Submitted:
18 February 2024
Posted:
19 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
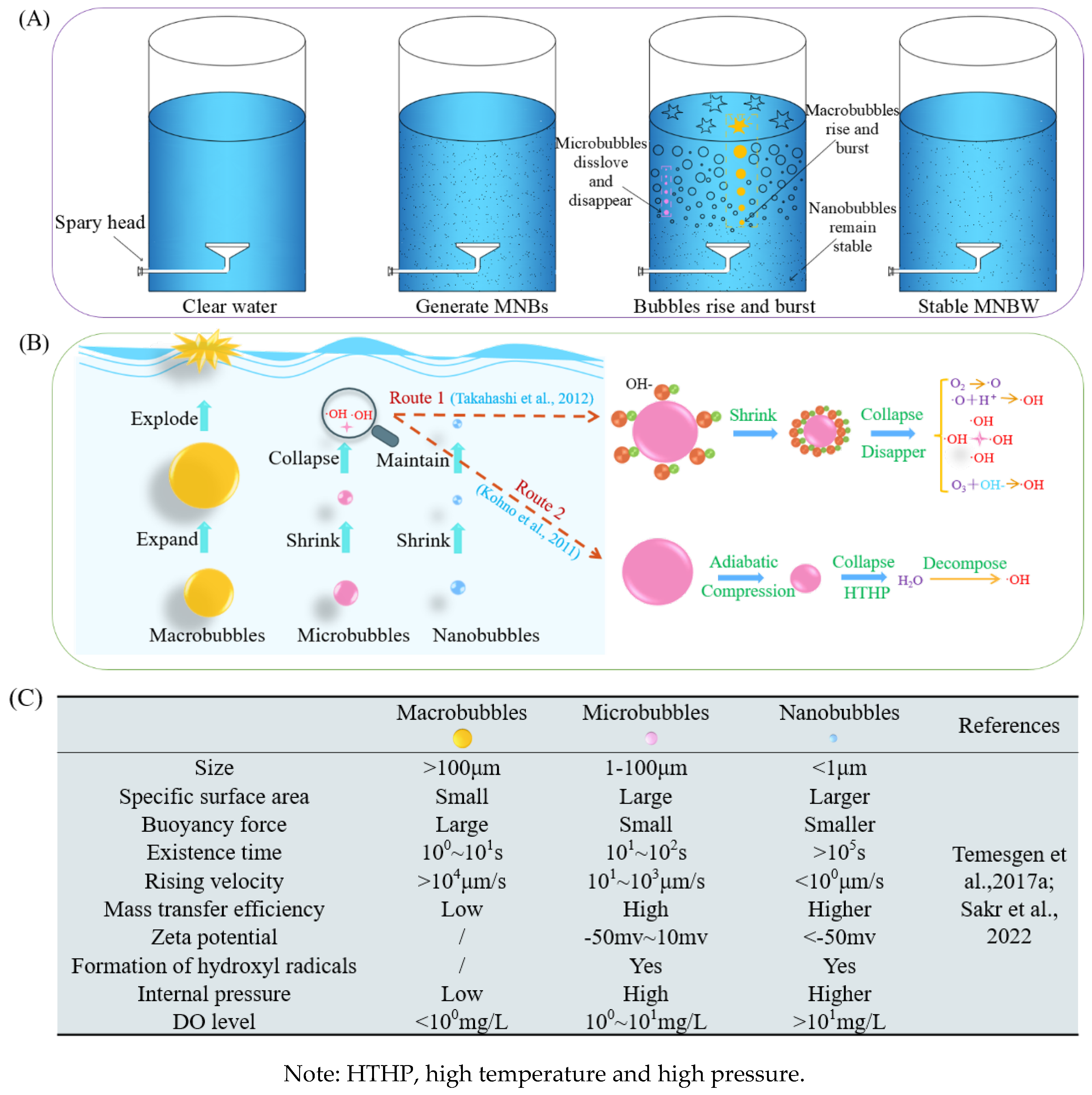
2. Generation Process and Characteristics of MNBs in Water
2.1. The Generation Process of MNBs in Water
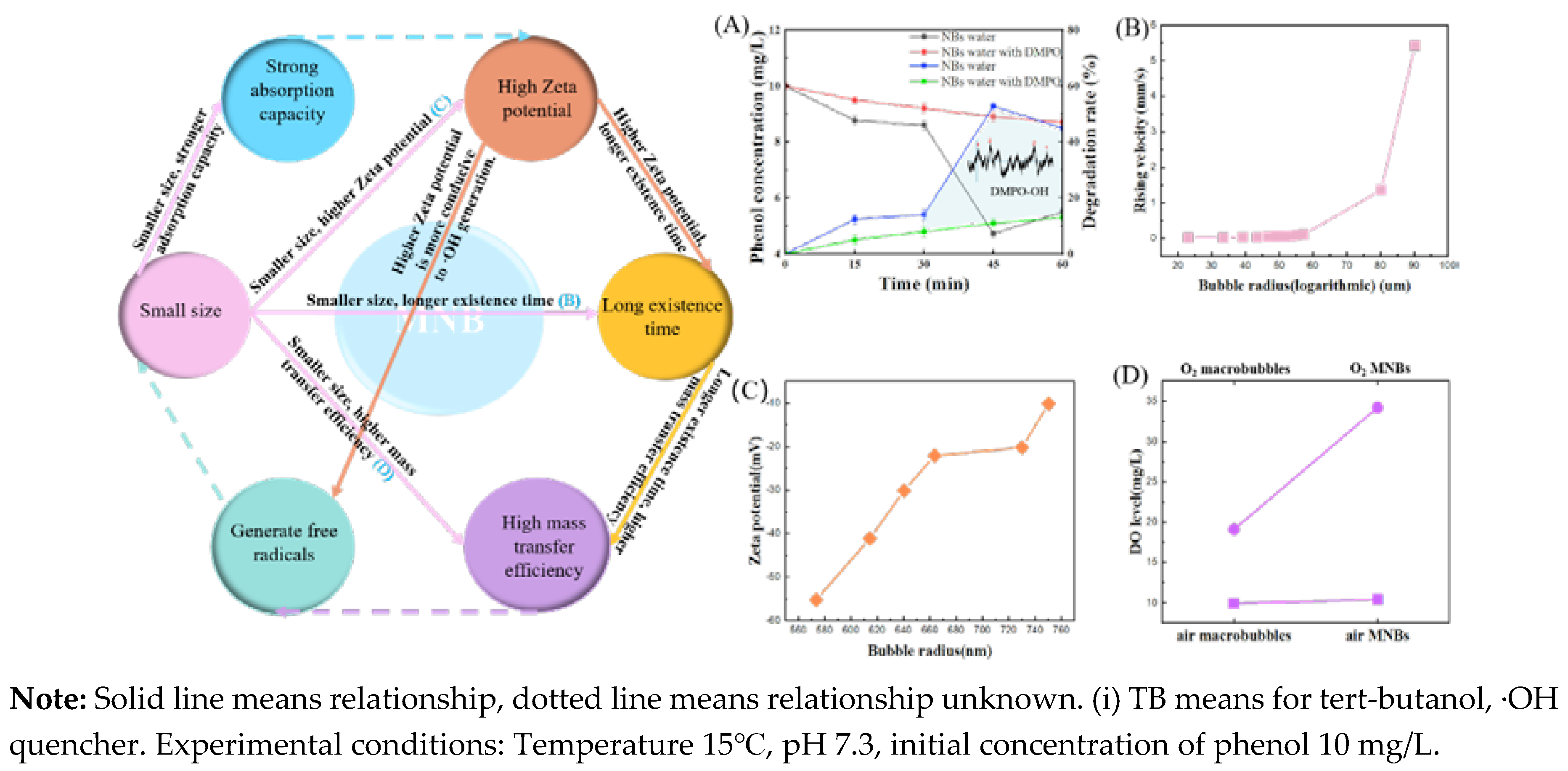
2.2. Characteristics of MNBs in Water
3. Characteristics of MNBs Collapse and Influencing Factors of Hydroxyl Radical Generation in MNBW
