Submitted:
28 February 2024
Posted:
28 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. MicroRNAs Expression Profile Analysis
2.2.1. MicroRNA Extraction from FFPE Tissues and FNAC Samples
2.2.2. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.3. Genetic Analysis
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. Mutational Screening
2.4. Clinicopathological Features
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Series Description
3.1.1. Epidemiologic Data
3.1.2. MiRNAS Profile in Cytology Samples
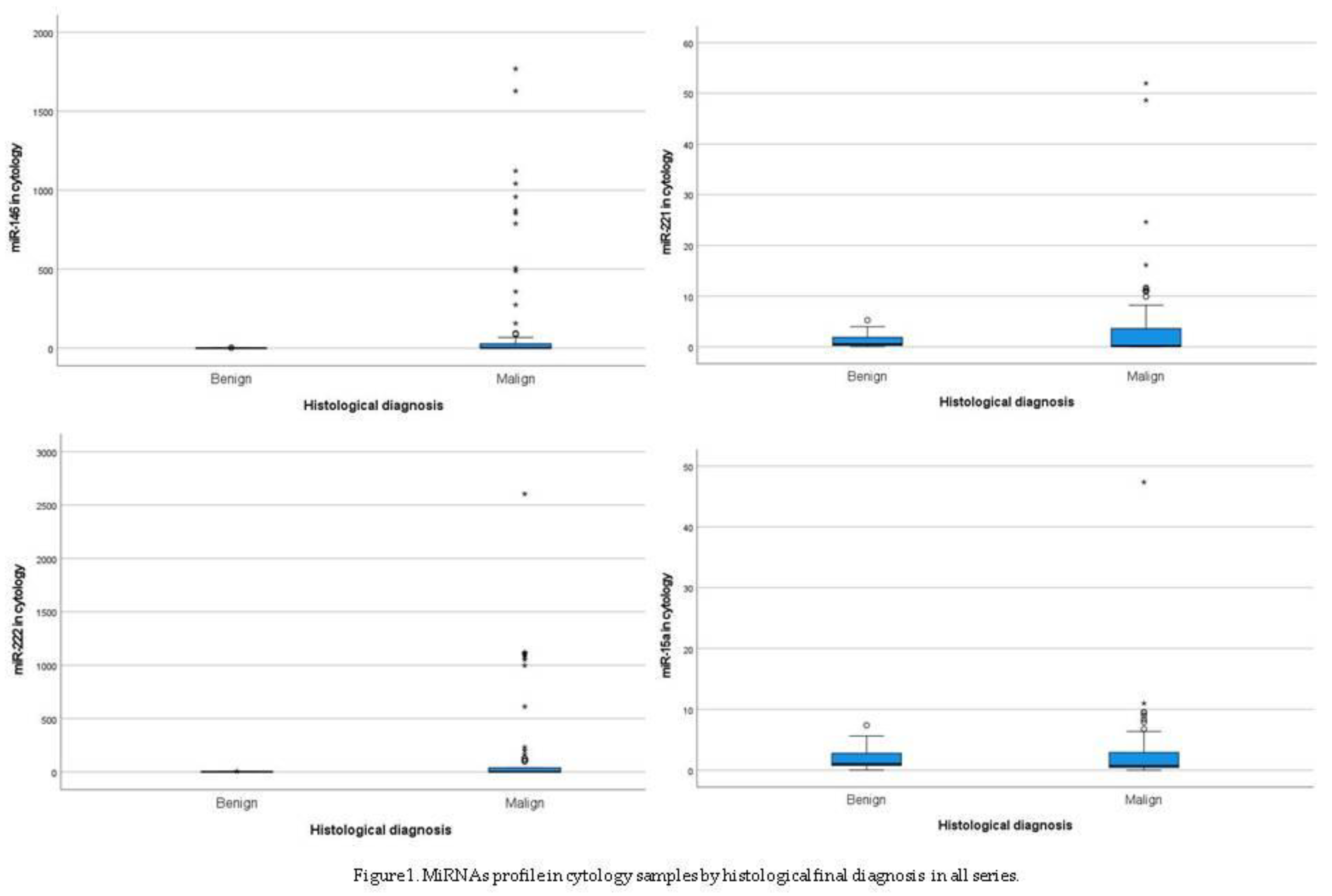
3.1.3. MiRNAs Profile in Histology Samples
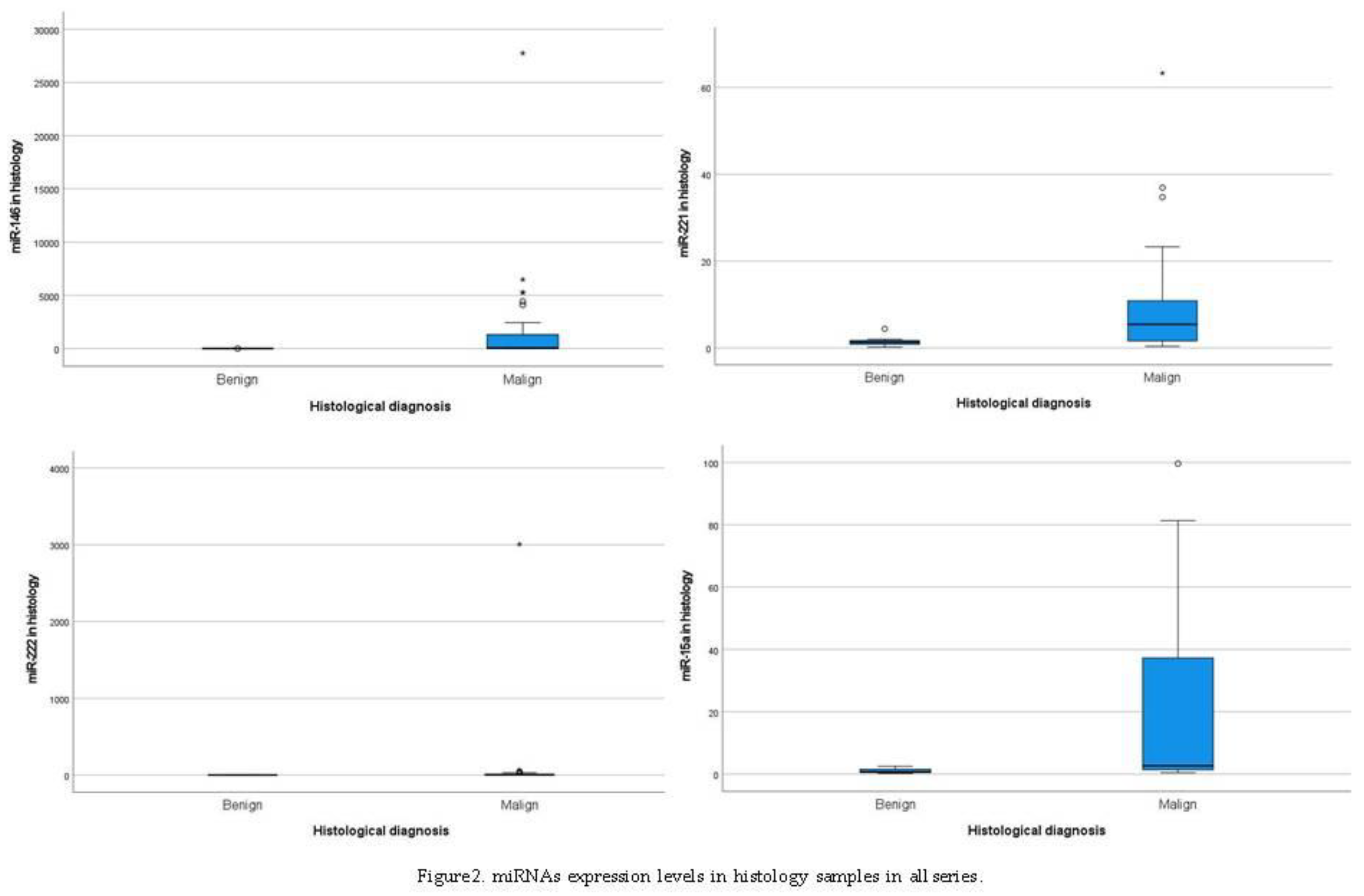
3.2. MiRNA Expression and Mutations in Cytology and Histology Samples in PTCs
3.3. MiRNA Expression and Clinicopatological Features in PTCs
3.4. The Discriminative Ability of miRNAs in Histology for the Diagnosis of Malignancy
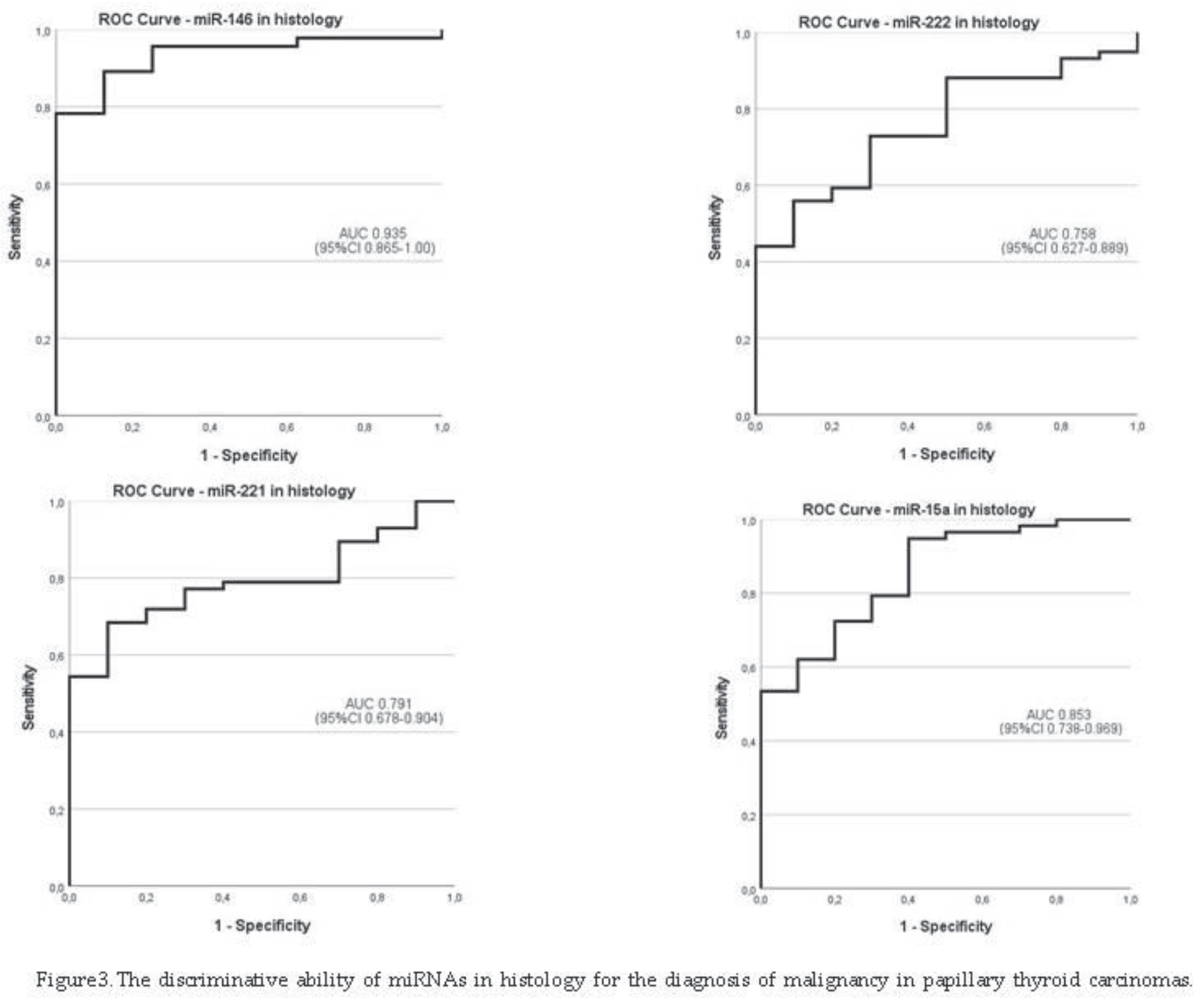
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlumberger, M.; Pacini, F.; Tuttle, R.M. Thyroid Tumors, 4th ed.; Institut Médico-Educatif: Paris, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grussendorf, M.; Ruschenburg, I.; Brabant, G. Malignancy rates in thyroid nodules: A long-term cohort study of 17,592 patients. Eur. Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e220027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Brito, J.P.; Vaccarella, S. Long-Term Declines of Thyroid Cancer Mortality: An International Age-Period-Cohort Analysis. Thyroid 2020, 30, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Filho, A.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Bray, F.; Cao, B.; Franceschi, S.; Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L. Thyroid Cancer Incidence Trends by Histology in 25 Countries: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; et al. Co-existence of BRAF (V600E) and TERT promoter mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma is associated with tumor aggressiveness, but not with lymph node metastasis. Cancer Manag Res 2018, 10, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlozek, J.; Pekova, B.; Rotnágl, J.; Holý, R.; Astl, J. Genetic Changes in Thyroid Cancers and the Importance of Their Preoperative Detection in Relation to the General Treatment and Determination of the Extent of Surgical Intervention—A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.Z.; Cibas, E.S. The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology: Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Syed Z Ali 1, Zubair W Baloch 2, Beatrix Cochand-Priollet 3, Fernando C Schmitt 4, Philippe Vielh 5, Paul A VanderLaan 6. The 2023 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid 2023, 33, 1039–1044. [CrossRef]
