1. Introduction
In many brain perfusion studies, contrast agents are used [
1]. Although relatively low toxicity of current gadolinium-based contrast agents, the possibility of negative side effects in long term perspective are arising [
2]. A contrast-free MRI perfusion imaging method would improve clinical scanning protocols safety. Such possibility arises when considering IVIM based perfusion studies.
IVIM MRI at first was described by Le Bihan in 1986 [
3] as an extension of diffusion MRI (dMRI) that explores the random movement of molecules [
4], particularly water, within biological tissues. This movement, known as diffusion, results from molecular collisions and follows a random walk pattern or so called Brownian motion [
5]. A dMRI sequence, at first used a modified by Stejskal an Tanner [
6] spin-echo sequence, where MR echo signal was sensitized to water molecules diffusion speed by applying magnetic field gradient pulses. Resulting exponential decrease of measured MR signal depends on the product of the diffusion coefficient (
) and the magnitude of sensitization, the so-called
-value (later in this work referred as
or
-value).
In IVIM MRI, the movement of water caused by blood flow in the vessel network aligned in multiple directions within a voxel, can be considered as a fast (pseudo-diffusion,
) component. This pseudo-diffusion component, together with extravascular component (regular diffusion,
) contribute to MR signal attenuation, allowing both tissue diffusion and blood microcirculation to be detected and separated [
7]. Thus, the overall dMRI signal, as a combination of fast and regular components, can be described by a bi-exponential signal decay model given by Eq. (1)
Where:
represents the measured signal intensity in the DWI image for a given .
stands for b-value – diffusion weighting factor, determined by the strength and timing of diffusion gradients prior to signal echo.
is the signal intensity in the absence of diffusion weighting ().
represents the fraction of signal coming from quick diffusing water molecules, which are assumed to be circulating blood.
is the pseudo-diffusion coefficient, which reflects the diffusion of water in capillaries and small vessels.
represents the true diffusion coefficient, which characterizes the diffusion of extravascular water molecules.
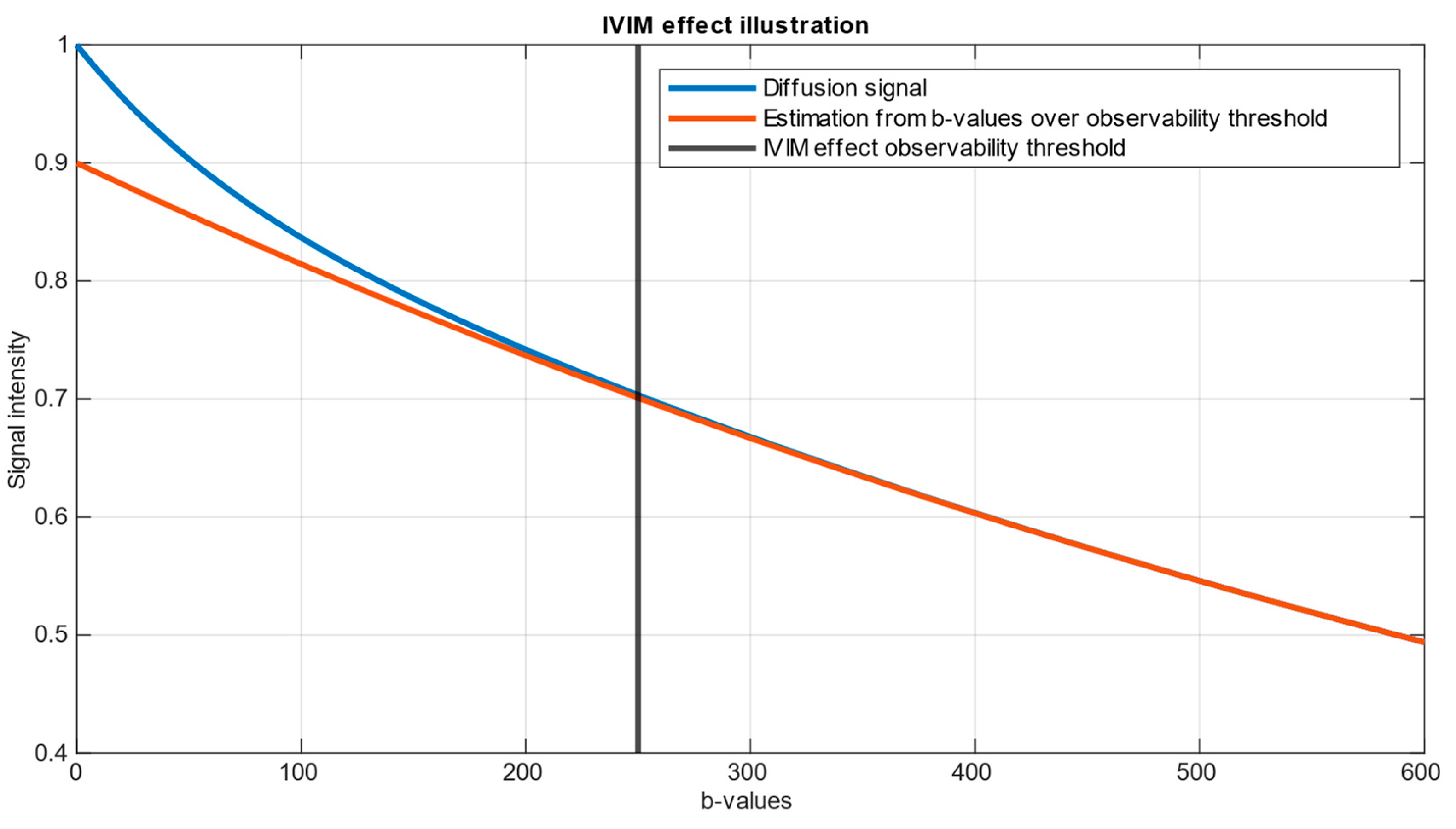
An illustration of example Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) dataset is presented on
Figure 1. The parameters chosen for this representation are
. These values were selected to demonstrate a clear and explanatory IVIM dataset, generated in accordance with Eq. (1)
The primary aim of this study was to investigate the impact of SNR on the estimation of f, D, and D* parameters with the IVIM technique. By employing multiple methods of parameter estimation, the study aims to compare their efficacy and identify potential strengths and weaknesses in particular SNR ranges and region sizes.
While previous studies have extensively explored the applications of the IVIM technique in various medical fields, especially in pathological conditions [
9,
10,
11], the influence of SNR on the accuracy of IVIM parameter determination remains insufficiently investigated in terms of clinical, time limited, whole brain scanning, only partially covered by simulations in silico [
12]. This study, in contrast to other studies that were conducted for IVIM specific exam, which took most of the scanner time, aims to assess quick IVIM scanning protocol as additional series to regular, clinical acquisition protocol. Quick IVIM protocols may be useful for example during the acute stroke phase, where imaging have to be completed in less than 10 minutes [
13] or as a DWI extension for additional screening that provides regular DWI measures but does not take too much excessive time.
One of the techniques that may help overcome SNR issues is voxel clustering or averaging signal from atlas-based regions of interest. Although in the context of brain imaging, where gray matter exhibits thicknesses of approximately 2-3 mm, in diffusion-weighted images this tissue effectively occupies nearly whole voxel between white matter (WM) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Quality of single voxel estimation rather than clustered approach should also be investigated, as in this tissue precise drawing large ROIs, may be difficult.
2. Materials and Methods
To estimate feasibility of whole brain IVIM studies in context of clinical, time limited protocols following steps were conducted:
To assess the chance of performing an accurate IVIM MRI parameters estimation, the SNR level must be known as a crucial factor determining the reliability and precision of estimation. Signal-to-noise ratio plays a significant role in DWI, influencing the ability to distinguish subtle signal variations, related to diffusion, from noise in the acquired images. A higher SNR allows for better discrimination between true signal changes related to perfusion effects and random fluctuations. Therefore, knowledge on the SNR level is essential for ensuring and estimating the robustness and validity of IVIM MRI analyses.
Considering this protocol to be as quick as possible, scanning duration was set with a maximum limit of 15 minutes. To ensure maximum available SNR level a MUSE sequence was used [
14]. While planning an experiment we tried selecting b-values accessible on the scanner, close to an optimized set [
15]. Under these conditions GE MR 3T Pioneer scanner with 21 channel head/neck coil was able to acquire images for 10
-values (1200 1000 700 500 200 120 80 50 20 10) measured in three orthogonal directions and five
(no diffusion weighing). Echo Time (TE) was set to 85 ms, Repetition Time (TR) 14,3 s. Voxel dimensions were 1x1 mm in plane resolution, 2 mm slice thickness, 72 slices (whole brain coverage), slice gap 0, phase acceleration factor was set to 2 and NEX 1 for all b-values. Two anatomical sequences were applied T1 MP-RAGE TR 1370.36 ms TE 2.228 ms TI 718.0 ms flip angle 7
1 mm cubic voxel; and CUBE T2, TE 71 ms, TR 2800 ms, 1mm cubic voxel, reconstructed to 0.5x0.5.x1mm voxel.
