1. Introduction
The Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (
S.
aureus) is a major human pathogen that can cause a wide variety of infections, from mild to life-threatening clinical conditions, including bacteremia, endocarditis, chronic osteomyelitis and pneumonia [
1,
2,
3]. Bacteremia refers to the presence of viable bacteria in the bloodstream, frequently arising from localized infections associated with implants or catheters [
4,
5]. Despite the considerable improvements in therapy, the mortality rates of
S.
aureus bacteremia are still high [
6], with more than one in four patients perishing within 3 months [
7]. The treatment of these infections is hampered by the emergence and widespread dissemination of antibiotic-resistant strains, namely methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (MRSA) [
3,
8,
9]. The gold standard for the clinical management of MRSA infections is vancomycin (VCM), a glycopeptide antibiotic that was approved for human use in 1958 [
1,
10,
11]. However, VCM application may be hindered by severe toxicity, low tissue penetration and slow antibacterial effect [
12]. In addition, resistance to VCM has been reported in clinical isolates of
S.
aureus [
8,
13].
Bacteria biofilms constitute another medical concern since the antibiotic penetration is weakened and the immune system action is prevented [
14,
15,
16]. Biofilm-organized
S.
aureus is surrounded by a protective and complex matrix containing proteins, polysaccharides and genomic material. In biofilm form, bacteria attach to host tissues or implanted devices, namely prosthetic joints and catheters, causing persistent infections that are resistant to treatment [
16,
17,
18].
These challenges have prompted the search for novel and more effective therapeutic approaches. On the one hand, this may be accomplished by the discovery of new antibacterial drugs, a time and cost-inefficient process. On the other hand, drug repurposing using nanotechnology has been accomplished mainly through the association of clinically-approved antibiotics to delivery systems, namely liposomes [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. Compared to the process of drug discovery and development, the repurposing of existing antibiotics entails shorter timelines and fewer costs [
19,
20].
Rifamycins are a class of antibiotics discovered in the 1950s and are highlighted for their activity against mycobacterial infections, comprising the clinically approved rifampicin, rifapentine, rifaximin and rifabutin (RFB) [
24,
25]. Among these, RFB has recently received special attention for its potential anti-staphylococcal activity in both planktonic and biofilm bacteria [
20,
24,
25,
26]. Compared to rifampicin, RFB has lower toxicity and longer half-life, as well as weaker induction of CYP450 enzymes that results in reduced drug–drug interactions [
24,
27]. Moreover, RFB displays higher tissue distribution and better intracellular uptake than rifampicin, probably due to its higher lipophilicity [
24]. As aforementioned, the use of lipid-based nanosystems for antibiotic delivery, namely RFB, has proven to be quite advantageous, providing protection from premature degradation and or elimination, promoting accumulation at infected sites, and enhancing the therapeutic effectiveness [
28,
29]. In the literature, several examples demonstrate the advantages of using liposomes as drug delivery systems against planktonic and biofilm
S.
aureus (reviewed in [
30,
31,
32,
33]). Considering the potential of RFB against
S.
aureus infections, here the aim was to develop RFB-loaded liposomes and assess the antibacterial potency against planktonic and biofilm MRSA strains of clinical origin. Furthermore, the in vivo therapeutic effect of developed formulations was confirmed in systemic MRSA infection models.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antibacterial Activity of free RFB and VCM against Planktonic S. aureus
Previous studies in planktonic and biofilm methicillin-sensitive
S.
aureus (MSSA) (ATCC
®25923
TM) demonstrated the superior antibacterial potency of RFB formulations, compared to the gold-standard VCM [
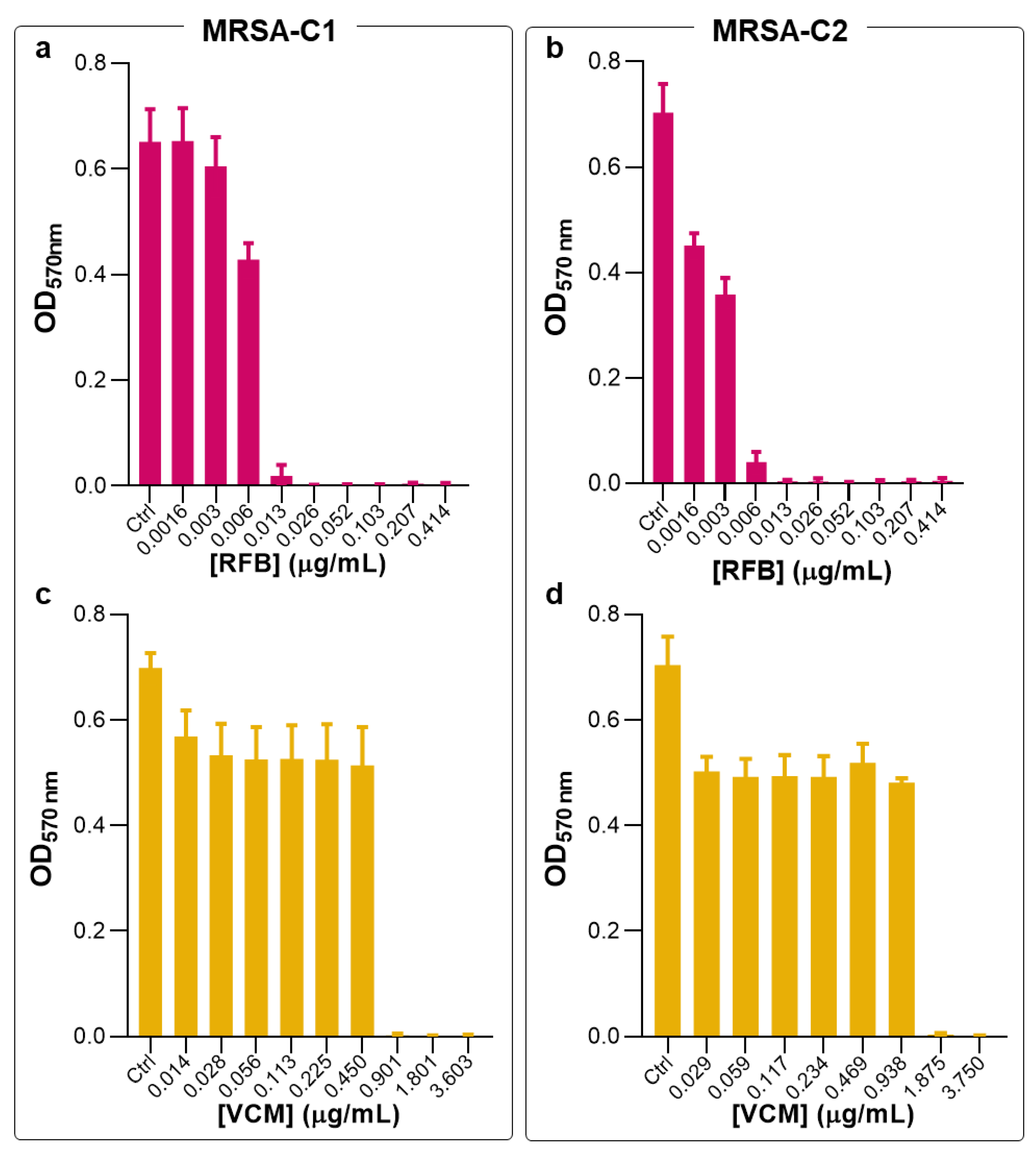
20]. In the present work, the antibacterial activity of RFB formulations was validated against MRSA clinical strains. First, susceptibility tests to RFB and VCM in the free form were performed in planktonic and biofilm clinical isolates, hereafter designated as MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2. In planktonic bacteria, free antibiotics were incubated for 24 h and antibacterial activity was determined through the broth microdilution method. In
Figure 1 are depicted the turbidity readings (OD
570nm), and in
Table 1 are the obtained MIC values.
Previously, these two antibiotics were tested against a MSSA strain, showing MIC values of 0.006 and 1.562 μg/mL for RFB and VCM, respectively [
20]. Here, similar antibacterial effect was obtained for RFB in the free form against MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2, with MIC values of 0.009 and 0.012 μg/mL, respectively (
Figure 1 and
Table 1). Of note, compared to the positive control VCM, RFB was 136- and 156-fold more potent towards MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2, respectively.
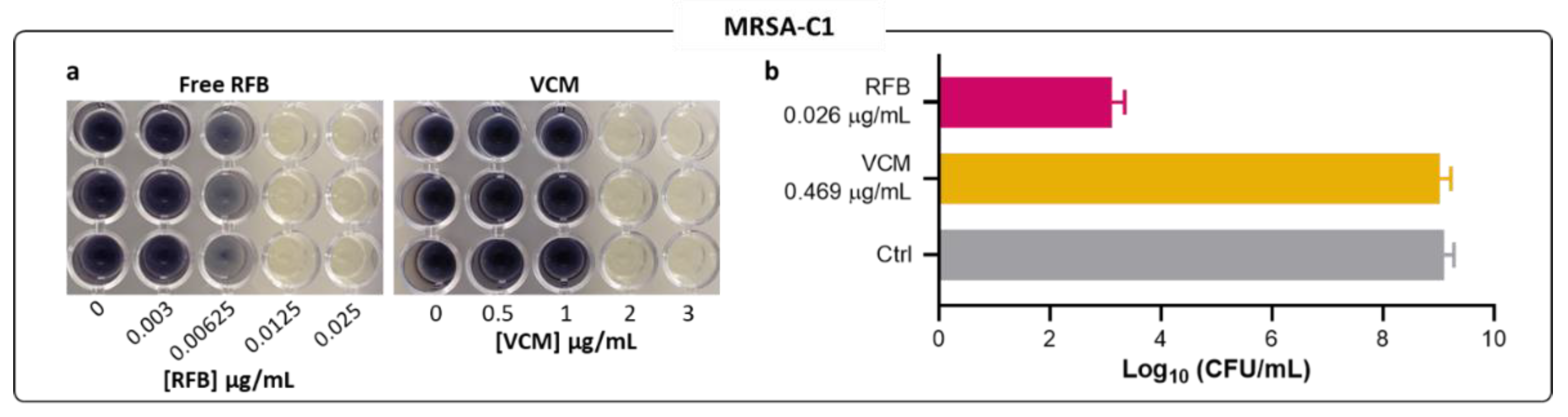
The results obtained by turbidity measurement for MRSA-C1 were confirmed by CFU counts and by the MTT assay (
Figure 2a,b). The visualization of color formation in MTT assay is an established methodology to determine MIC values in different bacteria species, including
S.
aureus [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. The yellow tetrazolium salt is irreversibly reduced to purple formazan crystals by metabolic active microbial cells. Here, the MIC value was defined as the minimum antibiotic concentration corresponding to the absence of color formation, compared to the negative control. MTT assay and CFU counting were also employed for planktonic MRSA-C1 incubated with VCM.
Similar MIC values were obtained among all three methods—turbidity, MTT assay and CFU counts. For RFB and VCM in MRSA-C1, the results obtained through the visualization of formazan coloration (
Figure 2a) were in accordance with those of turbidity measurements (
Table 1), validating this method for MIC determination. The RFB potency towards the clinical strain MRSA-C1 was further confirmed by CFU counts, as depicted in
Figure 2b. At 0.026 μg/mL, RFB induced a 6-log reduction of viable bacteria in relation to Control. In comparison, VCM at a 18-fold higher concentration than RFB, displayed negligible antibacterial activity.
