1. Introduction
Sensory systems like olfaction, vision, audition, etc., allow animals to interact with the external environment. Among these, olfaction is the oldest sensory system to evolve in organisms [
1]. Olfaction allows organisms with receptors for the odorant to identify food, potential mating partners, dangers, and enemies [
2]. In some nocturnal mammals like mice, as much as five percent of the genome is devoted to olfaction [
3]. Similar to animals, a mobile robot integrated with a chemical sensor can detect odors in the external environment. Robotic Odor source localization (OSL) is the technology that allows robots to utilize olfaction sensory inputs to navigate toward an unknown target odor source in the given environment [
4]. It has important applications including monitoring wildfires [
5], locating air pollution [
6], locating chemical gas leaks [
7], locating unexploded mines and bombs [
8], locating underground gas leaks [
9], and marine surveys such as finding hydrothermal vents [
10], etc.
Locating an unknown odor source requires an effective OSL algorithm guiding the robot based on sensor observations. Current OSL algorithms include bio-inspired methods that imitate animal olfactory behaviors, engineering-based methods that rely on mathematical models to estimate potential odor source locations and machine learning-based methods that use a trained model to guide the robot toward the odor source. The typical bio-inspired method includes moth-inspired algorithm that imitates male months mate-seeking behaviors [
11], where a robotic agent will follow a ‘surge/casting’ model [
12] to reach the odor source. Typical engineering-based methods includes the Particle Filter algorithm [
13], where the robot will use historic olfaction reading to predict the odor source location. Finally, typical machine learning-based OSL methods include deep supervised and reinforcement learning-based methods.
All of these approaches rely on olfaction (e.g., chemical and airflow) sensing to detect and navigate to the given odor source. However, approaches that rely solely on olfaction sensing struggle in turbulent airflow environments. In contrast, animals that operate in complex airflow environments often rely on multiple sensory systems like olfaction and vision for odor source localization. For example, humans often recognize the presence of an odor source of interest with olfaction (e.g., smelling a barbecue), and locate and navigate to the odor source using vision (e.g., locating the barbecue shop with vision). If there is no valid vision of the odor source, we may search for the source using olfaction sensing (e.g., moving towards the direction of greater odor concentration or against the direction of wind flow). Similarly, a robot with both olfaction and vision sensing capabilities (e.g., with a camera and chemical sensor) can find an unknown odor source more efficiently, compared to olfaction-only OSL navigation methods. Thus, this project departs from the existing OSL navigation methods in utilizing both robotic vision and olfaction for searching the odor source location. The core of this project involves designing an algorithm that utilizes both vision and olfaction sensing for locating an unknown odor source location.
The project proposes an effective sensor fusion approach that utilizes a vision method and bio-mimicking olfaction method to guide the robot toward an unknown odor source in a real-world obstacle-ridden search area with both laminar and turbulent airflow setups.
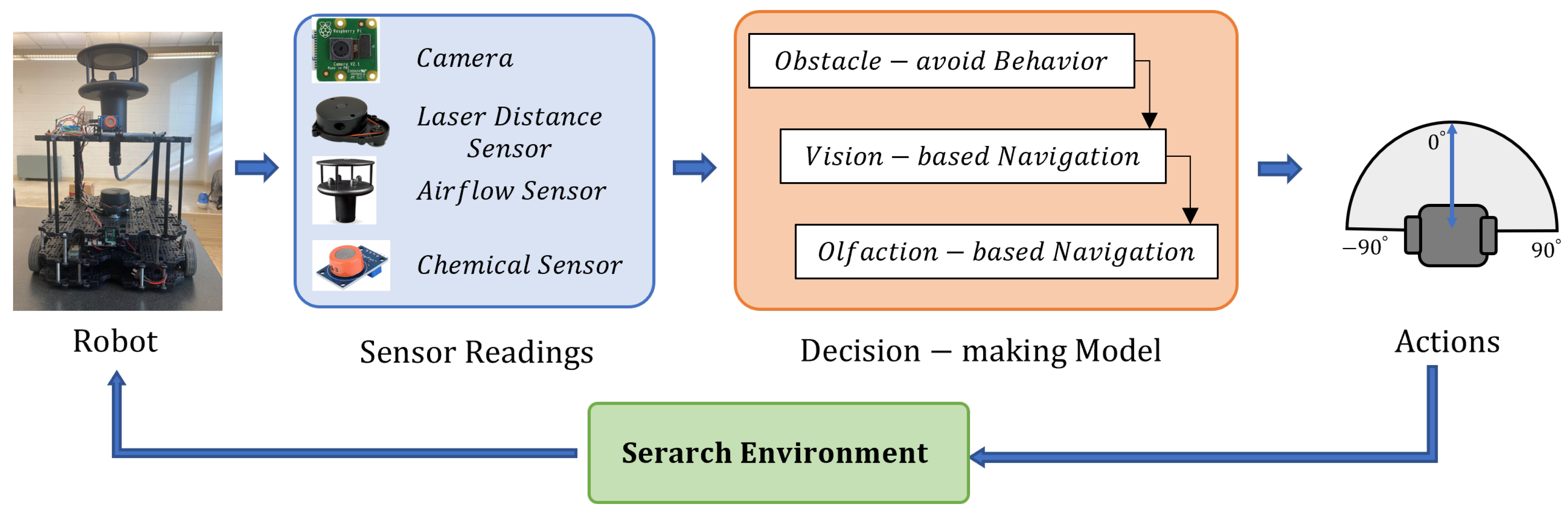
Figure 1 shows the proposed method, where we show the developed robot platform equipped with vision and olfaction sensors. The vision sensors include a camera, and the olfaction sensors include a chemical detector and anemometer. It also includes a Laser Distance Sensor (LDS) for obstacle detection. The sensor observations are transmitted to a decision-making model, which is implemented in a remote computer. The model selects Obstacle-avoid Navigation, Vision-based Navigation, or Olfaction-based Navigation behavior based on the sensor readings. In the proposed decision-making model, the robotic vision is achieved by a deep-learning vision model, and the robotic olfaction model is based on a bio-mimicking moth-inspired algorithm. Based on the current sensor reading, the active search behavior will calculate the robot heading commands, guiding the robot to approach the odor source location. Finally, the robot executes the heading command, collects new sensor readings at the new location, and repeats the loop until the odor source is detected.
In order to test the performance of our proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm, we conducted 30 real-world OSL experiments using Olfaction-only Navigation algorithm, Vision-only Navigation Algorithm, and the proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithms in both laminar and turbulent airflow environments. Contributions of this work can be summarized as:
Introduce vision as an additional sensing modality for odor source localization. For vision sensing, We trained a deep-learning-based computer vision model to detect odor sources from emitted visible plumes.
Develop a multimodal Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm with Obstacle-avoid Navigation capabilities for OSL tasks.
Compare the search performance of Olfaction-only and Vision-only navigation algorithms with the proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm in a real-world search environment with obstacles and turbulent airflow setups.
In the remaining of this paper,
Section 2 reviews the recent progress of olfactory-based navigation algorithms;
Section 3 reviews technical details of the proposed OSL algorithm;
Section 4 presents details of performing the real-world experiments;
Section 5 includes a discussion on the future research direction based on this work; and finally,
Section 6 includes overall conclusion of the work.
2. Related Works
Research on Robotic Odor Source Localization (OSL) has gained significant attention in recent decades [
14]. Technological advancements in robotics and autonomous systems have made it possible to deploy mobile robots for locating odor or chemical sources. Designing algorithms that mimic the navigation method of biological organisms is a typical approach in robotic odor source localization research. Organisms across various sizes rely on scent for locating objects. Whether it’s a bacterium navigating an amino acid gradient or a wolf tracking down prey, the ability to follow odors can be crucial for survival.
Chemotaxis is the simplest odor source localization approach in biological organisms, where they rely only on olfaction for navigation. For example, bacteria exhibit chemotaxis by adjusting their movement in response to changes in chemical concentration. When they encounter higher levels of an appealing chemical, their likelihood of making temporary turns decreases, promoting straighter movement. Conversely, in the absence of a gradient or when moving away from higher concentrations, the default turning probability is maintained [
15]. This simple algorithm enables single-celled organisms to navigate along a gradient of attractive chemicals through a guided random walk. Nematodes [
16] and crustaceans [
17] also, follow Chemotaxis-based odor source localization. Early attempts at robotic OSL focused on employing such simple gradient following chemotaxis algorithms. These methods utilized a pair of chemical sensors on plume-tracing robots, directing them to steer towards higher concentration measurements [
18]. Several early studies [
19,
20,
21,
22] validated the effectiveness of chemotaxis in laminar flow environments, characterized by low Reynolds numbers. However, in turbulent flow environments with high Reynolds numbers, alternative methods were proposed, drawing inspiration from both complex biological and engineering principles.
