Submitted:
29 February 2024
Posted:
29 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
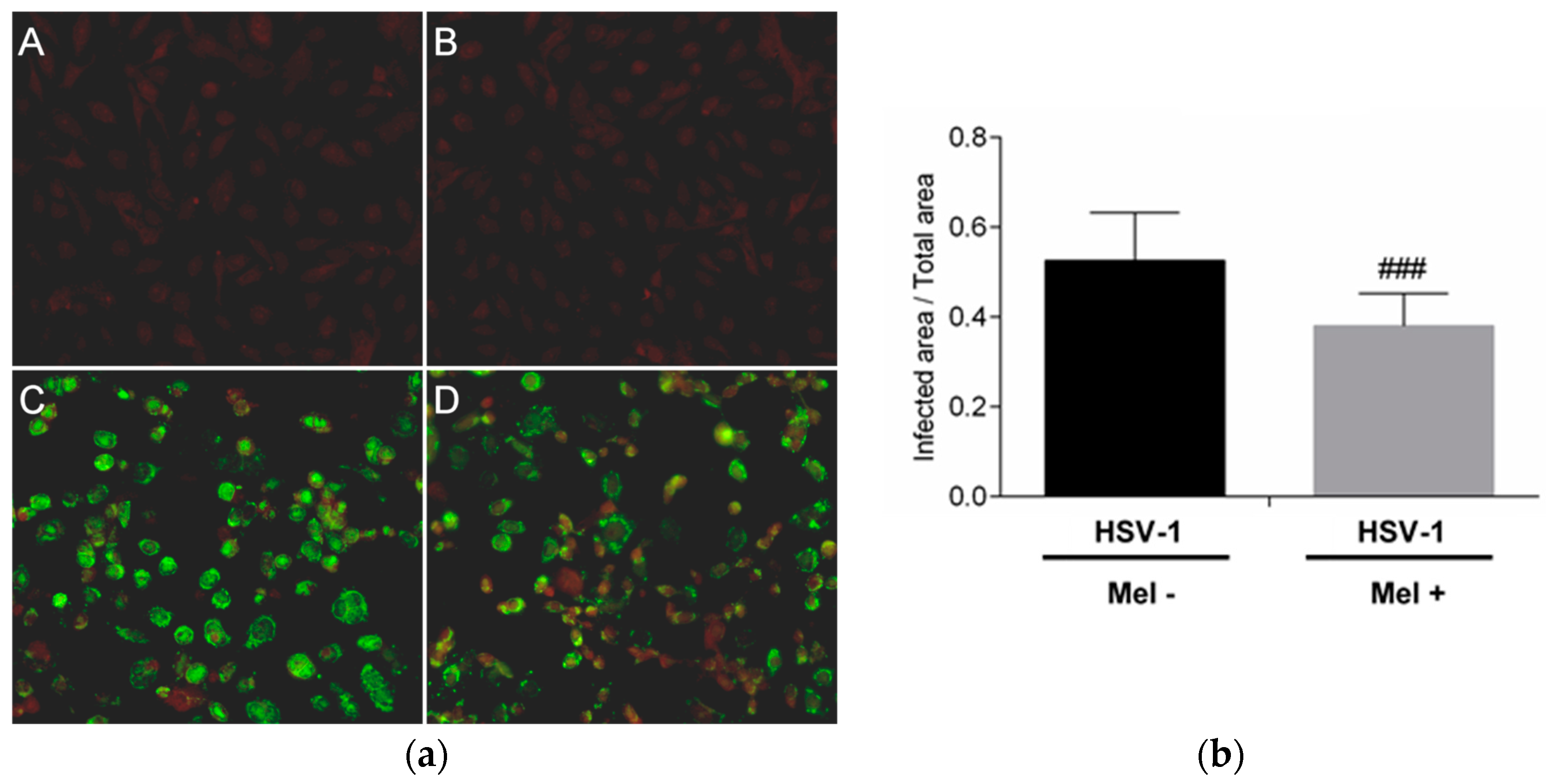
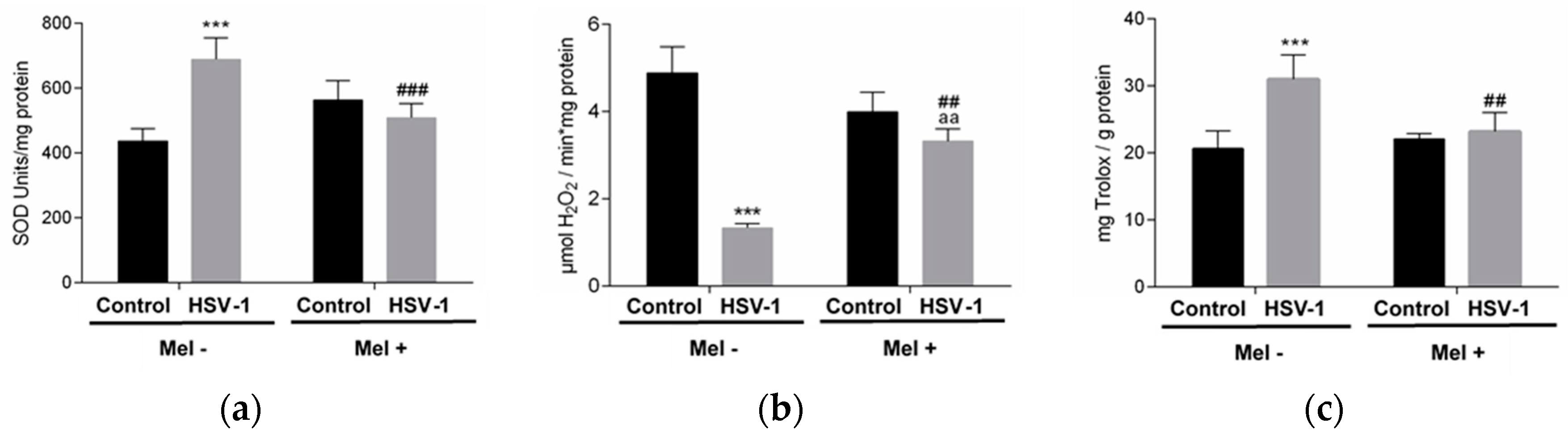
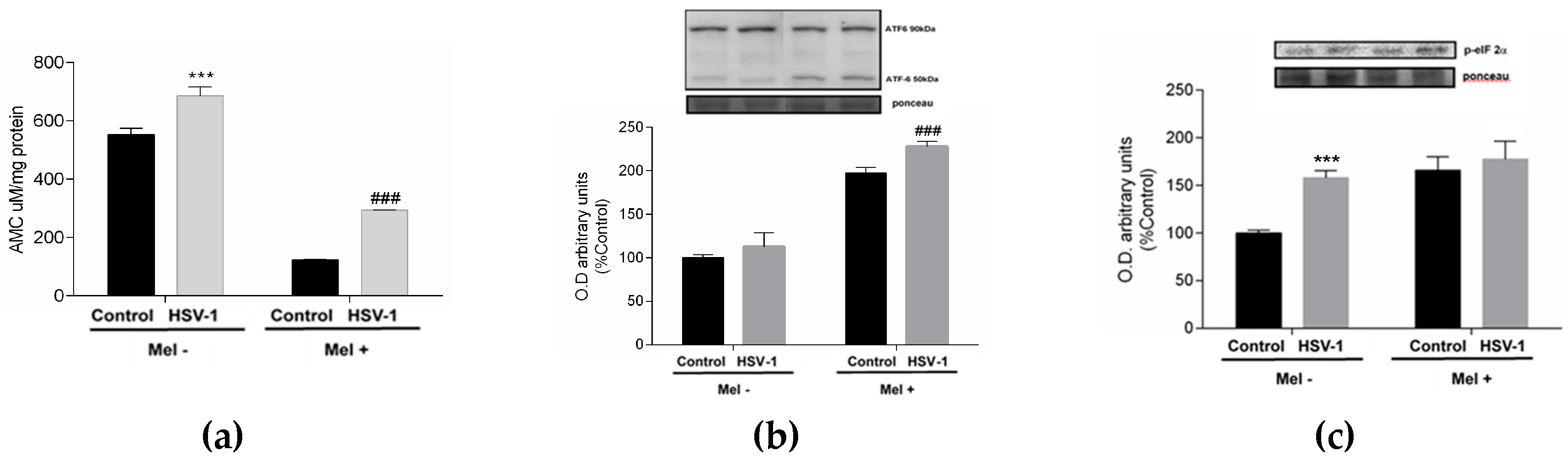
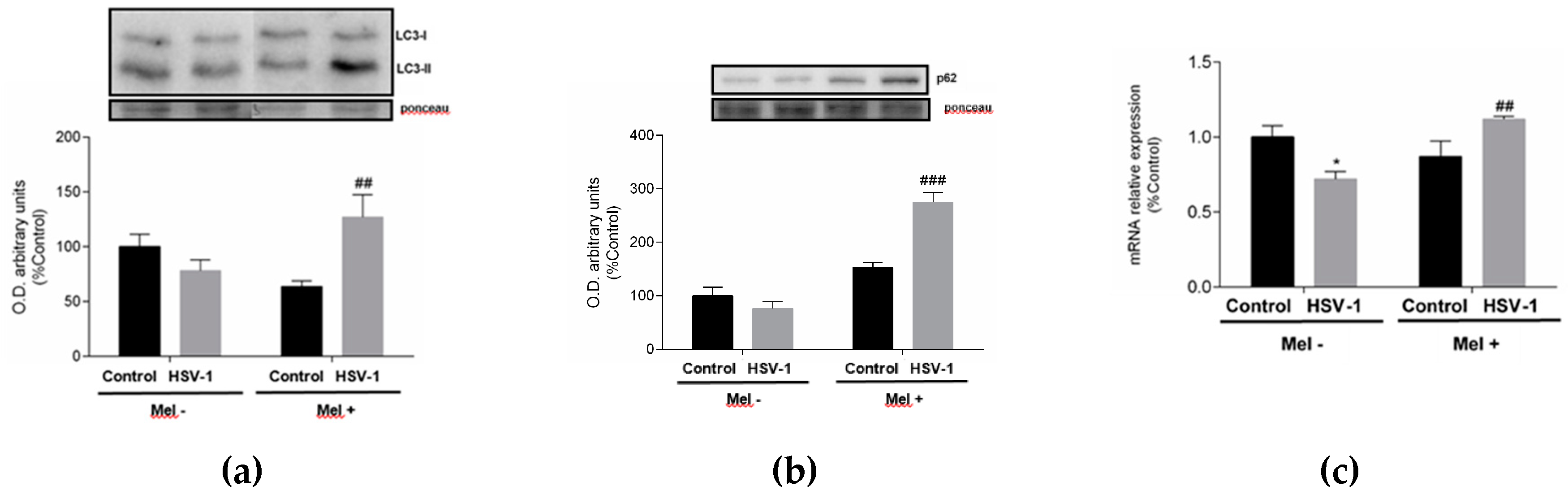
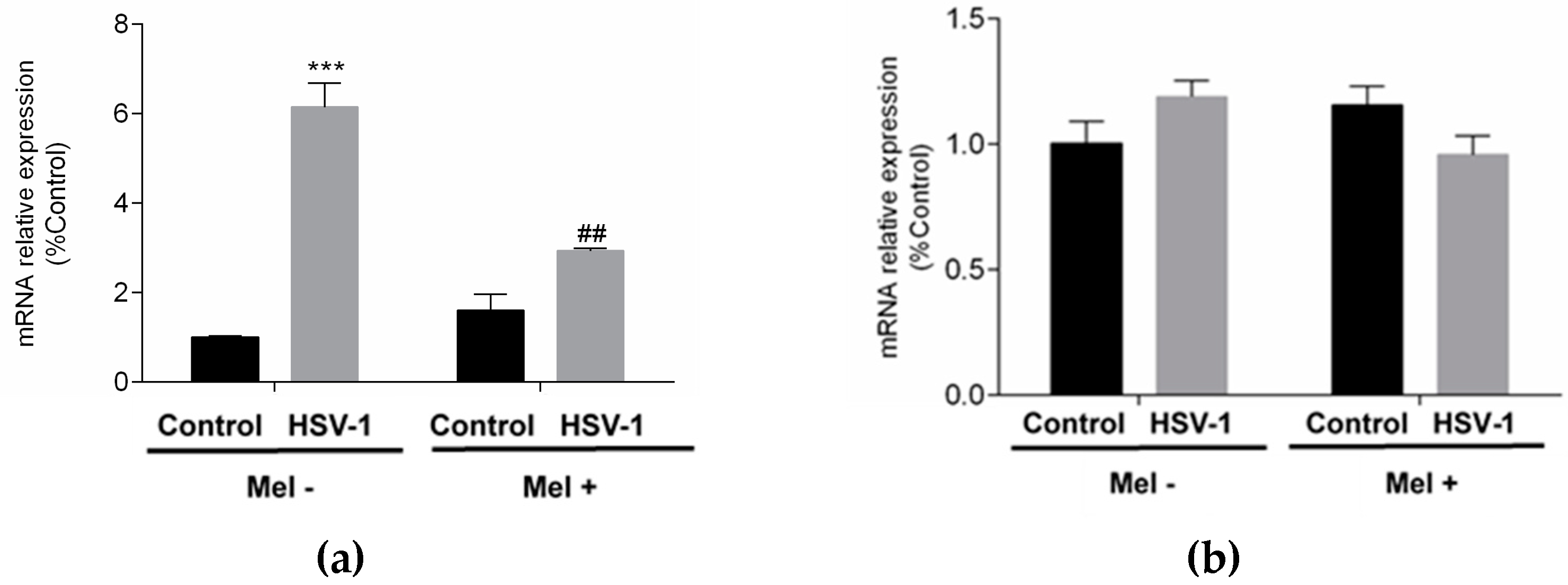
2. Results
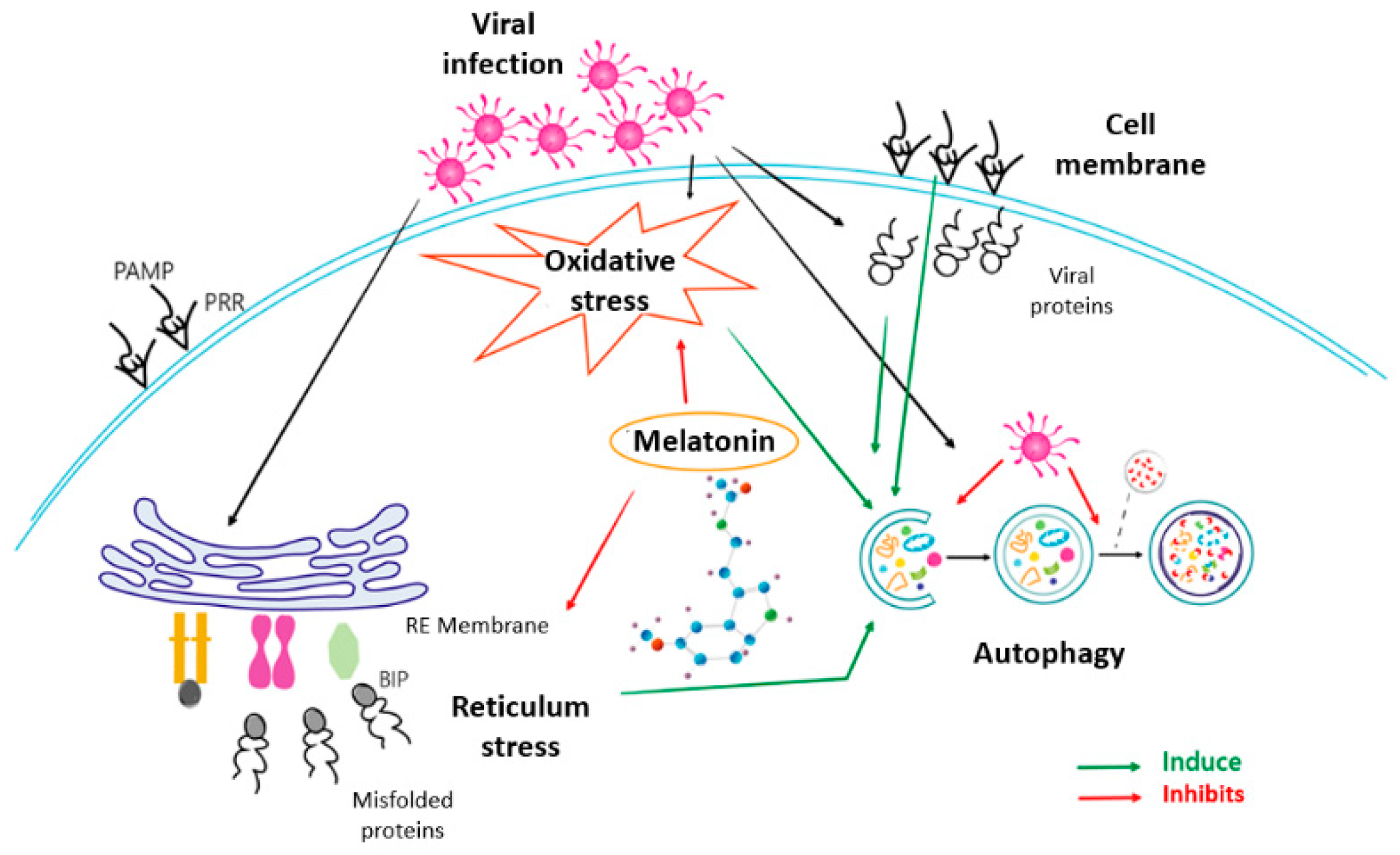
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Viruses
4.2. HSV-1 Antigen Detection
4.3. Antioxidant Activity and Enzymatic Assays
4.4. Immunoblotting
4.5. Proteasome Activity
4.6. Gene Expression Quantification
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arduino, P. G.; Porter, S. R. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 infection: overview on relevant clinico-pathological features. J Oral Pathol Med. 2008;37(2):107-121. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Viejo-Borbolla, A. Pathogenesis and virulence of herpes simplex virus. Virulence 2021;12(1):2670-2702. [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, LA.; Upadhyay, R.; Greeley, ZW.; Margulies, BJ. Current Drugs to Treat Infections with Herpes Simplex Viruses-1 and -2. Viruses. 2021;13(7):1228. [CrossRef]
- Gavilán, E.; Medina-Guzman, R.; Bahatyrevich-Kharitonik, B.; Ruano, D. Protein Quality Control Systems and ER Stress as Key Players in SARS-CoV-2-Induced Neurodegeneration. Cells 2024;13(2):123. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, R.Y. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a elicits heightened cytopathic effects despite robust ER-associated degradation. mBio 2024;15(1):e0303023. [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, G.M.; Pelham, R.W.; Pang, S.F.; Loughlin, L.