Introduction
Lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury can occur with vascular injuries due to trauma and various vascular diseases [
1], and it can also be seen during vascular or orthopedic surgeries during vascular clamp or tourniquet applications [
2] for clear vision in the surgical field. Ischemia occurs when arterial blood flow is blocked and blood flow to organs is restricted; as a result, cellular energy stocks are depleted, a serious imbalance occurs in cell metabolism, toxic metabolites accumulate and cell death may occur. Reperfusion injury may also occur when blood flow is restored to the ischemic tissue, which may lead to excessive damage and excessive immune response in the ischemic tissue [
3].
Ischemia causes hypoxia, dysfunction of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, decrease in ATP production, Na+-K+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase pump dysfunction. A decrease in ATP production induces anaerobic metabolism in mitochondria and causes a decrease in ATP and antioxidative agents in the cell. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) increases, and increasing lactic acid after anaerobic metabolism causes metabolic acidosis. Na+-K+-ATPase pump dysfunction causes Na retention in the cell and K accumulation outside the cell, reducing the increased intracellular Na Na+-H+ pump activity. The intracellular pH drops, and Ca2+-ATPase dysfunction also impairs Ca reuptake in the endoplasmic reticulum. Increased intracellular H, Ca, and Na cause hyperosmolarity. A decrease in pH affects enzymatic activities and protein synthesis in ribosomes is reduced. Increased ROS causes oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, DNA damage, and increased local inflammatory responses [
4].
Increased molecular oxygen in the tissue by restoring blood flow to the tissue in reperfusion; by causing a further increase in ROS production, it causes activation of multifactorial complex mechanisms such as Ca2+ loading, development of endothelial dysfunction, increased prothrombogenic appearance and exacerbation of immune response.Importantly, this situation affects both the local tissues where ischemia occurs but can also affect distant organs through the release of mediators accumulated in the ischemic tissue into the systemic circulation by blood flow being restored to the ischemic tissue [
5].
Dealing with diabetes and its complications is becoming a serious problem for the global health and economic sector [
6]. According to the estimates of the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the number of diabetics, which was 382 million in 2013, will increase to 592 million in 2035. In 2040, it is estimated that one in 10 adults will have diabetes (642 million) and healthcare expenditures for diabetes-related diseases will exceed 802 million USD [
7].
It is stated that in diabetes, endogenous ROS increases, antioxidant defense systems are depleted, and accordingly, basal oxidative stress is already high. As a result of all these, the effects of ischemia-reperfusion injury increase in diabetes [
8]. The development of new treatment approaches that can reduce the negative effects of IRI is of great importance, especially for patient groups under chronic oxidative stress.
For this purpose, nanoparticles have been the subject of many studies recently. One such nanoparticle is cerium oxide (CeO2). Cerium is a member of the lanthanide group and is the most abundant rare earth metal with atomic number 58, available in two oxidation states i.e. +3 and +4 [
9]. CeO2 nanoparticles mimic the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) and act as a catalyst that scavenges ROS or free radicals. With the highly reactive surface area provided by the fluorite crystal, the cerium oxide nanoparticle lattice structure helps neutralize free radicals [
10]. Various studies have shown in the literature that CeO2, with its antioxidant enzyme-like effect, reduces various organ and tissue damages caused by oxygen free radicals formed during ischemia-reperfusion periods [
11,
12,
13,
14].
The study aimed to investigate whether CeO2 has protective effects on skeletal muscles in lower extremity IRI in mice with streptozocin-induced diabetes.
Materials and Methods
The present study was conducted at the Gazi University Animal Experiments Laboratory (Ankara, Turkey) in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines. The study protocol was approved by the Animal Research Committee of Gazi University (G.Ü.ET-22.063). All of the animals were maintained in accordance with the recommendations of the National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
In this study, a total of 38 Swiss albino mice (20-25 g) were used. The mice were housed in the laboratory at 20-21°C for 12 hours in daylight-12 hours in darkness. Free access to food was allowed. For the experiment, fasting was provided for 2 hours before the application of anesthesia.The animals were randomly separated into five groups: control group (group C, n=6), diabetes group (group D, n=8), diabetes-CeO2, (group DCO, n=8), diabetes-ischemia/reperfusion (group DIR, n=8), and diabetes-ischemia/reperfusion-CeO2 (group DIRCO, n=8). The groups were set up in this way because the ethics committee allowed 38 animals for the study.