Odor-gated anemotaxis navigation is a more complex odor source localization method that utilizes senses of both odor and airflow for navigation. Moths [
23,
24,
25], birds [
26,
27], etc. organisms follow this type of navigation. In particular, mimicking the mate-seeking behavior of male moths led to the development of the moth-inspired method in robotic odor source localization. This method was successfully applied in various robotic OSL scenarios [
28]. Additionally, diverse bio-inspired search strategies like zigzag, spiral, fuzzy-inference, and multi-phase exploratory approaches have been introduced [
29] in odor-gate anemotaxis-based solutions. Recent bio-inspired OSL navigation methods also aimed to make the search environment more complicated. For instance, [
30] proposed a 3-dimensional (3-D) moth-inspired OSL search strategy that utilized cross-wind Lévy Walk, spiraling and upwind surge.
Engineering-based methods take a different approach than bio-mimicking algorithms, relying on mathematical models for estimating odor source locations. These methods are often times known as Infotaxis [
31]. These methods involve constructing source probability maps, dividing the search area into regions, and assigning probabilities indicating the likelihood of containing the odor source. Algorithms for constructing such maps include Bayesian inference, particle filters, stochastic mapping [
32], source term estimation [
33], information-based search [
34], partially observable Markov decision processes [
35], etc. Subsequently, robots are guided towards the estimated source via path planning algorithms such as artificial potential fields, A-star [
36,
37]. These models also rely on olfaction sensing for estimating the odor source.
Deep Learning (DL) based methods are increasingly utilized for OSL experiments. Recent developments involve the use of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) to predict gas leak locations from stationary sensor networks or employing reinforcement learning for plume tracing strategies. For instance, Kim et al. [
38] trained an RNN to predict potential odor source locations using data from stationary sensor networks obtained through simulation. Hu et al. [
39] presented a plume tracing algorithm based on model-free reinforcement learning, utilizing the deterministic policy gradient to train an actor-critic network for Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) navigation. Wang et al. [
40] trained an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) to solve the OSL problem in simulations, yet real-world validations are necessary to confirm its efficacy. In summary, despite the promising potential of DL technologies, their application in solving OSL problems is still in its early stages and warrants further research. Most DL-based methods are validated in virtual environments through simulated flow fields and plume distributions, necessitating real-world implementations to validate their effectiveness.
Fusing vision with olfaction for odor source localization task is common in complex organisms like mice [
41,
42]. Humans also use vision as a primary sensor for odor source navigation tasks. However, very few works have utilized vision for OSL tasks. Recent advances in computer vision techniques can allow robots to use vision as an important sensing capability for detecting visible odor sources or plumes. The added advantage of vision is that it can allow robots to navigate to odor sources without being affected by sparse odor plumes or turbulent airflow in the navigation path. The main contribution of this paper is designing a dynamic Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm for odor source localization in an obstacle-ridden turbulent airflow environment.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Overview of the Proposed OSL Algorithm
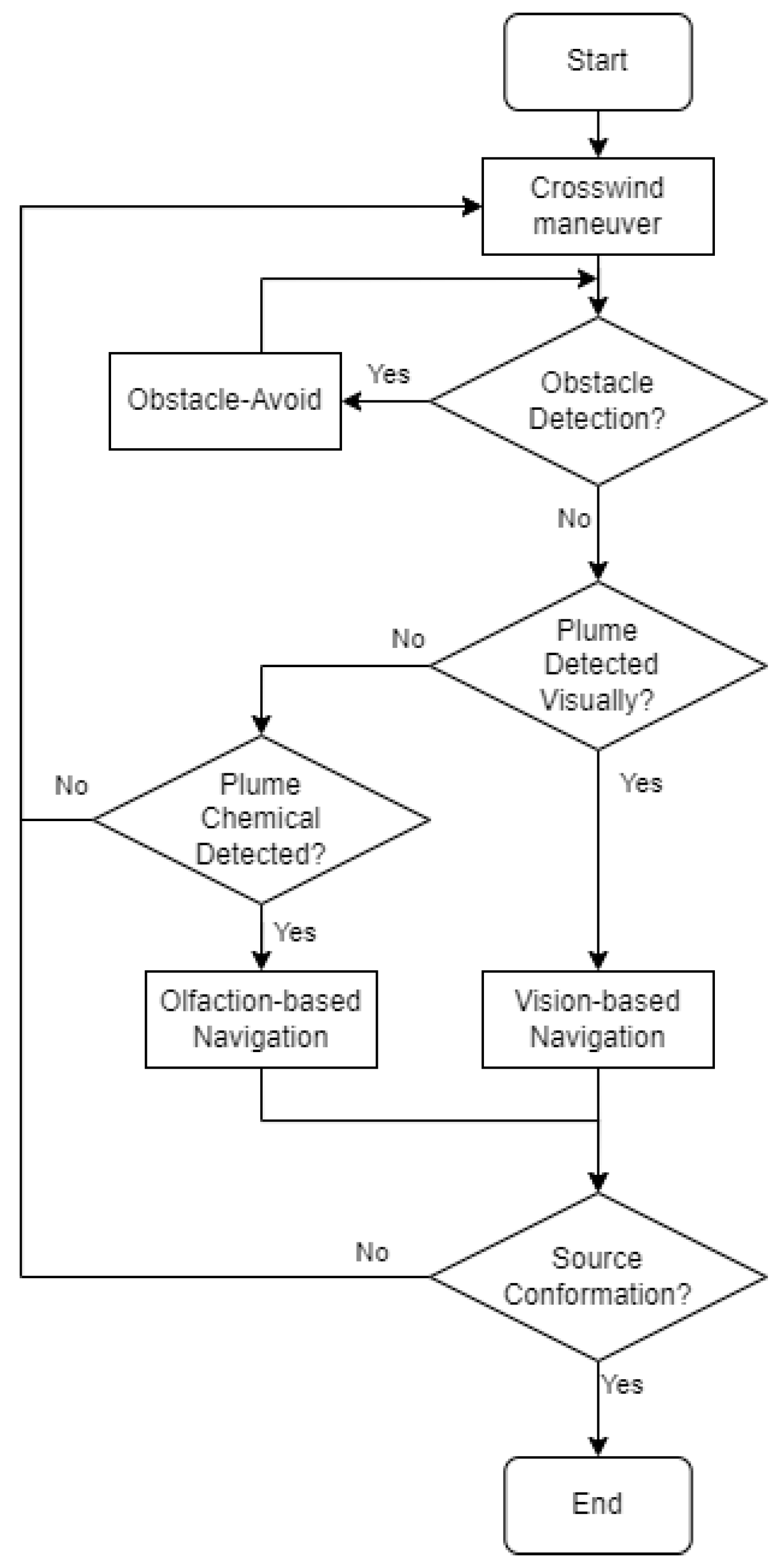
Figure 2 shows the flow diagram of the proposed navigation algorithm. In this work, the initial robot search behavior is the ‘Crosswind maneuver’ behavior, where the robot moves cross-wind to detect initial odor plumes. If the robot encounters obstacles in its surroundings, it switches to the ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ behavior, where the robot will move around to avoid obstacles. During the robot maneuver, the robot seeks valid visual and olfactory detection. If the robot obtains a valid visual detection, it employs Vision-based Navigation to approach the odor source location. Similarly, if the robot obtains sufficient olfactory detection, it employs Olfaction-based Navigation algorithm. If the robot is in the vicinity of the odor source, it is considered as the source declaration, i.e., the end of the search. Otherwise, the robot returns to the default ‘Crosswind maneuver’ behavior and repeats the above process.
In the following section, we present the design of the aforementioned search behaviors, including Crosswind maneuver (Subsection 3.2), Obstacle-avoid Navigation (Subsection 3.3), Vision-based Navigation (Subsection 3.4), and Olfactory-based Navigation (Subsection 3.5).
3.2. Crosswind maneuver Behavior
In an OSL task, the robot does not have any prior information on the odor source location. Thus, we define a ‘Crosswind maneuver’ behavior, as the default behavior, directing the robot to find initial odor plume detection or re-detect odor plumes when valid vision and olfaction observations are absent. Crosswind movement, where the robot heading is perpendicular to the wind direction, increases the chance of the robot detecting odor plumes [
43]. Denote that the wind direction in the inertial frame is
, thus, the robot heading command in the ‘Crosswind maneuver’ behavior can be defined as:
Besides, it is worth mentioning that we set the robot’s linear speed as a constant and only changed the heading commands in the ‘Crosswind maneuver’ behavior to simplify the robot control problem and save search time.
