Submitted:
28 February 2024
Posted:
28 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background and Context: Sentiment Analysis
2.1. Sentiment Analysis
2.1.1. Levels of Sentiment Analysis
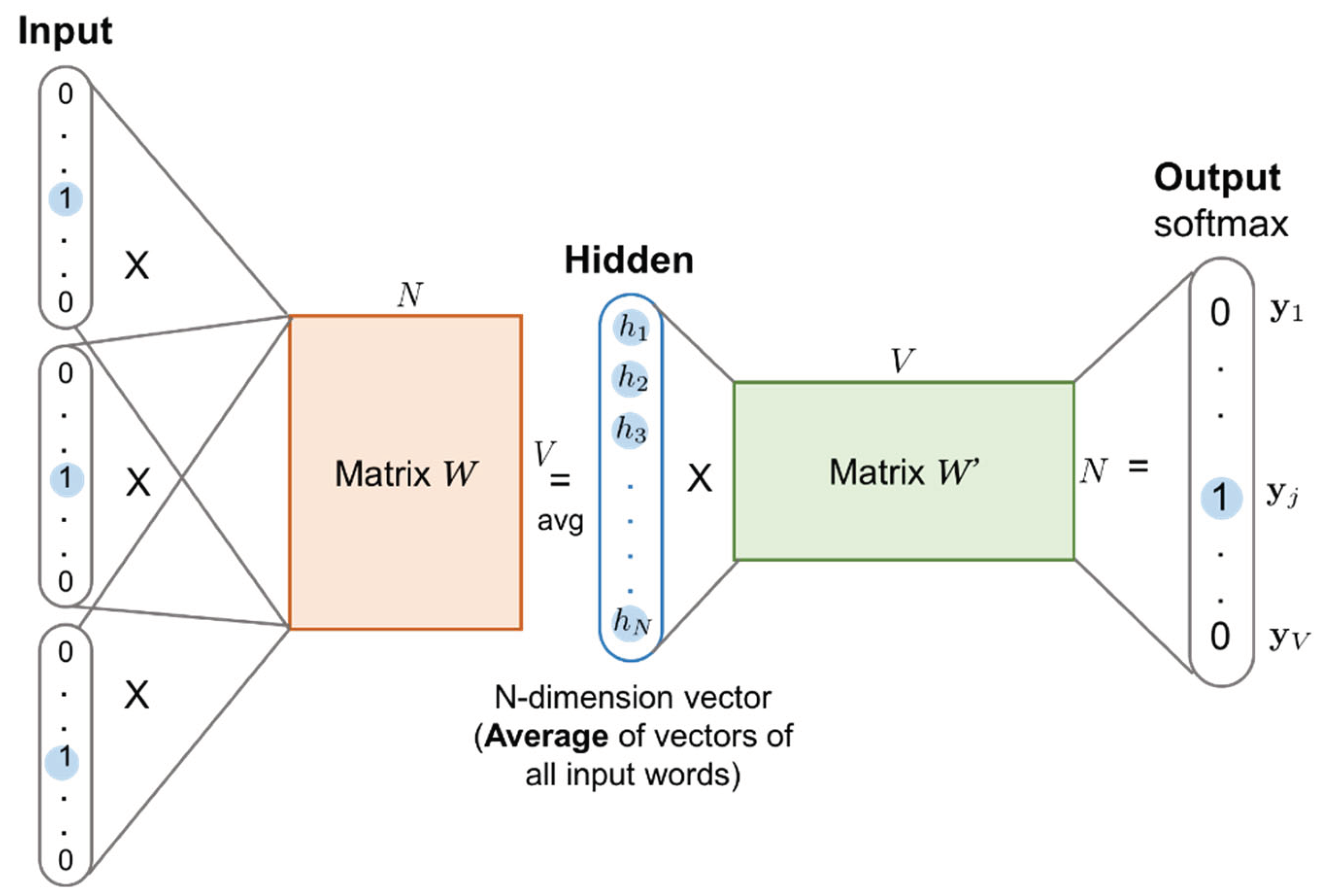
2.1.2. Word Embedding
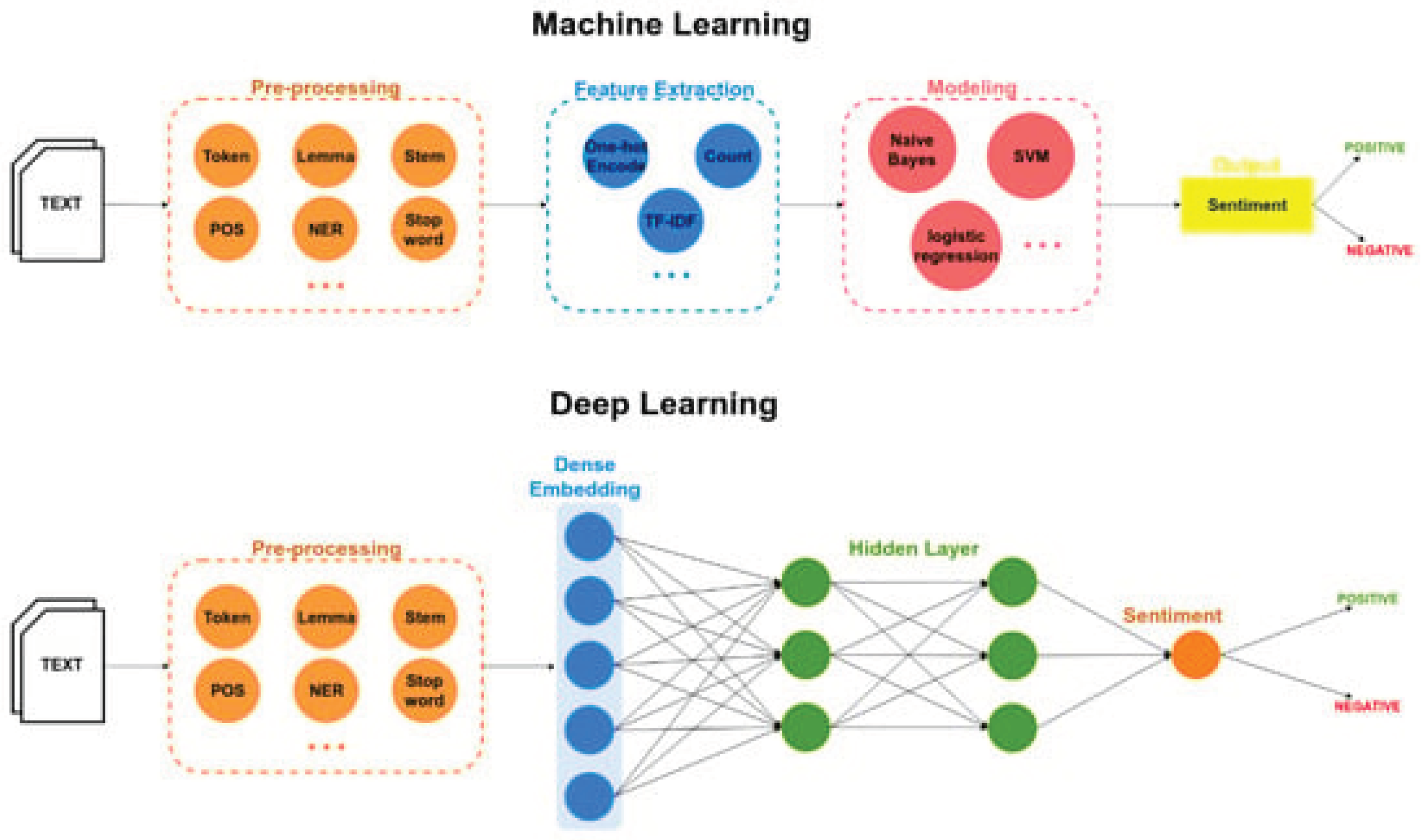