Diabetes was induced by a single injection of streptozotocin (STZ) (Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO, USA) administered 125 mg/kg intraperitoneally (i.p). The mice with fasting blood glucose (FBG) values higher than 250 mg/dL 72 hours after injection were classified as diabetic. Animals with FBG levels >250 mg/dL were included in the diabetic groups (group D, D-CeO2, DIR-CeO2). The mice were kept alive for 4 weeks after STZ injection to induce the development of chronic diabetes. The mice were kept alive for 4 weeks after the STZ injection to allow the development of chronic dia betes before the study. Before the experiment, all mice were anesthetized using 50 mg/kg intramuscular ketamine (Ketalar®; 1 mL = 50 mg; Pfizer, Istanbul, Turkey) and 10 mg/kg xylazine hydrochloride (Alfazyne® 2%, Ege Vet, Turkey). A heating lamp was used to prevent heat loss during the experiment. The procedures were performed with the mice in the supine position.
Group C and group D: After skin asepsis, a midline laparotomy was performed without additional surgical intervention.
Group DCO: CeO2 (Co aqueous nanoparticle dispersion, 100 ml; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was administered i.p (0.5 mg/kg) 30 min before the surgical procedure.
Group DIR: A midline laparotomy was performed, an atraumatic micro clamp was placed on the infrarenal abdominal aorta for 120 min, then clamp was withdrawn and the lower extremity was reperfused for another 120 min.
Group DIRCO: CeO2 was administered i.p 30 min before the IR procedure.
To avoid hypovolemia, an hourly 3 mL/kg i.p isotonic solution was administered. During the IR period, the abdomen was covered with a moistened sterile pad. At the end of the experiments, after the animals were euthanized, the left hind leg was dissected, the calf muscles were isolated, and the gastrocnemius muscle was dissected. Gastrocnemius tissue samples were taken for biochemical and histopathologic analyses. After 4 hours of follow-up, all mice received ketamine at a dose of 100 mg/kg intraperitoneally and sacrificed by collecting blood from their abdominal aortas. After the heartbeat and respiration ceased, the mice were monitored for a further 2 minutes to confirm death.
Histopathologic Assessment
Muscle tissue specimens were immersed in 10% neutral buffered formalin and fixed for 48 hours. Following fixation, tissue specimens were routinely processed and embedded in paraffin. Four-µm-thick sections were cut from the paraffin blocks using a microtome (Leica RM2245, Germany), and sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to assess the histologic changes. H&E-stained muscle sections were observed under 200× and 400× magnifications using a light microscope (Leica DM 4000B, Germany) equipped with a computer, and images were captured using the Leica LAS V4.9 software. Muscle injury was evaluated semi-quantitatively accounting for the extent of disorganization and degeneration of muscle fibers and inflammatory cell infiltration. Each parameter was scored between 0 and 3 (0, normal; 1, mild; 2, moderate; 3, severe), and then the degree of IRI was determined using the sum of the scores of these two parameters, corresponding to a value ranging between 0 and 6 [
15,
16].
Biochemical Assessment
Measurements of TAS/TOS
TAS Measurement
The TAS test kit (RelAssay Diagnostic
®, Turkey) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to measure the TAS levels. In brief, 30 μL of the sample was mixed with 500 μL of measurement buffer (reagent 1) in an Eppendorf tube, and 2 μL of that mixture was used to measure the absorbance at 660 nm (A
1) (NanoDrop
® ONE, Thermo Scientific). Then, 75 μL of coloured 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) (reagent 2) was added to the mixture, and incubation was performed at 37 °C for 5 min (ST 30, NUVE). The A
2 measurement was evaluated at an absorbance of 660 nm. Trolox Eq solution at a concentration of 1 mmol/L was used instead of samples to obtain the standard values. A
1 and A
2 measurements were performed three times for each sample, and the average values were calculated. The absorbance change (ΔAbs) was calculated by subtracting the first absorbance value (A
1) from the second absorbance value (A
2). The TAS level was calculated using the formula given in the kit and expressed as mmol Trolox Eq/L.