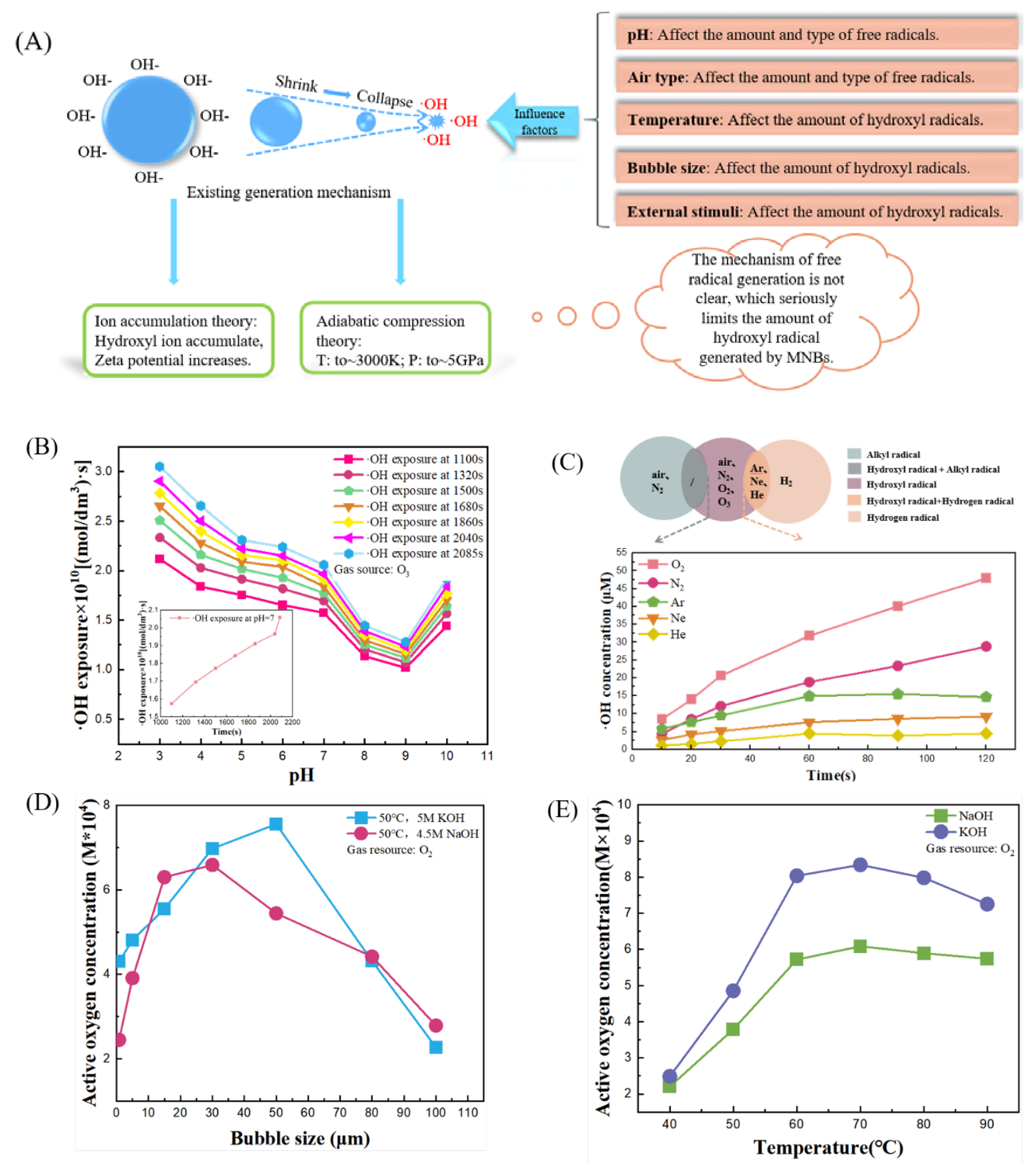
3.1. Characteristics of MNBs Collapse
3.2. Influencing Factors of ·OH Generation in MNBW
4. Effect Mechanism of MNBs on Pollutants and Biofilms in Water
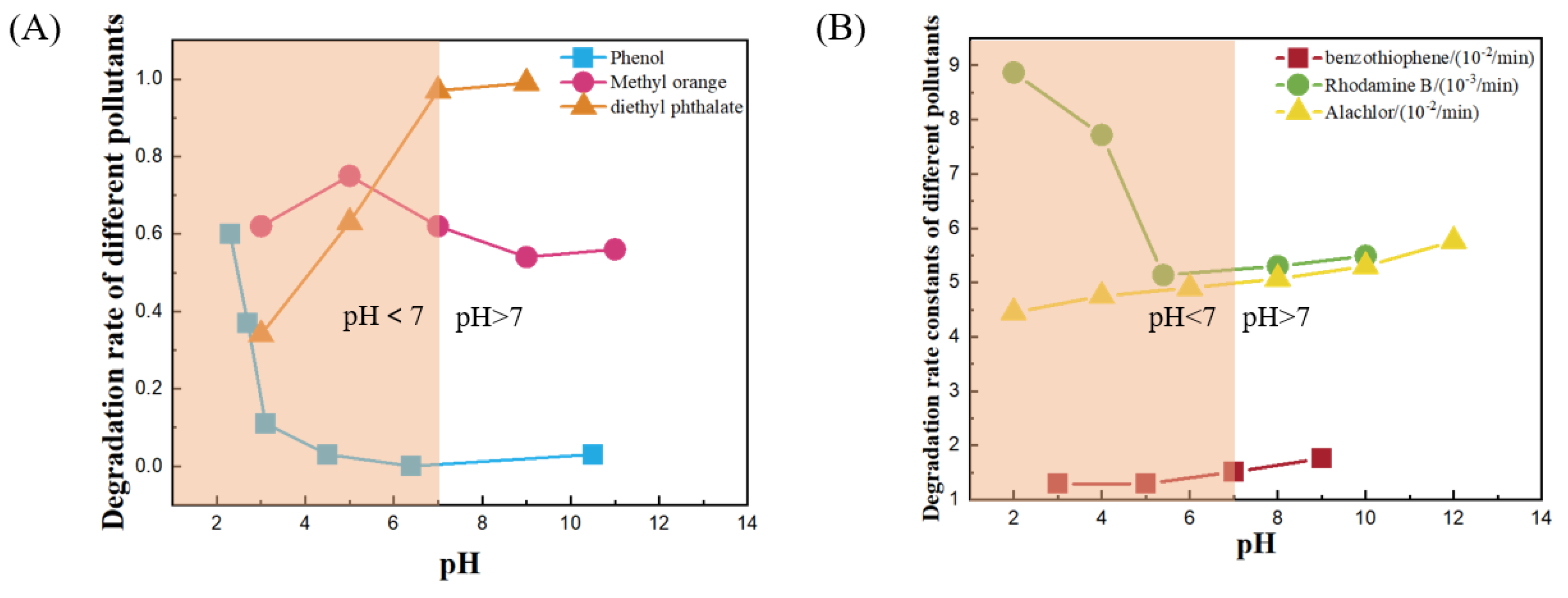
4.1. MNBs Remove Pollutants from Water
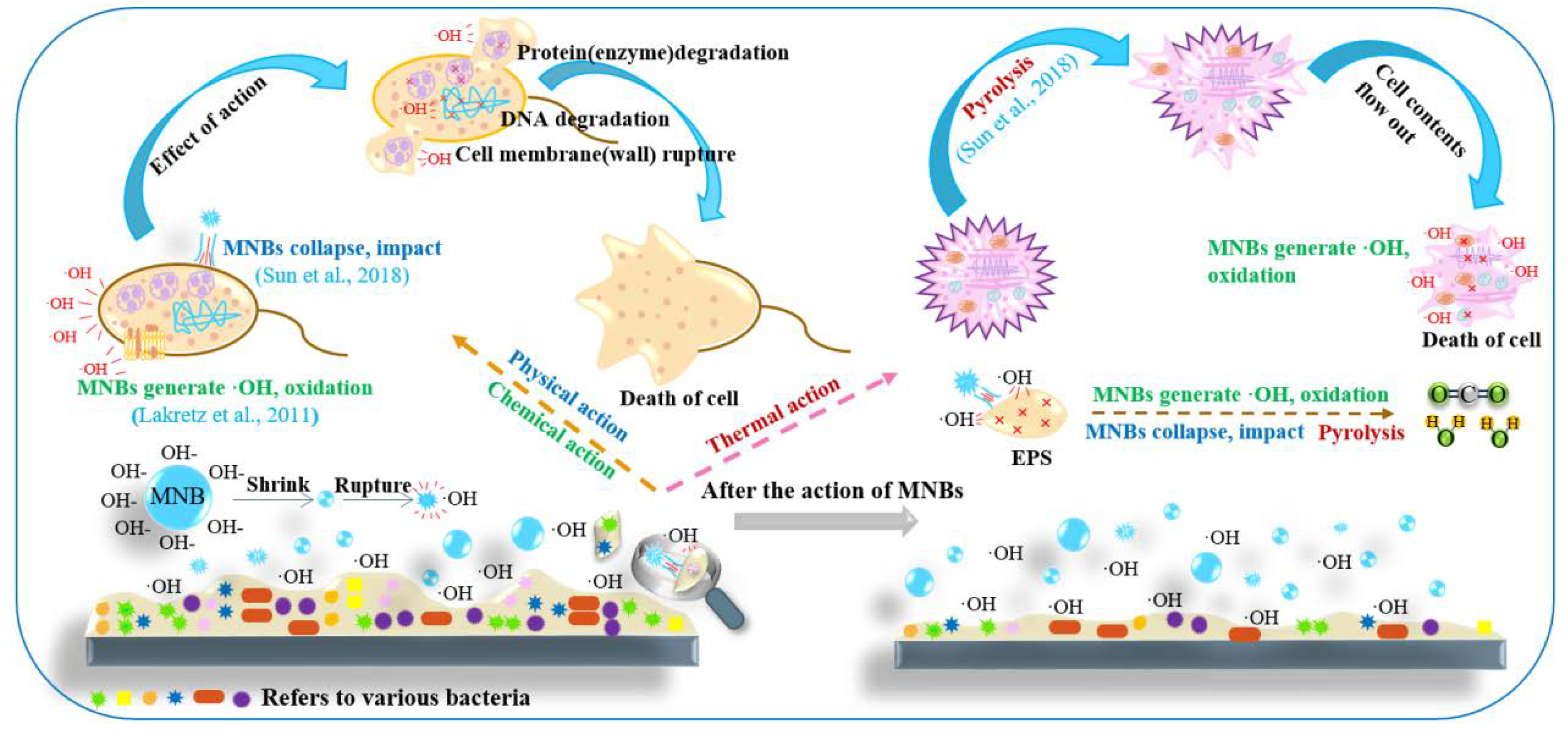
4.2. Control Mechanism of MNBs on Pipe Biofilm Growth
