1. Introduction
Culex quinquefasciatus is an efficient vector of several disease agents including those causing West Nile disease, lymphatic filariasis, and Japanese encephalitis and is a worldwide target for vector control operations [
1,
2,
3,
4]. This species has posed challenging for operational control but using the principles of integrated vector management (IVM) has been shown as the most effective way to manage mosquito populations including
Cx. quinquefasciatus [
5,
6,
7]. Monitoring insecticide resistance is a critical element of an effective IVM strategy as it can guide decision-making on appropriate and effective operational responses while helping to avoid interventions likely to be of low efficacy.
A 70-year history shows examples of insecticide resistance (IR) in
Cx. quinquefasciatus to a variety of active ingredients (AIs), including larvicides and adulticides. Laboratory testing on populations from Okinawa, Japan showed increasing resistance to DDT [
8]. Studies from Peru and Ecuador around the same time showed that
Cx. quinquefasciatus had a high level of “natural” resistance and that IR could be rapidly induced in the laboratory in as little as six generations although the specific mechanism was undetermined [
9,
10]. In a real-world demonstration of this same principle, Tanzanian populations taken from areas subject to intense pressure from malaria eradication by house spraying with dieldrin were 10-fold more resistant than a population collected from an untreated area [
11]. The initial reports of IR in US
Cx. quinquefasciatus populations from Texas and California were published in the 1960s [
12,
13]. Pyrethroids were initially effective against
Culex populations up through the mid-1970s [
14,
15,
16]. However, pyrethroid resistance was widely detected over the next decade and this increasing IR was linked to preexisting DDT resistance [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. In Florida, IR has been reported in
Cx. quinquefasciatus populations for a few decades and appears to be widespread and frequently intense [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26].
Studies of IR populations of
Cx. quinquefasciatus have implicated both target site resistance mutations and enzymatic resistance, the two primary IR mechanisms in mosquitoes, as responsible for the observed IR phenotype (reviewed in [
27]). Studies have identified SNPs that result in resistance across various insect orders by altering the binding of pesticides to the voltage gated sodium channel or acetylcholinesterase, the molecular targets of pyrethroids and organophosphates respectively [
27,
28,
29]. In
Aedes aegypti, the presence of specific knockdown resistance (
kdr) genotypes has been shown to strongly correlate with pyrethroid resistance intensity but this is not clear for
Cx. quinquefasciatus. Two adjacent SNPs in the sodium channel result in changes of the normal leucine at position 1014 (1014L) to either a phenylalanine or rarely a serine (1014F or 1014S) and both SNPs have been found in Florida
Cx. quinquefasciatus [
24,
26,
30,
31]. The 1014F mutation, the canonical
kdr mutation, has been shown in laboratory studies to result in resistance to pyrethroids and DDT. An acetylcholinesterase SNP resulting in a glycine to serine substitution (119G to 119S) has been detected in
Cx. quinquefasciatus populations in the Caribbean and shown to result in resistance to organophosphates [
28,
29].
Enzymatic resistance acts through enhanced degradation of pesticides and/or enhanced transport and excretion. In one Florida population (and 3 others from Alabama) resistance ratios up to nearly 300-fold were described when the known 1014F
kdr mutation was absent [
25]. A Vero Beach, Florida collection made in 1998 was resistant to pyrethroids, organophosphates, fipronil, imidacloprid and spinosad, but not
Bti [
23]. This broad resistance to multiple AIs was attributed to strong enzymatic activity and the relative importance of this mechanism seemed to be greater than the contribution from
kdr mutations [
24,
25]. Studies using a variety of synergists indicated that the resistance phenotype had a large enzymatic contribution [
18,
26,
32,
33]. Our recent study of IR in Miami-Dade
Cx. quinquefasciatus demonstrated only moderate correlation between phenotypic resistance and
kdr genotypes, implicating enzymatic resistance as a large factor [
31].
In this study, we sought to examine on a statewide scale whether
kdr frequency is a useful predictor of resistance intensity in
Cx. quinquefasciatus, as specific
kdr genotypes are in
Ae. aegypti [
34,
35,
36]. We examined phenotypic insecticide resistance by CDC bottle bioassay and
kdr frequency in 89
Cx. quinquefasciatus populations from the state of Florida, including 17 assessed recently in Miami-Dade County, to test for any correlation [
31]. We also conducted direct topical application on select populations from the Gulf Coast of Florida to quantify the level of resistance to permethrin observed in the bottle bioassay.
2. Materials and Methods
Mosquito collections. Egg rafts were collected from 89 locations across Florida by local vector control personnel and research staff then shipped to the Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory or the Center for Medical, Agricultural, and Veterinary Entomology (CMAVE). Specific collection information is in
Table S1. Rearing procedures and morphological identification followed the same methods as in [
31]. The CMAVE laboratory susceptible
Cx. quinquefasciatus strain was reared using a standard protocol previously described [
37].
Phenotypic resistance testing. Insecticide resistance testing was conducted using the standard CDC bottle bioassay using AI-specific diagnostic doses (DD) and diagnostic times (DT). This method as implemented in our laboratories has been described previously [
31,
38]. Briefly, four bottles were coated with technical grade permethrin at 43 µg/bottle, deltamethrin at 0.75 µg/bottle or malathion at 400 µg/bottle along with acetone only negative control bottles. Mosquitoes were aspirated into bottles and knockdown was scored at 0, 5, 10, and 15 min then every 15 min through 2 hr as specified by the protocol. A subset of bottles (permethrin testing conducted at Florida Medical Entomology Laboratory) was monitored with a final count at 24 hours to assess recovery [
26]. If sufficient mosquitoes were available, all three AIs were tested. Knockdown was converted to percent mortality per the CDC protocol. Data is found in
supplementary files S1 and S2
Topical application. Topical application of permethrin and malathion was conducted as previously described [
34,
36,
39]. Five to 10 days old post-emergence mosquitos from each strain were anesthetized with CO
2, sorted on ice, and then weighed to allow an average mass per female. Females were sorted into cohorts of 10-20 and then dosed with 0.5 µl of gravimetrically prepared permethrin doses using a PB600 repeater pipette with a 25 µl gas tight, blunt tip syringe (Hamilton Company, Reno, NV). The range of doses varied by strain to produce mortality between 0 and 100%. Control mosquitoes were treated with acetone only. Mortality was scored at 24 hr after application. The assay was repeated at least three times on different days. Topical bioassay data and fitting parameters are found in
supplementary file S3. Abbott’s corrected mortality data for each strain was fitted to a 4-parameter logistic regression using PRISM v10 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). Median lethal doses (LD
50), 95% confidence intervals, and fitting parameters for each strain were calculated by the software.