TOS Measurement
The TOS test kit (RelAssay Diagnostic
®, Turkey) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to measure the TOS levels. In brief, 75 μL of the sample was mixed with 500 μL of measurement buffer (reagent 1) in an Eppendorf tube, and 2 μL of that mixture was used to measure the absorbance at 530 nm (A
1) (NanoDrop
® ONE, Thermo Scientific). Then, 25 μL of pro-chromogenic solution (reagent 2) was added to the mixture, and incubation was performed at 37°C for 5 min (ST 30, NUVE). The A
2 measurement was evaluated at an absorbance of 530 nm. A standard solution containing 10 μmol/L of hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2) equivalent/litre given in the kit was used for the standard measurement. A
1 and A
2 measurements were performed three times for each sample, and the average values were calculated. The absorbance change (ΔAbs) was calculated by subtracting the first absorbance value (A
1) from the second absorbance value (A
2). The TOS level was calculated using the formula given in the kit and expressed as mmol H
2O
2 Eq/L.
Oxidative Stress Index
The OSI, which is shown as an indicator of oxidative stress, is expressed as the ratio of TOS to TAS levels. When calculating the OSI of the samples, TAS levels were multiplied by 100 to equalize the TOS levels and the units. The results were expressed as arbitrary units (AU).
Paraoxanase (PON) Measurement
Paraoxonase activities were measured spectrophotometrically using commercially available kits (RelAssay Diagnostic®, Turkey).
The rate of paraoxon hydrolysis (diethylpnitrophenylphosphate in 50 mM glycine/NaOH, pH 10.5 containing 1 mM CaCl2) was measured by monitoring the increase of absorption at 412 nm at 37 °C. The amount of generated p-nitrophenol was calculated from the molar absorption coefficient at pH 8.5, which was 18.290 M−1 cm−1 at pH 10.5. One enzyme unit was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzed the hydrolysis of 1 μmol of substrate at 37 °C (U/L).
Statistical Analysis
The SPSS 20.0 for Windows was used for statistical analyses. Each categorical variable was analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Datas were tested using the Kruskal-Wallis test, Bonferroni Correction test, and the Mann-Whitney U test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All data are expressed as mean±standard error (mean ± SE).
Results
Histopathologic Findings
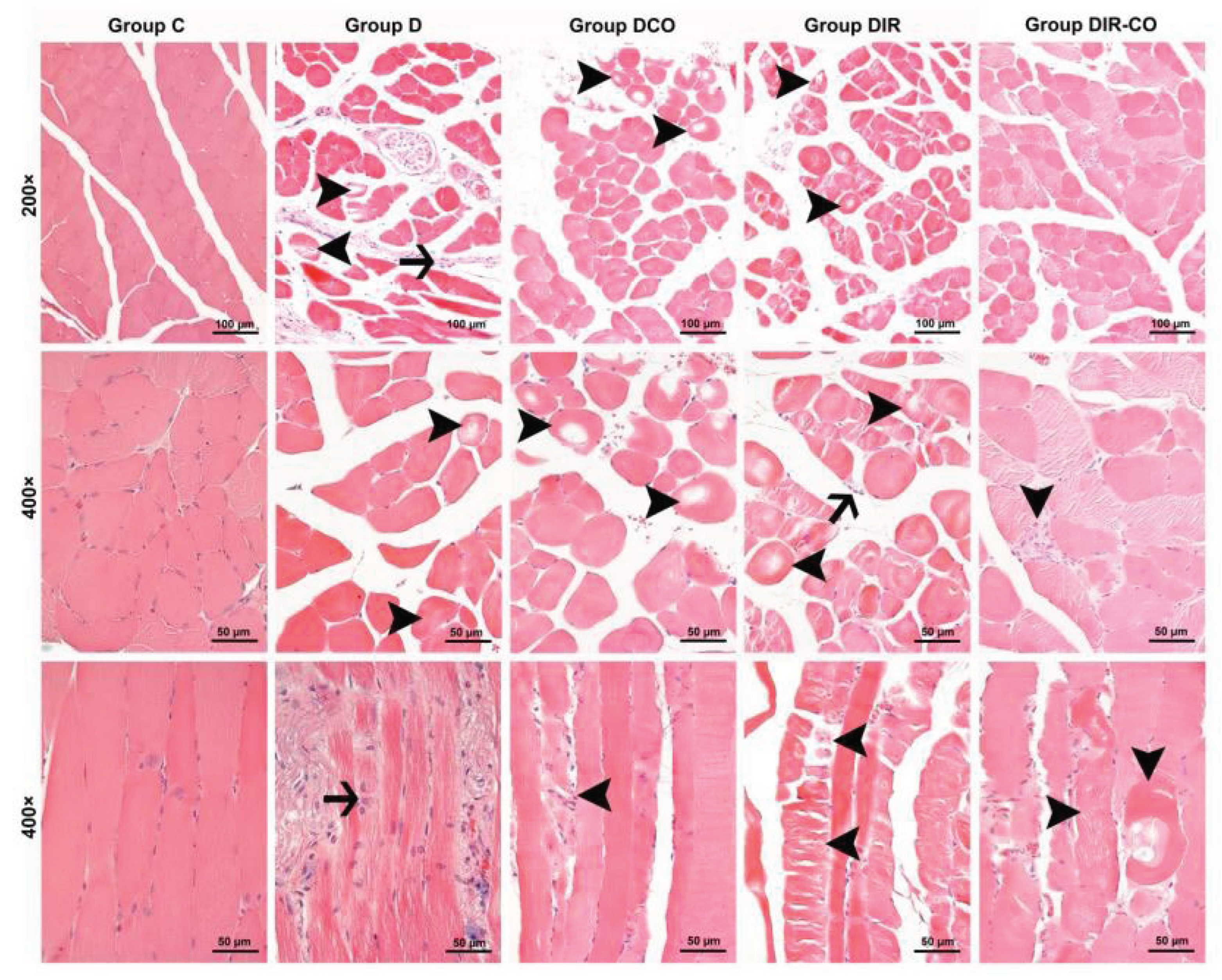
Muscle cells from the control group were observed to display a normal appearance with eosinophilic cytoplasms, polygonal shapes, cross striations, peripherally located nuclei, and forming regular fascicles (
Figure 1, group C). In contrast to control muscle cells, interstitial edema accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration within the fascicles, and also degenerative changes of muscle fibers such as hypereosinophilic cytoplasms, rounded outlines, and non-peripheral localization of nuclei, and large cytoplasmic defects in some cases were noted in the specimens of the diabetic mice (
