1. Introduction
Transcription factors play a critical role in the progression of myocardial changes including hypertrophy, fibrosis, genetic cardiomyopathy and neonatal posthypoxic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Recently, many studies have demonstrated the potential to regulate gene expression signaling pathways [
1,
2,
3]. Expression of transcription-activating genes plays a critical role in the myocardium, not only in cardiac hypertrophy but also in intrauterine cardiac differentiation and valve formation. [
4,
5] Consistent with this, our previous studies have shown that children with bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) overexpress of the nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1 (NFATC1) gene, the key transcriptional activator, depending on the degree of left ventricular hypertrophy. [
6,
7]. On the other hand, a number of substances that may be able to inhibit cardiac hypertrophy by this mechanism are currently in various stages of clinical trials. Some are components of gene therapy and are not yet applicable in pediatric practice. It should also be emphasized that the ability of already known and relatively safe pharmaceutical agents to modulate the activity of transcriptional and translational factors in the heart at different levels is not sufficiently exploited in practice. The type and duration of hypertrophic stimuli determine the transition from adaptive or physiological hypertrophy to pathological changes in the heart [
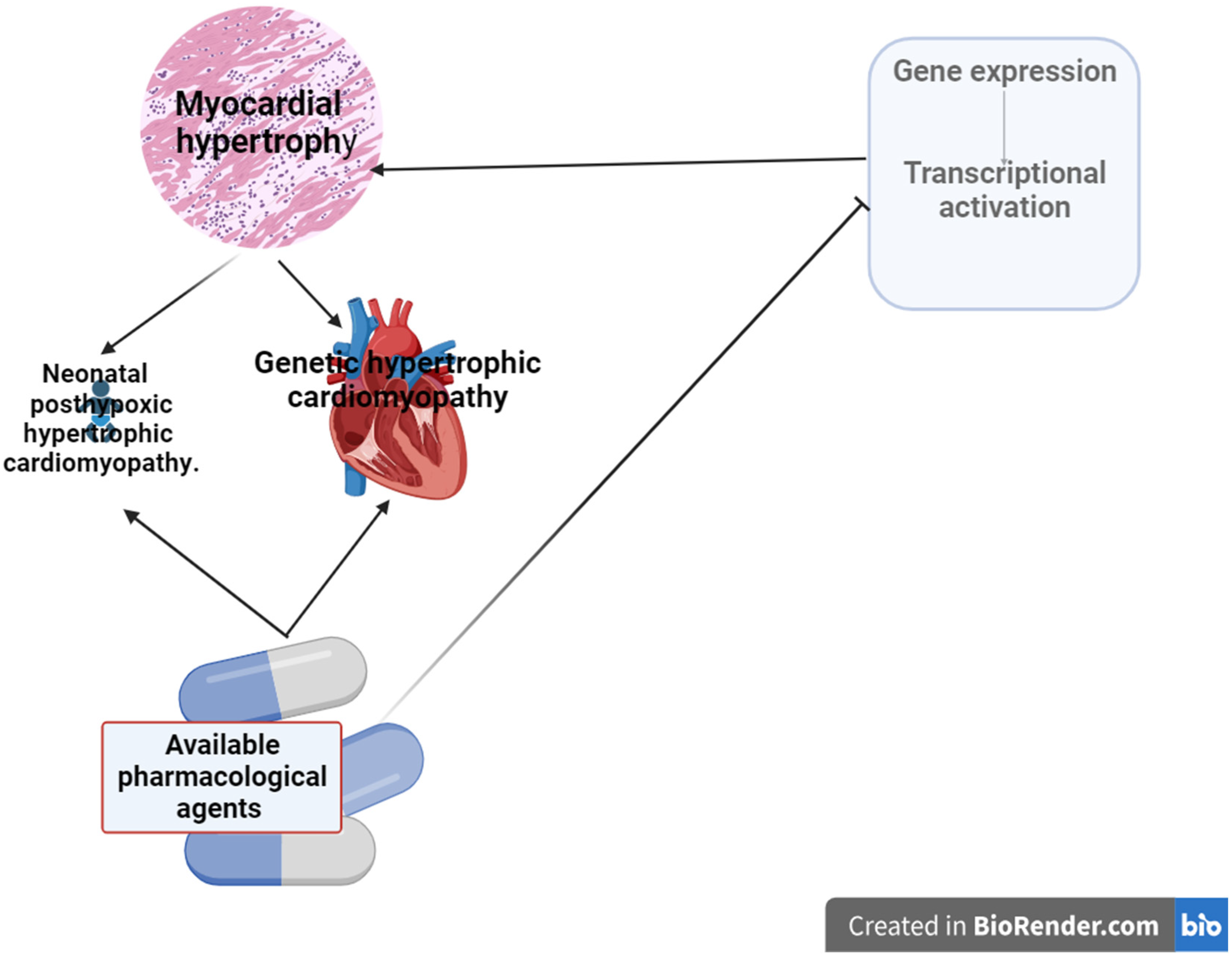
8]. This is of particular importance in children with a high adaptive potential and with a predominantly progressive and asymptomatic course of the myocardial changes. Therefore, the aim of our study was to analyze the current situation with regard to the possibility of existing drugs that could potentially be used in children to influence the translational and transcriptional pathways involved in cardiac hypertrophy. In order to achieve the goal set out in the study, we analyzed the expression of genes and their signaling pathways in relation to the most common primary hypertrophic heart conditions in children (
Figure 1). We then identified and assessed the applicability of the pharmaceutical agents that can affect gene expression pathways at different levels
2. Regulatory factors of gene expression in myocardial hypertrophy and approaches to pharmacological modulation
Experiments with human heart failure cardiomyocytes and transaortic banding have shown an increase in gene expression in adaptive myocardial hypertrophy and a decrease in gene expression in pathological hypertrophy. Overexpressed cardiac stress genes such as NPPB (natriuretic peptide) and MYH7 (beta myosin heavy chain) were identified. At the same time, downregulation of almost all mitochondrial genes in maladaptive cardiomyocytes reflects reduced transcriptional activity. However, RASL11B, a small GTPase protein with apoptotic activity in cancer cells, was found to be over-expressed in cardiomyocytes and to play a special role in increasing the activity of glycolytic enzyme genes such as PFKP (platelet isoform of phosphofructokinase) in failing cardiomyocytes. Authors have proposed inhibition therapeutic activity [
9]. Calcineurin, a Ca2+-dependent serine/threonine protein phosphatase, was found to have main functions in development of myocardial hypertrophy. It causes internalisation of NFATC into the nucleus of cardiomyocytes with consequent transcriptional activation. [
10,
11]. Long non-coding RNA (lnsRNAs) gene (H19) found to suppress pro hypertrophic NFATC sygnaling and to prevent pathological myocardial hypertrophy by restoring lnsRNAs in viral base gene therapy [
12,
13]. Using samples from failing hearts and aortic banding mice, nuclear localised protein 1 was shown to negatively regulate cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing NFATC3 transcription independently of calcineurin activity. [
14]. Theaflavin-3,3′-digallate (TF3), the main constituent of black tea, was found to reduce calcineurin (CaN) levels and increase p-NFATc3 protein expression. This suggests that TF3 inhibits the transmission of the hypertrophy signal, at least in part, through the CaN-NFAT pathway by reducing Ca2+ levels. In cardiomyocytes with pathological hypertrophy TF3 binds to both calmodulin and CaN, leading to downregulation and ultimately inhibition of CaN-NFAT pathway activation. [
15].
The balance between acetylation and deacetylation of histones by the enzymes histone acetylase (HAT) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) leads to post-translational modification of histones and HDAC1 down-regulates the expression of genes that inhibit cardiac hypertrophy. On the contrary, HDAC2, by binding to NFAT or GATA4, activates excessive gene expression that has led to the development of myocardial hypertrophy, while short-chain fatty acids are weak NFATC inhibitors with moderate selectivity for HDAC1, the hydroxamic acid has been shown to have the most zinc-chelating properties compared to other inhibitors and binds specifically to all types of HDACs. Simultaneously, benzamide and cyclic peptides are highly selective for HDAC 1-3 [
16]. It was also shown the HDAC inhibitors with more significantly for valproic acid could increase expression of calcium-activated potassium channel (KCa2.3) and potentiates vasodilatation [
17]. In general, HDAC inhibitors act through Zn2+ binding and exert their protective effects not only in myocardial hypertrophy but also in arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction and atrial fibrillation. [
18].