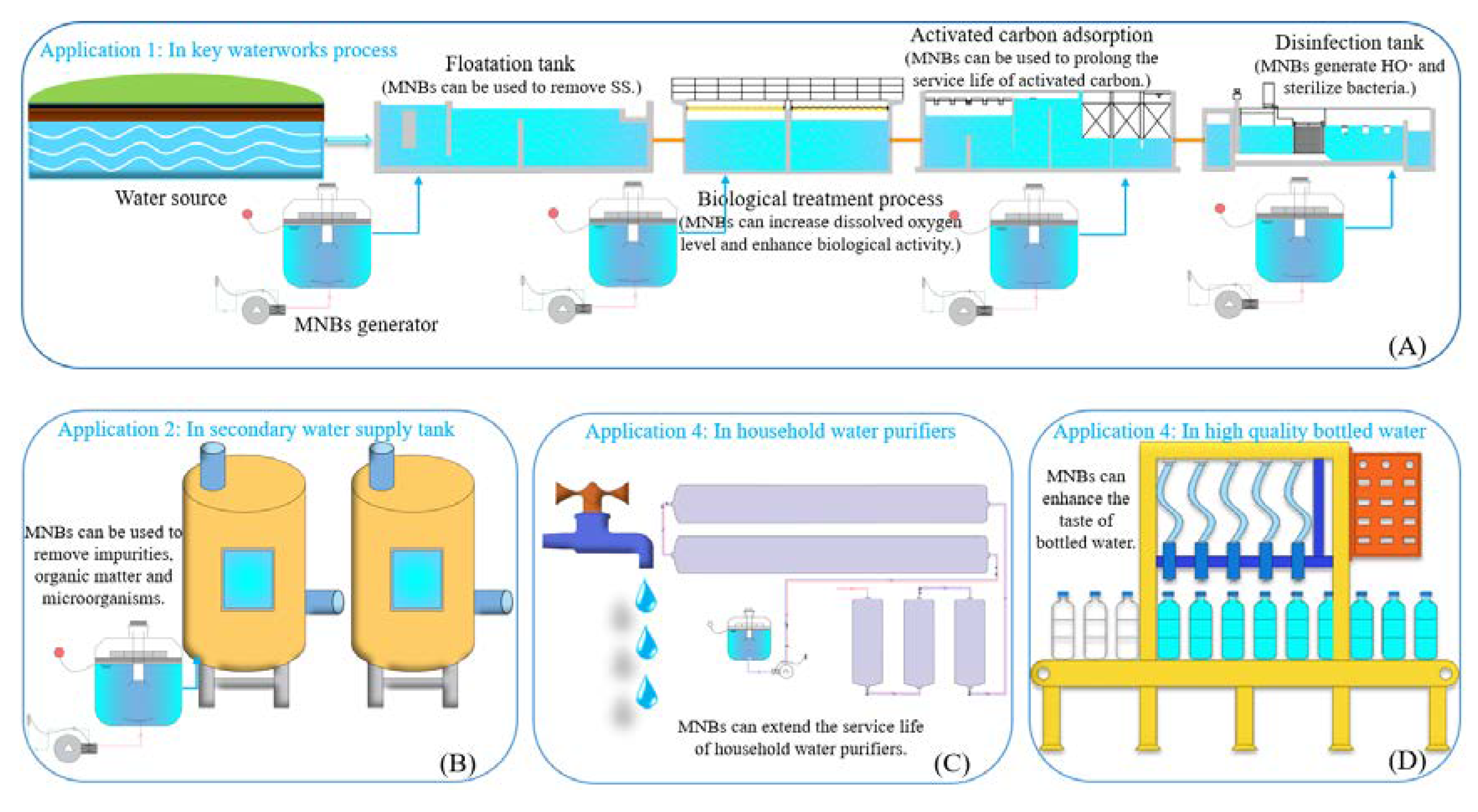
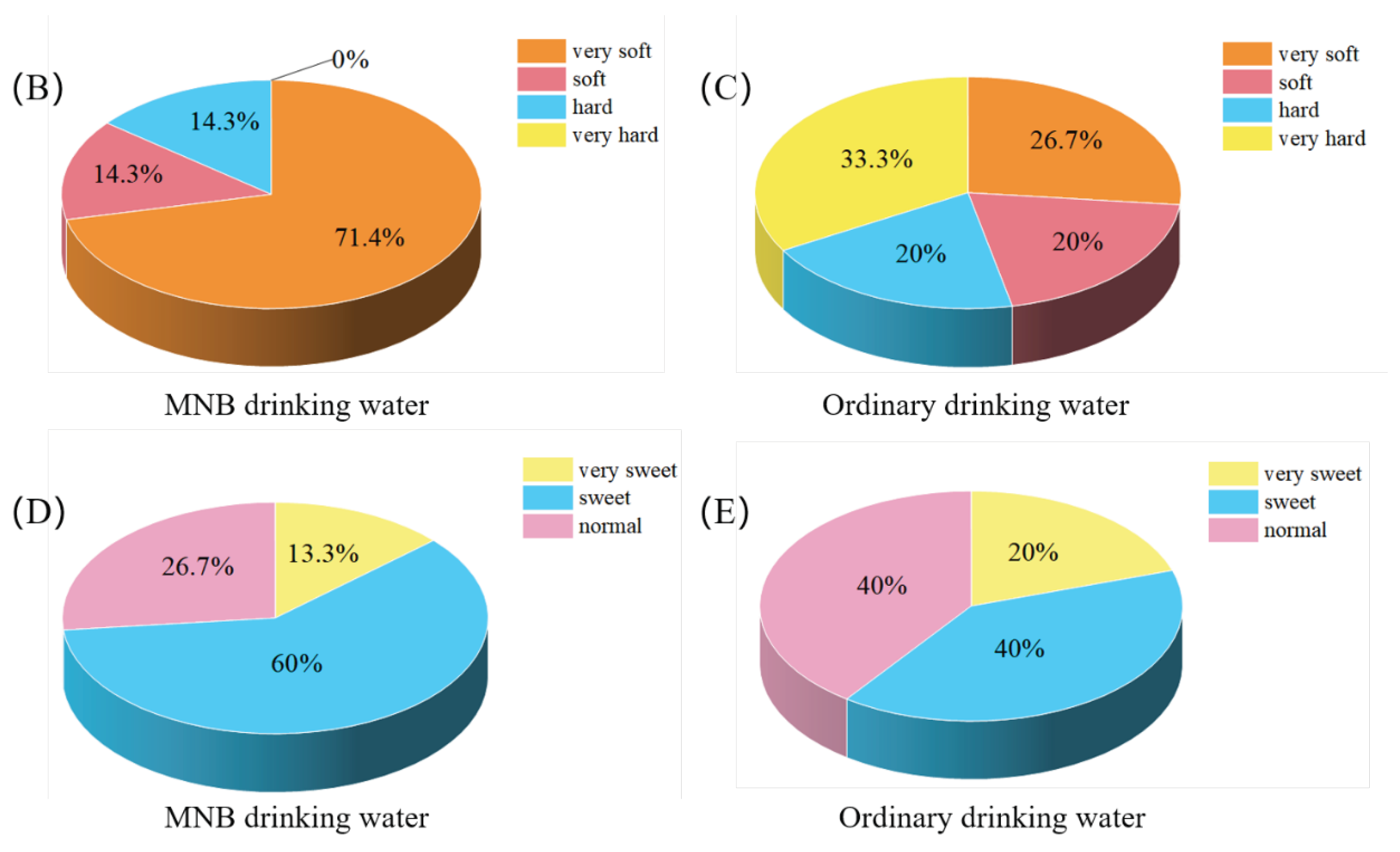
5. Application Prospect of MNBs in Drinking Water
6. Limitations and Prospects of MNBs
- The long-term stable existence of MNBs in water and the ·OH generation mechanism are highly controversial. Existing studies on the above two aspects remain at the surface and speculation level; hence, further discussion is needed.