Figure 1, group D). Degenerative changes of muscle fibers in the samples of diabetic animals that underwent ischemia-reperfusion were seen to be exacerbated. Varying degrees of degenerative changes such as hyalinization of muscle cells, extensive cytoplasmic vacuolization, and cytoplasmic fragmentation in which cell integrity was disrupted were observed beside the inflammatory cell infiltration in some areas (
Figure 1, groups DIR and DIR-CO).
When the scores for the histopathologic parameters were compared, disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells, inflammatory cell infiltration, and total injury scores were found significantly different between the groups (p<0.001, for all) (
Table 1). The degree of disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells in groups DCO, DIR, and DIR-CO were markedly more severe in comparison with group C (p=0.001, p<0.001, and p<0.001, respectively). Additionally, disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells in group DIR were significantly more prominent than in groups D and DCO (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively). The score for disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells in group DIR-CO was markedly higher than in group D, but was significantly lower than that in group DIR (p=0.017 and p=0.002, respectively) (
Table 1).
Inflammatory cell infiltration was significantly greater in all groups than in group C (p=0.034, p=0.001, p<0.001, and p=0.002, respectively). In addition, the inflammatory cell infiltration score in group DIR was markedly higher than in groups D and DCO (p=0.002 and p=0.033, respectively), whereas it was markedly milder in group DIR-CO in comparison with group DIR (p=0.034) (
Table 1).
Finally, the total injury scores of groups D, DCO, DIR, and DIR-CO were found to be higher than in group C (p=0.027, p<0.001, p<0.001, and p<0.001, respectively). Also, the total injury score of group DIR was notably higher than that of groups D and DCO (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively). Although the total injury score was markedly higher in group DIR-CO than in group D, it was significantly lower when compared with group DIR (p=0.027 and p=0.001, respectively). According to the total injury score, CeO2 appears to alleviate muscle injury (
Figure 1, group DIR-CO) (
Table 1).
Biochemical Findings
When the groups were compared with each other in terms of muscle tissue TAS levels, there was a significant difference between the groups (p=0.001). TAS levels were found to be significantly lower in all groups than in group C (p=0.007, p=0.012, p<0.001, and p=0.002, respectively) (
Table 2). In addition, TAS levels were significantly lower in group DIR than in groups D and DCO (p=0.047 and p=0.022, respectively) (
Table 2).