Overexpression of neurominidase 1 (NEU1) observed in cardiomiocytes, invading monocytes and lead to inflammation, heart hypertrophy and heart failure in ischemia -reperfusion heart injury in mice. The authors proposed specific inhibition of NEU1 as a promising therapeutic strategy. [
19]. The overexpression of neuraminidase 1 in hypertrophic cardiomyocytes and its interaction with the nuclear GATA4 gene promote the development of cardiac hypertrophy in mice. The homology modelling strategy has shown that the C-09 molecule is able to bind neurominidase 1 with subsequent reduction in activity of most cardiac hypertrophic genes, improvement in left ventricular mass, left ventricle posterior wall depth (LVPWd) and cardiac fibrosis. The study confirmed protective effect of the antiviral neurominidase inhibitors zanamivir and oseltamivir on both structural and hemodynamic heart parameters and on the development of cardiac fibrosis. [
20].
Lansoprazole, a proton pump H+/K+ adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) inhibitor, was shown to suppress pathological cardiac remodeling in mice after transverse aortic constriction, by inhibiting the up-regulated Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway without affecting blood pressure and angiotensin II receptors, by inhibiting angiotensin-stimulated cardiomyocytes and fibroblast remodeling independently of gastric proton pump and inhibiting oxidative stress by increasing hem oxygenase expression. [
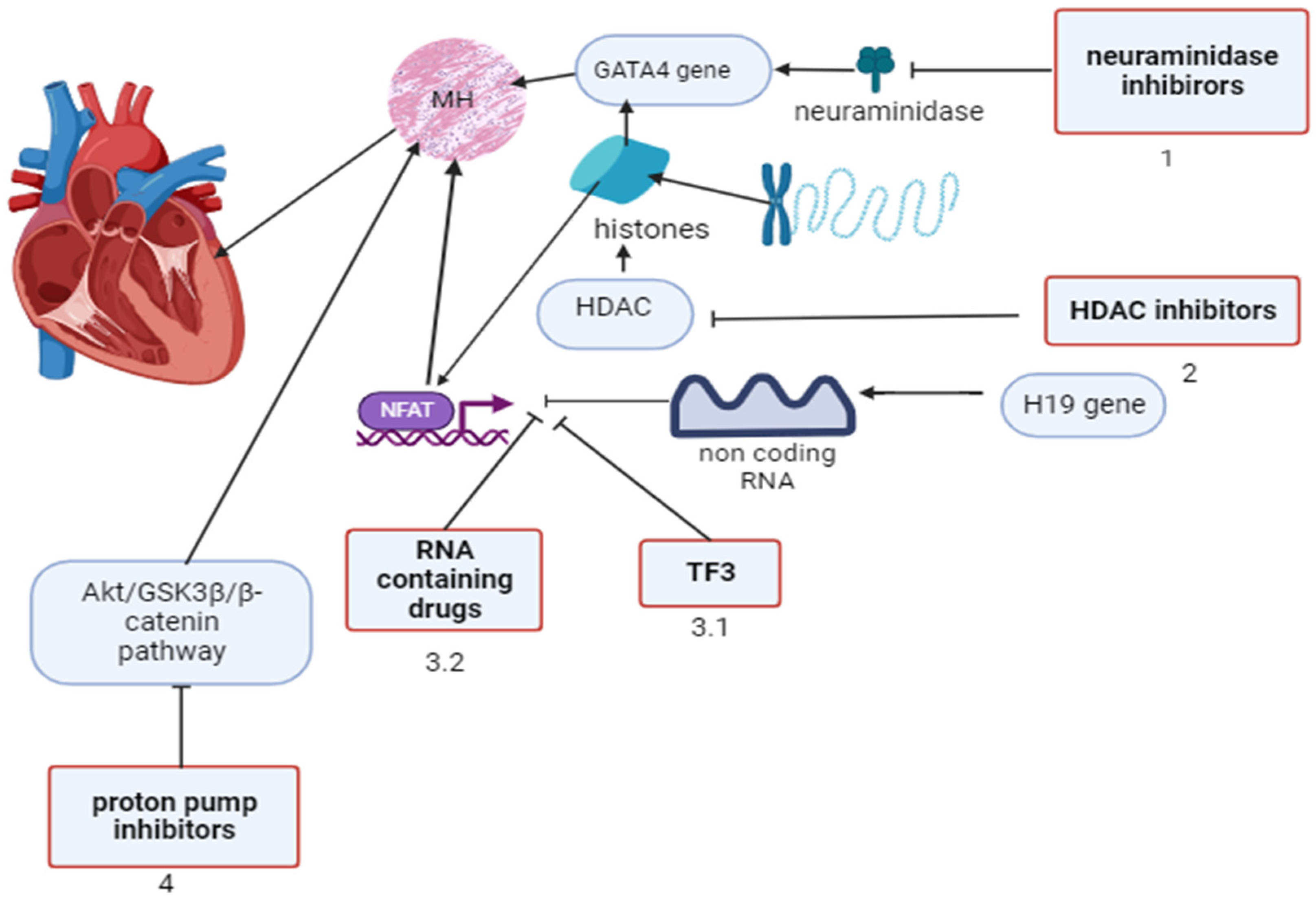
21]. Therefore, the modulation of myocardial hypertrophy on the basis of gene expression pathways for neuraminidase and HDAC inhibitors, RNA preparations, theaflavin and proton pump inhibitors seems to be promising for translation into practice (
Figure 2).
MH- myocardial hypertrophy, NFAT – nuclear factor of activated T-cell pathway, HDAC – histone deacetylase, TF3 - theaflavin-3,3′-digallate. This image was generated using Biorender.
3. Neonatal posthypoxic myocardial hypertrophy, factors of gene expression regulation and pharmacological modulation.
Posthypoxic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy was found in 62.2% of neonates with perinatal hypoxia, and echocardiography was recommended in the first week of life. Myocardial hypertrophy was found on echocardiography in 51% of the newborns, of whom 69% showed intraventricular septal enlargement. These changes are associated with increased troponin T levels. [
22,
23,
24]. It was also shown that left ventricular mass was two times more in the first 3 months after birth in preterm compared to term counterparts and these changes were associated with low gestational age and cardiovascular problems could be seen later in these children [
25].
Fetal hypoxia results in impaired autonomic regulation of the coronary vasculature, impaired energy metabolism (lack of ATP, ADP and creatine phosphate), dysregulation of the Krebs cycle, activation of anaerobic glycolysis and impaired mitochondrial ultrastructure, both in cardiomyocytes and in cells of the conducting system. [
26]. In the mouse model of perinatal hypoxia, transcriptomic and methylomic data showed the state of fetal hypermethylation compared to adult hypomethylation [
27].
Perinatal hypoxia (PH) in the postnatal period was found to significantly alter gene expression in congenital cyanotic heart disease in an experimental rodent model. In the up-regulated state the detected genes are responsible for cell cycle regulation, oxidative phosphorylation (subunit of cytochrome oxidase), glycolysis and anaerobic glycolysis, contractile function, sodium transmembrane influx, transcriptional activation (apoptosis in abnormal cells with reduced adhesion) and general apoptosis. Downregulated genes were those involved in collagen fibril assembly, excitation-contraction coupling, mitochondrial function, potassium transmembrane influx, oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase), SERCA pump (sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase), L-type Ca++ channel, endogenous inotropy, gap junction cell-cell interaction, transcriptional activation (fatty acid storage and glucose metabolism), contractile force and sarcomere structure. These changes, with no differences in septal and ventricular wall thickness, were associated with reduced contractility and reduced ejection fraction. [
28].