The diffusion data went through a preprocessing procedure, involving five steps: denoising, removal of Gibbs ringing artifacts, correction of susceptibility-induced distortions, eddy current correction, and DWI bias field correction. Denoising was performed using Marchenko-Pastur Principal Component Analysis [
16,
17,
18],while Gibbs ringing artifacts was mitigated through the method of local subvoxel-shifts [
19], and implemented in MRTrix [
20]; susceptibility induced distortions correction and eddy current correction was corrected using FSL [
21]; and B1 Inhomogeneity correction using N4 algorithm [
22] implemented in ANTs [
23]. Preprocessed data underwent brain extraction procedure with MRTrix. SNR was calculated from 5
scans as mean signal and standard deviation quotient in MATLAB [
24] for brain extracted images. Normalization of IVIM data to MNI152 space [
25] using MRTrix algorithms. To match structures in MNI space, patient’s
scan underwent extraction that was followed by brain masking. Subsequently, the histogram of the extracted image was non-linearly adjusted to match the histogram of symmetrical 1mm
3 T2 template. The image was then registered to the template using affine, followed by non-linear transformation. Two transformation matrices were computed: one for aligning the patient’s image to the template space and another for aligning the template to the patient’s space. Using abovementioned transform, Brodmann atlas aligned in MNI space [
26] was transformed to patient space and regridded to IVIM data using nearest neighbor interpolation method. Quality of matching was visually inspected. IVIM parameter estimations for 80 Brodmann areas (40 from left and 40 from right hemisphere) were computed based on the averaged signal from the specified region after normalizing each voxel to its maximal value.
FSL FMRIB’s Automated Segmentation Tool was used on T1 and T2 image to create white matter and gray matter maps. As T1 and IVIM MRI were acquired as first and last imaging sequence respectively, thus coregistration of T1 to
IVIM scan was necessary because of discrepancies in spatial alignment caused by patient movement. This coregistration was performed using SPM12 [
27] using Normalized Mutual Information objective function. Similarly to the above IVIM parameter estimations for white matter and grey matter were computed based on the averaged signal from the region after normalizing each voxel to its maximal value.
To evaluate the accuracy of the IVIM MRI parameter estimation methods, a simulated environment is created. The IVIM signal is generated in silico, mimicking real-world conditions, with known ground truth values assigned to key parameters such as perfusion fraction (
), diffusion coefficient (
), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (
), and baseline signal intensity (
). This allows for the latter comparison of estimated values with the true values, providing a controlled setting to assess the reliability of the estimation methods. These were conducted using MATLAB and included the generation of synthetic IVIM MRI data using the four-parametric model described by Eq. (1). According to literature, in grey matter (GM)
,
,
and are in range of, respectively
,
,
, which was summarized in [
28]. To conduct further study, values from mentioned ranges were chosen to represent IVIM parameter values as a sample from human brain. Following values were assigned as ground truth
.
To replicate the noise inherent in real-world MRI data, Rician noise is introduced to the simulated IVIM signals. The application of noise ensures that the simulated data resembles the complexities of experimental data, allowing for evaluation of the parameter estimation quality.
Random Rician-distributed noise, as shown in Eq. (2) was added to create a multiple realization of IVIM data. The amplitude of real and imaginary parts of Rician noise were adequately set to represent SNR levels from 15 to 50. Simulations finally consisted of
realizations for each SNR level.
Where:
represents the “ground truth” signal,
represents the noised signal,
are respectively real and imaginary parts of noise.
For every realization, parameters
,
,
and
were estimated with three methods commonly found in literature [
29]: one-step curve fitting, two-step curve fitting, two-step grid search algorithm. The one-step fitting method involves simultaneous estimation of all parameters, while the two-step methods separate the estimation into two distinct stages. First stage aims to estimate regular diffusion coefficient (D), for b-value greater than certain threshold, followed by the second stage where pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*) is estimated from remaining data, below threshold. This approach relies on observation that in data obtained for
-values above 250 blood fraction signal is close to 0 and below noise floor level [
8]. For both one-step (4-parameter) and two-step (2-parameter) fitting the Trust Regions nonlinear curve fitting method implemented in MATLAB Curve Fitting Tool [
30] was used, for grid search method an algorithm was implemented locally.
After estimation procedure, a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between estimated parameters
and known ground truth parameters was calculated according to Equation (3) for each parameter and SNR level:
Where:
is number of realizations,
is a prediction for given parameter from single realization,
is a corresponding ground truth parameter value.
For three analyzed methods relative to ground truth was plotted as a function of SNR. Additionally, to simulate neighboring voxel averaging, estimates were calculated for every 8 (2x2x2), 27 (3x3x3) and 64 (4x4x4) averaged realizations.
3. Results
3.1. Estimation of scanner specific Signal to Noise Ratio
A healthy subject (M, age 55) was scanned with previously described protocol. Subject gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committee for project NCN OPUS 2018/31/B/ST7/01888.
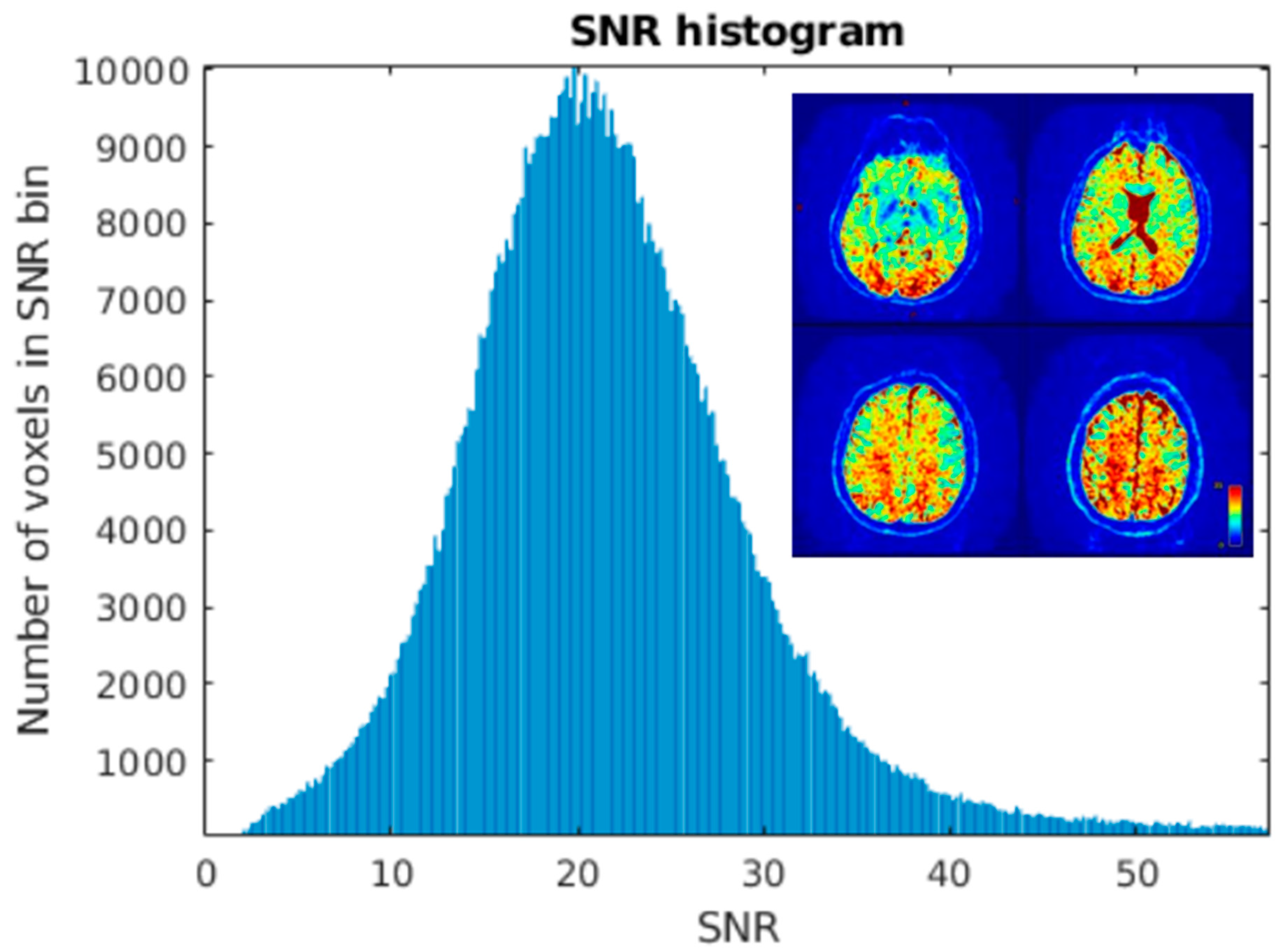
Brain extraction tool found brain occupying 1,011,294 of total 4,718,592 voxels (approx. 20% of scanned volume) and SNR in whole brain to have following parameters:
. Results are depicted on
Figure 2
SNR level was estimated for white matter and grey matter voxels separately, with use of FSL FAST segmentation with Tissue Probability Maps (TPM). Acquiring high resolution T2 data allowed for high precision separation of these two tissue types. The results were comparable to whole brain analysis and each other. Estimated parameters for white matter, based on 210523 voxels were as follows: . For grey matter, based on 68067 voxels .