When the groups were compared with each other in terms of muscle tissue TOS levels, there was a significant difference between the groups (p<0.001). TOS levels were significantly higher in all groups compared with group C (p=0.002, p=0.004, p<0.001, and p<0.001, respectively). Similarly, TOS levels were found to be significantly lower in group DIR than in groups D and DCO (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively) (
Table 2). In group DIRCO, TOS levels were significantly higher than in group DIR (p<0.001) (
Table 2).
When the groups were compared with each other in terms of muscle tissue OSIs, there was a significant difference between the groups (p<0.001). OSI levels were found to be significantly higher in all groups than in group C (p=0.010, p=0.016, p<0.001, and p=0.001, respectively). Similarly, the OSI was significantly lower in group DIR than in groups D and DCO (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively) (
Table 2).
When the groups were compared among themselves in terms of muscle tissue paraoxonase (PON-1) enzyme activity, there was a significant difference between the groups (p<0.001). PON-1 enzyme activity was found to be significantly increased in group DIR compared groups C, D, and DCO (p<0.001, p=0.002, and p<0.001, respectively). Similarly, PON-1 enzyme activity was significantly increased in group DIRCO compared with group C (p=0.032) (
Table 2).
Discussion
With this study, we wanted to contribute to the limited data in the literature on reducing the effects of ischemia and reperfusion injury on the diabetic group under chronic oxidative stress by evaluating the effects of CeO2 use 30 minutes before IR on muscle tissue in lower extremity IRI in diabetic mice. For this purpose, we examined both histopathologic, oxidative-antioxidative, and lipid peroxidation parameters in muscle tissue in IRI to investigate the effects of CeO2 on tissue damage. As a result of our study, we have shown that intraperitoneal CeO2 administration in diabetic mice in a lower extremity IRI model significantly reduces oxidative damage in muscle tissue and improves histopathologic findings.
Tourniquets are frequently used in orthopedic and plastic surgery to create a bloodless surgical field, provide safe and fast surgery, and reduce perioperative blood loss [
17]. Lower extremity IRI may occur during the use of a tourniquet, temporary clamping of the aorta in aortic surgery, and acute or bilateral acute femoral artery occlusion [
18]. Increasing knowledge of the mechanisms of IRI, developing new treatment strategies to reduce oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by IRI [
19] will reduce morbidity by reducing the known distant organ effects of lower extremity IRI [
20].
Studies in humans and experimental models indicate that basal oxidative stress is increased and mitochondrial dysfunction is present in diabetes [
21]. Increased basal oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes may cause an increase in the effects of increased ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction due to IRI. Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disease that can lead to macro and microvascular complications [
8]. It is known that diabetes is an important risk factor for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) and it accelerates the progression and increases the severity of the disease [
22].
In one study, it was stated that type 1 diabetes worsened IR-induced skeletal muscle injury, and mitochondrial respiration and oxidative stress were more impaired in animals with type 1 diabetes than in non-diabetic animals. This situation became more severe after IRI, and apoptosis and cell damage were more common in animals with diabetes [
21].
In our results, the TOS was significantly higher in the diabetic group (group D) than in the control group (group C). TAS was significantly lower in group D than in group C, and OSI was significantly higher in group D than in group C. These results show that oxidative stress is greater in animals with diabetes than in animals without diabetes. This seems to be consistent with our histopathologic results. Disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells were higher in group D than in group C, and the difference in terms of inflammatory cell infiltration and total injury score was significantly higher. According to these results, inflammatory cell infiltration and total injury scores appear to be more severe in subjects with diabetes.
Mitochondria have important functions such as ATP production, ROS production and detoxification, apoptosis regulation, cytoplasmic and mitochondrial matrix calcium regulation, metabolite synthesis and catabolism. Dysfunction of mitochondria also plays an important role in the pathogenesis of IRI.Decreased mitochondrial oxidative capacity and dysfunction associated with increased ROS production have also been demonstrated in experimental models of ischemia-reperfusion of the lower extremity using an aortic cross-clamp or leg tourniquet [
23].
Oxidative stress occurs as a result of insufficient endogenous catalytic mechanisms in the face of increased production of free radicals, and it causes the progression of the inflammatory process by directly activating the expression of proinflammatory genes and preventing tissue remodeling [
24]. We preferred to use TOS, TAS, OSI, and PON1 to analyze the oxidative stress situation. TAS and TOS can provide more accurate results by measuring unknown markers in serum [
25]. Because OSI is calculated as the ratio of TOS to TAS, it is a better indicator for systemic oxidative balance [
26]. Lipid peroxidation is a pathophysiologic process that occurs as a result of excessive ROS production in IRI and contributes to IRI [
27]. PON1 is an enzyme synthesized in the liver that inhibits the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in vitro [
28].
