Submitted:
27 February 2024
Posted:
28 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
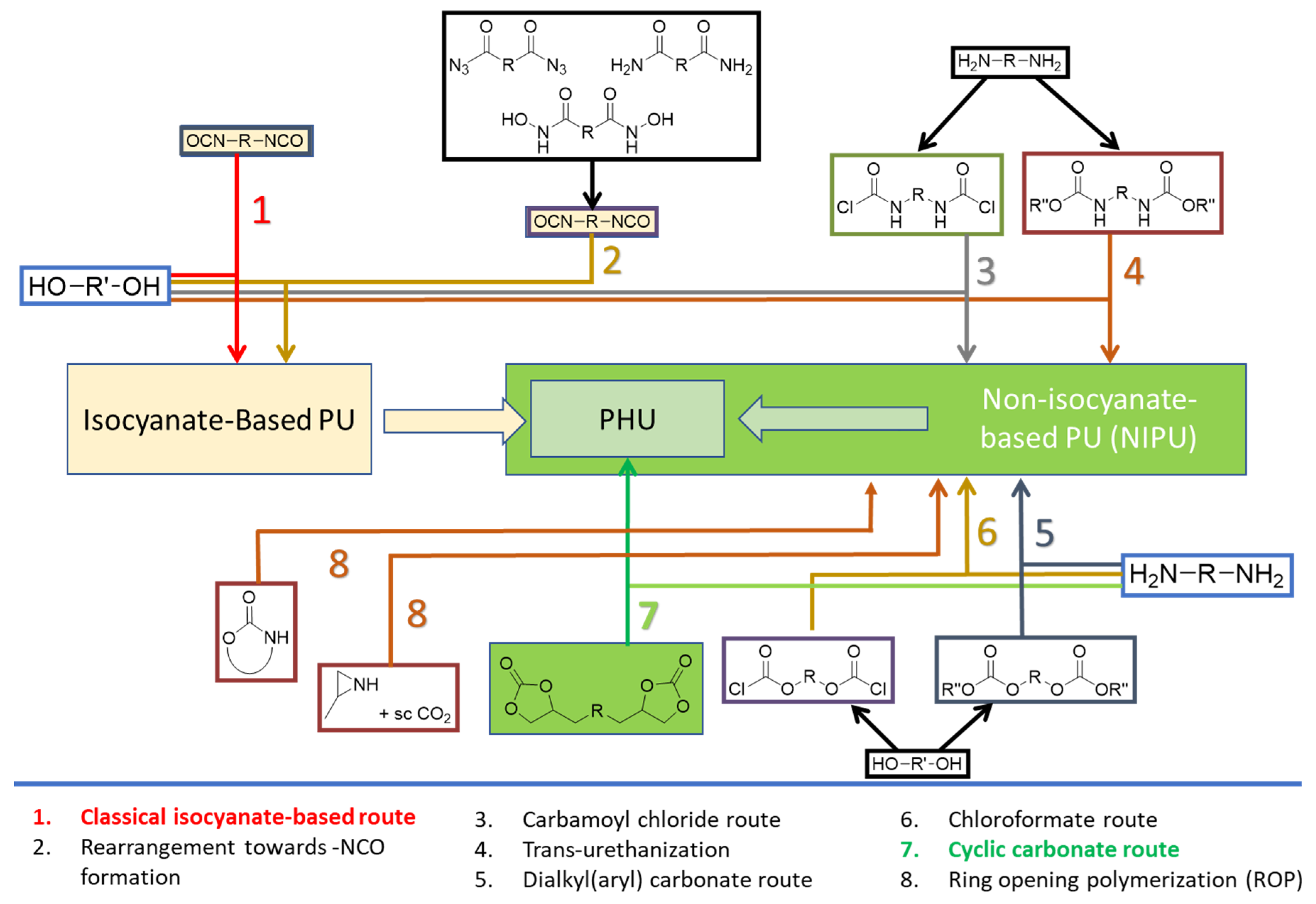
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and General Methods
2.2. Preparation of PHU by Means of Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane (NIPU) Methodology
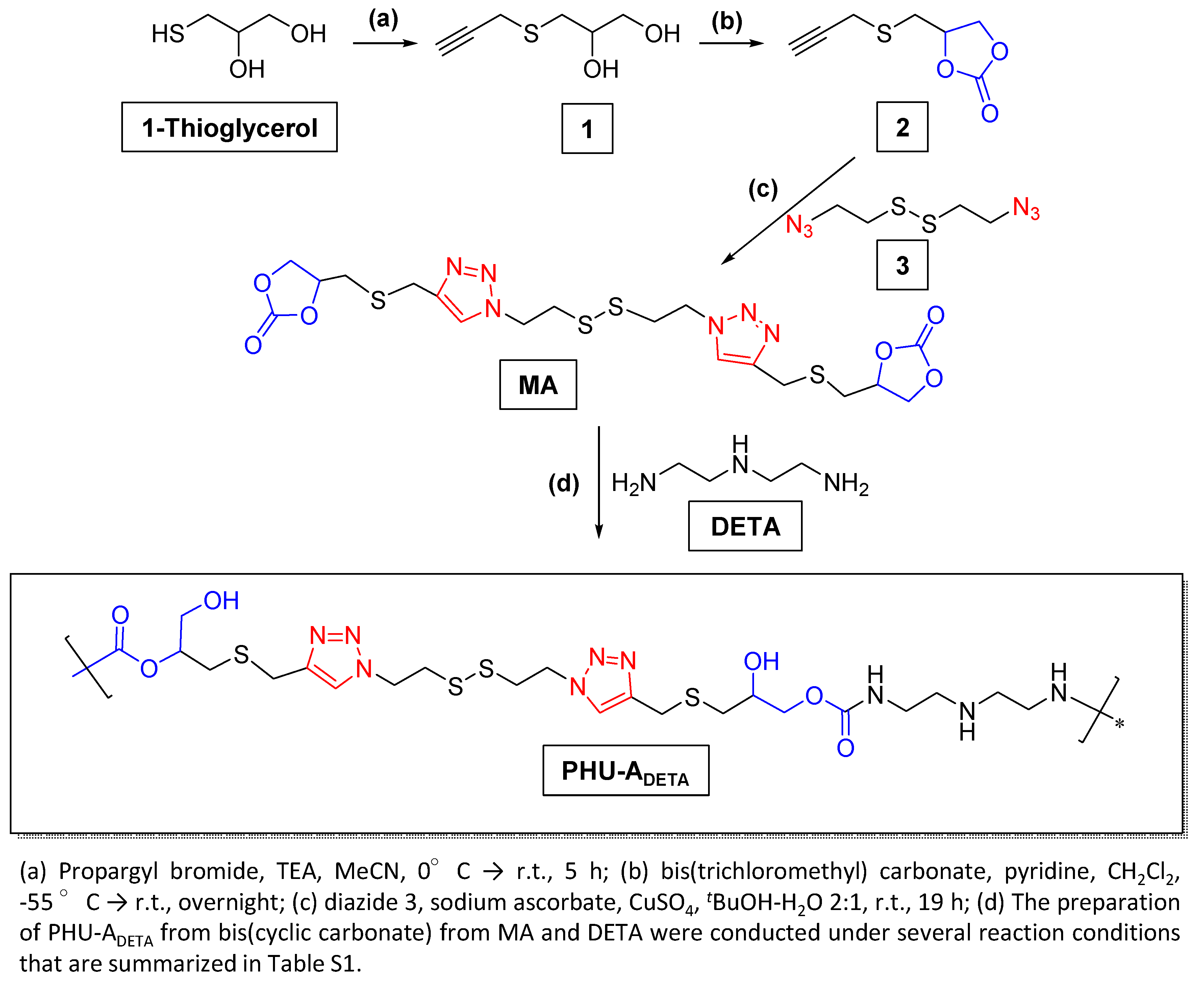
2.2.1. Preparation of PHU-ADETA from MA and DETA
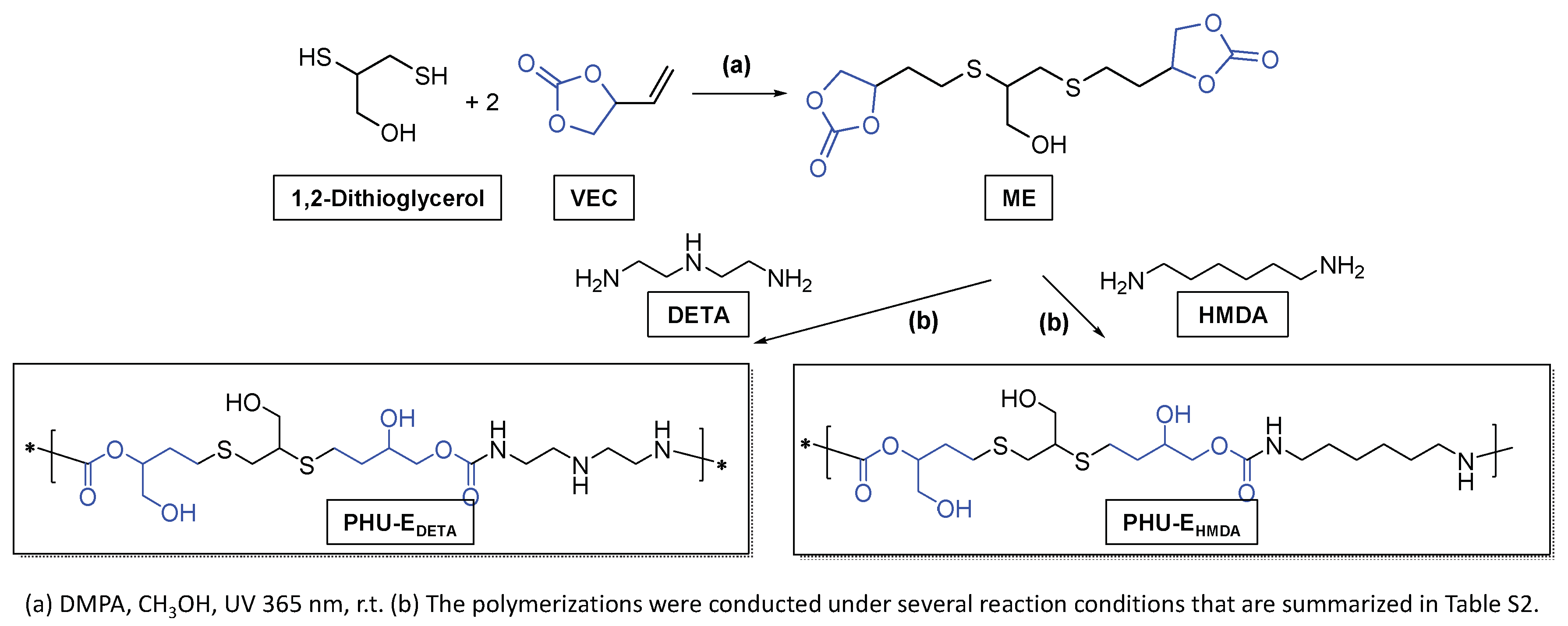
2.2.2. Preparation of PHU-EDETA and PHU-EHMDA
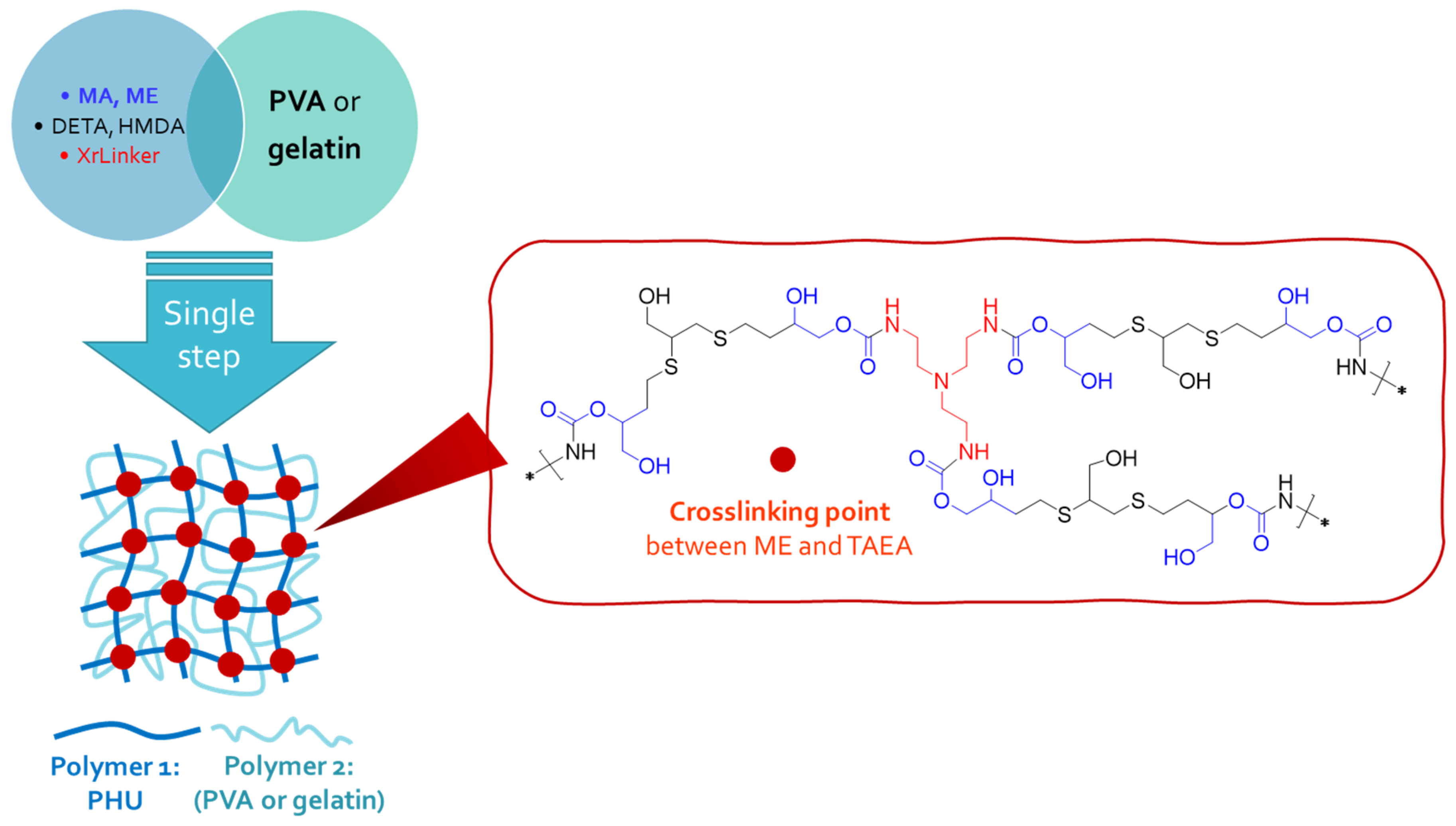
2.3. One-Step Procedure for the Manufacture of SIPN-Based Hydrogels. Characterization of the New Multicomponent Hydrogels.