3.3. Obstacle-avoid Navigation Behavior
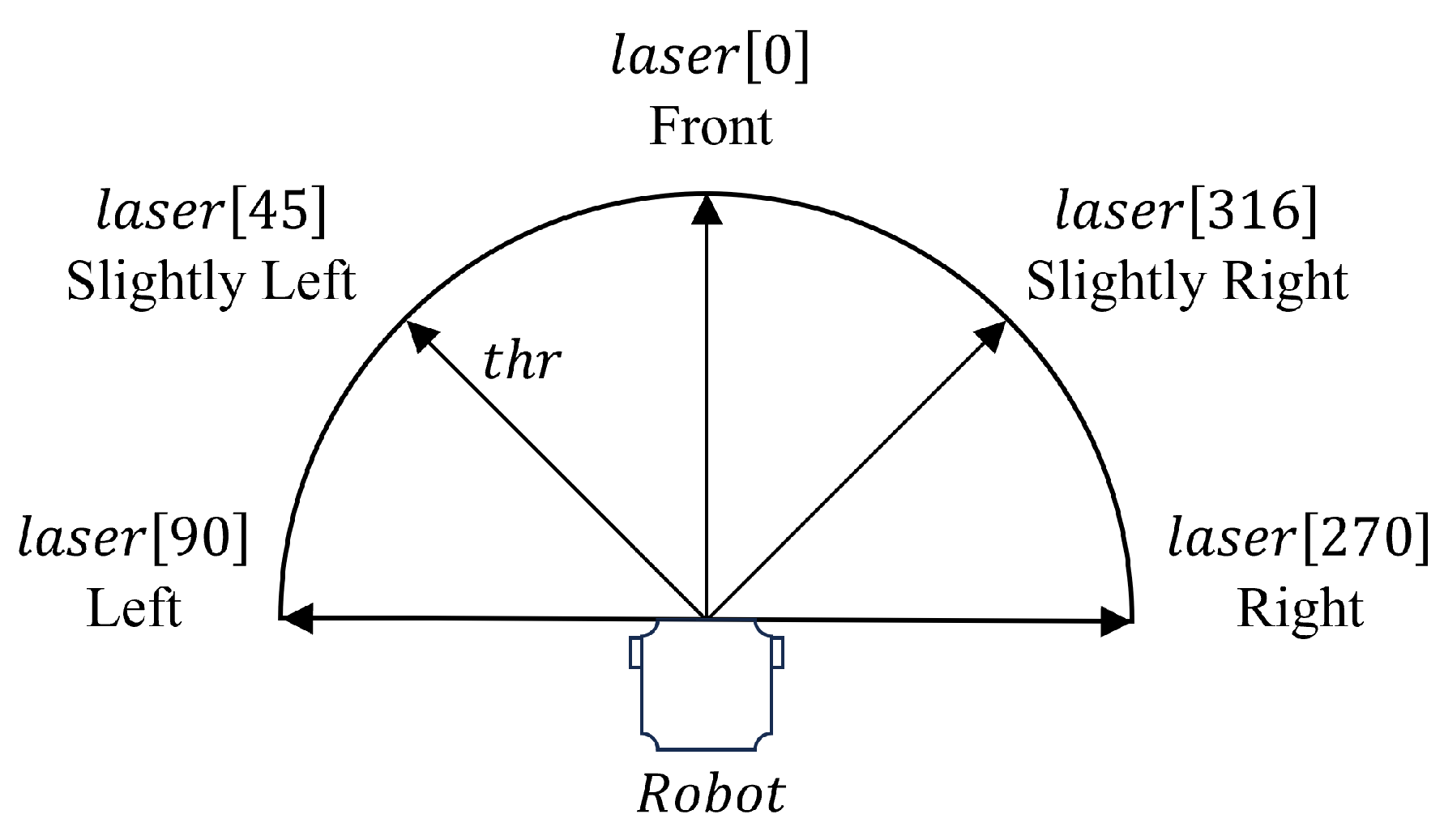
The ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ behavior is activated when the robot moves close to an obstacle object within the search environment, which directs the robot to move around and avoid the obstacles. In this work, the robot employs a Laser Distance Sensor (LDS) to measure the distances from the robot to any obstacles in five surrounding angles as presented in
Figure 3. Specifically, we denote
as the measured distance at angle
x, including Front (
), Slightly Left, (
), Slightly Right (
), Left (
), and Right (
). If the obstacle distance in any of the five angles is less than the threshold, the proposed ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ behavior is activated.
Algorithm 1 shows the pseudo-code for the ’Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ behavior. The main idea is to identify the relative location of obstacles to the robot and command the robot to move around to avoid obstacles. Specifically, the robot initially set the linear velocity and angular velocity as
and
, respectively. Positive values in
and
represent forward and left rotation, respectively, and negative values represent backward and right rotation, respectively. Initial values of
and
are set as 0.6 m/s and 0 rad/s in this work.
|
Algorithm 1 ’Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ Behavior |
- 1:
Set robot linear velocity as m/s1.35 - 2:
Set robot angular velocity as rad/s - 3:
if then
- 4:
rad/s - 5:
else - 6:
m/s and rad/s - 7:
if then
- 8:
if then
- 9:
rad/s - 10:
else
- 11:
rad/s - 12:
end if
- 13:
else if then
- 14:
if then
- 15:
rad/s - 16:
else
- 17:
rad/s - 18:
end if
- 19:
else
- 20:
m/s - 21:
end if
- 22:
end if |
In the ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’ behavior, the robot will always check if there is a clear path in the Front direction, i.e., ( is the threshold for obstacle detection, m in this work), and if it is true, the robot will move forward with rad/s. If the Front is blocked, the robot will stop and check Slightly Left or Slightly Right for a clear path (). If there is a clear path in either of these two directions, the robot will compare clearance in Slightly Left and Slightly Right and rotate left (i.e., rad/s) or right (i.e., rad/s) to face the greater clearance. If there is no clearance in Slight Left or Slight Right, the robot will check Left and Right for a clear path (). If there is a clear path, the robot will compare Left and Right clearance () and rotate left ( rad/s) or right ( rad/s) to face the greater clearance. If there is no clear path in all five directions, the robot will move back ( m/s) to escape the dead end.
3.4. Vision-based Navigation
In this work, we employ vision as the main approach to detect odor sources within the search environment. Vision sensing allows the robot to detect the plume source location in its visual field and approach it directly. Olfaction-only navigation methods often rely on airflow direction for navigating to the odor source. This can lead to failure in turbulent airflow environments. Given visual sensing is not guided by airflow direction, combining it with Olfaction-based Navigation can allow the robot to find the odor source in turbulent airflow environments.
The proposed Vision-based Navigation relies on computer vision techniques. Specifically, we train a deep learning-based object detection model, i.e., YOLOv7, to detect vapors emitted from the odor source. Vapors can be considered as a common and distinct feature for the odor source object, such as smoke for fire sources, chemical plumes for chemical leaks or hydrothermal vents, etc. It should be mentioned that if the odor source does not have a distinct plume feature (i.e., transparent vapors), the robot can still find the odor source using the proposed Olfaction-based Navigation algorithm. We also provided real-world performance comparison between the Olfaction-based Navigation and the Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithms.
In the proposed vision sensing method, we trained a YOLOv7 model to detect odor plumes in the continuously captured images. To generate training images, we extracted 243 observation frames with a resolution of
while the turtlebot was approaching the odor plumes in a variety of angles and lighting conditions.
Figure 4 shows two sample frames used for training the vision model. This data was split into training, validation, and testing datasets for training the model. Roboflow [
44] was utilized as the annotation tool for accurate bounding boxes and polygons delineation.
To assess YOLOv7 performance, diverse predefined augmentation techniques in Roboflow were systematically applied to ‘Dataset-1’. These included rotation (-10° to +10°), shear (±15° horizontally and vertically), hue adjustment (-25° to +25°), saturation adjustment (-25% to +25%), brightness adjustment (-25% to +25%), exposure adjustment (-25% to +25%), blur (up to 2.5px), and noise (up to 1% of pixels). Post-augmentation, the resulting augmented dataset, labeled as ‘Dataset-3’, enriched the training set for a comprehensive evaluation of YOLOv7’s robustness in detecting prescribed odor plumes. We set the number of training epochs to 100, with a batch size of 16. The resulting training accuracy was 98% and testing accuracy was 93%.
The implemented vision model returns a box bounding the plume in the image if it detects an odor plume. The output of the model also includes the horizontal and vertical location of the plume bounding box. If the model returns a plume bounding box, the robot continues moving forward (i.e., m/s) and checks if the horizontal location of the bounding box is in the left or the right half of the image. The model requires less than 1 second to generate output in our remote computer. The robot sends 30 image frames per second, and the robot picks every 30th frame as the input to the vision model.
Equation
2 calculates robot’s heading -
where c is the horizontal mid-point of the bounding box, and w is the horizontal resolution of the captured image. If the bounding box is in the left half of the image (i.e., ), the robot rotates left (i.e., rad/s) to face the plume. Otherwise, it rotates right ( rad/s) to face the plume.
3.5. Olfaction-based Navigation
If there is no valid visual detection but the robot can sense above-threshold odor concentration, Olfaction-based Navigation is employed to guide the robot to approach the odor source location.