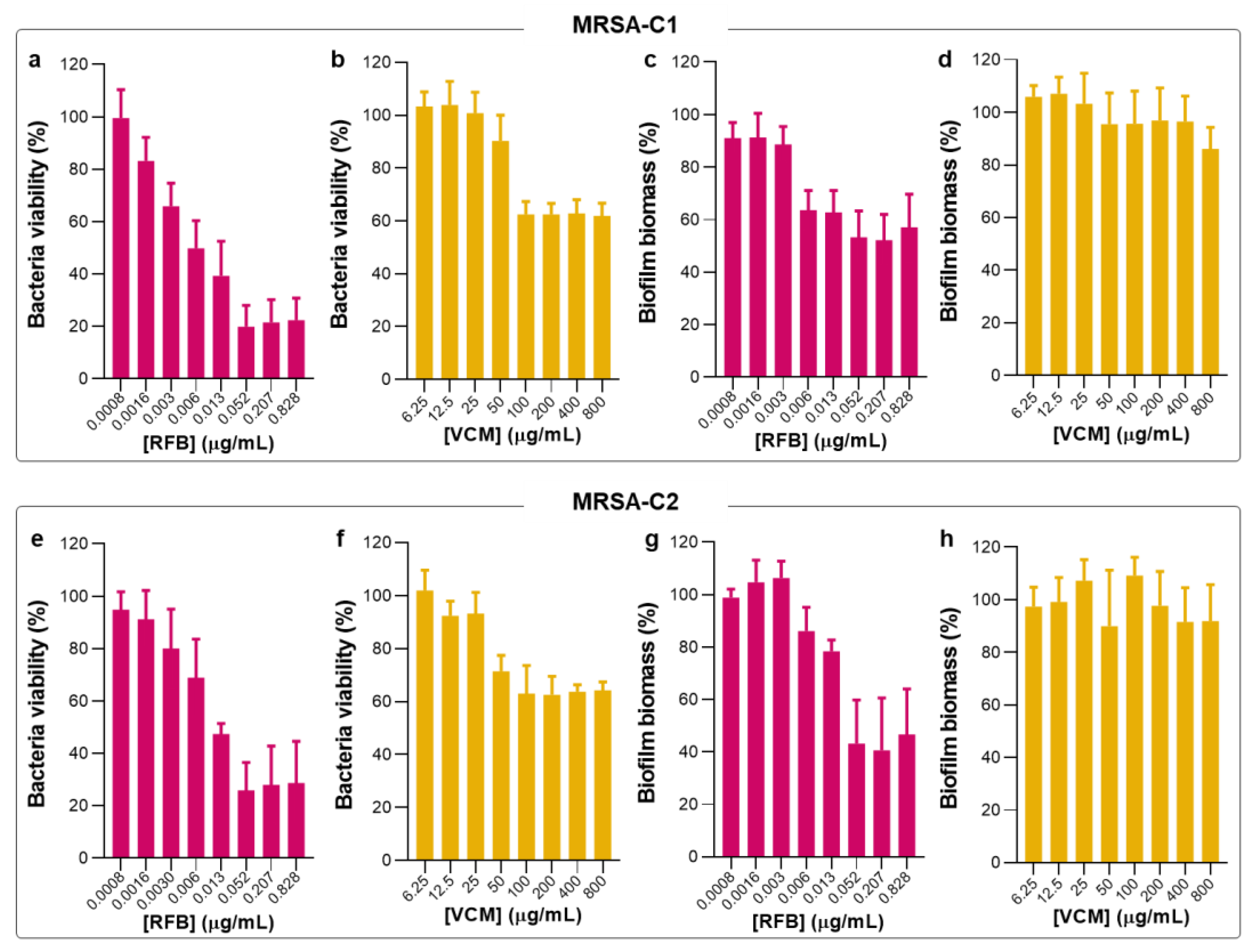
2.2. Antibacterial Activity of Free RFB and VCM against Biofilm S. aureus
Following the studies in planktonic MRSA clinical isolates, the biofilm susceptibility to RFB and VCM in the free form was evaluated by MTT and crystal violet (CV) assays (
Figure 3) that provide information of bacteria viability and biofilm biomass, respectively. These two assays are simple and with high reproducibility. However, it is not possible to establish a direct association between bacteria viability and biofilm biomass since CV is a nonspecific cationic dye that stains the biofilm matrix constituents and both viable and dead bacteria [
40,
41,
42]. In
Table 2 are depicted the values of MBIC
50 for tested antibiotics in the free form against the different
S.
aureus strains.
Biofilm-forming bacteria produces an extracellular matrix rich in polysaccharides, proteins and extracellular DNA that acts as a defense against stress conditions, promoting a faster adaptation to environmental changes and increasing bacterial virulence [
14,
15,
16]. Moreover, this complex barrier hinders the access of immune cells and antibiotics to bacteria residing within the biofilm structure, impairing the treatment effectiveness and increasing the persistence of bacterial infections [
14,
15,
16]. It is well documented that established biofilm infections are, in general, more resistant to antimicrobial agents than free-living bacteria [
20,
43,
44]. Nevertheless, several reports on the antibacterial effect of distinct compounds against MRSA have found MBIC
50 values similar [
45] or even inferior to MIC [
46,
47,
48,
49].
In the present work, RFB was equally effective against planktonic and biofilm MRSA, presenting MBIC
50 values of 0.010 and 0.012 μg/mL for MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2, respectively (
Table 2). Due to this similar antibacterial effect following studies were only performed with MRSA-C1. In turn, the positive control VCM did not exert an antibiofilm effect, even at the maximum tested concentration of 800 μg/mL. This lack of efficacy of VCM against
S.
aureus biofilm is in agreement with previous studies in MSSA (MBIC
50 > 200 μg/mL) [
20]. Also, exposure of MRSA to VCM has been reported to promote biofilm formation as a stress response [
50,
51]. Of note, it has been described that high concentrations of antibacterial drugs may promote bacteria survival and proliferation (reviewed in [
52]). This effect has been observed for different classes of antibiotics (e.g.,: β-lactams, glycopeptides, quinolones and aminoglycosides), in the presence of different microorganisms (e.g.,:
Staphylococcus spp.,
Streptococcus spp.,
Enterococcus spp.,
Mycobacterium spp., and Gram-negative bacteria) (reviewed in [
52]).
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of RFB-Loaded Liposomes
The current lack of specificity of antimicrobial agents and the high doses often required for a significant therapeutic outcome can cause severe toxicity and lead to drug resistance [
53]. This obstacle can be overcome by associating drugs to appropriate drug delivery systems that may promote a preferential targeting to infected sites of loaded antibiotics, decreasing the dose and administration frequency that are necessary to exert therapeutic efficacy. In particular, liposomes are highlighted as effective nanotechnological tools for the delivery of antibacterial agents [
20,
28,
31,
32,
54,
55]. These lipid-based nanosystems ensure the safety and improve the efficacy of loaded compounds, being able to change the pharmacokinetic and biodistribution profile of incorporated antibiotics [
28,
56]. Moreover, liposomes are able to preferentially accumulate at infected sites and can also enhance the interaction within biofilm matrix (reviewed in [
18,
31,
32,
57]). In the present work, RFB was incorporated with four different lipid compositions, and the obtained data are described in
Table 3.
As depicted in
Table 3, all RFB liposomal formulations exhibited high loading capacity (36-43 μg/µmol) and I.E. (43-55%). Previous work with RFB-loaded DMPC:DMPG (8:2) [
20] and DMPC:DMPG (7:3) [
28] showed similar loading capacity (36 and 47 µg/µmol, respectively) and I.E. (51 and 55%, respectively). Bilayer fluidity is an important factor to consider when designing liposomal formulations. These properties need to ensure the stability of associated compounds and appropriate incorporation parameters. In the present work, in addition to the moderately fluid phospholipids DMPC/DMPG (with a phase transition temperature (Tc) = +23 °C), RFB liposomes using DPPC/DPPG phospholipids, that have a Tc = +41 °C were also prepared. Early studies of our research team have demonstrated that the use of DPPC/DPPG lipid mixtures was able to promote high blood residence time of RFB and an effective accumulation at major organs such as liver, spleen and lungs [
28]. Although DMPC/DMPG liposomes may increase the loading capacity and I.E. of RFB, its stability is lower when compared to more rigid bilayers [
20,
28].
An average mean size below 120 nm was recorded for all RFB liposomes, displaying high homogeneity with a PdI<0.1. The inclusion of DSPE-PEG, that confers long blood circulating properties, did not affect the incorporation parameters of liposomes or the mean hydrodynamic size. In terms of surface charge, the presence of this polymer in RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2 resulted in a zeta potential close to neutrality (-5 ± 1 mV), as opposed to the negative charge of RFB-LIP3 (-14 ± 1 mV) and RFB-LIP4 (-15 ± 1 mV). For unloaded liposomes, a low mean size (108-121 nm) and high homogeneity (PdI<0.1) were also recorded. The zeta potential was equivalent to the RFB-loaded liposomes, with a neutral charge for unloaded-LIP1 and unloaded-LIP2, and a negative zeta potential for unloaded-LIP3 and unloaded-LIP4 (
Table 3).
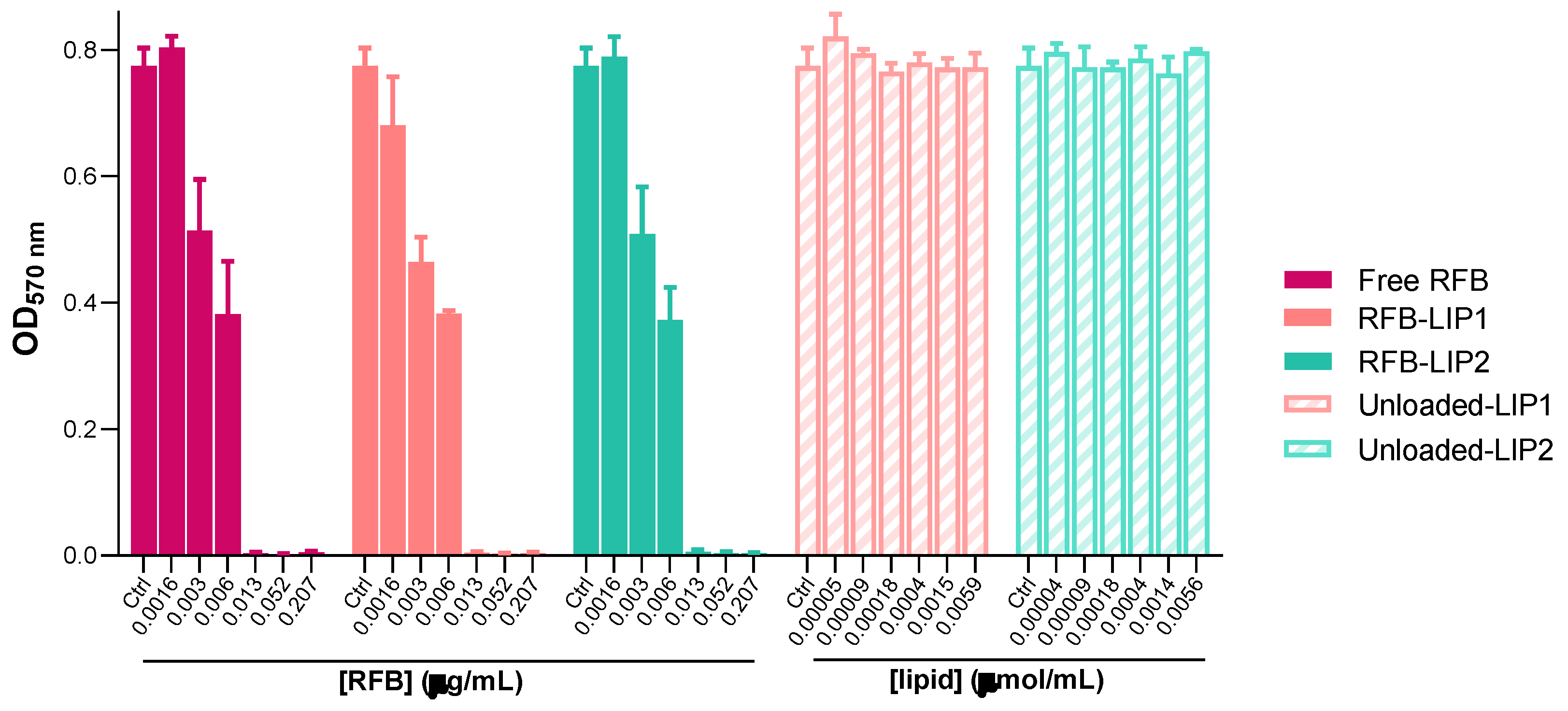
2.4. Susceptibility of Planktonic and Biofilm S. aureus to RFB-Loaded Liposomes
After the successful preparation and characterization of RFB-loaded liposomes, the antibacterial properties of these nanoformulations were assessed against both planktonic and biofilm MRSA-C1 (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5). As the main goal is to develop a therapeutic strategy against systemic
S.
aureus infection, liposomes with prolonged blood circulating times, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2, were selected for these studies. In parallel, unloaded liposomes with the same lipid compositions were also evaluated at the corresponding lipid concentrations.
