Submitted:
22 February 2024
Posted:
22 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Data fusion methods
- Liet al.[17] method
2.2. Validation of methods on in-ear measurements
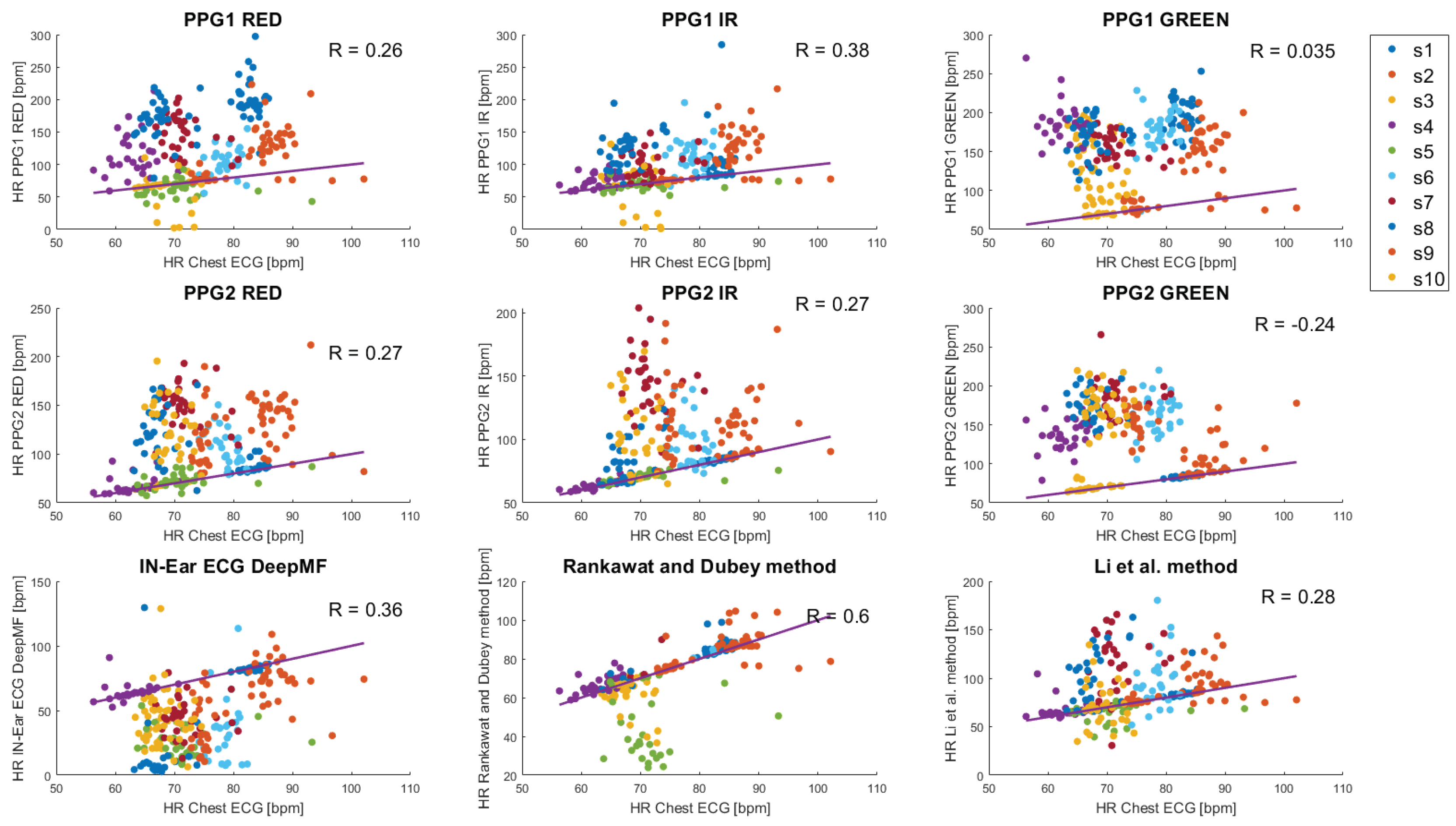
3. Results
4. Discussion
- 1.
- Enhancement of data fusion methods by refining the assessment of weights.
- 2.
- Development of PPG beat detector optimized for low-amplitude in-ear PPG signals.
- 3.
- Improvement of SQI estimation methods towards more reliable HR estimation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HR | heart rate |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| PPG | photoplethysmographm |
| SQI | signal quality index |
References
- Ruiz-Alias, S.A.; García-Pinillos, F.; Soto-Hermoso, V.M.; Ruiz-Malagón, E.J. Heart rate monitoring of the endurance runner during high intensity interval training: Influence of device used on training functions. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part P: Journal of Sports Engineering and Technology 2021, p. 17543371211037035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, D.; Garatachea, N.; Almeida, R.; Casajus, J.A.; Bailón, R. Validation of heart rate monitor Polar RS800 for heart rate variability analysis during exercise. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research 2018, 32, 716–725. [Google Scholar]
- Fariha, M.; Ikeura, R.; Hayakawa, S.; Tsutsumi, S. Analysis of Pan-Tompkins algorithm performance with noisy ECG signals. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2020, Vol. 1532, p. 012022.