- The relationship between synergistic and antagonistic effects of MNBs on microorganisms remains unclear. Because the MNBs can generate substantial oxidizing ·OH to destroy microorganisms and provide great potential for water disinfection. Moreover, due to high mass transfer efficiency, MNBs have good biological activity and can promote the biological purification function of water. These two statements are contradictory. Therefore, to better apply MNBs technology, it is required to explore under what circumstances, which side of the synergistic and antagonistic effects of MNBs on microorganisms is more dominant.
- It is difficult to quantitatively determine ·OH generated by MNBs. Recently, the detection methods of ·OH are all indirect methods, which are complicated in operation, and are inevitably interfered by many factors in the detection process, resulting in considerable errors. Future research should focus on direct detection of ·OH to reduce unnecessary interference items.
- MNBs generates a limited amount of ·OH. The ability of MNBs to generate free radicals is only one of its many outstanding properties, and the ·OH generated is only one of the many free radical products. At present, studies on the influence of various factors on the generation of ·OH by MNBs are relatively simple. It should continue to explore how to promote the generation of ·OH by MNBs, and simultaneously control the factors that affect ·OH generation under optimal conditions.
- NBs generation devices are expensive. NBs are superior to MBs in all aspects, but due to the high energy consumption and high price of NB generation devices, the application of NBs in various fields is limited to a certain extent. Hence, developing practical NB generation devices with low energy consumption, low cost, excellent performance and easy promotion is also a new direction of current research.
- The study of MNBs characteristics is not comprehensive enough. At present, the research on the characteristics of MNBs mainly focuses on the well-known aspects of free radical generation and high mass transfer efficiency. Other characteristics of MNBs, such as heat transfer and viscosity, are unknown and require more analysis.
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Achar J C, Nam G, Jung J, et al. Microbubble ozonation of the antioxidant butylated hydroxytoluene: Degradation kinetics and toxicity reduction. Environmental research 2020, 186, 109496.
- Agarwal A, Ng W J, Liu Y. Cleaning of biologically fouled membranes with self-collapsing microbubbles. Biofouling 2013, 29, 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Akcay M U, Avdan Z Y, Inan H. Effect of biofiltration process on the control of THMs and HAAs in drinking water. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 2546–2554. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo A, Etchepare R, Calgaroto S, et al. Aqueous dispersions of nanobubbles: Generation, properties and features. Minerals Engineering 2016, 94, 29–37. [CrossRef]
- Baig S, Liechti P A. Ozone treatment for biorefractory COD removal. Water Science and Technology 2001, 43, 197–204. [CrossRef]
- Baram S, Weinstein M, Evans J F, et al. Drip irrigation with nanobubble oxygenated treated wastewater improves soil aeration. Scientia Horticulturae 2022, 291, 110550. [CrossRef]
- Barton N A, Farewell T S, Hallett S H, et al. Improving pipe failure predictions: Factors affecting pipe failure in drinking water networks. Water research 2019, 164, 114926. [CrossRef]
- Bimakr F, Ginige M P, Kaksonen A H, et al. Assessing graphite and stainless-steel for electrochemical sensing of biofilm growth in chlorinated drinking water systems. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2018, 277, 526–534. [CrossRef]
- Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan M A. Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chemical reviews 2009, 109, 6570–6631. [CrossRef]
- Buttiglieri G, Malpei F, Daverio E, et al. Denitrification of drinking water sources by advanced biological treatment using a membrane bioreactor. Desalination. 2005; 178, 211–218. [CrossRef]
- Cai Y, Li D, Liang Y, et al. Autotrophic nitrogen removal process in a potable water treatment biofilter that simultaneously removes Mn and NH4+-N. Bioresource technology 2014, 172, 226–231. [CrossRef]
- Chang L, Lee J H W, Fung Y S. Prediction of lead leaching from galvanic corrosion of lead-containing components in copper pipe drinking water supply systems. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 436, 129169.
- Chaplin, M. Nanobubbles (ultrafine bubbles). Available online: www1.lsbu.ac.
- 2019. Available online: uk/water/nanobubble. html (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- Cheng W, Quan X, Li R, et al. Ozonation of phenol-containing wastewater using O3/Ca (OH) 2 system in a micro bubble gas-liquid reactor. Ozone: Science & Engineering 2018, 40, 173–182.
- Choi S J, Kim Y H, Jung I H, et al. Effect of Nano Bubble Oxygen and Hydrogen Water on Microalgae. Applied Chemistry for Engineering 2014, 25, 324–329.
- Ebina K, Shi K, Hirao M, et al. Oxygen and air nanobubble water solution promote the growth of plants, fishes, and mice. PLoS One 2013, 8, e65339. [CrossRef]
- Etchepare R, Azevedo A, Calgaroto S, et al. Removal of ferric hydroxide by flotation with micro and nanobubbles. Separation and Purification Technology 2017, 184, 347–353. [CrossRef]
- Fan W, Li Y, Lyu T, et al. A modelling approach to explore the optimum bubble size for micro-nanobubble aeration. Water Research 2023, 228, 119360. [CrossRef]
- Frontistis Z, Mantzavinos D. Sonodegradation of 17α-ethynylestradiol in environmentally relevant matrices: Laboratory-scale kinetic studies. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2012, 19, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Gao Y, Duan Y, Fan W, et al. Intensifying ozonation treatment of municipal secondary effluent using a combination of microbubbles and ultraviolet irradiation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2019, 26, 21915–21924. [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk C, Libra J A, Saupe A. Ozonation of water and waste water: A practical guide to understanding ozone and its applications. John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
- Gogate P R, Kabadi A M. A review of applications of cavitation in biochemical engineering/biotechnology. Biochemical Engineering Journal 2009, 44, 60–72. [CrossRef]
- Guo Z, Wang X, Wang H, et al. Effects of nanobubble water on the growth of Lactobacillus acidophilus 1028 and its lactic acid production. RSC advances 2019, 9, 30760–30767. [CrossRef]
- Hasan H A, Muhammad M H. A review of biological drinking water treatment technologies.
- for contaminants removal from polluted water resources. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2020, 33:101035.
- Hasan H A, Abdullah S R S, Kamarudin S K, et al. Response surface methodology for optimization of simultaneous COD, NH4+–N and Mn2+ removal from drinking water by biological aerated filter. Desalination. 2011, 275, 50–61.
- Hamamoto S, Takemura T, Suzuki K, et al. Effects of pH on nano-bubble stability and transport in saturated porous media. Journal of contaminant hydrology 2018, 208, 61–67. [CrossRef]
- Han M, Zhao Z, Gao W, et al. Study on the factors affecting simultaneous removal of ammonia and manganese by pilot-scale biological aerated filter (BAF) for drinking water pre-treatment. Bioresource technology 2013, 145, 17–24. [CrossRef]
- Han M, Zhao Z, Gao W, et al. Effective combination of permanganate composite chemicals (PPC) and biological aerated filter (BAF) to pre-treat polluted drinking water source. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 28240–28249. [CrossRef]
- Hanotu J, Kong D, Zimmerman W B. Intensification of yeast production with microbubbles. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2016, 100, 424–431. [CrossRef]
- Haris S, Qiu X, Klammler H, et al. The use of micro-nano bubbles in groundwater remediation: A comprehensive review. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2020, 11, 100463. [CrossRef]
- He S, Wang J, Ye L, et al. Removal of diclofenac from surface water by electron beam irradiation combined with a biological aerated filter. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 2014, 105, 104–108. [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard M J, Albrechtsen H J. Microbial pesticide removal in rapid sand filters for drinking water treatment–potential and kinetics. Water Research 2014, 48, 71–81. [CrossRef]
- Henry, W. Experiments on the quantity of gases absorbed by water, at different temperatures, and under different pressures[C]//Abstracts of the Papers Printed in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. London: The Royal Society, 1832, 103-104.
