Submitted:
16 February 2024
Posted:
18 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
EVs in Plant-Microbe Interactions: Biogenesis and Functional Insights
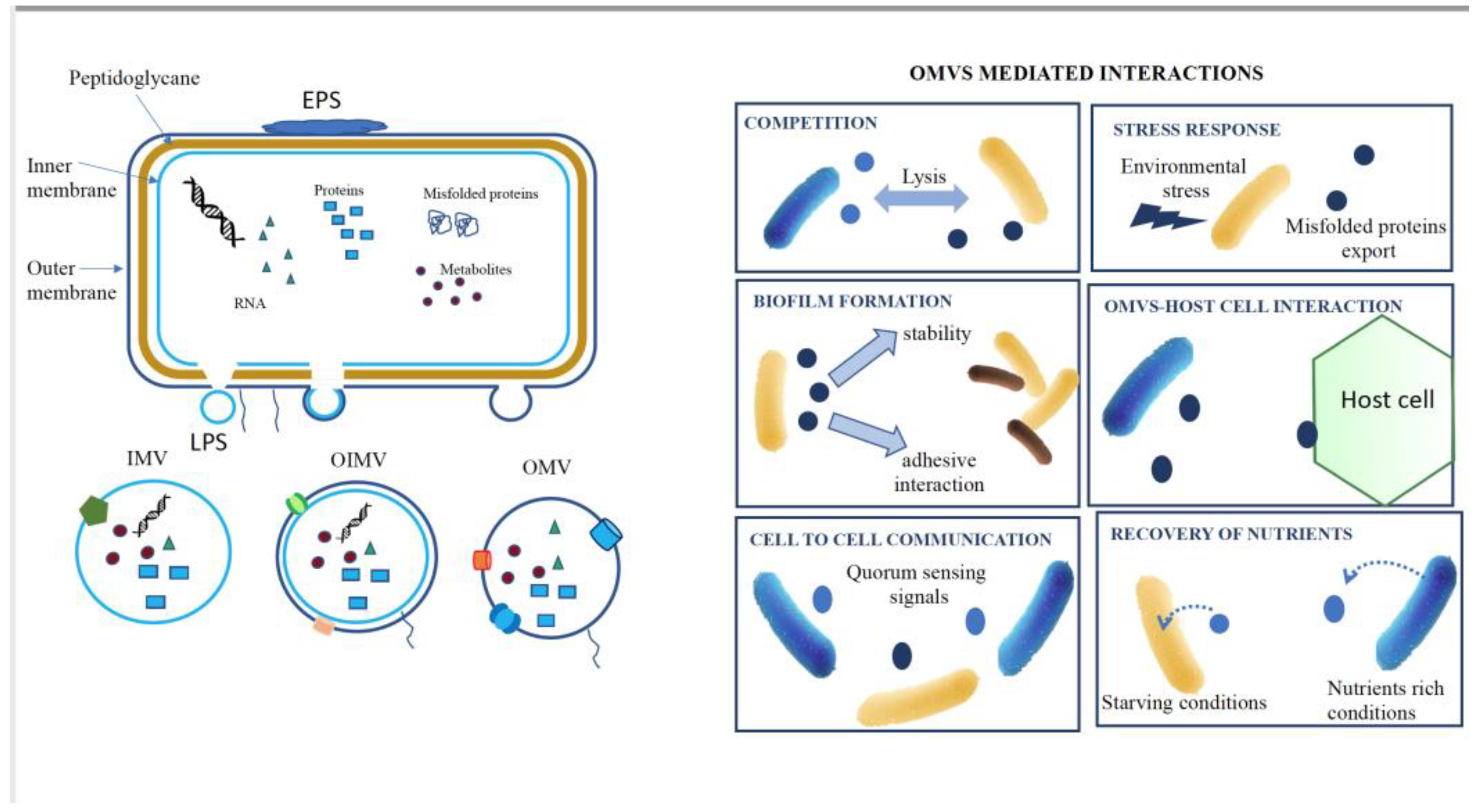
Bacterial EVs
Biogenesis, Secretion and Uptake of EVs
- Cell wall turnover: During routine cell wall recycling, lipoproteins between the outer membrane and the peptidoglycans dissociate, leading to membrane protrusion and the release of vesicles into the extracellular space [28].
