Submitted:
16 February 2024
Posted:
19 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- -
- hard abrasives in the zone of mating of machine components, which intensify abrasive processes,
- -
- saline waters, which tend to induce electrochemical corrosion processes,
- -
- dynamic excitations caused by start-up operations or sudden load changes which, in turn, can cause cracks in the microstructure, leading to material decohesion.
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- effect of the content of retained austenite on multifactorial wear, including impact-abrasion-corrosion,
- -
- relationship between multifactorial wear and service hardness of the surface layer.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Method
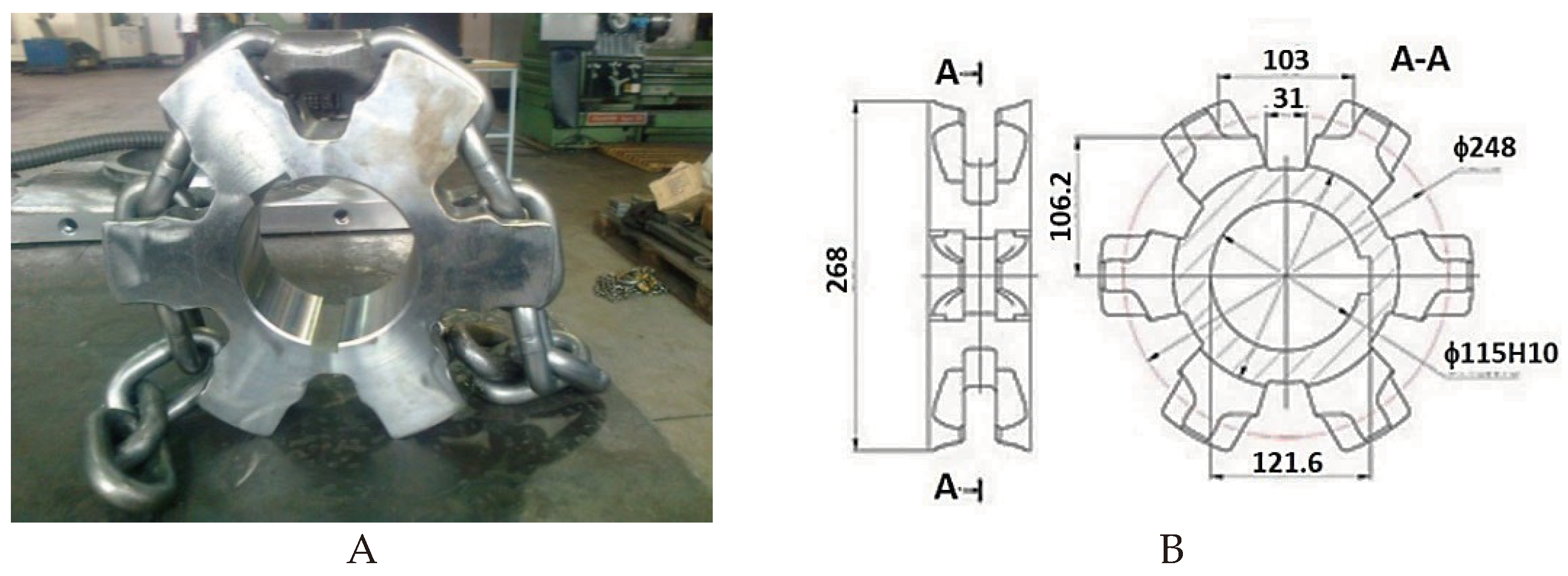
2.2. Object of Research
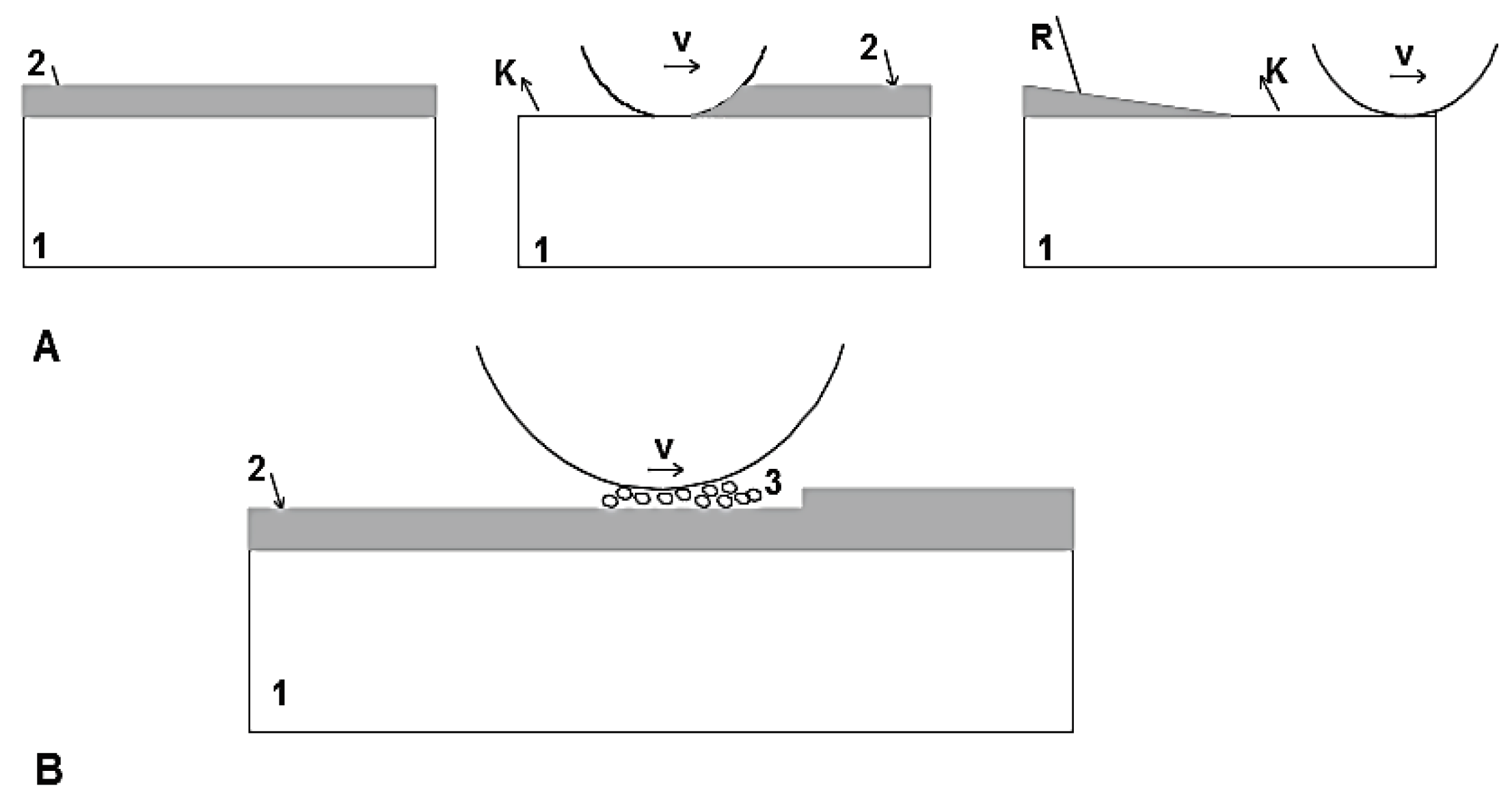
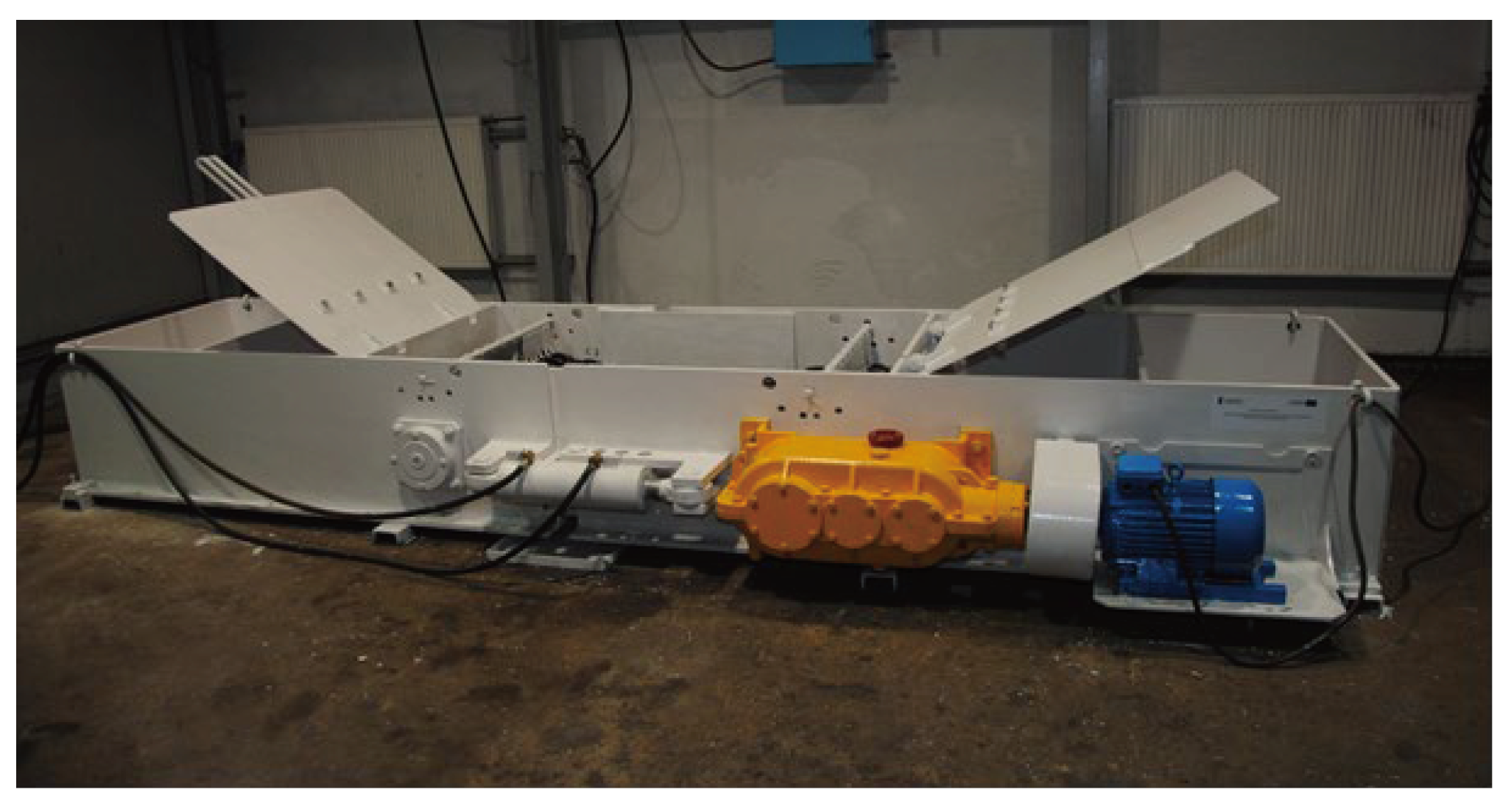
2.3. Wear testing station
- -
- peripheral velocity of chain drums: 0.7 m/s,
- -
- total test duration: 200 hours (100 hours for each direction of motor rotation),
- -
- pressure on surface between drum seat and chain link: 48.9 MPa.