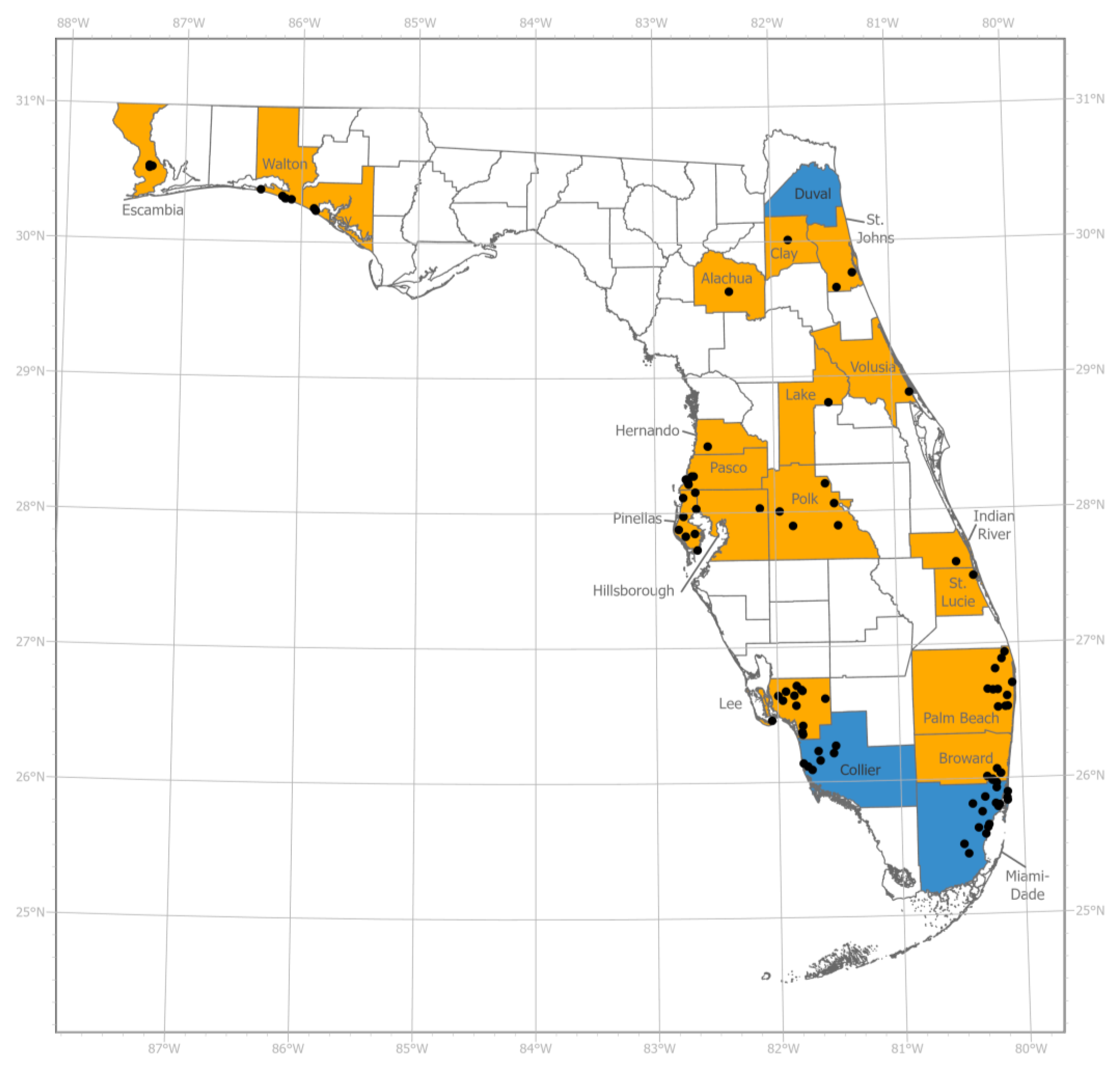
Figure 1.
Map of sampling locations used in this study. Individual sites are marked with solid black circles and counties that provided samples are in orange. Counties highlighted in blue are locations described in previous studies [
24,
26,
31]. Map created in ArcGIS Pro Version 3.1.2 using Florida county boundaries from the Florida Geographic Data Library. Detailed sample location data is in
Table S1.
Figure 1.
Map of sampling locations used in this study. Individual sites are marked with solid black circles and counties that provided samples are in orange. Counties highlighted in blue are locations described in previous studies [
24,
26,
31]. Map created in ArcGIS Pro Version 3.1.2 using Florida county boundaries from the Florida Geographic Data Library. Detailed sample location data is in
Table S1.
Knockdown resistance genotyping. Assessment of the 1014
kdr mutation used a previously described genotyping assay [
31,41]. Individual organisms, averaging 43 per location (range: 24-147) were homogenized in 400 µl of deionized water and used immediately as template for a SYBR Green based competitive PCR with variously GC-tailed primers for 1014L, 1014F, and 1014S and a common reverse primer. Each assay included a deionized water negative control. Genotype controls were homogenate or purified DNA from the CMAVE susceptible strain (1014LL), the LA resistant strain (1014FF), and an LA heterozygote (1014LF) or a surrogate heterozygote created by combining a 1014LL and a 1014FF mosquito [
31,
40]. Assays were assembled in 384-well plates on an epMotion 5750 liquid handling system (Eppendorf, Hamburg Germany) and cycled using default “FAST” conditions on a QuantStudio 6 Flex system (Thermo Fisher, Waltham MA) followed by a 60-95
oC melt curve phase. The presence or absence of the 1014L and 1014F alleles was determined by characteristic melting temperature (Tm) peaks of 86.0±0.4
oC and 82.2±0.4
oC respectively. The rare 1014S allele produces a Tm peak at ~84.5
oC. Heterozygosity at position 1014 was identified by the presence of a peak at both Tms. Calculation of allele frequencies was done using the equations:
Correlation analysis. Percent mortality from the bottle bioassay at each AI specific DT (permethrin: 30 min, deltamethrin: 60 min, malathion: 45 min), mortality at 120 min, genotype percentages, and allele frequencies were used as input for Spearman’s correlation analysis and 95% confidence interval calculation using PRISM v10. Data and correlation information is found in
supplementary files S1 and S4.
