Submitted:
19 February 2024
Posted:
20 February 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
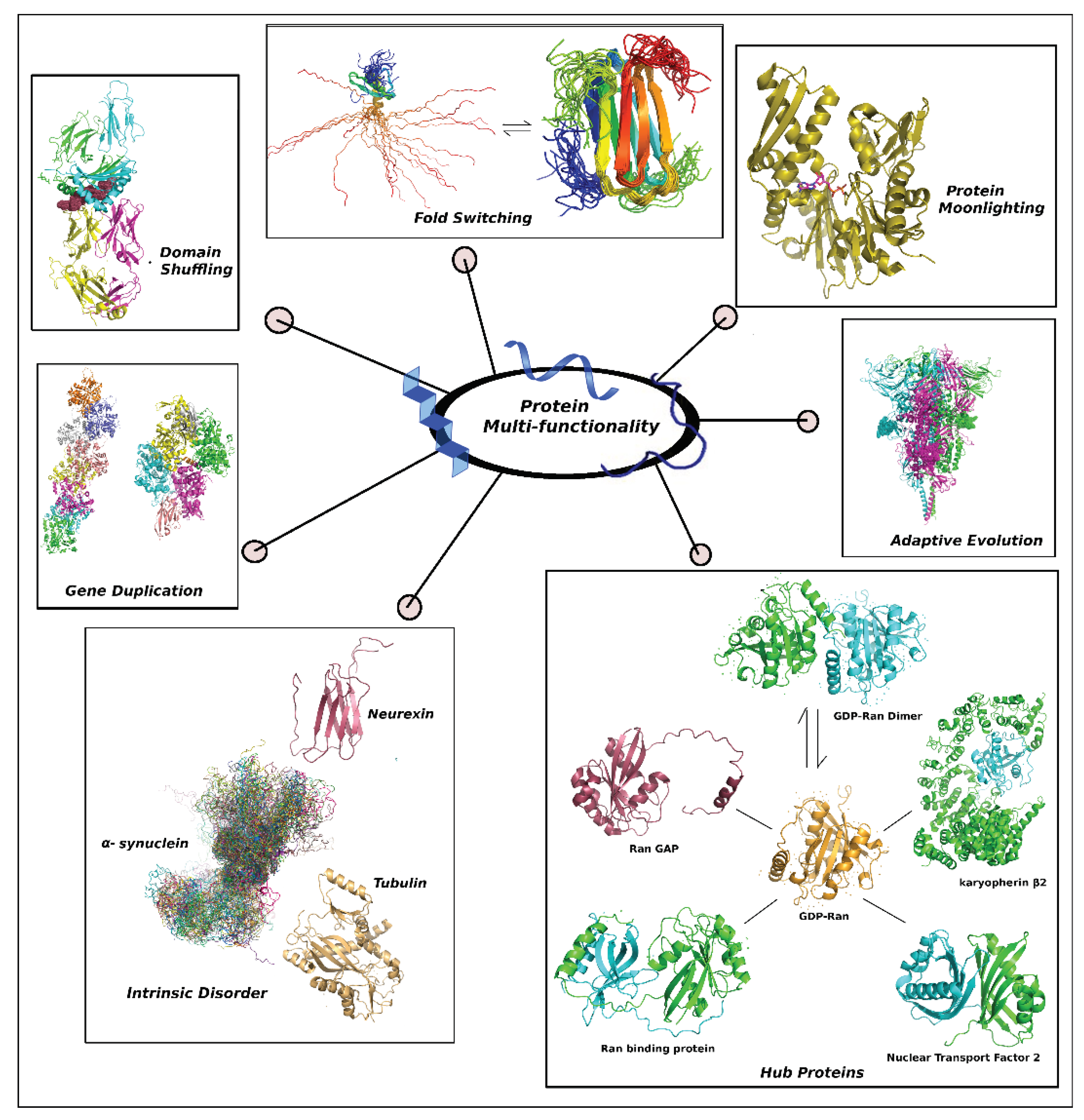
Protein Multi-Functionality from an Evolutionary Perspective
Biophysical Basis of Multi-Functionality in IDPs
Weaponry of Evolved Protein Multi-Functionality
Necessity of IDPs as SOS (Ad Hoc) Tools for Multi-Functionality in Higher Organisms
p53: Example of a Unique Idiosyncratic Multi-Functional Hybrid Protein with Functionally Crucial IDRs
Conclusion
References
- T. Sikosek, H.S. Chan, Biophysics of protein evolution and evolutionary protein biophysics, J R Soc Interface 11 (2014) 20140419. [CrossRef]
- N. Tokuriki, F. Stricher, L. Serrano, D.S. Tawfik, How Protein Stability and New Functions Trade Off, PLOS Comput Biol 4 (2008) e1000002. [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Cantú, D. Ascencio, F. Barona-Gómez, A. DeLuna, Gene duplication and the evolution of moonlighting proteins, Frontiers in Genetics 6 (2015). https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2015.00227 (accessed February 1, 2024).