Prenatal hypoxia altered gene expression, activating stress-adaptive pathways (endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway) leading to apoptosis and cardiomyocyte degeneration. [
29]. In rat model of newborn hypoxia it was shown significantly decreasing of cardiomyocytes proliferation with resultant significant reduction in cardiomyocyte number and increasing of hypoxia inducible 1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) transcription factor and pre-proET-1 (endothelin-1) mRNA elevation. Anoxia has no effect on binucleation or size of cardiomyocytes. Administration of ETA-receptor antagonist increases proliferation of cardiomyocytes and myocardial mass and significantly decreases the effects of hypoxia [
30]. If inadequately treated, focal dystrophy leading to focal cardiosclerosis may be the end result of hypoxic heart damage. Our studies showed that in 2-month-old rats subjected to perinatal hypoxia (PH) there is preexitation in cardiac rhythm and a significant dominance of parasympathetic innervation in the regulation of cardiac electrical activity. We cannot exclude that the decrease in HR after PH was caused by sinus blockade, which may also reflect parasympathetic regulation of the heart rather than normal sympathetic control of electrical activity.
Prolongation of ventricular electrical systole, which may be caused by impaired ventricular myocardial conduction, was observed in the development of abnormalities in cardiac bioelectrical activity after PH. Under these conditions, the ventricular electrical repolarizing force increased 5.5-fold, indicating significant problems in restoring the membrane potential of the ventricular cardiomyocytes. We obtained data on the efficacy of metabolitotropic cardioprotectors thiotriazolin (thiazotic acid), angiolin, mildronate and arginine in correcting post-PH cardiac bioelectric dysfunction. In normalising the electrical activity of the heart and restoring the neurogenic regulation of the sinus node automaticity function the angiolin (combination of metabolitotropic cardioprotector thiotriozolin and L-lysin) has been shown to be the most effective [
31].
Current evidence suggests that endothelial dysfunction and associated abnormalities in the NO system underlie the development of many cardiovascular diseases. Under the influence of hypoxia, infection and other harmful factors, nitroxidergic system functioning is disturbed, accompanied by development of pathology of organs and systems, including cardiovascular system. The role of the NO system in the development of neonatal cardiovascular pathologies and the potential cardioprotective effects of modulating the NO system is poorly documented in the literature. Suppression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, increase in the expression of its inducible form and activation of nitrosative stress were found to be persistent disturbances of the cardiac nitroxidergic system after PH [
32]. The abnormalities we found are consistent with modern views of myocardial damage mechanisms during ischaemia and hypoxia. [
33]. PH is known to reduce cardiac tolerance to ischaemia/reperfusion, impair endothelial vasodilatation/vasoconstriction mechanisms and contribute to cardiovascular pathology including hypertension, atherosclerotic vascular disease and heart failure [
34].
There is evidence to suggest reduced eNOS expression and activity in cardiomyocytes and endothelium and a risk of endothelial dysfunction following intrauterine hypoxia. Disturbances in eNOS activity could be explained by changes in interactions between eNOS and its regulatory partner proteins such as caveolin-1, calmodulin and Hsp90. Alterations in phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of key eNOS serine and threonine residues may also contribute to eNOS dysfunction [
35,
36]. Endothelium-dependent vasodilation was impaired in coronary arteries of male and female offspring subjected to PH at 4 and 9.5 months of age. This was associated with reduced eNOS and impaired SKCa and IKC channel function.[
37].
Low levels of eNOS are associated with impaired NO-dependent regulation of glutathione synthesis and reduced resistance to oxidative stress [
38]. Decreased eNOS may be linked to hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit (HIF-1a) deficiency. This factor activates inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression by phosphorylating a serine residue [
39]. Increased expression of iNOS was found to compensate for the decrease in eNOS after PH [
40]. However, this leads to the formation of cytotoxic NO derivatives in “parasitic” reactions under conditions of reduced thiol antioxidant deficiency. Such reactions may occur under conditions of L-arginine deficiency, antioxidant deficiency, mitochondrial dysfunction and increased iNOS expression. Uncontrolled formation of cytotoxic NO derivatives leads to nitrosylation of the most active sites of protein structures of ion channels, receptors, transmembrane pores, signalling molecules, i.e., development of nitrosative stress. An equally important consequence of myocardial ischaemia is the loss of NO-mediated effects such as suppressing cell proliferation, platelet aggregation and, most importantly, inhibiting monocyte activation by so-called adhesion molecules [
41].
Nitrosative stress also leads to heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) deficiency in the cell by depriving the glutathione linked of the thiol-disulphide system. Cytotoxic forms of NO not only lead to the modification (reversible and irreversible) of macromolecules, including HSP70 itself, but also reduce the expression activity of the genes encoding its synthesis [
42,
43]. Role of NO derivatives in suppressing gene activity and reducing levels of various transcription factors demonstrated [
44]. Apparently, excess forms of nitric oxide, such as peroxynitrite and nitrosonium ion, first nitrolyse the thiol-redox dependent regions of these genes, then oxidise them at increasing concentrations. Cytotoxic forms of NO have a direct toxic effect on the myocardium, activating the processes of interstitial growth and fibrosis, increasing the negative inotropic effect of NO on the myocardium. Peroxynitrite can inhibit the mitochondrial electron transport chain by oxidising thiols and binding to iron in cytochromes, exacerbating myocardial energy metabolism disorders [
45,
46].
NO in target cells can form active derivatives such as nitrosonium (NO+), nitroxyl (NO-) and peroxynitrite (ONOO-). Recent studies have shown that NO, and in particular its transformation products such as peroxynitrite (ONOO-), nitrosonium ion (NO+), nitroxyl (NO-) and diazotrioxide (N2O3), are the main factors in the implementation of nitrosative stress, resulting in direct interaction of NO with metals (haemoglobin, hem iron, myoglobin, iron-containing enzymes, and non-hem iron of iron-sulphur proteins and DNA), and indirect interaction of NO with myoglobin, iron-containing enzymes, copper and zinc of enzyme active centers), NO+ (S-, N-, O-nitrosation) with thiol, phenol, hydroxyl and amino groups of proteins and DNA [
47]. All this suggests and justifies the use of pharmacological agents - modulators of the NO system for the protection of the myocardium after PH [
48]. Therefore, the use of the NO substrate of L-arginine has been the focus of researchers and clinicians for the reduction of the adverse effects of PH [
49].
Our studies have shown a positive effect of arginine on the parameters of the NO system in the heart of 1 and 2 month old rats after PH. Pharmacological agents that combine the properties of positive modulators of NO and its transporters are promising. Thiotriazoline can increase NO bioavailability in excess of reactive oxygen species (ROS) , is an antioxidant, ROS scavenger, and NO increases the activity of glutathione-dependent enzymes and the level of reduced glutathione during myocardial ischemia. ROS also stimulate cellular apoptosis signalling kinase-1. This is a redox-sensitive kinase upstream of c- Jun N terminal nuclear kinase (JNK) and p38 (mitogen activated protein kinases family). Overexpression of apoptosis signal kinase-1 activates nuclear factor NF-kB to stimulate hypertrophy, whereas genetic suppression of apoptosis signal kinase-1 inhibits hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II, norepinephrine and endothelin 1 [
50,
51,
52].
