].
D. Firdaus et al. [
17] proposed a DDoS detection method using Machine Learning with Ensemble Algorithm. Their study consists of two methodologies: clustering and classification, and Ensemble Algorithm clustering and classification. The researchers utilize Ensemble Algorithm K-means++ and Random Forest to achieve high detection accuracy and efficiency, obtaining a remarkable accuracy of 100% using 15 features out of the original dataset’s 84. Conversely, other researchers in [
8], [
19], and [
20] also achieved very high accuracies of 99.42%, 99.9961%, and 99.94% respectively, but they employed 48 or 56 features. A. Ibrahimy et al. [
19] used feature correlation to reduce the number of features in the InSDN dataset, while V. Hnamte and J. Hussain [
20] employed two 1D convolutional layers to capture important features from the input data. These layers are connected to a flattened layer, which converts the output of the convolutional layers into a 1D array. Subsequently, four fully connected dense layers are utilized, activated by the rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation function.
The researchers in [
15,
16] achieved an accuracy of 98.98% with 30 features and 98% with 20 features respectively. A. Zainudin et al. [
15] employed the LightGBM feature selection technique, which utilized three main modules: pre-block, depth-wiseConv, and stacked GRU. The depth-wiseConv module utilized a residual connection to enhance training model performance and address the issue of gradient vanishing. Additionally, a factorized convolution architecture was utilized to create a lightweight model structure.
3. Proposed Methodology
The number of features in an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) significantly influences its accuracy and performance. A larger feature set can provide a more detailed representation of the data, potentially leading to better detection of complex intrusion patterns. However, it can also introduce noise and irrelevant information, which can confuse the model, leading to overfitting and reduced generalization capabilities. Conversely, a smaller, well-curated feature set can result in a more streamlined and interpretable model, reducing the computational load and enabling the IDS to operate more efficiently, especially for IDS in IoT environments and resource limitations.
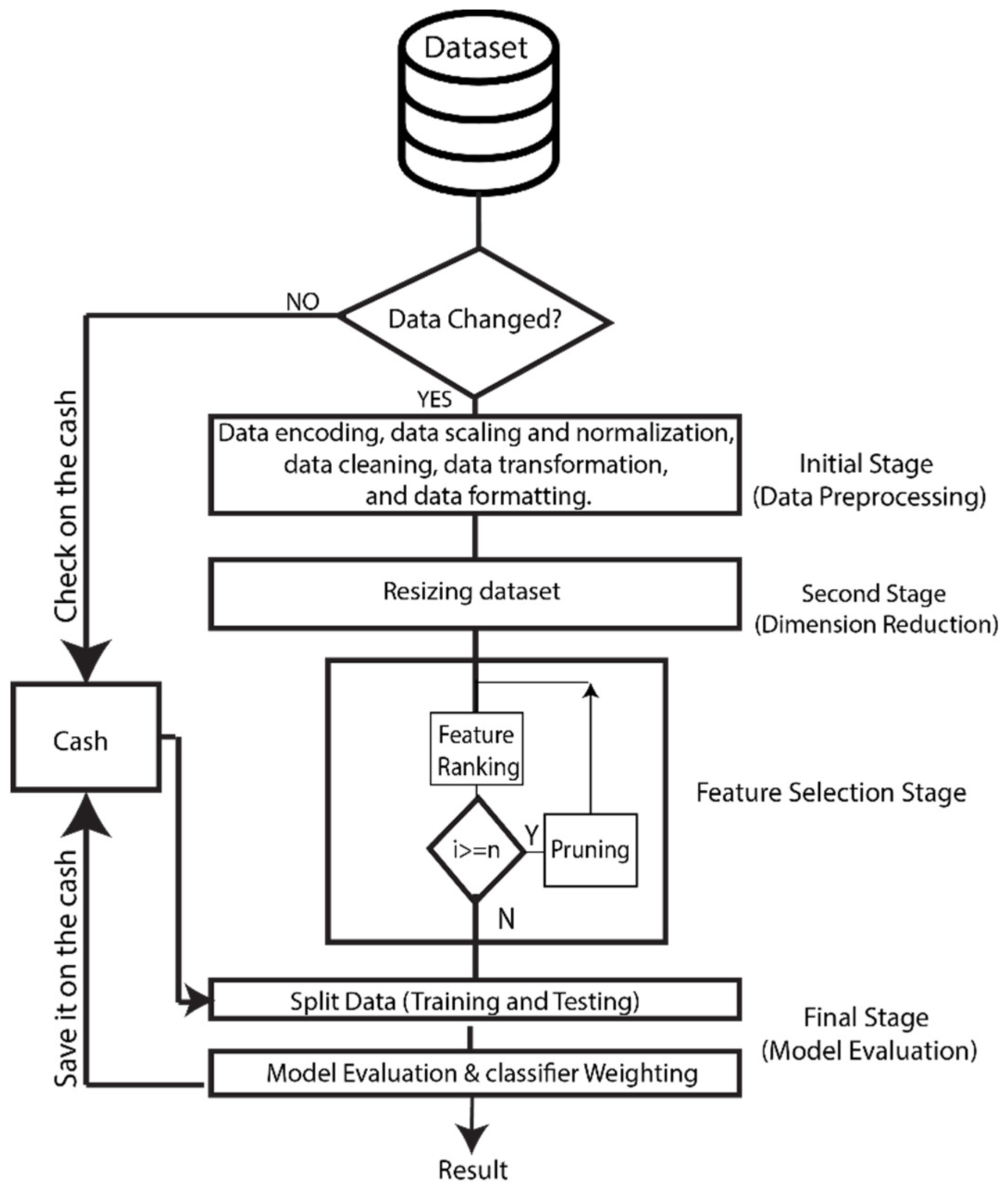
In this paper, we present a sophisticated hybrid feature selection approach specifically devised for the nuanced requirements of IoT environments. The proposed methodology unfolds across several defined stages:
Initial Stage (Data Preprocessing).
