Submitted:
27 February 2024
Posted:
28 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
| Study | Type | P | I | C | Risk model | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multifaceted | ||||||
| Anderson 1994 N = 798 |
Cluster RCT |
Medical and surgical |
CME only: grand rounds slide lecture with local data by physician expert + mailed materials + telephone line for immediate VTE consults. CME + QA: additionally, data from manual retrospective chart reviews reported at medical staff meetings, individual physician feedback concerning compliance. | Usual care |
Generic screening for the selection of high-risk patients and adequate thromboprophylaxis rates. Generic risk factor screening. | Changes in prophylaxis among the control, CME, and CME + QA hospitals maintained significance. Multivariate adjusted odds ratios were 2.1 (95% confidence limits, 1.6,2.9) for control hospitals, 3.6 (95% confidence limits, 2.7,4.7) for CME hospitals, and 3.8 (95% confidence limits, 2.9,5.0) for CME+QA hospitals. |
| Streubel 2009 N = 345 |
Pretest-posttest | Surgical | Prospective VTE protocol adherence and event rate monitoring. Results presented every two months. | Usual care |
N/A | VTE prophylaxis adherence failure reduction: 15% vs 1.6% (P = 0.002), VTE rates trend for improvement (P = 0.37). |
| Labarere 2007 N = 812 |
Cluster RCT |
Medical | Educational presentations with local data, educational material, audit/feedback components directed at physicians and nurses. | Physicians only | Evidence derived, non-validated | No significant differences in radiology-verified DVT (two-level OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.70 – 2.11; P = 0.50; intra-cluster correlation coefficient, 0.08). |
| Hinchey 2010 N = 2071 |
Cluster, Quasi-RCT |
Medical | Audit, feedback and benchmark information along with site-selected components from the below: evidence synthesis as educational resource, alerts, standing orders, grand round reporting of audits, individualized clinician feedback. Knowledge and attitude, barrier to adherence audit and discussion, with suggestions for improvement. | Audit with feedback | Unknown | Nonsignificant trend for appropriate thromboprophylaxis - no more data available. Extracted from figure with web plot digitizer (apps.automeris.io/wpd/): Intervention baseline 79%, outcome 87.1%. Control: baseline, 81%utcome, 86%. |
| Pai 2013 N = 2611 |
Pilot cluster RCT | Medical | Paper based VTE risk assessment forms, educational sessions and material for all staff, real-time chart audits within 24h of admission used for instructional feedback at 4, 12 and 16 weeks. | Usual care | non-validated, evidence derived ACCP 8th ed. | No significant difference in appropriate thromboprophylaxis, over- or under-prescription rates. Significant qualitative components: interviews and questionnaires of stakeholders, including patients. No significant difference rates of appropriate thromboprophylaxis between groups was found (OR = 0.80; 95% CI: 0.50, 1.28; P = 0.36). |
| Cavalcanti 2016 N = 6761 |
Cluster RCT | Medical and Surgical | Goals of care discussions at ICU level. Daily Checklist in daily grand rounds with single item confirming thromboprophylaxis orders. Online and offline education. Involvement of the whole clinical team. Checklist adherence feedback. Periodic text message reminders. Directors contacted when adherence was low. | Usual care | N/A | VTE prophylaxis rates 74.8% vs 75.0% of patient-days; adjusted RR, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.91-1.22; P = 0.5 favoring intervention. |
| Roy 2016 N = 15351 |
Cluster RCT | Medical | Educational lectures, educational resources. In a second phase, a CDSS with alerts incorporating medical diagnosis code for risk stratification and tailored thromboprophylaxis suggestions used in only 2 of 13 centers. | Usual care | Non-validated | No difference in VTE/major bleeding composite, thromboembolic events, major bleeding, and all-cause mortality. Thromboprophylaxis rates post-intervention similar between groups. Adjusted difference in thromboprophylaxis rates: 6.6% [1.6-11.6] favoring intervention. |
| Roberts 2017 NHS Centers in UK |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | See text. | Usual care | Paper-based, non-validated, evidence-derived national tool- lists of risk factors. | Median risk assessment rate 2010: 51% (IQR 27-71%), March 2012: 93% (IQR 91-96%). Hospitals with >90% assessment rate: 15% reduction in hospital associated thrombosis, 12% lower avoidable VTE, VTE related mortality reduction post-discharge: 15% for >3 days hospitalizations (95% CI 0.75-0.96), 39% for <3 days hospitalizations (CI 0.48-0.79), excluding outpatient. 90-day readmissions with VTE: 4% reduction, secondary VTE diagnosis: 9%reduction, mean mortality rate: 9% reduction, maintained at 8% less than 2012 estimates, long-term data unavailable. |
| Pre-Printed Order Sheets | ||||||
| Fontaine et al. 2006 N = 719 |
Cluster RCT | Medical | Evidence-derived, locally compiled thromboprophylaxis prescription guidelines. Anonymous anticoagulant prescription forms including patient characteristics (age, sex, body weight, date of admission), presence or absence of venous thromboembolic risk factors, 10 cm visual analogical scale of the patient’s risk of anticoagulation and hemorrhagic complications risk. | Usual care | Non-validated, evidence derived, weighted risk factor based | Overprophylaxis increased by 17% (from 22 to 26%) in the control group and decreased by 44% (from 25% to 15%) in the intervention group. Appropriate thromboprophylaxis rates were similar (around 63%) before and after the intervention. No differences in undertreatment, with both groups showing minor reductions. |