Specifically, the proposed Olfaction-based Navigation algorithm commands the robot to move upwind to approach the odor source location. This behavior is analogous to the ’Surge’ behavior of the bio-mimicking moth-inspired navigation OSL algorithm [
45]. In this behavior, the robot’s linear velocity is fixed at
m/s and the heading command, i.e.,
, is calculated as:
The robot will switch back to Vision-based Navigation once there is a valid vision detection.
3.6. Source Declaration
The robot is considered as successful if the robot position is within m of the odor source location. But if the robot fails to reach the odor source within 200 seconds, the trial run is considered as a failure.
6. Conclusion
The combination of computer vision and robotic olfaction provides a more comprehensive observation of the environment, enabling the robot to interact with the environment in more ways and enhancing navigation performance. This paper proposes the incorporation of vision sensing in OSL. Specifically, the paper proposes a Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm with Obstacle-avoid Navigation capability for 2-D odor source localization tasks for ground mobile robots. For conducting real-world experiments to test the proposed algorithm, a robot platform based on the Turtlebot3 mobile robot was developed with olfaction and vision-sensing capabilities. The proposed navigation algorithm had five behaviors, i.e., Crosswind maneuver behavior to find odor plume, Obstacle-avoid Navigation behavior to circumvent obstacles in the environment, Vision-based Navigation to approach the odor source using vision sensing, Olfaction-based Navigation to approach the odor source using olfaction sensing, and source declaration. For the Vision-based Navigation behavior, a YOLOv7-based vision model was trained to detect visible odor plumes. For Olfaction-based Navigation behavior, we used moth-inspired algorithm. To test the performance of the proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm, we tested the performance of the Olfaction-only navigation algorithm, Vision-only navigation algorithm, and the proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm separately in real-world experiment setups. Furthermore, we tested the performance of the three navigation algorithms in laminar and turbulent airflow environments to compare their strengths. We used five predefined starting robot positions for each navigation algorithm and repeated them for both airflow environments - resulting in 30 total experiment runs. The search results of the OSL experiments show that the proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm had a higher success rate, lower average search time, and lower average traveled distance for finding the odor source compared to Olfaction-only and Vision-only navigation algorithms in both laminar and turbulent airflow environments. The result of our experiment indicates that vision sensing is a promising addition to olfaction sensing in ground-mobile robot-based Odor Source Localization research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H. and L.W.; methodology, S.H. and L.W.; software, S.H. and K.M.; validation, L.W.; formal analysis, S.H.; investigation, S.H.; resources, L.W.; data curation, S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H.; writing—review and editing, L.W.; visualization, S.H.; supervision, L.W.; project administration, L.W.; funding acquisition, L.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the proposed method for OSL experiment. We utilized the Turtlebot3 robot platform. We equipped it with a camera, Laser Distance Sensor, Airflow sensor, Chemical sensor, etc. The robot utilizes 3 navigation behaviors - Obstacle-avoid Navigation, Vision-based Navigation, and Olfaction-based Navigation to output robot heading and linear velocity.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the proposed method for OSL experiment. We utilized the Turtlebot3 robot platform. We equipped it with a camera, Laser Distance Sensor, Airflow sensor, Chemical sensor, etc. The robot utilizes 3 navigation behaviors - Obstacle-avoid Navigation, Vision-based Navigation, and Olfaction-based Navigation to output robot heading and linear velocity.
Figure 2.
The flow diagram of the proposed OSL algorithm. There are four navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, ‘Vision-based Navigation’, and ‘Olfaction-based Navigation’.
Figure 2.
The flow diagram of the proposed OSL algorithm. There are four navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, ‘Vision-based Navigation’, and ‘Olfaction-based Navigation’.
Figure 3.
Five directions in the robot’s laser distance sensing, including Left, Slightly Left, Front, Slightly Right, and Right. denotes the distance between the robot and the object at the angle x, which is measured from the onboard laser distance sensor.
Figure 3.
Five directions in the robot’s laser distance sensing, including Left, Slightly Left, Front, Slightly Right, and Right. denotes the distance between the robot and the object at the angle x, which is measured from the onboard laser distance sensor.
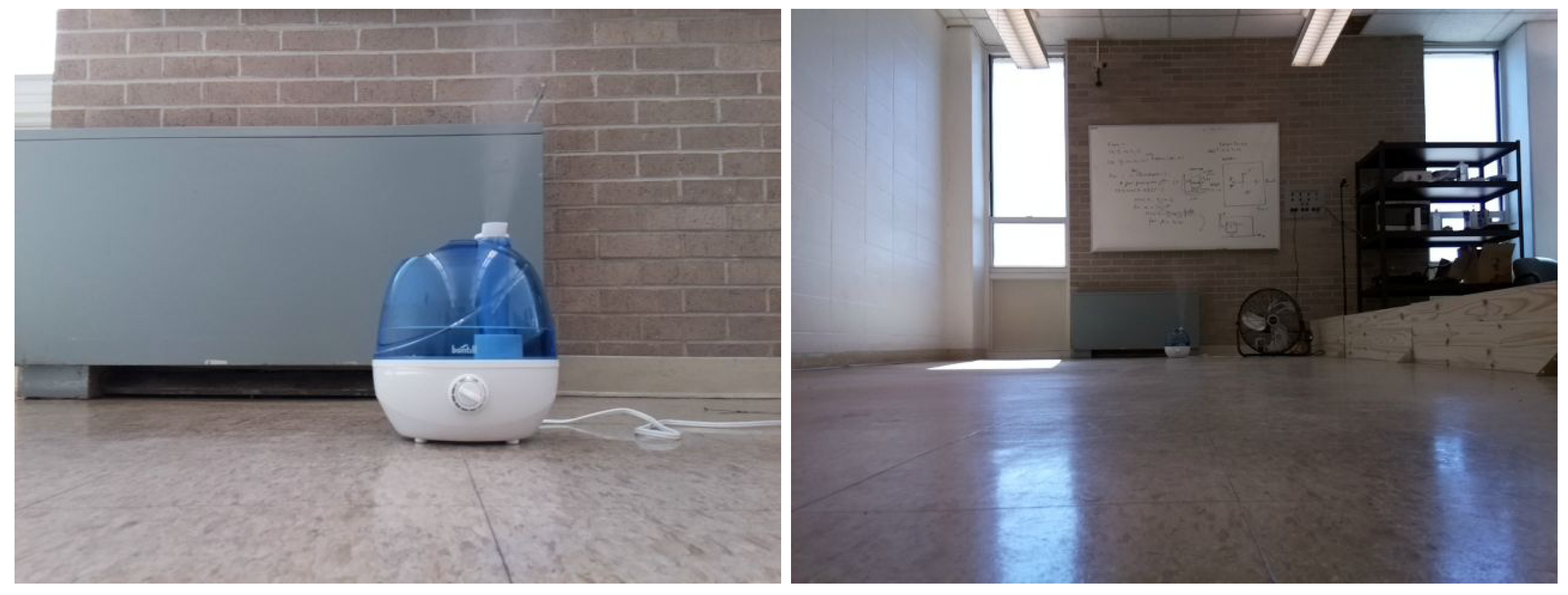
Figure 4.
Two sample frames that include humidifier odor plumes in different lighting and spatial conditions. The frames are sampled out of the total 243 frames used for training the vision model. All of the frames were captured by the Turtlebot robot in the experiment area.
Figure 4.
Two sample frames that include humidifier odor plumes in different lighting and spatial conditions. The frames are sampled out of the total 243 frames used for training the vision model. All of the frames were captured by the Turtlebot robot in the experiment area.