- Domain Shuffling - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics, (n.d.). https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/domain-shuffling (accessed February 1, 2024).
- A.K. Dunker, J.D. Lawson, C.J. Brown, R.M. Williams, P. Romero, J.S. Oh, C.J. Oldfield, A.M. Campen, C.M. Ratliff, K.W. Hipps, J. Ausio, M.S. Nissen, R. Reeves, C. Kang, C.R. Kissinger, R.W. Bailey, M.D. Griswold, W. Chiu, E.C. Garner, Z. Obradovic, Intrinsically disordered protein, Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling 19 (2001) 26–59. [CrossRef]
- H. Brüssow, C. Canchaya, W.-D. Hardt, Phages and the Evolution of Bacterial Pathogens: from Genomic Rearrangements to Lysogenic Conversion, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68 (2004) 560–602. [CrossRef]
- N.E. Davey, G. Travé, T.J. Gibson, How viruses hijack cell regulation, Trends Biochem Sci 36 (2011) 159–169. [CrossRef]
- P.T. Fersht Alan, Structure and Function of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins, Chapman and Hall/CRC, New York, 2009. [CrossRef]
- H. Hegyi, P. Tompa, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Display No Preference for Chaperone Binding In Vivo, PLOS Computational Biology 4 (2008) e1000017. [CrossRef]
- K. Sugase, H.J. Dyson, P.E. Wright, Mechanism of coupled folding and binding of an intrinsically disordered protein, Nature 447 (2007) 1021–1025. [CrossRef]
- S. Basu, D. Bhattacharyya, R. Banerjee, Self-Complementarity within Proteins: Bridging the Gap between Binding and Folding, Biophys J 102 (2012) 2605–2614. [CrossRef]
- C.J. Tsai, S. Kumar, B. Ma, R. Nussinov, Folding funnels, binding funnels, and protein function, Protein Sci 8 (1999) 1181–1190. [CrossRef]
- Y. Levy, S.S. Cho, J.N. Onuchic, P.G. Wolynes, A Survey of Flexible Protein Binding Mechanisms and their Transition States Using Native Topology Based Energy Landscapes, Journal of Molecular Biology 346 (2005) 1121–1145. [CrossRef]
- P.E. Wright, H.J. Dyson, Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm, J. Mol. Biol. 293 (1999) 321–331. [CrossRef]
- H.J. Dyson, P.E. Wright, Coupling of folding and binding for unstructured proteins, Curr Opin Struct Biol 12 (2002) 54–60. [CrossRef]
- H.J. Dyson, P.E. Wright, Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions, Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 6 (2005) 197–208. [CrossRef]
- V.N. Uversky, Natively unfolded proteins: a point where biology waits for physics, Protein Sci 11 (2002) 739–756. [CrossRef]
- B.A. Shoemaker, J.J. Portman, P.G. Wolynes, Speeding molecular recognition by using the folding funnel: the fly-casting mechanism, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97 (2000) 8868–8873. [CrossRef]
- P.C. Simister, F. Schaper, N. O’Reilly, S. McGowan, S.M. Feller, Self-Organization and Regulation of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins with Folded N-Termini, PLOS Biology 9 (2011) e1000591. [CrossRef]
- C.A. Waudby, C.M. Dobson, J. Christodoulou, Nature and Regulation of Protein Folding on the Ribosome, Trends in Biochemical Sciences 44 (2019) 914–926. [CrossRef]
- K. Kamagata, E. Mano, Y. Itoh, T. Wakamoto, R. Kitahara, S. Kanbayashi, H. Takahashi, A. Murata, T. Kameda, Rational design using sequence information only produces a peptide that binds to the intrinsically disordered region of p53, Sci Rep 9 (2019) 8584. [CrossRef]
- S. Saurabh, K. Nadendla, S.S. Purohit, P.M. Sivakumar, S. Cetinel, Fuzzy Drug Targets: Disordered Proteins in the Drug-Discovery Realm, ACS Omega 8 (2023) 9729–9747. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yi, W. Liu, J.H. Seo, J. Su, M.A. Alaoui-Jamali, J. Luo, R. Lin, J.H. Wu, Discovery of a Small-Molecule Inhibitor Targeting the Androgen Receptor N-Terminal Domain for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer, Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 22 (2023) 570–582. [CrossRef]
- T. Gruber, M. Lewitzky, L. Machner, U. Weininger, S.M. Feller, J. Balbach, Macromolecular Crowding Induces a Binding Competent Transient Structure in Intrinsically Disordered Gab1, Journal of Molecular Biology 434 (2022) 167407. [CrossRef]