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Sandock, K.L.; Vaughan, M.K.; Koslow, S.H.; Reiter, R.J. Nocturnal elevation of plasma melatonin and urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in young men: attempts at modification by brief changes in environmental lighting and sleep and by autonomic drugs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976;42(4):752-64. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, A.; Ordóñez, R.; Reiter, RJ.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, JL. Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(3):292-307. [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Reiter, RJ. Melatonin and its metabolites vs oxidative stress: From individual actions to collective protection. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(1):e12514. 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Chimenz, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Gitto, E. Use of Melatonin in Oxidative Stress Related Neonatal Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020;9(6):477. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anghel, L.; Baroiu, L.; Popazu, C.R.; Pătraș, D.; Fotea, S.; Nechifor, A.; Ciubara, A.; Nechita, L.; Mușat, C.L.; Stefanopol, I.A.; Tatu, A.L.; Ciubara, A.B. Benefits and adverse events of melatonin use in the elderly (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(3):219. Epub 2022 Jan 14. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Boga, J.A.; Coto-Montes, A.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Beneficial actions of melatonin in the management of viral infections: a new use for this "molecular handyman"? Rev Med Virol. 2012;22(5):323-338. [CrossRef]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Collin, F. Melatonin: action as antioxidant and potential applications in human disease and aging. Toxicology 2010;278(1):55-67. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barceló, E.J.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Clinical uses of melatonin: evaluation of human trials. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(19):2070-2095. [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Lopez-Burillo, S. Melatonin: reducing the toxicity and increasing the efficacy of drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2002;54(10):1299-1321. [CrossRef]
- Maestroni, G.J. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in immunodeficiency states, viral diseases, and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;467:217-226. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Nathan, D.; Maestroni, G.J.; Lustig, S.; Conti, A. Protective effects of melatonin in mice infected with encephalitis viruses. Arch Virol. 1995;140(2):223-230. [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, E.; Valero-Fuenmayor, N.; Pons, H.; Chacín-Bonilla, L. Melatonin protects mice infected with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997;53(5):430-434. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.C. Melatonin reduces mortality from Aleutian disease in mink (Mustela vison). J Pineal Res. 1996;21(4):214-217. [CrossRef]
- Nunes Oda, S.; Pereira Rde, S. Regression of herpes viral infection symptoms using melatonin and SB-73: comparison with Acyclovir. J Pineal Res. 2008;44(4):373-378. [CrossRef]
- Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Sánchez, D.I.; et al. Melatonin inhibits the sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling pathway in rabbits with fulminant hepatitis of viral origin. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(2):168-176. [CrossRef]
- Sebastiano, M.; Chastel, O.; de Thoisy, B.; Eens, M.; Costantini, D. Oxidative stress favours herpes virus infection in vertebrates: A meta-analysis. Curr Zool. 2016;62(4):325-332. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, G. The Differential Expression of Mitochondrial Function-Associated Proteins and Antioxidant Enzymes during Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Infection: A Potential Mechanism for Virus Infection-Induced Oxidative Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;7072917. [CrossRef]