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Monomer MA and Preliminary Studies on PHU-ADETA Formation
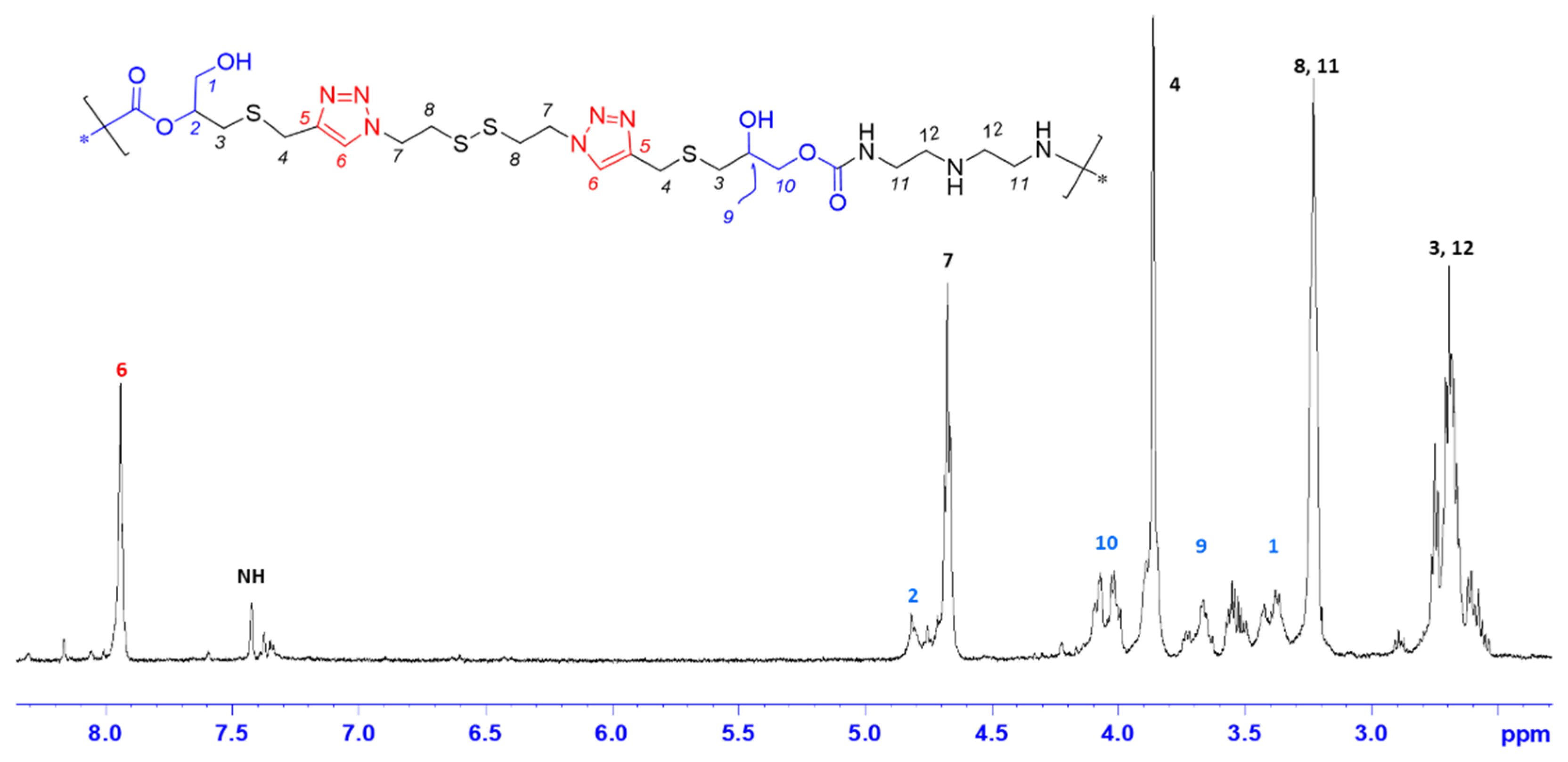
3.2. Optimization of Polymerization Conditions for PHU-ADETA Formation
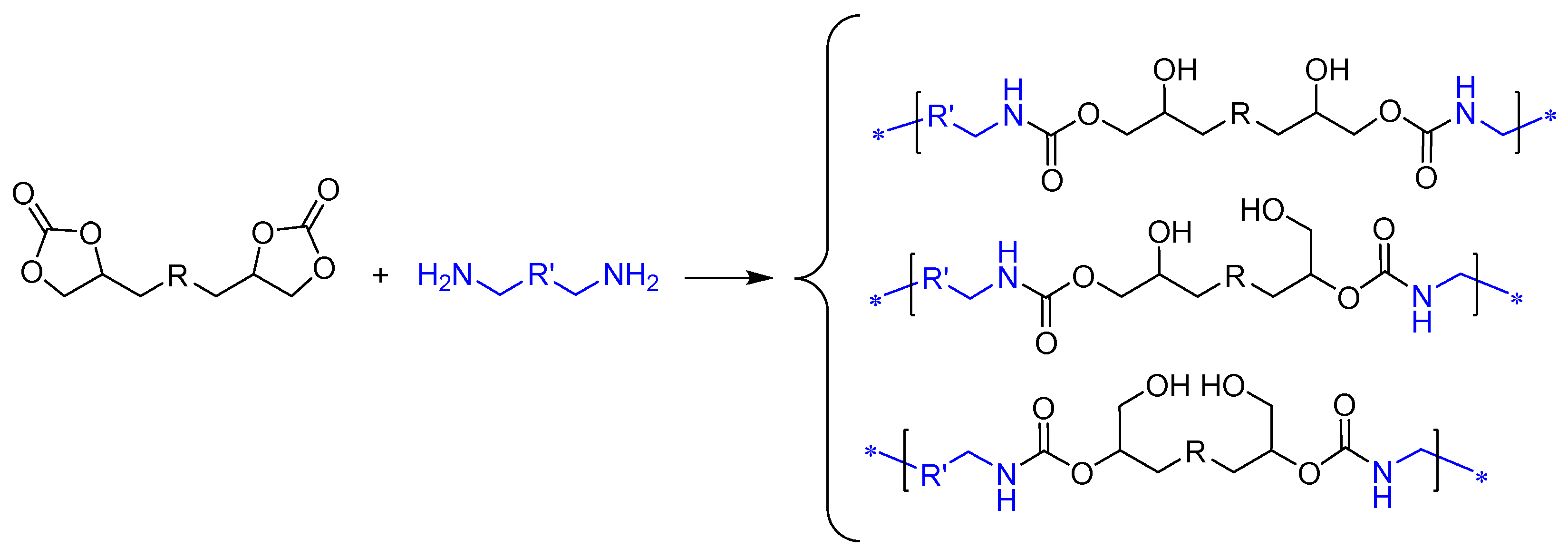
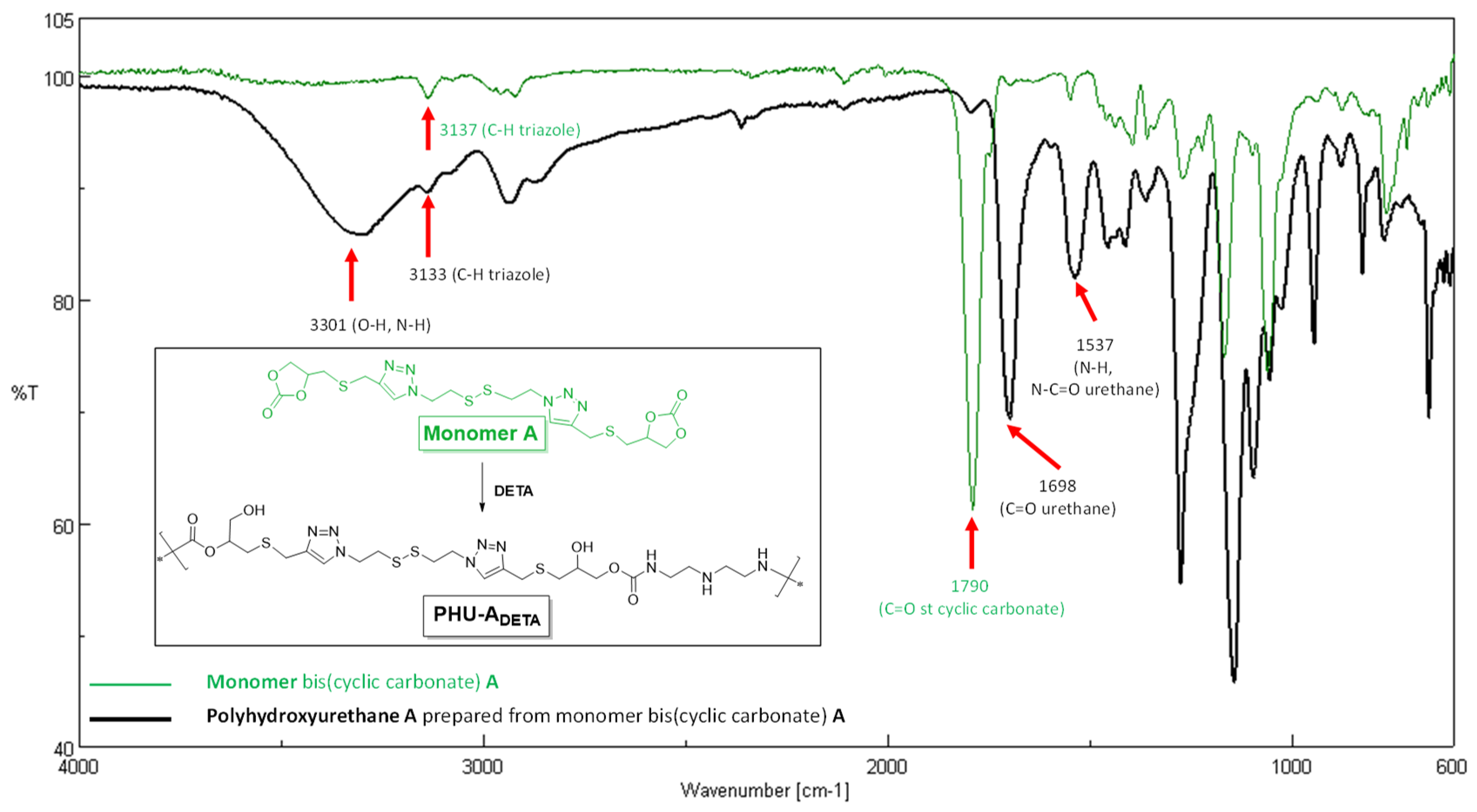
3.3. Synthesis of Bis(Cyclic Carbonate) Monomer ME and PHU-EDETA and PHU-EHMDA
3.4. One-Step Procedure for the Manufacture of PHU-Based Multicomponent Hydrogels
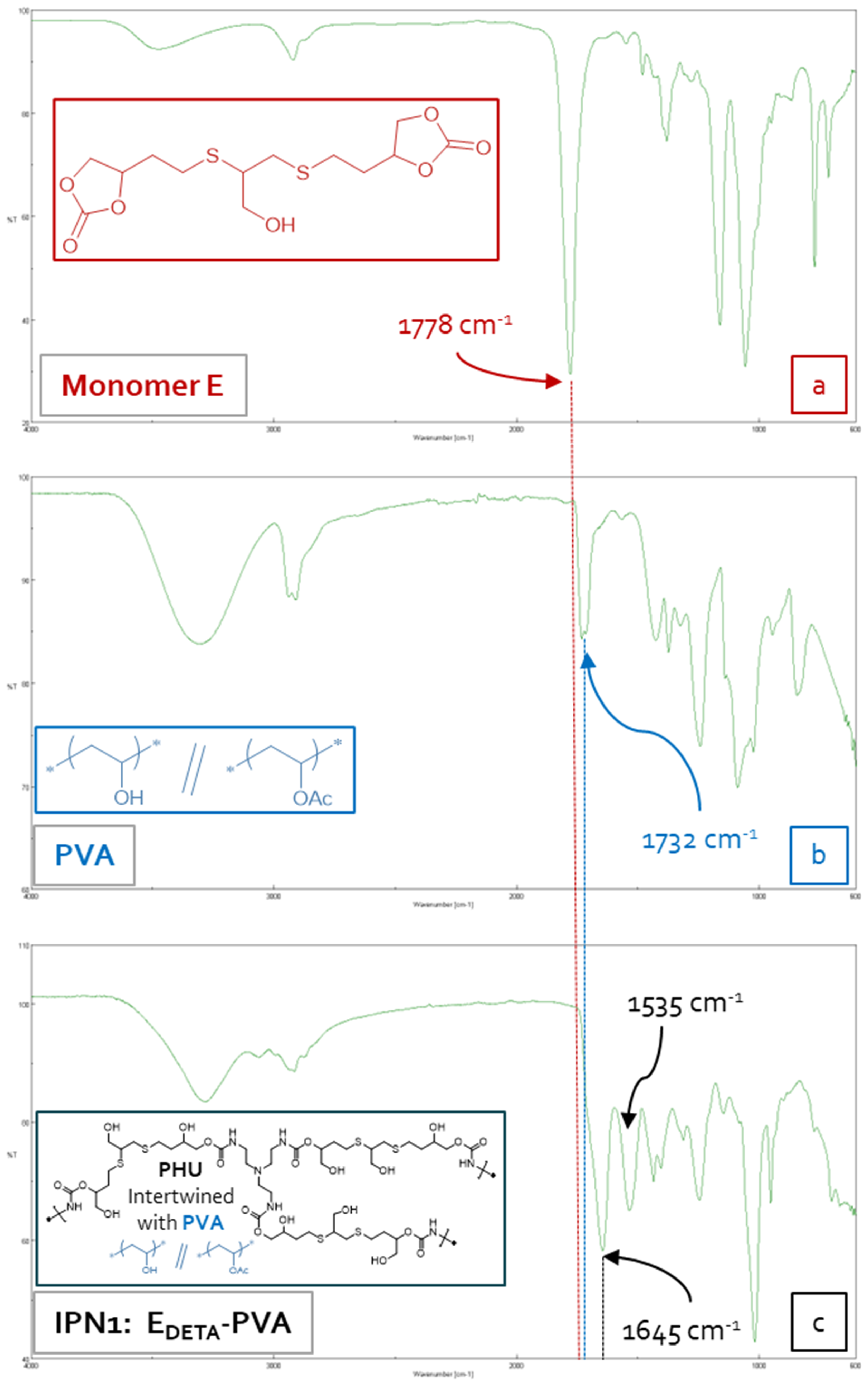
3.5. Characterization of Multicomponent Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Lau, H.K.; Kiick, K.L. Opportunities