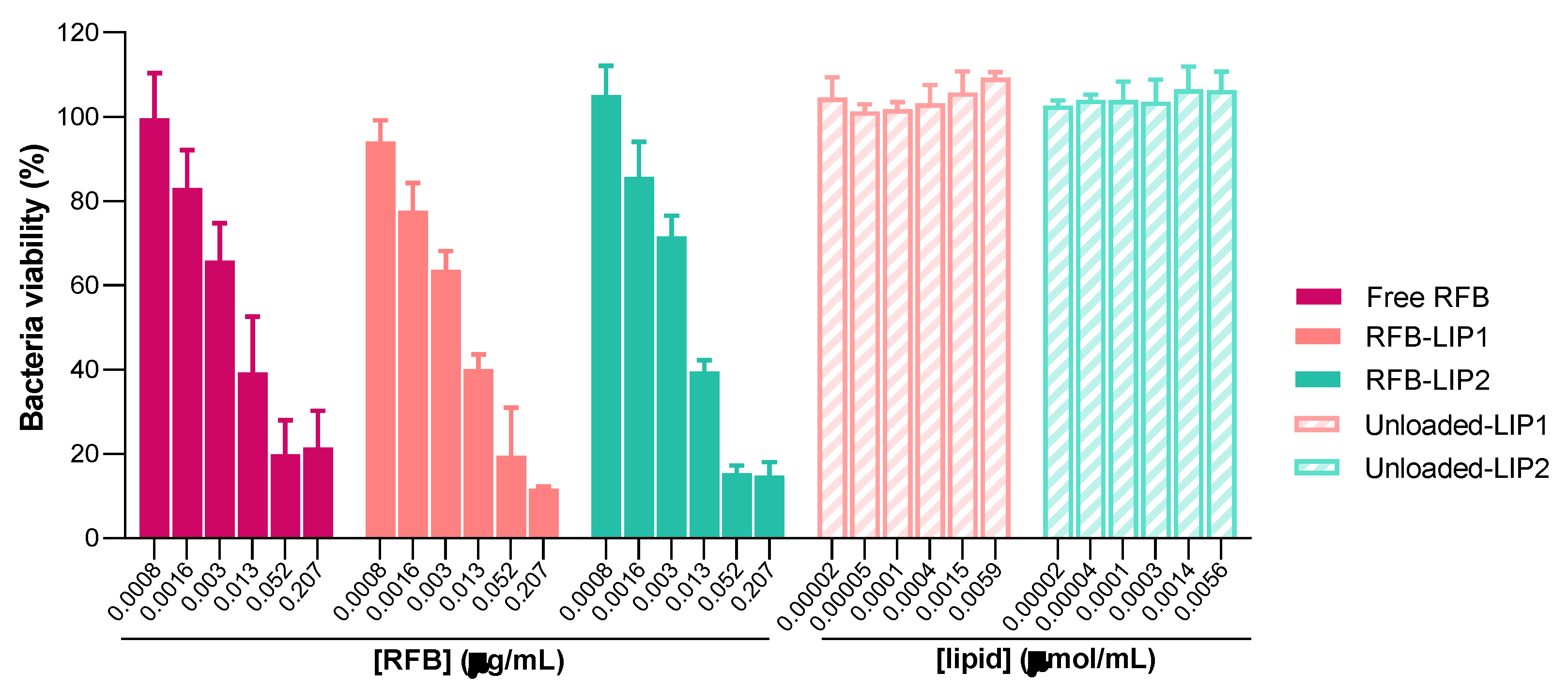
As shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, results demonstrated that both RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2 retained the antibacterial activity of RFB in the free form against planktonic and biofilm bacteria. As detailed in
Table 4, MIC values of 0.009, 0.013 and 0.013 μg/mL were obtained for Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2, respectively. Also, MBIC
50 values of 0.010, 0.008 and 0.008 μg/mL were achieved for Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2, respectively. In turn, unloaded liposomes tested at the corresponding lipid concentrations did not affect bacteria growth. This confirmed that the antibacterial effect was due to RFB action since unloaded liposomes were innocuous.
Several studies conducted in
S.
aureus reinforce the advantages of using antibiotic-loaded liposomes for enhanced antibacterial effect and improved safety, compared to the free drug (reviewed in [
30,
31,
32,
33]). Liposomes depending on their physicochemical properties are able to interact with biofilm-organized bacteria since they can penetrate the matrix and release loaded drugs [
53,
57]. Importantly, the release of associated antibiotics from liposomes is further promoted by MRSA-secreted toxins that, upon insertion into the bilayer is able to create pores and facilitate drug leakage [
58].
The successful antibiofilm activity of liposomes depends on several factors, including the presence of PEG at the liposomal surface [
57]. In a study comparing liposomes with and without PEG, researchers concluded that both formulations improved the antibacterial activity of nafcillin towards planktonic and biofilm MSSA, with PEGylated liposomes exerting a more potent effect (2-fold) compared to non-PEGylated ones [
59]. Moreover, in biofilms of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and
Staphylococcus epidermis, the inclusion of PEG in the lipid composition also increased [
60] or maintained [
61] the antibiofilm effectiveness of liposomes compared to those without the polymer. In the present study, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2, containing DSPE-PEG in the lipid composition, preserved the antibiofilm activity of free RFB (
Table 4).
2.5. Interaction of Unloaded and RFB-Loaded Liposomes with S. aureus Biofilm by Microscopy
As aforementioned, to overcome current challenges in antibiofilm therapy, the association of antibiotics to liposomes constitutes as an advantageous strategy to facilitate drug penetration into
S.
aureus biofilm, increasing the local concentration of antibiotic [
20,
53,
62]. Several reports have proved the importance of liposomes as antibiotic delivery systems, allowing to overcome bacteria resistance to drugs in the free form (reviewed in [
31,
32,
57]).
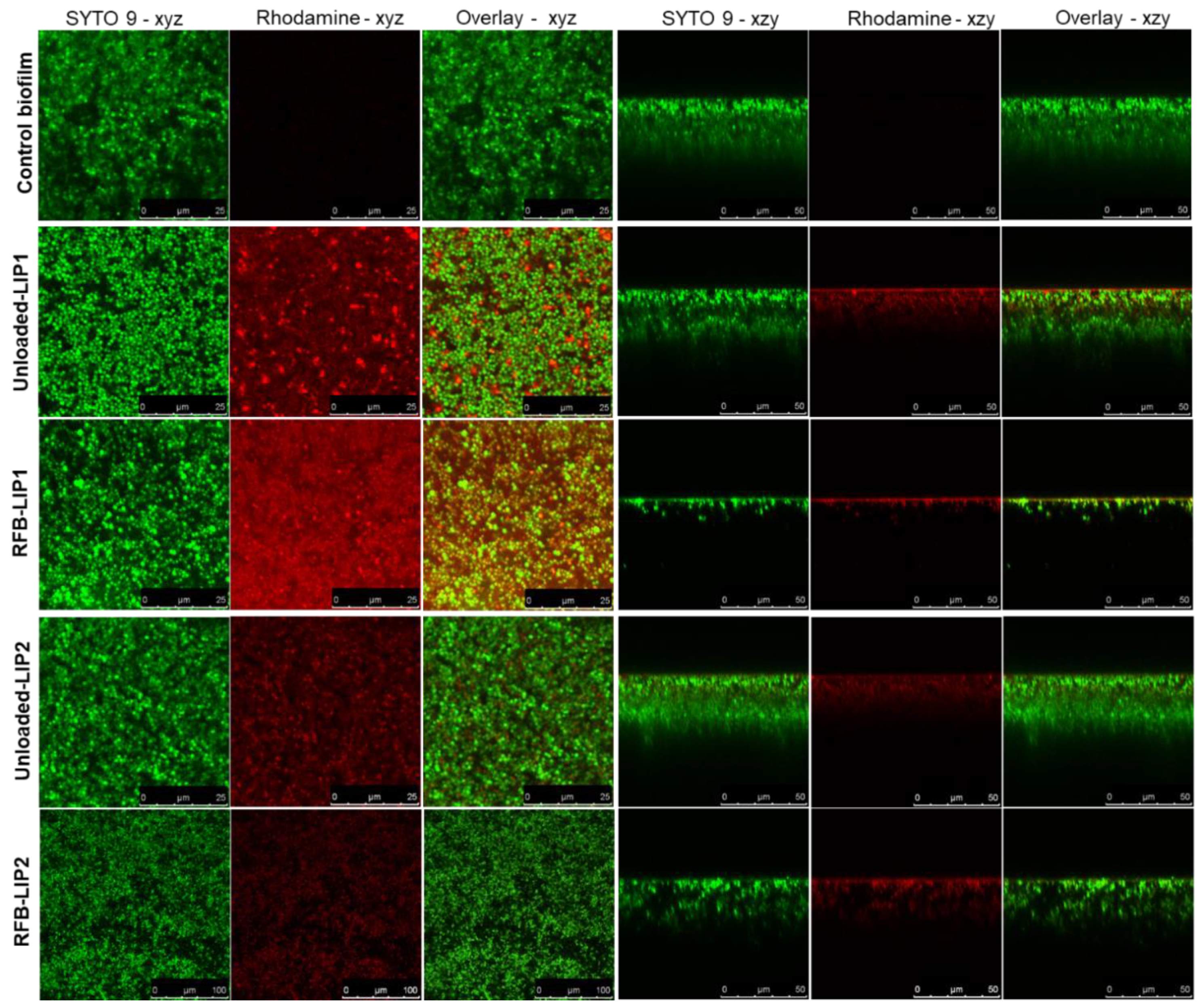
Here, to deeply understand the interaction of liposomes with the biofilm structure, we resorted to confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) to obtain high-resolution images of biofilms at different depths and planes. For this analysis, both unloaded and RFB-loaded liposomes labelled with rhodamine were incubated for 24 h. As depicted in
Figure 6 and
Figure S1, the presence of RFB did not hinder the interaction of liposomes with the biofilm matrix. Furthermore, while unloaded liposomes did not affect biofilm growth, the presence of RFB led to an evident reduction of biofilm thickness. These data were in accordance with the MTT assay, where RFB-loaded liposomes greatly decreased bacteria viability in a concentration-dependent manner, and unloaded liposomes were innocuous (
Figure 5). Previously, our research group has reported the successful interaction and internalization of liposomes within
S.
aureus biofilms [
20]. In particular, the positively charged liposomes DMPC:stearylamine (+13 mV), with a mean size 130 nm, showed high biofilm interaction [
20]. This has also been observed by other researchers evaluating liposomes composed of distearoyl phosphatidyl choline (DSPC) and dioleyl trimethylammonium propane (DOTAP) [
63]. These small mean size liposomes (<130 nm) with a very high positive charge (+59 mV) have also exhibited elevated levels of penetration in MSSA biofilms [
63].