- Conformational changes in outer membrane proteins (OMPs): Changes in the conformation of OMPs can promote vesicle formation. Specific proteins and lipids are locally enriched in areas with high vesicle abundance, while other proteins inhibiting vesiculation such as lipoproteins are reduced [29].
- Explosive cell lysis: A newly proposed mechanism suggests that vesiculation is a result of explosive cell lysis or bubbling cell death, [31], which involves the release of DNA-containing lytic EVs.
Functions of Bacterial EVs
Cell-Cell Communications and Quorum Sensing (QS)
Biofilm Formation
Transport and Delivery
Stress Response
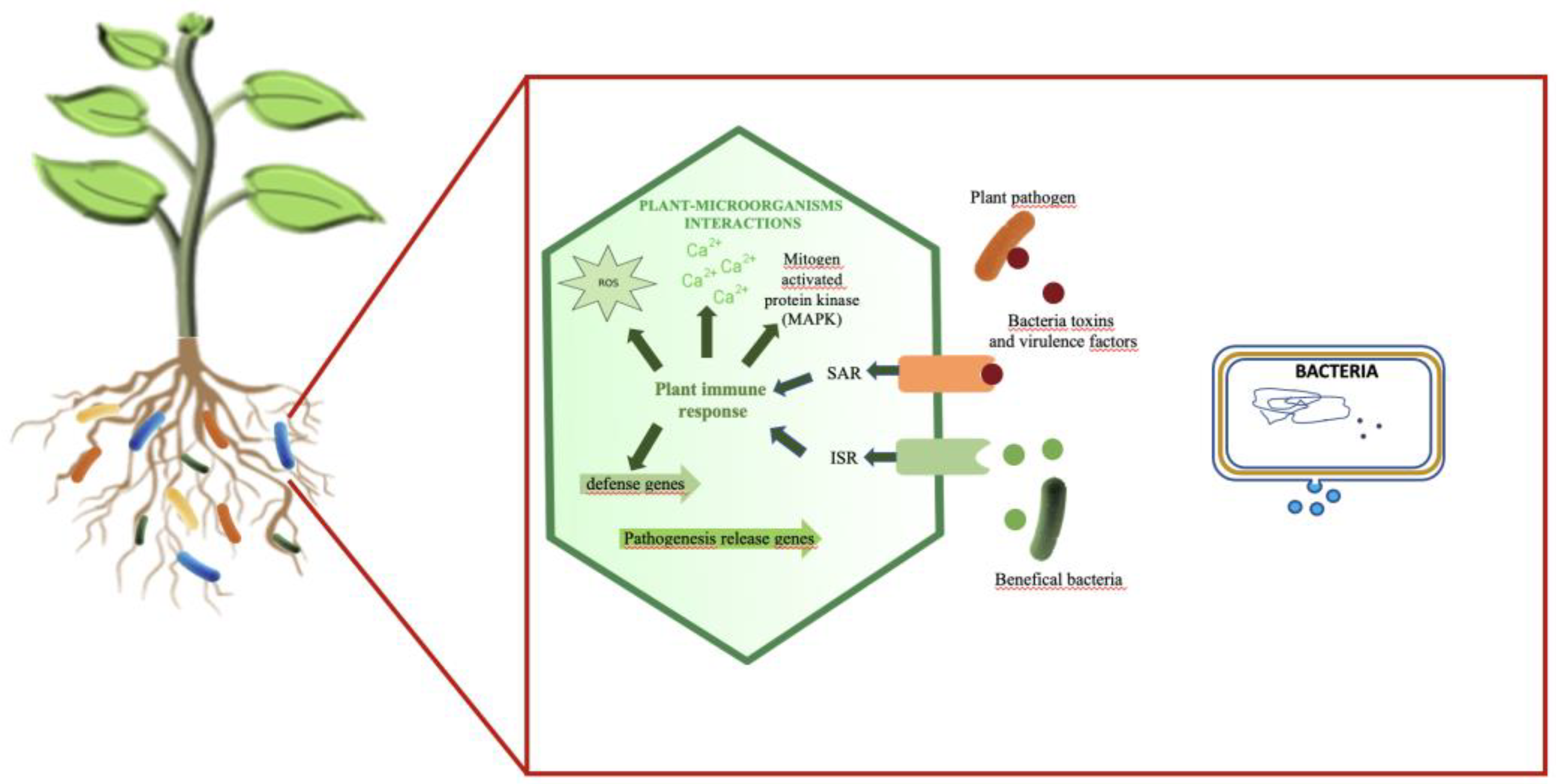
Role of EVs and sRNA in Plant-Microbe Interaction
Plant-Microbe Symbiosis
EV-Packed sRNA and Pathogenicity
Bacterial EVs: Activating Signal for Plant Immune Response
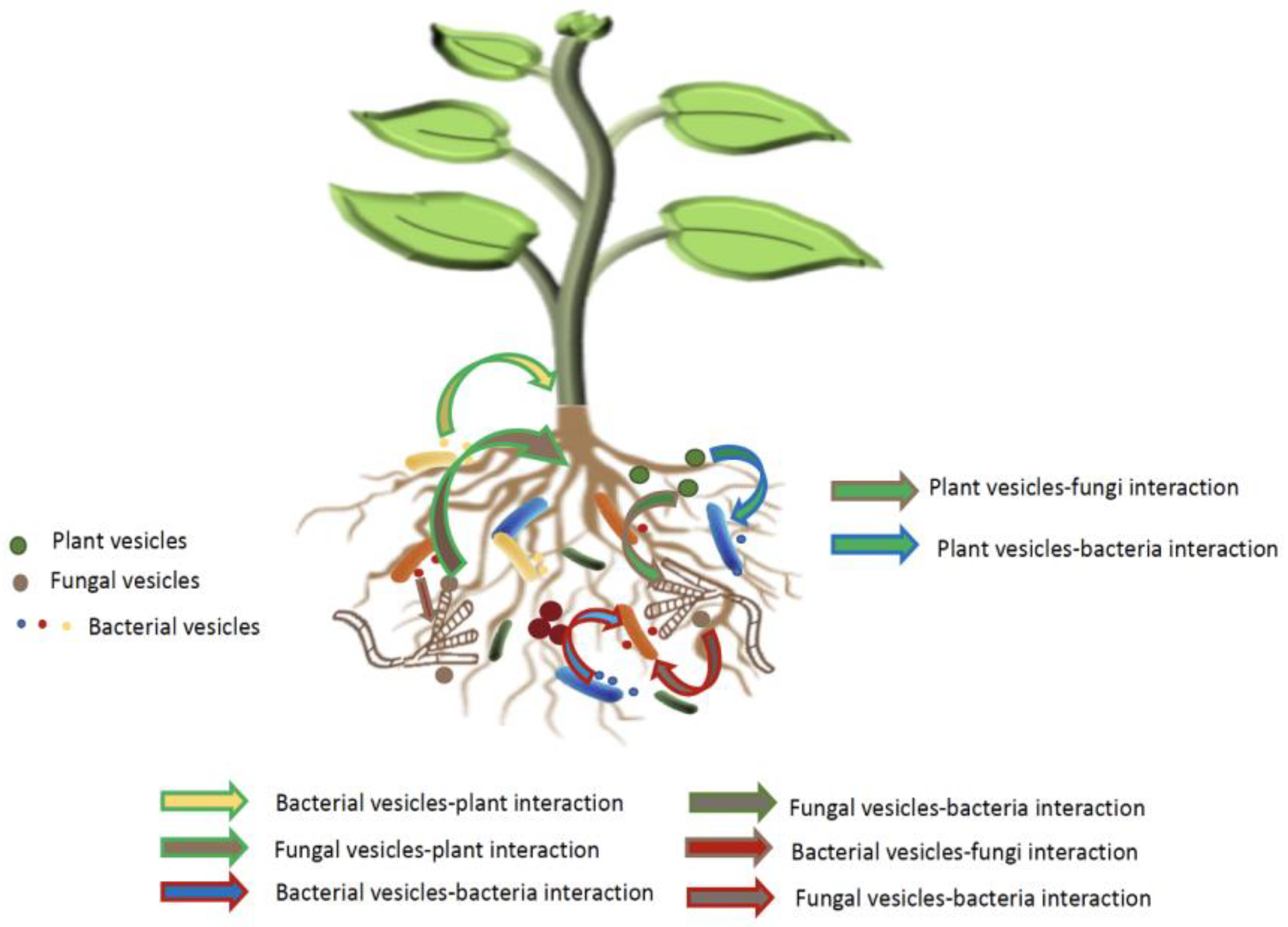
Plant-Microbiota Vesicle Interactions
2. Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassani, M.A.; Durán, P.; Hacquard, S. Microbial interactions within the plant holobiont. Microbiome 2018, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benidire, L., El Khalloufi, F., Oufdou, K., Barakat, M., Tulumello, J., Ortet, P., Heulin, T., Achouak, W. Phytobeneficial bacteria improve saline stress tolerance in Viciafaba and modulate microbial interaction network. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139020. [CrossRef]
- Tulumello, J.; Chabert, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Long, J.; Nalin, R.; Achouak, W.; Heulin, T. Rhizobium alamii improves water stress tolerance in a non-legume. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 797, 148895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, P.H.; Hochberg, M.E.; Burdon, J.J.; Bever, J.D. Coevolution of symbiotic mutualists and parasites in a community context. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T. R., James, E. K., and Poole, P. S. The plant microbiome. Genome Biol 2013, 14:209. [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Ayangbenro, A.S.; Glick, B.R.; Babalola, O.O. Plant health: feedback effect of root exudates-rhizobiome interactions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 103, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haichar, F.e.Z.; Santaella, C.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Root exudates mediated interactions belowground. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, A.; Harir, M.; Fochesato, S.; Tulumello, J.; Walker, A.; Barakat, M.; Ndour, P.M.S.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Cournac, L.; Laplaze, L.; et al. Unraveling the interplay between root exudates, microbiota, and rhizosheath formation in pearl millet. Microbiome 2024, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological Functions and Biogenesis of Secreted Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-W.; Um, J.-H.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J. Tiny RNAs and their voyage via extracellular vesicles: Secretion of bacterial small RNA and eukaryotic microRNA. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, E.J.; Krachler, A.M. Mechanisms of outer membrane vesicle entry into host cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1508–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-Y., Choi, D.-Y., Kim, D.-K., Kim, J.-W., Park, J. O., Kim, S., Kim, S.-H., Desiderio, D. M., Kim, Y.-K., Kim, K.