- Fulvio Basolo, Elisabetta Macerola, Anello Marcello Poma, and Liborio Torregrossa. The 5th edition of WHO classification of tumors of endocrine organs: changes in the diagnosis of follicular-derived thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine 2023, 80, 470–476. [CrossRef]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; et al. American Thyroid Association: Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosimo Durante, Laszlo Hegedüs, Agnieszka Czarniecka, Ralf Paschke, Gilles Russ, Fernando Schmitt, Paula Soares, Tamas Solymosi, and Enrico Papini. 2023 European Thyroid Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for thyroid nodule management. Eur Thyroid J. 2023, 12, e230067. [CrossRef]
- Oczko-Wojciechowska, M.; Kotecka-Blicharz, A.; Krajewska, J.; Rusinek, D.; Barczynski, M.; Jarzab, B.; Czarniecka, A. European perspective on the use of molecular tests in the diagnosis and therapy of thyroid neoplasms. Gland. Surg. 2020, 9 (Suppl. S2), S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Bar, Y.; Maurice-Dror, C.; Finkel, I.; Goldvaser, H.; Dudnik, E.; Goldstein, D.A.; Gordon, N.; Billan, S.; Gutfeld, O.; et al. Next-generation sequencing in thyroid cancers: Do targetable alterations lead to a therapeutic advantage: A multicenter experience. Medicine 2021, 100, e26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina Alina Silaghi 1, Vera Lozovanu 1, Carmen Emanuela Georgescu 1, Raluca Diana Georgescu 2, Sergiu Susman 3 4, Bogdana Adriana Năsui 5, Anca Dobrean 2 6, Horatiu Silaghi 7. Thyroseq v3, Afirma GSC, and microRNA Panels Versus Previous Molecular Tests in the Preoperative Diagnosis of Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol 2021, 12, 649522. [CrossRef]
- Sergei Titov 1 2, Pavel S Demenkov 3 4, Sergei A Lukyanov 5, Sergei V Sergiyko 5, Gevork A Katanyan 6, Yulia A Veryaskina 7 3, Mikhail K Ivanov 7 2 Preoperative detection of malignancy in fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) smears with indeterminate cytology (Bethesda III, IV) by a combined molecular classifier. J Clin Pathol. 2020, 73, 722–727. [CrossRef]