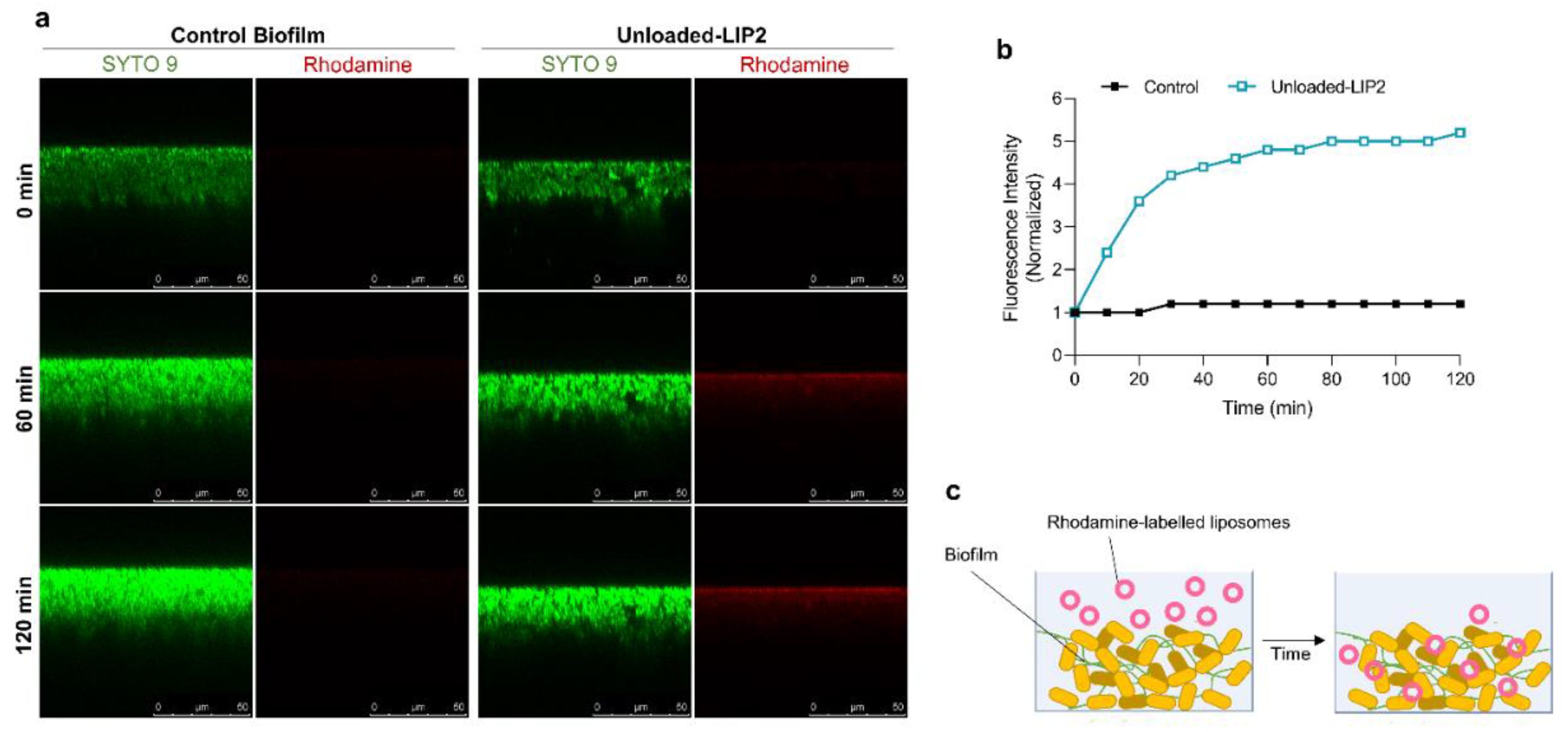
After assessing the behavior of liposomal formulations in MRSA-C1 biofilms, the next step was to investigate the kinetics of this interaction. This analysis was accomplished with rhodamine-labelled unloaded-LIP2 that was incubated with the biofilm at a lipid concentration of 1.5 μmol/mL. The distribution of liposomes was monitored during 120 min by CSLM (
Figure 7a) and the fluorescence intensity signal was normalized in relation to time = 0 min (
Figure 7b). The results showed that liposomes internalization within the biofilm structure was a rapid event, with a sharp increase in fluorescence intensity in the first 30 min, followed by a steady phase up to 120 min. The high antibiofilm efficacy of tested nanoformulation was supported by confocal microscopy, showing that liposomes successfully reached the inner layers of biofilm, releasing RFB within the vicinity of target bacteria (
Figure 7c).
2.6. Therapeutic Evaluation of RFB formulations against systemic MRSA infection
Considering the promising in vitro results of RFB formulations, their therapeutic potential was evaluated in murine models of systemic MRSA-C1 infection. In the preliminary study (designated as In Vivo Assay 1), mice were infected with 1.4×10
9 CFU/mouse and only Free RFB and RFB-LIP2 were evaluated (
Figure S2). Groups treated with these formulations at a dose of 20 mg/kg exhibited 100% survival, while the Control group reached 50% survival 7 days after infection induction (
Figure S2a). This was correlated with reduced weight loss (
Figure S2b) and significantly lower bacterial burden (
Figure S2c) and growth index values (
Figure S2d), compared to Control mice. Importantly, the antibacterial effect of RFB was greatly enhanced when incorporated in liposomes. RFB-LIP2 treatment decreased bacterial burden and growth index in all four major organs (liver, spleen, kidneys, and lung), while for Free RFB such effect was only observed in spleen and kidneys.
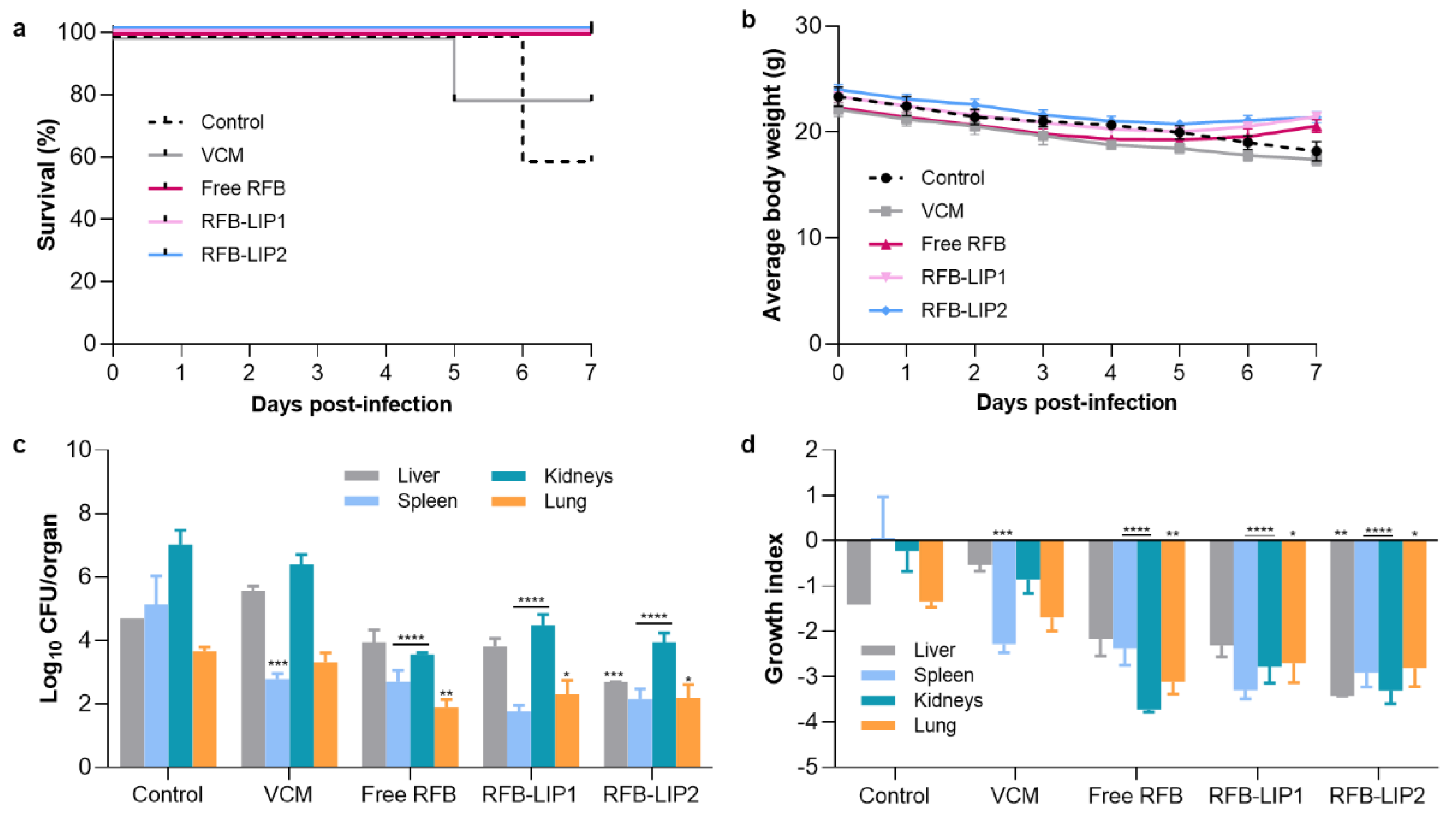
Ensuing this successful therapeutic evaluation, a second infection model (In Vivo Assay 2) was established to evaluate Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2, as well as the positive control, VCM. In particular one main objective was to assess the influence of two long blood circulating liposomes, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2. The obtained results are depicted in
Figure 8.
As in the previous assay (
Figure S2), in this In Vivo Assay 2 RFB formulations demonstrated a potent therapeutic effect against systemic MRSA-C1 infection, as shown in
Figure 8. Mice treated with RFB in the free and liposomal forms (RFB-LIP2) displayed 100% survival, compared to 80% for VCM and 60% for Control (
Figure 8a). The higher survival rate observed for the control group, when compared to the In Vivo Assay 1 (60% vs 50%), might be due to the lower infection dose used (3.4×10
8 CFU/mouse vs 1.4×10
9 CFU/mouse, respectively). In addition, the 100% survival rate observed for animals treated with RFB formulations was correlated with a recovery in body weight, which was not seen for positive and negative controls, as depicted in
Figure 8b. Furthermore, in terms of bacterial burden (
Figure 8c) and growth index (
Figure 8d), a significant reduction was attained in major organs of mice administered with RFB formulations. In the spleen, the Control group displayed a growth index of 0.066 ± 0.90, while Free RFB, RFB-LIP1, RFB-LIP2 and the positive control, VCM, presented values of -2.38 ± 0.37, -3.30 ± 0.19, -2.92 ± 0.31 and -2.29 ± 0.18, respectively. In the kidneys, the growth index of Control mice was -0.23 ± 0.45, and for the groups Free RFB, RFB-LIP1, RFB-LIP2 and VCM, values were -3.11 ± 0.62, -2.79 ± 0.35, -3.31 ± 0.29 and -0.86 ± 0.31, respectively. In the liver, only RFB-LIP2 significantly reduced the bacterial burden and growth index. It should be mentioned that the antibacterial effect of RFB formulations was achieved at a 2-fold lower dose than the positive control, VCM, further evidencing their antibacterial potential.