- Huang C, H. Preparation of nanobubbles by ultrasonic method and its effect on electric double layer on electrode surface [D]. Shanghai Normal University, 2016.
- Huang Q, Liu A R, Zhang L J. Characteristics of micro-nanobubbles and their applications in.
- soil environment improvement. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology 2022, 12, 1324–1332.
- Hu L, Xia Z. Application of ozone micro-nano-bubbles to groundwater remediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2018, 342, 446–453. [CrossRef]
- Hu Y Y, Zhu K Q, Xi B S. Numercial study of cavitation erosion on a rigid wall. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics 2004, 21, 22–25.
- Ilmasari D, Kamyab H, Yuzir A, et al. A Review of the Biological Treatment of Leachate: Available Technologies and Future Requirements for the Circular Economy Implementation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2022: 108605. [CrossRef]
- Jabesa A, Ghosh P. Removal of diethyl phthalate from water by ozone microbubbles in a pilot plant. Journal of Environmental Management 2016, 180, 476–484. [CrossRef]
- Jia W, Ren S, Hu B. Effect of water chemistry on zeta potential of air bubbles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2013, 8, 5828–5837. [CrossRef]
- Jin N, Zhang F, Cui Y,et al.Environment-friendly surface cleaning using micro-nano bubbles. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Kalumuck K M, Chahine G L. The use of cavitating jets to oxidize organic compounds in water. J. Fluids Eng. 2000, 122, 465–470. [CrossRef]
- Khadre M A, Yousef A E, Kim J G. Microbiological aspects of ozone applications in food: a review. Journal of food science 2001, 66, 1242–1252. [CrossRef]
- Khaled Abdella Ahmed A, Sun C, Hua L, et al. Colloidal properties of air, oxygen, and nitrogen nanobubbles in water: Effects of ionic strength, natural organic matters, and surfactants. Environmental Engineering Science 2018, 35, 720–727.
- Khuntia S, Majumder S K, Ghosh P. Quantitative prediction of generation of hydroxyl radicals from ozone microbubbles. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2015, 98, 231–239. [CrossRef]
- Kim I K, Huang C P. Sonochemical degradation of polycyclic aromatic sulfur hydrocarbons (PASHs) in aqueous solutions exemplified by benzothiophene. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers 2005, 28, 1107–1118.
- Kim J R, Huling S G, Kan E. Effects of temperature on adsorption and oxidative degradation of bisphenol A in an acid-treated iron-amended granular activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal 2015, 262, 1260–1267.
- Kondo T, Gamson J, Mitchell J B, et al. Free radical formation and cell lysis induced by ultrasound in the presence of different rare gases. International journal of radiation biology 1988, 54, 955–962. [CrossRef]
- Kohno M, Mokudai T, Ozawa T, et al. Free radical formation from sonolysis of water in the presence of different gases. Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition 2011, 49, 96–101. [CrossRef]
- Kröninger D, Köhler K, Kurz T, et al. Particle tracking velocimetry of the flow field around a collapsing cavitation bubble. Experiments in fluids 2010, 48, 395–408. [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan T A, Lo W, Chan G, et al. Biological processes for treatment of landfill leachate. Journal of Environmental Monitoring 2010, 12, 2032–2047.
- Lakretz A, Ron E Z, Mamane H. Biofilm control in water by a UV-based advanced oxidation process. Biofouling 2011, 27, 295–307. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Hu L, Song D, et al. Characteristics of micro-nano bubbles and potential application in groundwater bioremediation. Water Environment Research 2014, 86, 844–851. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Hu L, Song D, et al. Subsurface transport behavior of micro-nano bubbles and potential applications for groundwater remediation. International journal of environmental research and public health 2014, 11, 473–486. [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Study on the Water, Fertilization and aeration distribution characteristics of aerated drip irrigation, and the clogging of emitters[D]. Jiangsu University, 2020.
- Li J, Song Y, Yin J, et al. Investigation on the effect of geometrical parameters on the performance of a venturi type bubble generator. Nuclear Engineering and Design 2017, 325, 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Li P, Takahashi M, Chiba K. Enhanced free-radical generation by shrinking microbubbles using a copper catalyst. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1157–1160. [CrossRef]
- Li P, Takahashi M, Chiba K. Degradation of phenol by the collapse of microbubbles. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1371–1375. [CrossRef]
- Li P, Tsuge H, Itoh K. Oxidation of dimethyl sulfoxide in aqueous solution using microbubbles. Industrial & engineering chemistry research 2009, 48, 8048–8053. [CrossRef]
- Li T, Shang C, Xiang Y, et al. ClO2 pre-oxidation changes dissolved organic matter at the molecular level and reduces chloro-organic byproducts and toxicity of water treated by the UV/chlorine process. Water Research 2022, 216, 118341. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Chu H P. Membrane bioreactor for the drinking water treatment of polluted surface water supplies. Water research 2003, 37, 4781–4791.
- Li Y, J. Formation and characterization of bulk micro-/nanobubbles[D]. Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2020.
- Li Z, Dvorak B, Li X. Removing 17β-estradiol from drinking water in a biologically active carbon (BAC) reactor modified from a granular activated carbon (GAC) reactor. Water research 2012, 46, 2828–2836. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Tang Y. Application research of micro and nano bubbles in water pollution control[C]//E3S Web of Conferences. EDP Sciences. 2019; 136, 06028.
- Liu J, Chen H, Yao L, et al. The spatial distribution of pollutants in pipe-scale of large-diameter pipelines in a drinking water distribution system. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2016, 317, 27–35. [CrossRef]
- Liu S, Wang Q, Ma H, et al. Effect of micro-bubbles on coagulation flotation process of dyeing wastewater. Separation and purification Technology 2010, 71, 337–346. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Zhou Y, Wang T, et al. Micro-nano bubble water oxygation: Synergistically improving irrigation water use efficiency, crop yield and quality. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 222, 835–843. [CrossRef]
- Ljunggren S, Eriksson J C. The lifetime of a colloid-sized gas bubble in water and the cause of the hydrophobic attraction. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 1997, 129, 151–155. [CrossRef]
- Lu J, Huang X, Zhang Z, et al. Co-coagulation of micro-nano bubbles (MNBs) for enhanced drinking water treatment: A study on the efficiency and mechanism of a novel cleaning process. Water Research 2022, 226, 119245. [CrossRef]
- Maeda Y, Hosokawa S, Baba Y, et al. Generation mechanism of micro-bubbles in a pressurized dissolution method. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 2015, 60, 201–207. [CrossRef]
- Makuta T, Aizawa Y, Suzuki R. Sonochemical reaction with microbubbles generated by hollow ultrasonic horn. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2013, 20, 997–1001. [CrossRef]
- Marsidi N, Hasan H A, Abdullah S R S. A review of biological aerated filters for iron and manganese ions removal in water treatment. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2018, 23, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Mason T J, Joyce E, Phull S S, et al. Potential uses of ultrasound in the biological decontamination of water. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2003, 10, 319–323. [CrossRef]
- Masuda N, Maruyama A, Eguchi T, et al. Influence of microbubbles on free radical generation by ultrasound in aqueous solution: dependence of ultrasound frequency. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2015, 119, 12887–12893. [CrossRef]
- Matos C T, Velizarov S, Reis M A M, et al. Removal of bromate from drinking water using the ion exchange membrane bioreactor concept. Environmental science & technology 2008, 42, 7702–7708. [CrossRef]
- McKie M J, Andrews S A, Andrews R C. Conventional drinking water treatment and direct biofiltration for the removal of pharmaceuticals and artificial sweeteners: a pilot-scale approach. Science of the Total Environment 2016, 544, 10–17. [CrossRef]
- Meegoda J N, Aluthgun Hewage S, Batagoda J H. Stability of nanobubbles. Environmental Engineering Science 2018, 35, 1216–1227.