- Shipra Agarwal 1, Andrey Bychkov 2, Chan-Kwon Jung 3 4. Emerging Biomarkers in Thyroid Practice and Research. Cancers 2021, 14, 204. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marcos Tadeu Santos 1, Bruna Moretto Rodrigues 2, Satye Shizukuda 2, Andrei Félix Oliveira 2, Miriane Oliveira 2, David Livingstone Alves Figueiredo 3, Giulianno Molina Melo 4, Rubens Adão Silva 5, Claudio Fainstein 6, Gerson Felisbino Dos Reis 7, Rossana Corbo 8, Helton Estrela Ramos 9, Cléber Pinto Camacho 10, Fernanda Vaisman 11, Mário Vaisman 12. Clinical decision support analysis of a microRNA-based thyroid molecular classifier: A real-world, prospective and multicentre validation studies. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104137. [CrossRef]
- Lithwick-Yanai G1, Dromi N1, Shtabsky A2,3, Morgenstern S3,4, Strenov Y3,4, Feinmesser M3,4, Kravtsov V3,5, Leon ME6, Hajdúch M7, Ali SZ8, VandenBussche CJ8, Zhang X9,10, Leider-Trejo L2,3, Zubkov A2, Vorobyov S11, Kushnir M1, Goren Y1,12, Tabak S1, Kadosh E1, Benjamin H13, Schnitzer-Perlman T1, Marmor H1, Motin M1, Lebanony D1, Kredo-Russo S1, Mitchell H13, Noller M13, Smith A13, Dattner O13, Ashkenazi K13, Sanden M13, Berlin KA13, Bar D1, Meiri E1. Multicentre validation of a microRNA-based assay for diagnosing indeterminate thyroid nodules utilising fine needle aspirate smears. J Clin Pathol. 2017, 70, 500–507. [CrossRef]
- Yuping Chen 1, Bingtian Dong 2, Lichun Huang 1, Huibin Huang 1 Serum microRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022, 22, 862–871. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi-Lin Xu 1, Yu-Yang Tian 2 3, Ying Zhou 3, Li-Qiao Liu 1 .Diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs in thyroid carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol 2020, 93, 489–498. [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova MN1, Chiosea SI, Nikiforov YE. MicroRNA expression profiles in thyroid tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2009, 20, 85–91. [CrossRef]
- Wójcicka, A.; Kolanowska, M.; Jażdżewski, K. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: MicroRNA in diagnostics and therapy of thyroid cancer. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016, 174, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvíková, M.; Kalfeřt, D.; Kholová, I. Pathobiology of MicroRNAs and Their Emerging Role in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration. Acta Cytol. 2015, 59, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.I.; Junit, S.M.; Leong Ng, K.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Karikalan, B.; Hashim, O.H. Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Genetic Alterations and Molecular Biomarker Investigations. International Journal of Medical Sciences 2019, 16, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Xue, Y.; et al. miRNA-15a regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma via regulating AKT pathway. OncoTargets and Therapy 2019, 12, 6217–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Luzi, E.; Brandi, M.L. MicroRNA Role in Thyroid Cancer Development. Journal of Thyroid Research, 2011, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Luzón-Toro, B.; Fernández, R.M.; Villalba-Benito, L.; et al. Influencers on Thyroid Cancer Onset: Molecular Genetic Basis. Genes 2019, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Chiosea, S.I.; Nikiforov, Y.E. MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Thyroid Tumors. Endocr Pathol 2009, 20, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Tseng, G.C.; Steward, D.; Diorio, D.; Nikiforov, Y.E. MicroRNA Expression Profiling of Thyroid Tumors: Biological Significance and Diagnostic Utility. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagna, M.G.; Marzocchi, C.; Pilli, T.; et al. MicroRNA expression profile of thyroid nodules in fine-needle aspiration cytology: a confirmatory series. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation 2019, 42, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Gao, AB.; Wang, Q.; et al. MicroRNA-221 promotes papillary thyroid carcinoma cell migration and invasion via targeting RECK and regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets and Therapy 2019, 12, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca Napoli 1, Ida Rapa 2, Umberto Mortara 3, Federica Massa 2, Stefania Izzo 2, Angelica Rigutto 1 4, Vanessa Zambelli 1, Claudio Bellevicine 5, Giancarlo Troncone 5, Mauro Papotti 1, Marco Volante 1. MicroRNA profiling predicts positive nodal status in papillary thyroid carcinoma in the preoperative setting. Cancer Cytopathol. 2022, 130, 695–704. [CrossRef]
- Jong-Lyul Park 1 2, Seon-Kyu Kim 2 3, Sora Jeon 4, Chan-Kwon Jung 4 5, Yong-Sung Kim 1,6. MicroRNA Profile for Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 632. [CrossRef]
- Viviana A Ruiz-Pozo 1, Santiago Cadena-Ullauri 1, Patricia Guevara-Ramírez 1, Elius Paz-Cruz 1, Rafael Tamayo-Trujillo 1, Ana Karina Zambrano 1 Differential microRNA expression for diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer. Review Front Med 2023, 10, 1139362. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Hu, J.; Wei, W.; Ma, B.; Wen, D. MicroRNA-15 regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by targeting Bcl-2. JBUON 2019, 24, 2114–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Laetitia Lebrun, Isabelle Salmon. Pathology and new insights in thyroid neoplasms in the 2022 WHO classification. Review Curr Opin Oncol. 2024, 36, 13–21. [CrossRef]