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Resistance Testing
3.1.1. CDC bottle bioassay
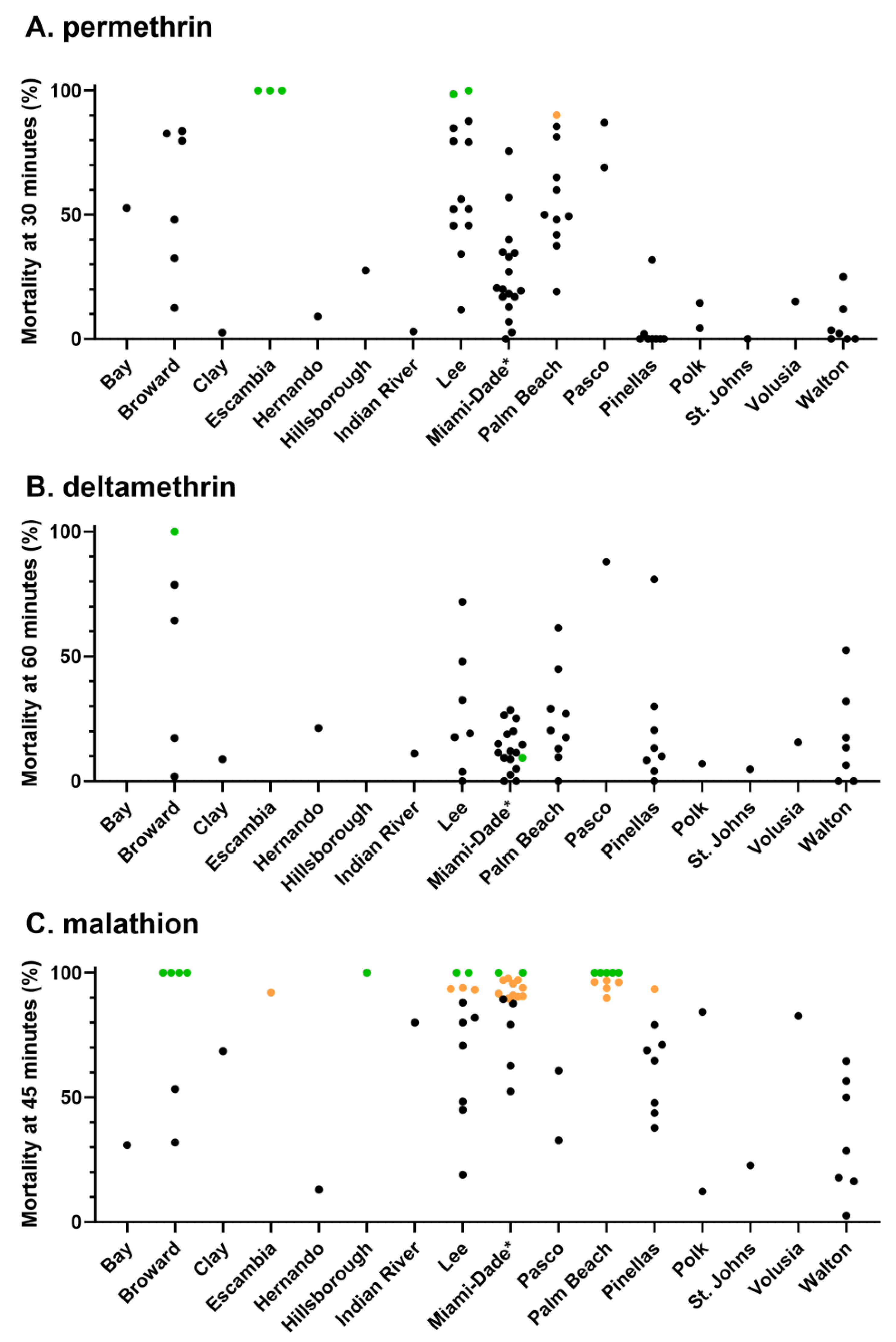
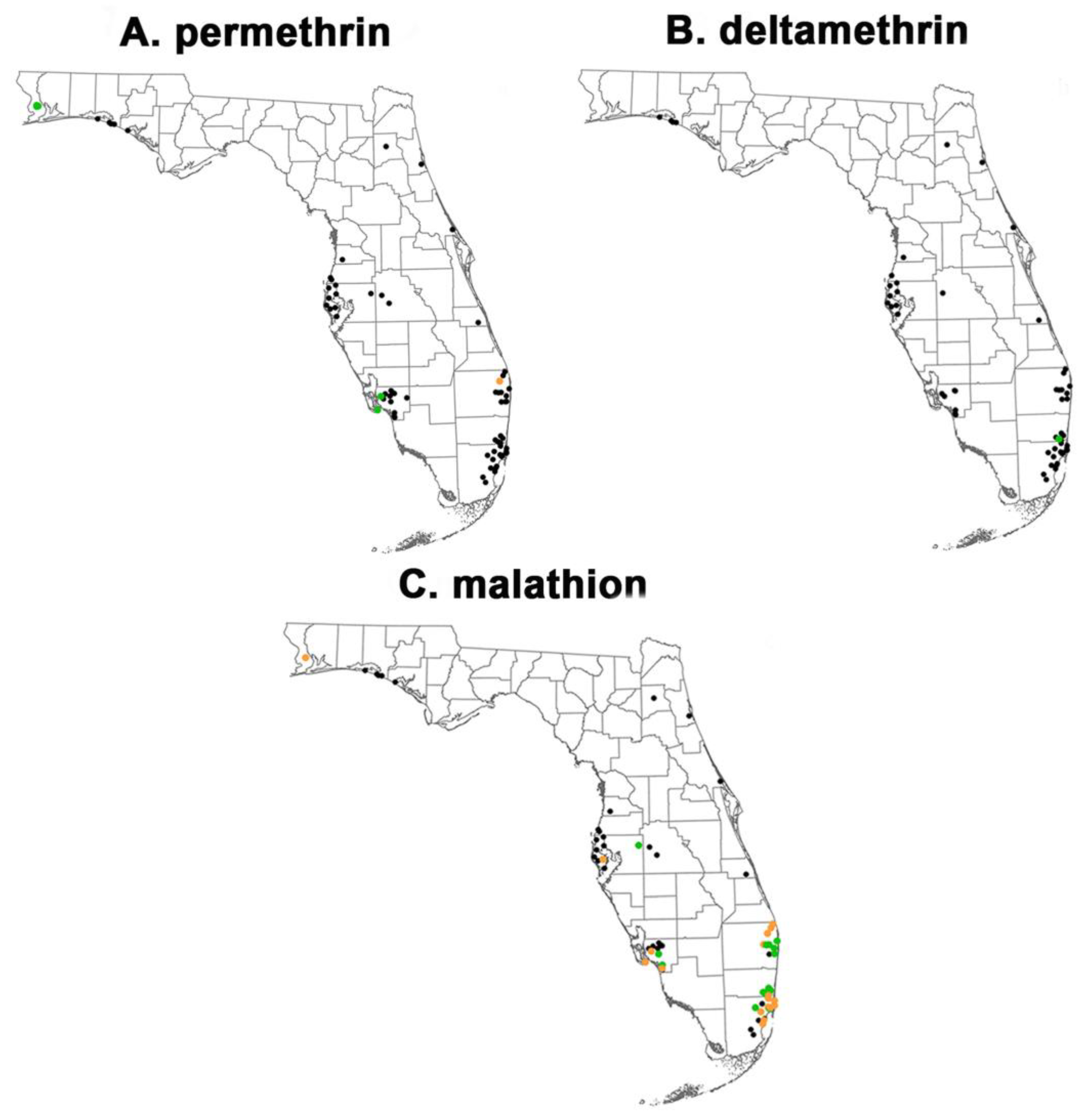
Bottle bioassay testing indicated resistance to all three AIs but the percentage of resistant populations varied. Testing of 75 populations with permethrin at the 43 µg/bottle DD and 30 min DT found 92% were resistant under CDC guidelines (
Figure 2A and
Figure 3A). Only 5 (6.7%) – 3 from Escambia County in the Florida Panhandle and 2 from Lee County in SW Florida – were susceptible. One population, from Palm Beach County, was susceptible but showed developing resistance. In both Lee and Palm Beach Counties, these susceptible populations represented only a fraction of the tested populations from these counties (2 of 13 and 1 of 11, respectively). We also noted varied recovery (less knockdown/mortality at 24 hours versus knockdown/mortality at 2 hrs) in populations with extended exposure to permethrin. This recovery averaged 21% across 27 populations (
File S2).
Testing with the type II pyrethroid deltamethrin showed similar results (
Figure 2B,
Figure 3B). Only one population, from Richmond Heights in Miami-Dade County, was susceptible at the DD and DT, while 57 populations were resistant. Notably, only 7 of the 58 tested had mortality above 50% at the diagnostic time. Even at 120 min, mortality was 50% or more in only 29% (17 of 58) of the populations.