Cerium exists in both trivalent (III) and tetravalent (IV) states and can easily switch between these two states; this low-energy change gives CeO2 nanoparticles unique catalytic properties. Cerium nanoparticles in the oxide form protect their fluorite structure through oxygen deficiency. In this way, sites for reduction-oxidation reactions are provided. Being able to easily switch between valence states enables CeO2 nanoparticles to mimic SOD, CAT, and specific enzyme functions such as phosphatase, oxidase peroxidase, and phosphotriesterase [
29]. CeO2 nanoparticles have been the subject of many studies with their antioxidant effects and immunomodulatory properties against the overproduction of tissue ROS with enzyme-mimetic effects such as CAT, SOD, and peroxidase [
30].
Ozdemirkan et al. [
31] examined the effects of desflurane and CeO2 on lung tissue following lower extremity limb IRI. In their results, they stated that when CeO2 was given in IRI, there were significant reductions in inflammation in histologic findings and oxidative damage indicator MDA and NO levels. Like this study, Tuncay et al. [
11] investigated the efficacy of CeO2 on lung tissue in lower extremity IRI in sevoflurane-administered rats, and MDA and NO levels, which are indicators of oxidative stress, were found to be significantly lower in CeO2-applied groups. The authors obtained more positive results in neutrophil infiltration/aggregation and lung tissue total injury scores compared with the IR group.
Ozdemirkan et al. [
31] and Tuncay et al. [
11] investigated the lung protective effect of 0.5 mg/kg i.p. CeO2 on lung injury 30 minutes before lower extremity IRI in rats and observed reduced inflammation histopathologically and oxidative stress biochemically. We applied 0.5 mg/kg i.p. CeO2 30 minutes before ischemia based on studies in the literature. We preferred the intraperitoneal route for the ease of application and rapid absorption [
32].
In our study, looking at the OSI, TOS, TAS, and PON1 activities in the muscle tissue, we achieved more positive results in group DCO than in group D. In terms of TAS, we have a positive result in group DIRCO compared with group DIR, and for TOS, OSI, and PON1, we see that the difference in this positive result is significant in group DIRCO compared with group DIR. In the histopathologic evaluation, in terms of disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells, inflammatory cell infiltration and total injury scores in group DIRCO had more positive results than group DIR and the difference was significant. In terms of the same criteria, we had more negative results in group DCO group than in group D, but the difference was not significant. In our study, CeO2 administration before IR prevented the increase in oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation markers, and disorganization and degeneration of muscle cells, inflammatory cell infiltration, and total injury score were significantly reduced. Our results are similar for muscle tissue.
Park et al. [
33] injected CeO2, prepared at 0.5, 1, 2 mg/mL, and 300 μL, resulting in CeO2 doses of 0.15, 0.3, and 0.6 mg intramuscularly (i.m.) in mice left hind limbs with ischemic injury created by ligating the femoral artery, and they monitored tissue reperfusion and hind limb salvage for 3 weeks. In their study, five of seven mice (71.4%) administered 0.6 mg i.m. on day 21 showed no limb loss or necrosis, and it was reported that CeO2 had a dose-dependent effect in hind limb salvage. The authors stated that CeO2 optimally upregulated the angiogenic growth factor at 0.6 mg and effectively improved endothelial survival by preventing excessive ROS increase in critical limb ischemia.
Byaraa et al. [
34] induced an ischemia model by ligating the proximal femoral artery and border vessels of mice. They used CeO2-decorated graphene oxide (CeGO) prepared in the form of nano-microlayers from mesenchymal stem cells into a spheroid structure. Compared with the other groups, the highest limb salvage rate was seen in the CeGO-Cell group, with four limb salvages, necrosis in two feet, and one limb loss. The researchers stated that proangiogenic events such as cell sprouting and expression of angiogenic markers (HIF1α, VEGF, FGF2, eNOS) of cellular spheroids increased with CeGO intercalation. In addition, the significantly higher fluorescence signal of ROS was significantly reduced only in the CeGO-Cell group, and they stated that CeGO had an effective role in clearing ROS.