3. Results
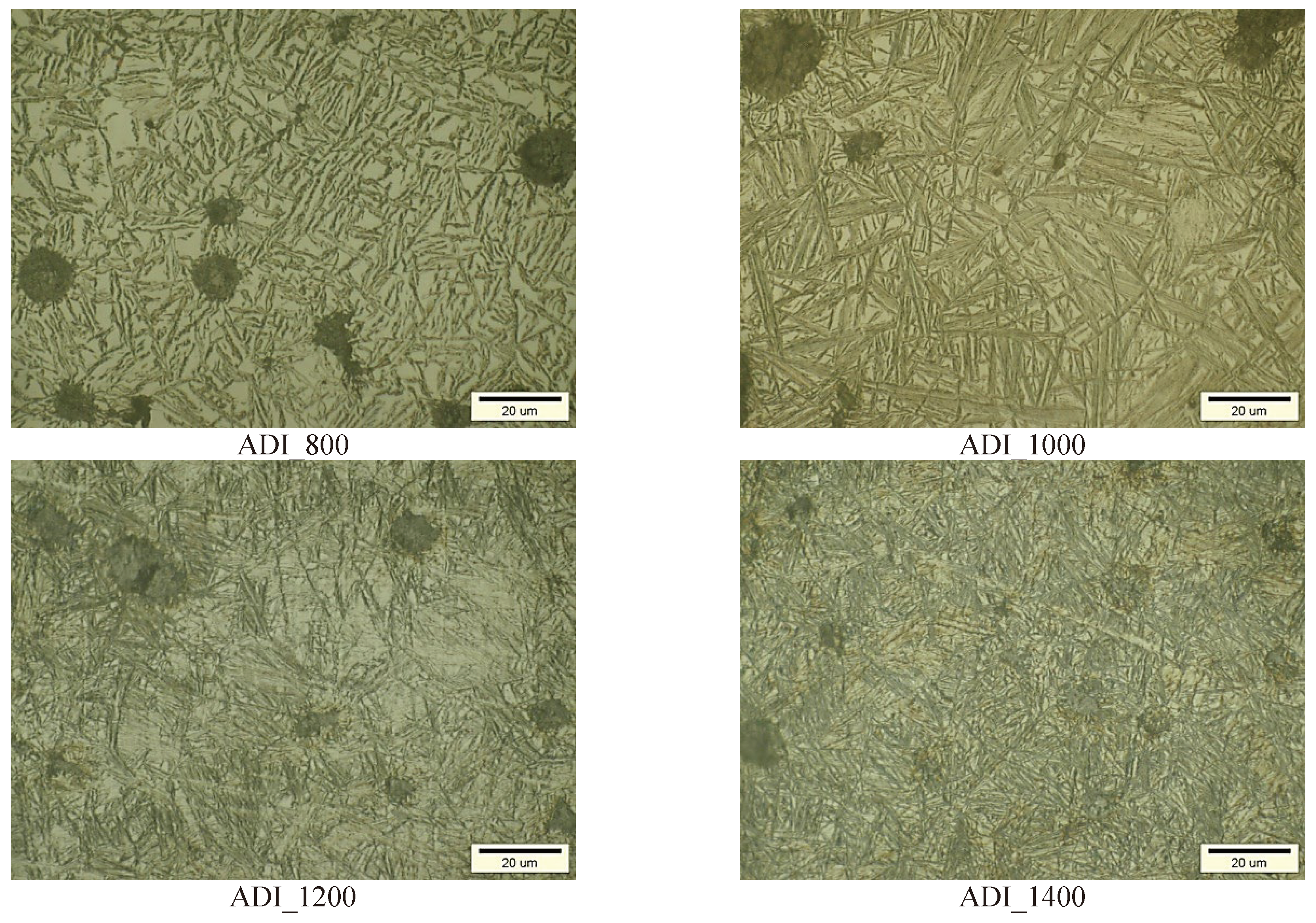
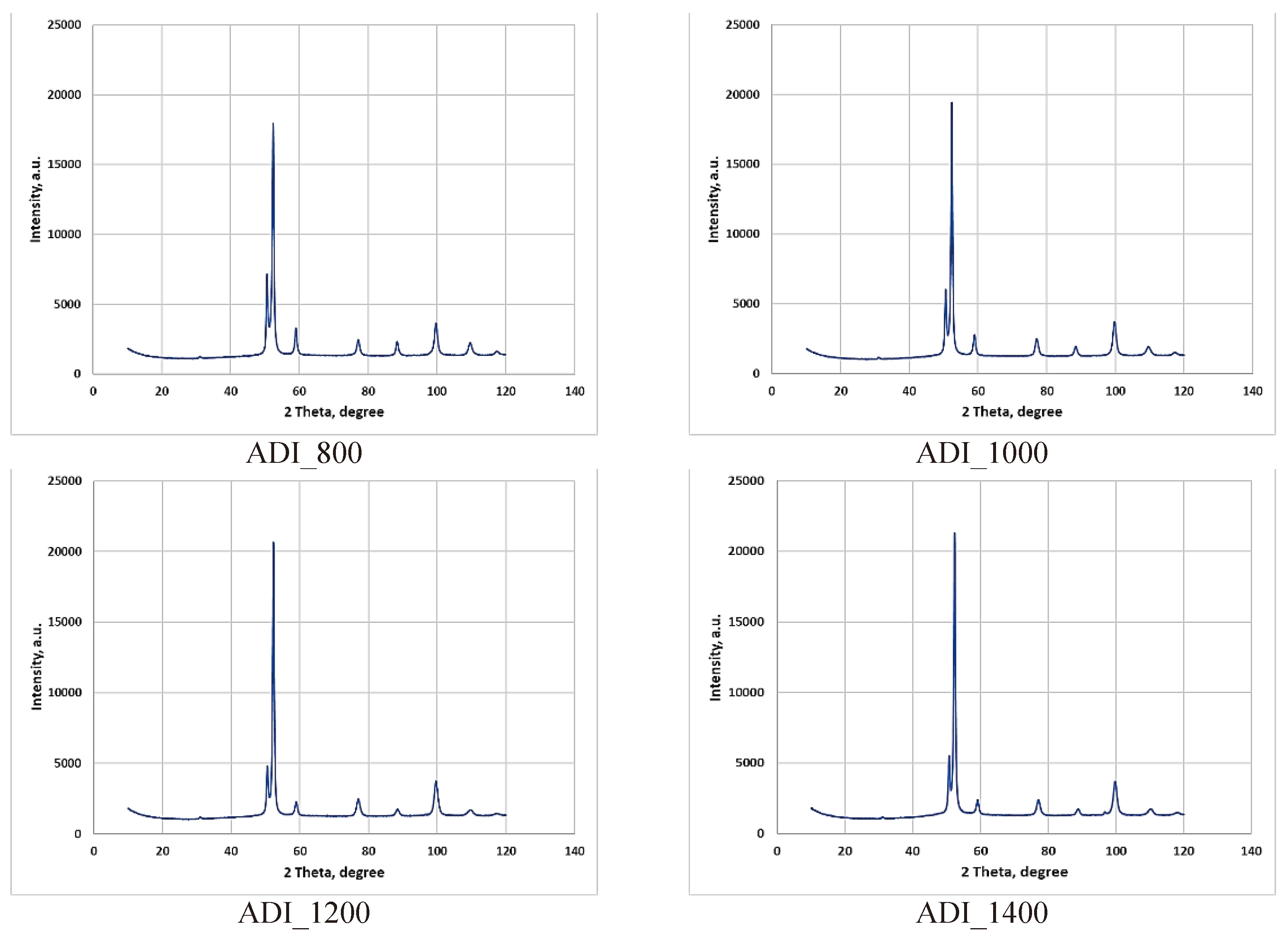
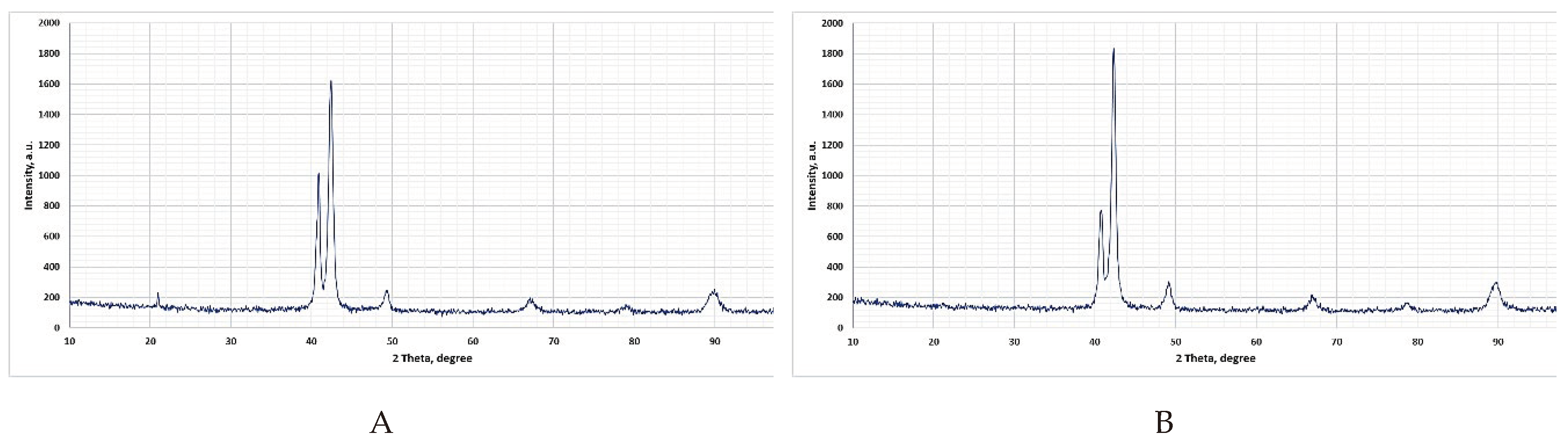
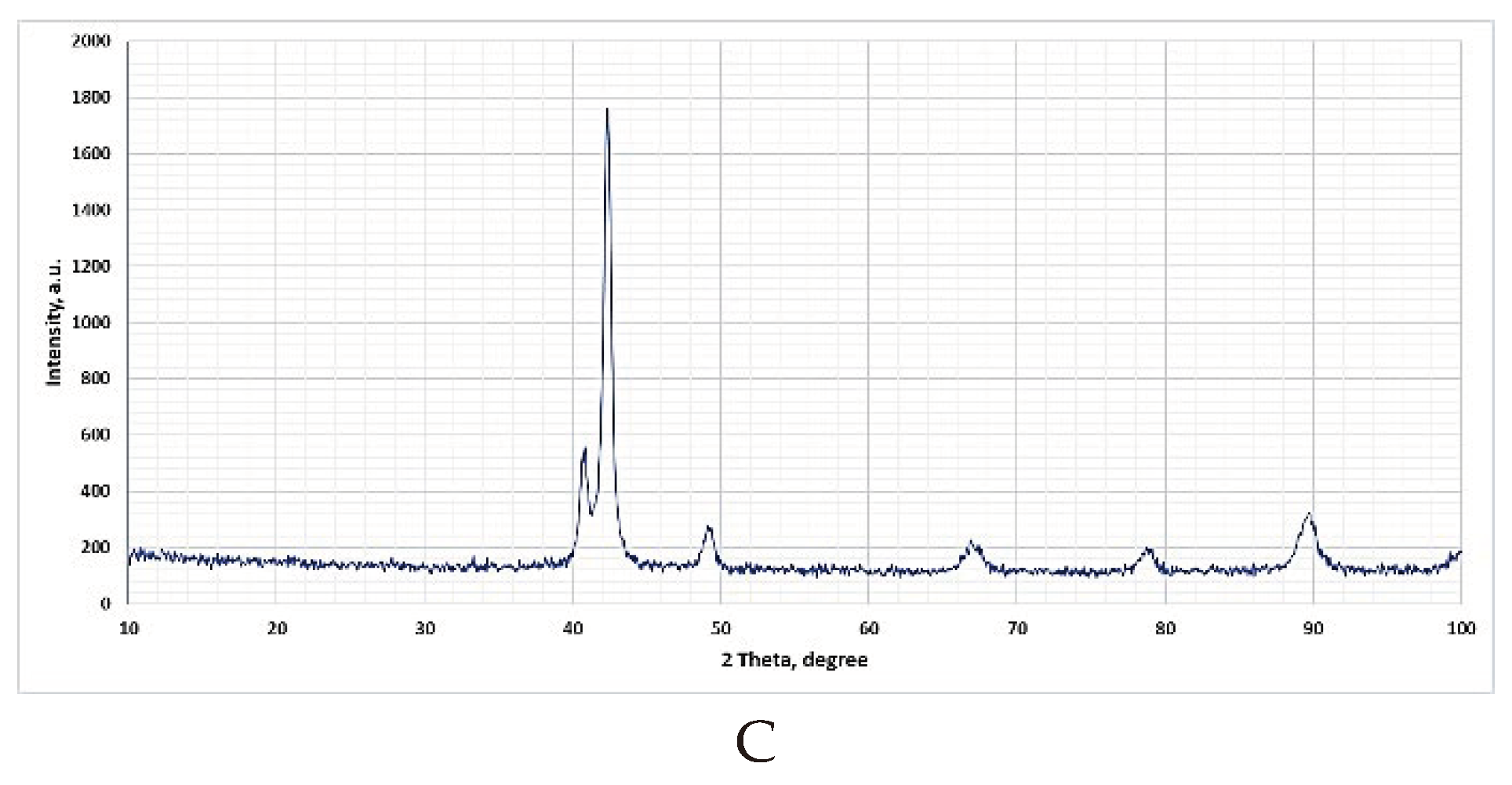
3.1. Identification of the Initial Structure of ADI and Their Corrosion Properties
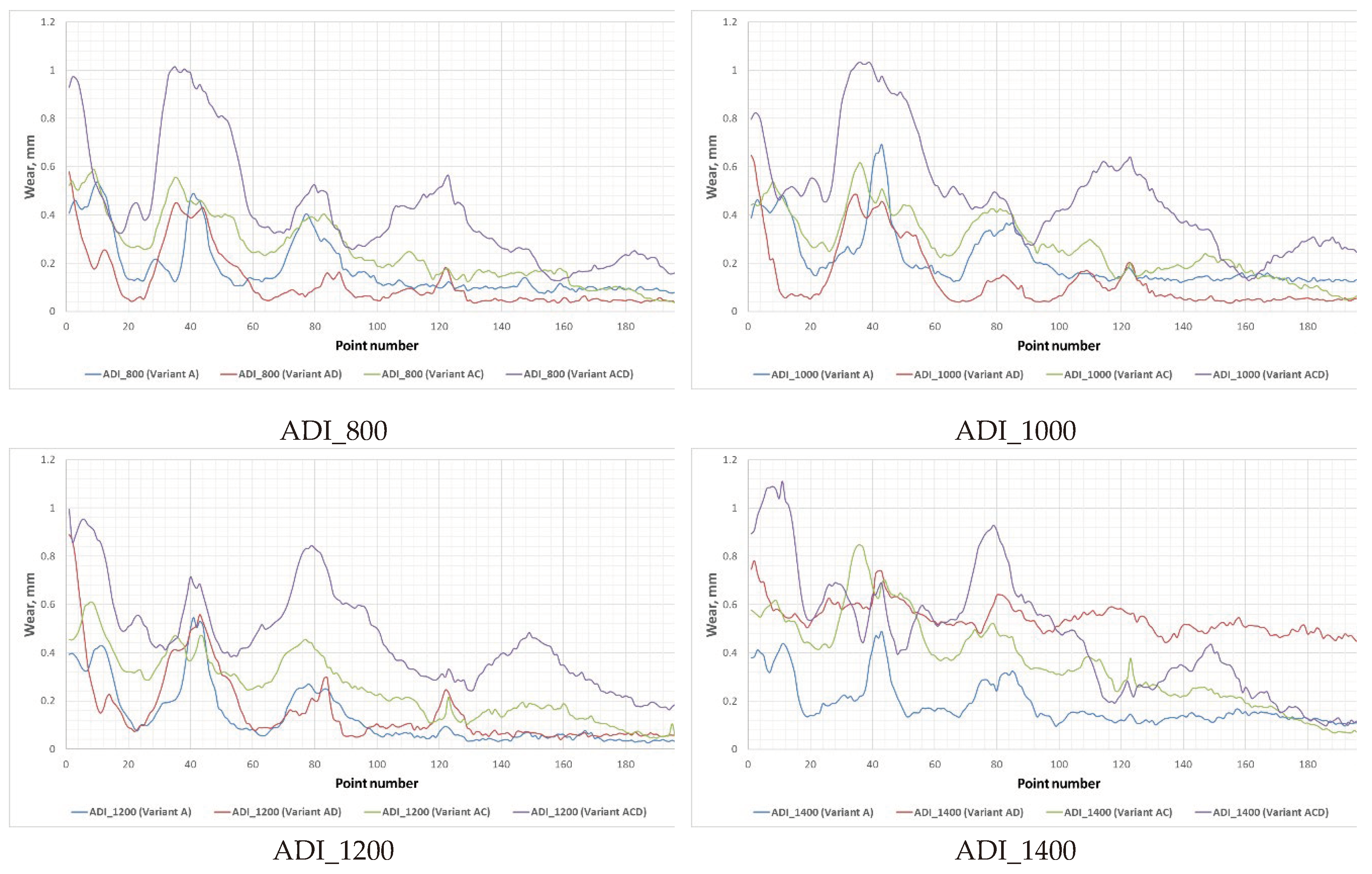