-P., Gho, Y. S. Gram-positive bacteria produce membrane vesicles: Proteomics-based characterization of Staphylococcus aureus-derived membrane vesicles. Proteomics 2009, 9:5425–5436. [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M.; Schild, S.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Eberl, L. Composition and functions of bacterial membrane vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, E.; Goes, A.; Garcia, R.; Panter, F.; Koch, M.; Müller, R.; Fuhrmann, K.; Fuhrmann, G. Biocompatible bacteria-derived vesicles show inherent antimicrobial activity. J. Control. Release 2018, 290, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBroom, A. J., and Kuehn, M. J. Release of outer membrane vesicles by Gram-negative bacteria is a novel envelope stress response: Outer membrane vesicles relieve envelope stress. Molecular Microbiology 2007, 63:545–558. [CrossRef]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaganza, E.-S., Rioux, D., Simard, M., Arul, J., and Tweddell, R. J. Ultrastructural Alterations of Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica Caused by Treatment with Aluminum Chloride and Sodium Metabisulfite. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70:6800–6808. [CrossRef]
- Solé, M.; Scheibner, F.; Hoffmeister, A.-K.; Hartmann, N.; Hause, G.; Rother, A.; Jordan, M.; Lautier, M.; Arlat, M.; Büttner, D. Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria Secretes Proteases and Xylanases via the Xps Type II Secretion System and Outer Membrane Vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2879–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, O.; Mordukhovich, G.; Luu, D.D.; Schwessinger, B.; Daudi, A.; Jehle, A.K.; Felix, G.; Ronald, P.C. Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles Induce Plant Immune Responses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interactions® 2016, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, M.; Zaini, P.A.; Baccari, C.; Tran, S.; da Silva, A.M.; Lindow, S.E. Xylella fastidiosa outer membrane vesicles modulate plant colonization by blocking attachment to surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, E3910–E3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, A.d.S.; Mendes, J.S.; dos Santos, C.A.; de Toledo, M.A.S.; Beloti, L.L.; Crucello, A.; Horta, M.A.C.; Favaro, M.T.d.P.; Munar, D.M.M.; de Souza, A.A.; et al. The Antitoxin Protein of a Toxin-Antitoxin System from Xylella fastidiosa Is Secreted via Outer Membrane Vesicles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roier, S., Leitner, D. R., Iwashkiw, J., Schild-Prüfert, K., Feldman, M. F., Krohne, G., Reidl, J., and Schild, S. Intranasal Immunization with Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae Outer Membrane Vesicles Induces Cross-Protective Immunity in Mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7:e42664. [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Wolf, J.M.; Prados-Rosales, R.; Casadevall, A. Through the wall: extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, U.; Tsatsaronis, J.A.; Le Rhun, A.; Stübiger, G.; Rohde, M.; Kasvandik, S.; Holzmeister, S.; Tinnefeld, P.; Wai, S.N.; Charpentier, E. A Two-Component Regulatory System Impacts Extracellular Membrane-Derived Vesicle Production in Group A Streptococcus. mBio 2016, 7, e00207-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, I.A.; Kuehn, M.J. Offense and defense: microbial membrane vesicles play both ways. Res. Microbiol. 2012, 163, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Comolli, L.R.; Downing, K.H.; Shapiro, L.; McAdams, H.H. The Caulobacter Tol-Pal Complex Is Essential for Outer Membrane Integrity and the Positioning of a Polar Localization Factor. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 4847–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, H.M.; Jagannadham, M.V. Biogenesis and multifaceted roles of outer membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology 2014, 160, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhenawy, W.; Bording-Jorgensen, M.; Valguarnera, E.; Haurat, M.F.; Wine, E.; Feldman, M.F. LPS Remodeling Triggers Formation of Outer Membrane Vesicles in Salmonella. mBio 2016, 7, e00940–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyofuku, M. Bacterial communication through membrane vesicles. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juodeikis, R., Simon, R. C. Outer Membrane Vesicles: Biogenesis, Functions, and Issues. Microbiology and Molecular Biology reviews 2022, 86(4). [CrossRef]
- Altindis, E.; Fu, Y.; Mekalanos, J.J. Proteomic analysis of Vibrio cholerae outer membrane vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, E1548-56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, M.; Shiota, T.; Ueno, S.; Takahara, M.; Haneda, K.; Tahara, Y.O.; Shintani, M.; Nakao, R.; Miyata, M.; Kimbara, K.; et al. Identification of genes involved in enhanced membrane vesicle formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: surface sensing facilitates vesiculation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1252155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashburn, L.M.; Whiteley, M. Membrane vesicles traffic signals and facilitate group activities in a prokaryote. Nature 2005, 437, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X. The Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS): Not Just for Quorum Sensing Anymore. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, M., Morinaga, K., Hashimoto, Y. Uhl, J., Shimamura, H., Inaba, H., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Eberl, L., Nomura, N. Membrane vesicle-mediated bacterial communication. ISME J 2017, 11:1504-1509. [CrossRef]
- Brameyer, S.; Plener, L.; Müller, A.; Klingl, A.; Wanner, G.; Jung, K. Outer Membrane Vesicles Facilitate Trafficking of the Hydrophobic Signaling Molecule CAI-1 between Vibrio harveyi Cells. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00740–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, Y.; Ichikawa, S.; Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Uchiyama, H.; Nomura, N. Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Affects Membrane Vesicle Production in not only Gram-Negative but also Gram-Positive Bacteria. Microbes Environ. 2010, 25, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Kiefer, P.; Charki, P.; Hedberg, C.; Seibel, J.; Vorholt, J.A.; Hilbi, H. The Legionella autoinducer LAI-1 is delivered by outer membrane vesicles to promote interbacterial and interkingdom signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciofu, O., Beveridge, T. J., Kadurugamuwa, J., Walther-Rasmussen, J., and Høiby, N. Chromosomal β-lactamase is packaged into membrane vesicles and secreted from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2000, 45:9–13. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, S.; Wen, R.