| Passive Alerts (Human or Electronic) | ||||||
| Dexter 2001 N = 1326 |
Cluster RCT | Medical | EHR order entry CDS providing rule-based reminders and prewritten orders with explanatory text. Rules integrated the demographics, EHR codes and pharmacy records to alert and provide decision support, that could be accepted or not by the physician. Disabled escape key and attention-grabbing color schemes used to increase use. Simulated use test and provider interviews for design. | Usual care | Non-validated, evidence derived | Appropriate LMWH ordering rates increased by 13.3% (18.9% vs 32.2%) favoring intervention (P < 0.001). |
| Kucher 2005 N = 2506 |
Quasi-RCT | Medical and surgical | CDS integrated into database performing daily automatic patient screening. Physicians of at-risk patients not on prophylaxis would receive alerts to physicians that had to be acknowledged and provide a list of generic prophylaxis order options. No forcing components. VTE guidelines made available in the EHR. | VTE guidelines made available in the EHR. | Weighted score based on common risk factors and lab results | VTE rates at 90 days favored intervention with a hazard ratio of 0.59 (95% CI, 0.43 to 0.81; P=0.001). Mortality and bleeding rates were similar. |
| Garcia 2009 N = 140 |
Cluster, Quasi RCT | Medical | Pharmacist manual chart review via a standardized risk-assessment form. Weighted and scored list of comorbidities/risk factors, contraindications, and relevant prophylaxis options. Standardized script for informing physician of patient VTE risk level, no specific therapy recommendations. No further alerts after the first. | Usual care | Weighted score based on common risk factors and lab results | Thromboprophylaxis rates similar (P = 0.15). In at-risk patients: Low-dose unfractionated heparin use rate: 56%. Prophylactic dose enoxaparin use: 11%. Sequential Compression Device use: 64% in intervention vs 50% in control group, often in combination with pharmacologic strategies. |
| Piazza 2009 N = 2493 |
RCT | Medical and surgical | Manual weighted screening for VTE risk factors based on ICD-9 codes and laboratory values by staff. Alerting physicians if at-risk patient had no prescription with a recommendation for mechanical prophylaxis. Contraindications and bleeding risk not considered. No specific modalities, agents, doses, frequencies, or durations were recommended. | Usual care | Weighted score based on common risk factors and lab results | Thromboprophylaxis rates increase: 25.35% (95% CI: 21.8-28.9%). No differences in hard outcomes overall or in high-risk subgroups. |
| Mahan 2011 N = 3525 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Rounds discusions, manual pharmacist VTE risk assessments, alerts to physicians, monthly performance reviews. Printed risk assessment forms assessing risk factors, overall risk level and contraindications, with prophylactic recommendations: enoxaparin, UFH, mechanical prophylaxis or none based on bleeding risk and eGFR. Risk assessment forms added to the patient records. In cases of non-compliance, contact was repeated by the lead pharmacist and then escalated to a physician champion. | Usual care | Paper-based, non-validated, guideline-derived risk assessment form. | Appropriate prophylaxis rates: OR 2.5 (critical care), 1.6 (surgical), 2.1 (medical), 1.8 (overall discharges), P < 0.0001. Preventable VTE rates reduction: 74%, P = 0.0006. Overall VTE reduction: 44%, P = 0.0624. |
| Piazza 2013 N = 2513 |
RCT | Medical | Pre-discharge manual screening of medical inpatients close to discharge. Staff page alerts and calls to attending physicians of high-risk patients with no active thromboprophylaxis orders. Contraindications, bleeding risk assessment and specific regimen recommendations not provided. | Usual care | Weighted score based on common risk factors and lab results | Intervention group thromboprophylaxis rates: 22.0% vs control 9.7%, P < 0.0001. Pharmacoprophylaxis rates: Intervention 19% vs control 7.7%, P < 0.0001. Symptomatic DVT/PE at 90 days: HR 1.12 (95% CI 0.74-1.69), not significantly different. Mortality and bleeding rates at 90 days similar. |
| Computerized CDSS | ||||||
| Galanter 2010 N = 38647 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Evidence-based, locally compiled, EMR-integrated mandatory VTE risk assessment form, launched via alert at order entry until risk assessment completed. Could be dismissed for first 8 hours. Form adapted based on previous answers and provided prophylaxis recommendations by risk level. Batch reviews of alerts printed at nursing station, if patients were found to be at risk and have no valid orders based on automatic screening. Same alerts also sent to the clinical EMR mailbox of treating physicians. | Usual care | Evidence-based, locally compiled, non-validated. | VTE pharmacoprophylaxis rate increased from 25.9% to 36.8% (p < 0.0001). Orthopedics only saw no increase. Intervention group prophylaxis rate higher for all medications except warfarin. Post-intervention odds of receiving prophylaxis: OR = 2.02, 95% CI = 1.92–2.13. Compared to medical patients, increased odds of prophylaxis for all patient types except obstetrics and gynecology. VTE rate declined from 0.51% to 0.43% (p = 0.22) Absolute VTE risk in medical patients declined from 0.55% to 0.33% (p = 0.02). NNT: 450 patients. Minor bleeding event rate post-CDS: 1.75% to 1.60% (p = 0.27). |