Second Stage (Dimension Reduction).
Feature Selection Stage.
Final Stage (Model Evaluation).
Caching mechanism.
Each stage contributes to the overarching goal of selecting the most pertinent features for use in the IDS. The resulting features are of pivotal importance in machine learning, directly influencing the model’s learning efficacy and predictive accuracy. Our methodological process, depicted in
Figure 2, underscores the critical nature of feature selection in enhancing IDS performance within IoT contexts.
Incorporating a caching mechanism significantly improves the efficiency of our feature selection methodology. Throughout our proposed approach, the system meticulously identifies and caches the most significant features for subsequent iterations. After each iteration, the system checks the dataset’s feature count. Unchanged counts prompt the retrieval of previously selected features from the cache, streamlining the process to the final evaluation stage. Conversely, any change in feature count mandates a fresh execution through all four stages, commencing with Data Preprocessing and culminating in Model Evaluation.
The data processing stage—data encoding, scaling, normalization, cleaning, transformation, and formatting—is essential for preparing the raw dataset and creating a refined dataset where the intrinsic patterns can be more easily and accurately discerned by the IDS, leading to improved detection accuracy and performance. Data encoding converts categorical data into a numerical format, which is necessary because most machine learning algorithms can only interpret numeric values. This ensures that valuable categorical information, such as protocol types or service names, is retained and can be used in the detection process. Data scaling and normalization are critical steps that adjust the range of the feature data. Scaling alters the range of the data to a common scale without distorting differences in the ranges of values, while normalization adjusts the data in such a way that its distribution will have a mean value of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. These steps are crucial to prevent features with larger scales from dominating those with smaller scales, thus ensuring that the IDS model treats all features equally.
Data cleaning is the process of detecting and correcting (or removing) corrupt or inaccurate records from a dataset, which might otherwise lead to incorrect conclusions. Data transformation involves converting data into a suitable format or structure for analysis, which could include generating polynomial features or interaction terms if needed. Finally, data formatting ensures that all data is consistently and correctly formatted, such as ensuring data times are in a uniform format, which is fundamental for time-series analysis in intrusion detection. One major challenge in IDS is dealing with high-dimensional and imbalanced data, which increases the cost of machine learning [
21]. Well-preprocessed data lowers the chance of overfitting, aids in the model’s learning of pertinent patterns, and produces predictions that are more reliable and accurate.
The second stage is the dataset resizing stage, which is a crucial step in data preprocessing, there are various methods used for dimensionality reduction such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to suit different needs. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) excels in classification tasks by using label information to maintain class distinctions. t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) shines in visualizing complex data but can be computationally demanding and sensitive to hyperparameters. Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) offers a faster alternative to t-SNE, suitable for large datasets while preserving data structure. Autoencoders (AE), leveraging neural networks, are powerful for non-linear transformations but require substantial data and computational resources. Random Projection provides a speedy, simple approach though it may yield less precise results due to its stochastic nature. Finally, Isomap is effective for unfolding manifolds by maintaining geodesic distances, albeit at a higher computational cost. The choice among these techniques hinges on the specific dataset and analytical objectives, balancing factors like visualization clarity, computational efficiency, and interpretability. In this stage, we use PCA because it gives us faster speed in data resizing compared with the other methods, while other methods gave us good results but it took more computational time.
After employing the dimension reduction algorithm in our proposed method, the preprocessed data will be fed into the Feature Selection Stage. Each line will undergo feature ranking and pruning after a specific number of iterations. The combination process may involve selecting the best features based on scoring metrics or aggregating results from different workers. The outcome of the Feature Selection stage will be cached, which offers a time-saving advantage for subsequent runs on similar datasets or during iterative model development.