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y. Membrane vesicles derived from Enterococcus faecalis promote the co-transfer of important antibiotic resistance genes located on both plasmids and chromosomes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 79, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaar, V.; Uddbäck, I.; Nordström, T.; Riesbeck, K. Group A streptococci are protected from amoxicillin-mediated killing by vesicles containing -lactamase derived from Haemophilus influenzae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 69, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbo, C.; Fernández-Moreira, E.; Merino, M.; Poza, M.; Mendez, J.A.; Soares, N.C.; Mosquera, A.; Chaves, F.; Bou, G. Horizontal Transfer of the OXA-24 Carbapenemase Gene via Outer Membrane Vesicles: a New Mechanism of Dissemination of Carbapenem Resistance Genes in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarten, T.; Sperling, S.; Seifert, J.; von Bergen, M.; Steiniger, F.; Wick, L.Y.; Heipieper, H.J. Membrane Vesicle Formation as a Multiple-Stress Response Mechanism Enhances Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1E Cell Surface Hydrophobicity and Biofilm Formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6217–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.J.; Kuehn, M.J. Contribution of bacterial outer membrane vesicles to innate bacterial defense. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 258–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Xiang, E.; Ivanovski, S.; Han, P. Saliva biofilm-derived outer membrane vesicles regulate biofilm formation and immune response of oral epithelial cells on titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Clarke, A.J.; Beveridge, T.J. Gram-Negative Bacteria Produce Membrane Vesicles Which Are Capable of Killing Other Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5478–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, P., Thiergart, T., Garrido-Oter, R., Agler, M., Kemen, E., Schulze-Lefert, P., and Hacquard, S. Microbial Interkingdom Interactions in Roots Promote Arabidopsis Survival. Cell 2018, 175:973-983.e14. [CrossRef]
- Rossoni, S.; Beard, S.; Segura-Bidermann, M.I.; Duarte-Ramírez, J.; Osorio, F.K.; Varas-Godoy, M.; Martínez-Bellange, P.; Vera, M.; Quatrini, R.; Castro, M. Membrane vesicles in Acidithiobacillia class extreme acidophiles: influence on collective behaviors of ‘Fervidacidithiobacillus caldus’. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1331363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Nakouzi, A.S.; Frases, S.; Nicola, A.; Casadevall, A. Bacillus anthracis produces membrane-derived vesicles containing biologically active toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19002–19007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.H.M.; Elgamoudi, B.; Colon, N.; Cramond, A.; Poly, F.; Ying, L.; Korolik, V.; Ferrero, R.L. Campylobacter jejuni extracellular vesicles harboring cytolethal distending toxin bind host cell glycans and induce cell cycle arrest in host cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0323223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, C.; Jagannadham, M.V. Virulence factors are released in association with outer membrane vesicles of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato T1 during normal growth. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, S.J.; Lundeen, R.A.; Hmelo, L.R.; Becker, K.W.; Arellano, A.A.; Dooley, K.; Heal, K.R.; Carlson, L.T.; Van Mooy, B.A.S.; Ingalls, A.E.; et al. Prochlorococcus extracellular vesicles: molecular composition and adsorption to diverse microbes. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 24, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, E.L.; Zavan, L.; Bitto, N.J.; Petrovski, S.; Hill, A.F.