3.2. Wear Test Results
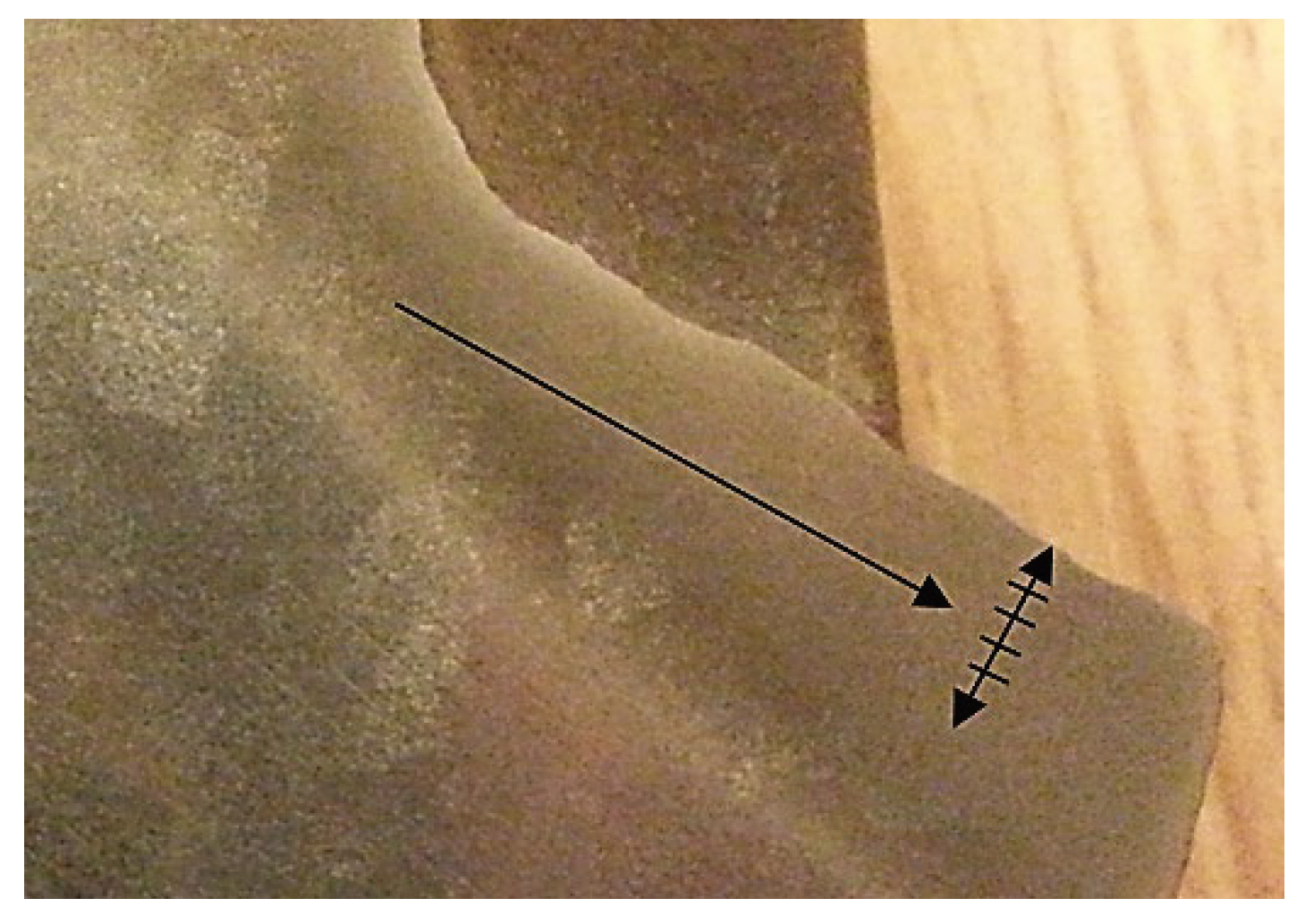
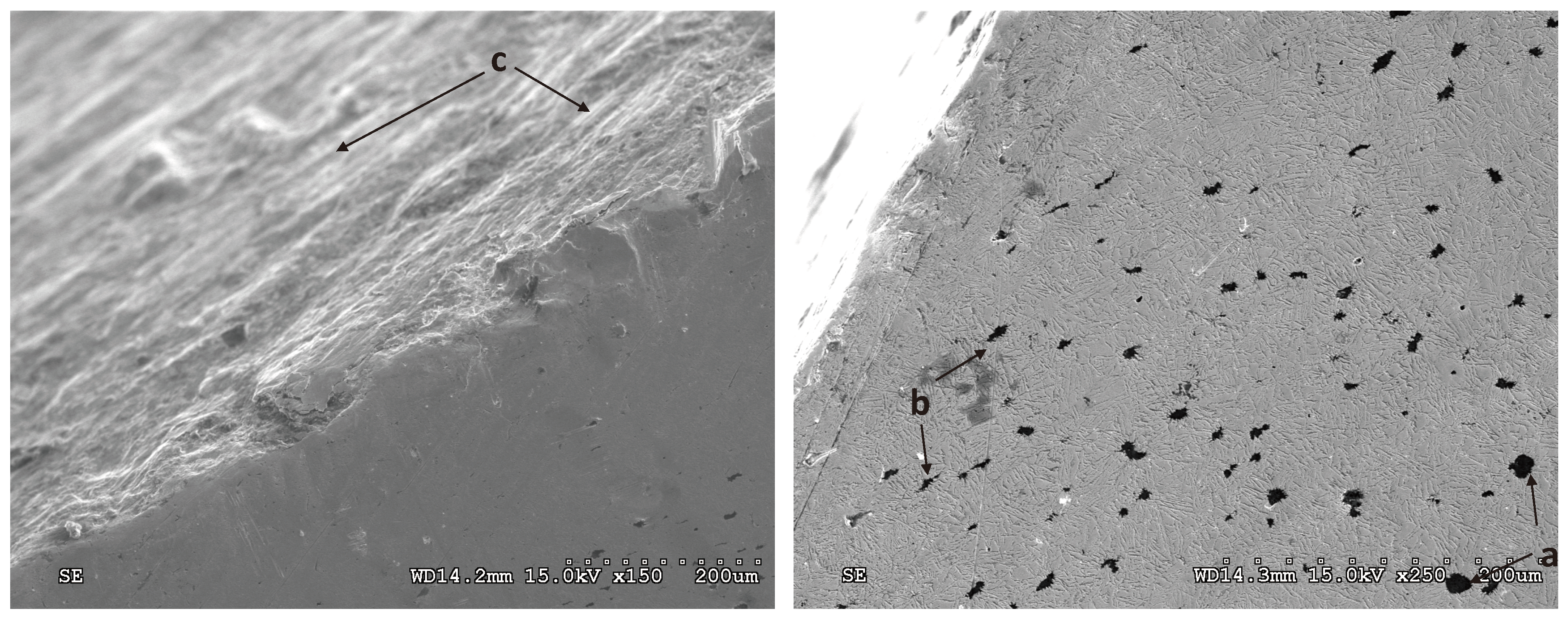
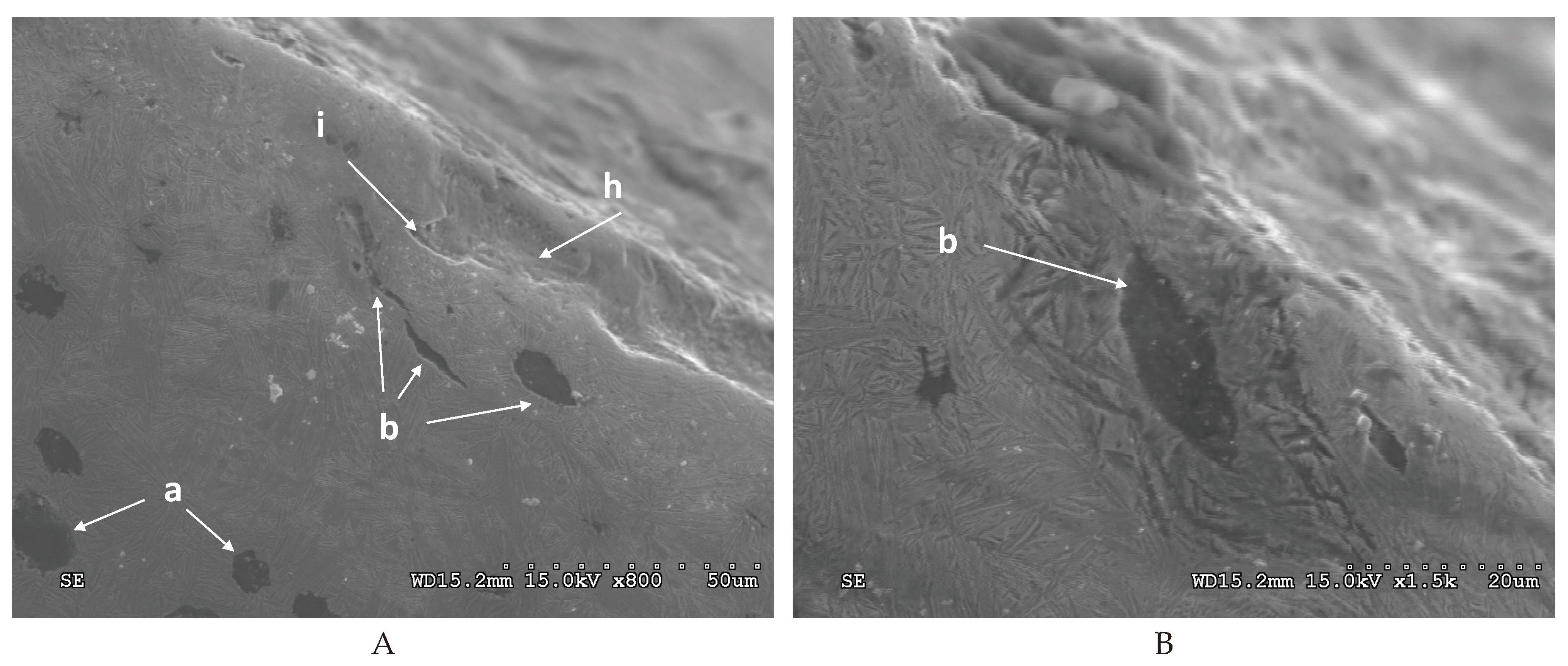
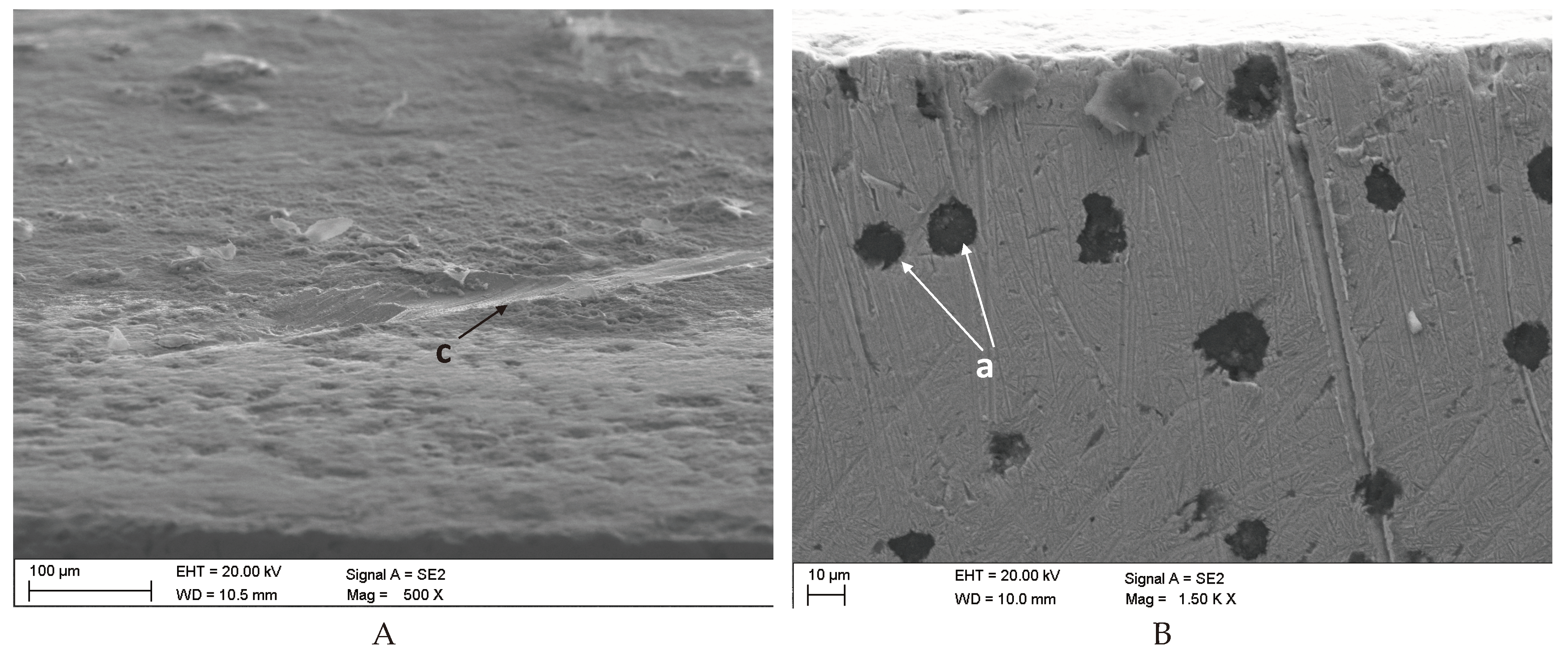
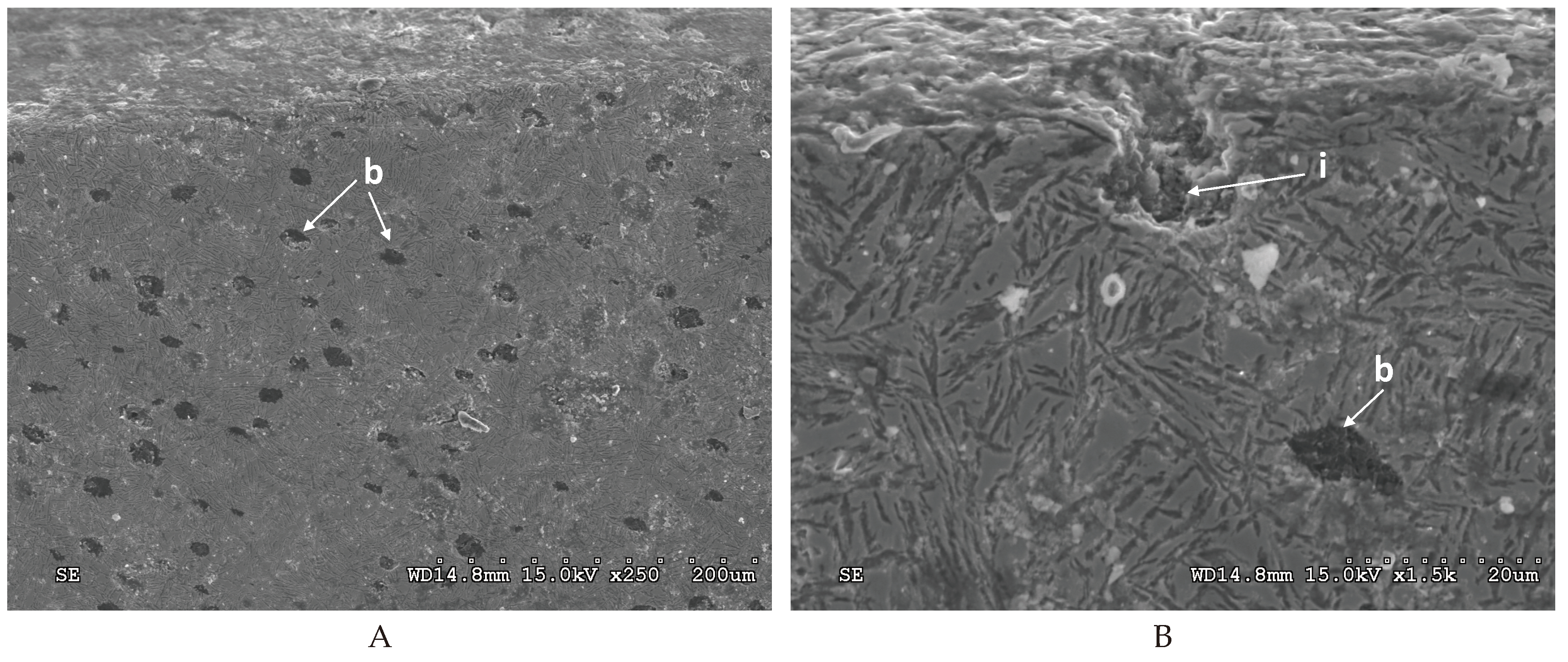
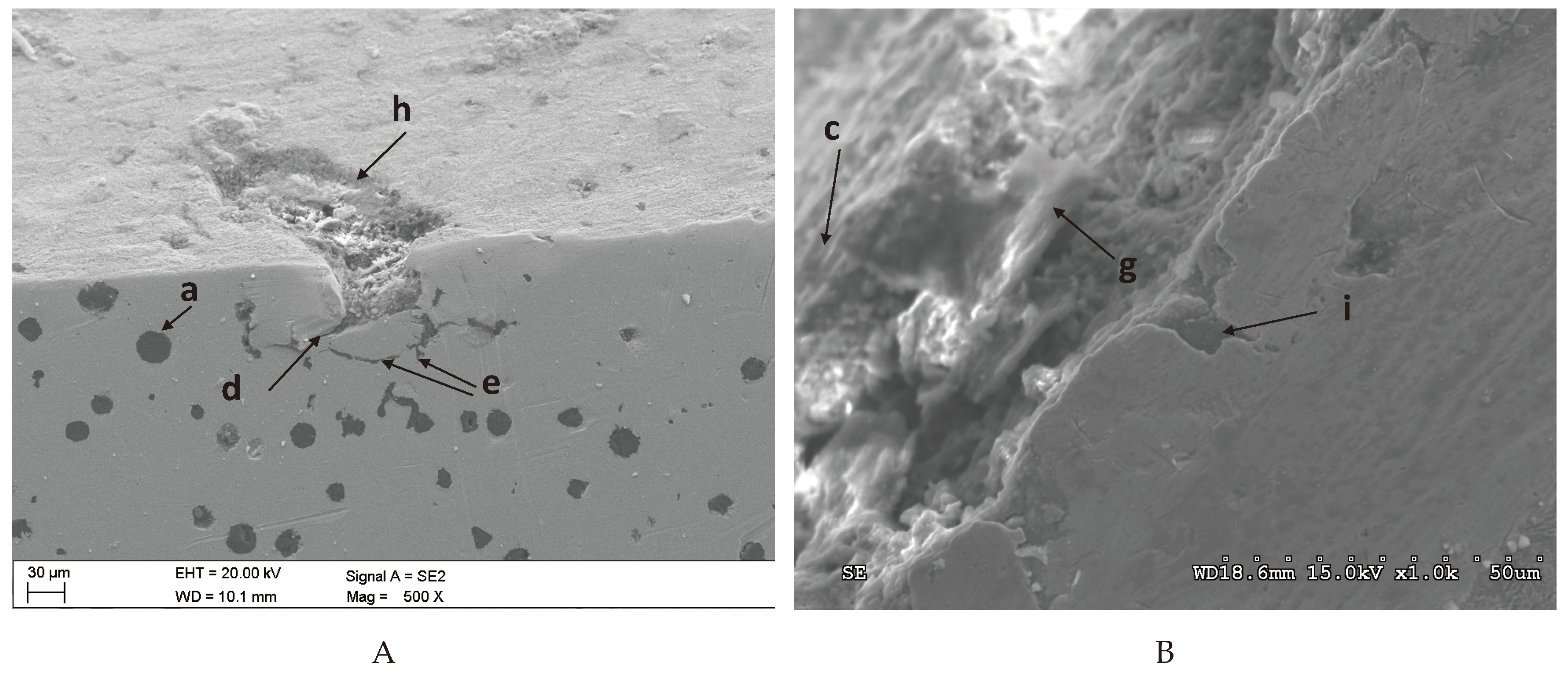
3.3. Damage Identification in the ADI Subject to Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Following a series of bench tests, making it possible to reproduce the processes of wear of chain wheels made of Ni-Cu alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron, one of the conclusions formulated in this paper is that the combined effect of dynamic forces, corrosion, and quartz sand-based abrasives causes increased surface degradation in the cast iron grades subject to the studies, as compared with processes characterised by a reduced number of degradation factors (i.e. one- or two-factor wear processes).