Our study had some limitations. There was a small number of animals in each group and we did not measure hemodynamic parameters such as arterial blood pressure or pulse. The data we obtained at the end of the experiment are descriptive. The specific mechanism of action was not studied in the experiment. The experiment only includes a 2-hour ischemia and 2-hour reperfusion period.We did not measure levels of markers indicating tissue damage such as creatine kinase, rather, we investigated ROS directly to assess the therapeutic effect of CeO2.
Our results confirm that CeO2 has protective effects against IR-induced skeletal muscle injury in diabetic mice. Future studies that will evaluate the mechanisms by which CeO2 affects different IR durations will provide us with more in-depth information on the effect of IRI-related tissue damage on the reduction of tissue damage, especially in the diabetic group. Our data show that prophylactic treatment with CeO2 nanoparticles may have a place as a new therapeutic strategy in the treatment of IRI, especially in chronic diseases such as diabetes.
Author Contributions
MA AÖ, NŞ and AK designed the study, and analyzed and interpreted data. AÖ, HB and YK performed the experiments. MA, ÇÖ and GK confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. NŞ, AK, MA and GK provided scientific and technical assistance, and critically revised the article for important intellectual content. ÇÖ and GK collected samples. ZY and ADD performed cellular and molecular experiments. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from Animal Research Committee of Gazi University (Ankara, Turkey; approval no. G.Ü.ET-22.063).
Patient Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Corrick RM, Tu H, Zhang D, Barksdale A.N, Muelleman R.L, Wadman M.C et al. Dexamethasone protects against tourniquet-induced acute ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse hindlimb. Front Physiol, 2018; 9: 244. [CrossRef]
- Dong X, Xing Q, Li Y, Han X, Sun L. Dexmedetomidine protects against ischemia reperfusion injury in rat skeletal muscle. J Surg Res 2014;186:240-5. [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig H.K, Eckle T. Ischemia and reperfusion–from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011 7;17(11):1391-401. [CrossRef]
- Wu M.Y, Yiang G.T, Liao W.T, Tsai A.P, Cheng Y.L, Cheng P.W et al. Current mechanistic concepts in ıschemia and reperfusion ınjury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1650-1667. [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris T, Baines C.P, Krenz M, Korthuis R. J. Cell Biology of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012; 298: 229–317. [CrossRef]
- Zheng Y, Ley S.H, Hu F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88–98. [CrossRef]
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, et al. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diab Res clin pract. 2014; 103(2): 137–149. [CrossRef]
- Lejay A, Fang F, John R,Van J.A.D, Barr M, Thaveau F. et al. Ischemia-reperfusion injury, ischemic conditioning and diabetes mellitus. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 2016; 91:11–22. [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar S, Naik P. Synthesis and biomedical applications of cerium oxide nanoparticles – A review. Biotechnology Reports 2018;17:1–5. [CrossRef]
- Singh K.R, Nayak V, Sarkar T, Singh R.P. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: properties, biosynthesis and biomedical application. RSC Adv. 2020;10(45):27194-27214. [CrossRef]
- Tuncay A, Sivgin V, Ozdemirkan A, Sezen S.C, Boyunaga H, Kucuk A et al. The effect of cerium oxide on lung tissue in lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury in sevoflurane administered rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:7481-7489. [CrossRef]
- Gobut H, Kucuk A, Şengel N, Arslan M, Ozdemir C, Mortas T et al. Effects of cerium oxide (CeO2) on liver tissue in liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats undergoing desflurane anesthesia. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023;23(1):40. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Yang Y, Wen Y, Zhao M, Dong Y. Effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles on myocardial cell apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022;68(3):43-50. [CrossRef]
- Yesil S, Ozdemir C, Arslan M, Gundogdu A.C, Kavutcu M, Atan A. Protective effect of cerium oxide on testicular function and oxidative stress after torsion/detorsion in adult male rats. Exp Ther Med. 2022 Nov 15;25(1):1. [CrossRef]