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Planktonic and Biofilm-Derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa Outer Membrane Vesicles Facilitate Horizontal Gene Transfer of Plasmid DNA. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0517922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wen, R.; Mu, R.; Chen, X.; Ma, P.; Gu, K.; Huang, Z.; Ju, Z.; Lei, C.; Tang, Y.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles of Avian PathogenicEscherichia coli Mediate the Horizontal Transmission of blaCTX-M-55. Pathogens 2022, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’annunziata, F.; Dell’aversana, C.; Doti, N.; Donadio, G.; Piaz, F.D.; Izzo, V.; De Filippis, A.; Galdiero, M.; Altucci, L.; Boccia, G.; et al. Outer Membrane Vesicles Derived from Klebsiella pneumoniae Are a Driving Force for Horizontal Gene Transfer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, D.; Bélanger, M. Protective effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis outer membrane vesicles against bactericidal activity of human serum. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 3004–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.J.; Nodwell, J.R. Streptomyces extracellular vesicles are a broad and permissive antimicrobial packaging and delivery system. J. Bacteriol. 2024, e0032523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaheb, N.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P. Membrane Vesicle Production as a Bacterial Defense Against Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.; Matinha-Cardoso, J.; Giner-Lamia, J.; Couto, N.; Pacheco, C.C.; Florencio, F.J.; Wright, P.C.; Tamagnini, P.; Oliveira, P. Extracellular vesicles as an alternative copper-secretion mechanism in bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Rosales, R.; Weinrick, B.C.; Piqué, D.G.; Jr., W.R.J.; Casadevall, A.; Rodriguez, G.M. Role for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Membrane Vesicles in Iron Acquisition. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1250–1256. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H, Yang, J., Cheng, J., Zeng, J., Ma, X., Lin, J. PQS and pyochelin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa share inner membrane transporters to mediate iron uptake. Microbiol Spectr. 2024, 12:e0325623. [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, K.; Nagakubo, T.; Nomura, N.; Toyofuku, M. Iron Delivery through Membrane Vesicles in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0122223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-García, P., Moreno-de Castro, N., Jiménez-Guerrero, I., Müsken, M., Arce-Rodríguez, A., Pérez-Montaño, F., Borrero-de Acuña, J. M. Isolation, Quantification, and Visualization of Extracellular Membrane Vesicles in Rhizobia Under Free-Living Conditions. Methods Mol Biol. 2024, 2751:219-228. [CrossRef]
- Taboada, H.; Meneses, N.; Dunn, M.F.; Vargas-Lagunas, C.; Buchs, N.; Castro-Mondragón, J.A.; Heller, M.; Encarnación, S. Proteins in the periplasmic space and outer membrane vesicles of Rhizobium etli CE3 grown in minimal medium are largely distinct and change with growth phase. Microbiology 2019, 165, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taboada, H.; Dunn, M.F.; Meneses, N.; Vargas-Lagunas, C.; Buchs, N.; Andrade-Domínguez, A.; Encarnación, S. Qualitative changes in proteins contained in outer membrane vesicles produced by Rhizobium etli grown in the presence of the nod gene inducer naringenin. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1173–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Tang, Z.; Xie, F.; Chen, D.; Lin, H.; Li, Y. Analysis of Outer Membrane Vesicles Indicates That Glycerophospholipid Metabolism Contributes to Early Symbiosis Between Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 and Soybean. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interactions® 2022, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, H.; Swamy, C.V.; Jagannadham, M. The proteome of the outer membrane vesicles of an Antarctic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae Lz4W. Data Brief 2015, 4, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, H.M.; Kuehn, M.J. Proteomic Profiling Reveals Distinct Bacterial Extracellular Vesicle Subpopulations with Possibly Unique Functionality. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0168622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turbant, F.; Waeytens, J.; Blache, A.; Esnouf, E.; Raussens, V.; Węgrzyn, G.; Achouak, W.; Wien, F.; Arluison, V. Interactions and Insertion of Escherichia coli Hfq into Outer Membrane Vesicles as Revealed by Infrared and Orientated Circular Dichroism Spectroscopies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koeppen., Hampton, T. H., Jarek, M., Scharfe, M., Gerber, S.A., Mielcarz, D. W., Demers, E. G., Dolben, E. L., Hammond, J. H., Hogan, D. A., Stanton, B. A. A Novel Mechanism of Host-Pathogen Interaction through sRNA in Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 112:e1005672. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J. Microbe-Host Communication by Small RNAs in Extracellular Vesicles: Vehicles for Transkingdom RNA Transportation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriano-Gutierrez, S.; Bongrand, C.; Essock-Burns, T.; Wu, L.; McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Ruby, E.G. The noncoding small RNA SsrA is released by Vibrio fischeri and modulates critical host responses. PLOS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D., Liu, S., Liu, J., Miao, L., Zhang, S., Pan, Y. sRNA23392 packaged by Porphyromonas gingivalis outer membrane vesicles promotes oral squamous cell carcinomas migration and invasion by targeting desmocollin-2. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2021, 36:182-191. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Nie, W.; Ahmad, I.; Sarris, P.F.; Chen, G.; Zhu, B. Suppression of host plant defense by bacterial small RNAs packaged in outer membrane vesicles. Plant Commun. 2024, 100817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F.; Li, M.; Gu, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane vesicle-packed sRNAs can enter host cells and regulate innate immune responses. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yin, S.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Gong, T.; Liu, Q. Insights into the regulatory role of bacterial sncRNA and its extracellular delivery via OMVs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R., Massé, M. E. New Perspectives on Crosstalks Between Bacterial Regulatory RNAs from Outer Membrane Vesicles and Eukaryotic Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2024, 2741:183-194. [CrossRef]