| MaCauely 2012 N = 4669 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Electronic admission order CDS. First screen: risk stratification as high, moderate, or low risk via point based VTE risk assessment displayed as text along with relative and absolute pharmacoprophylaxis contraindications. Second screen: alert displayed for patients with moderate or high risk and no VTE prophylaxis. Option to order or indicate contraindication. | Usual care | Caprini surgical score | Post-implementation cohorts: Low-risk: 48%, Moderate-risk: 31%, High-risk: 7%, Higher manual risk classification than computer-generated: 38%, Deferred/missing provider risk assessment: 14%, Pharmacoprophylaxis rate from 27% to 53%, Increase in VTE prophylaxis: 26% (P < 0.0001), VTE incidence declined from 0.98% to 0.42%, RRR 57%, P < 0.02) |
| Mitchell 2012 N = 5238 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Electronic alert in EMR history and physical note at admission. Asked whether patient is receiving prophylaxis, is low, medium, or high-risk for VTE. Displayed sample order choices for each level and listed contraindications. Note could not be saved without filling in the alert. Could not link to order screen due to software limitations. | Historical controls | None | Overall prophylaxis rate increase from 42.8% to 60.0%, P < 0.001. Not significant in renal failure, hip fracture/replacement patients. VTE rate decrease from 1.1% to 0.34%, P = 0.001. Non-significant DVT rate reduction from 0.42% to 0.13%, P = 0.053. Pulmonary embolism rate reduced from 0.74% to 0.22%, P = 0.009. Bleeding rate trend from 1.1% to 0.6%, P = 0.09. |
| Bhalla 2012 N = 36500 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Mandatory VTE risk alert in admission EHR note: prophylaxis status, risk level. Sample orders for each risk category and contraindications displayed. Alert completion required to save note. Direct linking to order screen restricted by software limitations. Repeated every 5 days if no prophylaxis. | Usual care | None | (Medicine services) VTE prophylaxis order rates: 61.9% to 82.1%, P < 0.001, pharmacologic VTE prophylaxis rate: 59.0% to 74.5%, P < 0.001, hospital acquired VTE incidence: 0.65% to 0.42%, P = 0.008, bleeding rates: 2.9% to 4.0%, P < 0.001. (Non-medicine services) VTE prophylaxis ordering rates: 70.5% to 73.6%, P < 0.001, pharmacologic prophylaxis rates: 59.3% to 63.3%, P < 0.001, bleeding rates: 7.7% to 8.6%, P = 0.043, hospital acquired VTE incidence change nonsignificant. |
| Umscheid 2012 N = 223062 |
Quasi-experimental pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | EHR integrated CDS tools: list of 11 risk factors simply presented along with option to accept or decline VTE prophylaxis based on informed intuitive assessment, along with display of contraindications. Upon declining thromboprophylaxis, a specific reason had to be provided as free text in the first of two periods, changed to a choice between prewritten options during the third. The system disallowed two anticoagulants to be ordered simultaneously. An eGFR calculator prevented LMWH use in patients with stage 4 or higher renal disease. Risk estimation was intuitive. | Usual care | None | Thromboprophylaxis rates (control, 1st intervention period, 2nd intervention period): 27.1% to 43.0% to 51.9%, P < 0.01. Appropriate thromboprophylaxis rates: 42.0% to 47.6% to 54.4%, P < 0.01. VTE incidence and bleeding rates: unchanged. DVT decrease: 1.77% to 1.75% to 1.15%, P < 0.01. Overall VTE decrease: 2.18 to 2.15 to 1.73, P < 0.01. PE incidence increase: 0.52 to 0.53 to 0.74, P < 0.01. Physician guideline adherence increase for positively predisposed: 89.0% to 93.8%, P < 0.01. Physician guideline adherence increase for not predisposed: 63.7% to 74.1%, P < 0.01. Non-compliance reasons: No risk factors 58%, on therapeutic anticoagulation 35%, peri-procedural concerns 4%, bleeding risk 2%. |
| Fuzinatto 2013 N = 523 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Educational lecture, consensus meeting, EHR-based CDS tool. At EHR launch every 48 hours thereafter, if no thromboprophylaxis was prescribed, the physician could choose between 3 risk levels and indicate if thromboprophylaxis was contraindicated, aided by displayed text. Each level of risk was linked to appropriate UFH regimens, automatically prescribed in the background. Physicians could override the CDS by providing written justification. | Usual care | Evidence-based, locally compiled, non-validated | Thromboprophylaxis rate increase: from 46.2% to 57.9%, difference: 11.7% (95% CI: 3.2% - 20.3%, P = 0.01). Surgical patient VTE prophylaxis increase not statistically significant. Appropriate VTE prophylaxis pre- to post-implementation in cancer patients: 18.1% to 44.1%, absolute difference 26%, 95% CI: 9.9% to 42.3%, p = 0.002. Surgical patients postoperative appropriate VTE prophylaxis pre- to post-implementation: 53.6% to 60.4%, absolute difference 6.8%, 95% CI: −13.6% to 27.2%, p = 0.6. Medical patients appropriate VTE prophylaxis pre- to post-implementation: 44.2% to 57.2%, absolute difference 13%, 95% CI: 3.0% to 23.1%, p = 0.011. |