Testing of 55 populations with the organophosphate malathion at 400 µg/bottle DD and 45 min DT showed a range of susceptibilities (
Figure 2C). Approximately 21.8% of populations were susceptible, 18.2% were categorized as developing resistance and 60% were resistant. Four of the five counties with malathion susceptible populations (Broward, Palm Beach, Miami-Dade, & Lee) were along the south Florida coast (
Figure 3C). Hillsborough County, home to the city of Tampa, also had a malathion susceptible population.
3.1.2. Topical application
To confirm and quantify the resistance to permethrin that we observed in the bottle bioassay, we conducted topical application of permethrin on six field strains from Pasco and Pinellas Counties that were provided in adequate quantity. In all six strains, we measured resistance relative to the CMAVE susceptible strain (
Table 1). Resistance ratios, determined by dividing the LD
50 by the LD
50 of the CMAVE strain, ranged from 20.3 in the Pinellas Cross Bayou population to 40.6 in the Pasco County strain. The Keller strain, collected from a wastewater treatment facility had a RR of 34.9. The very resistant Pasco and Keller strains had LD
50s of about 56 and 49 ng permethrin/mg mosquito respectively. Assuming an average weight of 2.2 mg, this is equivalent to a total dose of over 100 ng of permethrin needed to kill the average adult
Cx. quinquefasciatus from these areas.