for multicomponent hybrid hydrogels in biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 28–42. [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Kiick, K.L. Hybrid multicomponent hydrogels for tissue engineering. Macromolecular Bioscience 2009, 9, 140–156. [CrossRef]
- Derkus, B.; Okesola, B.O.; Barrett, D.W.; D’Este, M.; Chowdhury, T.T.; Eglin, D.; Mata, A. Multicomponent hydrogels for the formation of vascularized bone-like constructs in vitro. Acta Biomaterialia 2020, 109, 82–94. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, W.; Shigemitsu, H.; Fujisaku, T.; Kubota, R.; Minami, S.; Urayama, K.; Hamachi, I. Post-assembly Fabrication of a Functional Multicomponent Supramolecular Hydrogel Based on a Self-Sorting Double Network. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2019, 141, 4997–5004. [CrossRef]
- Galbis, J.A.; García-Martín, M. de G.; de Paz, M.V.; Galbis, E. Synthetic Polymers from Sugar-Based Monomers. Chemical Reviews 2016, 116, 1600–1636. [CrossRef]
- Galbis, J.A.; García-Martín, M.G.; De-Paz, M.-V.; Galbis, E. Bio-based Polyurethanes from Carbohydrate Monomers. In Aspects of Polyurethanes; Yilmaz, F., Ed.; Intech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 155–192 ISBN 978-953-51-3545-6.