The act of choosing a subset of the most pertinent features (input variables or attributes) from the initial collection of features is known as feature selection in machine learning. Improving the machine learning model’s efficiency, decreasing overfitting, and improving performance are the goals. Three primary approaches can be used to classify the many feature selection techniques into general categories:
Filter Methods: Filter approaches don’t need to train a machine learning model because they rely on statistical metrics. They evaluate each feature’s importance separately, without reference to the learning algorithm. Common filter methods include Correlation-based feature selection, Chi-squared test, and Information gain and mutual information.
Wrapper Methods: By training and evaluating machine learning models on various feature combinations, wrapper approaches assess feature subsets. Although they require more computing power than filter approaches, they may produce feature subsets that are better. Common wrapper methods include Forward selection, Backward elimination, and Recursive feature elimination (RFE).
Embedded Methods: Feature selection is a crucial step in the model training process that is carried out by embedded methods. Usually, they are employed with algorithms that facilitate feature selection by default. Common embedded methods include L1 Regularization (Lasso), Tree-based methods, and Feature importance from Support Vector Machines (SVMs).
In our proposed method, we utilize the filter method because we aim to enhance the speed of our IDS. Higher speed translates to lower power usage, reduced capacity requirements, and faster computational time. Filter methods are generally faster compared to wrapper methods. They preprocess the data independently of the learning algorithm. Common filter methods include mutual information, chi-squared test, and correlation-based feature selection. These methods can be highly efficient, particularly when dealing with high-dimensional data. They employ statistical or correlation-based techniques to rapidly evaluate the relevance of individual features without the need to train a machine learning model.
Common metrics for feature selection include mutual information, chi-squared, and correlation coefficients. In a study by researchers [
23], both filter and wrapper methods were compared, and it was found that wrapper methods often require more computing resources but provide higher accuracy. On the other hand, filter methods require fewer resources but lack optimization capabilities. Filter methods are known for their ease of implementation and faster execution compared to wrapper and hybrid methods. However, wrapper methods outperform filter methods in terms of accuracy, albeit at the cost of slower execution [
24]. Another study by Z. Zhanget. al [
11] also compared these feature selection methods and found that wrapper methods are closely tied to the classifier, which uses the performance of the classifier as an objective function to evaluate the current feature subset. Wrapper methods train a new model for each feature subset, resulting in a relatively higher computational cost.
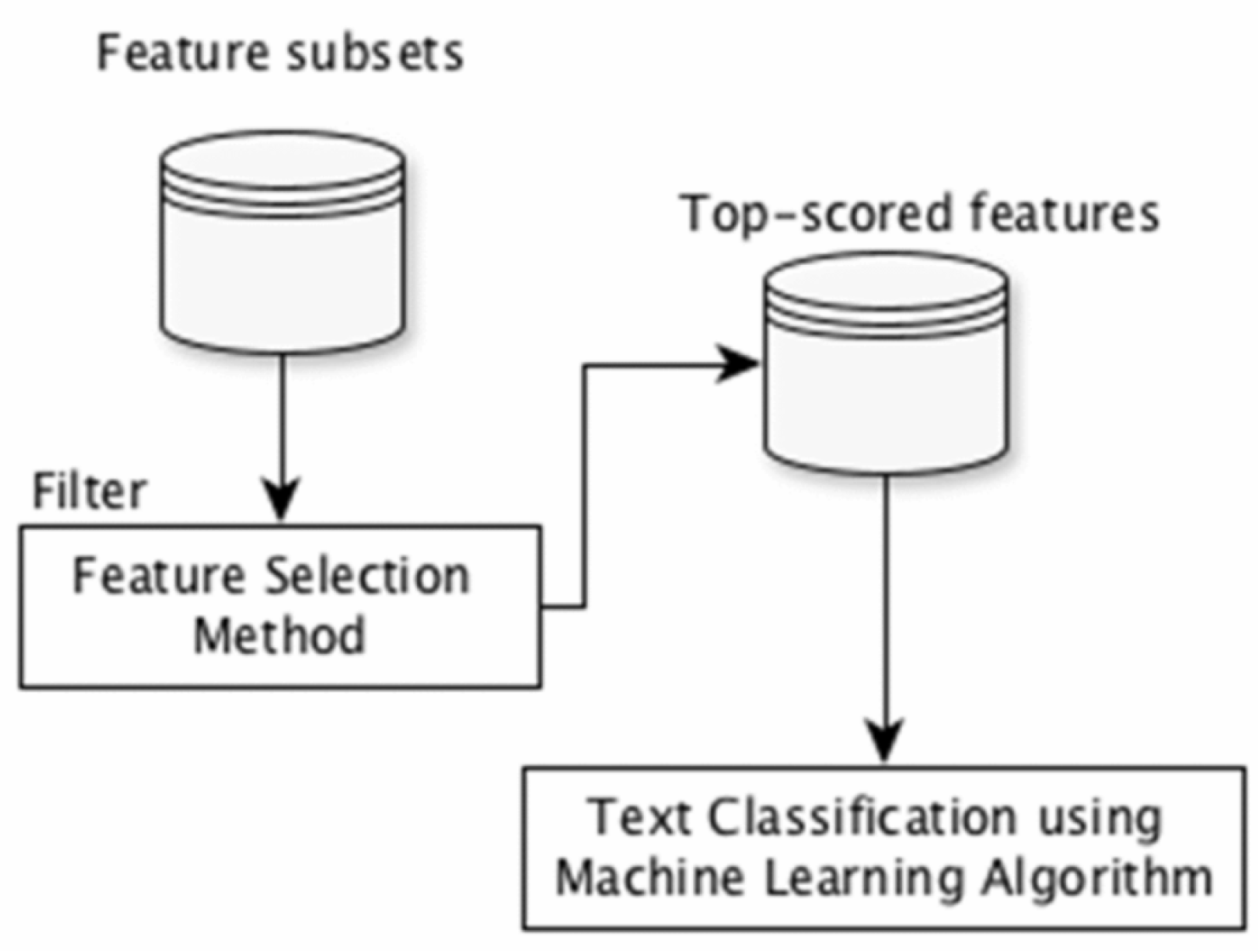
Figure 3.