3.2. Knockdown Resistance Testing
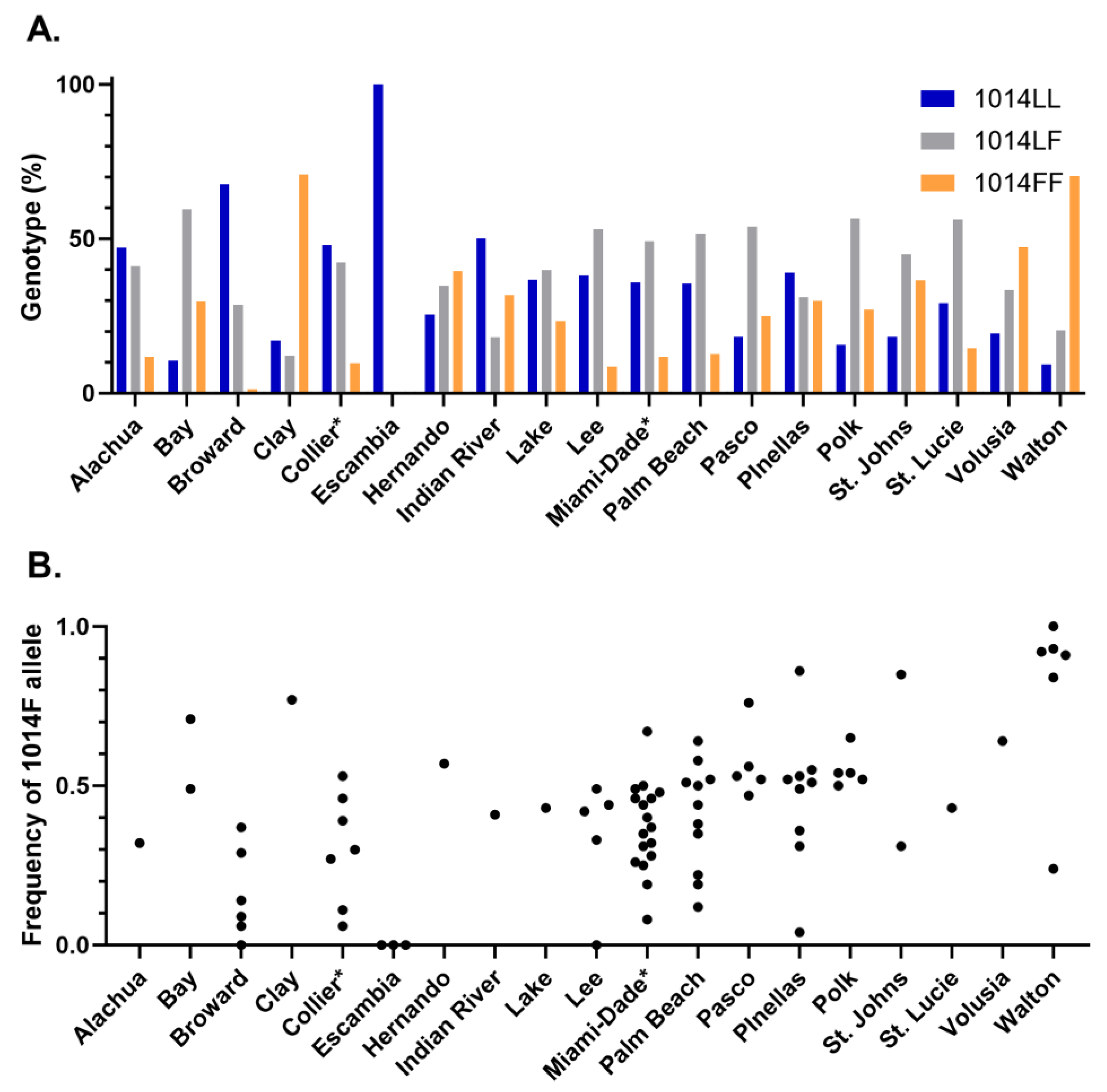
More than 3,300 individual
Cx. quinquefasciatus representing 79 populations from across 18 counties (1-17 populations/county) were genotyped for
kdr mutations at position 1014 using a melt curve assay (
Figure 4A,
File S1). We detected the 1014L and 1014F alleles but not the relatively rare 1014S allele.
Cx. quinquefasciatus averaged 35% 1014LL, 41.9% 1014LF and 23.1% 1014FF. Except for Escambia County, all counties had a mix of the 3 possible genotypes. The relative genotype percentages varied from county to county. In Escambia County, we did not detect either the 1014LF or 1014FF genotypes. At the other extreme, the 1014FF genotype was present at approximately 70% in Walton and Clay Counties.
We did observe individual populations within counties with skewed genotype percentages. Five locations, three in Escambia County and one each in Lee and Broward Counties, had only the 1014LL genotype. At the other extreme, only one location in Walton County was 100% 1014FF. The 1014FF genotype was absent from 18 samples, which were the five locations mentioned above that were 100% 1014LL and 13 locations that were a mix of 1014LL and 1014LF.
Allele frequencies were calculated from this genotyping data for each individual sampling location (
Figure 4B,
File S1). The frequency of the 1014F allele was variable by site but was completely penetrant at only one sampling site in Walton County. The 1014L allele was absent from 5 sites. The statewide 1014F allele frequency was 0.44.
3.3. Correlation between bottle bioassay and kdr genotype or allele frequency
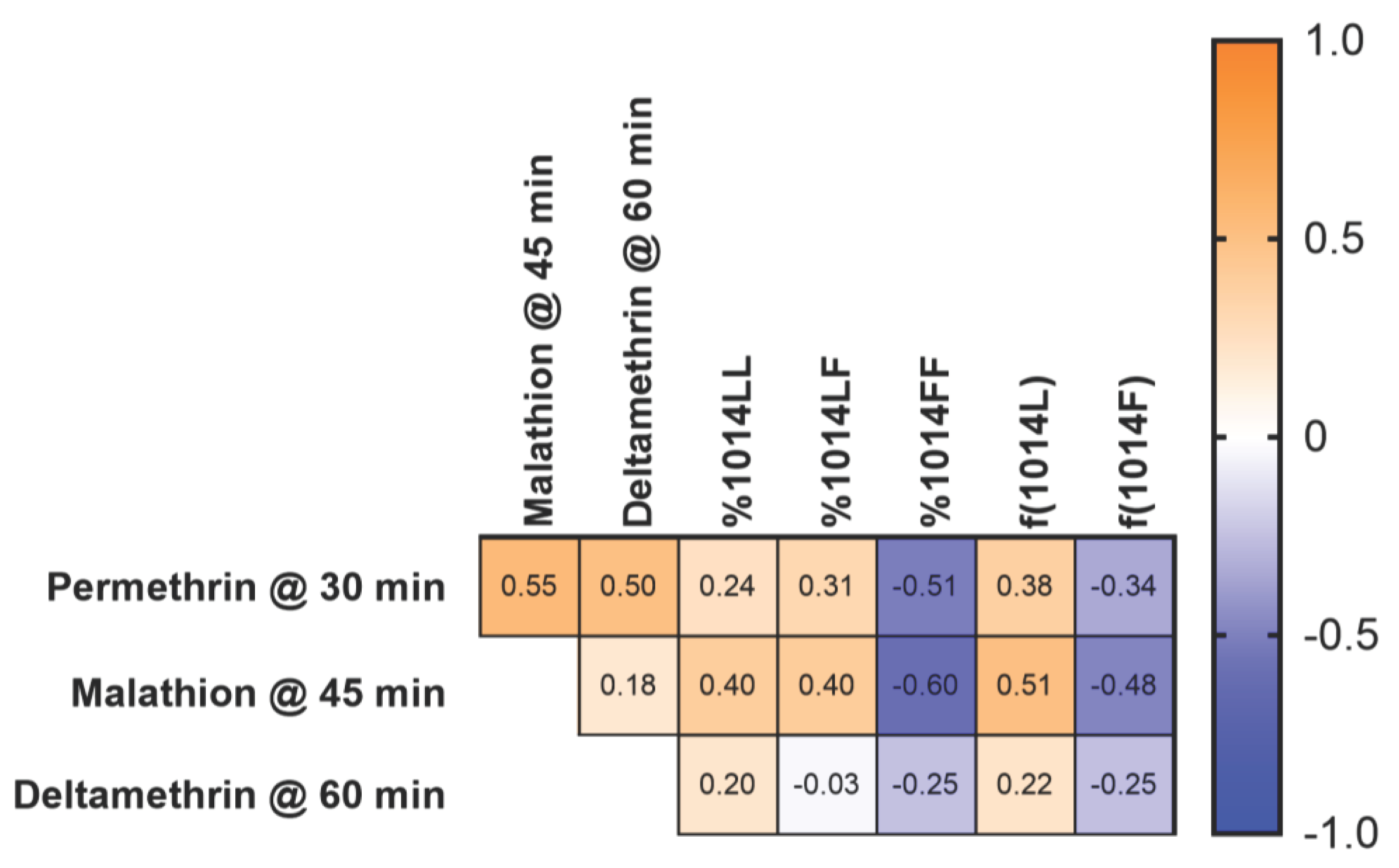
Correlation analysis of the percent mortality at DT, genotype percentages and allele frequencies indicated that there was a moderate negative correlation (-0.51) between permethrin mortality observed in the bottle bioassay and the 1014FF genotype percentage (
Figure 5). The negative correlation between mortality and 1014F allele frequency was weaker (-0.34). We observed a weak negative correlation between deltamethrin induced mortality and the 1014FF genotype or 1014F frequency (-0.25). Correlation coefficients for malathion induced mortality was slightly above that of permethrin with the 1014FF genotype percentage (-0.60) or 1014F allele frequency (-0.48). Notably, because of the matrix comparison, we observed that mortality between permethrin and malathion or deltamethrin were moderately correlated (0.55 & 0.50).
4. Discussion
This study sought to thoroughly examine the correlation between IR detected at the standard CDC specified DDs and DTs for three of the most common AIs in mosquito adulticides (permethrin, deltamethrin and malathion), and the genetic marker of pyrethroid IR in
Culex, the 1014
kdr mutation. The impetus for this study was, in part, driven by recent IR studies in field populations of Florida
Cx. quinquefasciatus which have shown limited phenotypic impact from this
kdr mutation [
26,
31]. Thus, we wanted to conduct a larger study with samples from across the state to see if the same conclusions that were drawn from these studies in SE and SW Florida were consistent across the more than 1,100-kilometer span of Florida. To do this, we collaborated with numerous mosquito control programs to provide egg rafts in sufficient quantity for CDC bottle bioassay testing from nearly 80 locations representing urban, suburban and agricultural areas in Florida. We also conducted permethrin topical application on a few populations to quantify the IR detected by the bottle bioassay. We further conducted testing to determine