Thiotriazoline prevents the irreversible inactivation of the transcription nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kB) by protecting the sensitive cysteine residues Cys 252, Cys 154 and Cys 61 in its DNA binding domains from the excess of ROS. Thiotriazoline may participate in reducing these groups during reversible inactivation by acting as Redox Factor-1. Thiotriazoline enhances the activation of the expression of redox-sensitive genes, which are essential for the cellular defence against oxidative stress. Thiotriazoline increases eNOS activity and reduces the intensity of nitrosative stress [
53]. The antioxidant mechanism of action of thiotriazolin consists in neutralizing of ROS and cytotoxic products of NO, regulating ROS-dependent transcriptional processes by acting on NF-kB [
54]. Therefore, the metabolitotropic cardioprotectors with endothelin-1 (ET1) inhibitors, by influencing both the ET1-induced vasoconstriction and the nitrosative stress, reduce the main effects of PH on the myocardium (
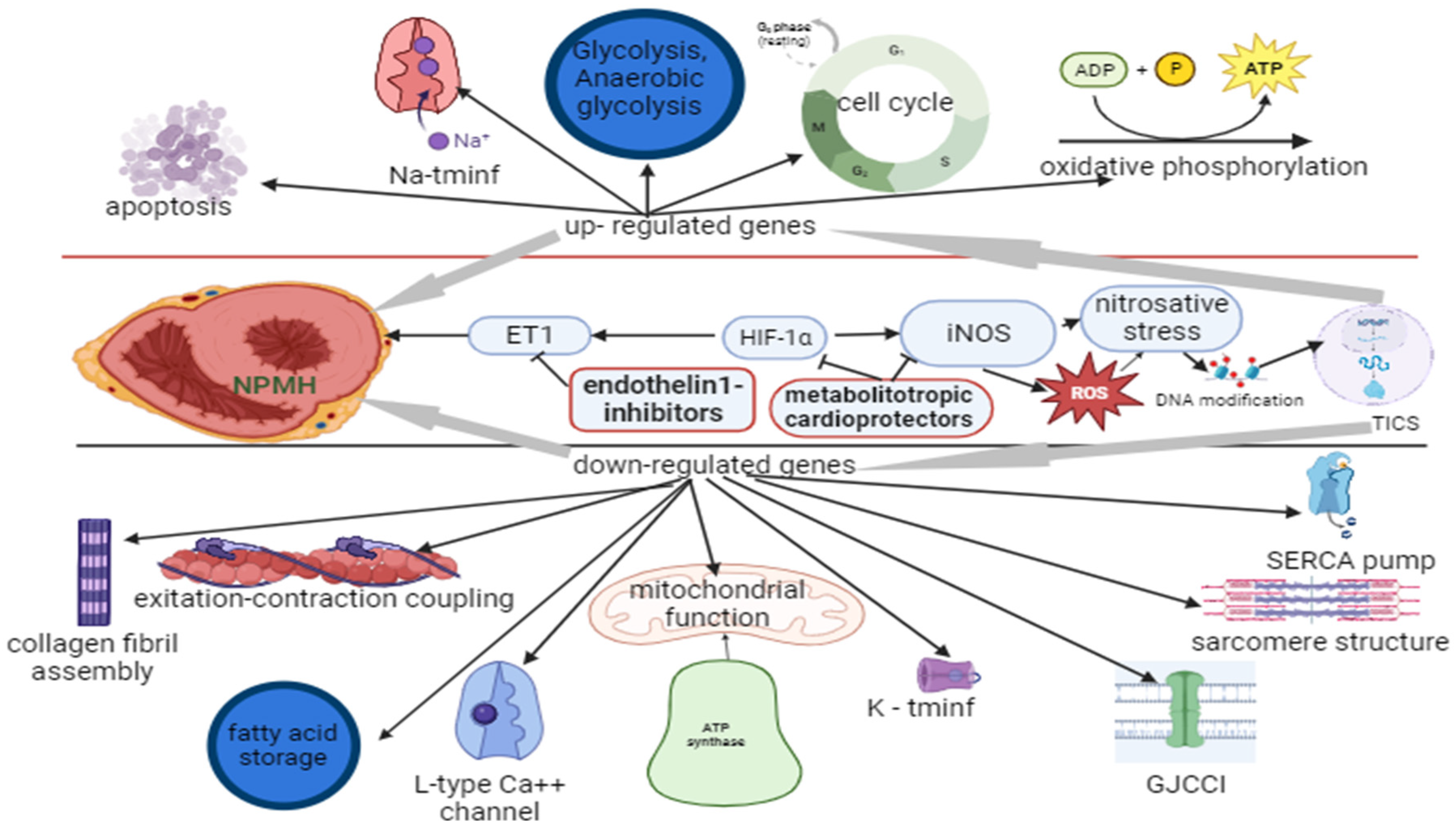
Figure 3). As shown in
Figure 3, the down-regulated gene expression was mainly related to the integrity of the myocardium, whereas the up-regulated genes were related to the energy metabolism.
In NPMH the nitrosative stress affects DNA modification (DNAm) and transcription-induced cell signalling (TICS), altering gene expression. MCs inhibit HIF-1alpha-induced ET-1 vasoconstriction and iNOS, preventing DNAm, endothelin-1 inhibitors - auxiliary inhibit ET-1.
Na-tminf -sodium transmembrane influx channel, K-tminf -potassium transmembrane influx channel, GJCC -gap junction cell-cell interaction, ROS – reactive oxygen species. This image was generated using Biorender.
4. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, transcriptional signaling pathways and options for the treatment.
Current pharmacological or interventional treatments for patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), although often effective in alleviating or preventing symptoms, do not target the underlying genetic defect or the key intermediate pathways involved in producing the phenotype. Therefore, this treatment is ineffective in the prevention or regression of cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. The development and testing of many pharmacological interventions is driven by the understanding of the molecular genetics and pathogenesis of HCM. Preliminary studies in animal models of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy have shown potential benefits of angiotensin II receptor blockers, statins, mineralocorticoid receptor blockers and N-acetylcysteine.
There are 9 chromosomal loci associated with the condition: beta myosin heavy chain, essential and regulatory myosin light chains, troponin T and I subunits, alpha troponin, cardiac myosin binding protein C, cardiac actin and titin. Mutations in sarcomeric genes (e.g., troponin1 gene, MyPBC3 (making cardiac myosin binding protein C), TNNT2 (gene provides instruction for making troponin T), TTN (provides instructions for making very large protein titin), myospryn (calcineurin interacting protein)) have been described in primary non-syndromic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). These genes encode proteins that are involved in the mechanism or control of contraction, so hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is classified as a cardiac sarcomere disease [
55,
56]. More than 107 mutations have been identified. More than half of them are found in the beta-myosin heavy chain (MyPBC3) gene. Some mutations are associated with a favorable prognosis, while others are associated with a high incidence of sudden cardiac death and severe hypertrophy [
57].
Heterozygous frameshift mutations in MyPBC3 result in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Long-term gene therapy of MyPBC3 in homozygous mice is underway. Delivery of MyPBC3 using an adeno-associated virus resulting in prevention of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mice. MyPBC3 gene therapy unexpectedly also suppresses the accumulation of mutant mRNAs. The first successful long-term gene therapy for HCM correcting both haploid insufficiency and noxious peptide production is reported in this study [
58]. Interfering RNAs targeting the mutant allele of MyPBC3 are being studied. Administration of iRNA delays manifestation of cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis [
59].
Another cause of HCM is a group of conditions called RASopathies or non-sarcomeric HCM caused by mutations in the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway, which controls cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis and is present in Noonan syndrome, Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML), Costello syndrome, cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome, neurofibromatosis type 1 and Legius syndrome. [
60]. RAF1 mutations (regulation of the RAS/MAPK signalling pathway) associated with Noonan and NSML as the cause of HCM in 65% of patients [
61]. RAS/MAPK activation leads to myocardial hypertrophy and cardiac fibers disorganization [
62]. Treatment with MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase belonging to the RAS/MAPK) inhibitors (kinase inhibitors) reduces the development of HCM caused by the RIT1 (RAS/MAPK activator) mutation in rats [
63]. A missens mutation of the PTPN11 (protein tyrosine phosphatase non receptor type 11) gene is another RAS/MAPK regulator that produces the SHP-2 (small heterodimer partner, intracellular transcription factor) protein is seen in NSML and is associated with HCM. This mutated gene increases the activity of the mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin)-PI3K (phosphoinositide 3 kinases)-AKT (makes AKT1 kinase protein, regulation cell growth, proliferation and differentiation) signalling pathway, which is important in regulating the cell cycle. Signs of HCM have been found to be reduced by mTOR-PI3K-AKT inhibitors such as rapamycin (immunosuppressive drug) [
64].