- Mekal A D, El-Shazly M M, Ragab M, et al. Comparison of modern and 40-year-old drinking water pipeline in northern Sinai region, Egypt: Characteristics and health risk assessment. Trace Elements and Minerals 2023, 5, 10078. [CrossRef]
- Mezule L, Tsyfansky S, Yakushevich V, et al. A simple technique for water disinfection with hydrodynamic cavitation: Effect on survival of Escherichia coli. Desalination. 2009, 248, 152–159. [CrossRef]
- Minamikawa K, Takahashi M, Makino T, et al. Irrigation with oxygen-nanobubble water can reduce methane emission and arsenic dissolution in a flooded rice paddy. Environmental Research Letters 2015, 10, 084012. [CrossRef]
- Moreira F C, Garcia-Segura S, Vilar V J P, et al. Decolorization and mineralization of Sunset Yellow FCF azo dye by anodic oxidation, electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton processes. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2013, 142, 877–890. [CrossRef]
- Nagayama G, Tsuruta T, Cheng P. Molecular dynamics simulation on bubble formation in a nanochannel. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 2006, 49, 4437–4443. [CrossRef]
- Nakashima T, Kobayashi Y, Hirata Y. Method to exterminate blue-green algae in a large pond and to improve plant growth by micro-nano bubbles in activated water[C]//XXVIII International Horticultural Congress on Science and Horticulture for People (IHC2010): International Symposium on 938. 2010: 391-400.
- Qiu J, Zou Z, Wang S, et al. Formation and stability of bulk nanobubbles generated by ethanol–water exchange. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1345–1350. [CrossRef]
- Pera-Titus M, García-Molina V, Baños M A, et al. Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2004, 47, 219–256. [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel D, Viraraghavan T. Biological filtration for removal of arsenic from drinking water. Journal of environmental management 2009, 90, 1956–1961. [CrossRef]
- Pramanik B K, Choo K H, Pramanik S K, et al. Comparisons between biological filtration and coagulation processes for the removal of dissolved organic nitrogen and disinfection by-products precursors. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 2015, 104, 164–169. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini M, Das I, Ghangrekar M M,et al.Advanced oxidation processes: Performance, advantages, and scale-up of emerging technologies. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316.
- Ricardo A R, Carvalho G, Velizarov S, et al. Kinetics of nitrate and perchlorate removal and biofilm stratification in an ion exchange membrane bioreactor. water research 2012, 46, 4556–4568. [CrossRef]
- Sakr M, Mohamed M M, Maraqa M A, et al. A critical review of the recent developments in micro–nano bubbles applications for domestic and industrial wastewater treatment. Alexandria Engineering Journal 2022, 61, 6591–6612. [CrossRef]
- Schijven J F, van den Berg H H J L, Colin M, et al. A mathematical model for removal of human pathogenic viruses and bacteria by slow sand filtration under variable operational conditions. Water research 2013, 47, 2592–2602. [CrossRef]
- Seddon J R T, Lohse D, Ducker W A, et al. A deliberation on nanobubbles at surfaces and in bulk. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2179–2187. [CrossRef]
- Shen D, Xie Z, Shentu J, et al. Enhanced oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons by ozone micro-nano bubble water: Mechanism and influencing factors. Environmental Chemical Engineering 2023, 11, 110281. [CrossRef]
- Shirgaonkar I Z, Lothe R R, Pandit A B.Comments on the mechanism of microbial cell disruption in high-pressure and high-speed devices. Biotechnology Progress 1998, 14, 657–660. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian G, Prakash H. Photo augmented copper-based Fenton disinfection under visible LED light and natural sunlight irradiation. Water Research 2021, 190, 116719. [CrossRef]
- Sumikura M, Hidaka M, Murakami H, et al. Ozone micro-bubble disinfection method for wastewater reuse system. Water Science and Technology 2007, 56, 53–61. [CrossRef]
- Sun X, Park J J, Kim H S, et al. Experimental investigation of the thermal and disinfection performances of a novel hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2018, 49, 13–23.
- Tan S Y, Shen Y, Liu Y Z, et al. Effects and mechanism of using Nanobubble to inhibit biofouling and scaling in biogas slurry drip irrigation emitters.. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(14).
- Takahashi M, Kawamura T, Yamamoto Y, et al. Effect of shrinking microbubble on gas hydrate formation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2003, 107, 2171–2173. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi Masayoshi. The ζ potential of microbubbles in aqueous solutions—Electrical properties of the gas-water interface. The Journal of Physical Chemistry 2005, 109, 21858–21864.
- Takahashi M, Chiba K, Li P. Formation of hydroxyl radicals by collapsing ozone microbubbles under strongly acidic conditions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2007, 111, 11443–11446. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi M, Chiba K, Li P. Free-radical generation from collapsing microbubbles in the absence of a dynamic stimulus. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2007, 111, 1343–1347. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi M, Ishikawa H, Asano T, et al. Effect of microbubbles on ozonized water for photoresist removal. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2012, 116, 12578–12583. [CrossRef]
- Tao H, Chun Y E, Chun-Hua L I, et al.Treatment effect of microbubble aeration technology on black-odor river water. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology 2011, 1, 20–25.
- Tan K A, Mohan Y, Liew K J, et al. Development of an effective cleaning method for metallic parts using microbubbles. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 261, 121076. [CrossRef]
- Tasaki T, Wada T, Fujimoto K, et al. Degradation of methyl orange using short-wavelength UV irradiation with oxygen microbubbles. Journal of hazardous materials 2009, 162, 1103–1110. [CrossRef]
- Tekerlekopoulou A G, Vayenas D V. Ammonia, iron and manganese removal from potable water using trickling filters. Desalination 2007, 210, 225–235. [CrossRef]
- Teo K C, Xu Y, Yang C. Sonochemical degradation for toxic halogenated organic compounds. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2001, 8, 241–246.
- Temesgen T, Bui T T, Han M, et al. Micro and nanobubble technologies as a new horizon for water-treatment techniques: A review. Advances in colloid and interface science 2017, 246, 40–51. [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, T. Enhancing gas-liquid mass transfer and) bio (chemical reactivity using ultrafine/nanobubble in water and waste water treatments. Civil and Environmental Engineering. Seoul, Korea: Seoul National University, 2017.
- Thompson L H, Doraiswamy L K. Sonochemistry: science and engineering. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 1999, 38, 1215–1249.
- Tian J, Liang H, Li X, et al. Membrane coagulation bioreactor (MCBR) for drinking water treatment. Water research 2008, 42, 3910–3920. [CrossRef]
- Tian J, Chen Z, Yang Y, et al. Hybrid process of BAC and sMBR for treating polluted raw water. Bioresource technology 2009, 100, 6243–6249. [CrossRef]
- Ushikubo F Y, Enari M, Furukawa T, et al. Zeta-potential of micro-and/or nano-bubbles in water produced by some kinds of gases. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2010, 43, 283–288. [CrossRef]
- Ushikubo F Y, Furukawa T, Nakagawa R, et al. Evidence of the existence and the stability of nano-bubbles in water. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2010, 361, 31–37.
- Wang B, Su H, Zhang B. Hydrodynamic cavitation as a promising route for wastewater treatment–A review. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 412, 128685. [CrossRef]
- Wang W, Fan W, Huo M, et al. Hydroxyl radical generation and contaminant removal from water by the collapse of microbubbles under different hydrochemical conditions. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 2018, 229, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Zhang Y. Degradation of alachlor in aqueous solution by using hydrodynamic cavitation. Journal of hazardous materials 2009, 161, 202–207. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Wang J, Guo P, et al. Chemical effect of swirling jet-induced cavitation: Degradation of rhodamine B in aqueous solution. Ultrasonics sonochemistry 2008, 15, 357–363. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Y. Mechanism and application research of the emitters clogging control method by micro-nano bubbles of drip irrigation systems with biogas slurry[D]. Shihezi University, 2020.
- Wu M, Song H, Liang X, et al. Generation of micro-nano bubbles by self-developed swirl-type micro-nano bubble generator. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification 2022, 181, 109136. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, Zhang X, Zhang X, et al. Nanobubbles influence on BSA adsorption on mica surface. Surface and Interface Analysis: An International Journal devoted to the development and application of techniques for the analysis of surfaces, interfaces and thin films 2006, 38, 990–995.
- Wu Z H, Zhang X H, Zhang X D, et al. In situ AFM observation of BSA adsorption on HOPG with nanobubble. Chinese Science Bulletin 2007, 52, 1913–1919.
- Xiao W, Xu G, Li G. Effect of nanobubble application on performance and structural characteristics of microbial aggregates. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 765, 142725. [CrossRef]
- Xiao W, Xu G. Mass transfer of nanobubble aeration and its effect on biofilm growth: Microbial activity and structural properties. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 703, 134976. [CrossRef]
- Xia Z, Hu L. Treatment of organics contaminated wastewater by ozone micro-nano-bubbles. Water 2018, 11, 55. [CrossRef]
- Xia Z, Hu L. Remediation of organics contaminated groundwater by ozone micro-nano bubble. Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication 2016, 2, 1978–1981. [CrossRef]
- Xia Z, Hu L, Kusaba S, et al. Remediation of TCE contaminated site by ozone micro-nano-bubbles[C]//The International Congress on Environmental Geotechnics. Springer, Singapore, 2018: 796-803.