- Sartori, G.; Jardim, N.S.; Sari, M.H.; Flores, E.F.; Prigol, M.; Nogueira, C.W. Diphenyl Diselenide Reduces Oxidative Stress and Toxicity Caused by HSV-2 Infection in Mice. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(5):1028-1037. [CrossRef]
- Crespo, I.; Miguel, B.S.; Laliena, A.; Alvarez, M.; Culebras, J.M.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Melatonin prevents the decreased activity of antioxidant enzymes and activates nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling in an animal model of fulminant hepatic failure of viral origin. J Pineal Res. 2010;49(2):193-200. [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, P.; et al. Melatonin inhibits Gram-negative pathogens by targeting citrate synthase. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(7):1430-1444. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casales, M.; Hernanz, R.; González-Carnicero, Z.; et al. The Melatonin Derivative ITH13001 Prevents Hypertension and Cardiovascular Alterations in Angiotensin II-Infused Mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024;388(2):670-687. [CrossRef]
- Macauslane, K.L.; Pegg, C.L.; Short, K.R.; Schulz, B.L. Modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress response pathways by respiratory viruses. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2023 7:1-19. Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.M.; Pritchard, S.M.; Wudiri, G.A.; Trammell, C.E.; Nicola, A.V. Early Steps in Herpes Simplex Virus Infection Blocked by a Proteasome Inhibitor. mBio 2019;10(3). pii: e00732-19. [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Greber, U.F. The endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response - homeostasis, cell death and evolution in virus infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2021;45(5):fuab016. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, BP.; McCormick, C. Herpesviruses and the Unfolded Protein Response. Viruses. 2019;12(1):17. [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Kropp, K.A.; Kirchner, M. et al. Herpes simplex virus type 1 modifies the protein composition of extracellular vesicles to promote neurite outgrowth and neuroinfection. mBio 2024;15(2):e0330823. [CrossRef]
- Burnett, H.F.; Audas, T.E.; Liang, G.; Lu, R.R. Herpes simplex virus-1 disarms the unfolded protein response in the early stages of infection. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012;17(4):473-483. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Feng, Z.; He, B. Herpes simplex virus 1 infection activates the endoplasmic reticulum resident kinase PERK and mediates eIF-2alpha dephosphorylation by the gamma(1)34.5 protein. J Virol. 2005;79(3):1379-1388. [CrossRef]
- Mulvey, M.; Arias, C.; Mohr, I. Maintenance of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells through the association of a viral glycoprotein with PERK, a cellular ER stress sensor. J Virol. 2007;81(7):3377-3390. [CrossRef]
- Kleber, A.; Kubulus, D.; Rössler, D.; Wolf, B.; Volk, T.; Speer, T.; Fink, T. Melatonin modifies cellular stress in the liver of septic mice by reducing reactive oxygen species and increasing the unfolded protein response. ExpMolPathol 2014;97(3):565-571. [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhai, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. The Cross-Linksof Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Autophagy, and Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:691881. [CrossRef]