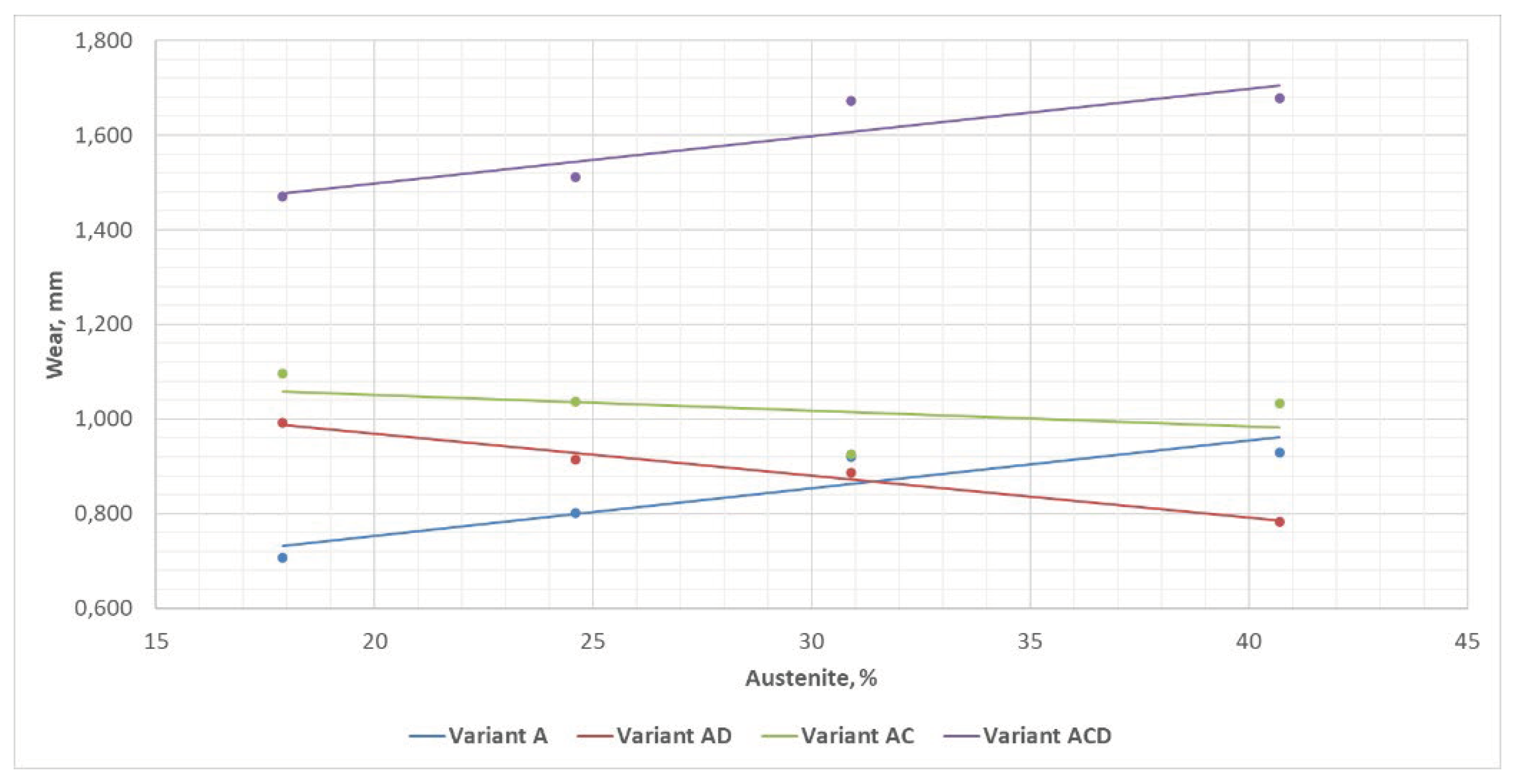
- The chain wheels made of ADI were found to have sustained the greatest damage under the impact-abrasion-corrosion (three-factor) wear scenario, while the wear was least advanced in the abrasion (one-factor) wear case. The two-factor wear was characterised by parameter values found to be intermediate between those obtained for the variants mentioned above, with a greater wear being observed for the tribocorrosion variant.
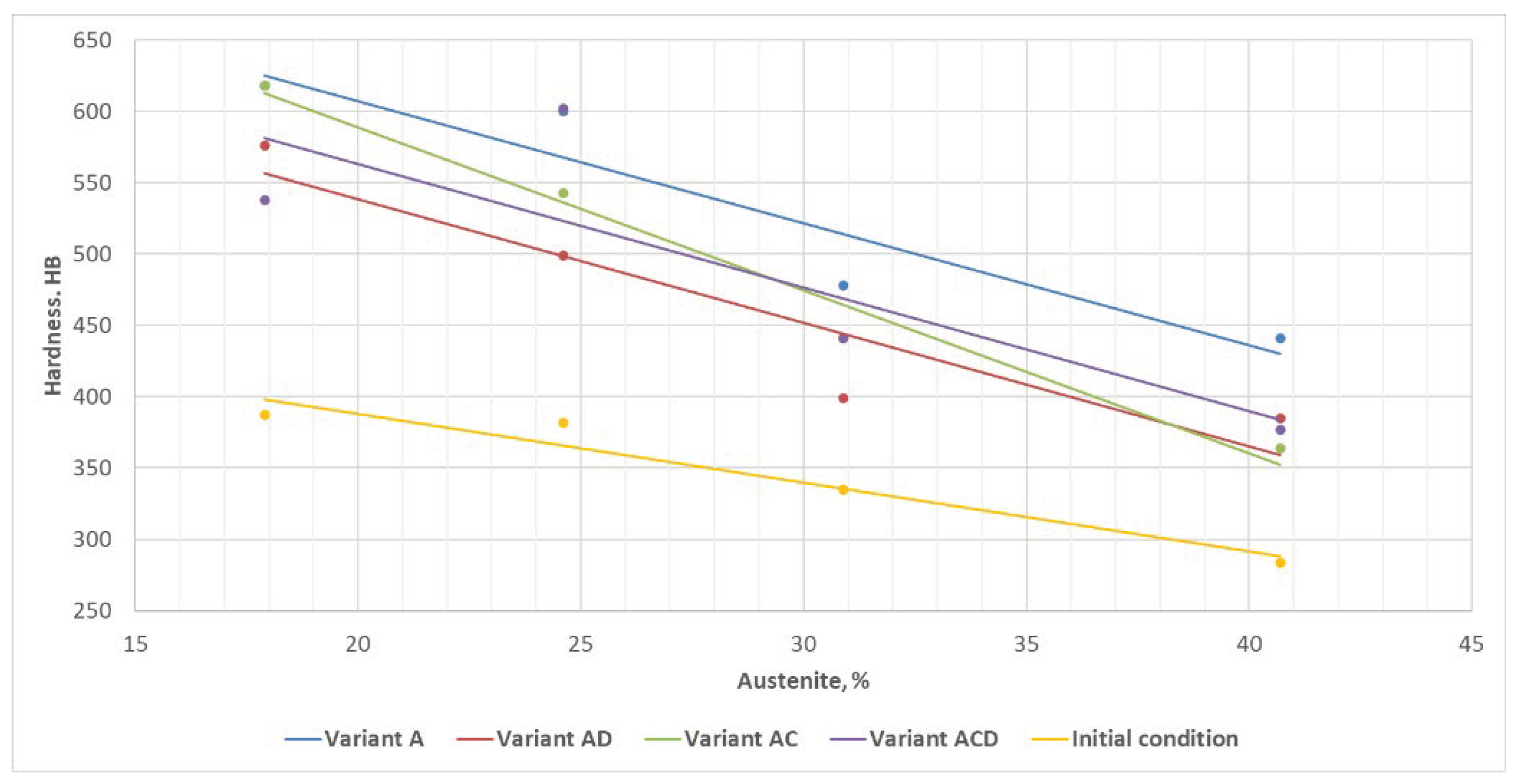
- The study has demonstrated an increasing service hardness of the surface layer of chain wheels made of ADI following wear processes compared to the hardness of unworn surface of the ductile irons.