- Xie S G, Wen D H, Shi D W, et al. Reduction of precursors of chlorination by-products in drinking water using fluidized-bed biofilm reactor at low temperature. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences 2006, 19, 360.
- Xu M Y, Lin Y L, Zhang T Y, et al. Chlorine dioxide-based oxidation processes for water purification: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 436, 129195.
- Yan C C, Cun H H, Zhang H Y, et al. Numerical simulation of effects of microbubble growth and collapse on adjacent microspheres. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics 2022, 36, 580–587.
- Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Kanematsu W. High temperature and pressure inside a dissolving oxygen nanobubble. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry 2019, 55, 308–312. [CrossRef]
- Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Kanematsu W, et al. Dynamic equilibrium model for a bulk nanobubble and a microbubble partly covered with hydrophobic material. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11101–11110. [CrossRef]
- Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Kanematsu W. Extreme conditions in a dissolving air nanobubble. Physical Review E, 2016b, 94(1): 013106. [CrossRef]
- Yasui K, Tuziuti T, Sivakumar M, et al. Theoretical study of single-bubble sonochemistry. Chemical Physics 2005, 122, 224706. [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K. Alternative model of single-bubble sonoluminescence. Physical Review E 1997, 56: 6750. [CrossRef]
- Yapsakli K, Mertoglu B, Çeçen F. Identification of nitrifiers and nitrification performance in drinking water biological activated carbon (BAC) filtration. Process Biochemistry 2010, 45, 1543–1549. [CrossRef]
- Yu X, Wang Z, Lv Y, et al. Effect of microbubble diameter, alkaline concentration and temperature on reactive oxygen species concentration. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 2017, 92, 1738–1745. [CrossRef]
- Yüksel S, Kabay N, Yüksel M. Removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from water by various nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. Journal of hazardous materials 2013, 263, 307–310. [CrossRef]
- Zhai H, He X, Zhang Y, et al. Disinfection byproduct formation in drinking water sources: A case study of Yuqiao reservoir. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 224–231. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Lin H, Li Q, et al. Removal of refractory organics in wastewater by coagulation/flocculation with green chlorine-free coagulants. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 787, 147654. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L J, Chen H, Li Z X, et al. The longevity of nanobubbles stems from their high internal density. Scientia Sinica: G series 2007, 37, 556–560.
- Zhang M, Qiu L, Liu G. Basic characteristics and application of micro-nano bubbles in water treatment[C]//IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing. 2020; 510, 042050.
- Zhang, T. The development of drinking water treatment technology. China High-Tech Enterprises, 2013, 6-8.
- Zhang X H, Maeda N, Craig V S J. Physical properties of nanobubbles on hydrophobic surfaces in water and aqueous solutions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5025–5035. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X X, Zhang Z Y, Ma L P, et al. Influences of hydraulic loading rate on SVOC removal and microbial community structure in drinking water treatment biofilters. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2010, 178, 652–657.
- Zhao L, Sun L, Mo Z, et al. Effects of the divergent angle on bubble transportation in a rectangular Venturi channel and its performance in producing fine bubbles. International Journal of Multiphase Flow 2019, 114, 192–206. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Wakisaka M. Effect of air nanobubble water on the growth and metabolism of Haematococcus lacustris and Botryococcus braunii. Journal of nutritional science and vitaminology, 2019, 65(Supplement): S212-S216. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Z, Shan L, Li X, et al. Effects of interspecific interactions on biofilm formation potential and chlorine resistance: Evaluation of dual-species biofilm observed in drinking water distribution systems. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2020, 38, 101564. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Z B, Pei Y Y, Shan L L, et al. Microbial interspecific interaction and its influencing factors in biofilm of drinking water distribution systems: A review. Environmental Engineering 2023, 41, 210–221.
- Zwaan E, Le Gac S, Tsuji K, et al. Controlled cavitation in microfluidic systems. Physical review letters 2007, 98, 254501. [CrossRef]

| Treatment Methods | Pollutants Removed from Drinking Water | Advantages | Disadvantages | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physico- chemical methods |
Adsorption | Organic pollutants (Bisphenol A) |
Simple and effective. | Adsorbent regeneration, high cost; The adsorption capacity of regenerated adsorbent decreases and the service life is short. | Kim et al., 2015 |
| Membrane separation technology | Particles, Sediments, Algae, Bacteria, Protozoa, Small colloid, Virus, Dissolved organics, Divalent ions Monovalent ions, COD |
No secondary pollution. | High energy consumption, complex equipment, high intake water quality requirements; Membrane fouling. | Yüksel et al., 2013 | |
| Coagulation/flocculation | Refractory organics | Economical and practical. | Produce secondary pollution. | Zhang et al., 2021 | |
| Ultrasonic decomposition | Particles, Organic pollutants | Short reaction time, simple process facilities. | Relatively low efficiency. | Zhang,2013 | |
| Photocatalytic technology | Dissolved organic carbon (DOC), Bacteria | Semiconductors are cheap, can mineralize refractory compounds, clean and safe. | Still in the development stage and immature. | Pera-Titus et al., 2004 | |
| Chemical methods | Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) |
Organic micro-pollutants | Has the environmental compatibility, versatility, high efficiency, safety. | Relatively low efficiency. Formation of stable by-products. |
Brillas et al., 2009; Moreira et al., 2013 |
| O3 based oxidation process | Organic pollutants (chlorophenols), Bacteria | Economical and efficient, harmless to most organisms, no harmful by-products generation. | Harmful to human health; High energy demand. | Pera-Titus et al., 2004; Baig et al., 2001 | |
| H2O2 based oxidation process | Organic pollutants (chlorophenols), Bacteria | Safe, efficient and easy to use; Widely used to prevent pollution and improve biodegradability. | The reaction process is affected by many factors, and the reaction time is long. | Pera-Titus et al., 2004 | |
| Chlorine based oxidation process | Organic matter, Bacteria Micropollutants, Viruses |
Chlorine remains in the water as residual chlorine, and the activity is persistent. High yield of active species, broad-spectrum, safe and effective. |
Taste and smell are not ideal, forming more than 40 DBPs. Disinfection effect is not ideal, used for secondary disinfection. |
Zhai et al., 2017; Li et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022; Subramanian et al., 2021 |
|
| Biological methods | Biological sand filtration (BSF) |
Viruses, Bacteria, Heavy metals, Nitrogenous compounds, Pesticides, Organic chemicals, Dissolved organic carbon (DOC), NOM, etc. | Easy operation, efficient and reliable operation, low cost. | (ⅰ) Microorganisms have high selectivity to pollutants, and the biodegradation time is long and the equipment is complex. (ⅱ) The uncontrolled growth of microorganisms may lead to health problems. (ⅲ) The application of biological sand filtration has high requirements on terrain and limited application scenarios. |
Pokhrel et al., 2009; Schijven et al., 2013; Hedegaard et al., 2014; Cai et al., 2014; Pramanik et al., 2015 |
| Biological activated carbon (BAC) | Nitrogenous compounds, Organic carbon, Micropollutants. |
The dual functions of adsorption and biodegradation improve the effectiveness of drinking water. | Li et al., 2012; Yapsakli et al., 2010; Zhang et al., 2010; McKie et al., 2016; Akcay et al., 2016 | ||
| Trickling filter (TF) | NH3-N, Fe, Mn. | No external air supply required. | Tekerlekopoulou et al.,2007 | ||
| Biological aerated filter (BAF) | COD, NH4+-N, Fe, Mn, Diclofenac. | Economical and effective. | Hasan et al., 2011; Han et al., 2013, 2016; He et al., 2014; Marsidi et al., 2018 | ||