- Blache. A, Achouak., W. Extraction and Purification of Outer Membrane Vesicles and Their Associated RNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2024, 2741:11-24. [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, R.; Fernã¡Ndez, S.; Zayas, C.; Acosta, A.; Sarmiento, M.E.; Ferro, V.A.; Rosenqvist, E.; Campa, C.; Cardoso, D.; Garcia, L.; et al. Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles and Vaccine Applications. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, J.C.; Walper, S.A. Bacterial Membrane Vesicles as Mediators of Microbe – Microbe and Microbe – Host Community Interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildermuth, M.C.; Dewdney, J.; Wu, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Isochorismate synthase is required to synthesize salicylic acid for plant defence. Nature 2001, 414, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazebrook, J. Contrasting Mechanisms of Defense Against Biotrophic and Necrotrophic Pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2005, 43, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalupowicz, L.; Mordukhovich, G.; Assoline, N.; Katsir, L.; Sela, N.; Bahar, O. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles induce a transcriptional shift in arabidopsis towards immune system activation leading to suppression of pathogen growth in planta. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.; Chng, C.-P.; Pu, X.; Ma, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Miao, Y. Potentiation of plant defense by bacterial outer membrane vesicles is mediated by membrane nanodomains. Plant Cell 2021, 34, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, H.M.; Zebell, S.G.; Ristaino, J.B.; Dong, X.; Kuehn, M.J. Protective plant immune responses are elicited by bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108645–108645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced Systemic Resistance by Beneficial Microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zhou, J.-M. Plant–bacterial pathogen interactions mediated by type III effectors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomovatskaya, L.A.; Romanenko, A.S. Secretion Systems of Bacterial Phytopathogens and Mutualists (Review). Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Klessig, D.F. DAMPs, MAMPs, and NAMPs in plant innate immunity. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, M., and Adi A. The receptor for the fungal elicitor ethylene-inducing xylanase is a member of a resistance-like gene family in tomato. The Plant Cell 2004, 16:1604-1615.
- Monaghan, J.; Zipfel, C. Plant pattern recognition receptor complexes at the plasma membrane. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.-M. Receptor Kinases in Plant-Pathogen Interactions: More Than Pattern Recognition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 618–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, B.; Zhou, J.-M.; Tang, D. Plant immune signaling: Advancing on two frontiers. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, B.D.; Innes, R.W. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from the Leaf Apoplast Carry Stress-Response Proteins. Plant Physiol. 2016, 173, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutrot, F.; Zipfel, C. Function, Discovery, and Exploitation of Plant Pattern Recognition Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhital, S.; Deo, P.; Stuart, I.; Naderer, T. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and host cell death signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Peng, W.; Mai, Y.; Li, K.; Wei, W.; Hu, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, H.; Jie, W.; Wei, Z.; et al. Outer membrane vesicles enhance tau phosphorylation and contribute to cognitive impairment. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 235, 4843–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