kdr genotypes and frequencies in many of these same populations.
Our primary observations from the resistance testing portion of this study are straightforward and agree with previous studies in the SE US. Most populations of
Cx. quinquefasciatus have resistance, often strong resistance, to pyrethroid AIs [
26,
31]. In this study, we found more than 93% of the populations were resistant to permethrin and more than 98% of the populations were resistant to deltamethrin. Quantification of permethrin resistance in a subset of strains by topical application showed that this IR was intense, requiring up to 40 times more to reach the LD
50 than the susceptible CMAVE laboratory strain. We also observed some level of recovery to extended exposure to permethrin as has been observed in a previous FL study [
26]. The operational impact of this ability to recover from exposure is unclear and needs to be thoroughly investigated.
With respect to malathion, our testing showed that IR was much more variable than with the pyrethroids. In this study, nearly a quarter of the populations we tested were susceptible and likely to be well controlled by commercial adulticides containing OPs. About a quarter of the populations were in the CDC “developing resistance” category which may indicate that OP resistance is widely increasing. This certainly calls for additional IR monitoring from these sites to determine if levels of IR are increasing over time.
We note one additional observation from the malathion testing; populations with susceptibility to malathion were found in Miami-Dade, Broward, Lee, Palm Beach, and Pinellas Counties. These are among the most urbanized and densely populated counties in Florida and have large mosquito control programs, yet they have some of the most susceptible populations of
Cx. quinquefasciatus. Our previous study noted that malathion IR was more intense in industrial and agricultural areas than the urban areas of Miami-Dade and this current study appears to support this [
31]. In these locations, operational mosquito control may not be the primary driver of strong OP resistance in
Culex populations, and it is certainly an area for additional study.
Assessment of the 1014
kdr mutation showed, on a statewide scale, the same patterns we had previously observed locally in Miami-Dade
Cx.
quinquefasciatus. First, we did not observe the 1014S mutation in the testing we conducted. It appears to still be rare, as it was even during the initial detection in Jacksonville in 2009, and it is thus unlikely to be an important factor in operational control [
26,
30,
31]. Second, we found the frequency of the 1014F allele was not generally high across the state (0.44) and is more often found as the 1014LF heterozygote (~41%) rather than as the homozygous 1014FF (~23%). This is notably different than in Florida populations of
Ae. aegypti where the 1534C
kdr mutation has reached near fixation [
34]. Selection for this mutation may not be as strong in
Cx. quinquefasciatus if other mechanisms are responsible for a large portion of the IR phenotype.