2.2. Deep Learning
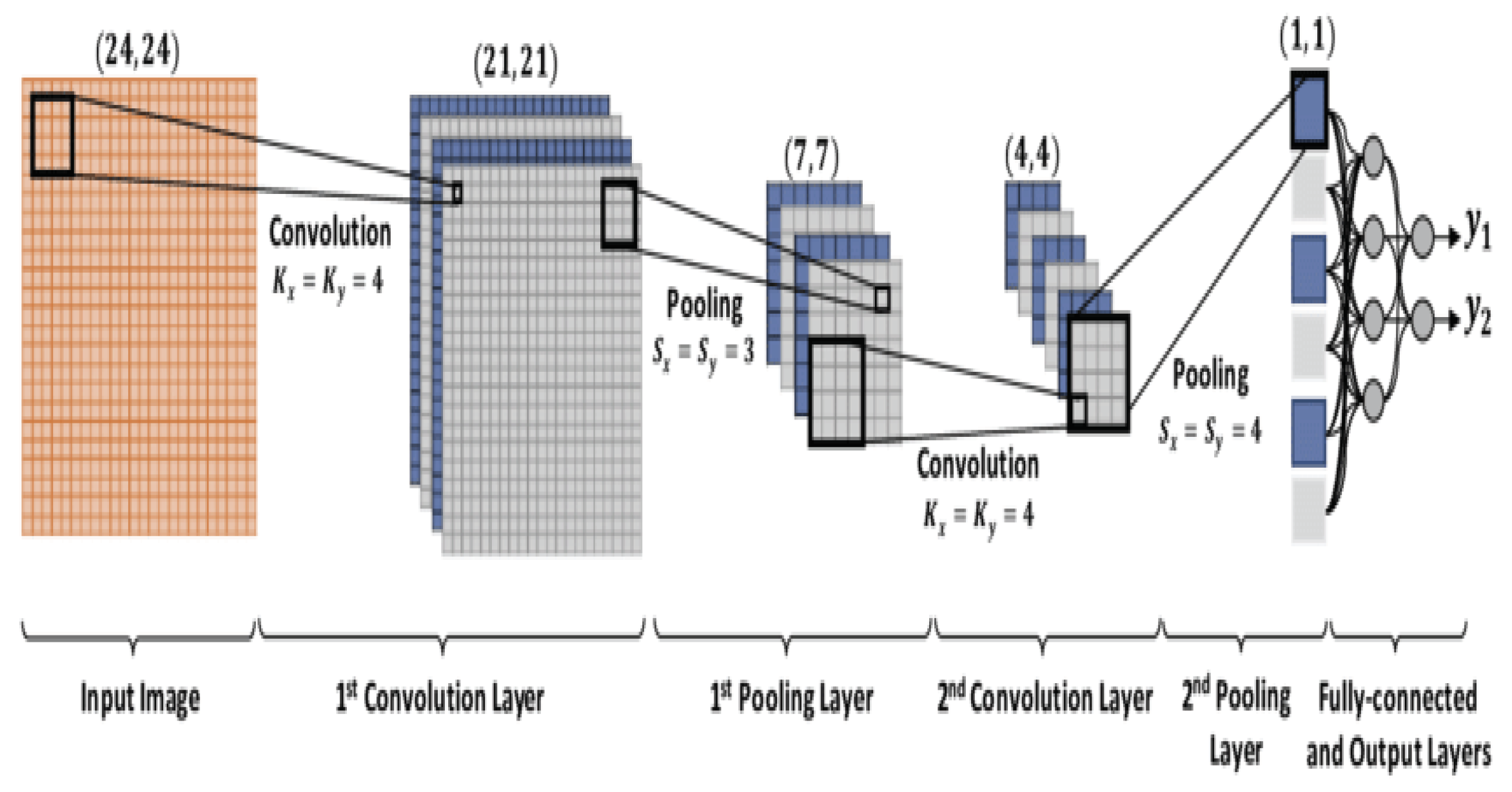
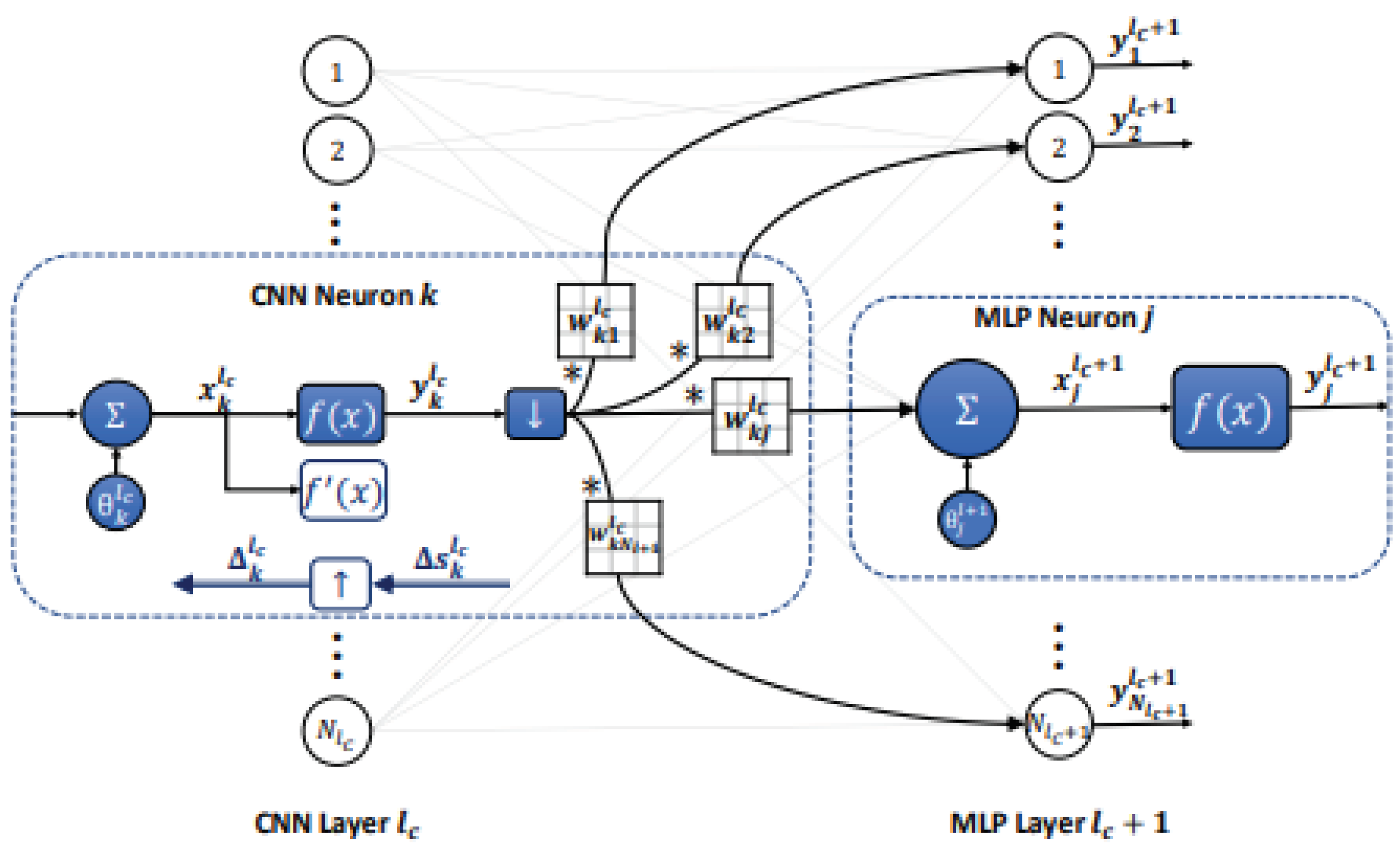
2.2.1. CNN
2.2.2. RNN-LSTM
2.2.3. RNN-BiLSTM
3. Related Works
3.1. Short Text Sentiment Analysis
3.2. Document Level Sentiment Analysis
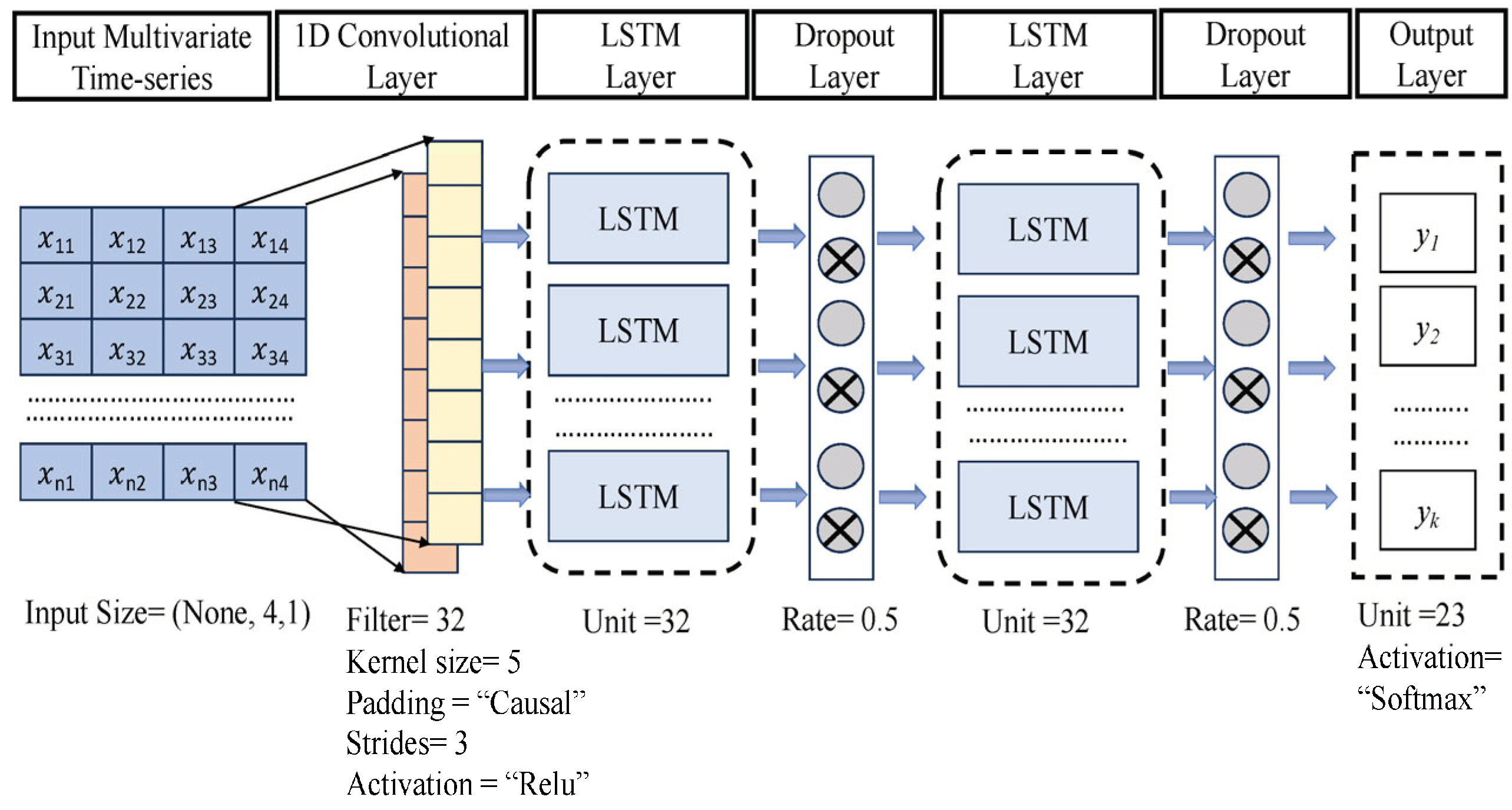
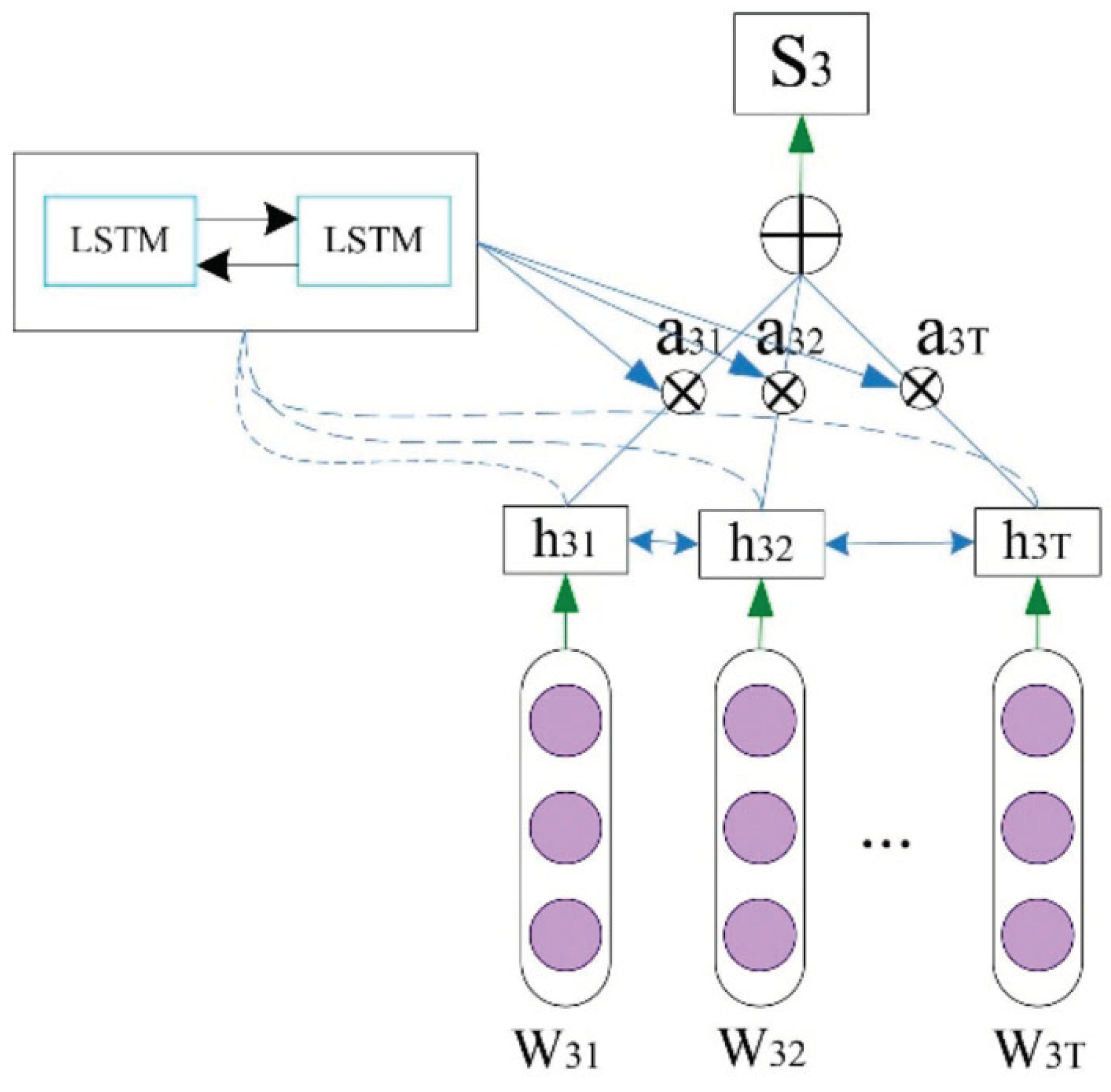