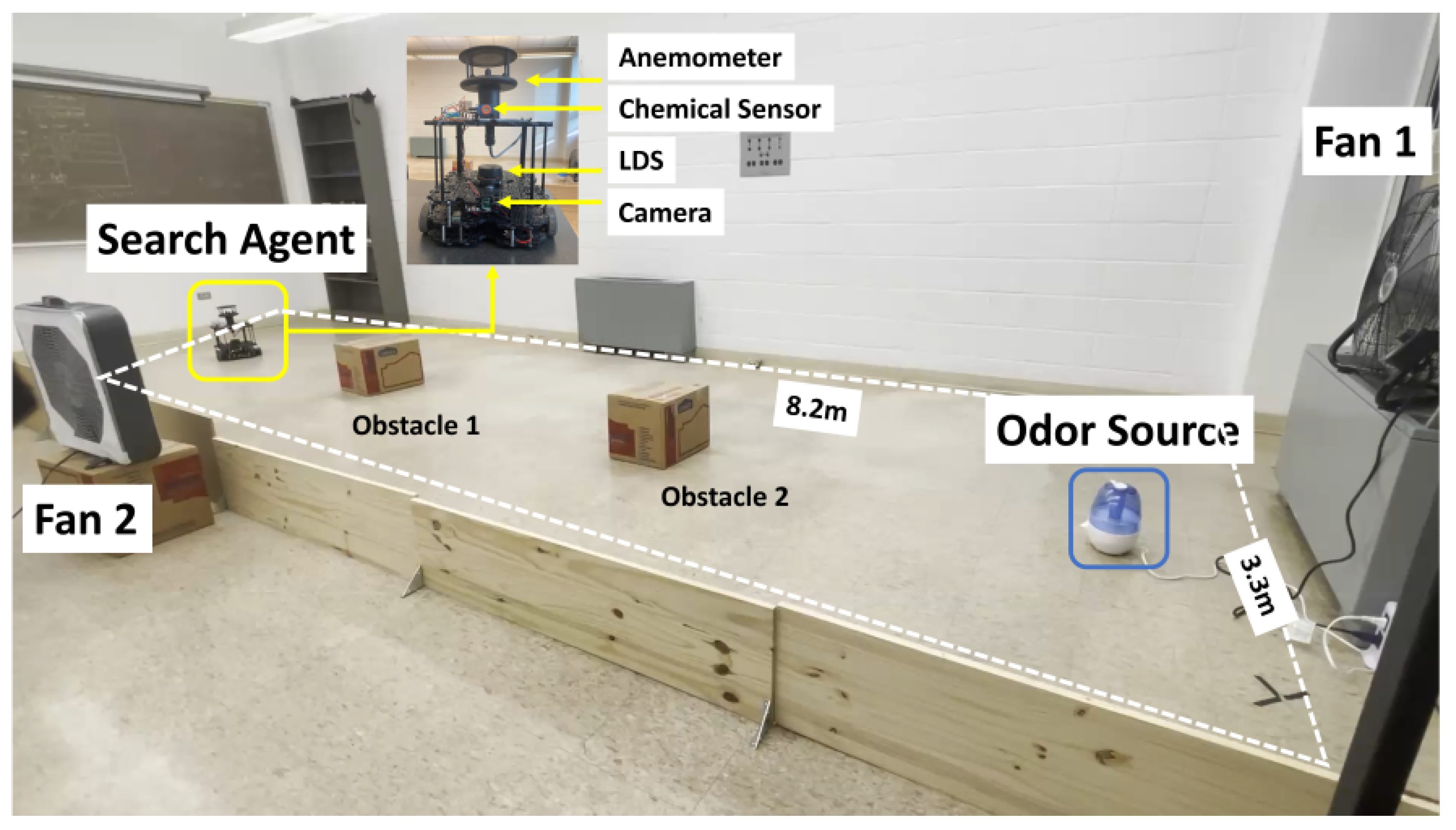
Figure 5.
The experiment setup. The Turtlebot3 waffle pi mobile robot is used in this work. In addition to the camera and Laser Distance sensor, the robot is equipped with a chemical sensor and an anemometer for measuring chemical concentration, wind speeds, and directions. The robot is initially placed in a downwind area with the object of finding the odor source. A humidifier loaded with ethanol is employed to generate odor plumes. Two electric fans are placed perpendicularly to create artificial wind fields. Two obstacles are placed in the search area.
Figure 5.
The experiment setup. The Turtlebot3 waffle pi mobile robot is used in this work. In addition to the camera and Laser Distance sensor, the robot is equipped with a chemical sensor and an anemometer for measuring chemical concentration, wind speeds, and directions. The robot is initially placed in a downwind area with the object of finding the odor source. A humidifier loaded with ethanol is employed to generate odor plumes. Two electric fans are placed perpendicularly to create artificial wind fields. Two obstacles are placed in the search area.
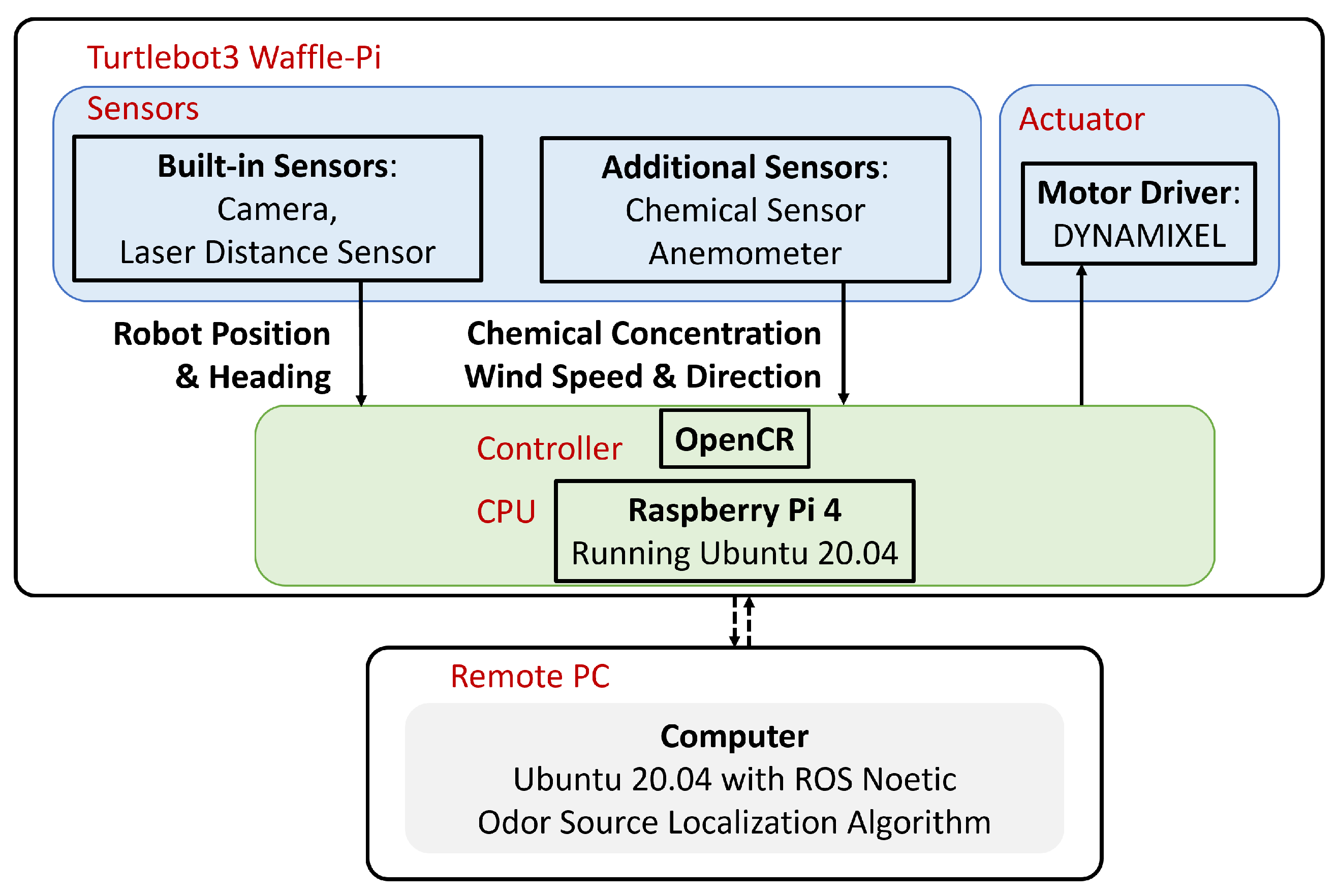
Figure 6.
System configuration. This system contains two main components, including the Turtlebot3 and the remote PC. The solid connection line represents physical connection, and the dotted connection line represents wireless link.
Figure 6.
System configuration. This system contains two main components, including the Turtlebot3 and the remote PC. The solid connection line represents physical connection, and the dotted connection line represents wireless link.