The negative correlation between permethrin mortality and the 1014FF genotype was the strongest that we observed among the two pyrethroids, but it was moderate and not comparable to the strong/very strong correlation between the dilocus
kdr genotype and permethrin LD
50 or resistance ratio (ρ=0.90) in
Ae. aegypti [
34,41,42]. The correlation between deltamethrin mortality and 1014FF in these
Culex populations was even weaker. Additionally, we also observed that the correlation between the 1014FF genotype and mortality from malathion, an OP with a mode of action different than the pyrethroids, was equally as strong (-0.60) as that of permethrin and that permethrin and malathion mortality were positively correlated. Taken together, this suggests that using the
kdr genotype is not a rigorous predictor of pyrethroid resistance intensity in these Florida
Culex quinquefasciatus. Clearly
kdr plays a role and is beneficial for surviving insecticide pressure but this data set suggests factors other than
kdr play a large role in the observed pyrethroid resistance making the value of using
kdr genotype as a surrogate for strong IR in
Cx. quinquefasciatus potentially dubious and requires further investigation in other locations than Florida.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded from the US Department of Agriculture AgData Commons, DOI: 10.15482/USDA.ADC/25044353. Table S1: Collection and data source information for samples used in this study; File S1: Summary data for phenotypic and genetic testing; File S2: CDC bottle bioassay data; File S3: Median Lethal dose data and fitting results; File S4: Correlation analysis results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte, Stephanie Mundis and Eva Buckner; Data curation, Alden Estep and Eva Buckner; Formal analysis, Alden Estep and Stephanie Mundis; Funding acquisition, Alden Estep and Eva Buckner; Investigation, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte, Stephanie Mundis, Ana Romero-Weaver, Troy Fedirko, Natalie Kendziorski, Kyle Kosinski and Daviela Ramirez; Methodology, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte and Eva Buckner; Resources, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte, Jason Stuck, Isik Unlu, Agne Prasauskas, Stephanie Mundis and Eva Buckner; Supervision, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte, Isik Unlu, Agne Prasauskas and Eva Buckner; Visualization, Alden Estep and Stephanie Mundis; Writing – original draft, Alden Estep; Writing – review & editing, Alden Estep, Neil Sanscrainte, Jason Stuck, Isik Unlu, Agne Prasauskas, Stephanie Mundis, Ana Romero-Weaver, Troy Fedirko, Natalie Kendziorski, Kyle Kosinski, Daviela Ramirez and Eva Buckner. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, grant number NU50CK000420-04-04 to EAB and US Department of Agriculture, National Program 104 (NP-104) to ASE.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study and used in the correlation analysis are available in the manuscript, the
Supplementary files at DOI: 10.15482/USDA.ADC/25044353 and/or previous publications [
26,
31].
Acknowledgments
The Authors acknowledge the assistance of the many Florida Mosquito Control Programs that provided samples for this study. We also acknowledge the assistance of Marah Clark from the Florida Department of Agriculture & Consumer Services for encouraging Florida Mosquito Control Programs to participate in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Farajollahi, A.; Fonseca, D.M.; Kramer, L.D.; Kilpatrick, A.M. “Bird biting” mosquitoes and human disease: a review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect Genetics Evol 2011, 11(7), 1577–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muturi, E.J.; Muriu, S.; Shililu, J.; Mwangangi, J.M.; Jacob, B.G.; Mbogo, C.; Githure, J.; Novak, R.J. Blood-feeding patterns of Culex quinquefasciatus and other culicines and implications for disease transmission in Mwea rice scheme, Kenya. Parasitol Res 2008, 102, 1329–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitatpattana, N.; Apiwathnasorn, C.; Barbazan, P.; Leemingsawat, S.; Yoksan, S.; Gonzalez, J. First isolation of Japanese encephalitis from Culex quinquefasciatus in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2005, 36(4), 875. https://www.tm.mahidol.ac.th/seameo/2005_36_4/10-3604.pdf. [PubMed]
- Molaei, G.; Andreadis, T.G.; Armstrong, P.M.; Bueno, R.; Dennett, J.A.; Real, S.V.; Sargent, C.; Bala, A.; Randle, Y.; Guzman, H.; Da Rosa, A.T. Host feeding pattern of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) and its role in transmission of West Nile virus in Harris County, Texas. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007, 77(1), 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Mosquito Control Association. Available online: https://www.mosquito.org/assets/pdf/hr_november_2021_amca_bmp_ma/ (accessed on 04 February 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/mosquitocontrol/joint-statement-mosquito-control-united-states (accessed on 04 February 2024).
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/69745/WHO_HTM_NTD_VEM_2008.2_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 04 February 2024).
