1. Introduction
A literature review shows that interest fly ash-based geopolymers concrete first emerged in the 1980s and continues worldwide.
The technology for producing lightweight geopolymer concrete based on fly ash and alumino-silicate artificial aggregate was developed with sustainable development in mind, aiming to reduce negative human impact on the environment. Sustainable development is based on proper resource management and caring for the natural environment. To achieve a sustainable state of development, developing specific consumer behaviors that would ensure a balance between human needs and environmental possibilities is essential. The starting point in achieving these goals is to minimize the negative impact of factors in the industrial and construction sectors on the environment.
In developing the research program, the elimination of Portland cement, previously the main component of concrete, was a priority. Studies have shown that producing one ton of cement releases 0.9 tons of CO2, accounting for 5% to 7% of global CO2 emissions [4,14,19]. Many studies have shown that geopolymer concrete is an alternative to cement-based concrete, and its synthesis is a process that consumes half the energy required for Portland cement production and releases 80% less carbon dioxide [3,11,13,23]. Geopolymer production can, therefore, significantly reduce the environmental burden by reducing gas emissions.
In addition to gas emissions, the use of some waste products from the energy, mining, and metallurgical sectors, including fly ash, is also essential. Fly ash is a highly dispersed material consisting of spherical particles represented by hollow aluminosilicate balls with a diameter of 0.1-100 μm, responsible for the binding properties in alkali-activated lightweight concrete [1,10,28,32,33]. It allows the elimination of the problem of waste stacking on specially prepared landfills, which has a significant impact on the environment.
Cement-free building materials were also obtained using ground perlite raw material using alkaline activation, outlined in a 2022 article by Acar M.C., Çelik A.I., Kayabaşı R., et al. [2]. Several tests were carried out, including compressive strength, which came out at the level of 6 - 16 MPa. Cementless paste and mortar were produced based on the alkaline activation of raw perlite and proved suitable as building materials. However, the durability of the mixes decreased with increasing water content in both paste and mortar. Most importantly, cement-free pastes and mortars can be produced environmentally friendly, requiring no high energy and no greenhouse gas emissions [2].
Equally important is replacing natural aggregates, because of unwillingness to extract raw materials from protected natural environments, with recycled aggregates [5,9,18,24] or artificial aggregates made from industrial waste or by-products [26,29]. There are two techniques for producing artificial aggregates [6]: sintering [17,30] and cold bonding [15,22]. The aggregate used in the study was obtained by sintering with simultaneous granulation, resulting in a lightweight, porous ceramic aggregate with high thermal insulation [12,25] and resistance to atmospheric and chemical factors as well as fungi, insects, and rodents. In addition, it is odorless, highly crush-resistant, and has relatively low water absorption.
Replacing Portland cement in concrete with fly ash and natural aggregates with alumino-silicate artificial aggregate required the research to demonstrate that the resulting product meets the requirements of norms and regulations and has similarities to traditional concrete. The fly ash was combined with artificial aggregate using an alkaline solution, resulting in a geopolymer, or artificial concrete. The production of geopolymers can thus lead to a significant reduction in environmental impact by reducing emissions, utilizing certain waste products from the energy, mining, and metallurgical sectors, as well as replacing natural raw materials with artificial fly ash aggregate, which can prove particularly useful in sustainable development-based construction [21].
In 2008, Obada Kayali conducted research using fly ash lightweight aggregates to produce high-strength concretes. Concrete produced using these aggregates was about 22% lighter and obtained strengths of 40-60 MPa. However, cement and natural aggregate were used in its production [16].
Anja Terzic, Lato Pezo, and others 2015 [31] analyzed the impact of using granulated aggregates based on fly ash obtained by various processing techniques on the behavior of lightweight concretes. The experimental plan assumed the use of four lightweight artificial aggregates. The performance of lightweight concrete was compared with traditional concrete by testing, inter alia, compressive strength. An increase in concrete strength was observed due to increased ash fineness, which also affected the granules' sintering time and the reduction of the sintering temperature. The 28- and 56-day-old lightweight concrete samples were characterized by properties meeting the requirements for traditional concretes and amounted to 56 - 58 MPa. Cement, water, natural aggregate, and artificial aggregate were used to produce concrete in these studies [31].
The compressive strength test is essential in the context of the conducted analyses. Many publications have been released in which researchers focused on preparing cement-free composites based on alkali-activated fly ash and testing their basic properties. Eric Asa, Monisha Shrestha, Edmund Baffoe-Twum, and Bright Awuku researched cement-free composites based on fly ash and described their findings in an article in 2020. They focused on developing sustainable building materials using 100% calcium and potassium hydroxide (KOH) alkaline solution and examining the engineering properties of the resulting fly ash-based geopolymer concrete. They conducted laboratory tests to determine the mechanical properties of geopolymer concrete, such as compressive and bending strength. In the study's first phase, carbon nanotubes (CNT - Carbon Nanotubes) were added to the mixture to determine their influence on the strength of geopolymer mortar. The results of the experiments showed that the mortar and concrete made entirely from fly ash require an alkaline solution to obtain strength properties comparable to those of Portland cement. However, it was found that increasing the amount of KOH generates a significant amount of heat, causing the concrete to set too quickly. The study also showed that adding CNT to the mixture makes the geopolymer concrete harder than traditional concrete without CNT [7].