4. Proposed Model: CNN - LSTM and Doc2vec for Document-Level Sentiment Analysis
4.1. Model Overview and Motivation
4.2. Document Representation
4.3. Convolution Layer
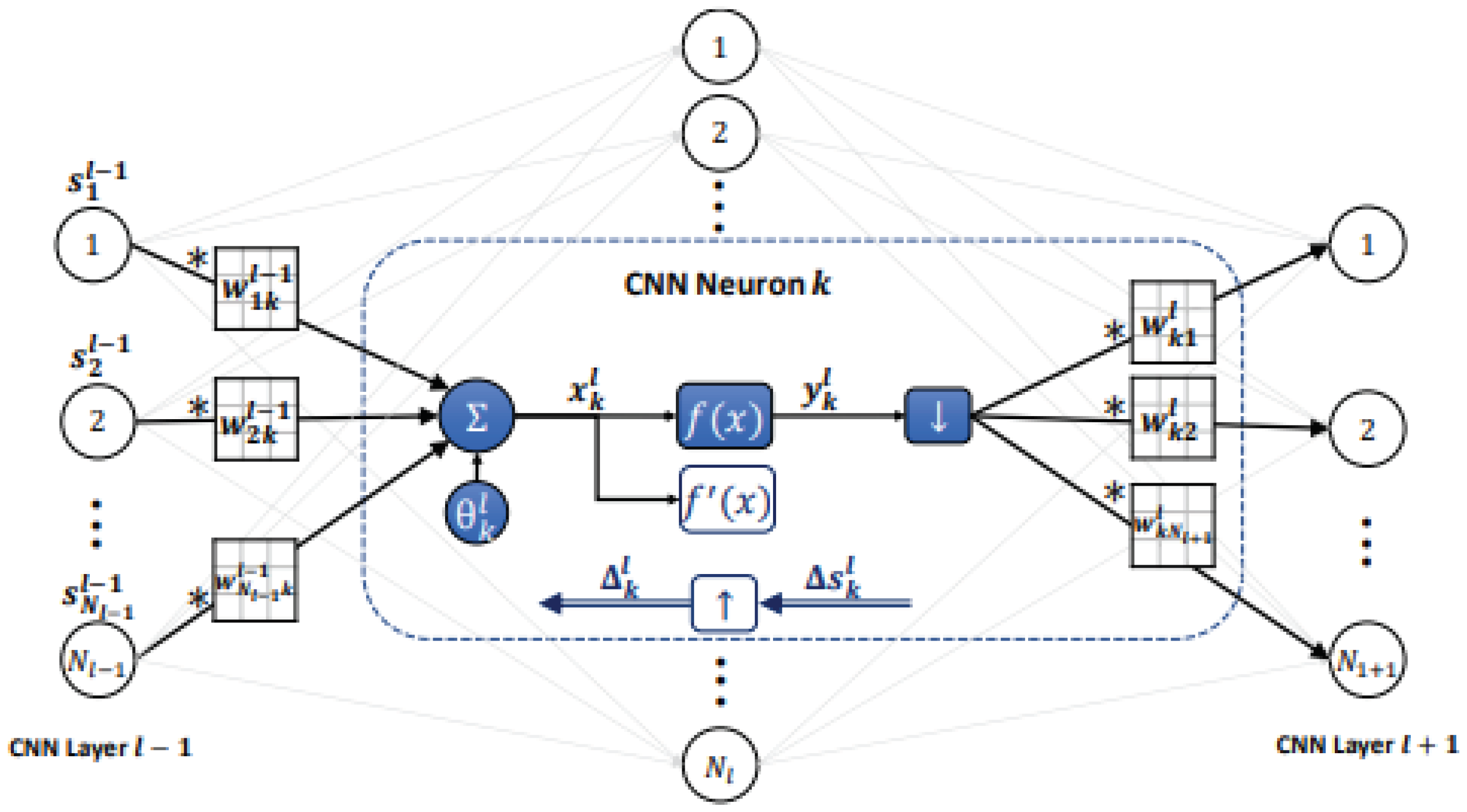
- 1)
- Initialize weights and biases (e.g., randomly, ~U(-0.1, 0.1)) of the network.
- 2)
-
For each BP iteration DO:
- a.
- For each PCG beat in the dataset, DO:
- FP: A layer's neuron outputs may be found by forward propagation from the input layer to the output layer.
- Update: Update the weights and biases by the (accumulation of) sensitivities scaled with the learning factor.