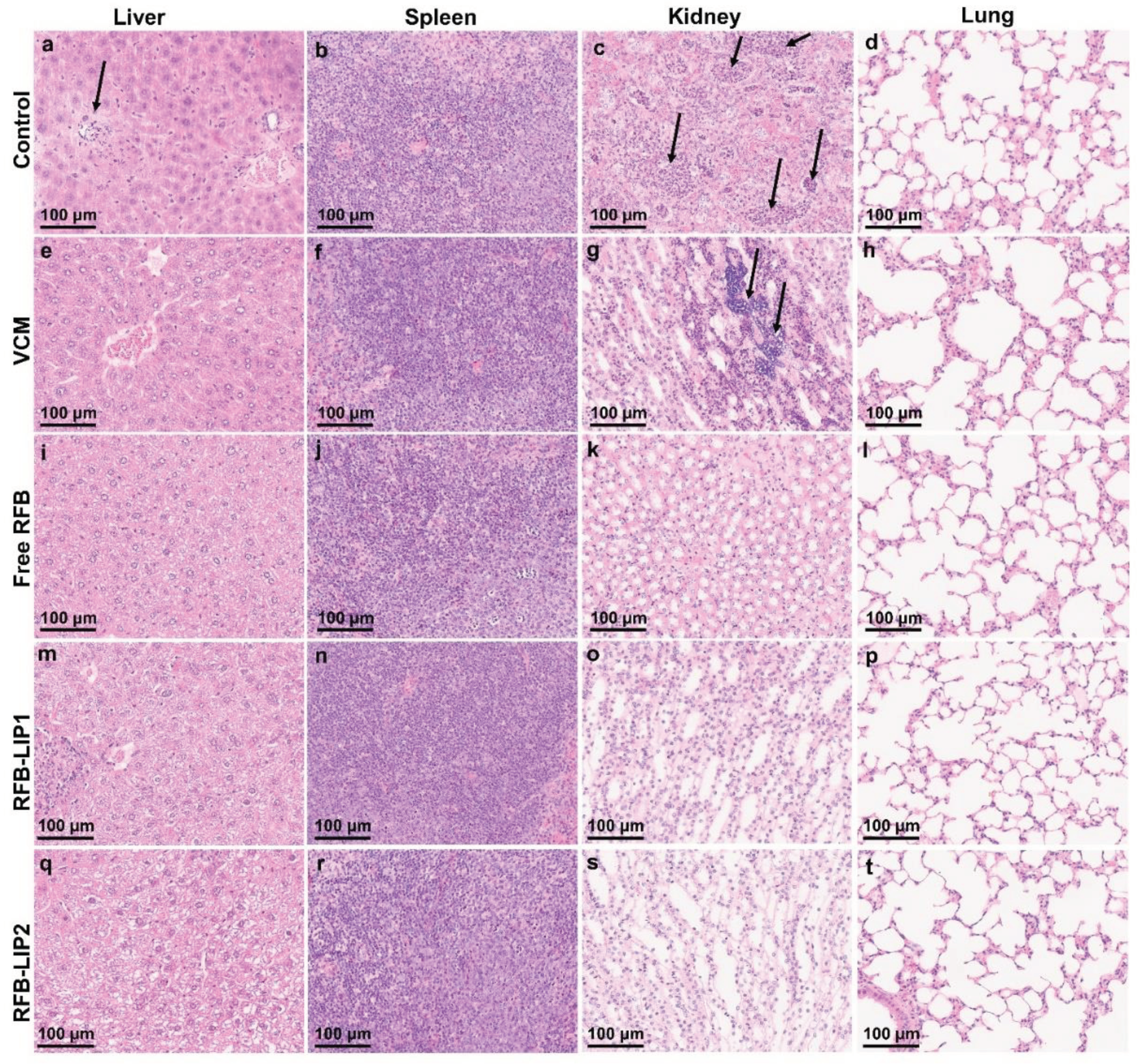
The histopathological analysis of liver, spleen, kidneys, and lung was performed using H&E staining (
Figure 9). Systemic
S.
aureus infection can form abscesses and persist in different organs. The kidneys are frequently the most affected ones, displaying high bacterial burdens [
64]. In the present study, the main lesions were identified in the liver and kidneys as foci of neutrophil infiltration with abscess formation. In the liver, the abscesses were multifocal and small. In the kidneys, the inflammatory infiltrates were mainly located in the medulla, with Control and VCM groups exhibited the highest scores for inflammation/necrosis (
Table S2). In the spleen, the presence of germinal center apoptotic bodies was indicative of reactivity (
Table S2).
Tissue index was evaluated as a safety parameter in both models of systemic
S.
aureus infection (
Table S1). Organ weight changes are frequently assessed as an indicator of toxicity. On the one hand, increased tissue index values may be associated with hypertrophy, congestion, or edema. On the other hand, lower values are indicative of organ atrophy or degeneration [
65,
66,
67]. In the present study, among the different experimental groups, no major changes in the analysed organs were detected compared to naïve mice, thus demonstrating the safety of tested formulations.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and VCM were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and RFB from Pharmacy Biotech AB (Uppsala, Sweden). The pure phospholipids, dimyristoyl phosphatidyl choline (DMPC), dimyristoyl phosphatidyl glycerol (DMPG), dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl choline (DPPC), dipalmitoyl phosphatidyl glycerol (DPPG) and distearoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine covalently linked to poly(ethylene glycol)2000 (DSPE-PEG) were purchased from Lipoid (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Rhodamine covalently linked to phosphatidylethanolamine (Rho-PE) were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL, USA). Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT), crystal violet (CV) and glycerol were obtained from Panreac AppliChem, ITW Reagents (Darmstadt, Germany). Culture media Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) and Mueller-Hinton Broth (MHB) were obtained from Oxoid, Ltd. (Basingstoke, UK) and Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) from Biokar (Pantin, France). The fluorescent stain SYTO 9 was obtained from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR, USA). D(+)-glucose monohydrate was acquired to Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and ethanol absolute anhydrous were obtained from Carlo Erba Reagents S.A.S. (Val de Reuil, France). All other reagents were of analytical grade.
3.2. Animals
Male Balb/c mice (6-8 weeks old) were obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Barcelona, Spain). Animals were kept under standard hygiene conditions, in ventilated cages on a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle, at 20-24 °C and 50-65% humidity. Mice had free access to sterilized diet and acidified water. All animal experiments were conducted according to the Animal Welfare Organ of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Universidade de Lisboa, approved by the competent national authority Direção-Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária (DGAV) and in accordance with the EU Directive (2010/63/UE) and Portuguese laws (DR 113/2013, 2880/2015, 260/2016 and 1/2019) for the use and care of animals in research.
3.3. Preparation of RFB-Loaded Liposomes
A remote loading technique, based on an ammonium sulfate gradient, was used to encapsulate RFB in pre-formed empty liposomes, as previously described [
28]. The tested lipid compositions were DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (65:30:5; LIP1), DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (65:30:5; LIP2), DMPC:DMPG (80:20; LIP3) and DPPC:DPPG (80:20; LIP4). Briefly, in a round-bottomed flask, selected phospholipids were dissolved in chloroform and dried in a rotary evaporator (Buchi R-200, Flawil, Switzerland) to form a thin lipid film. Afterwards, the lipid film was dispersed with deionized water for a final lipid concentration of 30 μmol/mL. The obtained lipid suspensions were frozen at -70 °C and lyophilized (freeze-dryer, Edwards, CO, USA) overnight. The lyophilized product was rehydrated with a buffer solution containing 120 mM of ammonium sulphate (pH 5), within a temperature set above the phase transition temperature (T
c) of the selected phospholipids. Then, using an extruder device (Lipex: Biomembranes Inc., Vancouver, Canada), the dispersions were sequentially filtered through polycarbonate membranes, under nitrogen pressure (10–500 lb/in2), to achieve an average vesicle size around 100 nm. An ammonium sulfate gradient was established by replacing the extraliposomal medium with HEPES buffer pH 6.9 (10 mM HEPES, 140 mM NaCl), using a desalting column (Econo-Pac
® 10 DG; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). A RFB solution at 0.5 mg/mL was prepared in the same buffer and, subsequently, incubated at 100 nmol/μmol of lipid with unloaded liposomes for 1 h, under stirring, at a temperature above the T
c of the phospholipids mixture. Non-encapsulated RFB was removed by ultracentrifugation at 250,000
g, for 120 min, at 15 °C in a Beckman LM-80 ultracentrifuge (Beckman Instruments, Inc, Fullerton, CA, USA). The obtained pellets were suspended in HEPES buffer pH 6.9. Unloaded liposomes were prepared following the same methodology. Fluorescent liposomes were obtained by including in the lipid composition Rho-PE at 0.1 mol% [
68].
3.4. Characterization of RFB-Loaded Liposomes
Liposomes were characterized in terms of RFB and lipid contents, mean size and zeta potential. For RFB quantification by spectrophotometry, liposomes were disrupted with ethanol and absorbance was read at 500 nm [
28]. Phospholipid content was determined following a colorimetric technique defined by Rouser [
69]. Loading capacity was defined as the final RFB to lipid ratio (RFB/Lip)f and the incorporation efficiency (I.E.), in percentage, was determined according to equation 1:
The mean size of liposomes and respective polydispersity index (PdI) were determined by dynamic light scattering in a Zetasizer Nano S (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK). The zeta potential was determined by laser doppler spectroscopy in a Malvern Zetasizer Nano Z (Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK).
3.5. S. aureus Strains and Culture Conditions
Clinical MRSA isolates, MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2, were kindly provided by Centro Hospitalar Universitário de Lisboa Central (CHULC, EPE), under a collaborative project. From 24 h bacterial cultures in MHA, stocks were prepared in MHB with 20% glycerol and stored at -80 °C. From these frozen stocks and for each assay, fresh cultures were grown 24 h in MHA, at 37 °C.
3.6. Susceptibility of Planktonic S. aureus to Antibiotics
The antibacterial activity of RFB formulations and VCM was evaluated by the broth microdilution assay, in accordance with the guidelines of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [
70], followed by turbidity assessment [
20]. RFB was quantified by spectrophotometry at 500 nm [
28] and VCM concentration was determined using the Lowry and Folin method [
71,
72]. RFB and VCM formulations diluted in MHB were tested at concentrations ranging from 0.0016-0.414 μg/mL and 0.014-3.750 μg/mL, respectively. To prepare the inoculum, bacteria from 24 h cultures were diluted in MHB and, by measuring the optical density (OD) at 600 nm (Shimadzu UV 160A, Shimadzu Corporation, Japan), turbidity was adjusted to 0.5 in a McFarland scale, corresponding to, approximately, 10
8 colony forming units per mL (CFU/mL). Bacterial suspensions were placed in non-adherent 96-well U-bottom polystyrene plates for a final concentration of 5×10
5 CFU/mL (MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2). Tested formulations were added to the respective wells and incubated at 37 °C, for 24 h, under static conditions. Negative controls were bacteria in MHB without antibiotics and sterile controls were MHB alone. Empty liposomes were also assayed using the same lipid concentrations as the ones tested for the respective RFB-loaded liposomes. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined spectrophotometrically at 570 nm in a microplate reader (iMark
TM, Bio-Rad laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA), being defined as the lowest antibiotic concentration that inhibited visible bacterial growth. For MRSA-C1, the obtained MIC values of Free RFB and VCM were further confirmed by CFU counting and MTT assay (visualization). For CFU counting, after incubation period, 50 μL of wells (in triplicate) were collected, serially diluted in sterile PBS, seeded in MHA plates and individual colonies were counted after 24 h at 37 °C. In MTT assay, after the incubation period, plates were centrifuged at 800 g, for 10 min, at room temperature. Medium was carefully removed and 200 μL/well of MTT solution at 125 μg/mL in PBS was added, followed by incubation at 37 °C until color formation (5-15 min). The MIC value was defined as the minimum concentration of antibiotic where no coloration was observed, compared to the negative control.
3.7. Susceptibility of S. aureus Biofilm to Antibiotics
Cultures of 24 h of each strain, MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2, were diluted in TSB 0.25% and placed in 96-well F-bottom polystyrene plates at a final concentration of 1×10
6 CFU/mL (200 μL/well) [
20]. Biofilms were grown at 37 °C, for 24 h, under static conditions. Tested antibiotic formulations were added and incubated for 24 h, at 37 °C, with RFB and VCM at concentrations ranging from 0.0008-0.828 μg/mL and 6.25-800 μg/mL, respectively. Negative controls were bacteria in TSB 0.25% without antibiotics and sterile controls were TSB 0.25% alone. Unloaded liposomes were also tested using the lipid concentrations corresponding to the respective RFB-loaded liposomes.