An infant patient with rapidly progressive HCM in NSML and evidence of PTPN11 mutation was treated with rapamycin analogue and cardiac improvement was demonstrated after 12 weeks of low dose administration [
65]. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) a drug from the group of thiol antioxidants with properties of ROS and nitric oxide scavenger, increases glutathione level and activity of glutathione-dependent enzymes - glutathione peroxidase and glutathioreductase, reduces iNOS overexpression, regulates IL-1b receptor sensitivity. NAC reduced cardiac fibrosis and associated ventricular hypertrophy in male neonates on the background of maternal obesity, possibly by reducing oxidative stress. NAC restored normal Akt-mTOR signalling in offspring [
66]. Administration of NAC to β-MyHC-Q403 transgenic rabbits and cTnT-Q92 transgenic mice normalised myocardial and blood levels of oxidised glutathione. It reversed cardiac hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis and prevented left ventricular systolic dysfunction [
67].
Mitochondrial disfunction plays an important role in formation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Several proteins are responsible for the integrity of mitochondrial structure and function, most of which are encoded by nuclear DNA (nDNA) and a small proportion by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) [
68]. As the heart muscle is one of the tissues that requires a lot of energy, damage to the heart muscle (i.e., mitochondrial cardiomyopathy) occurs in about 20-40% of children with mitochondrial diseases and can occur as an isolated feature or as part of a multi-organ lesion [
69]. In addition to the classical mitochondrial syndrome, several other mitochondrial disorders have been identified in association with HCM, which can be classified as mitochondrial diseases caused by deficiency of one or more respiratory chain complexes, CoQ10 (coenzyme Q10) deficiency, mitochondrial transporter deficiency, the disorders characterised by 3-methylglutaconium aciduria (e.g., Bart’s syndrome) and disorders of mitochondrial iron metabolism (e.g., Friedreich’s ataxia) [
70]. In mitochondrial cardomyopathies (MCM) the involvement of different molecular pathways take place resulting in formation of hypertrophic, dilated and arrhythmogenic cardomyopathies development.
Mice deficient in the AMT1 gene (adenine nucleotide translocator type 1) show myocardial hypertrophy and proliferation of mitochondria, similar to the MCM seen in humans. Mutations in Med30 (mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 30) negatively affect the transcription of genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation, resulting in progressive cardiomyopathy. Inhibiting mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) damages oxidative phosphorylation and increases ROS, leading to cell cycle inhibition. Mutations in CHCHD10 (coiled-coil helix domain/chain, activate transcription in hypoxia and normoxia) result in oxidative stress, iron dysregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction. In the management of MCM along with standard symptomatic therapy the pharmacological approach considered is resveratrol and epicatechin. These polyphenols are potent antioxidants that activate sirtuin 1-3 genes (deacetylate mitochondrial proteins regulate an ATP production) and eNOS, activate PGC1 alpha (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator, mitochondrial transcription factor), and NRFs (nuclear respiratory factors). Nicotinamide riboside, given as a dietary supplement, was found to activate sirtuin 1 and reduce cardiac hypertrophy in a mouse model [
71].
Metformin has been shown to enhance AKT (A- kinase C-terminal domain, protein kinase B) and activate RISK (reperfusion injury salvage kinases, responsible for cardioprotection in reperfusion) pathways, restore decreased PGC1 alpha levels, increase eNOSser1177 phosphorylation, improve mitochondrial metabolism and cardiovascular injury after ischemia. Metformin supports myocardial energy metabolism by activating AMPK pathway (adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase) and controlling lipid and glucose metabolism in cardiomyocytes, increasing NO bioavailability, limiting interstitial fibrosis and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ischaemia, improves the autophagic function of the ageing heart muscle [
72,
73,
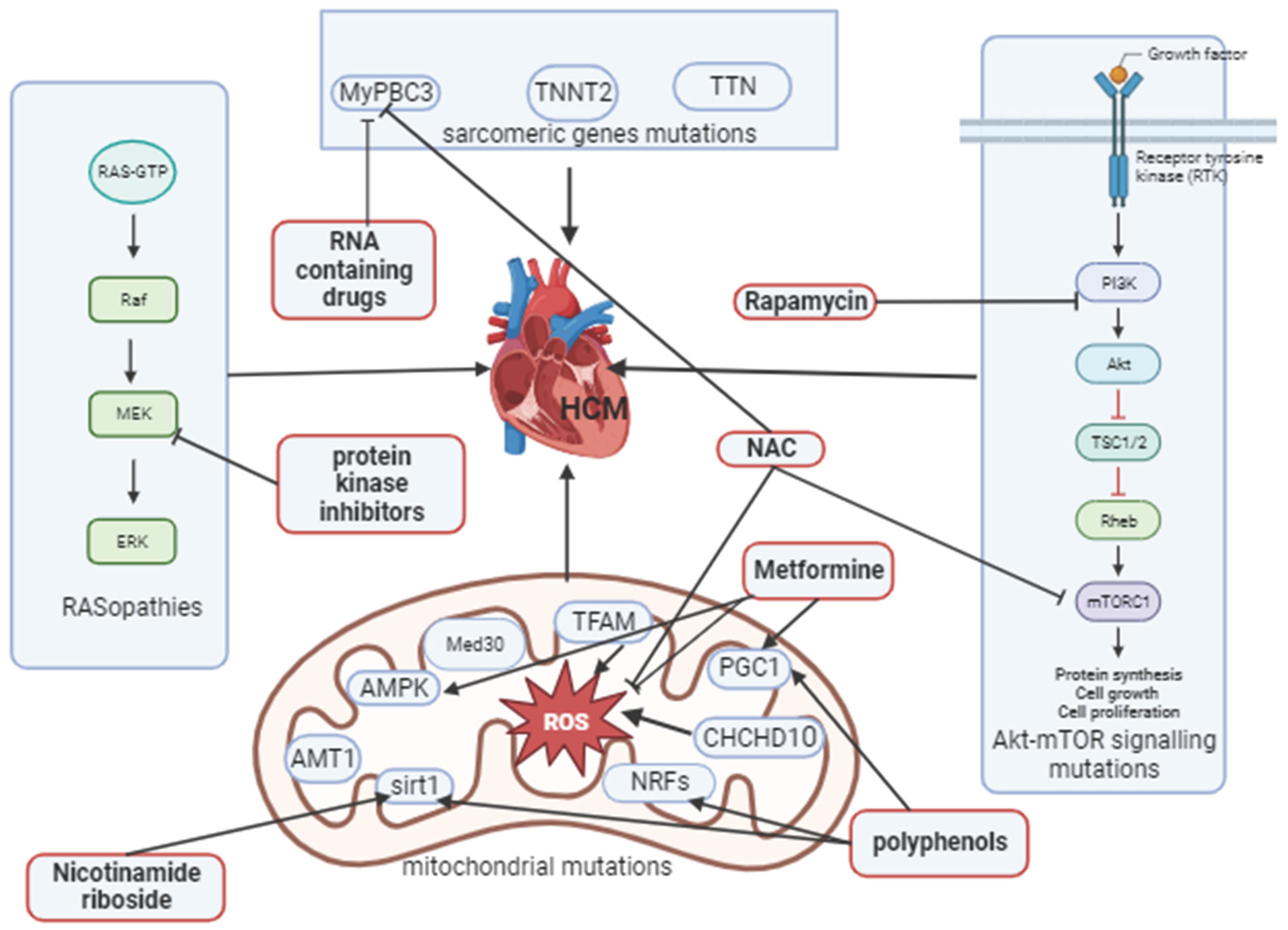
74]. Thus, pharmacological agents could have a differential impact on specific pathogenetic mechanisms involved in the development of HCM (
Figure 4).