3.2. Evaluation of accuracy
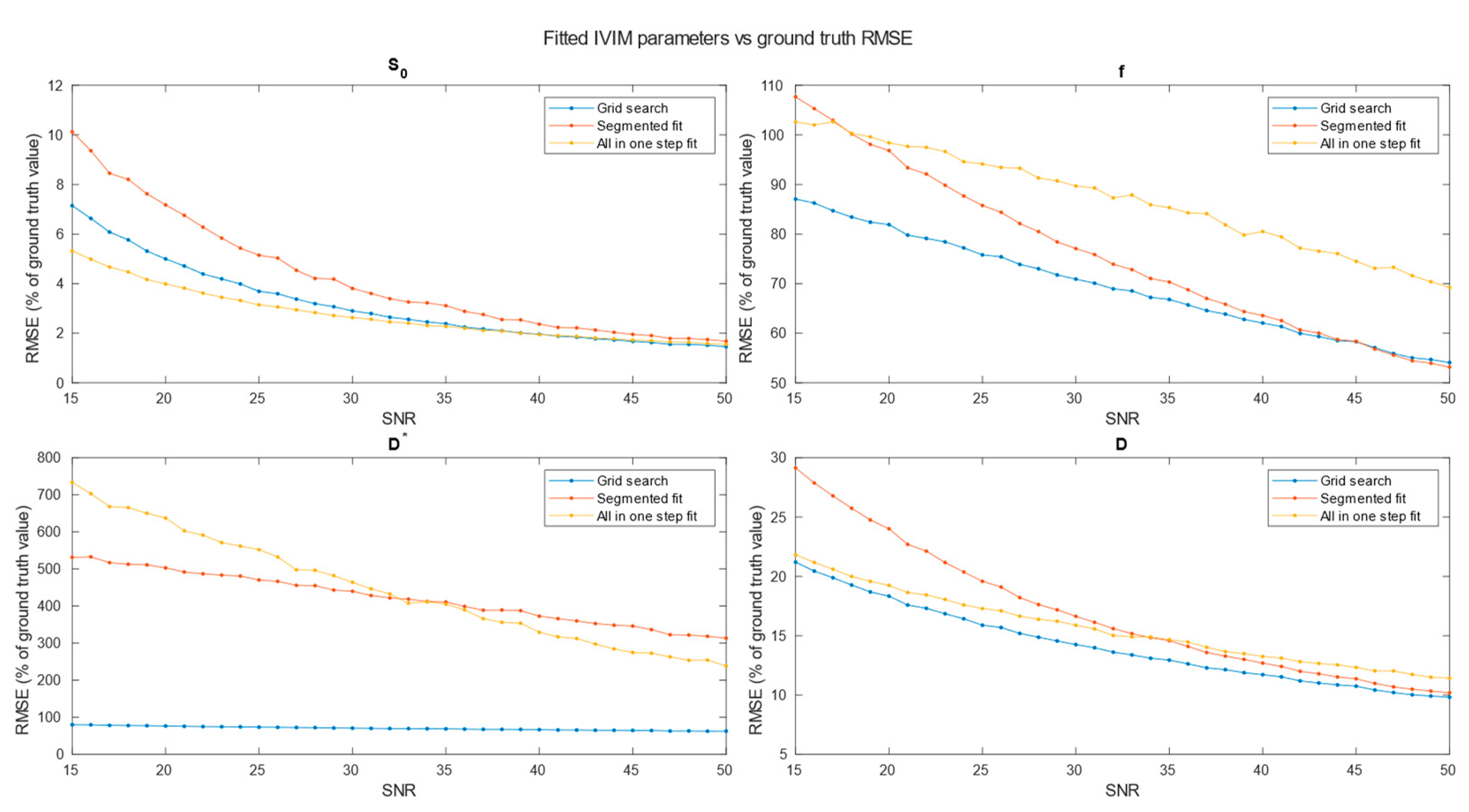
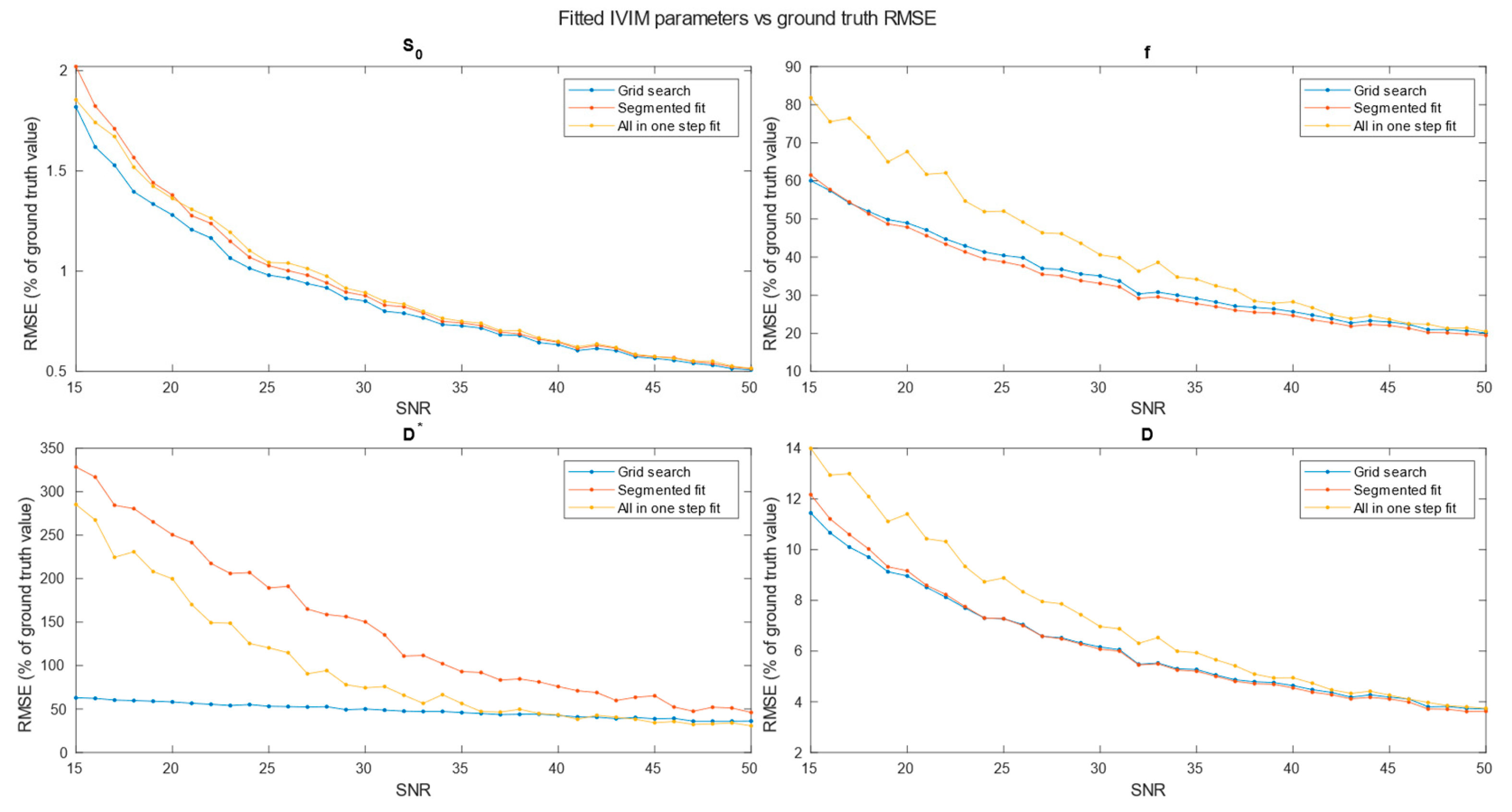
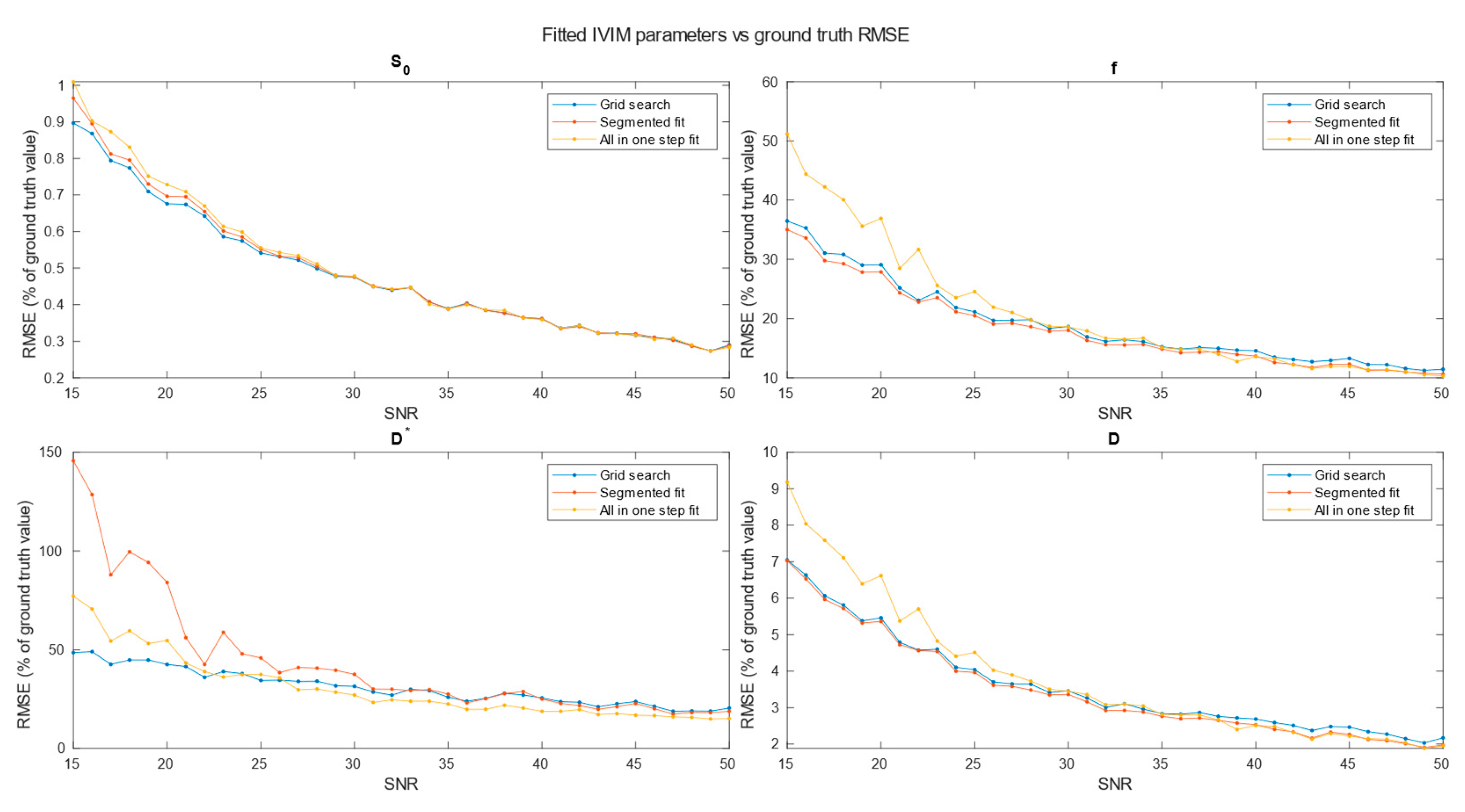
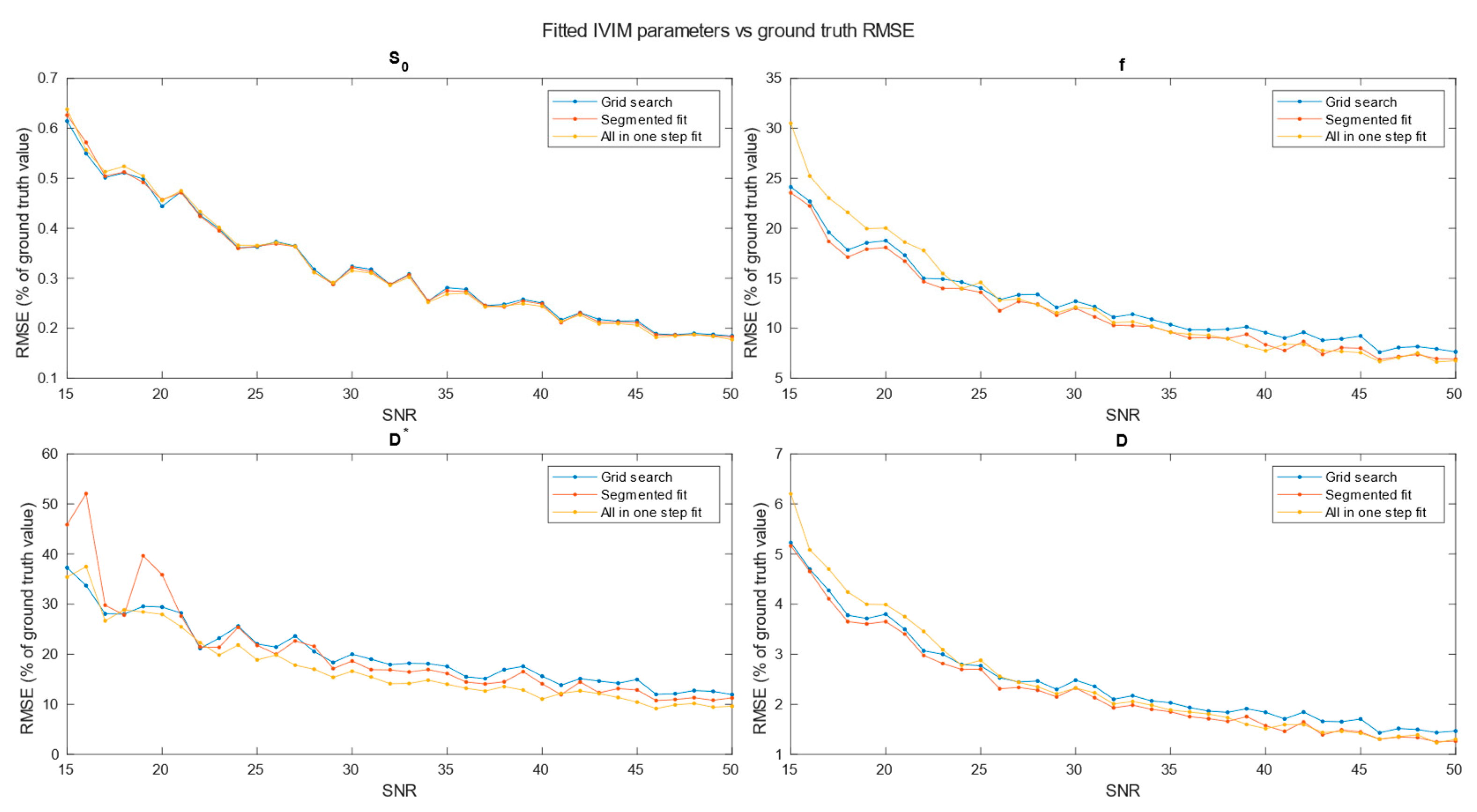
A comparison of RMSE in the function of SNR for three analyzed methods is shown on
Figure 4. Further tests included averaging simulation data before estimation for 2x2x2 (
Figure 5), 3x3x3 (
Figure 6), 4x4x4 (
Figure 7) neighboring voxels, which would be an equivalent of 2x2x4, 3x3x6 and 4x4x8 mm voxels/regions of interest respectively.
Values of relative RMSE, for SNR 20, closest to average SNR in conducted study, are presented in
Table 1.