4.4. Activation Layer
4.5. Regularization
4.6. Optimization
4.7. BiLSTM Layer
5. Experimental Results
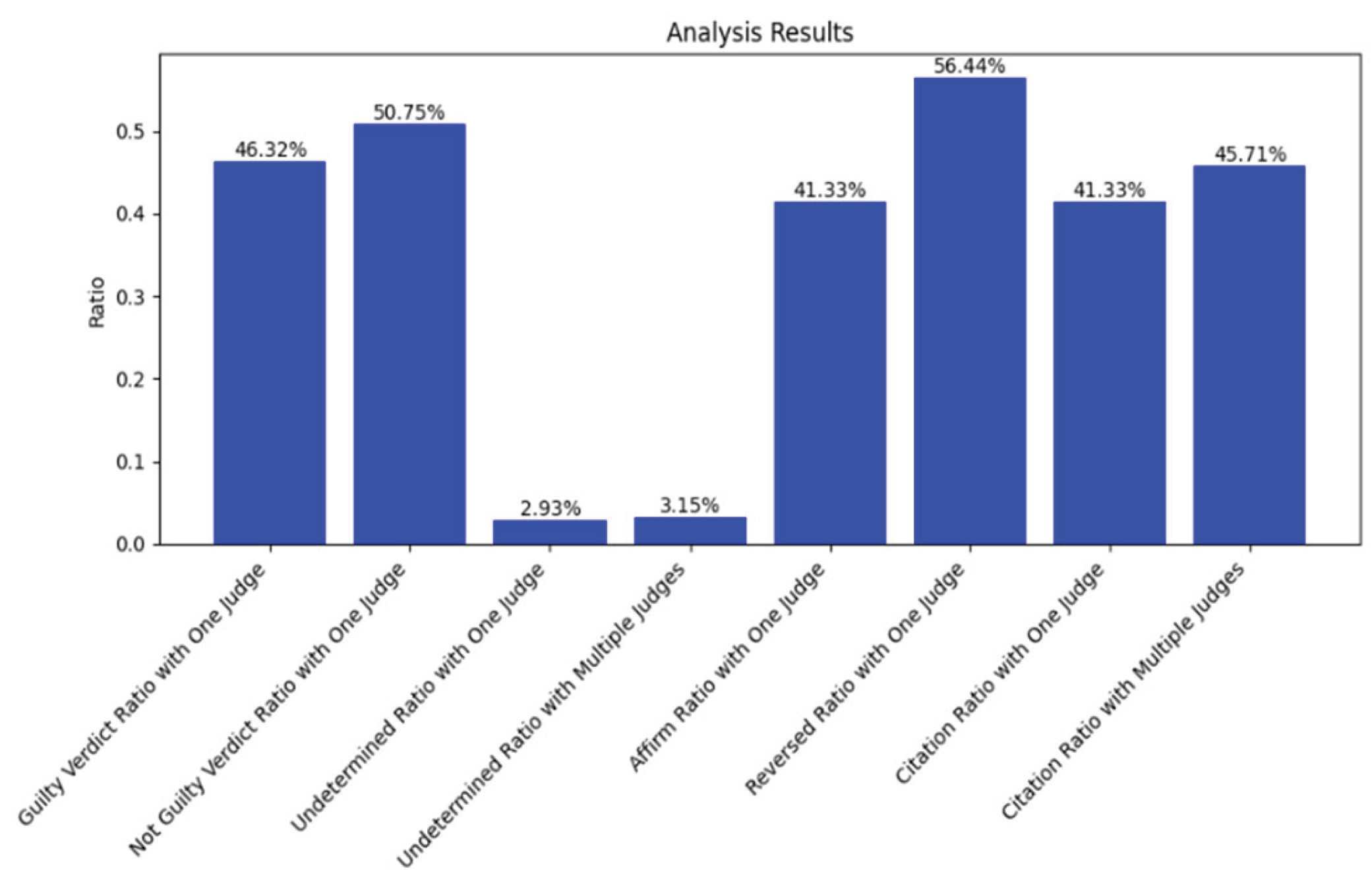
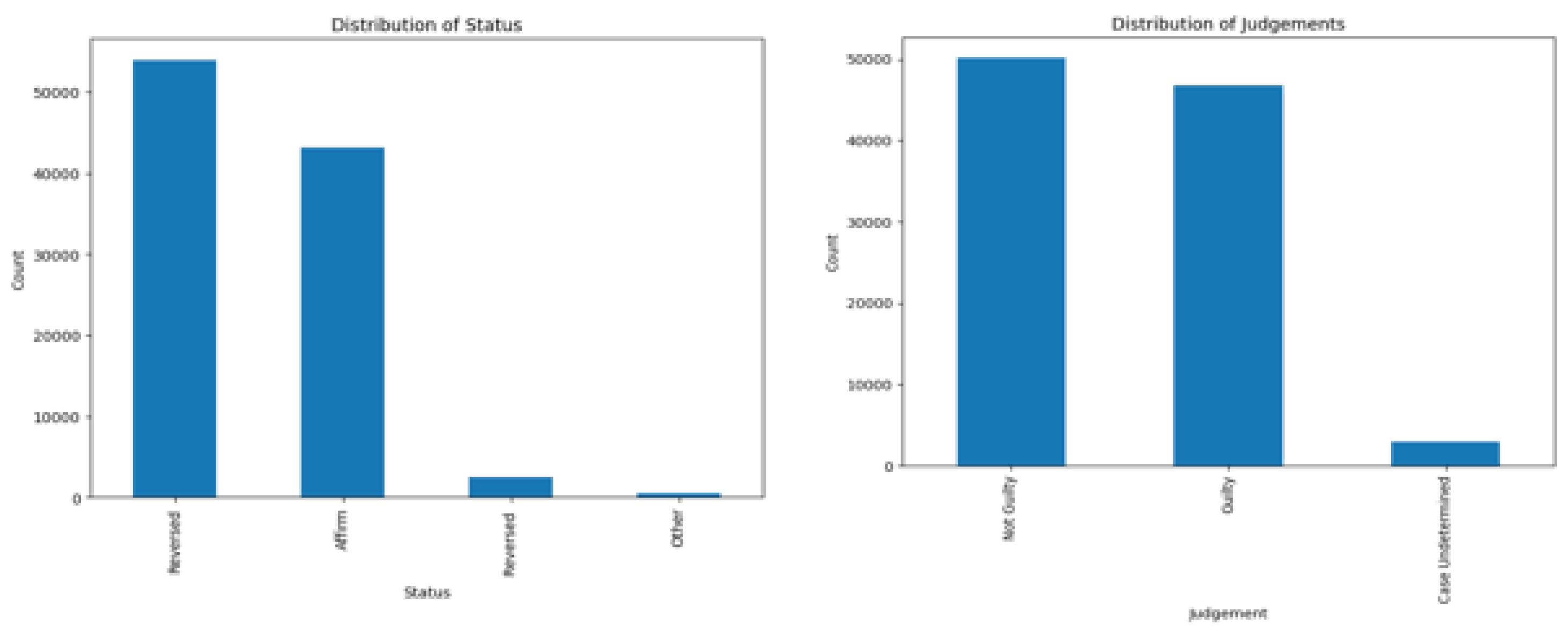
5.1. Data Set
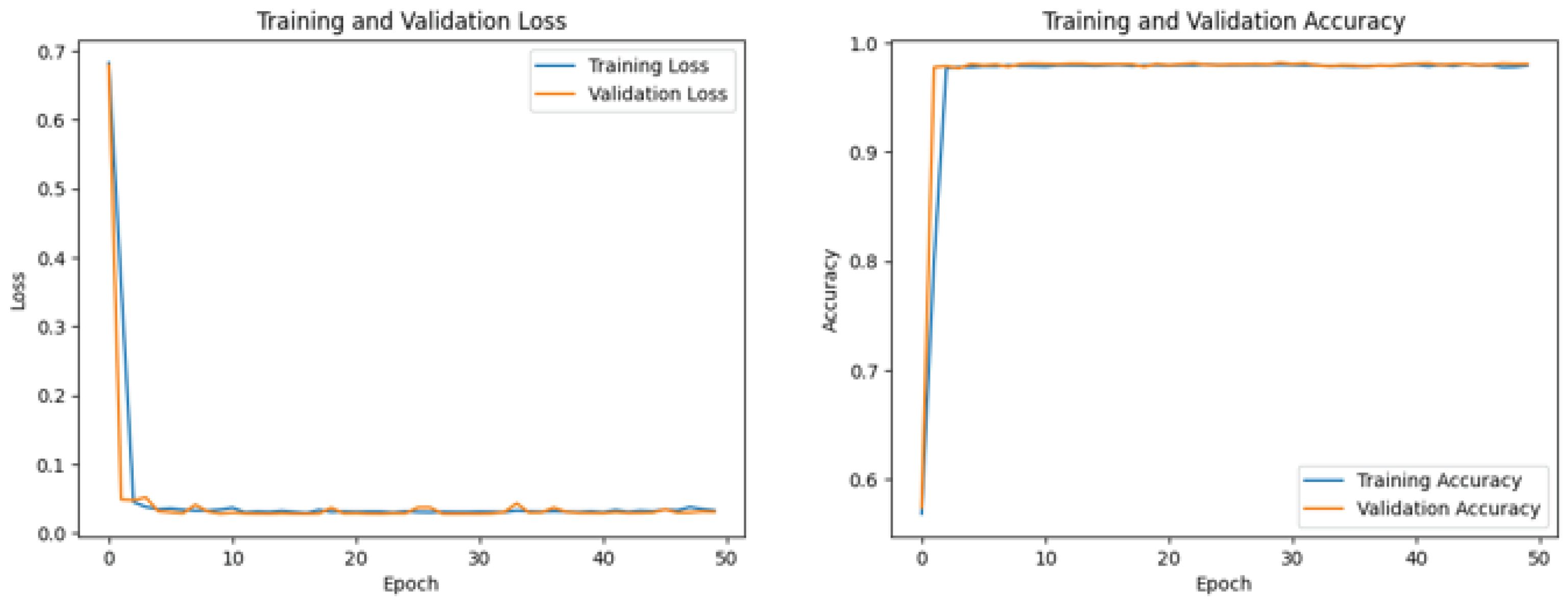
5.2. Results
5.3. Comparison
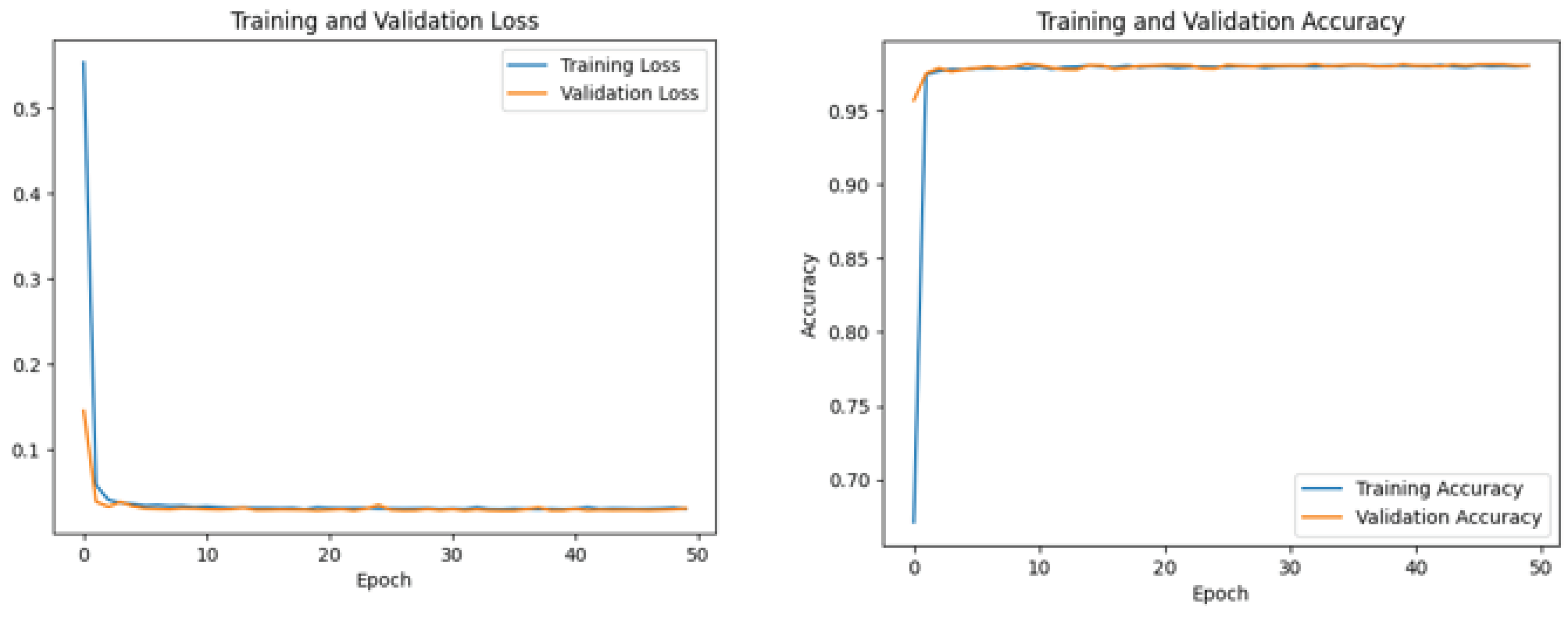
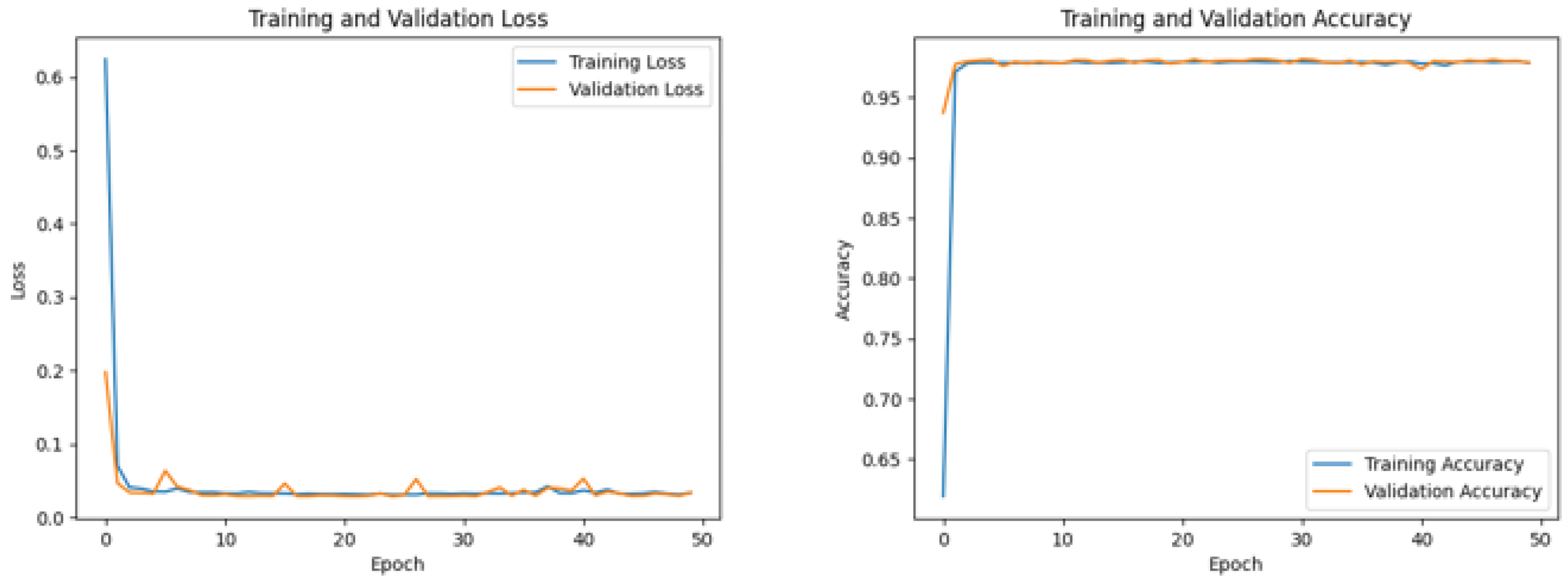
5.3.1. CNN Model
5.3.2. LSTM Models
5.3.3. CNN-LSTM Model
| Model | Test Accuracy |
|---|---|
| CNN+LSTM model 1 | 98.01% |
| CNN+LSTM model 2 | 97.94% |
| CNN+LSTM model 3 | 98.05% |
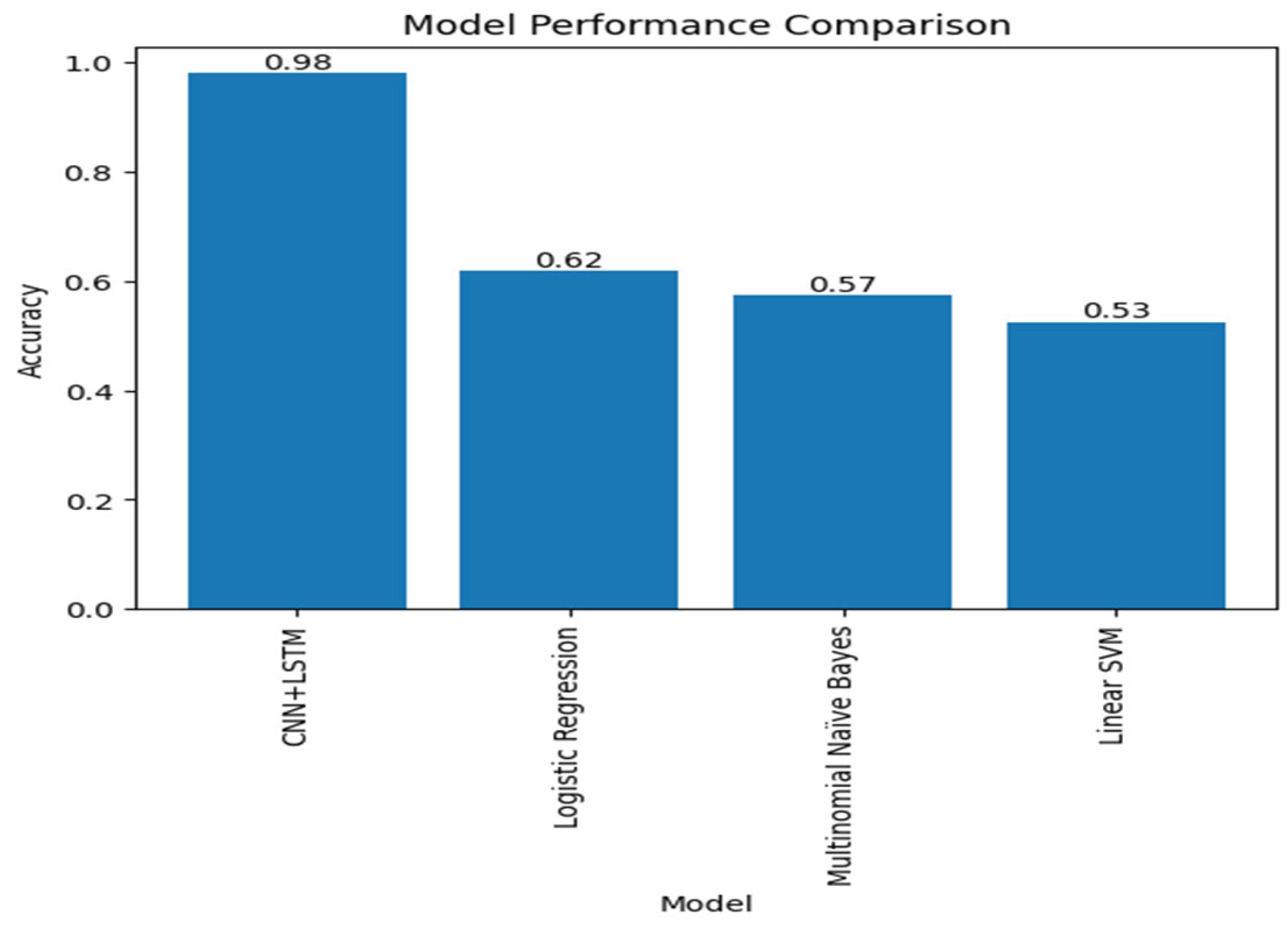
5.4. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- B. Liu, Sentiment analysis and opinion mining. Springer Nature, 2022.