- Santerre, J.P.; Woodhouse, K.; Laroche, G.; Labow, R.S. Understanding the biodegradation of polyurethanes: from classical implants to tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7457–70. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, C.; de Paz, M.V.; Aguilar-de-Leyva, A.; Caraballo, I.; Galbis, J.A. Reduction-sensitive functionalized copolyurethanes for biomedical applications. Polymer Chemistry 2014, 5, 2370–2381. [CrossRef]
- Benito, E.; Romero-Azogil, L.; Galbis, E.; De-Paz, M.V.; García-Martín, M.G. Structurally simple redox polymersomes for doxorubicin delivery. European Polymer Journal 2020, 137, 109952 (1–11). [CrossRef]
- De Paz, M.V.; Marin, R.; Zamora, F.; Hakkou, K.; Alla, A.; Galbis, J.A.; Munoz-Guerra, S. Linear polyurethanes derived from alditols and diisocyanates. Journal of Polymer Science, Part A: Polymer Chemistry 2007, 45, 4109–4117. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Kumar, V.; Bhunia, H.; Upadhyay, S.N. Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid): A Review. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part C 2005, 45, 325–349. [CrossRef]
- Robert, J.L.; Aubrecht, K.B. Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide To Form a Biodegradable Polymer. Journal of Chemical Education 2008, 85, 258. [CrossRef]
- Valette, V.; Kébir, N.; Tiavarison, F.B.; Burel, F.; Lecamp, L. Preparation of flexible biobased non-isocyanate polyurethane (NIPU) foams using the transurethanization approach. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2022, 181. [CrossRef]
- Wołosz, D.; Parzuchowski, P.G.; Świderska, A. Synthesis and characterization of the non-isocyanate poly(carbonate-urethane)s obtained via polycondensation route. European Polymer Journal 2021, 155. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, X.; Wan, Q.; Bo, G.; Yan, Y. Solvent- and catalyst-free synthesis, hybridization and characterization of biobased nonisocyanate polyurethane (NIPU). Polymers 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Monie, F.; Grignard, B.; Thomassin, J.M.; Mereau, R.; Tassaing, T.; Jerome, C.; Detrembleur, C. Chemo- and Regioselective Additions of Nucleophiles to Cyclic Carbonates for the Preparation of Self-Blowing Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Foams. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2020, 59, 17033–17041. [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.I.; Chen, C.W.; Yan, H.C.; Rwei, S.P. Synthesis and characteristics of nonisocyanate polyurethane composed of bio-based dimer diamine for supercritical CO2 foaming applications. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2022, 139. [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Liang, C.; Wang, J.; Kang, M.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y. Promising approaches to improve the performances of hybrid non-isocyanate polyurethane. Polymer International 2019, 68, 651–660. [CrossRef]
- Cornille, A.; Auvergne, R.; Figovsky, O.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. A perspective approach to sustainable routes for non-isocyanate polyurethanes. European Polymer Journal 2017, 87, 535–552. [CrossRef]