- S. Mallik, D.S. Tawfik, E.D. Levy, How gene duplication diversifies the landscape of protein oligomeric state and function, Curr Opin Genet Dev 76 (2022) None. [CrossRef]
- T. Kawashima, S. Kawashima, C. Tanaka, M. Murai, M. Yoneda, N.H. Putnam, D.S. Rokhsar, M. Kanehisa, N. Satoh, H. Wada, Domain shuffling and the evolution of vertebrates, Genome Res 19 (2009) 1393–1403. [CrossRef]
- P.N. Bryan, J. Orban, Proteins that switch folds, Curr Opin Struct Biol 20 (2010) 482–488. [CrossRef]
- C.J. Jeffery, Protein moonlighting: what is it, and why is it important?, Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 373 (2018) 20160523. [CrossRef]
- M. Higurashi, T. Ishida, K. Kinoshita, Identification of transient hub proteins and the possible structural basis for their multiple interactions, Protein Sci 17 (2008) 72–78. [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S. Basu, Criticality in the conformational phase transition among self-similar groups in intrinsically disordered proteins: Probed by salt-bridge dynamics, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 1868 (2020) 140474. [CrossRef]
- Evolution by Gene Duplication | SpringerLink, (n.d.). https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-642-86659-3 (accessed January 23, 2024).
- A.L. Hughes, R. Friedman, Parallel Evolution by Gene Duplication in the Genomes of Two Unicellular Fungi, Genome Res 13 (2003) 794–799. [CrossRef]
- A.N. Nguyen Ba, B. Strome, J.J. Hua, J. Desmond, I. Gagnon-Arsenault, E.L. Weiss, C.R. Landry, A.M. Moses, Detecting Functional Divergence after Gene Duplication through Evolutionary Changes in Posttranslational Regulatory Sequences, PLoS Comput Biol 10 (2014) e1003977. [CrossRef]
- S.W. Fewell, J.L. Woolford, Ribosomal protein S14 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae regulates its expression by binding to RPS14B pre-mRNA and to 18S rRNA, Mol Cell Biol 19 (1999) 826–834. [CrossRef]
- M. Lynch, A. Force, The probability of duplicate gene preservation by subfunctionalization, Genetics 154 (2000) 459–473. [CrossRef]
- X. He, J. Zhang, Rapid subfunctionalization accompanied by prolonged and substantial neofunctionalization in duplicate gene evolution, Genetics 169 (2005) 1157–1164. [CrossRef]
- M. Fadri, A. Daquinag, S. Wang, T. Xue, J. Kunz, The Pleckstrin Homology Domain Proteins Slm1 and Slm2 Are Required for Actin Cytoskeleton Organization in Yeast and Bind Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate and TORC2, Mol Biol Cell 16 (2005) 1883–1900. [CrossRef]
- C.J. Jeffery, Multifunctional proteins: examples of gene sharing, Ann Med 35 (2003) 28–35. [CrossRef]
- C.J. Jeffery, Moonlighting proteins, Trends Biochem Sci 24 (1999) 8–11. [CrossRef]
- J. Piatigorsky, Gene Sharing and Evolution: The Diversity of Protein Functions, in: Gene Sharing and Evolution, Harvard University Press, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Baruah, P. Biswas, Designing pH induced fold switch in proteins, J. Chem. Phys. 142 (2015) 185102. [CrossRef]
- A.K. Kim, L.L. Porter, Functional and Regulatory Roles of Fold-Switching Proteins, Structure 29 (2021) 6–14. [CrossRef]
- N.A. Bernhardt, U.H.E. Hansmann, Multifunnel Landscape of the Fold-Switching Protein RfaH-CTD, J Phys Chem B 122 (2018) 1600–1607. [CrossRef]
- A.F. Moutinho, F.F. Trancoso, J.Y. Dutheil, The Impact of Protein Architecture on Adaptive Evolution, Mol Biol Evol 36 (2019) 2013–2028. [CrossRef]
- Hasiów-Jaroszewska, M.A. Fares, S.F. Elena, Molecular evolution of viral multifunctional proteins: the case of potyvirus HC-Pro, J Mol Evol 78 (2014) 75–86. [CrossRef]
- S. Roy, P. Ghosh, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Basu, Capturing a Crucial ‘Disorder-to-Order Transition’ at the Heart of the Coronavirus Molecular Pathology—Triggered by Highly Persistent, Interchangeable Salt-Bridges, Vaccines 10 (2022) 301. [CrossRef]
- P. Balaram, The murky origins of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of the COVID-19 pandemic, CURRENT SCIENCE 120 (2021) 4.