A schema of filter method [
24].
Figure 3.
A schema of filter method [
24].
| Algorithm 1: Rank features using a Random Forest classifier pseudocode. |
# Step 1: Initialize the VarianceThreshold object with a threshold value threshold_value = 0.1 variance_selector = VarianceThreshold(threshold=threshold_value) # Step 2: Fit the selector to your data variance_selector.fit(X) # Step 3: Get the indices of the features selected selected_feature_indices = variance_selector.get_support(indices=True) # Step 4: Use the selected features selected_features = X[:, selected_feature_indices] |
The provided Rank feature pseudo code outlines a procedure for ranking features using a combination of a variance threshold method and a Random Forest classifier. The pseudo-code stops short of detailing the application of the Random Forest classifier; however, in typical usage, the Random Forest would be employed post-variance threshold application to rank the features according to their importance. This importance is gleaned from how much the features contribute to the accuracy of the Random Forest model. By combining the variance threshold with Random Forest ranking, the algorithm aims to enhance the feature selection process, potentially improving the predictive power of the subsequent machine learning models and offering a deeper understanding of the features’ influence within the dataset. The algorithm commences by initializing a VarianceThreshold object with a predefined threshold value, set here at 0.1. This threshold acts as a filter to remove features with low variance, under the assumption that features with a lower variance may contain less information. The variance_selector is then fitted to the dataset denoted as X, where it computes the variance for each feature.
Subsequently, the algorithm retrieves the indices of the features that surpass the variance threshold by invoking the get_support method with indices=True, which returns an array of indices. These indices represent the features that have been deemed important enough to retain based on their variance. In the final step, the algorithm selects the features from the dataset X using the obtained indices, creating a subset of X that only includes features with significant variance. This subset, denoted as selected_features, can be used for further processing or directly in the Random Forest classifier for ranking based on feature importance.
Use filter methods to select features based on their statistical properties. Common filter methods include:
Correlation: Calculate the correlation between features and remove highly correlated or redundant ones.
Variance Threshold: Remove features with low variance as they often contain little information.
Statistical Tests: Utilize statistical tests (e.g., chi-squared, ANOVA) to select features that significantly contribute to the classification.
You can use several different methods and approaches to increase the feature selection process speed. Choosing features can be computationally costly, particularly when working with big datasets or intricate feature spaces. It is challenging for IoT characteristics to exploit the features and attributes of IDS to ensure self-protection [
5]. Here are some methods used in the proposed method (
Figure 2) to enhance the speed of your feature selection process:
Feature Ranking: In this manner, you might not need to assess every feature in the dataset and instead concentrate on the most promising features first.
Pruning: Early in the feature subset evaluation process, prune or remove any subsets that don’t seem promising. This expedites the feature selection process and shrinks the search space. In the proposed methodology, feature ranking is performed in each round, while pruning is conducted every n number of iterations.
Caching: Implementing a caching mechanism can significantly enhance the efficiency of our feature selection methodology. During our proposed method journey, the system meticulously identifies and selects the most significant features, which are then cached for subsequent iterations. The system checks the dataset’s feature count after each iteration. If there is no change in the number of features, the system will swiftly retrieve the previously selected features from the cache, skipping unnecessary steps and advancing directly to the final evaluation stage. Conversely, any alteration in feature count necessitates a fresh execution through all four stages—beginning with Data Preprocessing and culminating in Model Evaluation.
It is important to note that while these methods are generally faster, they may not always yield the best subset of features for a specific problem. The choice of feature selection method should consider factors such as the nature of the data, the complexity of the problem, the desired trade-off between speed and model performance, and the specific goals of the analysis. Sometimes, a slightly slower method may yield better results in terms of model accuracy and generalization.