3.3. Results from study
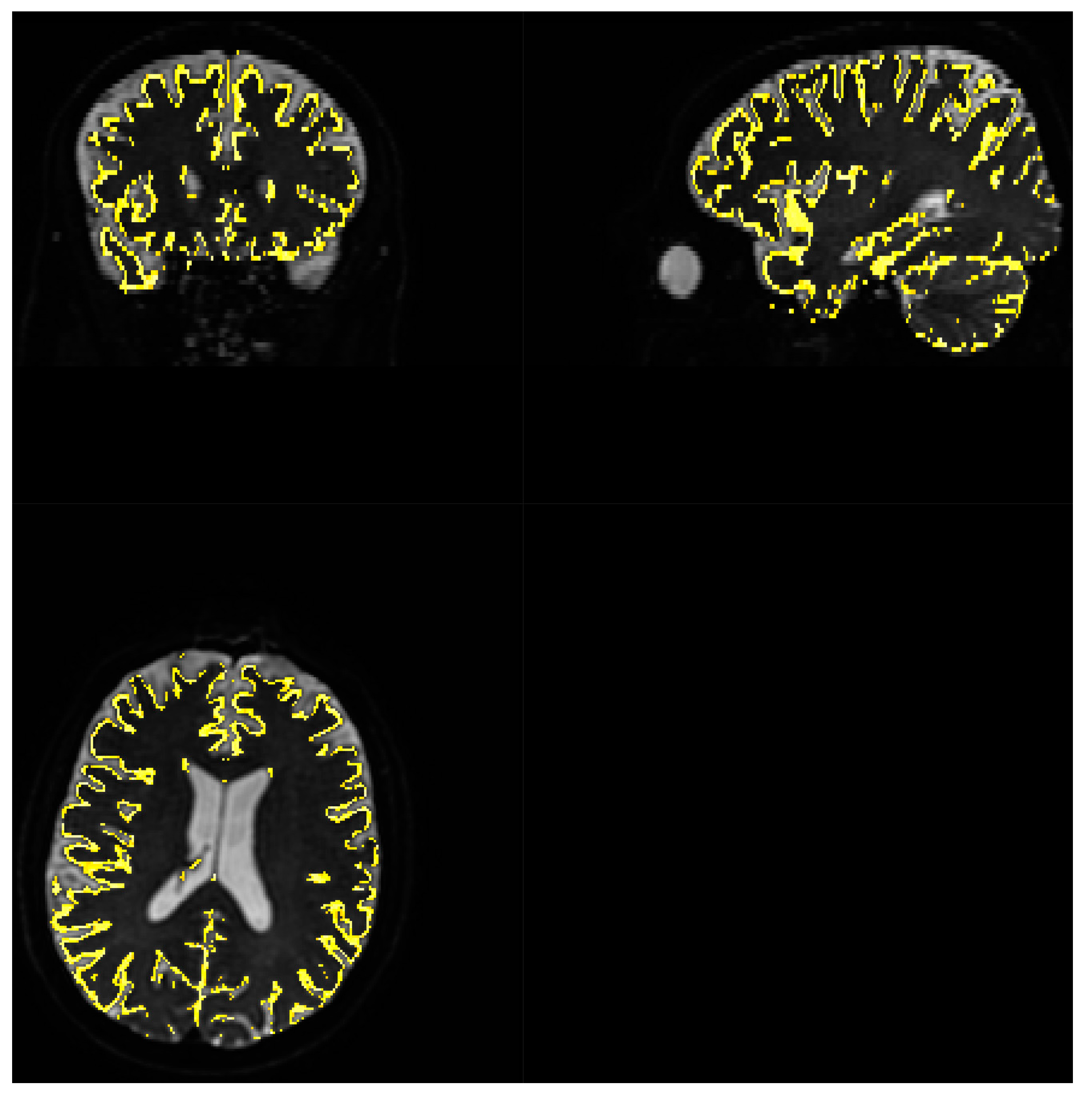
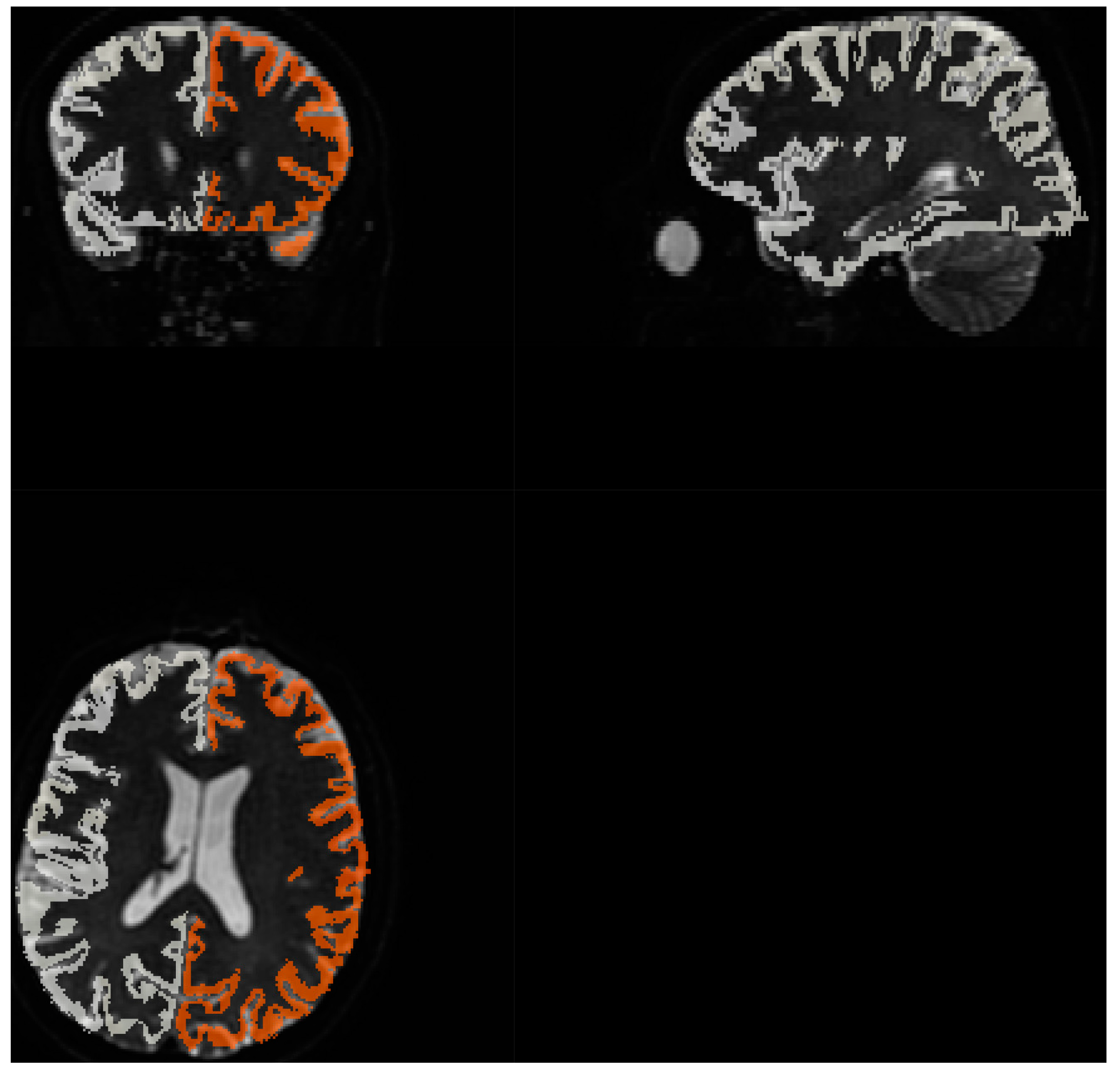
3.3.1. Quality of matching subject IVIM DWI data to T2 MNI template.
Fitting to template performed using MRTRix. Results are depicted on
Figure 8
3.3.2. Calculation of IVIM parameters
Calculation of IVIM parameters was performed in three ways: for white matter and grey matter, for each of Brodmann areas and single voxel. Results for WM and GM are presented in
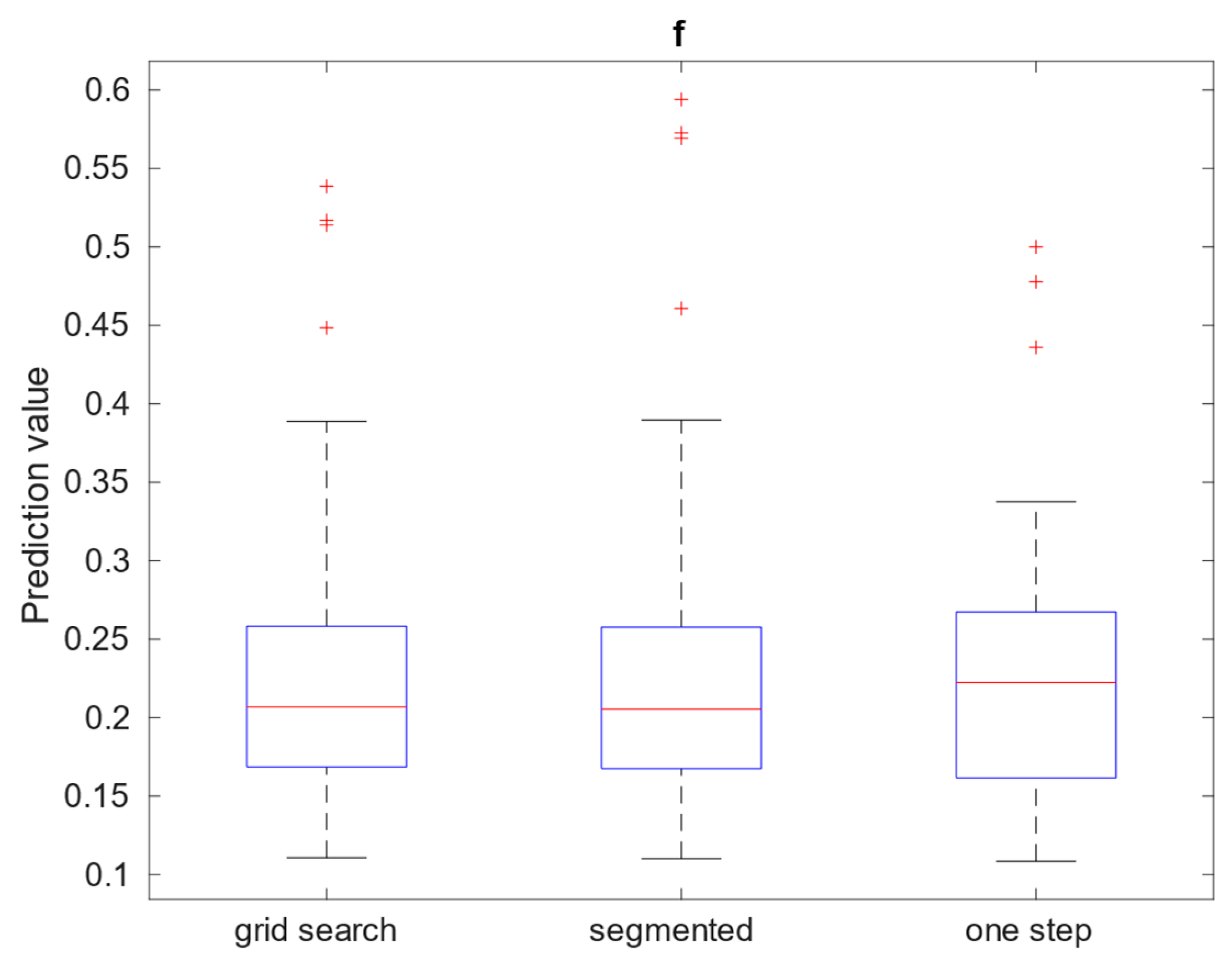
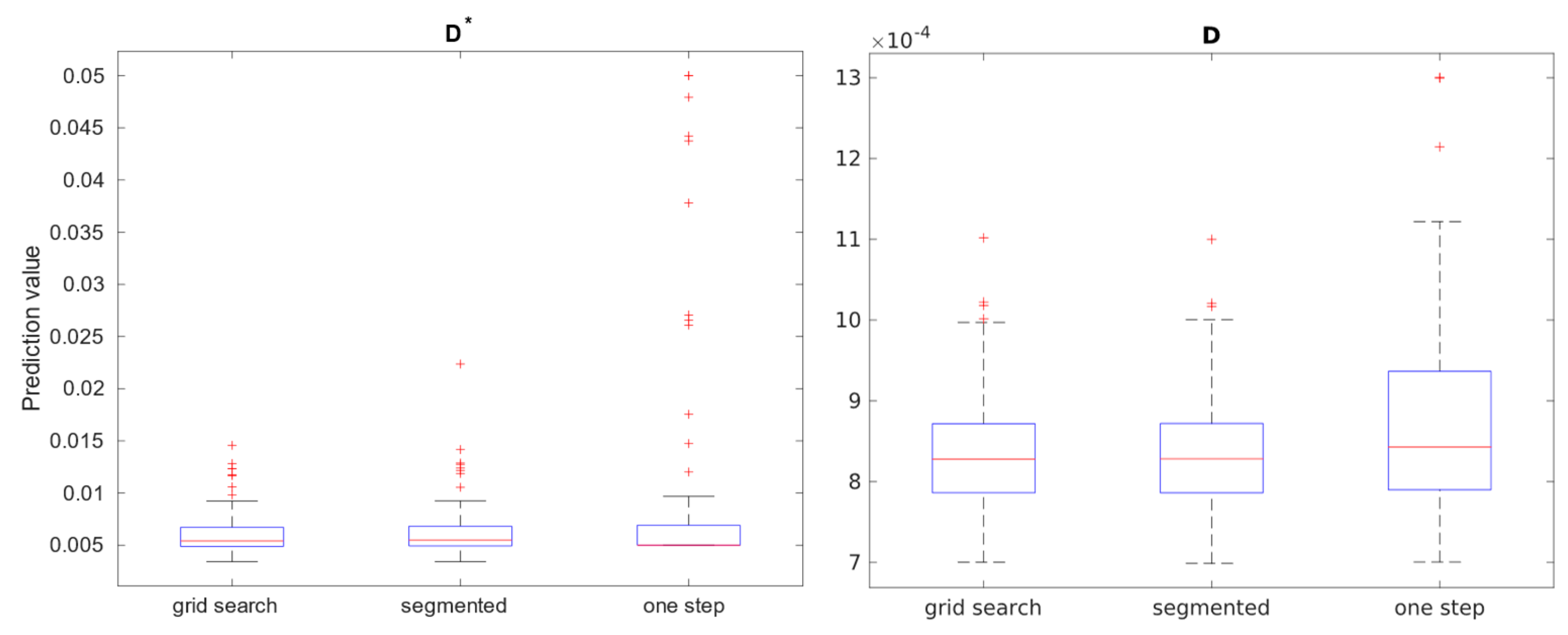
Table 2. The calculation of IVIM parameters for Brodmann areas is summarized using boxplots across all three methods. Three separate plots, containing 3 boxplots each, were prepared to illustrate results:
Figure 9 presents blood fraction estimation results and
Figure 10 presents pseudo-diffusion and diffusion estimation results. Each boxplot within single axes represents estimates from all 80 regions, calculated with given method. Within each boxplot, the central red mark signifies the median estimate, while the lower and upper edges denote the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively. The whiskers extend to the most extreme data points that are not considered outliers, with outliers plotted individually using the ’+’ marker symbol.
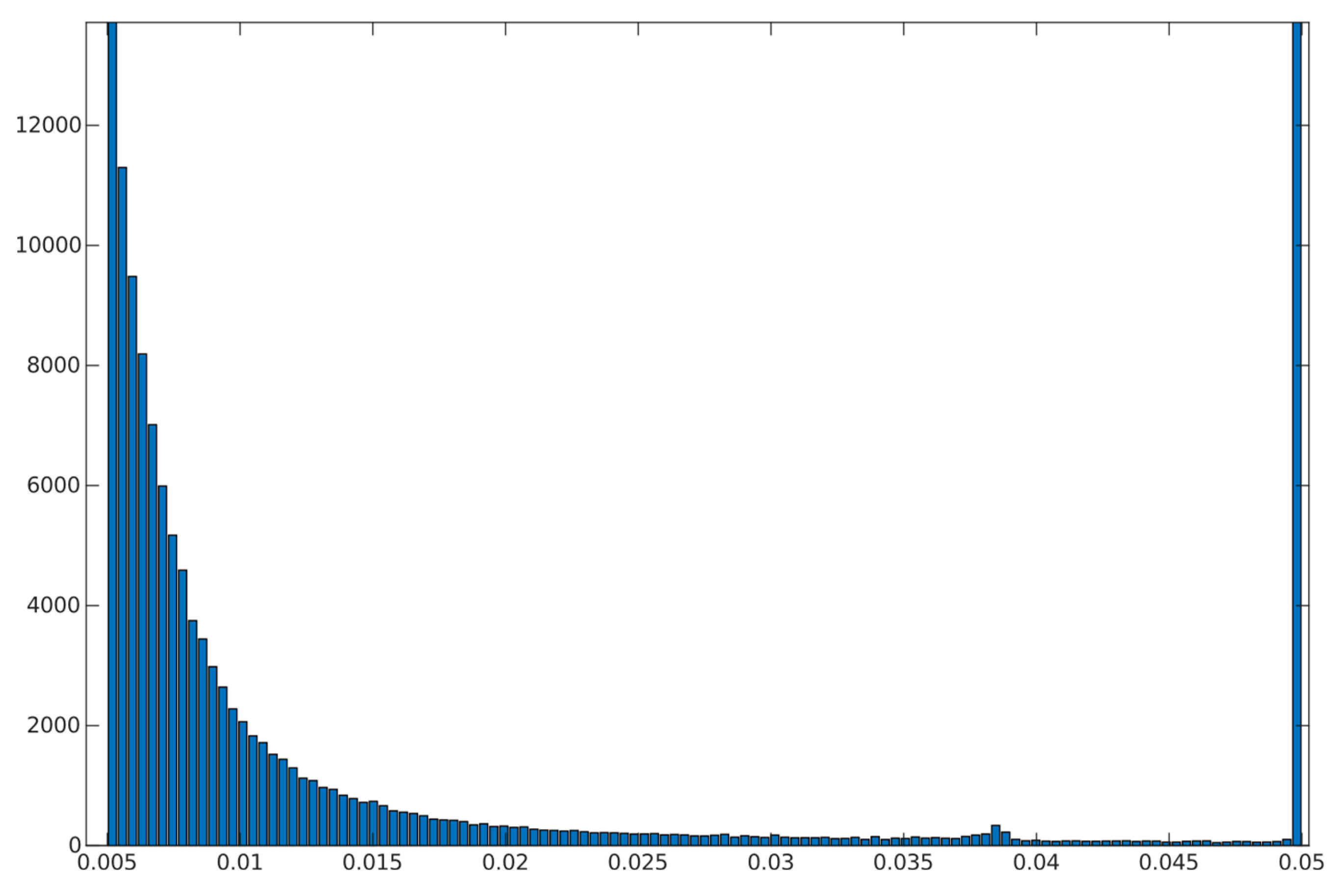
Out of 369832 voxels estimates from 56989 (approx. 15.42 %) were outliers that reached near 0 blood fraction . 70.02% of estimations fell in range .