- Magalhães-Novais, S.; Bermejo-Millo, J.C.; Loureiro, R.; Mesquita, K.A.; Domingues, M.R.; Maciel, E.; Melo, T.; Baldeiras, I.; Erickson, J.R.; Holy, J.; Potes, Y.; Coto-Montes, A.; Oliveira, P.J.; Vega-Naredo, I. Cell quality control mechanisms maintain stemness and differentiation potential of P19 embryonic carcinoma cells. Autophagy 2020;16(2):313-333. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gobeil, PA.; Leib, D.A. Herpes simplex virus γ34.5 interferes with autophagosome maturation and antigen presentation in dendritic cells. mBio 2012;3(5):e00267-12. [CrossRef]
- Cavignac, Y.; Esclatine, A. Herpesviruses and autophagy: catch me if you can! Viruses 2010;2(1):314-333. [CrossRef]
- Boga, J.A.; Caballero, B.; Potes, Y.; Perez-Martinez, Z.; Reiter, R.J.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Coto-Montes, A. Therapeutic potential of melatonin related to its role as an autophagy regulator: A review. J Pineal Res. 2019;66(1):e12534. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, G.; Wada, K.; Okuno, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Nukina, N. Serine 403 phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 regulates selective autophagic clearance of ubiquitinated proteins. Mol Cell. 2011;44(2):279-89. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bursch, W.; Ellinger, A.; Gerner, C.; Fröhwein, U.; Schulte-Hermann, R. Programmed cell death (PCD). Apoptosis, autophagic PCD, or others? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;926:1-12. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shenk, T.E. Viruses and apoptosis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995;5(1):105-111. [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Al-Shorbagy, M.Y.; Saad, M.A. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Chem Biol Interact 2021;335:109368. [CrossRef]