The in vitro activity of tested antibiotic formulations was assessed through the MTT assay, as described in literature [
73], with some modifications. After rinsing the attached bacteria twice with PBS (200 μL/well), MTT solution at 125 μg/mL in PBS was added (200 μL/well) and incubated at 37 °C, for 1 h. Afterwards, the MTT solution was discarded and 200 μL of DMSO were added to each well to solubilize the purple formazan crystals. The OD was measured at 570 nm in a microplate reader (iMark
TM, Bio-Rad laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Bacteria viability, in percentage, was calculated according to equation 2, where OD
t refers to the OD values of bacteria incubated with the tested formulations, and OD
ctrl are the OD values of negative control that corresponds to 100% viability.
Minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) was defined as the lowest antibiotic concentration able to inhibit 50% of bacterial growth, relative to negative controls (MBIC
50). The determination of MBIC
50 was performed by sigmoidal fitting analysis using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.1 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA,
www.graphpad.com).
Quantification of biofilm biomass was performed through CV staining method [
20,
74]. Briefly, medium was discarded and attached bacteria were washed twice with PBS (200 μL/well), followed by drying at room temperature for 15 min. Then, biofilms were incubated with 200 μL of a CV solution at 0.0125% (w/v in water) at room temperature, during 10 min, followed by two washing steps with PBS. After drying at 37 °C for 10 min, stained biofilms were dissolved with 200 μL ethanol and absorbance was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader (iMark
TM, Bio-Rad laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA). Negative control was the biofilm in the presence of TSB 0.25% only, representing 100% growth. Biofilm biomass (%) was calculated using equation 3, where OD
t corresponds to the biofilms incubated with the tested formulations and OD
ctrl refers to the negative control (100% biofilm biomass).
3.8. Interaction of RFB Liposomes with S. aureus Biofilm by Microscopy
Confocal scanning laser microscopy (CSLM) was used to evaluate the interaction of developed liposomal formulations with 24 h-old MRSA-C1 biofilms. For this assay, liposomes fluorescently labelled with Rho-PE (unloaded and RFB-loaded) were used. Biofilms were established in 8-well chambered coverslips (Ibidi GmbH, Munich, Germany), with 200 μL/well of MRSA-C1 bacteria inoculum at 1×10
6 CFU/mL in TSB supplemented with 0.25% of glucose (TSB 0.25%), and incubated at 37 °C, for 24 h [
75]. For these assays, liposomes at a lipid concentration of 1.5 µmol/mL in TSB 0.25% were used. Control biofilm corresponded to bacteria in TSB 0.25% medium.
In the first assay, RFB-LIP1, RFB-LIP2, RFB-LIP3, RFB-LIP4, as well as unloaded liposomes, were incubated for 24 h with MRSA-C1 biofilms. Afterwards, biofilms were washed with PBS and stained with SYTO 9 (3 µM), for 30 min in the dark, at room temperature. In the kinetics study, mature biofilms were stained with SYTO 9 (3 µM), incubated with unloaded-LIP2 and monitored over a period of 120 min, with 10 min intervals. Biofilms were visualized using a Leica TCS SP5 inverted microscope (Leica Mycrosystems CMS GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) equipped with a continuous Ar ion laser (Multi-line LASOS® LGK 7872 ML05). Image acquisition was performed at 512 by 512 pixels, with a scan rate of 100 Hz per frame. A 63x1.2 N.A. water immersion objective was used (HCX PL APO CS 63.0 × 1.20 WATER UV). SYTO 9 images were recorded with a 488 nm excitation line and emission was recorded at 501–570 nm. Rho-PE images were collected with a 514 nm excitation line and emission was recorded at 610–760 nm. For each condition, planes xzy and xyz were analysed.
3.9. Therapeutic evaluation of RFB formulations in murine models of systemic MRSA infection
The antibacterial effect of RFB formulations was assessed in systemic murine models of MRSA-C1 infection using male Balb/c mice (6-8 weeks old), obtained from Charles River Laboratories (Barcelona, Spain). Two independent infection models were tested: 1.4×109 CFU/mouse, designated as In Vivo Assay 1, and 3.4×108 CFU/mouse, corresponding to In Vivo Assay 2. Bacteria inoculum was given intravenously in the lateral tail vein. In the In Vivo Assay 1 (1.4×109 CFU/mouse), only Free RFB and RFB-LIP2 were assessed. In the In Vivo Assay 2 (3.4×108 CFU/mouse), Free RFB, RFB-LIP1, RFB-LIP2 and VCM were evaluated. RFB formulations were administered at 20 mg/kg and VCM at a dose of 40 mg/kg. Control mice group received buffer by intravenous route.
In both models, three days after infection induction, 3 to 5 animals were sacrificed and organs of interest (liver, spleen, kidneys, and lungs) were aseptically collected, homogenized, and serially diluted in PBS for CFU counting in MHA plates. Colonies were counted after 24 h of incubation at 37 °C. Growth index was determined as the difference between the log
10CFU at the end of the protocol and the log
10CFU at the beginning of treatment. Tissue index was calculated using equation 4:
Simultaneously, the treatment schedule was initiated. Groups received i.v. administrations of tested formulations, once per day, for three consecutive days. Two days after the last treatment, mice were sacrificed and liver, spleen, kidneys, and lung were collected and processed for CFU counting as abovementioned. For histology, organs were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, and sections were stained and examined by the H&E method. Whole-slide images were obtained using the NanoZoomer-SQ Digital slide scanner (Hamamatsu Photonics). Tissue indexes were calculated using equation 4. The antibacterial effectiveness of the formulations was determined in terms of average body weight, percentage of survival, bacterial burden, and growth index.
3.10. Statistical Analysis
Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) or standard error mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed with Two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnet’s Post-Hoc test using GraphPad Prism version 8.0.1 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, California USA,
www.graphpad.com). p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4. Conclusions
The present results are very encouraging, emphasizing the application of liposomes for the delivery of RFB against S. aureus infections, especially for the more resistant biofilm-organized bacteria. We successfully designed four liposomal formulations using phospholipids with distinct Tc (DMPC/DMPG = +24°C/+23ºC and DPPC/DPPG = +41°C) with high RFB loadings. DSPE-PEG was included in the lipid composition to achieve prolonged blood circulation times. In vitro studies demonstrated that RFB retained its antibacterial effect when nanoformulated. Importantly, RFB nanoformulations were more effective than the gold standard antibiotic, VCM. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of RFB liposomes against planktonic and biofilm-organized bacteria was confirmed to be solely due to the antibiotic presence since unloaded liposomes did not exert any effect.
The antibiofilm activity of RFB liposomes was correlated with the successful interaction of nanoformulations with MRSA-C1 biofilm as demonstrated by confocal microscopy studies. Furthermore, the presence of either DSPE-PEG and/or RFB did not hinder this interaction. Following these promising in vitro data, the proof-of-concept was performed in murine models of systemic MRSA-C1 infection. A significant reduction on bacterial burden and improvement on survival rates was achieved for mice treated with RFB formulations using a 2-fold lower dose than VCM, thus evidencing the potential of this therapeutic strategy. Continuous efforts should be made to provide new solutions against MRSA, particularly biofilm-organized bacteria, and RFB formulations emerge as an effective and safe option.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Representative CSLM images of 24 h-old MRSA-C1 biofilms after incubation with rhodamine-labelled LIP3 and LIP4 liposomes, unloaded and RFB-loaded, at a lipid concentration of 1.5 µmol/mL, for 24 h. Biofilms were stained with the green dye SYTO 9 at 3 µM. Untreated biofilm was used as a control (Control biofilm). Images in the left panels correspond to xyz section, and images in the right panels correspond to xzy orthogonal section. The overlay of the green and red channels from each plane image is presented as Overlay—xyz and Overlay—xzy. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG (RFB-LIP3 and Unloaded-LIP3); DPPC:DPPG (RFB-LIP4 and Unloaded-LIP4), Figure S2: In Vivo Assay 1—Preliminary evaluation of RFB formulations in a murine model of systemic MRSA-C1 infection. infection was induced intravenously in male Balb/c mice with a MRSA-C1 inoculum at 1.4×109 CFU/mouse. Three days after infection induction mice received i.v. administrations of RFB formulations (Free RFB and RFB-LIP2) at dose of 20 mg/kg. Control group received buffer by intravenous route. (a) percentage of survival (Kaplan-Meier analysis), (b) average body weight, (c) bacterial burden in major organs at the end of treatment protocol, and (d) growth index. RFB-LIP2: DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=4-5). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 vs Control group, Table S1: Tissue indexes of liver, spleen, kidneys, and lung of healthy mice (naïve) and mice infected with systemic MRSA-C1 and treated with tested formulations. In Vivo Assay 1 corresponds to mice induced with 1.4×109 CFU/mouse and In Vivo Assay 2 to animals induced with 3.4×108 CFU/mouse. Results are expressed as AVG ± SEM (n=4-5), Table S2: In Vivo Assay 2—Score of analysed organs in terms of inflammation/necrosis (liver, kidney, and lung) and reaction to infection (spleen).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.G. S.N.P., S.I.A.; Methodology, J.O.P., M.F., M.M.G., S.N.P., S.I.A., M.C.; Formal Analysis, J.O.P., M.F, S.N.P., M.C.; Investigation, J.O.P., S.N.P., S.I.A., M.M.G.; Resources, S.N.P., S.I.A., M.M.G.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, J.O.P.; Writing—Review & Editing, S.I.A., M.M.G. S.N.P.; Supervision, M.M.G.; Project Administration, M.M.G.; Funding Acquisition, M.M.G.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Protocols involving mice were carried out according to Directive 2010/63/EU and Portuguese laws (DR 113/2013, 2880/2015, 260/2016 and 1/2019) for the use and care of animals in research. All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Lisboa (Animal Welfare Organ—ORBEA-FFUL) and licensed by the Portuguese competent authority (Direção Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária, license number: 003866, 10th of March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Sandra I. Aguiar was affiliated to Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Animal Health (CIISA), Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Universidade de Lisboa at the time of this work but currently works in AstraZeneca.