- Erkanlı K, Kayalar N, Erkanlı G, Ercan F, Sener G, Kırali K. Melatonin protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. J. Pineal Res. 2005; 39:238–242. [CrossRef]
- Hsieh K.F, Shih J.M, Shih Y.M, Pai M.H, Yeh S.L. Arginine administration increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells and attenuates tissue injury in a mouse model of hind limb ischemia/reperfusion. Nutrition 2018; 55-56: 29–35. [CrossRef]
- Kumar K, Railton C, Tawfic Q. Tourniquet Application during Anesthesia: “What We Need to Know?”. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016;32(4):424-430. [CrossRef]
- Orhan M, Tuna A.T, Ünal Y,Arslan M,Yazar H, Sezen Ş.C et al. The effects of amantadine on lung tissue in lower limb ischemia/reperfusion injury model in rats Turkish Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2021;29(1):77-83. [CrossRef]
- Mansour Z, Charles A.L, Kindo M, Pottecher J, Chamaraux-Tran T N, Lejay A et al. Remote effects of lower limb ischemia-reperfusion: Impaired lung, unchanged liver, and stimulated kidney oxidative capacities. Biomed Res Int 2014; 2014:392390. [CrossRef]
- Kao M.C, Yang C.H, Chou W.C, Sheu J.R, Huang C.J Cepharanthine mitigates lung injury in lower limb ischemia-reperfusion. J Surg Res. 2015;199(2):647-56. [CrossRef]
- Pottecher J, Adamopoulos C, Anne Lejay A, Bouitbir J, Charles A.L, Meyer A et al. Diabetes worsens skeletal muscle mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and apoptosis after lower-limb ischemia-reperfusion: Implication of the RISK and SAFE pathways? Front Physiol. 2018 22;9:579. [CrossRef]
- Barnes J.A, Eid M.A, Creager M.A, Goodney P.P. Epidemiology and risk of amputation in patients with diabetes mellitus and peripheral artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020; 40(8):1808-1817. [CrossRef]
- Lejay A, Meyer A, Schlagowski A.I, Charles A.L, Singh F, Bouitbir J et al. Mitochondria: mitochondrial participation in ischemia-reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2014;50:101-105. [CrossRef]
- Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou M.C, Rahu N. Oxidative stress and inflammation: What polyphenols can do for us? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2016; 2016:7432797. [CrossRef]
- Erel O. A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem. 2005;38(12):1103–1111. [CrossRef]
- Karapinar O.S, Pinar N, Özcan O, Özgür T, Dolapçıoğlu K. Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid in methotrexate-induced ovarian oxidative injury and decreased ovarian reserve in rats. Gynecol Endocrinol 2017;33:653–9. [CrossRef]
- 27. Cannistrà M, Ruggiero M, Zullo A, Gallelli G, Serafini S, Maria M et al. Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury: A systematic review of literature and the role of current drugs and biomarkers. Int J Surg. 2016;33:57–70. [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak M.P, Iskra M, Majewski W, Budzyń-Napierała M, Gryszczyńska B, Strzyżewski K et al. PON1 status evaluation in patients with chronic arterial occlusion of lower limbs due to atherosclerosis obliterans. Arch Med Sci. 2014;10(6):1101-8. [CrossRef]
- Nyoka M, Choonara Y.E, Kumar P, Kondiah P.P.D, Pillay V. Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using various methods: Implications for biomedical applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(2):242. [CrossRef]
- Casals E, Zeng M, Parra-Robert M, Fernández-Varo G, Morales-Ruiz M, Jiménez W. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Advances in biodistribution, toxicity and preclinical exploration. Small. 2020;16(20):e1907322. [CrossRef]
- Ozdemirkan A, Kucuk A, Gunes I, Arslan M, Tuncay A, Sivgin V et al. The effect of cerium oxide on lung injury following lower extremity ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats under desflurane anesthesia. Saudi Med J. 2021;42(11):1247-1251. [CrossRef]
- Al Shoyaib A, Archie S.R, Karamyan V.T. Intraperitoneal route of drug administration: should it be used in experimental animal studies? Pharm Res 2020; 37: 12. [CrossRef]
- Park I.S, Mahapatra C, Park J.S, Dashnyam K, Kim J.W, Ahn J.C et al. Revascularization and limb salvage following critical limb ischemia by nanoceria-induced Ref-1/APE1-dependent angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2020;242:119919. [CrossRef]
- Bayaraa O, Dashnyam K, Singh R.J, Mandakhbayar N, Lee J.H, Park J.T et al. Nanoceria-GO-intercalated multicellular spheroids revascularize and salvage critical ischemic limbs through anti-apoptotic and pro-angiogenic functions. Biomaterials. 2023;292:121914. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).