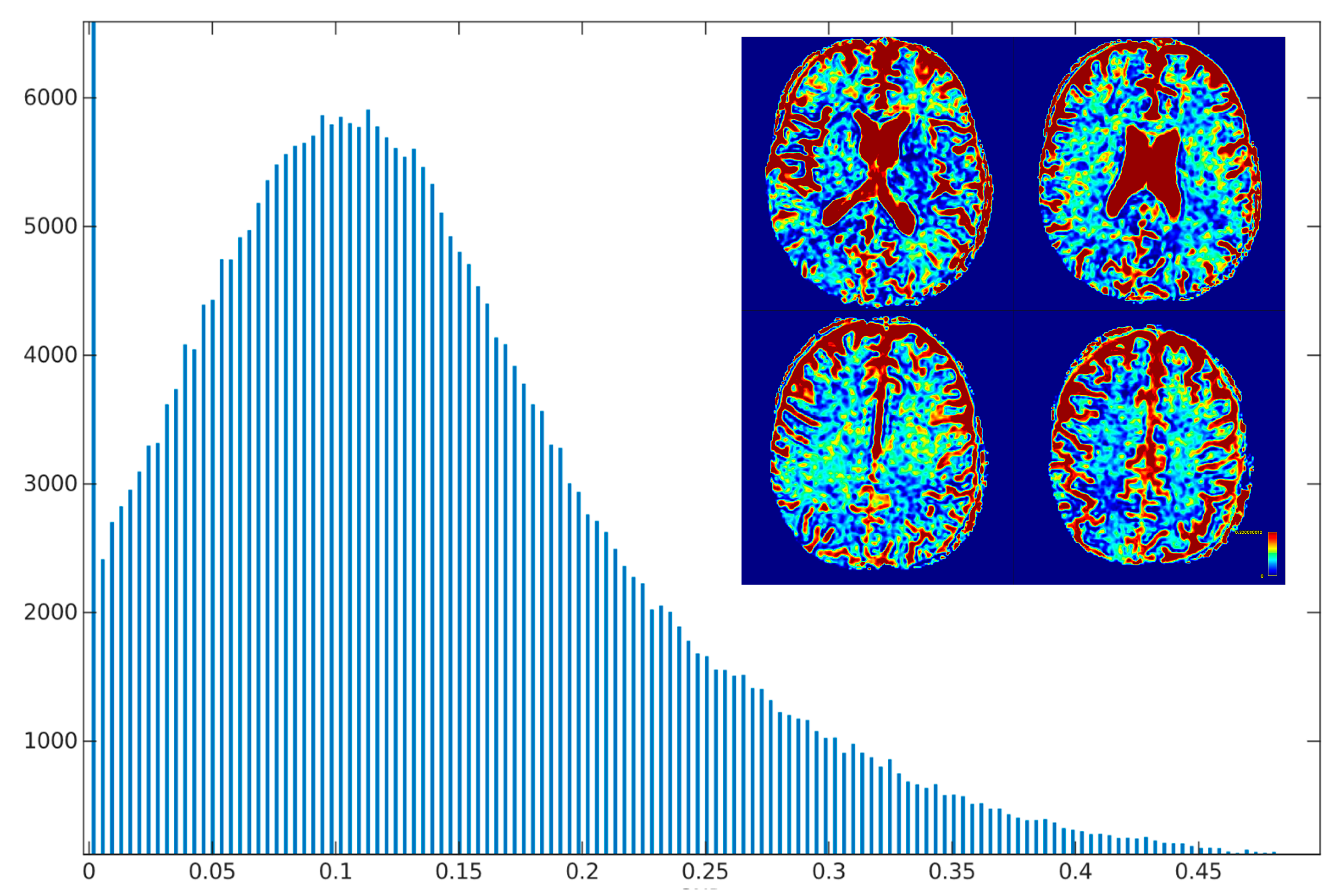
Figure 12.
Histogram and heatmap of estimate value (x-axis) on white and grey matter (sum of >70% TPM maps) voxels using grid search calculation method.
Figure 12.
Histogram and heatmap of estimate value (x-axis) on white and grey matter (sum of >70% TPM maps) voxels using grid search calculation method.
Over 54.82% of the estimates from voxels are considered outliers. 33.21% fell in range .
4. Discussion
The purpose of this study was to investigate IVIM estimation procedures in various SNR levels at medical conditions. Evaluation of accuracy was performed for commonly used techniques [
29]. SNR level is a factor of great importance whilst predicting IVIM parameters. Unfortunately, it is hard to achieve high while applying quick scanning techniques. One of the solutions is voxel clusterization. In many IVIM related papers such technique is used [
10,
12,
28,
31]. Another option for improving SNR is using multiple excitations for single Voxel as mentioned in [
15]. In all these works sizes of the voxels are much higher than in this paper (i. e. 1,8x1,8x5 mm [
28], 1,2x1,2x4 mm [
10], 2,75x2,75x5mm [
12], 1.14x1.14x4mm [
15], 1.5x1.5x6 mm [
32]) and have nonzero slice gap or are limited to lesser number of slices, both resulting in worse segmentation capabilities. Although in most publications
level is presented to be in range 10-30 for
, there are publications that states
in range 35-53 on
-value 1000 [
29] or even
[
15] which corresponds with
which is very unlikely to achieve in any scanning. To achieve precise results at high SNR level, one of the work total acquisition time was 52 min [
12]. Similar [
32] presents an optimal
vector for 12 minutes lasting sequence, but number of slices it is not clearly defined, so the brain coverage remains unknown. This raises the question of how to effectively implement a universal and repeatable IVIM diagnostic sequence.
We showed that high-resolution
and
estimates are consistent with the values reported in the literature for clustered or large voxel studies. Results are more consistent for segmented methods, while one step method requires better SNR level. IVIM estimates from signal averaged over white and grey matter ROIs, fit well with reports from previous studies [
28], also the vast majority of estimations for Brodmann areas fell within the ranges reported in the literature.
Some of the values presented appear to be outliers, which may stem from small areas or locally imperfect segmentation. All outliers may also have multiple causes like imperfect acquisition or patient movement (which was observed between scans). Patient movement is another factor emphasizing the importance to keep acquisition time in tight constraints.
High-resolution IVIM estimates from voxels mainly occupied by vessels, such as small arterials with relatively high blood flow [
33,
34], may yield high
and
estimates. Consequently, this could potentially result in categorizing them as outliers.
Our interpretation is that the lower estimation than in most of the literature may be a result of improved sampling precision in grey matter and Brodmann areas and thus lower CSF share in overall signal from tissue.
Specifically for our scanner, with measured SNR=20, RMSE of and on single voxel estimations reached 80-100% and 350-500% respectively. Ultimately on a better system achieving higher SNR level near 50 would lead to RMSE of single voxel blood fraction fit near 55%. RMSE of Blood pseudo-diffusion coefficient fit in all cases was above 70%, reaching 500-600% for curve fitting methods.
On the other hand, combining signal from 27 1x1x2 mm voxels in SNR range near estimated for our scanner RMSE of blood fraction parameter estimation was able to achieve level of 25% while estimation of improved from hundred percent relative RMSE error to roughly 60%. This suggests high potential for ROI based estimations, which was partially confirmed with estimations done on Brodmann areas.