- Smital, L.; Haider, C.R.; Vitek, M.; Leinveber, P.; Jurak, P.; Nemcova, A.; Smisek, R.; Marsanova, L.; Provaznik, I.; Felton, C.L.; others. Real-time quality assessment of long-term ECG signals recorded by wearables in free-living conditions. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2020, 67, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamis, H.; Weiss, R.; Xie, Y.; Chang, C.W.; Lovell, N.H.; Redmond, S.J. QRS detection algorithm for telehealth electrocardiogram recordings. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2016, 63, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, S. Performance analysis of ten common QRS detectors on different ECG application cases. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiou, K.; Larentzakis, A.V.; Khamis, N.N.; Alsuhaibani, G.I.; Alaska, Y.A.; Giallafos, E.J. Can wearable devices accurately measure heart rate variability? A systematic review. Folia Medica 2018, 60, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Rosenberg, W.; Chanwimalueang, T.; Goverdovsky, V.; Peters, N.S.; Papavassiliou, C.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Feasibility of recording cardiac rhythms from head and in-ear locations. Royal Society Open Science 2017, 4, 171214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarici, M.; Von Rosenberg, W.; Hammour, G.; Davies, H.; Amadori, P.; Ling, N.; Demiris, Y.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: feasibility of recording cardiac rhythms from single in-ear locations. Royal Society Open Science 2024, 11, 221620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverdovsky, V.; Von Rosenberg, W.; Nakamura, T.; Looney, D.; Sharp, D.J.; Papavassiliou, C.; Morrell, M.J.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Multimodal physiological in-ear sensing. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Occhipinti, E.; Nassibi, A.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Heart Rate Variability from Ear Electrocardiogram and Ear Photoplethysmogram (Ear-ECG and Ear-PPG). 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2023.
- Occhipinti, E.; Davies, H.J.; Hammour, G.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Artefact removal in Ear-EEG for continuous 24/7 monitoring. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2022, pp. 1–6.
- Hammour, G.; Yarici, M.; von Rosenberg, W.; Mandic, D.P. Hearables: Feasibility and validation of in-ear electrocardiogram. 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2019, pp. 5777–5780.
- Passler, S.; Müller, N.; Senner, V. In-ear pulse rate measurement: A valid alternative to heart rate derived from electrocardiography? Sensors 2019, 19, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlini, A.; Montanari, A.; Min, C.; Li, H.; Sassi, U.; Kawsar, F. In-ear PPG for vital signs. IEEE Pervasive Computing 2021, 21, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkow, K.J.; Dang, T.; Ferlini, A.; Ma, D.; Mascolo, C. hEARt: Motion-resilient Heart Rate Monitoring with In-ear Microphones. the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom). IEEE, 2023, pp. 200–209.
- Li, Q.; Mark, R.G.; Clifford, G.D. Robust heart rate estimation from multiple asynchronous noisy sources using signal quality indices and a Kalman filter. Physiological Measurement 2007, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankawat, S.A.; Dubey, R. Robust heart rate estimation from multimodal physiological signals using beat signal quality index based majority voting fusion method. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2017, 33, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankawat, S.A.; Rankawat, M.; Dubey, R. ECG artifacts detection in noncardiovascular signals using Slope Sum Function and Teager Kaiser Energy. 2015 International Conference on BioSignal Analysis, Processing and Systems (ICBAPS). IEEE, 2015, pp. 6–10.
- Welch, G.F. Kalman filter. Computer Vision: A Reference Guide 2020, pp. 1–3.
- Vest, A.N.; Da Poian, G.; Li, Q.; Liu, C.; Nemati, S.; Shah, A.J.; Clifford, G.D. An open source benchmarked toolbox for cardiovascular waveform and interval analysis. Physiological Measurement 2018, 39, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, H.J.; Hammour, G.; Zylinski, M.; Nassibi, A.; Mandic, D.P. A Deep Matched Filter For R-Peak Detection in Ear-ECG. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14102 2023.