- Paschke, R.; Cantara, S.; Crescenzi, A.; Jarzab, B.; Musholt, T.J.; Sobrinho Simões, M. European Thyroid Association Guidelines regarding Thyroid Nodule Molecular Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology Diagnostics. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Sobrinho-Simões, M. New WHO classification of thyroid tumors: a pragmatic categorization of thyroid gland neoplasms. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr. 2018, 65, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; et al. Identification of key miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma based on data mining and bioinformatics methods. Biomed Rep 2020, 12, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. Dynamic monitoring of circulating microRNAs as a predictive biomarker for the diagnosis and recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncol Lett 2017, 13, 4252–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.; da Rocha, A.G.; Batista, R.; Vinagre, J.; Martins, M.J.; Costa, G.; Ribeiro, C.; Carrilho, F.; Leite, V.; Lobo, C.; et al. TERT, BRAF, and NRAS in Primary Thyroid Cancer and Metastatic Disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017, 102, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, M.; Rosignolo, F.; Maggisano, V.;et al. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Thyroid Carcinoma. International Journal of Genomics, 2017, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Elisabetta Macerola, 1 Anello Marcello Poma, 1 Paola Vignali, 1 Agnese Proietti, 1 Clara Ugolini, 1 Liborio Torregrossa, 1 Alessio Basolo, 2 Rossella Elisei, 2 Ferruccio Santini, 2 and Fulvio Basolo. Predictive Biomarkers in Thyroid Cancer. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 901004. [CrossRef]
- Maria Papaioannou 1, Angeliki G Chorti 2, Anthoula Chatzikyriakidou 3, Kleanthis Giannoulis 2, Sohail Bakkar 4, Theodosios S Papavramidis 2. MicroRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: What Is New in Diagnosis and Treatment. Review Front Oncol. 2022, 11, 755097. [CrossRef]