- The value of the surface layer hardness increase following wear tests depends on the combination of degradation factors, and the largest hardness increase has been established for the abrasive wear variant.
-
The predominant forms of surface damage are as follows:
- –
- for abrasion wear – micro-scratching,
- –
- for impact-abrasion wear – micro-scratching and matrix cracking,
- –
- for tribocorrosion wear – micro-scratching and corrosion,
- –
- for impact-abrasion-corrosion wear – micro-scratching and matrix cracking.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuszynski, W.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Michalak, M.; Michalczewski, R.; Wieczorek, A. The effect of WC/C coating on the wear of bevel gears used in coal mines. Mater. Sci. (Medžiagotyra) 2015, 21, 358–363. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.N. Designing machinery and equipment in accordance with the principle of sustainable development. Manag. Syst. Prod. Eng. 2015, 1, 28–34. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z. Safety management of coal mining process. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 2020, 598. [CrossRef]
- Szewerda, K.; Tokarczyk, J.; Wieczorek, A. Impact of Increased Travel Speed of a Transportation Set on the Dynamic Parameters of a Mine Suspended Monorail. Energies 2021, 14, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Angeles, E.; Kumral, M. Optimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining Equipment. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2020, 20, 1408–1416. [CrossRef]
- Zum Gahr, K.H. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; Tribology series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987.
- Xia, R.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L. Screening the Main Factors Affecting the Wear of the Scraper Conveyor Chute Using the Plackett–Burman Method. Hindawi, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Kirchgaßner, M.; Badisch, E.; Franek, F. Behaviour of iron-based hardfacing alloys under abrasion and impact. Wear 2008, 265, 772–779. [CrossRef]
- Saha, G., Valtonen, K., Saastamoinen, A., Peura, P., & Kuokkala, V. T. Impact-abrasive and abrasive wear behavior of low carbon steels with a range of hardness-toughness properties. Wear, 2020, 450, 203263. [CrossRef]
- Widder, L., Varga, M., Adam, K., Kuttner, A., Development of Impact Energy Distribution of Various Abrasives during Cyclic Impact/Abrasion Testing. Solid State Phenomena 2017, 267, 234-242. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, DM; Helali, M; Hashmi, MSJ Dynamic abrasion resistance of coatings applied to engineering materials. Surface and Coatings Technology 1994, 68–69, 477-481. [CrossRef]
- Ratia V, Valtonen K, Kuokkala V-T. Impact-abrasion wear of wear-resistant steels at perpendicular and tilted angles. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part J: Journal of Engineering Tribology 2013; 227, 8, 868-877. [CrossRef]
- Teeri T, Kuokkala VT, Siitonen P, Kivikyto P, Liimatainen J (2006) Impact wear in mineral crushing. Proc. Estonian Acad Sci Eng 12(4): 408-418. [CrossRef]
- Ratia V., Valtonen K., Kemppainen A., Kuokkala V.-T. High Stress Abrasion and Impact-Abrasion Testing of wear Resistant Steels. Tribology Online 2013, 8, 2, 152–161. [CrossRef]
- Chintha, A. R., Valtonen, K., Kuokkala, V. T., Kundu, S., Peet, M. J., Bhadeshia, H. K. D. H. Role of fracture toughness in impact-abrasion wear. Wear 2019), 428, 430-437. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.N. Operation-oriented studies on wear properties of surface-hardened alloy cast steels used in mining in the conditions of the combined action of dynamic forces and an abrasive material. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017, 62, 2381–2389. [CrossRef]
- Sundström, A.; Rendón, J.; Olsson, M. Wear behaviour of some low alloyed steels under combined impact/abrasion contact conditions. Wear, 2001, 250, 744-754. [CrossRef]
- Ratia, V.; Heino, V.; Valtonen, K.; Vippola, M.; Kemppainen, A.; Siitonen, P.; Kuokkala, V.T. Effect of abrasive properties on the high-stress three-body abrasion of steels and hard metals. TRIBOLOGIA - Finnish Journal of Tribology 2014, 32, 1, 3-18.
- Wilson, R. D.; Hawk, J. A. Impeller wear impact-abrasive wear test. Wear 1999, 225, 1248-1257. [CrossRef]
- Mindivan F, Yildirim M.P., Bayindir F., Mindivan H., Corrosion and Tribocorrosion Behavior of Cast and Machine Milled Co-Cr Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Acta Physica Polonica 2016, A 129, 4, 701-704. [CrossRef]
- Mischler S., Triboelectrochemical techniques and interpretation methods in tribocorrosion: A comparative evaluation. Tribology International 2008, 41, 573-583. [CrossRef]
- Watson S.W., Friedersdorf F.J., Madsen B.W., Cramer S.D., Methods of measuring wear-corrosion synergism. Wear 1995, 181–183, 476-484. [CrossRef]
- Jemmely, P., Mischler, S., Landolt, D., Electrochemical modeling of passivation phenomena in tribocorrosion. Wear 237, 63–76, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Cao S., Mischler S., Modeling tribocorrosion of passive metals – A review. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 22, 4, 127-141, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Ponthiaux P., Wenger F., Celis J.P., Tribocorrosion: material behaviour under combined conditions of corrosion and mechanical loading. Corrosion Resistance, 2012, Dr Shih (Ed.).
- Stack M.M., Mapping tribo-corrosion processes in dry and in aqueous conditions: some new directions for the new millennium. Tribology International 2002, 35, 10, 681-689. [CrossRef]
- Dalmau A., Richard C., Igual – Muñoz A., Degradation mechanisms in martensitic stainless steels: Wear, corrosion and tribocorrosion appraisal. Tribology International 2018, 121, 167-179. [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh A., Salehi F.M., Bryant M., Neville A., A New Asperity-Scale Mechanistic Model of Tribocorrosive Wear: Synergistic Effects of Mechanical Wear and Corrosion. Journal of Tribology 2019, 141, 021601, 1-33. [CrossRef]
- Fallahnezhad K., Feyzi M., Ghadirinejad K., Hashemi R., Taylor M., Finite element-based simulation of tribocorrosion at the head-neck junction of hip implants. Tribology International 2021, 107284. [CrossRef]
- Songbo Y., Li D.Y., A new phenomenon observed in determining the wear-corrosion synergy during a corrosive sliding wear test. Tribology Letters 2008, 29, 45-52. [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak A., Tyczewski P., Zwierzycki W., The application of wear maps for analyzing the results of research into tribocorrosion. Wear 352–353, 146-154, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Munoz A.I., Espallargas N., Mischler S., Tribocorrosion, Springer 2020.
- Wang X.Y, Li D.Y., Investigation of the synergism of wear and corrosion using an electrochemical scratch technique. Tribology Letters 11, 2, 117-120, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Bainite in Steels, The Institute of Materials, Cambridge , GB, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Caballero, F.G.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Very Strong Bainite. Curr. Opinoin Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 251–257. [CrossRef]
- Hayrynen, K.L.; Keough, J.R.; Pioszak, G.L. Designing with Austempered Ductile Iron. AFS Trans. 2010, 129, 1–15.
- Myszka, D. Cast Iron–Based Alloys. In High-Performance Ferrous Alloys; Rana, R., Ed.; Springer Cham: Cham, Switzerland 2020, 153–210. [CrossRef]
- Massone J., Boeri R., Sikora J., Production of ADI by hot shake out – Microstructure and mechanical properties. International Journal Cast Metals Resarch 1999, 11, 419–424. [CrossRef]
- Guzik E., ADI cast iron and its variants as modern structural alloys. Engineering Forum "Development of ADI cast iron technology in Poland", Foundry Research Institute in Cracow, 2009, 37–49.