- Coto-Montes A, Boga JA, Rosales-Corral S, Fuentes-Broto L, Tan DX, Reiter RJ. Role of melatonin in the regulation of autophagy and mitophagy: A review. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;361(1-2):12-23. Epub 2012 May 1. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.P.; Dailey, M.; Sugarman, E. Negative and positive assays of superoxide dismutase based on hematoxylin autoxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987;255(2):329-336. [CrossRef]
- Lubinsky, S.; Bewley, G.C. Genetics of Catalase in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER: Rates of Synthesis and Degradation of the Enzyme in Flies Aneuploid and Euploid for the Structural Gene. Genetics 1979;91(4):723-742. [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254.
- Arnao, M.B.; Cano, A.; Acosta, M. The hydrophilic and lipophilic contribution to total antioxidant activity. Food Chemistry 2001;73(2):239–244. [CrossRef]
- de Gonzalo-Calvo, D.; Neitzert, K.; Fernández, M.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Caballero, B.; García-Macía, M.; Suárez, F.M.; Rodríguez-Colunga, M.J.; Solano, J.J.; Coto-Montes, A. Differential inflammatory responses in aging and disease: TNF-alpha and IL-6 as possible biomarkers. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49(5):733-737. [CrossRef]
- Potes, Y.; Pérez-Martinez, Z.; Bermejo-Millo, J.C.; Rubio-Gonzalez, A.; Fernandez-Fernández, M.; Bermudez, M.; Arche, J.M.; Solano, J.J.; Boga, J.A.; Oliván, M.; Caballero, B.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Coto-Montes, A. Overweight in the Elderly Induces a Switch in Energy Metabolism that Undermines Muscle Integrity. Aging Dis. 2019; 1;10(2):217-230.
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001;25(4):402-408. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