| Eijgenraam 2015 N = 128 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical | Button on first EHR, launching a risk assessment form, including a non-validated bleeding risk assessment model. Neither mandatory nor linked to the ordering system. Suggested appropriate prophylaxis regimens. | Usual care | Padua VTE risk score | Guideline adherence pre- and post-intervention: 59.4%, underprophylaxis decrease: OR 0.48 (95% CI: 0.18-1.30, P = 0.14), overprophylaxis increase: OR 1.66 (95% CI: 0.74–3.73, P = 0.22), CDS LMWH dose non-adherence: 12.5%, Physician self-reported non-adherence reason mean, SD: 2.4/5, 0.5 due to patient preferences. CDS mistrusted for complicated cases by 2/5 physicians, 3/5 questioned evidence base 3/5, 4/5 perceived improved patient outcomes, 2/5 believed automated ordering would reduce errors. |
| Amland 2015 N = 45046 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Three distinct periods separated by washout: 1. Nursing staff workflow standardized (thromboprophylaxis orders, interventions, documentation, outcome tracking) 2. CDS tool for risk stratification, contraindication documentation, evidence-based recommendations 3. Alert if patient not assessed or at increased VTE risk, given that initial tool utilization was non-measurable. | Usual care | Evidence-derived, non-validated risk assessment | VTE risk assessment rates within 24 hours from admission: increased from 49.7% to 78.4%, percentage of at-risk patients identified: increased from 42.8% to 64%, at-risk patients prescribed thromboprophylaxis: increased from 25.4% to 47.7%, VTE rates per 1000 patient days at baseline: 0.954, after nursing intervention: 0.734, after CDS availability: 0.790, after alert implementation: 0.434 (55% lower than baseline), sustained VTE rate at study end: 0.407 per 1000 patient days. Full implementation reduced VTE prevalence from 0.36% to 0.17% (OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.49-0.87, p = 0.0039), likelihood of VTE per patient after full intervention 35% lower compared to baseline, alerts crucial for significant results. |
| Spirk 2017 N = 1593 |
RCT | Medical | EHR alert 24 hours after admission prompting physicians to verify whether patient was on/had indications for therapeutic anticoagulation. EHR alert repeated at most three times promted risk stratification. A few patient characteristics were prepopulated (e.g. age). Anticoagulation recommendations for LMWH, UFH or mechanical prophylaxis based on creatinine clearance and bleeding risk, if appropriate based on risk. | Usual care | Geneva risk score | Similar rates of thromboprophylaxis, over- and underprophylaxis, and hard outcomes. 55.5% with inconsistent risk assessment leading to 9.2% lower rates of appropriate prophylaxis (62.6% vs 71.8%, P = 0.006) |
| Mathers 2017 N = 576 |
Observational pretest-posttest | Medical and surgical | Single-issue EHR-integrated alert at admission, mandating validated risk assessment. If patients were classified as medium or high risk, thromboprophylaxis prescription was required. The CDS could be overridden in cases of critical bleed or coagulopathy (INR > 2). | Usual care | Caprini surgical score | Pharmacoprophylaxis overall rate increase: 60% to 81.2% (P < 0.001), Medical service increase: 26.3% to 62.8% (P < 0.001), Surgical service increase: 83.7% to 95.5% (P < 0.001), Non-adherence in medical patients: 12.7%, Non-adherence in surgical patients: 3.6%, Common reasons for missing doses: patient preference (57%), provider overrides (25%), patient absence (15%), Hospitalization post-CDS associated with higher pharmacoprophylaxis odds: OR 4.72 (95% CI 2.94-7.57), Admission in surgical service associated with higher odds: OR 14.3 (95% CI 8.62-24.39), Blood transfusions associated with lower pharmacoprophylaxis odds: OR 0.28 (95% CI 0.12-0.63). |
| Spyropoulos 2023 N = 10699 |
Cluster RCT | Medical | EHR-agnostic CDS tool incorporating a validated VTE risk score for medical inpatient classification as low-, moderate- and high-risk. Multiple trigger points (admission, VTE prophylaxis order entry, discharge medication reconciliation). Automatically populating risk score calculator. Directed prescribers to order-entry for appropriate pharmacologic thromboprophylaxis, including extended post-discharge thromboprophylaxis. System overrides available only for patients at high bleed risk and non-medical inpatients. | Education | IMPROVE-DD - validated for medical patients | Inpatient thromboprophylaxis rates increased: 80.1% vs 72.5%, OR 1.52, 95% CI 1.39 to 1.67, P < 0.001. Appropriate discharge thromboprophylaxis rates in high-risk patients: 13.6% vs 7.5%, OR 1.93, 95% CI 1.60-2.33, P < 0.001. ATE events: 0.25% vs 0.70%, OR 0.35, P < 0.001. Mortality in the intervention group: 9.1% vs 7.0%, OR 1.32, P < 0.001. Outpatient arterial thromboembolic events: 0.86% to 0.32%, OR 0.37, 95% CI 0.21-0.65, P < 0.001. Total thromboembolic events: 4.5% to 3.3%, OR 0.72, 95% CI 0.59-0.88, P = 0.001. Mortality or VTE readmission rates at intervention sites: 4.9% vs 3.7%, OR 1.34, 95% CI 1.10-1.63, P < 0.004. |
3.1. Multifaceted Interventions
3.2. Preprinted Order Sets
3.3. Passive Alerts (Human or Electronic)
3.4. Computerized CDS System (CDSS) Interventions
3.5. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