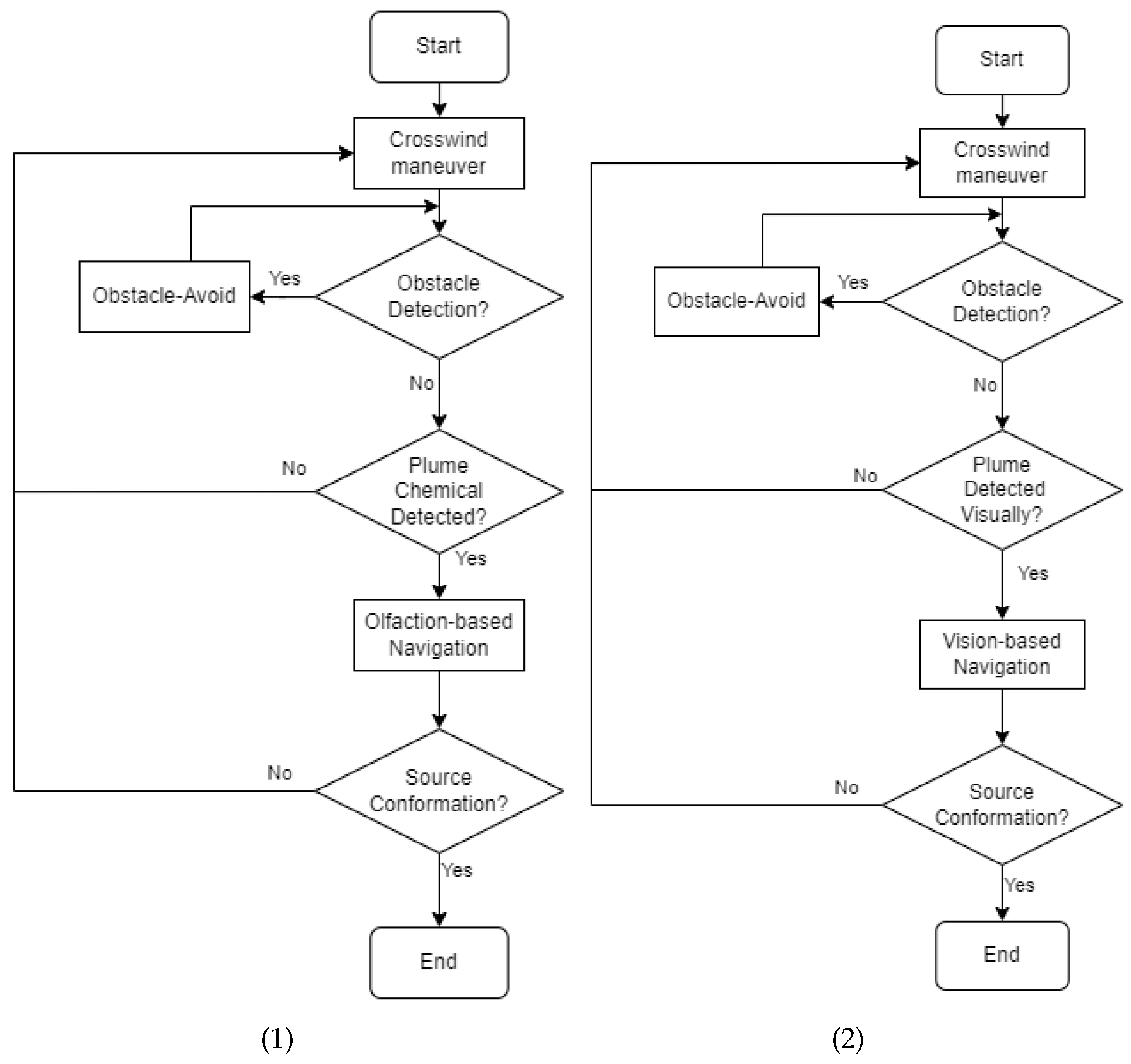
Figure 7.
(1) The flow diagram of the Olfaction-only navigation algorithm. There are three navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, and ‘Olfaction-based Navigation’. (2) The flow diagram of the Vision-only navigation algorithm. There are three navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, and ‘Vision-based Navigation’.
Figure 7.
(1) The flow diagram of the Olfaction-only navigation algorithm. There are three navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, and ‘Olfaction-based Navigation’. (2) The flow diagram of the Vision-only navigation algorithm. There are three navigation behaviors, including ‘Crosswind maneuver’, ‘Obstacle-avoid Navigation’, and ‘Vision-based Navigation’.
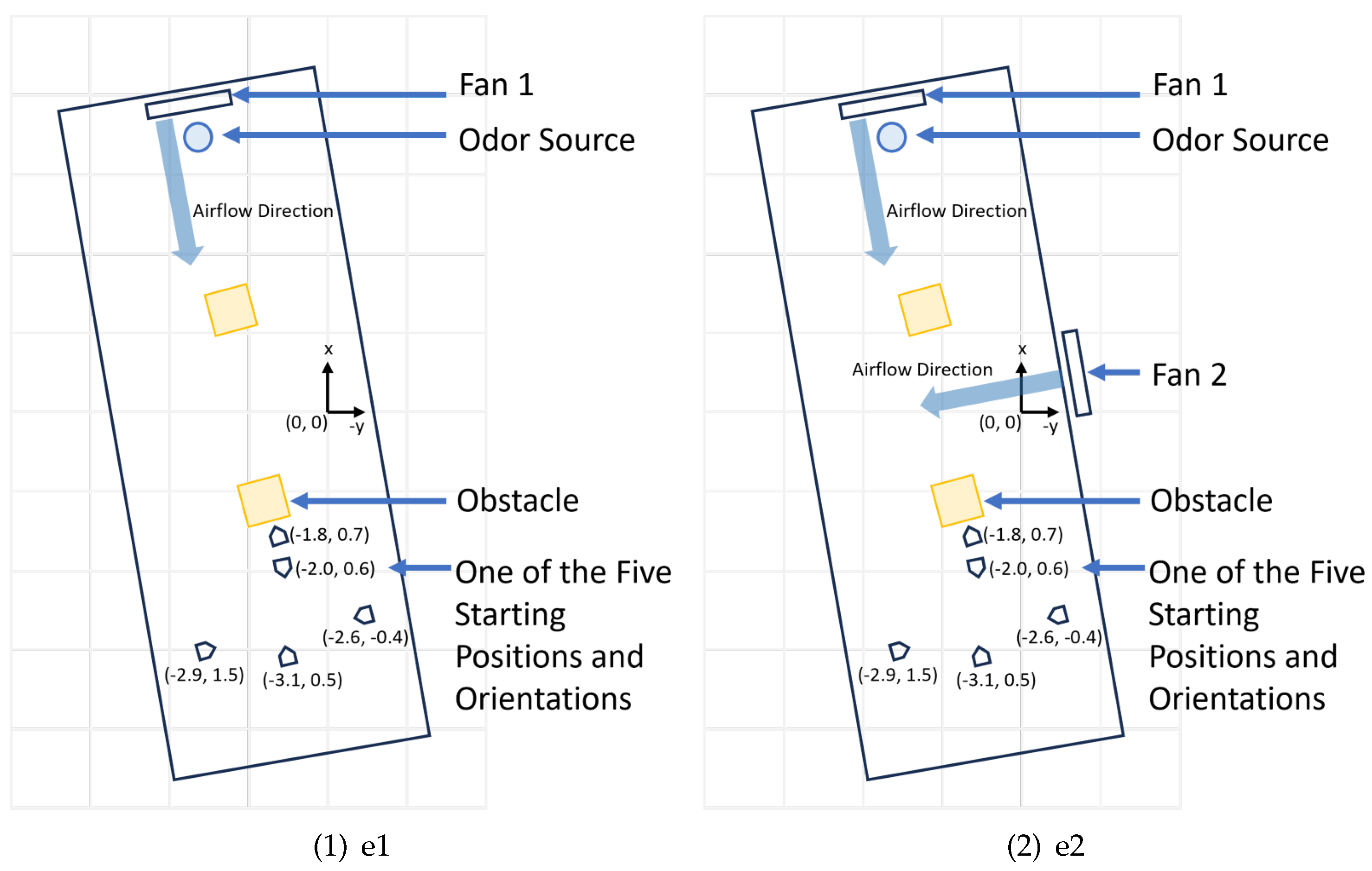
Figure 8.
(1) The schematic diagram of the search area with e1 - laminar airflow setup. The five robot starting positions are used for testing the performance of the Olfaction-based Navigation, Vision-based Navigation, and Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation tests. (2) The schematic diagram of the search area with e2 - turbulent airflow setup.
Figure 8.
(1) The schematic diagram of the search area with e1 - laminar airflow setup. The five robot starting positions are used for testing the performance of the Olfaction-based Navigation, Vision-based Navigation, and Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation tests. (2) The schematic diagram of the search area with e2 - turbulent airflow setup.