References
- Dayan, G.H.; Mohamed, N.; Scully, I.L.; Cooper, D.; Begier, E.; Eiden, J.; Jansen, K.U.; Gurtman, A.; Anderson, A.S. Staphylococcus aureus: The current state of disease, pathophysiology and strategies for prevention. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 1373–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.H.; Howden, B.P. Diagnosis and management of Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Intern. Med. J. 2005, 35, S17–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Jensen, S.O.; Vaska, V.L.; Espedido, B.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Gosbell, I.B. Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 362–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, M.Z.; Daum, R.S. Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections. In Staphylococcus aureus: Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology,; Bagnoli, F., Rappuoli, R., Grandi, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; Volume 409, pp. 325–383. ISBN 978-3-319-72063-0. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.D.; Lo, C.K.L.; Komorowski, A.S.; Suresh, M.; Guo, K.; Garg, A.; Tandon, P.; Senecal, J.; Del Corpo, O.; Stefanova, I.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuinness, W.A.; Malachowa, N.; DeLeo, F.R. Vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Purrello, S.M.; Garau, J.; Giamarellos, E.; Mazzei, T.; Pea, F.; Soriano, A.; Stefani, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A review of the currently available treatment options. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.P. Vancomycin: A history. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, S5–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, E.; Keynan, Y. Vancomycin revisited—60 years later. Front. Public Heal. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Hal, S.; Tong, S. Combination antibiotic treatment of serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 003–016. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, Y.; Yang, S.; Rao, X. Vancomycin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A review of case updating and clinical features. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 21, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vor, L.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Strijp, J.A.G. Staphylococci evade the innate immune response by disarming neutrophils and forming biofilms. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2556–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal biofilms. In Bacterial Biofilms. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, vol 322; Romeo, T., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008; pp. 207–228. ISBN 978-3-540-75418-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, L.; Bisen, M.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S.; Azizov, S.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Kumar, D. Advances in nanotechnology for biofilm inhibition. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21391–21409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Aguiar, S.; Bettencourt, A.; Gaspar, M.M. Lipid-based nanosystems for targeting bone implant-associated infections: Current approaches and future endeavors. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X. Thermosensitive nanotherapeutics for localized photothermal ablation of MRSA-infected osteomyelitis combined with chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 12842–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Pinto, S.N.; Aires-da-Silva, F.; Bettencourt, A.; Aguiar, S.I.; Gaspar, M.M. Liposomes as a nanoplatform to improve the delivery of antibiotics into Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhariri, M.; Azghani, A.; Omri, A. Liposomal antibiotics for the treatment of infectious diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, A.A.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Abd-Allah, A.R.A.; Bayomi, M.A. Treatment of experimental osteomyelitis by liposomal antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, A.; Chaudhari, B.B.; Chaudhari, P.; Ananthamurthy, K.; Aranjani, J.; Moorkoth, S.; Ghate, V.; Lewis, S. In vitro antibacterial activity and in vivo pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered amikacin-loaded liposomes for the management of bacterial septicaemia. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2022, 220, 112892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabol, Y.; Catherinot, E.; Veziris, N.; Jullien, V.; Lortholary, O. Rifabutin: Where do we stand in 2016? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doub, J.B.; Heil, E.L.; Ntem-Mensah, A.; Neeley, R.; Ching, P.R. Rifabutin use in Staphylococcus biofilm infections: A case series. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, L.; Josse, J.; Tasse, J.; Lustig, S.; Ferry, T.; Diot, A.; Laurent, F.; Valour, F. Antibiofilm and intraosteoblastic activities of rifamycins against Staphylococcus aureus: Promising in vitro profile of rifabutin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristoff, P.A.; Garcia, G.A.; Kirchhoff, P.D.; Hollis Showalter, H.D. Rifamycins – Obstacles and opportunities. Tuberculosis 2010, 90, 94–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Cruz, A.; Penha, A.F.; Reymão, J.; Sousa, A.C.; Eleutério, C.V.; Domingues, S.A.; Fraga, A.G.; Filho, A.L.; Cruz, M.E.M.; et al. Rifabutin encapsulated in liposomes exhibits increased therapeutic activity in a model of disseminated tuberculosis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Neves, S.; Portaels, F.; Pedrosa, J.; Silva, M.T.; Cruz, M.E.M. Therapeutic efficacy of liposomal rifabutin in a Mycobacterium avium model of infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwabuife, J.C.; Pant, A.M.; Govender, T. Liposomal delivery systems and their applications against Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Ogren, M.; Dias, J.N.R.; Silva, M.; Gil, S.; Tavares, L.; Aires-da-Silva, F.; Gaspar, M.M.; Aguiar, S.I. Liposomes as antibiotic delivery systems: A promising nanotechnological strategy against antimicrobial resistance. Molecules 2021, 26, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.M.; Lopes-de-Campos, D.; Martins, M.C.L.; Van Dijck, P.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Impact of nanosystems in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms treatment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 622–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhlouf, Z.; Ali, A.A.; Al-Sayah, M.H. Liposomes-based drug delivery systems of anti-biofilm agents to combat bacterial biofilm formation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requena, R.; Vargas, M.; Chiralt, A. Study of the potential synergistic antibacterial activity of essential oil components using the thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. LWT 2019, 101, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekinejad, H.; Bazargani-Gilani, B.; Tukmechi, A.; Ebrahimi, H. A cytotoxicity and comparative antibacterial study on the effect of Zataria multiflora Boiss, Trachyspermum copticum essential oils, and Enrofloxacin on Aeromonas hydrophila. Avicenna J. Phytomedicine 2012, 2, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Vipra, A.; Desai, S.N.; Junjappa, R.P.; Roy, P.; Poonacha, N.; Ravinder, P.; Sriram, B.; Padmanabhan, S. Determining the minimum inhibitory concentration of bacteriophages: Potential advantages. Adv. Microbiol. 2013, 03, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.S.; ElMasry, S.A.; Fahim, N.A.E.M.M.; Abd ElSattar, M.A.; Shaker, O.A. Detection of antibiotic susceptibility by colorimetric minimum inhibitory concentration in staphylococcal isolates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moodley, S.; Koorbanally, N.A.; Moodley, T.; Ramjugernath, D.; Pillay, M. The 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay is a rapid, cheap, screening test for the in vitro anti-tuberculous activity of chalcones. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 104, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarai, Z.; Kadri, A.; Ben Chobba, I.; Ben Mansour, R.; Bekir, A.; Mejdoub, H.; Gharsallah, N. The in-vitro evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic properties of Marrubium vulgare L. essential oil grown in Tunisia. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, E.; Nelis, H.J.; Coenye, T. Comparison of multiple methods for quantification of microbial biofilms grown in microtiter plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, E.; Trimble, M.; Cheng, J.; Vallé, Q.; Hancock, R. Critical assessment of methods to quantify biofilm growth and evaluate antibiofilm activity of host defence peptides. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macia, M.D.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Oliver, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisian, S.A.; Janssen, M.J.; Matta, H.; Henry, G.E.; LaPlante, K.L.; Rowley, D.C. Inhibition of bacterial growth and biofilm production by constituents from Hypericum spp. Phyther. Res. 2012, 26, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilieva, Y.; Marinov, T.; Trayanov, I.; Kaleva, M.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Yocheva, L.; Kokanova-Nedialkova, Z.; Najdenski, H.; Nedialkov, P. Outstanding antibacterial activity of Hypericum rochelii—Comparison of the antimicrobial effects of extracts and fractions from four Hypericum species growing in Bulgaria with a focus on prenylated phloroglucinols. Life 2023, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Sulaiman, J.E.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, R.; Malit, J.J.; Wong, W.C.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.-X.; Chen, F.; et al. Mode of action of elasnin as biofilm formation eradicator of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottola, C.; Matias, C.S.; Mendes, J.J.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Tavares, L.; Cavaco-Silva, P.; Oliveira, M. Susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in diabetic foot infections. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.N.C.; Yildiz, F.H. Biofilm matrix proteins. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirani, Z.A.; Jamil, N. Effect of sub-lethal doses of vancomycin and oxacillin on biofilm formation by vancomycin intermediate resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Basic Microbiol. 2011, 51, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yuan, F.; Lu, F.; Yin, Y.; Cao, J. Vancomycin-induced biofilm formation by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus is associated with the secretion of membrane vesicles. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 110, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyoputri, A.; Jarrad, A.M.; Cooper, M.A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. The Eagle Effect and antibiotic-induced persistence: Two sides of the same coin? Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forier, K.; Raemdonck, K.; De Smedt, S.C.; Demeester, J.; Coenye, T.; Braeckmans, K. Lipid and polymer nanoparticles for drug delivery to bacterial biofilms. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavina, Z.; Vanić, Ž. Current trends in development of liposomes for targeting bacterial biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2016, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.; Cruz, A.; Fraga, A.; Castro, A.; Cruz, M.; Pedrosa, J. Developments on drug delivery systems for the treatment of mycobacterial infections. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.M.; Calado, S.; Pereira, J.; Ferronha, H.; Correia, I.; Castro, H.; Tomás, A.M.; Cruz, M.E.M. Targeted delivery of paromomycin in murine infectious diseases through association to nano lipid systems. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology, Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Y.; van der Mei, H.C.; Ren, Y.; Busscher, H.J.; Shi, L. Lipid-based antimicrobial delivery-systems for the treatment of bacterial infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpattananangkul, D.; Zhang, L.; Olson, S.; Aryal, S.; Obonyo, M.; Vecchio, K.; Huang, C.-M.; Zhang, L. Bacterial toxin-triggered drug release from gold nanoparticle-stabilized liposomes for the treatment of bacterial infection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4132–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Raza, A.; Adelnia, H.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H. PEG-grafted liposomes for enhanced antibacterial and antibiotic activities: An in vivo study. NanoImpact 2022, 25, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibaraki, H.; Kanazawa, T.; Chien, W.-Y.; Nakaminami, H.; Aoki, M.; Ozawa, K.; Kaneko, H.; Takashima, Y.; Noguchi, N.; Seta, Y. The effects of surface properties of liposomes on their activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO-1 biofilm. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadas-Sharif, N.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Khameneh, B.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. The effect of nanoliposomal formulations on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scriboni, A.B.; Couto, V.M.; Ribeiro, L.N. de M.; Freires, I.A.; Groppo, F.C.; de Paula, E.; Franz-Montan, M.; Cogo-Müller, K. Fusogenic liposomes increase the antimicrobial activity of vancomycin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Thomas, N.; Thierry, B.; Vreugde, S.; Prestidge, C.A.; Wormald, P.-J. Distribution and inhibition of liposomes on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0131806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, T.; Reimers, D.; Lory, N.C.; Schmidt, C.; Schmid, J.; C. Heinig, L.; Bradtke, P.; Rattay, G.; Zielinski, S.; Hellmig, M.; et al. Kidney-resident innate-like memory γδ T cells control chronic Staphylococcus aureus infection of mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2023, 120, e2210490120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, B.; Yano, B.; Sellers, R.S.; Perry, R.; Morton, D.; Roome, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Schafer, K. Evaluation of organ weights for rodent and non-rodent toxicity studies: A review of regulatory guidelines and a survey of current practices. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, J.O.; Matias, M.; Godinho-Santos, A.; Amaral, J.D.; Mendes, E.; Perry, M.J.; Francisco, A.P.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Gaspar, M.M. A step forward on the in vitro and in vivo assessment of a novel nanomedicine against melanoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 640, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, R.S.; Mortan, D.; Michael, B.; Roome, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Yano, B.L.; Perry, R.; Schafer, K. Society of toxicologic pathology position paper: Organ weight recommendations for toxicology studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Gaspar, M.M.; Scholz, D.; Almeida, A.J.; Brayden, D.J. Track analysis of the passage of rhodamine-labeled liposomes across porcine jejunal mucus in a microchannel device. Ther. Deliv. 2018, 9, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouser, G.; Fleischer, S.; Yamamoto, A. Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids 1970, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
CLSI Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018.
- Gaspar, M.M.; Perez-Soler, R.; Cruz, M.E.M. Biological characterization of L-asparaginase liposomal formulations. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 38, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, L.Z.S.; Endo, E.H.; Cortez, D.A.G.; Dias Filho, B.P. Anti-biofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus MRSA and MSSA of neolignans and extract of Piper regnellii. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2017, 27, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, C.; Alves, M.; Santos, C.; Ribeiro, M.H.; Gonçalves, L.; Bettencourt, A.F.; Ribeiro, I.A.C. Can sophorolipids prevent biofilm formation on silicone catheter tubes? Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, S.; Dias, S.A.; Cruz, A.F.; Mil-Homens, D.; Fernandes, F.; Valle, J.; Andreu, D.; Prieto, M.; Castanho, M.A.R.B.; Coutinho, A.; et al. The mechanism of action of pepR, a viral-derived peptide, against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2 to RFB and VCM in the free form. The broth microdilution method, followed by turbidity measurement, was performed 24 h after incubation with antibiotics. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative control (Ctrl). RFB (a, b) and VCM (c, d). RFB and VCM concentrations ranged from 0.0016-0.414 μg/mL and 0.014-3.750 μg/mL, respectively. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3-4).
Figure 1.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2 to RFB and VCM in the free form. The broth microdilution method, followed by turbidity measurement, was performed 24 h after incubation with antibiotics. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative control (Ctrl). RFB (a, b) and VCM (c, d). RFB and VCM concentrations ranged from 0.0016-0.414 μg/mL and 0.014-3.750 μg/mL, respectively. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3-4).