4. Critical Synthesis and Discussion
4.1. Multifaceted
4.2. Preprinted Order Sets
4.3. Passive Alerts (Human or Electronic) and Order Entry Components
4.2. Computerized CDS Systems
5. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolberg, A.S.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Weitz, J.I.; Jaffer, I.H.; Agnelli, G.; Baglin, T.; Mackman, N. Venous Thrombosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2015, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raskob, G.E.; Angchaisuksiri, P.; Blanco, A.N.; Buller, H.; Gallus, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kakkar, A.; Konstantinides, S.V.; McCumber, M.; et al. Thrombosis: A Major Contributor to Global Disease Burden. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.R.; Lim, W.; Dunn, A.S.; Cushman, M.; Dentali, F.; Akl, E.A.; Cook, D.J.; Balekian, A.A.; Klein, R.C.; Le, H.; et al. Prevention of VTE in Nonsurgical Patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th Ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 2012, 141, e195S–e226S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, M.; Chan, N.; Bhagirath, V.; Ginsberg, J. Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in 2020 and Beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, C.E.; Holdsworth, M.T.; Welch, S.M.; Borrego, M.; Spyropoulos, A.C. Deep-Vein Thrombosis: A United States Cost Model for a Preventable and Costly Adverse Event. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 106, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Cushman, M.; Burnett, A.E.; Kahn, S.R.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Spencer, F.A.; Rezende, S.M.; Zakai, N.A.; Bauer, K.A.; Dentali, F.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Nonhospitalized Medical Patients. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 3198–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbar, S.; Noventa, F.; Rossetto, V.; Ferrari, A.; Brandolin, B.; Perlati, M.; Bon, E.D.; Tormene, D.; Pagnan, A.; Prandoni, P. A Risk Assessment Model for the Identification of Hospitalized Medical Patients at Risk for Venous Thromboembolism: The Padua Prediction Score. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Lipardi, C.; Xu, J.; Peluso, C.; Spiro, T.E.; De Sanctis, Y.; Barnathan, E.S.; Raskob, G.E. Modified IMPROVE VTE Risk Score and Elevated D-Dimer Identify a High Venous Thromboembolism Risk in Acutely Ill Medical Population for Extended Thromboprophylaxis. TH Open 2020, 04, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, V.; Hu, H.M.; Henke, P.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Campbell, D.A.J.; Caprini, J.A. A Validation Study of a Retrospective Venous Thromboembolism Risk Scoring Method. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, S.A.; Greene, M.T.; Grant, P.; Kaatz, S.; Paje, D.; Lee, B.; Barron, J.; Chopra, V.; Share, D.; Bernstein, S.J. Hospital Performance for Pharmacologic Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis and Rate of Venous Thromboembolism : A Cohort Study. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, C.E.; Fisher, M.D.; Mills, R.M.; Fields, L.E.; Stephenson, J.J.; Fu, A.-C.; Spyropoulos, A.C. Thromboprophylaxis Patterns, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Care in the Medically Ill Patient Population. Thromb. Res. 2013, 132, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, A.; Fareed, J.; Kakkar, A.K.; Comerota, A.J.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Hull, R.; Myers, K.; Samama, M.; Fletcher, J.; Kalodiki, E.; et al. Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism: International Consensus Statement (Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence). Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2013, 19, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.M.; Woller, S.C.; Kreuziger, L.B.; Bounameaux, H.; Doerschug, K.; Geersing, G.-J.; Huisman, M.V.; Kearon, C.; King, C.S.; Knighton, A.J.; et al. Executive Summary: Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. CHEST 2021, 160, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Anderson, F.A.; FitzGerald, G.; Decousus, H.; Pini, M.; Chong, B.H.; Zotz, R.B.; Bergmann, J.-F.; Tapson, V.; Froehlich, J.B.; et al. Predictive and Associative Models to Identify Hospitalized Medical Patients at Risk for VTE. CHEST 2011, 140, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, C.E.; Liu, Y.; Turpie, A.G.; Vu, J.T.; Heddle, N.; Cook, R.J.; Dairkee, U.; Spyropoulos, A.C. External Validation of a Risk Assessment Model for Venous Thromboembolism in the Hospitalised Acutely-Ill Medical Patient (VTE-VALOURR). Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 112, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.T.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Chopra, V.; Grant, P.J.; Kaatz, S.; Bernstein, S.J.; Flanders, S.A. Validation of Risk Assessment Models of Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Medical Patients. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 1001.e9–1001.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nendaz, M.R.; Chopard, P.; Lovis, C.; Kucher, N.; Asmis, L.M.; Dörffler, J.; Spirk, D.; Bounameaux, H. Adequacy of Venous Thromboprophylaxis in Acutely Ill Medical Patients (IMPART): Multisite Comparison of Different Clinical Decision Support Systems. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Raskob, G.E. New Paradigms in Venous Thromboprophylaxis of Medically Ill Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskob, E.G.; Day, I.S.C. for W.T. Venous Thromboembolism: A Call for Risk Assessment in All Hospitalised Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, K.; Dong, F.; Fang, F.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, L.; Wang, W.; Yang, P.; Jia, C.; Liu, P.; et al. Evaluation of In-Hospital Venous Thromboembolism Prevention and Management System Using Hospital-Level Metrics: A Nationwide Cross-Sectional Survey in China. J. Patient Saf. 2022, 18, e626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, T.J.; Wong, A.; Dhurjati, R.; Bristow, E.; Bastian, L.; Coeytaux, R.R.; Samsa, G.; Hasselblad, V.; Williams, J.W.; Musty, M.D.; et al. Effect of Clinical Decision-Support Systems. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.N.; Durkin, M.; Arya, R. Annotation: Developing a National Programme for VTE Prevention. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucher, N.; Koo, S.; Quiroz, R.; Cooper, J.M.; Paterno, M.D.; Soukonnikov, B.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Electronic Alerts to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism among Hospitalized Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.; Rosenbaum, E.J.; Pendergast, W.; Jacobson, J.O.; Pendleton, R.C.; McLaren, G.D.; Elliott, C.G.; Stevens, S.M.; Patton, W.F.; Dabbagh, O.; et al. Physician Alerts to Prevent Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients. Circulation 2009, 119, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karajizadeh, M.; Hassanipour, S.; Sharifian, R.; Tajbakhsh, F.; Saeidnia, H.R. The Effect of Information Technology Intervention on Using Appropriate VTE Prophylaxis in Non-Surgical Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Digit. Health 2022, 8, 20552076221118828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spyropoulos, A.C.; Goldin, M.; Koulas, I.; Solomon, J.; Qiu, M.; Ngu, S.; Smith, K.; Leung, T.; Ochani, K.; Malik, F.; et al. Universal EHRs Clinical Decision Support for Thromboprophylaxis in Medical Inpatients. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, M.; Lloyd, N.S.; Cheng, J.; Thabane, L.; Spencer, F.A.; Cook, D.J.; Haynes, R.B.; Schünemann, H.J.; Douketis, J.D. Strategies to Enhance Venous Thromboprophylaxis in Hospitalized Medical Patients (SENTRY): A Pilot Cluster Randomized Trial. Implement. Sci. IS 2013, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.-M.; Rachas, A.; Meyer, G.; Gal, G.L.; Durieux, P.; Kouri, D.E.; Honnart, D.; Schmidt, J.; Legall, C.; Hausfater, P.; et al. Multifaceted Intervention to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients Hospitalized for Acute Medical Illness: A Multicenter Cluster-Randomized Trial. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0154832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarere, J.; Bosson, J.-L.; Sevestre, M.-A.; Sellier, E.; Richaud, C.; Legagneux, A. Intervention Targeted at Nurses to Improve Venous Thromboprophylaxis. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2007, 19, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchey, J.A.; Shephard, T.; Tonn, S.T.; Ruthazer, R.; Hermann, R.C.; Selker, H.P.; Kent, D.M. The Stroke Practice Improvement Network: A Quasiexperimental Trial of a Multifaceted Intervention to Improve Quality. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 19, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Writing Group for the CHECKLIST-ICU Investigators and the Brazilian Research in Intensive Care Network (BRICNet); Cavalcanti, A.B.; Bozza, F.A.; Machado, F.R.; Salluh, J.I.F.; Campagnucci, V.P.; Vendramim, P.; Guimaraes, H.P.; Normilio-Silva, K.; Damiani, L.P.; et al. Effect of a Quality Improvement Intervention With Daily Round Checklists, Goal Setting, and Clinician Prompting on Mortality of Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 315, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streubel, P.N.; Pachón, M.; Kerguelén, C.A.; Navas, J.; Portocarrero, J.; Pesantez, R.F.; Zayed, G.; Carrillo, G.; Llinás, A.M. Prospective Monitoring Improves Outcomes of Primary Total Hip Replacement: A Cohort Study. Patient Saf. Surg. 2009, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, F.A.; Wheeler, H.B.; Goldberg, R.J.; Hosmer, D.W.; Forcier, A.; Patwardhan, N.A. Changing Clinical Practice. Prospective Study of the Impact of Continuing Medical Education and Quality Assurance Programs on Use of Prophylaxis for Venous Thromboembolism. Arch. Intern. Med. 1994, 154, 669–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, A.; Mahé, I.; Bergmann, J.F.; Fiessinger, J.N.; Dhote, R.; Cohen, P.; Vinceneux, P. Effectiveness of Written Guidelines on the Appropriateness of Thromboprophylaxis Prescriptions for Medical Patients: A Prospective Randomized Study. J. Intern. Med. 2006, 260, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, P.R.; Perkins, S.; Overhage, J.M.; Maharry, K.; Kohler, R.B.; McDonald, C.J. A Computerized Reminder System to Increase the Use of Preventive Care for Hospitalized Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.A.; Highfill, J.; Finnerty, K.; Varoz, E.; McConkey, S.; Hutchinson, K.; Libby, E. A Prospective, Controlled Trial of a Pharmacy-Driven Alert System to Increase Thromboprophylaxis Rates in Medical Inpatients. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2009, 20, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.; Anderson, F.A.; Ortel, T.L.; Cox, M.J.; Rosenberg, D.J.; Rahimian, S.; Pendergast, W.J.; McLaren, G.D.; Welker, J.A.; Akus, J.J.; et al. Randomized Trial of Physician Alerts for Thromboprophylaxis after Discharge. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanter, W.L.; Thambi, M.; Rosencranz, H.; Shah, B.; Falck, S.; Lin, F.-J.; Nutescu, E.; Lambert, B. Effects of Clinical Decision Support on Venous Thromboembolism Risk Assessment, Prophylaxis, and Prevention at a University Teaching Hospital. Am. J. Health. Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MaCauley, M.J.; Showalter, J.W.; Beck, M.J.; Chuang, C.H. The Effect of a Provider-Enhanced Clinical Decision Support Tool for Guiding Venous Thromboembolism Pharmacoprophylaxis in Low-Risk Patients. Hosp. Pract. 2012, 40, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Collen, J.F.; Petteys, S.; Holley, A.B. A Simple Reminder System Improves Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Rates and Reduces Thrombotic Events for Hospitalized Patients1. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umscheid, C.A.; Hanish, A.; Chittams, J.; Weiner, M.G.; Hecht, T.E. Effectiveness of a Novel and Scalable Clinical Decision Support Intervention to Improve Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis: A Quasi-Experimental Study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2012, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, R.; Berger, M.A.; Reissman, S.H.; Yongue, B.G.; Adelman, J.S.; Jacobs, L.G.; Billett, H.; Sinnett, M.J.; Kalkut, G. Improving Hospital Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis with Electronic Decision Support. J. Hosp. Med. 2013, 8, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzinatto, F.; Waldemar, F.S.D.; Wajner, A.; Elias, C.A.A.; Fernandez, J.F.; Hopf, J.L.D.S.; Barreto, S.S.M. A Clinical Decision Support System for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis at a General Hospital in a Middle-Income Country. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2013, 39, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amland, R.C.; Dean, B.B.; Yu, H.; Ryan, H.; Orsund, T.; Hackman, J.L.; Roberts, S.R. Computerized Clinical Decision Support to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism Among Hospitalized Patients: Proximal Outcomes from a Multiyear Quality Improvement Project. J. Healthc. Qual. JHQ 2015, 37, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijgenraam, P.; Meertens, N.; Van Den Ham, R.; Ten Cate, H.; Ten Cate-Hoek, A.J. The Effect of Clinical Decision Support on Adherence to Thrombosis Prophylaxis Guidelines in Medical Patients; A Single Center Experience. Thromb. Res. 2015, 135, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirk, D.; Stuck, A.K.; Hager, A.; Engelberger, R.P.; Aujesky, D.; Kucher, N. Electronic Alert System for Improving Appropriate Thromboprophylaxis in Hospitalized Medical Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2017, 15, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, B.; Williams, E.; Bedi, G.; Messaris, E.; Tinsley, A. An Electronic Alert System Is Associated With a Significant Increase in Pharmacologic Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Rates Among Hospitalized Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. J. Healthc. Qual. JHQ 2017, 39, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R.; Morrison, D.R.; Cohen, J.M.; Emed, J.; Tagalakis, V.; Roussin, A.; Geerts, W. Interventions for Implementation of Thromboprophylaxis in Hospitalized Medical and Surgical Patients at Risk for Venous Thromboembolism. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.R.; Diendéré, G.; Morrison, D.R.; Piché, A.; Filion, K.B.; Klil-Drori, A.J.; Douketis, J.; Emed, J.; Roussin, A.; Tagalakis, V.; et al. Effectiveness of Interventions for the Implementation of Thromboprophylaxis in Hospitalised Patients at Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: An Updated Abridged Cochrane Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenchus, J.D. Transitions in the Prophylaxis, Treatment and Care of Patients with Venous Thromboembolism. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Ann Hawkins, T.; Lange, I.R.; Gibson, P.S. Compliance With a Perinatal Prophylaxis Policy for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism After Caesarean Section. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2008, 30, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, G.M.; Drake, C.I.; Jupe, D.M.L.; Vial, J.H.; Wilkinson, S. Educational Campaign to Improve the Prevention of Postoperative Venous Thromboembolism. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1999, 24, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellier, E. Effectiveness of a Guideline for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Elderly Post–Acute Care Patients: A Multicenter Study With Systematic Ultrasonographic Examination. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieux, P.; Nizard, R.; Ravaud, P.; Mounier, N.; Lepage, E. A Clinical Decision Support System for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism: Effect on Physician Behavior. JAMA 2000, 283, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.W.; Adams, R. Impact of Introducing Anticoagulation-Related Prescribing Guidelines in a Hospital Setting Using Academic Detailing. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobesh, P.P.; Stacy, Z.A. Effect of a Clinical Pharmacy Education Program on Improvement in the Quantity and Quality of Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis for Medically Ill Patients. J. Manag. Care Pharm. 2005, 11, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.T.; Thursz, M.R.; Razvi, N.A.; Voller, R.; Orchard, T.; Rashid, S.T.; Shlebak, A.A. Venous Thromboprophylaxis in UK Medical Inpatients. 2005; 98. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.M.; McKenzie, C.A.; Mires, G.J. Use of a Computerised Maternity Information System to Improve Clinical eVectiveness: Thromboprophylaxis at Caesarean Section. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McEleny, P.; Bowie, P.; Robins, J.B.; Brown, R.C. Getting a Validated Guideline into Local Practice: Implementation and Audit of the Sign Guideline on the Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis in a District General Hospital. Scott. Med. J. 1998, 43, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock-Palmer, R.P.; Weiss, S.; Hyman, C. Innovative Approaches to Increase Deep Vein Thrombosis Prophylaxis Rate Resulting in a Decrease in Hospital-acquired Deep Vein Thrombosis at a Tertiary-care Teaching Hospital. J. Hosp. Med. 2008, 3, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; DeCaire, K.; Friedrich, J.O. Medical Admission Order Sets to Improve Deep Vein Thrombosis Prophylaxis Rates and Other Outcomes. J. Hosp. Med. 2009, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R. A Computerized Reminder for Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Surgical Patients. Proc. AMIA Symp. 1998, 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- Mosen, D.; Elliott, C.G.; Egger, M.J.; Mundorff, M.; Hopkins, J.; Patterson, R.; Gardner, R.M. The Effect of a Computerized Reminder System on the Prevention of Postoperative Venous Thromboembolism. Chest 2004, 125, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedgwick, P.; Greenwood, N. Understanding the Hawthorne Effect. BMJ 2015, h4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiumara, K.; Piovella, C.; Hurwitz, S.; Piazza, G.; Niles, C.; Fanikos, J.; Paterno, M.; Labreche, M.; Stevens, L.-A.; Baroletti, S.; et al. Multi-Screen Electronic Alerts to Augment Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, G.A.; Morris, T.A.; Jenkins, I.H.; Stone, S.; Lee, J.; Renvall, M.; Fink, E.; Schoenhaus, R. Optimizing Prevention of Hospital-acquired Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Prospective Validation of a VTE Risk Assessment Model. J. Hosp. Med. 2010, 5, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecumberri, R.; Marqués, M.; Díaz-Navarlaz, M.; Panizo, E.; Toledo, J.; García-Mouriz, A.; Páramo, J.A. Maintained Effectiveness of an Electronic Alert System to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism among Hospitalized Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jaghbeer, M.; Dealmeida, D.; Bilderback, A.; Ambrosino, R.; Kellum, J.A. Clinical Decision Support for In-Hospital AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2018, 29, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaides, A.; Fareed, J.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Kakkar, A.K.; Antignani, P.; Avgerinos, E. Prevention and Management of Venous Thromboembolism. Int. Angiol. 2024. (In press) [Google Scholar]
- Hostler, D.C.; Marx, E.S.; Moores, L.K.; Petteys, S.K.; Hostler, J.M.; Mitchell, J.D.; Holley, P.R.; Collen, J.F.; Foster, B.E.; Holley, A.B. Validation of the International Medical Prevention Registry on Venous Thromboembolism Bleeding Risk Score. Chest 2016, 149, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D.J.; Press, A.; Fishbein, J.; Lesser, M.; McCullagh, L.; McGinn, T.; Spyropoulos, A.C. External Validation of the IMPROVE Bleeding Risk Assessment Model in Medical Patients. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 116, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
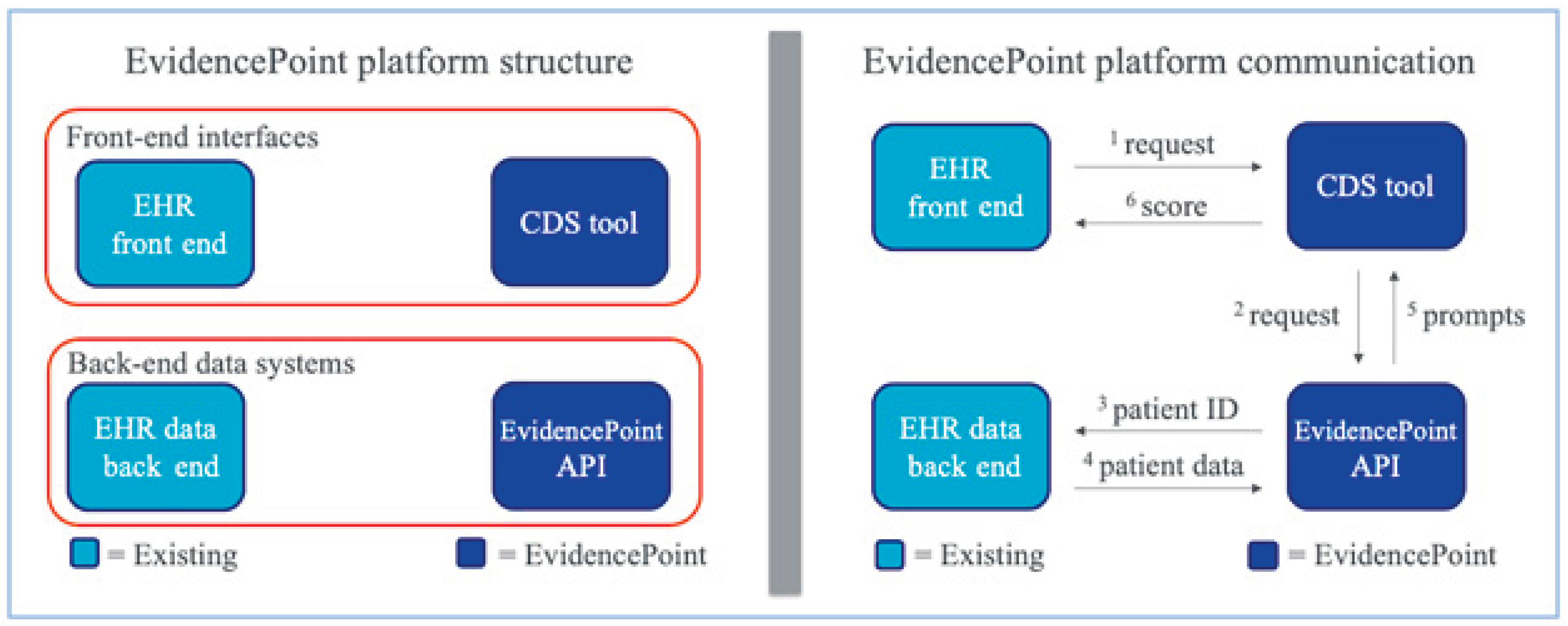
- Solomon, J.; Dauber-Decker, K.; Richardson, S.; Levy, S.; Khan, S.; Coleman, B.; Persaud, R.; Chelico, J.; King, D.; Spyropoulos, A.; et al. Integrating Clinical Decision Support Into Electronic Health Record Systems Using a Novel Platform (EvidencePoint): Developmental Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2023, 7, e44065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.C.; Kreda, D.A.; Mandl, K.D.; Kohane, I.S.; Ramoni, R.B. SMART on FHIR: A Standards-Based, Interoperable Apps Platform for Electronic Health Records. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2016, 23, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenders, J.A.O. , Jonathan Teich, Donald Levick, Luis Saldana, Ferdinand Velasco, Dean Sittig, Kendall Rogers, Robert Improving Outcomes with Clinical Decision Support: An Implementer’s Guide, Second Edition; 2nd ed.; HIMSS Publishing: New York, 2012; ISBN 978-0-367-80612-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ramgopal, S.; Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Horvat, C.M.; Carroll, M.S.; Luo, Y.; Florin, T.A. Artificial Intelligence-Based Clinical Decision Support in Pediatrics. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