| Membrane bioreactor (MBR) |
Nitrate, Total organic carbon (TOC), Deamination, Macro pollutants, Anionic micropollutants (perchlorate, bromate, nitrate) | Overcomes the problem of microbial contamination and supports the growth of selected microorganisms. | Buttiglieri et al., 2005; Li et al., 2003; Ricardo et al., 2012; Matos et al., 2008 |
||
| Fluidized bed biofilm reactor (FBBR) | TOC, THM, Ammonia. | No backwash required, easy to manage. | Xie et al., 2006 | ||
| Integrated/ combining technologies |
Microorganism, Particle, Nitrate, Phosphate, Organic matter, Ammonium | Higher treatment efficiency. Improve the quality of treated water and reduce membrane pollution. |
Tian et al., 2008; Tian et al., 2009 |
||
| Application fields | Main function | Gas type | Bubble size(nm) | Bubble concentration(one/mL) | Characteristics of applied MNBs | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochemical process | Promote the growth of microalgae and increase the output of many high-value products. | air | <200 | / | ④ | Zhu and Wakisaka, 2019; Choi et al., 2014 |
| Improve biofilm structure and promote aerobic metabolism; Improve COD and ammonia removal rate and reduce aeration. | air | <225 | / | ④ | Xiao et al., 2021; Xiao and Xu, 2020 |
|
| Improve the production efficiency of probiotics through fermentation, mainly in the lag stage and logarithmic stage of strain growth. | air | 180~220 | (3.59±1.14)×107 | ⑥ | Guo et al.,2019 | |
| Improve the production efficiency and recovery rate of yeast. | air | ≈3×105 | / | ④ | Hanotu et al., 2016 | |
| Groundwater remediation | Improve the mass transfer efficiency of O3 and the in-situ remediation efficiency of organically contaminated groundwater. | O3 | 10~1000 | (1~1000)×106 | ③,④ | Hu and Xia., 2018 |
| Surface cleaning | Prevent and remove protein adsorbed on solid surface. | air | 25~35 | / | ⑦ | Wu et al., 2006; Wu et al., 2007 |
| Remove oil stain on metal surface. | air | (2~6)×104 | / | ①,② | Tan et al., 2020 | |
| Agronomy | Improve irrigation water use efficiency, crop yield and quality. | air | 124~148 | (6~7)×108 | ④ | Liu et al., 2019 |
| Improve plant growth; Purifying blue-green algae pollution. | air | 200~2200 | / | ④ | Nakashima et al., 2010 | |
| Soil environment | Change the redox conditions of submerged paddy soil to reduce methane emission. | O2 | 128~242 | (6~8)×107 | ④ | Minamikawa et al., 2020 |
| Remove metal pollutants from soil. | O2 | <103 | / | ④ | Minamikawa et al., 2015 | |
| Improve the availability of oxygen in clay or sandy soil and improve the soil anoxic environment. | O2 | 190~210 | (0.5~1.5)×109 | ④ | Baram et al., 2022 | |
| Marine animals and food | Significantly promote the growth of plants, fish and mice. | O2 | <200 | / | ④ | Ebina et al., 2013 |
| air | / | |||||
| Water pollution treatment | Aeration to improve oxygen mass transfer efficiency. | air | 102~105 | / | ④ | Li et al., 2014 |
| Disinfect and can effectively remove bacteria and viruses. | O3 | (3~6)×104 | / | ⑤ | Sumikura et al., 2007 | |
| Flotation to improve the treatment effect of printing and dyeing wastewater. | air | <6×104 | / | ②,③,④,⑤ | Liu et al., 2010 | |
| Degradation of organic pollutants (see Table 4) | ||||||
| Generation methods | Generation process | Influence factor | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic cavitation | When a large pressure difference is generated in the moving fluid, hydrodynamic cavitation will be observed, resulting in MNBs. | Pressure difference. | High efficiency and low energy consumption. | Bubble size is not easy to control. | Etchepare et al., 2017; Maeda et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2022; Sakr et al.,2022 |
| Ultrasonic cavitation | Apply sound field to make the liquid generate tensile stress and negative pressure. If the pressure is too saturated, MBs will be generated. | Ultrasonic time, frequency. | The bubble size is small and uniform. | Complex operation for large-scale treatment. | |
| Optic cavitation | A certain wavelength of light is irradiated on the photocatalysis material, which makes the electrons transit, and MNBs precipitate. | Wavelength of light. | No secondary pollution. | High cost, not conducive to mass production. | |
| Jet dispersion method | The air-liquid mixture is formed after the air compressor is injected or inhaled by itself, and then injected at high speed, relying on the turbulence between the air and liquid to generate MNBs. | Air intake. | Rapid generation of MNBs with uniform size. | The air intake is difficult to control. | |
| Compressed air passing through diffusion plate method | The pressurized air enters the liquid phase through the micropores with a certain size on the special diffusion plate, and the gas forms MNBs under the shear of the micropores. | Size of micropore. | Relatively simple operation, easy to form MNBs. | Expensive device, pores are easy to block. | |
| Mechanical force high-speed shearing air method | The larger bubbles in the liquid are divided into MNBs by using the shear effect generated by the high-speed rotating impeller. | Impeller rotation. | Rapid generation of a large number of MNBs. | Unstable bubble size, high energy consumption. | |
| Dissolved gas release method | First, pressurize the gas to make it supersaturated and dissolved, and then decompress the gas to release, thus producing MNBs. | Pressure and nozzle cavitation mode. | Simple operation and low energy consumption. | Discontinuous gas dissolution and release, low efficiency. | |
| Aeration method | Directly use various micro nano bubble generators to aerate in water, producing MNBs. | MNBs generator type. | Easy to operate, non-toxic and residue free. | The instrument is expensive. | |
| Chemical reaction method | Add chemical reagents to the solution to make it react violently, producing MNBs. | Type of reactant. | High bubble generation efficiency. | Bring secondary pollution | |
| Electro-chemical method | Electrolyze water through electrode to form MNBs on the positive and negative plates. | Voltage size, electrolytic time . | The size of bubbles can be controlled. | High energy consumption and low efficiency. |
| Bubble type | T | P | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| MNBs | >5000K | / | Takahashi et al., 2007b |
| Air NBs | 3000K | 5GPa | Yasui et al., 2019 |
| Oxygen NBs | 2800K | 4.5GPa | |
| MNBs | 500~15000 K | 100~5000 Pa | Wang et al., 2021 |
| MNBs | 2000–6000 K | / | Sun et al., 2018 |
| Pollutants | Generation of MNBs | Type of air source | Reaction time(min) | Initial concentration/(mg/L) | pH | Temperature | Degradation rate constant/degradation rate/lnc/c0 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alachlor | Swirling jet-induced cavitation. | air | 100 | 50 | 5.9 | 40℃ | 4.90×10−2min-1 | Wang and Zhang, 2009 |
| Rhodamine B | Swirling jet-induced cavitation. | air | 180 | 5 | 5.4 | 40℃ | 62%/5.13×10−3min-1 | Wang et al., 2008 |
| Diethyl phthalate | Aeration method | O3 | 30 | 222 | 9 | 25℃ | 98% | Jabesa et al., 2016 |
| Phenol | Dissolved gas release method. | O2 | 120 | 18.8 | 2.3 | 35℃ | 83%/2.67×10−2min-1 | Li et al., 2009b |
| Dissolved gas release method. | air | 180 | / | <7 | <50℃ | 30% | Takahashi et al., 2007 | |
| Micro bubble ozonation reactor. | O3+Ga(OH)2 | 40 | 450 | / | 25℃ | 99% | Cheng et al., 2018 | |
| Methyl orange | Spiral liquid flow coupled pressurized dissolution | O3 | 30 | 10 | / | 20℃ | 96% | Xia and Hu, 2016 |
| Aeration method | O3 | 30 | 50 | 3~11 | 20℃ | >90% | Xia and Hu., 2018 | |
| Spiral liquid flow-type. | O3 | 30 | 10 | / | / | 98% | Hu and Xia, 2018 | |
| Photoresist | Dissolved gas release method. | O3 | 9.6 | / | / | 22℃ | 100% | Takahashi et al., 2012 |
| Butylated hydroxytoluene | Aeration method | O3 | 0.5 | <2 | 7 | / | 97% | Achar et al., 2020 |
| Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Aeration method | O3 | / | / | / | / | 7.0×10-4-1.9×10-3s-1 | Li et al., 2009c |
| P-chlorophenol | Ultrasonic cavitation. | air | 120 | / | / | 38℃ | 0.00899min-1/-0.83 | Teo et al., 2001 |
| P-nitrophenol | Jet cavitation reactor. | air | 90 | 8 | 3.5 | / | 50% | Kalumuck and Chahine, 2000 |
| Trichloroethylene | Aeration method | O3 | 20 | 14 | / | / | 100% | Xia et al., 2018 |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | Dissolved gas release method. | O3 | 120 | / | <7 | <35℃ | 30% | Takahashi et al., 2007 |
| Benzothiophene | Ultrasonic cavitation. | air | 60 | / | 5 | 25℃ | 0.0492min-1 | Kim et al., 2005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