- Grosso, R.; Benito, E.; Carbajo-Gordillo, A.I.; García-Martín, M.G.; Perez-Puyana, V.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; De-Paz, M.-V. Biodegradable Guar-Gum-Based Super-Porous Matrices for Gastroretentive Controlled Drug Release in the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori: A Proof of Concept. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 2281 (1–23). [CrossRef]
- Matricardi, P.; Di Meo, C.; Coviello, T.; Hennink, W.E.; Alhaique, F. Interpenetrating polymer networks polysaccharide hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2013, 65, 1172–1187. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cid, P.; Romero, A.; Díaz, M.J.; De-Paz, M. V.; Perez-Puyana, V. Chitosan-based hydrogels obtained via photoinitiated click polymer IPN reaction. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2023, 379, 121735 (1–11). [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.Y.; Noh, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Ji, Y.B.; Ju, H.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Lee, B.; Kim, M.S. An injectable click-crosslinked hydrogel that prolongs dexamethasone release from dexamethasone-loaded microspheres. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 438. [CrossRef]
- León-Campos, M.I.; Claudio-Rizo, J.A.; Rodriguez-Fuentes, N.; Cabrera-Munguía, D.A.; Becerra-Rodriguez, J.J.; Herrera-Guerrero, A.; Soriano-Corral, F. Biocompatible interpenetrating polymeric networks in hydrogel state comprised from jellyfish collagen and polyurethane. Journal of Polymer Research 2021, 28, 291. [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Raza, Z.A.; Batool, S.R.; Zahid, M.; Onder, O.C.; Rafique, A.; Nazeer, M.A. Preparation, properties, and applications of gelatin-based hydrogels (GHs) in the environmental, technological, and biomedical sectors. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 218, 601–633. [CrossRef]
- Bray D. Critical Point Drying of Biological Specimens for Scanning Electron Microscopy. In: Williams JR, Clifford AA, editors. Supercritical Fluid Methods and Protocols. Methods In Biotechnology. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press; 2000. p. 235-43. [CrossRef]
- Carbajo-Gordillo, A.I.; Benito, E.; Galbis, E.; Grosso, R.; Iglesias, N.; García-Martín, M.-G.; De-Paz, M.-V. Spectra and GPC Data for Polyhydroxyurethanes Formation from Bis(cyclic carbonate) Monomers in Multicomponent Semi-IPN Hydrogels Fabrication [Dataset] 2024, 1–90. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, J.; Ruymbeke, E. van; Keunings, R.; Bailly, C. Evaluation of different methods for the determination of the plateau modulus and the entanglement molecular weight. Polymer 2006, 47, 4461–4479. [CrossRef]
- Baumgaertel, M.; Winter, H.H. Interrelation between continious and discrete time spectra. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics 1992, 44, 15–36. [CrossRef]
- Besse, V.; Foyer, G.; Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; Boutevin, B.; Burk, R.M.; Roof, M.B. A safe and efficient method for conversion of 1,2- and 1,3-diols to cyclic carbonates utilizing triphosgene. Tetrahedron Letters 1993, 51, 3284–3296. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, N.; Du, F.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Tan, Y.X.; Ji, S.P.; Liang, D.H.; Li, Z.C. Reduction-degradable linear cationic polymers as gene carriers prepared by Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 66–74. [CrossRef]