N- acetylcysteine (NAC) restoring Akt-mTOR signaling, together with RNA containing drugs inhibits MyPBC3 and oxidative stress. Metformine potentiates AMPK and PGC1 with polyphenols, inhibits oxidative stress, polyphenols also potentiate NRFs and activate sirt1 with nicotinamide riboside, protein kinase inhibitors act on MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase) in RAS/MAPK pathway.
HCM- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, MyPBC3 - beta-myosin heavy chain, TNNT2- troponin T, TTN -titin, NAC- N-acetylcysteine, ROS- reactive oxygen species, TFAM - mitochondrial transcription factor A, Med30- mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 30, AMPK- adenosine monophosphate- activated protein kinase, AMT1- adenine nucleotide translocator type 1, sirt1-sirtuin1, NRFs - nuclear respiratory factors, CHCHD10 -coiled-coil helix domain/chain 2, PGC1 –1 alpha - peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator. This image was generated using Biorender.
5. Conclusions and future perspectives.
The experimental data analyzed, and some clinical data from recent studies reflect the possibilities available for the application of known pharmacological agents that modulate different signaling pathways in some conditions associated with hypertrophic processes in the heart. It should also be noted that these agents, although reasonably available, are not part of standard treatment programs. At the same time, there are insufficient data on the clinical efficacy of these modulators of genes transcriptional pathways activated in myocardial hypertrophy, especially in children. In our review, we outlined both directions on further clinical studies of practical applicability and the options for combining different remedies, taking into account the points of their application in relation to the specific signaling pathways involved in the pathological process.
In our opinion, this approach is most relevant to the slowly developing hypertrophic processes in the myocardium with little or no manifestation, which is most common in childhood. For example, in children with BAV with slowly progressive left ventricular hypertrophy and calcineurin pathway (NFAT) gene activation, noncoding RNAs show significant inhibitory activity. Using RNAi-based drugs is considered one of the most promising areas, including heart diseases [
75]. The same signaling pathway is inhibited by theaflavin, which is naturally derived and could be safely used in addition to RNA drugs in the future. Neuraminidase inhibitors, widely used as antivirals, also inhibit GATA signaling in the heart and could therefore be considered for viral heart damage (e.g., myocarditis), which is quite common in childhood. HDAC inhibitors are synergistic with neurominidase inhibitors for the GATA pathway and with RNAi drugs and theaflavin for the NFATC pathway. However, the most specific of these, such as hydroxamic acid, benzamides and cyclic peptides, may not be promising because of their safety profile and side effects, although short-chain fatty acids, being weak inhibitors, may be applicable in children with myocardial hypertrophy in combination with inhibitors of other specific pathways.
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are of particular interest in this context. In addition to their well-known role as regulators of gastric secretion, PPIs can directly influence myocardiocytes proliferation and remodeling by inhibiting the Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway independently of gastric proton pump. In spite of the predominantly experimental data, PPIs can be regarded as a promising approach, especially in view of the comorbid hyperacidity in pediatric patients.
In NPMH the experimental data indicate that many genes and their activated pathways are involved in the pathological process and that their expression is altered by oxidative stress. The down-regulated genes were mostly related to myocardial structure and integrity, while the up-regulated genes were associated with compensatory activation of energy metabolism, cell cycle and apoptosis. Depending on the intensity and duration of hypoxic exposure, these changes are generally considered as dystrophic. In this respect, there may be a large number of metabolitotropic cardioprotective agents available, including in the neonatal period.
Given the safety profile of these agents the derivatives of thiazotic acid in combination with L-arginine and L-lysine may be considered optimal for use in this category of patients, In addition, although endothelin-1 inhibitors require further study of their clinical efficacy in children, they can be considered a promising direction of therapy in combination with metabolitotropic cardioprotectors, potentiating antihypoxic effect and enhancing cardiomyocyte proliferation. On this basis, these agents may have a regulatory and normalizing effect on gene expression under hypoxic conditions by inhibiting nitrosative stress-induced DNA modification.
In HCM, the clinical evidence for the efficacy of long-term low-dose administration of immunosuppressive drugs (e.g., rapamycin), although used in one pediatric patients, reflects areas for future study regarding reduced immunosuppression and specific inhibition of the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in the heart. In sarcomeric HCM, the RNA-containing drugs may specifically inhibit the mutated MyPBC3 gene, preventing myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. In RASopathies (syndromic HCM), protein kinase inhibitors reduce the MEK activity of RAS/MAPK signaling in the heart. However, these agents belong to the antitumor class with systemic cytostatic effects and have less prospects for use in pediatric HCM. In mitochondrial HCM, mutations in mitochondrial genes with systemic phenotypic involvement and cardiac damage lead to impaired energy metabolism and cause oxidative stress that increases ROS. Metformine has been found to have multiple effects on mitochondrial function, affecting key signaling pathways of AMPK, PGC1 and reducing ROS.
Polyphenols have a synergistic effect on PGC1 and, with nicotinamide riboside, also on sirt1. Overall, these agents potentiate normal mitochondrial signaling and may compensate for altered gene function in mitochodriopathies. NAC has a threefold role in this context, affecting Akt-mTOR signaling, MyPBC3 function in sarcomeric HCM and reducing oxidative stress. Because of its safety and minimal side effects, NAC can be used in combination with RNA drugs and metformin in various forms of HCM. Non-selective drugs (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antiarrhythmics, ACE II receptor antagonists, valsartan, trimetazidine) have been proposed for the treatment of HCM.
Specific drugs known as myosin inhibitors (mavacamten, aficamten) have passed the first stage of clinical trials in adults and are targeting the structure of the sarcomere in acquired HCM [
76]. In this review we have summarized recent breakthroughs in modulating of gene signaling pathways, including mutations involved in some types of genetic heart conditions development, focusing on available and relatively safe pharmacological agents that allows them to be combined for specific hypertrophic myocardial changes in children and to translate these data in future clinical studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K., I.B. in consultation with co-authors; Writing -original draft preparation, A.K., I.B., V.O. and O.K. Writing -Review and Editing, A.K., I.B., V.O. and O.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, L.; Hu, J.; Lei, H.; Qin, H.; Wang, C.; Gui, Y.; Xu, D. Regulatory T Cells in Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2023, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, R.M.; Nikolova, A.P. A Surprising Noncanonical Role for Calcineurin in Pressure-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mognol, G.; Carneiro, F.; Robbs, B.K.; Faget, B.V.; Viola, J.P.B. Cell cycle and apoptosis regulation by NFAT transcription factors: New roles for an old player. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, F.; Gentile, A.; Gauvrit, S.; Didier YRBensimon-Brito SBensimon-Brito, A. NFATC1 Promotes Interstitial Cell Formation During Cardiac Valve Development in Zebrafish. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan MG, Linneweh M, Liebscher S, Van Handel B, Layland SL, Schenke-Layland K. Endocardial-to-mesenchymal transformation and mesenchymal cell colonization at the onset of human cardiac valve development. Development. 2016 Feb 1;143(3):473-82. [CrossRef]
- Kamenshchyk A.V., Kamyshny A.M., Ivanko O.G. Gene expression of nuclear factor of activated T-cells in children with bicuspid aortic valve. Medical perspectives. 2016, V. 21, 3. - p. 29-33. http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Mp_2016_21_3_7.
- Kamenshchyk A, Gonchar M, Oksenych V, Kamyshnyi A. Association of Myocardial Changes and Gene Expression of the NFATC1 and NFATC4—Calcineurin Signaling Pathway in Children with Bicuspid Aortic Valve. Children. 2023; 10(9):1434. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M., Sadoshima, J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018; 15, 387–407. [CrossRef]
- Marta Vigil-Garcia and others, Gene expression profiling of hypertrophic cardiomyocytes identifies new players in pathological remodelling, Cardiovascular Research, 2021; Volume 117, Issue 6, Pages 1532–1545. [CrossRef]
- Malay Chaklader, Beverly A. Rothermel. Calcineurin in the heart: New horizons for an old friend. Cellular Signalling. 2021; Volume 87, 110134. [CrossRef]
- Bazgir, F.; Nau, J.; Nakhaei-Rad, S.; Amin, E.; Wolf, M.J.; Saucerman, J.J.; Lorenz, K.; Ahmadian, M.R. The Microenvironment of the Pathogenesis of Cardiac Hypertrophy. Cells 2023; 12, 1780. [CrossRef]
- Janika Viereck and others, Targeting muscle-enriched long non-coding RNA H19 reverses pathological cardiac hypertrophy, European Heart Journal, 2020; Volume 41, Issue 36, 21, Pages 3462–3474.