In the same year, Zijian Su, Wei Hou, and others conducted research in which they synthesized a foamed geopolymer from fly ash to produce lightweight geopolymer concrete (GLWC - Geopolymeric Lightweight Concrete). The fly ash was activated with a sodium silicate solution, and aluminum powder was used as a foaming agent. The synthesized mortars were cured at 40°C for 28 days, resulting in a product with a bulk density ranging from 600 to 1600 kg/m3. The results showed that GLWC had higher mechanical strength than commercial cellular concrete and achieved 80–90% of its 28-day strength after seven days of curing. In addition, for densities ranging from 600 to 1200 kg/m3, the thermal conductivity decreased from 0.70 to 0.22 W/m·K, much better than its counterpart, ordinary Portland cement (OPC) concrete [27].
The article presented geopolymer concrete produced using various waste additives, different concentrations of NaOH solution, and a range of curing conditions involving varying times and temperatures. The resulting conclusion emphasized the significantly improved physico-mechanical properties displayed by geopolymer composites when compared to traditional Portland cement-based concretes. The research results allowed for obtaining a patent [8]. Based on available domestic and international literature sources, a decision was made to conduct research into lightweight concretes formulated by incorporating alkali-activated fly ash, supplemented by the inclusion of alumino-silicate artificial aggregates. It is worth noting that the literature review did not yield any information regarding waste additives in the form of such aggregates. Previous studies exclusively employed natural aggregates, with artificial aggregates taking the form of fibers, chips, sawdust, or foam. The literature analysis unequivocally confirmed that, as of the present date, no research has been undertaken in the field of integrating alumino-silicate artificial aggregates into geopolymer concretes. Based on research conducted by K. Kalinowska-Wichrowska et al. 2022 [31], who proposed a solution to improve the adhesion of geopolymer grout to coarse artificial aggregate with high porosity by impregnating the 4-8 mm fraction of the aggregate with an alkali solution, it was decided to use surface impregnation of coarse aggregate.
A hypothesis was put forward that it is possible to monolithically bind the alkali-activated precursor with artificial lightweight aggregate, which would improve the properties of lightweight concrete and eliminate the need for Portland cement. The aim was to develop a recipe for cement-free composites based on raw waste energy materials activated by alkalis and to investigate their properties.
3. Results
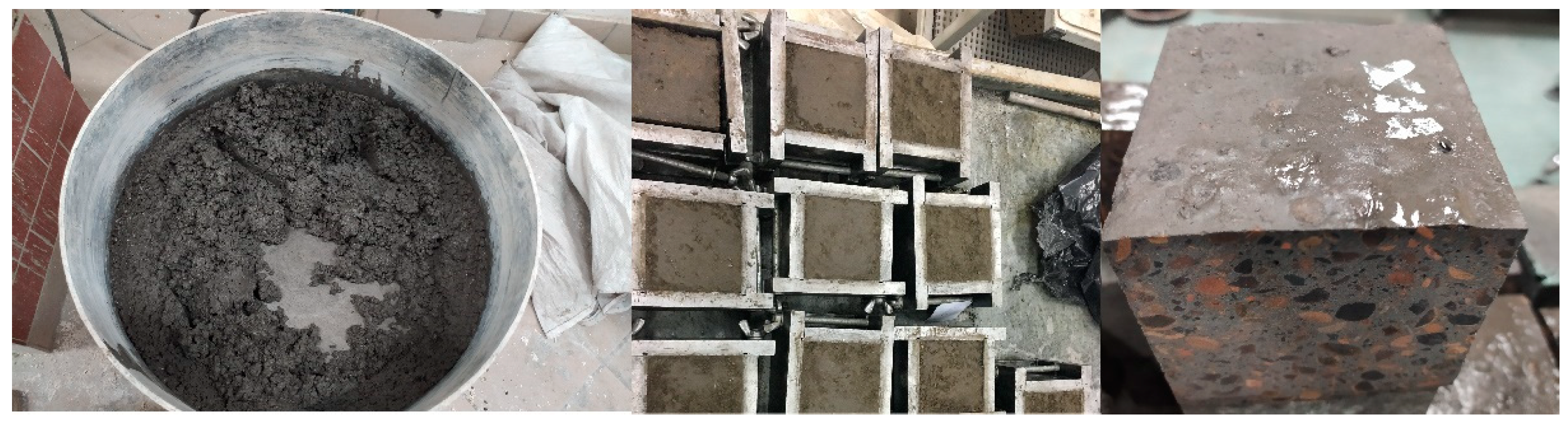
The influence of coarse ash aggregate surface impregnation on the properties of lightweight concrete based on alkali-activated waste materials was investigated.