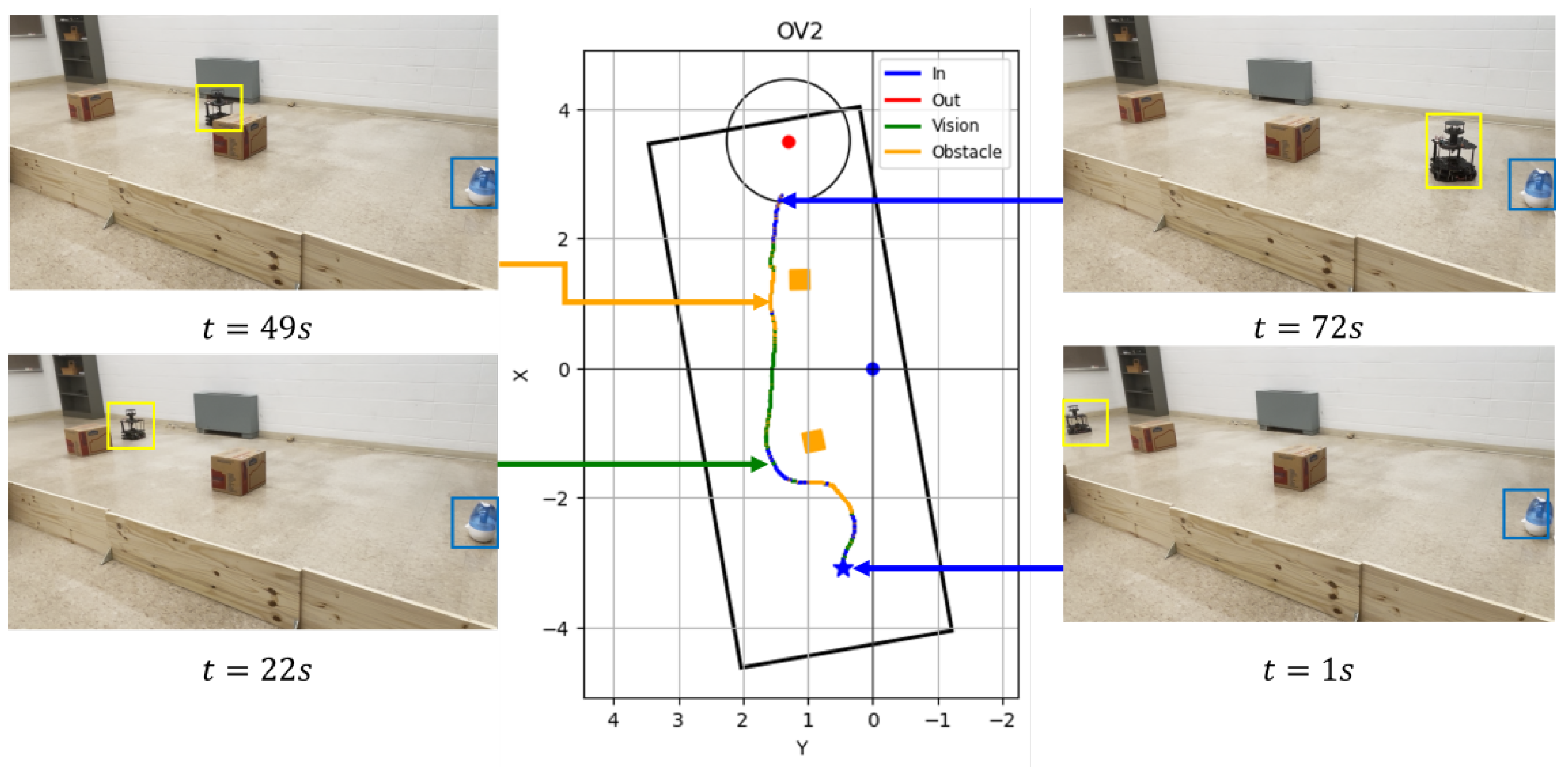
Figure 9.
Robot trajectory graphs and snapshots of OSL tests with the Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm in turbulent airflow environment.
Figure 9.
Robot trajectory graphs and snapshots of OSL tests with the Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm in turbulent airflow environment.
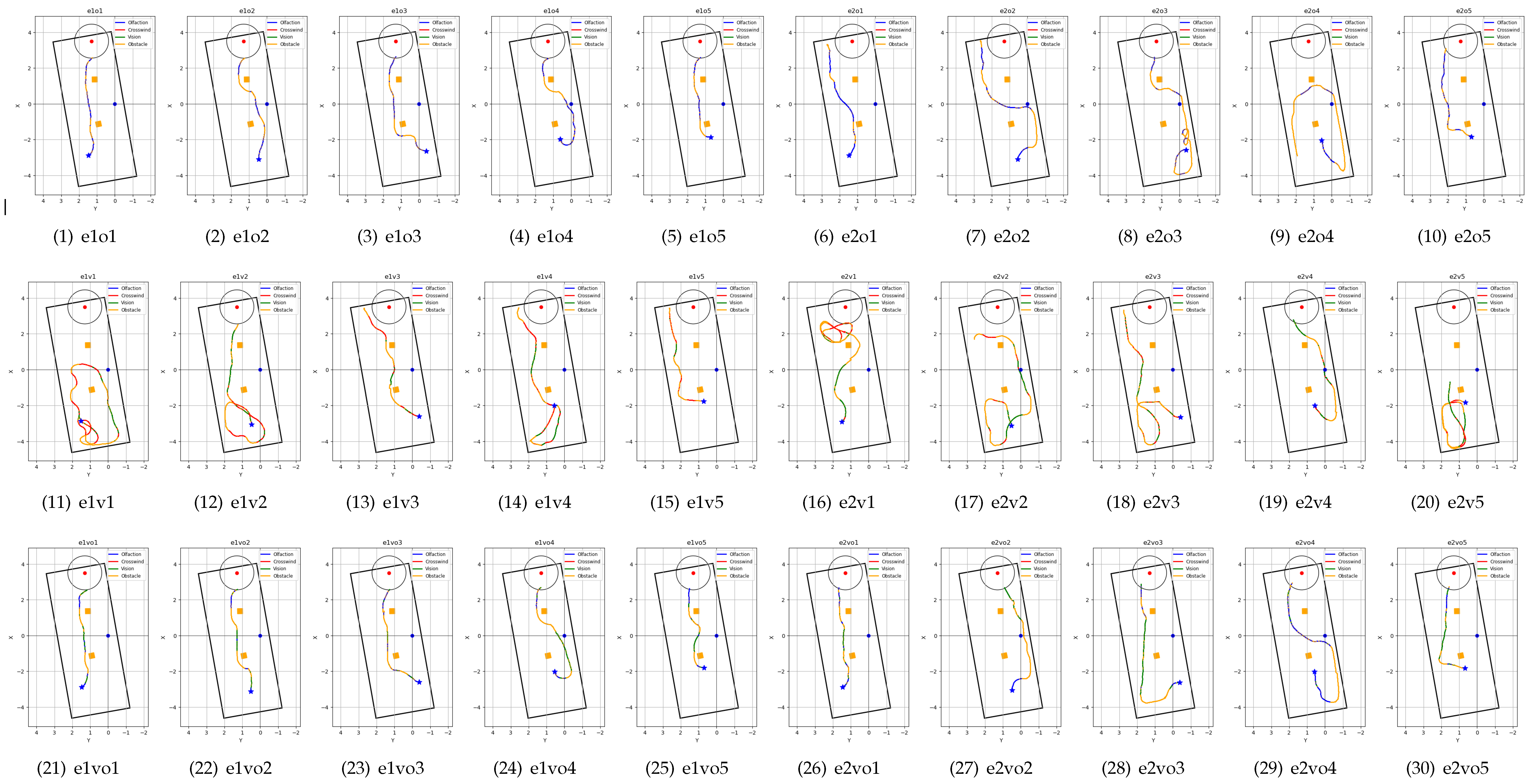
Figure 10.
Trajectories of OSL repeat experiments. Olfaction-only Navigation algorithm trials (o1-o5) in - (1-5) laminar airflow environment (e1), and (6-10) turbulent airflow environment (e2). Similarly, Vision-only Navigation algorithm trials (v1-v5) in e1 (11-15) and e2 (16-20), Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm trials (vo1-vo5) in - e1 (21-25) and e2 (26-30). The behaviors that the robot was following under the three navigation algorithms are Crosswind - crosswind maneuver behavior, Obstacle - Obstacle-avoid Navigation behavior, Olfaction - Olfaction-based Navigation behavior, and Vision - Vision-based Navigation behavior. Robot starting positions are highlighted with a blue star, the obstacles are the orange boxes, and the odor source is the red point with the surrounding circular source declaration region.
Figure 10.
Trajectories of OSL repeat experiments. Olfaction-only Navigation algorithm trials (o1-o5) in - (1-5) laminar airflow environment (e1), and (6-10) turbulent airflow environment (e2). Similarly, Vision-only Navigation algorithm trials (v1-v5) in e1 (11-15) and e2 (16-20), Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm trials (vo1-vo5) in - e1 (21-25) and e2 (26-30). The behaviors that the robot was following under the three navigation algorithms are Crosswind - crosswind maneuver behavior, Obstacle - Obstacle-avoid Navigation behavior, Olfaction - Olfaction-based Navigation behavior, and Vision - Vision-based Navigation behavior. Robot starting positions are highlighted with a blue star, the obstacles are the orange boxes, and the odor source is the red point with the surrounding circular source declaration region.
Figure 11.