- Yang, J.; Putatunda, S.K. Effect of microstructure on abrasion wear behavior of austempered ductile cast iron (ADI) processed by a novel two-step austempering process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 406, 217–228. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Putatunda, S.K. Influence of a novel two-step austempering process on the strain-hardening behaviour of austempered ductile cast iron (ADI). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 382, 265–279. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.R.F.; Garboggini, A.A.; Tschipitschin, A.P. Effect of austenite grain refinement on morphology of product of bainitic reaction in austempered ductile iron. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1993, 9, 705–710. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, R.; Hassan, I.; Ghorbani, A.; Dioszegi, A. Austempered compacted graphite iron—influence of austempering temperature and time on microstructural and mechanical properties. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2019, 767, 138434. [CrossRef]
- Bayati H., Elliot R., The concept of an austempered heat treatment processing window. International Journal Cast Metals Resarch 1999, 11, 413–417. [CrossRef]
- Colin-García, E.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Romero-Serrano, J.A.; Sánchez-Alvarado, R.G.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, V.H.; Reyes-Castellanos, G. Nodule count effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of hypo-eutectic adi alloyed with nickel. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2021, 57, 115–124. [CrossRef]
- Myszka D., Cybula L., Wieczorek A.N., Influence of heat treatment conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of austempered ductile iron after dynamic deformation test. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2014, 59, 1181-1189. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.N. Influence of Shot Peening on Abrasion Wear in Real Conditions of Ni-Cu-Ausferritic Ductile Iron. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 1985–1990. [CrossRef]
- Zammit, A.; Abela, S.; Wagner, L.; Mhaede, M.; Grech, M. Tribological behavior of shot peened Cu-Ni austempered ductile iron. Wear 2013, 302, 829–836. [CrossRef]
- Zammit, A.; Bonnici, M.; Mhaede, M.; Wan, R.; Wagner, L.; Shot peening of austempered ductile iron gears. Surf. Eng. 2017, 33, 679–686. [CrossRef]
- Zammit, A.; Mhaede, M.; Grech, M.; Abela, S.; Wagner, L. Influence of shot peening on the fatigue life of Cu-Ni austempered ductile iron. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 545, 78–85. [CrossRef]
- Sevillano, J.G.; Aldazabal, J. Ductilization of nanocrystalline materials for structural applications. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 795–800. [CrossRef]
- Rementeria, R.; Aranda, M.M.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Caballero, F.G. Improving wear resistance of steels through nanocrystalline structures obtained by bainitic transformation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 3, 308-312. [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.; Skołek, E.; Wieczorek, A. Manufacture of toothed elements in nanoausferritic ductile iron. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 1227–1231. [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.; Wasiluk, K.; Skołek, E.; Swiatnicki, W. Nanoausferritic matrix of ductile iron. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 829–834. [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, S. Development of Nanostructured Austempered Ductile Cast Iron. Ph.D. Thesis, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA, 2017; 1856. Available online: https://digitalcommons.wayne.edu/oa_dissertations/1856 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Myszka D., Technological aspects of deformation-induced transformation in austempered ductile iron. Scientific Works of the Warsaw University of Technology. Mechanics, 265, Warsaw 2014.
- Soliman, M.; Palkowski, H.; Nofal, A. Multiphase ausformed austempered ductile iron. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2017; 62, 3, 1493–1498. [CrossRef]
- Myszka D., Austenite-martensite trasformation in austempered ductile iron, Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2007, 52, 475–480.
- Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Shirazi, H. Austempered ductile cast iron: bainitic transformation. Encyclopedia of Iron, Steel, and Their Alloys; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015, 217-230. [CrossRef]
- Ritha Kumari U., Prasad Rao P., Study of wear behaviour of austempered ductile iron. Journal of Materials Science 2009, 44, 1082–1093. [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.; Wieczorek, A.N. An assessment of the applicability of austempered ductile iron containing Mo and Ni for mining machines parts. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2013, 58, 967–970. [CrossRef]
- Hayrynen, K.L.; Keough, J.R. Wear Properties of Austempered Ductile Cast Irons. AFS Trans. 2005, 187, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Sellamuthu, P.; Samuel, D.G.; Dinakaran, D.; Premkumar, V.P.; Li, Z.; Seetharaman, S. Austempered ductile iron (ADI): Influence of austempering temperature on microstructure, mechanical and wear properties and energy consumption. Metals 2018, 8, 53. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadabadi, M.N.; Ghasemi, H.M.; Osia, M. Effects of successive austempering on the tribological behavior of ductile cast iron. Wear 1999, 231, 293–300. [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Hsui, I.C.; Chen, L.H.; Lui, T.S. Effects of heat treatment on the erosion behavior of austempered ductile irons. Wear 2006, 260, 783–793. [CrossRef]
- Myszka, D.; Wieczorek, A.N. Effect of phenomena accompanying wear in dry corundum abrasive on the properties and microstructure of austempered ductile iron with different chemical composition. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 483–490. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, D.; Song, Q. Wear and friction behavior of austempered ductile iron as railway wheel material. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 815–822. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek A.N. The role of operational factors in shaping of wear properties of alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron. Part I. Experimental studies abrasive wear of Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) in the presence of loose quartz abrasive. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2014, 59, 1665-1674. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek A.N., The role of operational factors in shaping of wear properties of alloyed Austempered Ductile Iron. Part II. An assessment of the cumulative effect of abrasives processes and the dynamic activity on the wear property of Ausferritic Ductile Iron. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2014, 59, 4, 1675-1683. [CrossRef]
- Carlos Humberto Navarro-Mesa and Maryory Gómez-Botero and Mateo Montoya-Mejía and Oscar Ríos-Diez and Ricardo Aristizábal-Sierra Wear resistance of austempered grey iron under dry and wet conditions}, Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2022, 21, 4174-4183. [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak A., Wieczorek A.N., Comparative tribocorrosion tests of 30CrMo12 cast steel and ADI spheroidal cast iron. Tribology International 2021, 155, 106763. [CrossRef]
- EN 1564:2012; Standard-Austempered Ductile Cast Irons. iTeh, Inc.: Newark, DE, USA, 2011.
- Wieczorek, A. N.; Polis, W., Operation-oriented method for testing the abrasive wear of mining chain wheels in the conditions of the combined action of destructive factors. Management Systems in Production Engineering 2015, 19, 175-178. [CrossRef]
- Putatunda, S.K.; Bingi, G.A. Influence of step-down austempering process on the fracture toughness of austempered ductile iron. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2005, 5, 39−70.
- Ravishankar, K.S.; Rajendra Udupa, K.; Prasad Rao, P. Development of Austempered Ductile Iron for High Tensile and Fracture toughness by Two Step Austempering Process. 68th WFC - World Foundry Congress 2008, 35-40.


| Research Variant And Its Designation | Destructive Factors | Simulated Type of Wear |
|---|---|---|
| Variant A | quartz sand | abrasive wear |
| Variant AD | quartz sand and dynamic force | abrasive- dynamic wear |
| Variant AC | quartz sand and water | tribocorrosion wear |
| Variant ACD | quartz sand, water and dynamic force | abrasive-corrosion-dynamic wear |
| C | Si | Mn | S | P | Mg | Cr | Cu | Ni | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.50 | 2.54 | 0.16 | 0.013 | 0.041 | 0.047 | 0.026 | 0.50 | 1.40 | 0.24 |
| Heat treatment parameters | ADI_1400 | ADI_1200 | ADI_1000 | ADI_800 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitising temperature,⁰C | 950 | |||
| Austenitising time, min | 180 | |||
| Austempering temperature,⁰C | 240 | 270 | 310 | 360 |
| Austempering time, min | 150 | |||
| Mechanical Properties | ADI_1400 | ADI_1200 | ADI_1000 | ADI_800 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength TS, MPa | 1507 | 1372 | 1132 | 1028 |
| Yield Strength YS, MPa | 1072 | 936 | 804 | 652 |
| Impact Toughness K, J | 54 | 72 | 84 | 124 |
| Elongation A5, % | 3 | 4 | 5 | 10 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Ammonium ion (NH4+) | <0.05 mg/dm3 |
| Nitrites (NH2-) | <0.03 mg/dm3 |
| Manganese (Mn) | <4.0 mg/dm3 |
| Iron (Fe) | <60.0 mg/dm3 |
| pH | 7.2 |
| Fractions of Individual Phases | ADI_1400 | ADI_1200 | ADI_1000 | ADI_800 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 72.1± | 75.4± | 69.1± | 59.3± |
| γ | 17.9±0.7 | 24.6±1.9 | 30.9±1.2 | 40.7±2.5 |
| Parameters | ADI_800 | ADI_1000 | ADI_1200 | ADI_1400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| , mV (SCE) | -590 ± 15 | -501 ± 16 | -493 ± 12 | -676 ± 16 |
| , µA/cm2 | 16.1 ± 2.1 | 13.8 ± 1.5 | 12.4 ± 1.8 | 14.8 ± 2.1 |
| WCORR | 0.0041± 0.0001 | 0.0041± 0.0001 | 0.0044± 0.0009 | 0.0048± 0.0001 |
| Grade of Cast Iron | δMAX, A (Variant A) |
δMAX, AD (Variant AD) |
δMAX, AC (Variant AC) |
δMAX, ACD (Variant ACD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADI_1400 | 0.707 ± 0.080 | 0.993 ± 0.137 | 1.096 ± 0.254 | 1.471 ± 0.089 |
| ADI_1200 | 0.801 ± 0.079 | 0.914 ± 0.130 | 1.037 ± 0.159 | 1.511 ± 0.125 |
| ADI_1000 | 0.920 ± 0.079 | 0.886 ± 0.118 | 0.926 ± 0.206 | 1.672 ± 0.158 |
| ADI_800 | 0.930 ± 0.123 | 0.783 ± 0.097 | 1.033 ± 0.144 | 1.678 ± 0.114 |
| HB | Initial state | Variant A | Variant AD | Variant AC | Variant ACD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADI_1400 | 387 ± | 618 ± | 576 ± | 618 ± | 538 ± |
| ADI_1200 | 382 ± | 600 ± | 499 ± | 543 ± | 602 ± |
| ADI_1000 | 335 ± | 478 ± | 399 ± | 441 ± | 441 ± |
| ADI_800 | 284 ± | 441 ± | 385 ± | 364 ± | 377 ± |
| Variant A | Variant AD | Variant AC | Variant ACD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | -0.921 | 0.989 | 0.757 | -0.876 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