- Gentry, J.W.; Hubert, A.A. Resistance of Culex quinquefasciatus to Chlorinated Hydrocarbons on Okinawa. Mosq News 1957, 17(2). [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Castillo, R. The Appearance of Resistance to Residual Insecticides in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus [fatigans] in the City of Guayaquil. Rev Ecuatoriana Entomol Parasitol 1953, 1(4), 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, M. Physiological resistance to insecticides in Culex pipiens fatigans. Rev Med Peruana 1961, 30(330). [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A. Dieldrin resistance in Culex pipiens fatigans in north eastern Tanganyika. Indian J Malariology 1959, 12(4). [Google Scholar]
- Micks, D.W.; Cox, W.M.; McNeill, J.C. The Status of Insecticide Resistance in some Mosquito Species of Texas. Mosq News 1961, 21(3), 229–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pennell, J.T.; Hoskins, W.M. The monofactorial inheritance of resistance to dieldrin in larval and adult Culex quinquefasciatus Say. Bull Wld Hlth Org 1964, 31(5), 669–77. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.W.A. Meeting the resistance problem: Vector control prospects in the light of present knowledge of insecticide resistance. Bull Wld Hlth Org 1963, 29 (Suppl), 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.W.A. The present status of control of Culex pipiens fatigans. Bull Wld Hlth Org 1967, 37(2), 297–9. [Google Scholar]
- Georghiou, G.P.; Ariaratnam, V.; Pasternak, M.E.; Lin, C.S. Organophosphorus multiresistance in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus in California. J Econ Entomol 1975, 68(4), 461–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priester, T.M.; Georghiou, G.P. Induction of high resistance to permethrin in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus. J Econ Entomol 1978, 71(2), 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priester, T.M.; Georghiou, G.P. Cross-resistance spectrum in pyrethroid-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus. Pesticide Sci. 1980, 11(6), 617–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priester, T.M.; Georghiou, G.P. Penetration of permethrin and knockdown in larvae of pyrethroid-resistant and-susceptible strains of the southern house mosquito. J Econ Entomol 1980, 73(1), 165–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnin, M.; Marboutin, E.; Pasteur, N. Insecticide resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) in West Africa. J Med Entomol 1988, 25(2), 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.M.; Hemingway, J. Preliminary investigation of the mechanisms of DDT and pyrethroid resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus Say (Diptera: Culicidae) from Saudi Arabia. Bull Entomol Res 1989, 79(3), 361–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, J.K.; Knight, J.W.; Munstermann, L.E. Temporal and geographic genetic variation in Culex pipiens quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) from Florida. J Med Entomol 2003, 40(6), 882–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cupp, E.W.; Micher, K.M.; Guo, A.; Liu, N. Insecticide resistance and cross-resistance in Alabama and Florida strains of Culex quinquefaciatus. J Med Entomol 2004, 41(3), 408–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lawrence, G.G.; Vineis, J.H.; McAllister, J.C.; Wirtz, R.A.; Brogdon, W.G.3. Detection of broadly distributed sodium channel alleles characteristic of insect pyrethroid resistance in West Nile virus vector Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in the United States. J Med Entomol 2009, 46(2), 321–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, T.; He, L.; Zhang, L. Permethrin resistance and target site insensitivity in the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus in Alabama. J Med Entomol 2009, 46(6), 1424–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.J.; Bales, R.B.; McCoy, K.; Weldon, C. Oxidase, esterase, and KDR-associated pyrethroid resistance in Culex quinquefasciatus field collections of Collier County, Florida. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 2020, 36(1), 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Yoshimizu, M.H.; Kasai, S. Pyrethroid resistance in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Pest Biochem Physiol 2015, 120, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, M.; Lutfalla, G.; Mogensen, K.; Chandre, F.; Berthomieu, A.; Berticat, C.; Pasteur, N.; Philips, A.; Fort, P.; Raymond, M. Insecticide resistance in mosquito vectors. Nature 2003, 423(6936), 136–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, M.; Malcolm, C.; Chandre, F.; Mogensen, K.; Berthomieu, A.; Marquine, M.; Raymond, M. The unique mutation in ace-1 giving high insecticide resistance is easily detectable in mosquito vectors. Insect Mol Biol 2004, 13(1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, J.C.; Godsey, M.S.; Scott, M.L. Pyrethroid resistance in Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus from Port-au-Prince, Haiti. J Vector Ecol 2012, 37(2), 325–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unlu, I.; Buckner, E.A.; Medina, J.; Vasquez, C.; Cabrera, A.; Estep, A.S. Insecticide resistance of Miami-Dade Culex quinquefasciatus populations and initial field efficacy of a new resistance-breaking formulation. PLOS One 2024, 19(2), e0296046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.L.; Balanay, J.A.G.; Fields, M.; Vandock, K. Baseline insecticide susceptibility screening against six active ingredients for Culex and Aedes (Diptera: Culicidae) mosquitoes in the United States. J Med Entomol 2017, 54(3), 682–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, A.S.; Babcock, E.; Lucas, K.J. Ornamental bromeliads of local botanical gardens serve as production sites for pyrethroid-resistant Culex quinquefasciatus (Say) in Collier County, Florida. J FL Mosq Control Assoc 2020, 68(1), 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, A.S.; Sanscrainte, N.D.; Waits, C.M.; Bernard, S.J.; Lloyd, A.M.; Lucas, K.J.; Buckner, E.A.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Morreale, R.; Conti, L.A.; Becnel, J.J. Quantification of permethrin resistance and kdr alleles in Florida strains of Aedes aegypti (L.) and Aedes albopictus (Skuse). PLOS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12(10), e0006544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, L.K.; Kelly, E.T.; Lee, Y.; Brisco, K.K.; Shen, K.V.; Zahid, A.; van Schoor, T.; Cornel, A.J.; Attardo, G.M. Frequency of sodium channel genotypes and association with pyrethrum knockdown time in populations of Californian Aedes aegypti. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep III, A.; Kissoon, K.; Saldana, M.; Fredregill, C. Persistent variation in insecticide resistance intensity in container breeding Aedes (Diptera: Culicidae) co-collected in Houston, TX. J Med Entomol 2023, 60(4), 725–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridgeon, J.W.; Pereira, R.M.; Becnel, J.J.; Allan, S.A.; Clark, G.G.; Linthicum, K.J. Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti, Culex quinquefasciatus Say, and Anopheles quadrimaculatus Say to 19 pesticides with different modes of action. J Med Entomol 2008, 45(1), 82–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONUS Manual for Evaluating Insecticide Resistance in Mosquitoes Using the CDC Bottle Bioassay Kit. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mosquitoes/pdfs/CONUS-508.pdf (accessed on 05 February 2024).
- Jensen, B.M.; Althoff, R.A.; Rydberg, S.E.; Royster, E.N.; Estep, A.; Huijben, S. Topical application bioassay to quantify insecticide toxicity for mosquitoes and fruit flies. J Vis Exp 2022, (179), e63391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess IV, E.R.; Lopez, K.; Irwin, P.; Jaeger, C.P.; Estep, A.S. Assessing pyrethroid resistance status in the Culex pipiens complex (Diptera: Culicidae) from the northwest suburbs of Chicago, Illinois using Cox regression of bottle bioassays and other detection tools. PLOS ONE 2022, 17(6), e0268205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoglu, H. User's guide to correlation coefficients. Turkish J Emergency Med 2018, 18(3), 91–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.H. Biostatistics 104: correlational analysis. Singapore Med J 2003, 44(12), 614–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).