Robot trajectories of repeated tests in six navigation algorithm and airflow environment combinations. Trajectories in laminar airflow environments are - (1) e10 - Olfaction-only navigation algorithm, (2) e1v - Vision-only navigation algorithm, and (3) e1vo - Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm. Trajectories in turbulent airflow environment are - (4) e20 - Olfaction-only navigation algorithm, (5) e2v - Vision-only navigation algorithm, (6) e2vo - Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm. The behaviors that the robot was following under the three navigation algorithms are shown in the trajectory. These behaviors include Crosswind - crosswind maneuver behavior, Obstacle - Obstacle-avoid Navigation behavior, Olfaction - Olfaction-based Navigation behavior, and Vision - Vision-based Navigation behavior. Five robot starting positions are highlighted with a blue star, the obstacles are the orange boxes, and the odor source is the red point with the surrounding circular source declaration region.
Figure 11.
Robot trajectories of repeated tests in six navigation algorithm and airflow environment combinations. Trajectories in laminar airflow environments are - (1) e10 - Olfaction-only navigation algorithm, (2) e1v - Vision-only navigation algorithm, and (3) e1vo - Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm. Trajectories in turbulent airflow environment are - (4) e20 - Olfaction-only navigation algorithm, (5) e2v - Vision-only navigation algorithm, (6) e2vo - Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation algorithm. The behaviors that the robot was following under the three navigation algorithms are shown in the trajectory. These behaviors include Crosswind - crosswind maneuver behavior, Obstacle - Obstacle-avoid Navigation behavior, Olfaction - Olfaction-based Navigation behavior, and Vision - Vision-based Navigation behavior. Five robot starting positions are highlighted with a blue star, the obstacles are the orange boxes, and the odor source is the red point with the surrounding circular source declaration region.
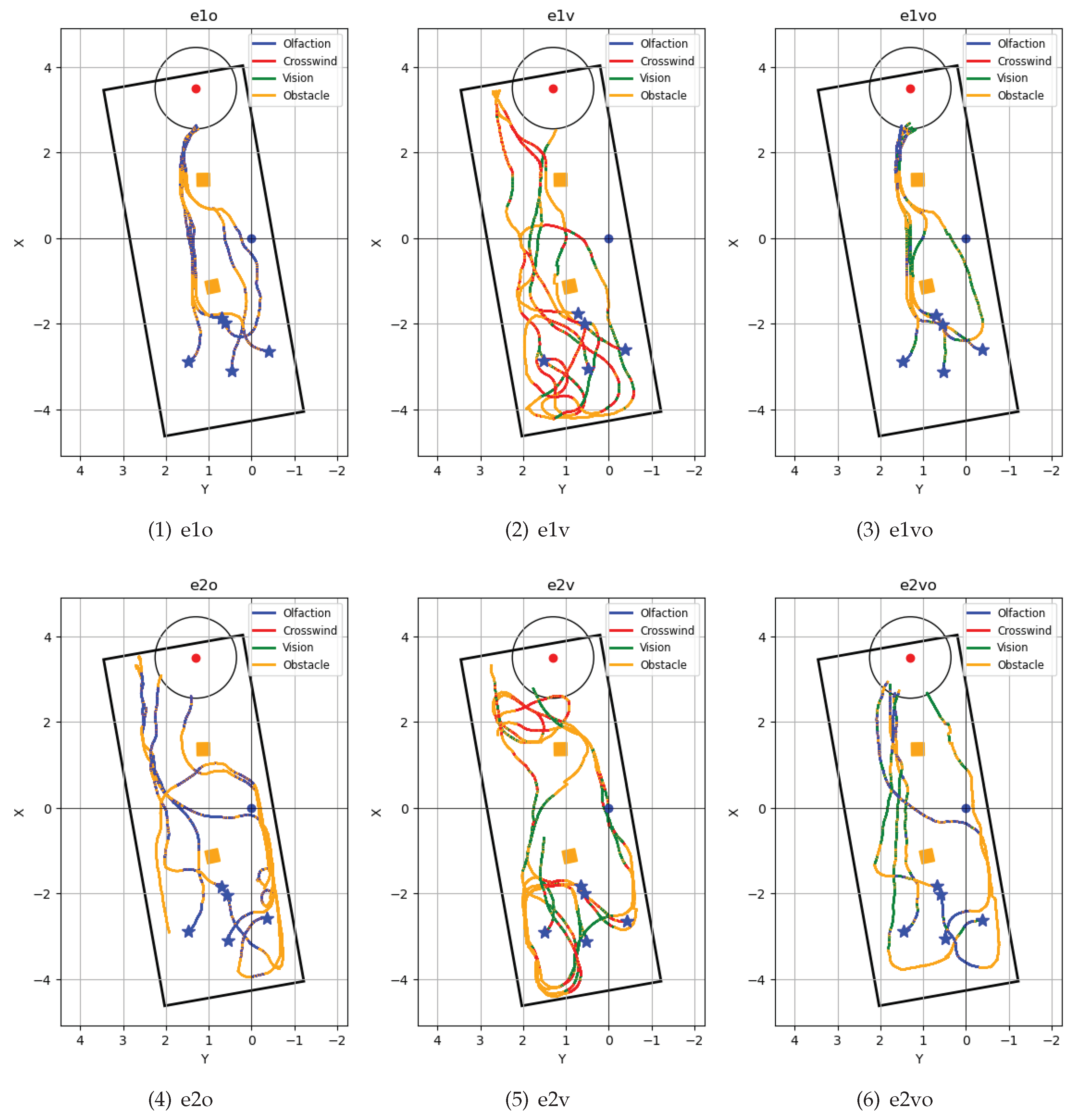
Table 1.
Type, name, and specification of the built-in camera, laser distance sensor, and added anemometer, chemical sensor.
Table 1.
Type, name, and specification of the built-in camera, laser distance sensor, and added anemometer, chemical sensor.
| Source |
Sensor Type |
Module Name |
Specification |
| Built-in |
Camera |
Raspberry pi
camera v2 |
Video Capture:
1080p30, 720p60
and VGA90. |
Laser Distance
Sensor |
LDS-02 |
Detection Range:
360-degree.
Distance Range:
160 ∼8,000 mm. |
| Added |
Anemometer |
WindSonic,
Gill Inc. |
Speed: 0-75m/s.
Wind direction:
0-360 degrees. |
Chemical
Sensor |
MQ3 alcohol
detector |
Concentration:
25 – 500 ppm. |
Table 2.
Search Time of the Vision-only, Olfaction-only, and the Proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation Algorithms.
Table 2.
Search Time of the Vision-only, Olfaction-only, and the Proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation Algorithms.
| |
Robot Initial
Position (x, y),
Orientation (z, w) |
Olfaction-only
Navigation
Algorithm (s) |
Vision-only
Navigation
Algorithm (s) |
Vision and Olfaction
Fusion Navigation
Algorithm (s) |
Laminar
Airflow
Env.
|
(-2.9, 1.5),
(-0.6, 1.0) |
63.1 |
- |
63.9 |
(-3.1, 0.5),
(0.0, 35.0) |
71.3 |
149.3 |
69.9 |
(-2.6, -0.4),
(0.7, 0.7) |
74.3 |
- |
67.5 |
(-2.0, 0.6),
(1.0, -0.1) |
73.8 |
- |
75.7 |
(-1.8, 0.7),
(0.0, 0.1) |
59.1 |
- |
61.1 |
Turbulent
Airflow
Env.
|
(-2.9, 1.5),
(-0.6, 1.0) |
- |
- |
64.0 |
(-3.1, 0.5),
(0.0, 35.0) |
- |
- |
113.1 |
(-2.6, -0.4),
(0.7, 0.7) |
196.4 |
- |
130.7 |
(-2.0, 0.6),
(1.0, -0.1) |
- |
102.8 |
131.9 |
(-1.8, 0.7),
(0.0, 0.1) |
72.3 |
- |
68.5 |
Table 3.
Result Statistics, i.e., Success Rate and Average Search Time of Vision-based Navigation, Olfaction-based Navigation, and the Proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation Algorithms.
Table 3.
Result Statistics, i.e., Success Rate and Average Search Time of Vision-based Navigation, Olfaction-based Navigation, and the Proposed Vision and Olfaction Fusion Navigation Algorithms.
Airflow
Environment |
Navigation
Algorithm |
Success
Rate |
Avg. Search
Time (s) |
Avg. Travelled
Distance (m) |
| Laminar |
Olfaction-only |
5/5 |
68.3 |
6.1 |
| Vision-only |
1/5 |
189.9 |
11.7 |
Vision and
Olfaction Fusion
|
5/5 |
67.6 |
6.2 |
| Turbulent |
Olfaction-only |
2/5 |
173.7 |
9.7 |
| Vision-only |
1/5 |
180.6 |
13.7 |
Vision and
Olfaction Fusion
|
5/5 |
101.6 |
7.8 |
| Combined |
Olfaction-only |
7/10 |
121.0 |
7.9 |
| Vision-only |
2/10 |
185.2 |
12.7 |
Vision-Olfaction
Fusion
|
10/10 |
84.6 |
7.0 |