- Zubair W Baloch 1, Sylvia L Asa 2, Justine A Barletta 3, Ronald A Ghossein 4, C Christofer Juhlin 5 6, Chan Kwon Jung 7, Virginia A LiVolsi 8, Mauro G Papotti 9, Manuel Sobrinho-Simões 10, Giovanni Tallini 11 12, Ozgur Mete 13 .Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Thyroid Neoplasms. Review Endocr Pathol. 2022, 33, 27–63. [CrossRef]
- Pallante, P.; Visone, R.; Ferracin, M.; et al. MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2006, 13, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panebianco, F.; Mazzanti, C.; Tomei, S.; Aretini, P.; Franceschi, S.; Lessi, F.; Di Coscio, G.; Bevilacqua, G.; Marchetti, I. The combination of four molecular markers improves thyroid cancer cytologic diagnosis and patient management. BMC Cancer. 2015, 15, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikholeslami, S.; et al. Overexpression of mir-129-1, miR-146b, mir-183, and mir-197 in follicular thyroid carcinoma and adenoma tissues. Mol Cell Probes 2020, 51, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; et al. miR-146a and miR-146b in the diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2017, 38, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina Pamedytyte 1, Vaida Simanaviciene 1, Dalia Dauksiene 2, Enrika Leipute 1, Aurelija Zvirbliene 1, Valdas Sarauskas 3, Albertas Dauksa 4, Rasa Verkauskiene 2, Birute Zilaitiene 2. Association of MicroRNA Expression and BRAFV600E Mutation with Recurrence of Thyroid Cancer Biomolecules. 2020, 10, 625. [CrossRef]
- John Woody Sistrunk 1, Alexander Shifrin 2, Marc Frager 3, Ricardo H Bardales 4, Johnson Thomas 5, Norman Fishman 6, Philip Goldberg 7, Richard Guttler 8, Edward Grant 9. Clinical impact of testing for mutations and microRNAs in thyroid nodules. Diagn Cytopathol. 2019, 47, 758–764. [CrossRef]
- Visone, R.; Russo, L.; Pallante, P.; De Martino, I.; Ferraro, A.;et al. MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Gang, Q.; Shen, S.; Zhang, J.; Lun, Y.; Xu, D.; Duan, Z.; Xin, S. Interstitial fibrosis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma and its association with biological behavior. Oncology Letters 2018, 15, 4937–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournaud, C.; Descotes, F.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; et al. TERT promoter mutations identify a high-risk group in metastasis-free advanced thyroid carcinoma. European Journal of Cancer 2019, 108, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.M.; Abi-Raad, R.; Garritano, J.; Cai, G.; Prasad, M.L.; Adeniran, A.J. RAS mutation and associated risk of malignancy in the thyroid gland: An FNA study with cytology-histology correlation. Cancer Cytopathol. 