Figure 2.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 to free RFB and VCM. (a) Representative images of MTT assay 24 h after incubation with the antibiotics in the free form. (b) CFU countings of selected antibiotic concentrations were performed to determine viable bacteria recovered after the same incubation period (24 h). Concentrations of RFB and VCM ranged from 0.0008-0.026 μg/mL and 0.117-3.75 μg/mL, respectively. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative control. Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).
Figure 2.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 to free RFB and VCM. (a) Representative images of MTT assay 24 h after incubation with the antibiotics in the free form. (b) CFU countings of selected antibiotic concentrations were performed to determine viable bacteria recovered after the same incubation period (24 h). Concentrations of RFB and VCM ranged from 0.0008-0.026 μg/mL and 0.117-3.75 μg/mL, respectively. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative control. Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).
Figure 3.
Susceptibility of biofilm MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2 to free RFB and VCM. (a, b, e, f) Bacteria viability (%) was assessed through the MTT assay and MBIC50 was defined as the antibiotic concentration that inhibits 50% of bacterial growth related to negative control. (c, d, g, h) Biofilm biomass (%) was assessed through the CV assay. Mature biofilms were incubated with RFB and VCM at concentrations ranging from 0.0008-0.828 μg/mL and 6.25-800 μg/mL, respectively. Bacteria in TSB 0.25% corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).
Figure 3.
Susceptibility of biofilm MRSA-C1 and MRSA-C2 to free RFB and VCM. (a, b, e, f) Bacteria viability (%) was assessed through the MTT assay and MBIC50 was defined as the antibiotic concentration that inhibits 50% of bacterial growth related to negative control. (c, d, g, h) Biofilm biomass (%) was assessed through the CV assay. Mature biofilms were incubated with RFB and VCM at concentrations ranging from 0.0008-0.828 μg/mL and 6.25-800 μg/mL, respectively. Bacteria in TSB 0.25% corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).
Figure 4.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 to RFB formulations, Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2. RFB concentrations ranged from 0.0016-0.207 μg/mL. Unloaded liposomes were tested at the same lipid concentrations as corresponding RFB-loaded liposomes. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). The susceptibility to tested formulations was assessed by turbidimetry. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 4.
Susceptibility of planktonic MRSA-C1 to RFB formulations, Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2. RFB concentrations ranged from 0.0016-0.207 μg/mL. Unloaded liposomes were tested at the same lipid concentrations as corresponding RFB-loaded liposomes. Bacteria in MHB corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). The susceptibility to tested formulations was assessed by turbidimetry. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 5.
Susceptibility of biofilm MRSA-C1 to RFB formulations, Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2. RFB concentrations ranged from 0.0008-0.207 μg/mL. Unloaded liposomes were tested at the same lipid concentrations as corresponding RFB-loaded liposomes. Bacteria in TSB 0.25% corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). The susceptibility to tested formulations was assessed by MTT assay. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 5.
Susceptibility of biofilm MRSA-C1 to RFB formulations, Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2. RFB concentrations ranged from 0.0008-0.207 μg/mL. Unloaded liposomes were tested at the same lipid concentrations as corresponding RFB-loaded liposomes. Bacteria in TSB 0.25% corresponds to negative controls (100% growth). Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). The susceptibility to tested formulations was assessed by MTT assay. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 6.
Representative CSLM images of mature MRSA-C1 biofilms after 24 h incubation with rhodamine-labelled LIP1 and LIP2 liposomes, unloaded and RFB-loaded, at a lipid concentration of 1.5 µmol/mL. Biofilms were stained with the green dye SYTO 9 at 3 µM. Untreated biofilm was used as a negative control (Control biofilm). Images in the left panels correspond to to x–y plane images taken at the inner layer of MRSA stained biofilms, and images in the right panels correspond to x–z orthogonal plane images. The overlay of the green and red channels from each plane image is presented as Overlay—x–y and Overlay—x–z. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 6.
Representative CSLM images of mature MRSA-C1 biofilms after 24 h incubation with rhodamine-labelled LIP1 and LIP2 liposomes, unloaded and RFB-loaded, at a lipid concentration of 1.5 µmol/mL. Biofilms were stained with the green dye SYTO 9 at 3 µM. Untreated biofilm was used as a negative control (Control biofilm). Images in the left panels correspond to to x–y plane images taken at the inner layer of MRSA stained biofilms, and images in the right panels correspond to x–z orthogonal plane images. The overlay of the green and red channels from each plane image is presented as Overlay—x–y and Overlay—x–z. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1 and Unloaded-LIP1); DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2 and Unloaded-LIP2).
Figure 7.
Interaction of rhodamine-labelled unloaded-LIP2 with MRSA-C1 biofilm. Liposomes were incubated at a lipid concentration of 1.5 μmol/mL. Untreated 24 h-old biofilm was used as negative control (Control Biofilm). (a) Representative CSLM xzy orthogonal views of MRSA biofilms at time points 0, 60 and 120 min. Biofilms were stained with the green dye SYTO 9 at 3 µM. xzy sections) were taken every 10 min for a total of 120 min (b) Relative changes in the average of rhodamine fluorescence intensity over time. (c) Schematic representation of the interaction of rhodamine-labelled liposomes with S. aureus biofilm. LIP2: DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG.
Figure 7.
Interaction of rhodamine-labelled unloaded-LIP2 with MRSA-C1 biofilm. Liposomes were incubated at a lipid concentration of 1.5 μmol/mL. Untreated 24 h-old biofilm was used as negative control (Control Biofilm). (a) Representative CSLM xzy orthogonal views of MRSA biofilms at time points 0, 60 and 120 min. Biofilms were stained with the green dye SYTO 9 at 3 µM. xzy sections) were taken every 10 min for a total of 120 min (b) Relative changes in the average of rhodamine fluorescence intensity over time. (c) Schematic representation of the interaction of rhodamine-labelled liposomes with S. aureus biofilm. LIP2: DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG.
Figure 8.
In Vivo Assay 2—Therapeutic evaluation of RFB and VCM formulations in a murine model of systemic MRSA-C1 infection. Infection was induced intravenously in male Balb/c mice with a MRSA-C1 inoculum at 3.4×108 CFU/mouse. Three days after infection induction mice received i.v. administrations of VCM (40 mg/kg) and RFB formulations (Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2; 20 mg/kg). Control group received buffer by intravenous route. (a) percentage of survival (Kaplan-Meier analysis), (b) average body weight, (c) bacterial burden in major organs at the end of treatment protocol, and (d) growth index. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1) and DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=5-6). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 vs Control group.
Figure 8.
In Vivo Assay 2—Therapeutic evaluation of RFB and VCM formulations in a murine model of systemic MRSA-C1 infection. Infection was induced intravenously in male Balb/c mice with a MRSA-C1 inoculum at 3.4×108 CFU/mouse. Three days after infection induction mice received i.v. administrations of VCM (40 mg/kg) and RFB formulations (Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2; 20 mg/kg). Control group received buffer by intravenous route. (a) percentage of survival (Kaplan-Meier analysis), (b) average body weight, (c) bacterial burden in major organs at the end of treatment protocol, and (d) growth index. Lipid compositions: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP1) and DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG (RFB-LIP2). Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=5-6). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 vs Control group.
Figure 9.
In Vivo Assay 2—Representative images of histological analysis of major organs collected from mice induced with systemic MRSA-C1 infection (3.4×108 CFU/mouse): Buffer-treated (Control), treated with VCM at a dose of 40 mg/kg of body weight, and with RFB formulations (Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2) at a dose of 20 mg/kg of body weight. Black arrows indicate affected regions. (a) small single abscess; (c) extended coalescing foci of abscesses in the medulla with pyelonephritis; (g) large abscess in the medulla with presence of bacteria; (b, f, j, n, r) white pulp germinal center apoptosis minimal; (s) minimal inflammatory infiltrates in the interstitium. LIP1: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG; LIP2: DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Figure 9.
In Vivo Assay 2—Representative images of histological analysis of major organs collected from mice induced with systemic MRSA-C1 infection (3.4×108 CFU/mouse): Buffer-treated (Control), treated with VCM at a dose of 40 mg/kg of body weight, and with RFB formulations (Free RFB, RFB-LIP1 and RFB-LIP2) at a dose of 20 mg/kg of body weight. Black arrows indicate affected regions. (a) small single abscess; (c) extended coalescing foci of abscesses in the medulla with pyelonephritis; (g) large abscess in the medulla with presence of bacteria; (b, f, j, n, r) white pulp germinal center apoptosis minimal; (s) minimal inflammatory infiltrates in the interstitium. LIP1: DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG; LIP2: DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Table 1.
Susceptibility of planktonic S. aureus strains to RFB and VCM in the free form, assessed by turbidity.
Table 1.
Susceptibility of planktonic S. aureus strains to RFB and VCM in the free form, assessed by turbidity.
| |
MIC (μg/mL) |
|
S. aureus strain |
RFB |
VCM |
| MRSA-C1 |
0.009 ± 0.004 |
1.226 ± 0.459 |
| MRSA-C2 |
0.012 ± 0.001 |
1.875 ± 0.000 |
Table 2.
Susceptibility of biofilm S. aureus strains to RFB and VCM in the free form.
Table 2.
Susceptibility of biofilm S. aureus strains to RFB and VCM in the free form.
| |
MBIC50 (μg/mL) |
|
S. aureus strain |
RFB |
VCM |
| MRSA-C1 |
0.010 ± 0.006 |
>800 |
| MRSA-C2 |
0.012 ± 0.002 |
>800 |
Table 3.
Physicochemical properties of RFB liposomal formulations.
Table 3.
Physicochemical properties of RFB liposomal formulations.
| Formulation |
Lipid composition
(molar ratio) |
Loading capacity
(μg RFB/µmol lipid) |
I.E.
(%) |
Ø (nm)
(PdI) |
ζ pot.
(mV) |
| RFB-LIP1 |
DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG
(65:30:5) |
43 ± 5 |
55 ± 9 |
108 ± 8
(<0.1) |
-5 ± 1 |
| RFB-LIP2 |
DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG
(65:30:5) |
36 ± 4 |
43 ± 7 |
110 ± 6
(<0.1) |
-5 ± 1 |
| RFB-LIP3 |
DMPC:DMPG
(80:20) |
36 ± 2 |
54 ± 3 |
108 ± 9
(<0.1) |
-14 ± 1 |
| RFB-LIP4 |
DPPC:DPPG
(80:20) |
37 ± 4 |
47 ± 8 |
116 ± 4
(<0.1) |
-15 ± 1 |
| Unloaded-LIP1 |
DMPC:DMPG:DSPE-PEG
(65:30:5) |
N.A. |
N.A. |
110 ± 11
(<0.1) |
-5 ± 1 |
| Unloaded-LIP2 |
DPPC:DPPG:DSPE-PEG
(65:30:5) |
N.A. |
N.A. |
114 ± 7
(<0.1) |
-5 ± 1 |
| Unloaded-LIP3 |
DMPC:DMPG
(80:20) |
N.A. |
N.A. |
108 ± 12
(<0.1) |
-15 ± 2 |
| Unloaded-LIP4 |
DPPC:DPPG
(80:20) |
N.A. |
N.A. |
121 ± 3
(<0.1) |
-15 ± 3 |
Table 4.
Susceptibility of planktonic and biofilm MRSA-C1 to tested RFB formulations.
Table 4.
Susceptibility of planktonic and biofilm MRSA-C1 to tested RFB formulations.
| Formulation |
MIC (μg/mL) |
MBIC50 (μg/mL) |
| Free RFB |
0.009 ± 0.004a
|
0.010 ± 0.006 |
| RFB-LIP1 |
0.013a |
0.008 ± 0.001 |
| RFB-LIP2 |
0.013a
|
0.008 ± 0.001 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).