- Y. Araf, F. Akter, Y.-D. Tang, R. Fatemi, M.S.A. Parvez, C. Zheng, M.G. Hossain, Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: Genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines, J Med Virol 94 (2022) 1825–1832. [CrossRef]
- S.Q. Maulud, D.A. Hasan, R.K. Ali, R.F. Rashid, A.A. Saied, M. Dhawan, Priyanka, O.P. Choudhary, Deltacron: Apprehending a new phase of the COVID-19 pandemic, Int J Surg 102 (2022) 106654. [CrossRef]
- V.N. Uversky, Dancing Protein Clouds: The Strange Biology and Chaotic Physics of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins, J Biol Chem 291 (2016) 6681–6688. [CrossRef]
- X. Sun, E.H.A. Rikkerink, W.T. Jones, V.N. Uversky, Multifarious Roles of Intrinsic Disorder in Proteins Illustrate Its Broad Impact on Plant Biology, The Plant Cell 25 (2013) 38–55. [CrossRef]
- S. Basu, P. Biswas, Salt-bridge dynamics in intrinsically disordered proteins: A trade-off between electrostatic interactions and structural flexibility, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 1866 (2018) 624–641. [CrossRef]
- M. Már, K. Nitsenko, P.O. Heidarsson, Multifunctional Intrinsically Disordered Regions in Transcription Factors, Chemistry – A European Journal 29 (2023) e202203369. [CrossRef]
- K.M. Reid, H. Poudel, D.M. Leitner, Dynamics of Hydrogen Bonds between Water and Intrinsically Disordered and Structured Regions of Proteins, J Phys Chem B 127 (2023) 7839–7847. [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.J. Brown, A.K. Dunker, V.N. Uversky, Intrinsically disordered regions of p53 family are highly diversified in evolution, Biochim Biophys Acta 1834 (2013) 725–738. [CrossRef]
- E.A. Cino, R.C. Killoran, M. Karttunen, W.-Y. Choy, Binding of disordered proteins to a protein hub, Sci Rep 3 (2013) 2305. [CrossRef]
- G.W. Beadle, E.L. Tatum, Genetic Control of Biochemical Reactions in Neurospora*, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 27 (1941) 499–506. [CrossRef]
- P. Portin, A. Wilkins, The Evolving Definition of the Term “Gene,” Genetics 205 (2017) 1353–1364. [CrossRef]
- V.N. Uversky, p53 Proteoforms and Intrinsic Disorder: An Illustration of the Protein Structure–Function Continuum Concept, Int J Mol Sci 17 (2016) 1874. [CrossRef]
- S.A. Clark, N. Jespersen, C. Woodward, E. Barbar, Multivalent IDP assemblies: Unique properties of LC8-associated, IDP duplex scaffolds, FEBS Letters 589 (2015) 2543–2551. [CrossRef]
- M. Sickmeier, J.A. Hamilton, T. LeGall, V. Vacic, M.S. Cortese, A. Tantos, B. Szabo, P. Tompa, J. Chen, V.N. Uversky, Z. Obradovic, A.K. Dunker, DisProt: the Database of Disordered Proteins, Nucleic Acids Res 35 (2007) D786–D793. [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.H. Torpey, R.L. Isaacson, Intrinsically disordered proteins: modes of binding with emphasis on disordered domains, Open Biol 11 (n.d.) 210222. [CrossRef]
- W. Basile, M. Salvatore, C. Bassot, A. Elofsson, Why do eukaryotic proteins contain more intrinsically disordered regions?, PLoS Comput Biol 15 (2019) e1007186. [CrossRef]
- J.A. Zamora-Briseño, A. Pereira-Santana, S.J. Reyes-Hernández, D. Cerqueda-García, E. Castaño, L.C. Rodríguez-Zapata, Towards an understanding of the role of intrinsic protein disorder on plant adaptation to environmental challenges, Cell Stress and Chaperones 26 (2021) 141–150. [CrossRef]
- P.E. Wright, H.J. Dyson, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in Cellular Signaling and Regulation, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16 (2015) 18–29. [CrossRef]
- V.N. Uversky, Unusual biophysics of intrinsically disordered proteins, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1834 (2013) 932–951. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