2022, 130, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.d.L.; Pinto, M.; Alves, M.; Canberk, S.; Gonçalves, A.; Bugalho, M.J.; Papoila, A.L.; Soares, P. Comparative CytoHistological Genetic Profile in a Series of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.I.; Choi, Y.S. Expressions of miRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Their Associations with the BRAFV600EMutation and Clinicopathological Features. Kosin Medical Journal 2020, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; et al. Expression of miRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas Is Associated with BRAF Mutation and Clinicopathological Features in Chinese Patients. Int J Endocrinol. 2013, 128735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole A Cipriani 1, Daniel N Johnson 2, David H Sarne 3, Peter Angelos 4, Ward Reeves 5, Tatjana Antic 5. The Significance of RAS-Like Mutations and MicroRNA Profiling in Predicting Malignancy in Thyroid Biopsy Specimens. Endocr Pathol. 2022, 33, 446–456. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna B Banizs 1, Jan F Silverman 1. The utility of combined mutation analysis and microRNA classification in reclassifying cancer risk of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. Diagn Cytopathol. 2019, 47, 268–274. 201. [CrossRef]
| Cytology diagnosis n=106 |
Histology diagnosis n=106 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | WDT-UMP | NIFT | PTC | FTC | HCC | Total | ||
| 1.ND 2.Benign 3.AUS 4.FN 5.SM 6.Malignant |
||||||||
| 0 (0%) 12 (11.3%) 0 (0%) 1 (0.9%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) |
0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 2 (1.9%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) |
1 (0.9%) 2 (1.9%) 0 (0%) 1 (0.9%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) |
2 (1.9%) 7 (6.6%) 23 (21.7%) 23 (21.7%) 12 (11.3%) 14 (13.2%) |
0 (0%) 1 (0.9%) 0 (0%) 1(0.9%) 2 (1.9%) 0 (0%) |
0 (0%) 1(0.9%) 0 (0%) 1 (0.9%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) |
3 (2.8%) 23 (21.7%) 23 (21.7%) 29 (27.4%) 14 (13.2%) 14 (13.2%) |
||
| Total | 13 (12.3%) | 2 (1.9%) | 4 (3.8%) | 81 (76.4%) | 4 (3.8%) | 2 (1.9%) | 106 (100%) | |
| miRNAs in cytology | Frequencies of miRNAs expression by histology diagnosis |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final diagnosis |
Median | Under max-value n= (%) |
Over max-value n= (%) |
Total n= (%) |
|