Using Random Forest (RF) or L1 regularization (Lasso) can offer faster feature selection compared to other techniques. With Random Forest, you can assess feature importance, which is often faster than running more computationally intensive wrapper methods like recursive feature elimination with cross-validation (RFECV). Random Forest models can achieve high prediction accuracy with a small overhead in terms of computational resource usage [
25]. In the proposed method, we use Random Forest as a supervised ML model for detecting attacks. Its advantages, such as handling both continuous and categorical data, addressing missing and outlier values, and shorter training time, led us to choose it as the classifier [
26].
L1 regularization (Lasso) is commonly used in linear models to encourage sparsity in feature selection. It can be relatively fast, especially when combined with optimization techniques like coordinate descent.
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
This paper introduces an improved feature selection methodology aimed at achieving high accuracy while utilizing a reduced number of features. The focus on a lower feature count is particularly relevant for wireless networks, which often have resource constraints. In this section, we present a hybrid feature selection approach designed to enhance the performance of intrusion detection system (IDS) classification. We demonstrate the application of our methodology on the InSDN dataset. Software-defined networking (SDN) has been developed to reduce network complexity by centralizing control and management of the entire network [
8]. SDN-based Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) networks utilize a centralized controller, which can make them vulnerable to DoS/DDoS attacks and susceptible to single points of failure [
18].
The dataset used in this research is called the InSDN dataset, which was published in 2020 by M. Elsayd et al. [
8]. The purpose of creating the InSDN dataset was to reduce its size compared to other IDS datasets. The researchers collected real-world network traffic from an SDN environment and classified it based on the presence of DDoS attacks. Unlike NSL-KDD and KDD99, InSDN provides a realistic representation of traffic in an SDN environment [
17].
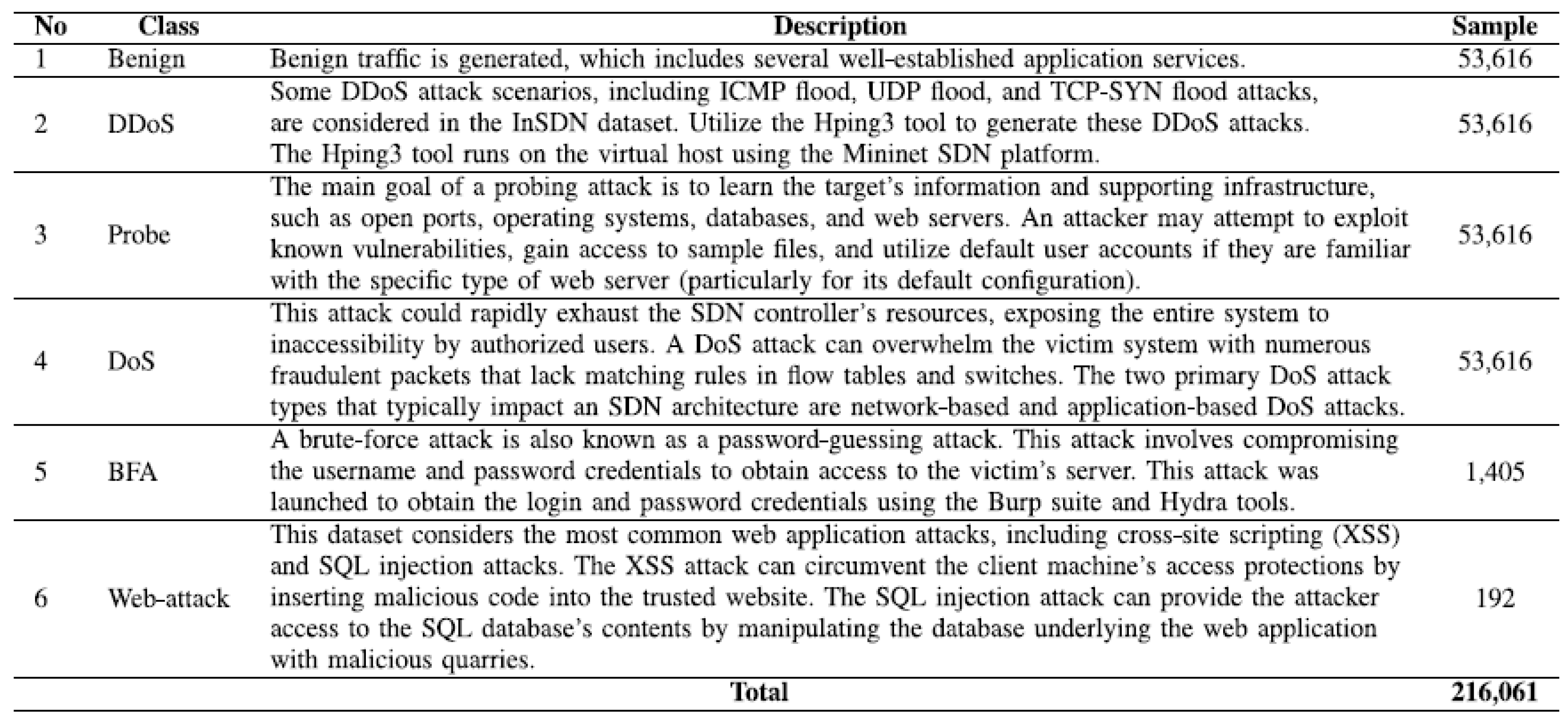
The dataset consists of a total of 343,889 data records with 84 features. Of these, 127,828 records correspond to ordinary traffic, while 216,061 records correspond to attack traffic. InSDN includes various attack scenarios, such as SYN floods and TCP, UDP, and ICMP floods, which are all included in the dataset.