5. Conclusions
The diffusion-based Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) method undoubtedly offers a non-invasive means to gain insights into blood flow parameters in perfused tissues. In this study, we estimated accuracy using the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) measure of a quick, high-resolution IVIM imaging protocol with three reconstruction methods, under the assumption of not exceeding a 15-minute scanning time. We demonstrated that it is possible to acquire IVIM data and estimate perfusion parameters from it. Despite the relative RMSE of IVIM estimates and results from human studies showing that all single voxel reconstruction methods are significantly error-prone at low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) levels, the measurements were still able to fall within expected ranges. Despite a significant number of outlier values, the estimation of is feasible in high-resolution quick IVIM, especially when considering the use of small ROIs. In terms of fitting for , the single voxel method appears to be not applicable. Simulations suggested high error value, which was confirmed with human study as over 50% of estimations reach the boundaries of estimation.
Acquiring high resolution IVIM DWI allowed for precise spatial alignment with template/atlas, as evidenced on
Figure 8. Visual observation leads to conclusion that Brodmann areas atlas is mostly well aligned with cortical structures.
The decision to average small voxel data rather than acquiring larger voxels may initially appear incongruent with the pursuit of high-resolution IVIM outcomes. However rather than decreasing spatial resolution, averaging data from multiple precisely selected voxels could improve diagnostic value of the data. Utilization of smaller voxels proves to be more beneficial, given the fact that with high resolution imaging sequence, it is possible to draw precise ROI for any structure. With imaging sequences that have more than 3 mm slice thickness or in plane resolution it is impossible to catch gray matter specific voxels, because of partial volume effects. Acquiring high resolution IVIM images allows to distinguish between WM, GM and CSF and limit the partial volume effect influence on parameter estimation.
Regarding selection of fitting techniques, in terms of precision estimation, in general it is advised to use segmented parameters fitting methods. In all SNR cases grid search and segmented curve fitting represent similar quality in terms of prediction, with favor for grid search algorithm at single voxel fitting. All in one step fitting becomes feasible only for high SNR and clustered voxels. In case of single voxel fitting, it is advised to use grid search, as the other methods become reliable for clustered voxel approach at significantly higher SNR levels or large clusters. Even for relatively large ROIs, such as Brodmann areas, fitting may produce imperfect results. These outlier values were estimated from the smallest Brodmann ROIs and also from the frontal cortex, which, considering the patient’s supine position, may be subject to greater movement.
This study may be continued and extended in terms of gathering more data on patients, search for applications and testing multiple scanners and scanning techniques towards finding an optimal whole brain quick scanning protocol. Advancements in this field would have potential to improve all perfusion related diagnostics as well as patients comfort and safety.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, K.L. and P.B..; methodology K.L and P.B.; software, K.L..; validation, K.L. and P.B.; formal analysis, P.B.; investigation, P.B.; resources, K.L. and P.B.; data curation, K.L. and P.B; writing—original draft preparation, K.L. writing—review and editing, P.B.; visualization, K.L.; supervision, P.B.; project administration, P.B.; funding acquisition, P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research was funded by Narodowe Centrum Nauki, grant number OPUS 2018/31/B/ST7/01888.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the local Ethics Committee of Narodowe Centrum Nauki OPUS 2018/31/B/ST7/01888.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
10.5281/zenodo.10599942.
Acknowledgments
Thank all of CNS Lab.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Essig, M.; Shiroishi, M.S.; Nguyen, T.B.; Saake, M.; Provenzale, J.M.; Enterline, D.; Anzalone, N.; Dörfler, A.; Rovira, À.; Wintermark, M.; et al. Perfusion MRI: The Five Most Frequently Asked Technical Questions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Grenier, P.; Cabanis, E.; Laval-Jeantet, M. MR Imaging of Intravoxel Incoherent Motions: Application to Diffusion and Perfusion in Neurologic Disorders. Radiology 1986, 161, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. On the Movement of Small Particles Suspended in Stationary Liquids Required by the Molecular-Kinetic Theory of Heat. Ann. Phys. 1905, 322, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R., XXVII. A Brief Account of Microscopical Observations Made in the Months of June, July and August 1827, on the Particles Contained in the Pollen of Plants; and on the General Existence of Active Molecules in Organic and Inorganic Bodies. Philos. Mag. 1828, 4, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, E.O.; Tanner, J.E. Spin Diffusion Measurements: Spin Echoes in the Presence of a Time-Dependent Field Gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 1965, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D.; Breton, E.; Lallemand, D.; Aubin, M.L.; Vignaud, J.; Laval-Jeantet, M. Separation of Diffusion and Perfusion in Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging. Radiology 1988, 168, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, D. What Can We See with IVIM MRI? NeuroImage 2019, 187, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iima, M. Perfusion-Driven Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) MRI in Oncology: Applications, Challenges, and Future Trends. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federau, C.; O’Brien, K.; Meuli, R.; Hagmann, P.; Maeder, P. Measuring Brain Perfusion with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM): Initial Clinical Experience. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 39, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Cercueil, J.-P.; Yuan, J.; Chen, W.; Loffroy, R.; Wáng, Y.X.J. Liver Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Comprehensive Review of Published Data on Normal Values and Applications for Fibrosis and Tumor Evaluation. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2017, 7, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydhög, A.S.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Lindgren, E.; Nilsson, M.; Lätt, J.; Ståhlberg, F.; Wirestam, R.; Knutsson, L. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Imaging at Different Magnetic Field Strengths: What Is Feasible? Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birenbaum, D.; Bancroft, L.W.; Felsberg, G.J. Imaging in Acute Stroke. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 12, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Pei, Y.; Liu, W.V.; Liu, W.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Zhong, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Masokano, I.B.; et al. MRI: Evaluating the Application of FOCUS-MUSE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Pancreas in Comparison With FOCUS, MUSE, and Single-Shot DWIs. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 57, 1156–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, C.; Zampini, M.A.; Morelli, L.; Buizza, G.; Fontana, G.; Anemoni, L.; Imparato, S.; Riva, G.; Iannalfi, A.; Orlandi, E.; et al. Optimizing B-values Schemes for Diffusion MRI of the Brain with Segmented Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Model. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraart, J.; Fieremans, E.; Novikov, D.S. Diffusion MRI Noise Mapping Using Random Matrix Theory. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veraart, J.; Novikov, D.S.; Christiaens, D.; Ades-Aron, B.; Sijbers, J.; Fieremans, E. Denoising of Diffusion MRI Using Random Matrix Theory. NeuroImage 2016, 142, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero-Grande, L.; Christiaens, D.; Hutter, J.; Price, A.N.; Hajnal, J.V. Complex Diffusion-Weighted Image Estimation via Matrix Recovery under General Noise Models. NeuroImage 2019, 200, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E.; Dhital, B.; Kiselev, V.G.; Reisert, M. Gibbs-Ringing Artifact Removal Based on Local Subvoxel-Shifts. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, J.-D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.-H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A Fast, Flexible and Open Software Framework for Medical Image Processing and Visualisation. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkinson, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.J.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M. FSL. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avants, B.; Tustison, N.J.; Song, G. Advanced Normalization Tools: V1.0. Insight J. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks Inc. MATLAB Version: R2023a 2023.
- Fonov, V.; Evans, A.; McKinstry, R.; Almli, C.; Collins, D. Unbiased Nonlinear Average Age-Appropriate Brain Templates from Birth to Adulthood. NeuroImage 2009, 47, S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijnenburg, R.; Scholtens, L.H.; Ardesch, D.J.; de Lange, S.C.; Wei, Y.; van den Heuvel, M.P. Myelo- and Cytoarchitectonic Microstructural and Functional Human Cortical Atlases Reconstructed in Common MRI Space. NeuroImage 2021, 239, 118274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 27. In Statistical Parametric Mapping: The Analysis of Funtional Brain Images, Friston, K.J., Ed.; 1st ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam; Boston, 2007; ISBN 978-0-12-372560-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chabert, S.; Verdu, J.; Huerta, G.; Montalba, C.; Cox, P.; Riveros, R.; Uribe, S.; Salas, R.; Veloz, A. Impact of b-Value Sampling Scheme on Brain IVIM Parameter Estimation in Healthy Subjects. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, E.M.; Novak, J.; Withey, S.B.; Zarinabad, N.; Dehghani, H.; Peet, A.C. Evaluation of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Fitting Methods in Low-Perfused Tissue: IVIM Fitting in Low-Perfused Tissue. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The MathWorks Inc. Curve Fitter 2023.
- Bisdas, S.; Klose, U. IVIM Analysis of Brain Tumors: An Investigation of the Relaxation Effects of CSF, Blood, and Tumor Tissue on the Estimated Perfusion Fraction. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2015, 28, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merisaari, H.; Federau, C. Signal to Noise and B-Value Analysis for Optimal Intra-Voxel Incoherent Motion Imaging in the Brain. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, M.J. Anatomy and Ultrastructure. In The Cerebral Circulation; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, 2009.
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Chang, C.; Fan, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, G. Caliber of Intracranial Arteries as a Marker for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).