- de Paz, M.V.; Zamora, F.; Begines, B.; Ferris, C.; Galbis, J.A. Glutathione-Mediated Biodegradable Polyurethanes Derived from L -Arabinitol. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 269–276. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Bailén, M.; Galbis, E.; Carmona, A.T.; De-Paz, M.-V.; Robina, I. Preparation of water-soluble glycopolymers derived from five-membered iminosugars. European Polymer Journal 2019, 119, 213–221. [CrossRef]
- Blain, M.; Yau, H.; Jean-Gérard, L.; Auvergne, R.; Benazet, D.; Schreiner, P.R.; Caillol, S.; Andrioletti, B. Urea-and thiourea-catalyzed aminolysis of carbonates. ChemSusChem 2016, 9, 2269–2272. [CrossRef]
- Mhd. Haniffa, M.A.C.; Munawar, K.; Ching, Y.C.; Illias, H.A.; Chuah, C.H. Bio-based Poly(hydroxy urethane)s: Synthesis and Pre/Post-Functionalization. Chemistry – An Asian Journal 2021, 16, 1281–1297. [CrossRef]
- Blattmann, H.; Fleischer, M.; Bähr, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Isocyanate- and phosgene-free routes to polyfunctional cyclic carbonates and green polyurethanes by fixation of carbon dioxide. Macromolecular Rapid Communications 2014, 35, 1238–1254. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Gatti, F.J.; Luitz, M.; Ritter, B.S.; Bruchmann, B.; Mülhaupt, R. Erythritol dicarbonate as intermediate for solvent-and isocyanate-free tailoring of bio-based polyhydroxyurethane thermoplastics and thermoplastic elastomers. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2296–2303. [CrossRef]
- Blain, M.; Cornille, A.; Boutevin, B.; Auvergne, R.; Benazet, D.; Andrioletti, B.; Caillol, S. Hydrogen bonds prevent obtaining high molar mass PHUs. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2017, 134, 44958. [CrossRef]
- Cornille, A.; Blain, M.; Auvergne, R.; Andrioletti, B.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. A study of cyclic carbonate aminolysis at room temperature: effect of cyclic carbonate structures and solvents on polyhydroxyurethane synthesis. Polymer Chemistry 2017, 8, 592–604. [CrossRef]
- Cornille, A.; Guillet, C.; Benyahya, S.; Negrell, C.; Boutevin, B.; Caillol, S. Room temperature flexible isocyanate-free polyurethane foams. European Polymer Journal 2016, 84, 873–888. [CrossRef]
- Guzmán Agudelo, A.F.; Pérez-Sena, W.Y.; Kebir, N.; Salmi, T.; Ríos, L.A.; Leveneur, S. Influence of steric effects on the kinetics of cyclic-carbonate vegetable oils aminolysis. Chemical Engineering Science 2020, 228. [CrossRef]
- Almdal, K.; Dyre, J.; Hvidt, S.; Kramer, O. Towards a phenomenological definition of the term “gel.” Polymer Gels and Networks 1993, 1, 5–17. [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Critical exponents for sol-gel transition in aqueous alginate solutions induced by cupric cations. Carbohydrate Polymers 2006, 65, 544–551. [CrossRef]
- Sachlos, E.; Wahl, D.A.; Triffitt, J.T.; Czernuszka, J.T. The impact of critical point drying with liquid carbon dioxide on collagen-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia 2008, 4, 1322–1331. [CrossRef]