- Li, Q.; Clifford, G.D. Signal quality and data fusion for false alarm reduction in the intensive care unit. Journal of Electrocardiology 2012, 45, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Jonkman, M.; De Boer, F. Frequency Bands Effects on QRS Detection. Biosignals 2010, 2003, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Karmakar, C.; Natgunanathan, I.; Yearwood, J.; Palaniswami, M. Robustness of electrocardiogram signal quality indices. Journal of the Royal Society Interface 2022, 19, 20220012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Qin, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, C. A novel attentional deep neural network-based assessment method for ECG quality. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 79, 104064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhong, G.; He, J.; Yang, C. Multi-task cascaded assessment of signal quality for long-term single-lead ECG monitoring. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 83, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, D.T.; Villajuan, S.O.; Edkins, L.; Cleary, S.; Saleem, J.J. Wearable heart rate monitor technology accuracy in research: A comparative study between PPG and ECG technology. Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting. SAGE Publications Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA, 2017, Vol. 61, pp. 1292–1296.
- Charlton, P.H.; Kotzen, K.; Mejía-Mejía, E.; Aston, P.J.; Budidha, K.; Mant, J.; Pettit, C.; Behar, J.A.; Kyriacou, P.A. Detecting beats in the photoplethysmogram: Benchmarking open-source algorithms. Physiological Measurement 2022, 43, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, S.M.; Ercole, A. Multi-scale peak and trough detection optimised for periodic and quasi-periodic neuroscience data. Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI. Springer, 2018, pp. 189–195.
- Galli, A.; Frigo, G.; Narduzzi, C.; Giorgi, G. Robust estimation and tracking of heart rate by PPG signal analysis. IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–6.
- Sjoding, M.W.; Dickson, R.P.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Gay, S.E.; Valley, T.S. Racial bias in pulse oximetry measurement. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, 2477–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermond, M.; Davies, H.J.; Occhipinti, E.; Nassibi, A.; Mandic, D.P. Reducing racial bias in SpO2 estimation: The effects of skin pigmentation. 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2023.
- Hartmann, V.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Qiu, Q.; Hughes, S.; Zheng, D. Quantitative comparison of photoplethysmographic waveform characteristics: Effect of measurement site. Frontiers in Physiology 2019, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Source type | SQI ≥ 0.9 | 0.9>SQI ≥ 0.8 | 0.8>SQI ≥ 0.7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular signals | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| Non-cardiovascular signals | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| PPG1 | PPG2 | In-Ear ECG | Data fusion | ||||||
| Subject | RED | IR | GREEN | RED | IR | GREEN | DeepMF | Rankawat and Dubey | Li et al. |
| 1 | 119 | 19 | 113 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 107 | 39 | 124 | 16 | 46 | 65 | 17 | 14 | 35 |
| 3 | 1.6 | 9.0 | 94 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 2.3 | 26 | 3.5 | 1.3 |
| 4 | 53 | 12 | 124 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 73 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| 5 | 13 | 7.3 | - | 5.6 | 2.4 | - | 45 | 27 | 7.6 |
| 6 | 26 | 36 | 98 | 28 | 19 | 85 | 48 | 1.6 | 25 |
| 7 | 74 | 29 | 84 | 80 | 73 | 108 | 28 | 6.6 | 44 |
| 8 | 101 | 55 | 101 | 55 | 15 | 107 | 57 | 2.7 | 32 |
| 9 | 6.1 | 3.3 | 5.9 | 38 | 35 | 78 | 37 | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| 10 | 45 | 49 | 16 | 56 | 37 | 106 | 30 | 16 | 17 |
| Mean | 54 | 26 | 84 | 29 | 23 | 69 | 29 | 8.0 | 17 |
| std | 40 | 19 | 50 | 28 | 24 | 42 | 17 | 8.4 | 16 |
| PPG1 | PPG2 | In-Ear ECG | Data fusion | ||||||
| Subject | RED | IR | GREEN | RED | IR | GREEN | DeepMF | Rankawat and Dubey | Li et al. |
| 1 | 50 | 51 | 73 | 30 | 4.6 | 2.8 | 32 | 2.2 | 5.8 |
| 2 | 71 | 63 | 82 | 71 | 71 | 8.8 | 31 | 14 | 12 |
| 3 | 18 | 28 | 101 | 65 | 29 | 12 | 58 | 31 | 15 |
| 4 | 56 | 51 | 76 | 56 | 22 | 9.5 | 13 | 4.1 | 14 |
| 5 | 43 | 36 | - | 28 | 24 | - | 77 | 16 | 34 |
| 6 | 34 | 33 | 44 | 51 | 53 | 44 | 71 | 28 | 23 |
| 7 | 20 | 18 | 31 | 15 | 13 | 25 | 72 | 24 | 18 |
| 8 | 20 | 22 | 41 | 55 | 60 | 51 | 79 | 3.6 | 34 |
| 9 | 22 | 17 | 21 | 18 | 22 | 35 | 63 | 11 | 14 |
| 10 | 20 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 31 | 15 | 26 | 15 | 14 |
| Mean | 35 | 33 | 54 | 40 | 33 | 23 | 52 | 15 | 18 |
| std | 19 | 17 | 33 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 24 | 10 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