Table 1 presents the distribution of samples within the InSDN dataset.
The dataset includes a variety of attack scenarios, such as TCP, UDP, and ICMP floods, as well as SYN flood and Slowloris attacks. The InSDN dataset was generated using multiple virtual machines with an SDN network architecture. The standard Ubuntu system represents regular users, while the Kali system represents attackers performing various types of attacks on the SDN network [
20].
In this section, we present the outcomes of our extensive investigation into the effectiveness of the proposed methodology. Our experiments involve extracting crucial features from the InSDN dataset through the suggested stages. We evaluate the performance using classification matrices, which include metrics such as accuracy, loss, and AUC score.
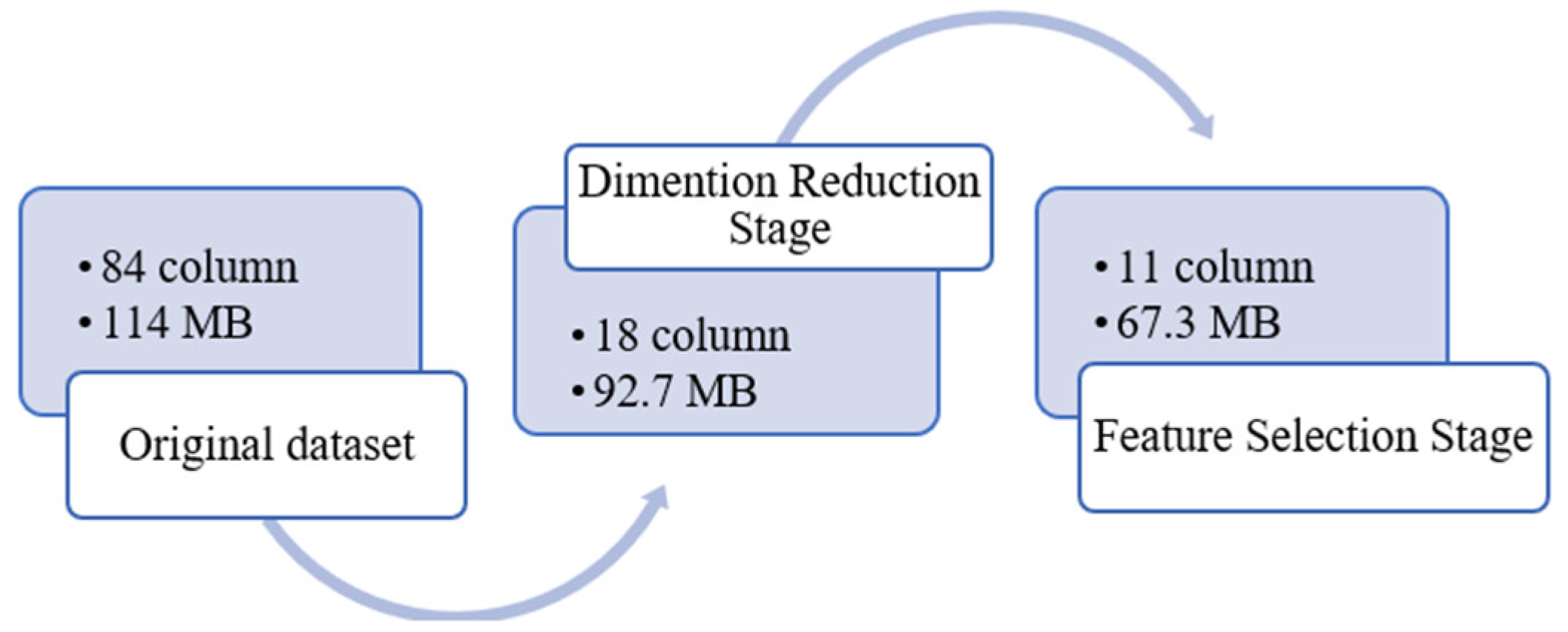
In our proposed system, we have different stages: the Initial Stage (Data Preprocessing), Second Stage (Dimension Reduction), Feature Selection Stage, and Final Stage (Model Evaluation). After each stage, we preserved the dataset for size comparison, as illustrated in
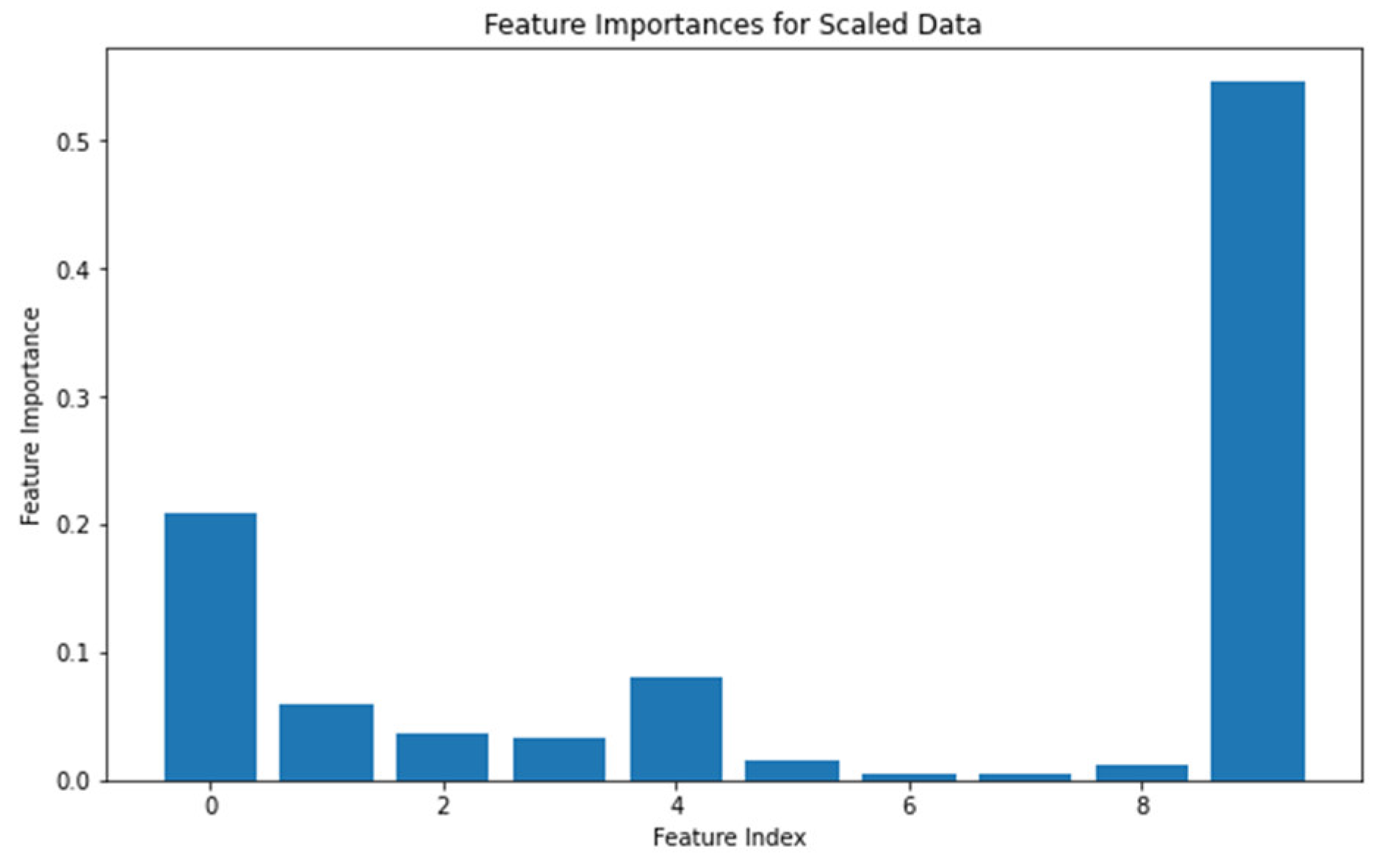
Figure 4. The original InSDN dataset consists of 84 features. However, after applying the dimension reduction algorithm in the second stage, the dataset is reduced to only 18 columns. The ultimate dataset is further refined, retaining the top 11 features. The most important features are shown in
Figure 5.
By selecting the most relevant features and eliminating irrelevant or redundant ones, you can enhance the performance of the IDS. This reduces computational complexity and improves its ability to accurately detect and classify intrusions. Metrics for evaluating Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are used to assess the performance of IDS solutions in detecting and preventing network or system intrusions and security breaches. These metrics help security professionals understand the effectiveness and efficiency of their IDS solutions. Here are some common IDS evaluation metrics:
True Positive (TP): The number of correctly detected intrusions or attacks by the IDS.
True Negative (TN): The number of correctly identified normal or non-malicious network activities by the IDS.
False Positive (FP): The number of normal activities incorrectly classified as intrusions or attacks by the IDS. This is also known as a “false alarm.”