- He, J., Luo, Y., Song, J., Tan, T., Zhu, H. Non-coding RNAs and Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy. In: Xiao, J. (eds) Non-coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 2020; vol 1229. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Lei, F., Wang, X. M., Deng, K. Q., Ji, Y. X., Zhang, Y., et al. NULP1 Alleviates Cardiac Hypertrophy by Suppressing NFAT3 Transcriptional Activity. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020; 9 (16), e016419. [CrossRef]
- Zhou H, Xia C, Yang Y, Warusawitharana HK, Liu X, Tu Y. The Prevention Role of Theaflavin-3,3’-digallate in Angiotensin II Induced Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy via CaN-NFAT Signal Pathway. Nutrients. 2022; 14(7):1391. [CrossRef]
- Yu Han, Jiali Nie, Dao Wen Wang, Li Ni. Mechanism of histone deacetylases in cardiac hypertrophy and its therapeutic inhibitors. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine, 2022; Volume 9,. [CrossRef]
- Kolski-Andreaco A, Balut CM, Bertuccio CA, Wilson AS, Rivers WM, Liu X, Gandley RE, Straub AC, Butterworth MB, Binion D, Devor DC. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) increase expression of KCa2.3 (SK3) in primary microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022; 322(3):C338-C353. [CrossRef]
- Chun P. Therapeutic effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on heart disease. Arch Pharm Res. 2020; Dec;43(12):1276-1296. [CrossRef]
- Heimerl M, Sieve I, Ricke-Hoch M, Erschow S, Battmer K, Scherr M, Hilfiker-Kleiner D. Neuraminidase-1 promotes heart failure after ischemia/reperfusion injury by affecting cardiomyocytes and invading monocytes/macrophages. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020; Sep 25;115(6):62. PMID: 32975669; PMCID: PMC7519006. [CrossRef]
- Qian-Qian Chen and others, Neuraminidase 1 is a driver of experimental cardiac hypertrophy, European Heart Journal, 2021; Volume 42, Issue 36, 21, Pages 3770–3782. [CrossRef]
- Hairuo Lin and others, Lansoprazole alleviates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure in mice by blocking the activation of β-catenin, Cardiovascular Research, 2020; Volume 116, Issue 1, Pages 101–113. [CrossRef]
- Dimitiru L, Dimitiru A, Stamatin M. Hypoxic Perinatal Cardiomyopathy-Diagnosis and Evolution Archives of Disease in Childhood. 2012; 97: A331. [CrossRef]
- L. Dimitriu , A.G. Dimitriu, Particular aspects of diagnosis and evolution of hypoxic myocardial injury in newborn infant, European Heart Journal, 2013; Volume 34, Issue suppl_1, P3011. [CrossRef]
- L. Dimitriu , A.G. Dimitriu, Detection of myocardial injury in perinatal asphyxia by echocardiography and cardiac biomarkers. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases Supplements. 2021;Volume 13, Issue 1, 2021, Page 144. [CrossRef]
- Aye, C., Lewandowski, A., Lamata, P. et al. Disproportionate cardiac hypertrophy during early postnatal development in infants born preterm. Pediat Res. 2017; 82, 36–46. [CrossRef]
- Hutter D, Kingdom J, Jaeggi E. Causes and Mechanisms of Intrauterine Hypoxia and Its Impact on the Fetal Cardiovascular System: A Review. Int J Pediatr. 2010; [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., Zhang, L. & Wang, C. Prenatal hypoxia-induced epigenomic and transcriptomic reprogramming in rat fetal and adult offspring hearts. Sci Data. 2019;6,238. [CrossRef]
- Romanowicz J, Guerrelli D, Dhari Z, Mulvany C, Reilly M, Swift L, Vasandani N, Ramadan M, Leatherbury L, Ishibashi N, Posnack NG. Chronic perinatal hypoxia delays cardiac maturation in a mouse model for cyanotic congenital heart disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021; 320(5):H1873-H1886. [CrossRef]
- Lei Huang, Xin Chen, Chiranjib Dasgupta, Wanqiu Chen, Rui Song, Charles Wang, Lubo Zhang, Foetal hypoxia impacts methylome and transcriptome in developmental programming of heart disease, Cardiovascular Research, 2019; Volume 115, Issue 8, 2019, Pages 1306–1319. [CrossRef]
- Paradis AN, Gay MS, Wilson CG, Zhang L Newborn Hypoxia/Anoxia Inhibits Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Decreases Cardiomyocyte Endowment in the Developing Heart: Role of Endothelin-1. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10(2): e0116600. [CrossRef]
- Popazova O, Belenichev I, Abramov A, Bukhtiyarova N, Chereshniuk I, Skoryna D. Indicators of Bioelectrical Activity of the Rat Heart After Prenatal Hypoxia and Pharmacological Correction. Innov Biosyst Bioeng [Internet]. 2023; 6(3-4):148-60. Available from: http://ibb.kpi.ua/article/view/268504. /.
- Ferreiro CR, Chagas AC, Carvalho MH, Dantas AP, Jatene MB, Bento De Souza LC, Lemos Da Luz P. Influence of hypoxia on nitric oxide synthase activity and gene expression in children with congenital heart disease: a novel pathophysiological adaptive mechanism. Circulation. 2001 May 8;103(18):2272-6. [CrossRef]
- Belenichev I,. Abramov A. , Puzyrenko A., et al. Molecular mechanisms of myocardial damage in the hypertensive rats and hypertensive rats with metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis). RRP. 2022; Vol.8 (4):25-33. [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Kane, A.D.; Lusby, C.M.; Allison, B.J.; Chua, Y.Y.; Kaandorp, J.J.; Nevin-Dolan, R.; Ashmore, T.J.; Blackmore, H.L.; Derks, J.B.; et al. Maternal Allopurinol Prevents Cardiac Dysfunction in Adult Male Offspring Programmed by Chronic Hypoxia During Pregnancy. Hypertension. 2018, 72, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson AJ, Zhang L. Hypoxia and fetal heart development. Curr Mol Med. 2010; 10(7):653-66. [CrossRef]
- Hauton, D. Ousley, V. Prenatal hypoxia induces increased cardiac contractility on a background of decreased capillary density. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2009, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hula, N.; Liu, R.; Spaans, F.; Pasha, M.; Quon, A.; Kirschenman, R.; Cooke, C.-L.M.; Davidge, S.T. The Long-Term Effects of Prenatal Hypoxia on Coronary Artery Function of the Male and Female Offspring. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pascali F, Hemann C, Samons K, Chen CA, Zweier JL. Hypoxia and reoxygenation induce endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in endothelial cells through tetrahydrobiopterin depletion and S-glutathionylation. Biochemistry. 2014;53(22):3679-88. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Yao, L., Yang, J., Wang, Z., & Du, G. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Molecular Medicine Reports, 2018;18, 3547-3554. [CrossRef]
- Jung F, Palmer LA, Zhou N, Johns RA. Hypoxic regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase via hypoxia inducible factor-1 in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 2000;86(3):319-25. [CrossRef]
- Belenichev I, Gorbachova S, Pavlov S, Bukhtiyarova N, Puzyrenko A, Brek O. Neurochemical status of nitric oxide in the settings of the norm, ishemic event of central nervous system, and pharmacological intervention. Georgian Med News. 2021; (315):169-176. [PubMed]
- Dattilo, S., Mancuso, C., Koverech, G. et al. Heat shock proteins and hormesis in the diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Immun Ageing, 2015; 12, 20. [CrossRef]
- Belenichev IF, Aliyeva OG, Popazova OO, Bukhtiyarova NV. Involvement of heat shock proteins HSP70 in the mechanisms of endogenous neuroprotection: the prospect of using HSP70 modulators. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1131683. [CrossRef]
- Bogdan C. Nitric oxide and the regulation of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol. 2001; 11(2):66-75. [CrossRef]