- T. Nasukawa and J. Yi, "Sentiment analysis: Capturing favorability using natural language processing," in Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on Knowledge capture, 2003, 70-77. [CrossRef]
- X. Bai, "Predicting consumer sentiments from online text," Decision Support Systems, 2011, 50, 732-742. [CrossRef]
- U. Naseem, I. Razzak, K. Musial, and M. Imran, "Transformer based Deep Intelligent Contextual Embedding for Twitter sentiment analysis," Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 113, 58-69. [CrossRef]
- N. N. Yusof, A. Mohamed, and S. Abdul-Rahman, "Context Enrichment Model Based Framework for Sentiment Analysis," in Soft Computing in Data Science: 5th International Conference, SCDS 2019, Iizuka, Japan, August 28–29, 2019, Proceedings 5, 2019: Springer, pp. 325-335.
- P. Vijayaragavan, R. Ponnusamy, and M. Aramudhan, "An optimal support vector machine based classification model for sentimental analysis of online product reviews," Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 111, 234-240. [CrossRef]
- T. Mikolov, M. Karafiát, L. Burget, J. Cernocký, and S. Khudanpur, "Recurrent neural network based language model," in Interspeech, 2010, vol. 2, no. 3: Makuhari, pp. 1045-1048.
- M. Rhanoui, M. Mikram, S. Yousfi, and S. Barzali, "A CNN-BiLSTM model for document-level sentiment analysis," Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 2019, 1, 832-847.
- A. Tripathy, A. Anand, and S. K. Rath, "Document-level sentiment classification using hybrid machine learning approach," Knowledge and Information Systems, 2017, 53, 805-831.
- K. NEWMYER and M. Zaccagnino, "VOLUME 52 FEBRUARY 2021 NUMBER 4," 2021.