| miRNA146 |
Benign Malignant |
0.308 0.489 |
≤ 4.394 11 (100) 55 (64.7) |
> 4.394 - 30 (35.3) |
96 (100) 11 (11.5) 85 (88.5) |
| miRNA221 | Benign Malignant |
0.535 0.172 |
≤ 5.242 11 (100) 70 (81.4) |
> 5.242 - 16 (18.6) |
97 (100) 11 (11.3) 86 (88.7) |
| miRNA222 | Benign Malignant |
0.914 1.460 |
≤ 6.358 11 (100) 56 (65.1) |
> 6.358 - 30 (34.9) |
97 (100) 11 (11.3) 86 (88.7) |
| miRNA15a | Benign Malignant |
1.053 0.686 |
≤ 7.39 11 (100) 77 (88.5) |
> 7.39 - 10 (11.5) |
98 (100) 11 (11.2) 87 (88.8) |
| miRNAs in histology | By histology diagnosis | |||||||||
| n | histology | Median* | P25 - P75 | min - max value | p-value** | |||||
| miRNA146 | 60 08 52 |
Benign Malignant |
0.660 44.529 |
0.392 –2.455 3.215 – 907.373 |
0.322 – 5.341 0.016 – 27755.76 |
0.002 | ||||
| miRNA221 | 76 10 66 |
Benign Malignant |
1.312 4.297 |
0.781 –1.798 1.475 – 9.695 |
0.192 –4.395 0.012 – 63.304 |
0.008 | ||||
| miRNA222 | 78 10 68 |
Benign Malignant |
1.067 3.409 |
0.645 – 2.544 1.075 – 13.027 |
0.328 – 4.347 0.114 – 3006.772 |
0.017 | ||||
| miRNA15a | 77 10 67 |
Benign Malignant |
0.683 2.111 |
0.510 – 1.619 1.204 – 37.237 |
0.282 – 2.513 0.230 – 99.640 |
0.002 | ||||
| miRNAs in histology | ||||||||
|
Genetic mutations in histology | ||||||||
| miRNA-146 | miRNA-221 | miRNA-222 | miRNA15a | |||||
| n | Median | n | Median | n | Median | n | Median | |
|
TERTp Absent Present p-value |
54 48 06 |
29.856 60.203 0.563 |
67 59 08 |
2.990 6.310 0.451 |
69 61 08 |
3.076 3.958 0.708 |
68 60 08 |
1.981 37.494 0.033 |
|
BRAF Absent Present p-value |
54 39 15 |
9.900 133.574 0.020 |
67 49 18 |
1.820 8.625 0.001 |
69 50 19 |
1.548 14.006 <0.001 |
68 50 18 |
2.087 2.257 0.792 |
|
RAS Absent Present p-value |
54 41 13 |
26.511 716.144 0.016 |
67 53 14 |
2.464 10.900 0.010 |
69 55 14 |
2.325 5.284 0.144 |
68 54 14 |
1.713 24.767 0.026 |
| miRNAs in Histology | Papillary thyroid carcinomas | |||||
| (n) | cutoff | AUC (95%CI) | Se % (95%CI) | Sp % (95%CI) | PPV % (95%CI) | NPV % (95%CI) |
| miRNA-146b | 3. 070 | 93.5 (86.5-100) | 89.1 (76.4-96.3) | 87.5 (84-99.2) | 97.6 (84-99.2) | 58.3 (35.6-98.4) |
| miRNA-221 | 1.762 | 79.1 (67.8-90.4) | 71.9 (58.5-83) | 80 (44.4-97.5) | 95.3 (80.4-97.5) | 33.3 ( 21.5-82.9) |
| miRNA-222 | 1.392 | 75.8 (62.7-88.9 | 72.9 (59.7-83.6) | 70 ( 34.8-93.3) | 93.5 ( 76.6-96.5) | 30.4 ( 19.5-72.4) |
| miRNA-15a | 1.537 | 85.3 (73.8-96.9) | 72.4 (59.1-83.3) | 80 (44.4-97.5) | 95.5 (80.7-97.6) | 33.3 (21.6-82.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