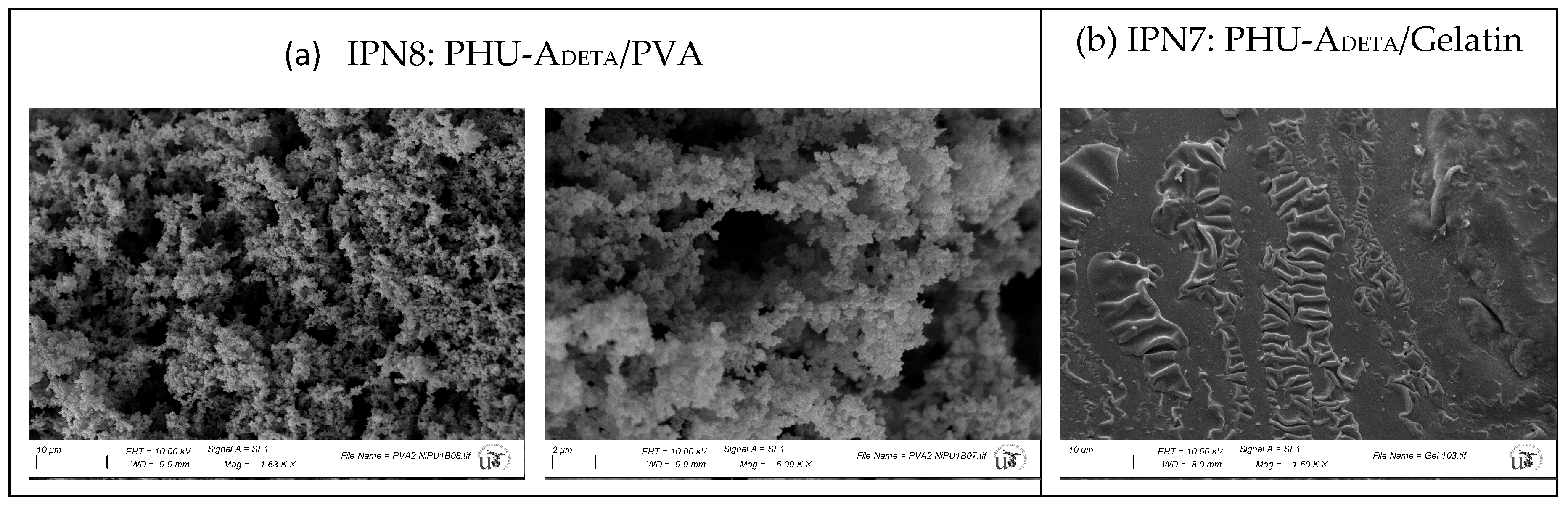
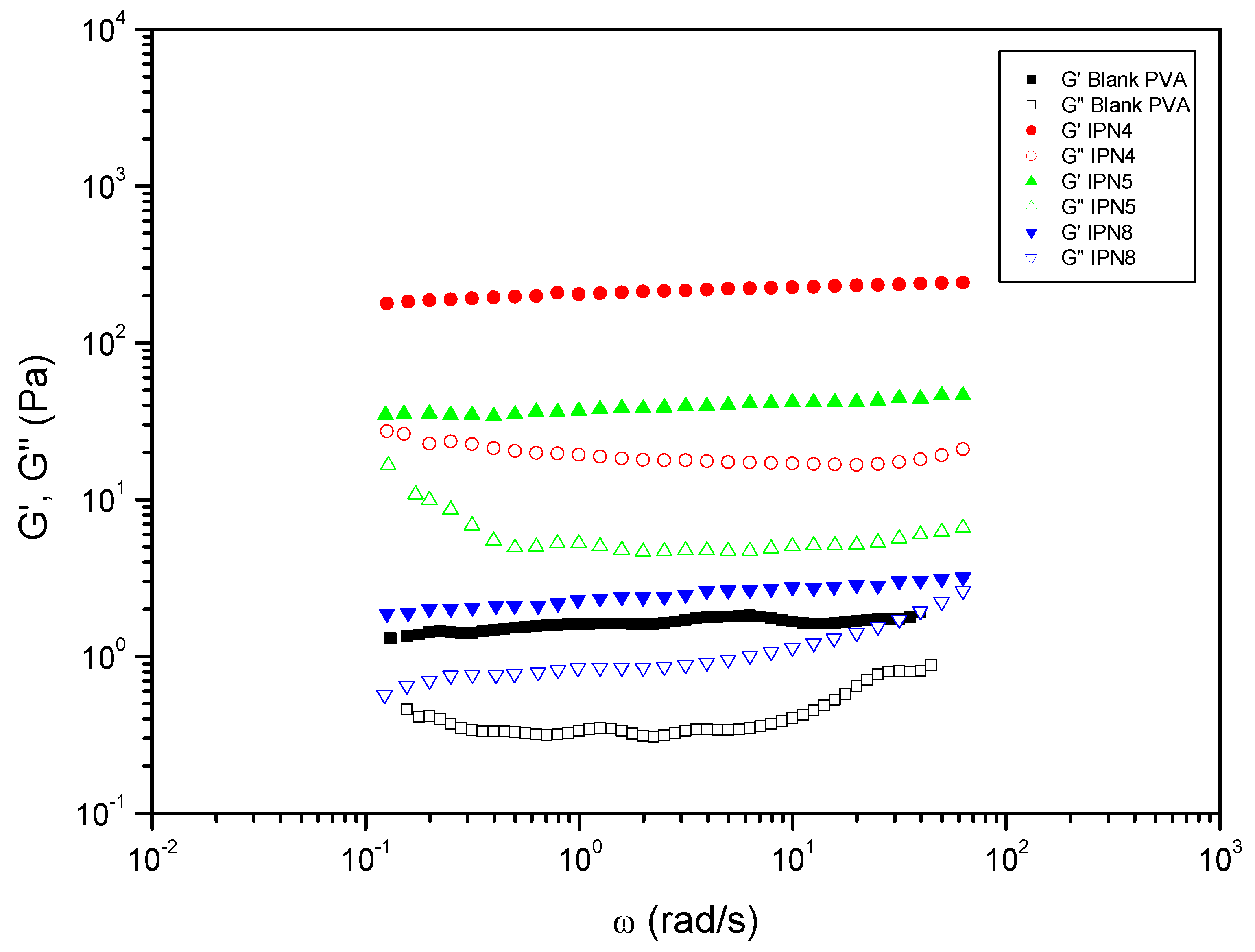
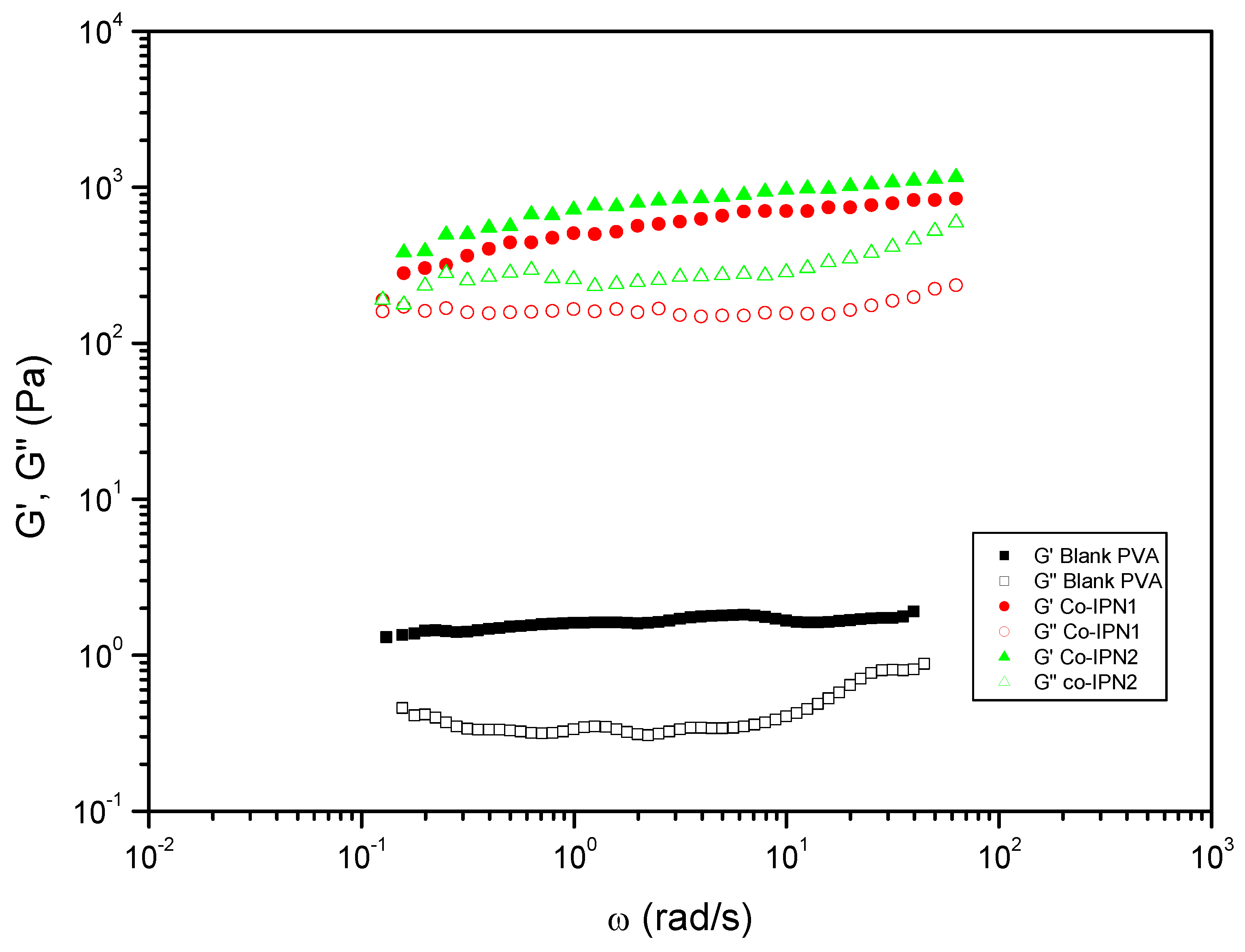
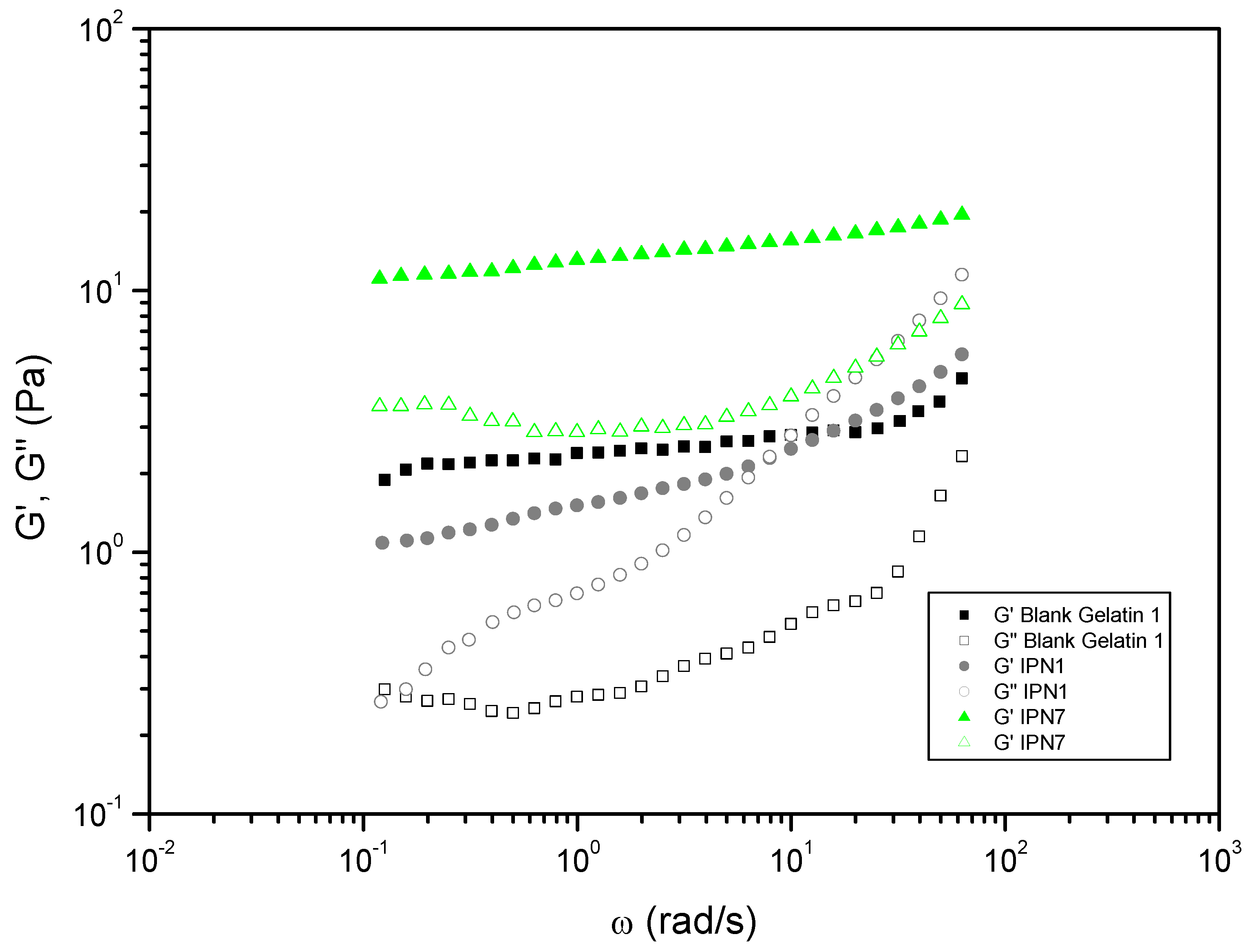

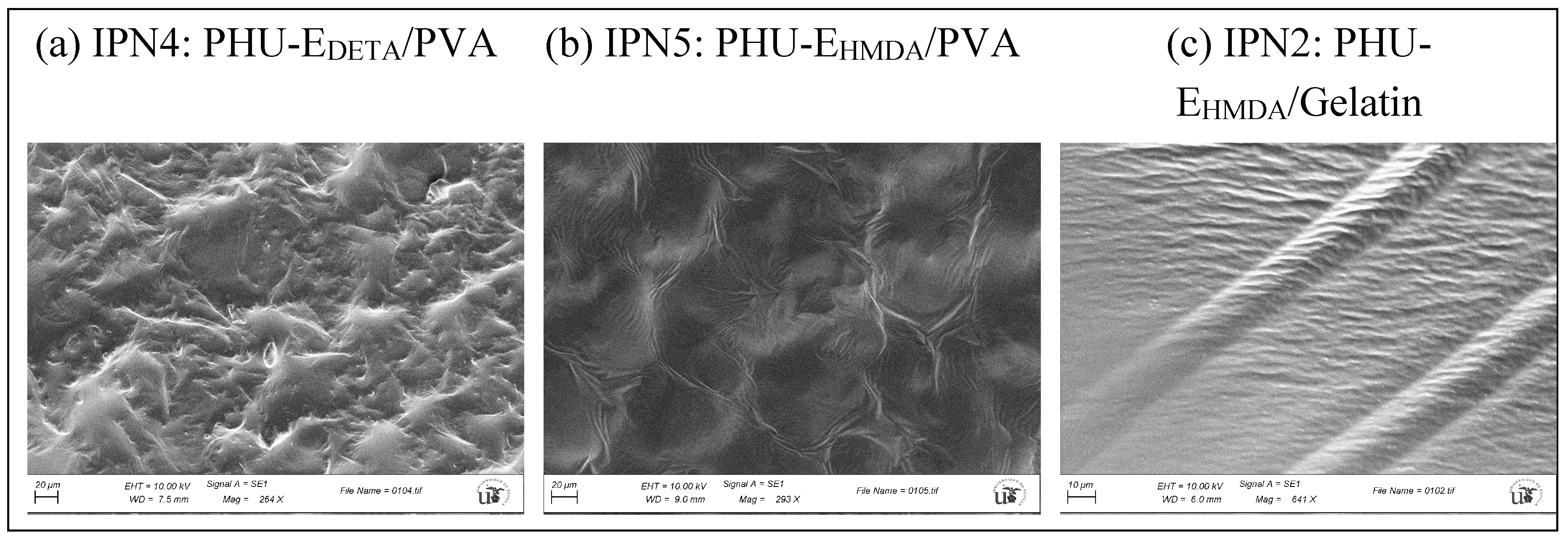
| Entry | Hydrogels prepared and blanks | Polymer 1 (PHU) Conc.: 10% w/v |
Polymer 2 (Polymer scaffold) Conc.: 10% w/v |
Solvents | Catalyst |
(Pa) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer 1 (bisCC) |
Monomer 2 (diamine) |
|||||||
| 1 | Blank | --- | --- | Gelatin 1 | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | 2.24 | 0.10 | |
| 2 | Blank | --- | --- | Gelatin 1 | EtOH-H2O 1:1 | 1240.46 | 0.12 | |
| 3 | Blank | --- | --- | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | 1.86 | 0.21 | |
| 4 | Blank | --- | --- | PVA | EtOH-H2O 1:1 | 11.9 | 0.35 | |
| 5 | IPN1 | ME | DETA | Gelatin 1 | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 1.45 | 0.44 |
| 6 | IPN2 | ME | HMDA | Gelatin 1 | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 4.29 | 0.20 |
| 7 | IPN3 | ME | DETA | Gelatin 1 | EtOH-H2O 1:1 | TU | 5.19 | 0.81 |
| 8 | IPN4 | ME | DETA | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 225.44 | 0.09 |
| 9 | IPN5 | ME | HMDA | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 40.97 | 0.14 |
| 10 | IPN6 | ME | DETA | PVA | EtOH-H2O 1:1 | TU | 8.28 | 0.19 |
| 11 | IPN7 | MA | DETA | Gelatin 1 | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 14.34 | 0.22 |
| 12 | IPN8 | MA | DETA | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 2.39 | 0.38 |
| 13 | co-IPN1 | ME80/MA20 | DETA | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 742.12 | 0.32 |
| 14 | co-IPN2 | ME20/MA80 | DETA | PVA | DMSO-H2O 1:1 | DBU | 958.39 | 0.35 |
| (a) (): Plateau modulus; (b) tan (δ) at 1 rad/s DBU: 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene; DETA: diethylenetriamine; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; EtOH: ethanol; HMDA: 1,6-hexamethylenediamine; MA: monomer bisCC A; ME: monomer bisCC E; TU: N′-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-cyclohexylthiourea. | ||||||||
| Sample | BisCC | Diamine | [Monomer] | Solvent- | Temp. (°C) |
Catalyst |
g/mol |
(°C) |
(°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADETA-13(d) | MA | DETA | 1.8 mol/L | TFE | 25 | TU | 16,400 | -3.0 | -- |
| EDETA-4(e) | ME | DETA | 1.8 mol/L | EtOH | 50 | TU | 29,600 | -10.3 | -- |
| EHMDA-2(e) | ME | HMDA | 1.8 mol/L | DMSO | 50 | DBU | 34,100 | 14.2 | -- |
| (a) Weight average molecular weight () calculated by gel permeation chromatography (GPC); (b) Glass transition temperature () determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC); (c) Melting temperature () determined by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC); (d) Table S1; (e) Table S2; DBU: 1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene; DETA: diethylenetriamine; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; EtOH: ethanol; HMDA: 1,6-hexamethylenediamine; MA: monomer A; ME: monomer B; TFE: 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol; TU: N′-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-N-cyclohexylthiourea. | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