- Kröncke KD. Nitrosative stress and transcription. Biol Chem. 2003;384(10-11):1365-77. [CrossRef]
- Bielenichev IF., Vizir VA.,, Mamchur VYo., Kuriat OV. Place of tiotriazoline in the gallery of modern metabolitotropic medicines. February. Zaporozhye Medical Journal. 2019; 21(1),118-128. [CrossRef]
- Anavi S, Tirosh O. iNOS as a metabolic enzyme under stress conditions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;146:16-35. [CrossRef]
- Hsu CN, Tain YL. Impact of Arginine Nutrition and Metabolism during Pregnancy on Offspring Outcomes. Nutrients. 2019; 11(7):1452. [CrossRef]
- Bednov A, Espinoza J, Betancourt A, Vedernikov Y, Belfort M, Yallampalli C. L-arginin prevents hypoxia-induced vasoconstriction in dual-perfused human placental cotyledons. Placenta. 2015;36(11):1254-9. [CrossRef]
- Kwon SH, Pimentel DR, Remondino A, Sawyer DB, Colucci WS. H(2)O(2) regulates cardiac myocyte phenotype via concentration-dependent activation of distinct kinase pathways. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35(6):615-21. [CrossRef]
- Amin JK, Xiao L, Pimental DR, Pagano PJ, Singh K, Sawyer DB, Colucci WS. Reactive oxygen species mediate alpha-adrenergic receptor-stimulated hypertrophy in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33(1):131-9. [CrossRef]
- Hirotani S, Otsu K, Nishida K, Higuchi Y, Morita T, Nakayama H, Yamaguchi O, Mano T, Matsumura Y, Ueno H, Tada M, Hori M. Involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in G-protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circulation. 2002;105(4):509-15. [CrossRef]
- Belenichev IF, Bak1 PG., Popazova OO, Bukhtiyarova N, Yadlovsky OE. Nitric oxide- dependent mechanism of endothelial dysfunction formation is a promising target link for pharmacological management I Biopolymers and Cell. 2022 Vol. 38. N 3. P 145–157.
- Belenichev IF, Nagornaya EA, Gorbacheva SV, Gorchakova NA, Bukhtiyarova NV. Thiol-disulfide system: role in endogenous cyto-and organoprotection, pathways of pharmacological modulation. 2020; Euston Publishing House, Kiev, 232.
- Lipshultz SE, Law YM, Asante-Korang A, Austin ED, Dipchand AI, Everitt MD, et al. Cardiomyopathy in children: classification and diagnosis: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation. 2019;140:e9–68. [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Kumar V, Kim JJ. Sarcomeric Gene Variants and Their Role with Left Ventricular Dysfunction in Background of Coronary Artery Disease. Biomolecules. 2020; 12;10(3):442. [CrossRef]
- Ramírez CD, Padrón R. Cardiomiopatia hipertrófica familiar: genes, mutaciones y modelos animales. Revisión Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: genes, mutations and animal models. A review. Invest Clin. 2004;45(1):69-99. Spanish. PMID: 15058760.
- Mearini G, Stimpel D, Geertz B, Weinberger F, Krämer E, Schlossarek S, Mourot-Filiatre J, Stoehr A, Dutsch A, Wijnker PJ, Braren I, Katus HA, Müller OJ, Voit T, Eschenhagen T, Carrier L. Mybpc3 gene therapy for neonatal cardiomyopathy enables long-term disease prevention in mice. Nat Commun. 2014; 2;5:5515. [CrossRef]
- Jiang J, Wakimoto H, Seidman JG, Seidman CE. Allele - specific silencing of mutant Myh6 transcripts in mice suppresses hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Science. 2013; 342(6154):111-4. [CrossRef]
- Monda E, Rubino M, Lioncino M, Di Fraia F, Pacileo R, Verrillo F, Cirillo A, Caiazza M, Fusco A, Esposito A, Fimiani F, Palmiero G, Pacileo G, Calabrò P, Russo MG, Limongelli G. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Children: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Non-sarcomeric Causes. Front Pediatr. 2021;25;9:632293. [CrossRef]
- Pandit B, Sarkozy A, Pennacchio LA, Carta C, Oishi K, Martinelli S, et al. Gain-of-function RAF1 mutations cause Noonan and LEOPARD syndromes with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet. 2007; 39:1007–12. [CrossRef]
- Calcagni G, Adorisio R, Martinelli S, Grutter G, Baban A, Versacci P, et al. Clinical presentation and natural history of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in rasopathies. Heart Fail Clin. 2018; 14:225–35. [CrossRef]
- Wu X, Simpson J, Hong JH, Kim KH, Thavarajah NK, Backx PH, et al. MEK-ERK pathway modulation ameliorates disease phenotypes in a mouse model of Noonan syndrome associated with the Raf1(L613V) mutation. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:1009–25. [CrossRef]
- Marin TM, Keith K, Davies B, Conner DA, Guha P, Kalaitzidis D, et al. Rapamycin reverses hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a mouse model of LEOPARD syndrome-associated PTPN11 mutation. J Clin Invest. 2011; 121:1026–43. [CrossRef]
- Hahn A, Lauriol J, Thul J, Behnke-Hall K, Logeswaran T, Schänzer A, Böğürcü N, Garvalov BK, Zenker M, Gelb BD, von Gerlach S, Kandolf R, Kontaridis MI, Schranz D. Rapidly progressive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in an infant with Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines: palliative treatment with a rapamycin analog. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167A(4):744-51. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Cao L, Tan Y, Zheng Y, Gui Y. N-acetylcysteine protects neonatal mice from ventricular hypertrophy induced by maternal obesity in a sex-specific manner. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:110989. [CrossRef]
- Zafarullah M, Li WQ, Sylvester J, Ahmad M. Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003; 60(1):6-20. [CrossRef]
- Craven L, Alston CL, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM. Recent Advances in Mitochondrial Disease. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2017; 31;18:257-275. [CrossRef]
- Brunel-Guitton C, Levtova A, Sasarman F. Mitochondrial Diseases and Cardiomyopathies. Can J Cardiol. 2015;31(11):1360-76. [CrossRef]
- Menezes MJ, Riley LG, Christodoulou J. Mitochondrial respiratory chain disorders in childhood: insights into diagnosis and management in the new era of genomic medicine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(4):1368-79. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, S. Duan, F., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Lian, B.; Kou, M., Chiang, Z., Li, Z., Lian, Q. Mitochondrial Cardiomyopathy: Molecular Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Models, and Therapeutic Management. Cells 2022, 11, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, Christin, Bamitale, Kayode D. S., Kazi, Aniessa, Olla, Mehnaaz, Nyane, Ntsoaki A. B., Owira, Peter M. O. Cardioprotective Effects of Metformin. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 2018; 72(2): p.121-127, August. [CrossRef]
- Dziubak A, Wójcicka G, Wojtak A, Bełtowski J. Metabolic Effects of Metformin in the Failing Heart. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; Sep 21;19(10):2869. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Mu N, Gu C, Liu M, Yang Z, Yin Y, Chen M, Wang Y, Han Y, Yu L, Ma H. Metformin mediates cardioprotection against aging-induced ischemic necroptosis. Aging Cell. 2020;19(2):e13096. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, X. et al. RNA-based therapeutics: an overview and prospectus. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13, 644. [CrossRef]
- Palandri C, Santini L, Argirò A, Margara F, Doste R, Bueno-Orovio A, Olivotto I, Coppini R. Pharmacological Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: From Bench to Bedside. Drugs. 2022; Jun;82(8):889-912. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).