- R. F. Southcott and K. A. Walsh, "Canadian maritime law update: 2006," J. Mar. L. & Com., 2007, 38, 335.
- O. M. Brandes and D. Curran, "Changing currents: A case study in the evolution of water law in Western Canada," Water policy and governance in Canada, 2017, 45-67.
- A. Christodoulou and J. Echebarria Fernández, "Maritime Governance and International Maritime Organization instruments focused on sustainability in the light of United Nations’ sustainable development goals," in Sustainability in the Maritime Domain: Towards Ocean Governance and Beyond: Springer, 2021, pp. 415-461.
- V. Gavrilov, R. Dremliuga, and R. Nurimbetov, "Article 234 of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the law of the sea and reduction of ice cover in the Arctic Ocean," Marine Policy, 2019, 106, 103518. [CrossRef]
- S. Undavia, A. Meyers, and J. E. Ortega, "A comparative study of classifying legal documents with neural networks," in 2018 Federated conference on computer science and information systems (FedCSIS), 2018: IEEE, pp. 515-522.
- B. Abimbola, Q. Tan, and J. R. Villar, "Introducing Intelligence to the Semantic Analysis of Canadian Maritime Case Law: Case Based Reasoning Approach," in International Workshop on Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications, 2022: Springer, pp. 587-595.
- M. Ghorbani, M. Bahaghighat, Q. Xin, and F. Özen, "ConvLSTMConv network: a deep learning approach for sentiment analysis in cloud computing," Journal of Cloud Computing, 2020, 9, 1-12.
- Z. Jin, Y. Yang, and Y. Liu, "Stock closing price prediction based on sentiment analysis and LSTM," Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32, 9713-9729. [CrossRef]
- F. Gers, "Long short-term memory in recurrent neural networks," Verlag nicht ermittelbar, 2001.
- S. Sohangir, D. Wang, A. Pomeranets, and T. M. Khoshgoftaar, "Big Data: Deep Learning for financial sentiment analysis," Journal of Big Data, 2018, 5, 1-25. [CrossRef]
- M. Schuster and K. K. Paliwal, "Bidirectional recurrent neural networks," IEEE transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45, 2673-2681.
- K. S. Tai, R. Socher, and C. D. Manning, "Improved semantic representations from tree-structured long short-term memory networks," arXiv preprint arXiv:1503.00075, 2015.
- A. Sadia, F. Khan, and F. Bashir, "An overview of lexicon-based approach for sentiment analysis," in 2018 3rd International Electrical Engineering Conference (IEEC 2018), 2018, pp. 1-6.
- S. Guo and G. Zhang, "Using machine learning for analyzing sentiment orientations toward eight countries," Sage Open, 2020, 10, 2158244020951268. [CrossRef]
- E. C. ATEŞ, G. E. BOSTANCI, and M. Serdar, "Big data, data mining, machine learning, and deep learning concepts in crime data," Journal of Penal Law and Criminology, 2020, 8, 293-319. [CrossRef]
- A. Kaur and B. Bozic, "Convolutional Neural Network-based Automatic Prediction of Judgments of the European Court of Human centers," in AICS, 2019, pp. 458-469.
- X. Li, X. Kang, C. Wang, L. Dong, H. Yao, and S. Li, "A neural-network-based model of charge prediction via the judicial interpretation of crimes," IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 101569-101579. [CrossRef]
- M. Medvedeva, M. Vols, and M. Wieling, "Using machine learning to predict decisions of the European Court of Human centers," Artificial Intelligence and Law, 2020, 28, 237-266. [CrossRef]
- K. Machová, M. Mikula, X. Gao, and M. Mach, "Lexicon-based sentiment analysis using the particle swarm optimization," Electronics, 2020, 9, 1317. [CrossRef]
- A. Alghazzawi, O. Bamasag, A. Albeshri, I. Sana, H. Ullah, and M. Z. Asghar, "Efficient prediction of court judgments using an LSTM+ CNN neural network model with an optimal feature set," Mathematics, 2022, 10, 683. [CrossRef]
- A. Bramantoro and I. Virdyna, "Classification of divorce causes during the COVID-19 pandemic using convolutional neural networks," PeerJ Computer Science, 2022, 8, e998. [CrossRef]
- J. Watson, G. Aglionby, and S. March, "Using machine learning to create a repository of judgments concerning a new practice area: a case study in animal protection law," Artificial Intelligence and Law, 2023, 31, 293-324. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Da Silva et al., "Document type classification for Brazil’s supreme court using a convolutional neural network," in 10th International Conference on Forensic Computer Science and Cyber Law (ICoFCS), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2018, pp. 29-30.
- V. G. Pillai and L. R. Chandran, "Verdict prediction for indian courts using bag of words and convolutional neural network," in 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), 2020: IEEE, pp. 676-683.
- D. L. Chen and J. Eagel, "Can machine learning help predict the outcome of asylum adjudications?," in Proceedings of the 16th edition of the International Conference on Articial Intelligence and Law, 2017, pp. 237-240.
- K. Lum, "Limitations of mitigating judicial bias with machine learning," Nature Human Behaviour, 2017, 1, 0141. [CrossRef]
- A. Tasdelen and B. Sen, "A hybrid CNN-LSTM model for pre-miRNA classification," Scientific reports, 2021, 11, 14125.
- F. Muhlenbach, L. N. Phuoc, and I. Sayn, "Predicting Court Decisions for Alimony: Avoiding Extra-legal Factors in Decision made by Judges and Not Understandable AI Models," arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.04824, 2020.
- A. Alsayat, "Improving sentiment analysis for social media applications using an ensemble deep learning language model," Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2022, 47, 2499-2511. [CrossRef]
- J. T. Lam, D. Liang, S. Dahan, and F. H. Zulkernine, "The Gap between Deep Learning and Law: Predicting Employment Notice," in NLLP@ KDD, 2020, pp. 52-56.
- B. Abimbola, "Sentiment Analysis of Canadian Maritime Case Law: A Sentiment Case Law and Deep Learning Approach " Mendeley Data, vol. V1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Alzahrani, T. H. Aldhyani, S. N. Alsubari, M. M. Althobaiti, and A. Fahad, "Developing an intelligent system with deep learning algorithms for sentiment analysis of E-commerce product reviews," Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
| Word Embedding | Level | Model | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| WORD2VEC | Word level Document level Sentence level |
CNN-LSTM BERT KNN SSR |
84.9% 84.7% 89.0% 85.01% |
| GLOVE | Document level Word level Sentence level |
CNN-BiLSTM KNN CNN |
88.9% 82.7% 81.0% 91.01% |
| BOMW | Sentence level Word level Document level |
BOMW BERT CNN SR-LSTM |
92.9% 78.7% 86.0% 80.01% |
| Case Year | The year the case was registered. |
|---|---|
| Majority Opinion | Opinion of the majority of judges engaged in the case. |
| Minority Opinion | Opinion of the minority of judges engaged in the case. |
| Number of judges | The total number of judges hearing the case. |
| Court Judgment | Final court judgment on the case (whether the decision is affirmed or not). |
|
Number of cited documents (Court decision legislation data) |
The number of laws and judicial jurisprudence cited by the judges to support their decision. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