False Negative (FN): The number of intrusions or attacks that the IDS failed to detect or classify as normal. This is also known as a “missed detection.”
Accuracy: The ratio of correctly identified instances (TP + TN) to the total number of instances. It provides an overall measure of the IDS’s correctness.
F1 Score: The harmonic mean of precision and recall. It balances the trade-off between false positives and false negatives [
1].
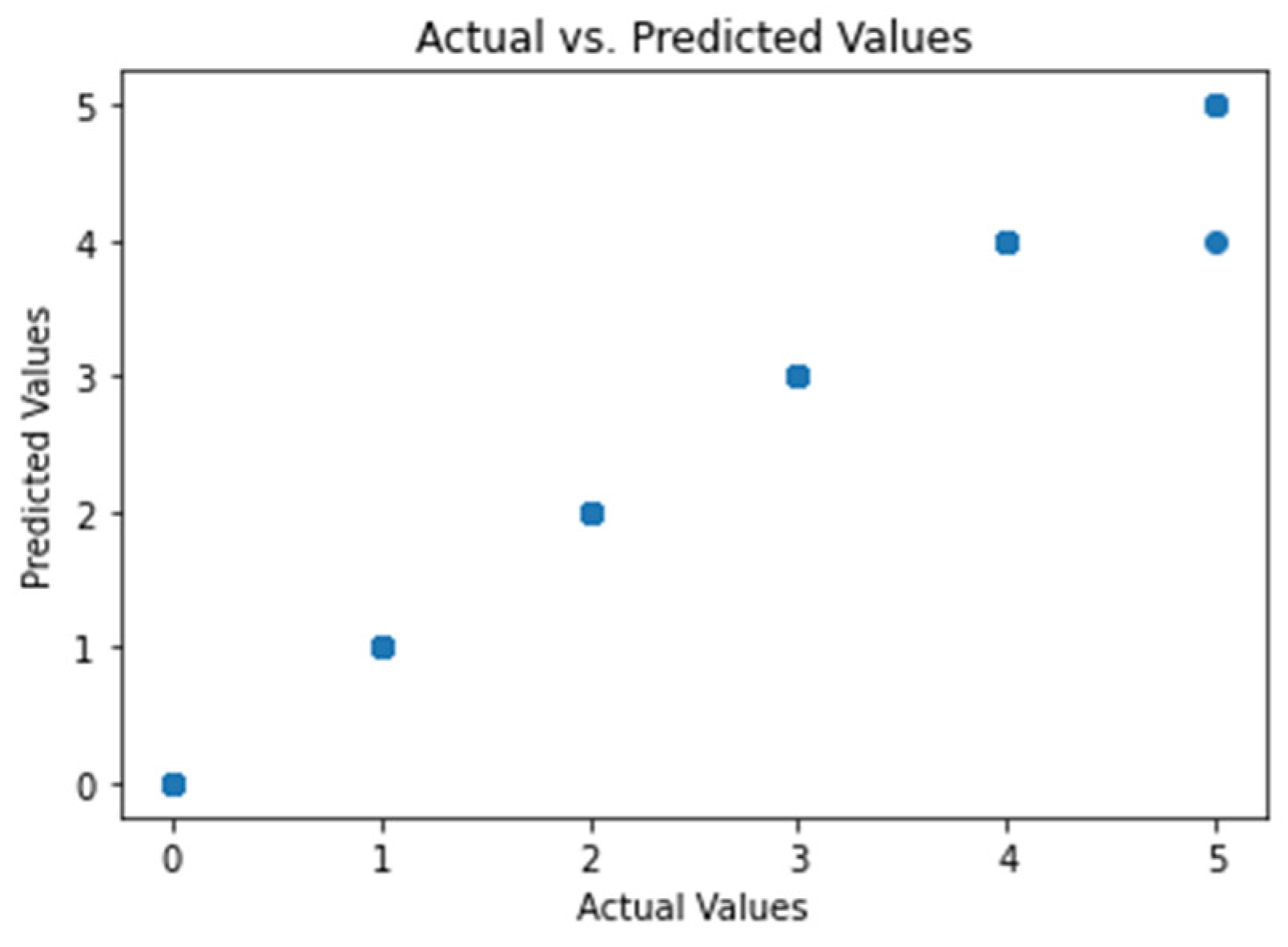
The proposed model achieved excellent results with an accuracy of 99.99%, precision of 99.99%, recall of 99.99%, ROC score of 0.99997, and a computation cost of 0.8599 seconds when using 11 features.
Figure 6 depicts the module results with actual versus predicted values.
Table 2 presents a comparison between our methodology and existing approaches. Our methodology achieves a remarkably high accuracy of 99.99% with a minimal number of features, using only 11. Additionally, we achieve a high computational speed of less than a second, specifically 0.8599 seconds. This makes our methodology suitable for wireless networks, particularly in limited resource environments such as IoT.