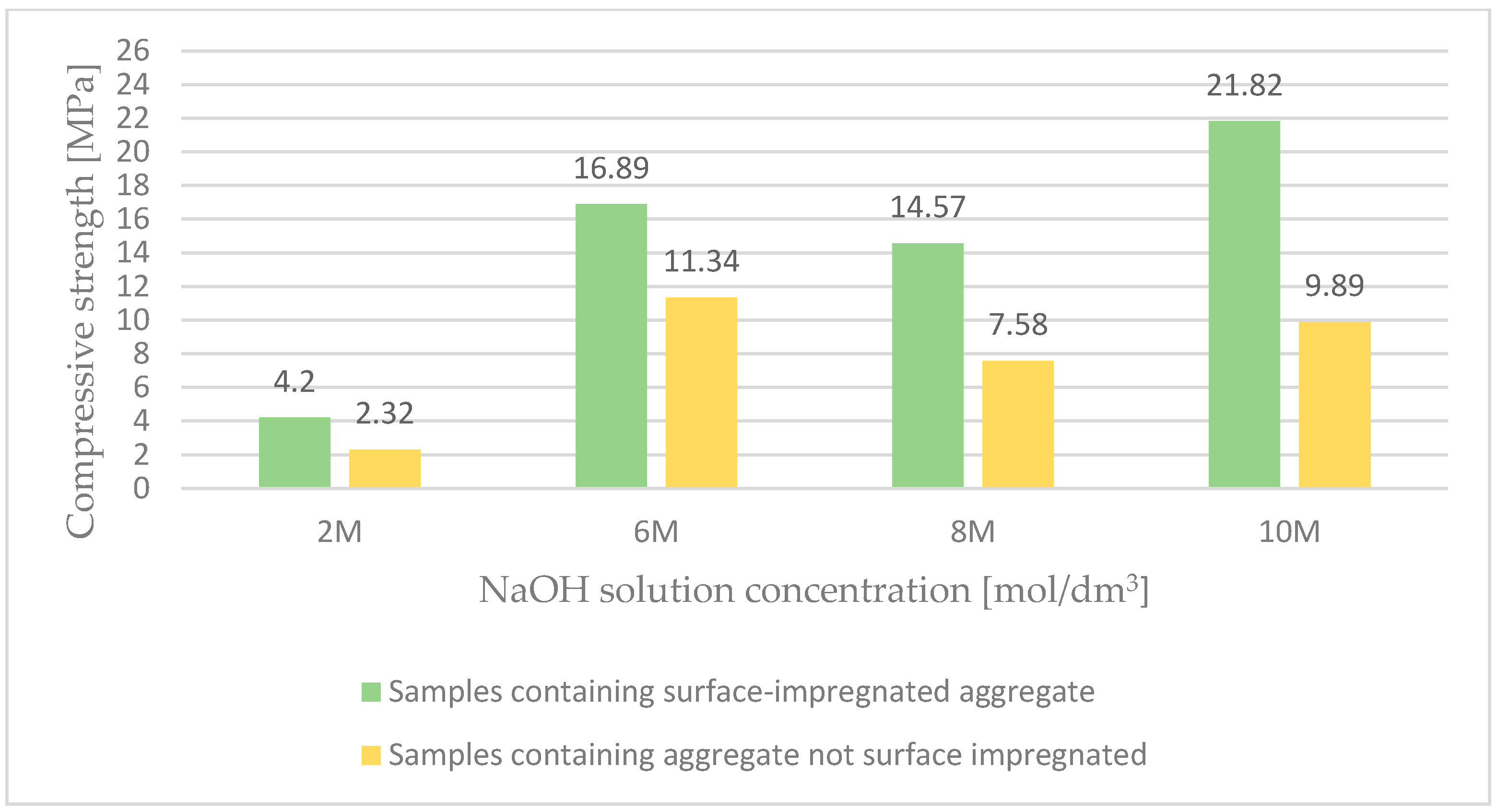
Figure 3 presents the results of the compressive strength of lightweight geopolymer concrete based on surface-impregnated artificial aggregate and fly ash. The analysis of the test results, aimed at examining the effect of the activator concentration on the properties of geopolymer concrete, allowed to conclude that the surface impregnation of coarse aggregate with the activator causes an almost two-fold increase in compressive strength. These premises meant that the main tests were carried out using coarse ash porous aggregate impregnated on the surface. Surface impregnation of the lightweight aggregate allowed to obtain a mixture of appropriate workability and consistency, thus improving the properties of ready-made lightweight geopolymer composites based on waste energy raw materials activated with alkali.
Figure 4.
The results of the compressive strength of lightweight geopolymer concrete based on surface-impregnated Certyd and fly ash.
Figure 4.
The results of the compressive strength of lightweight geopolymer concrete based on surface-impregnated Certyd and fly ash.
The initial analysis focused on the influence of the concentration of NaOH solution, amount of activator, and curing temperature on the compressive strength, water absorption and bulk density of geopolymer composites. One-dimensional significance tests were conducted to obtain average boundary values, which allowed determining the explanatory influence of the indicated variables on strength, water absorption and bulk density.
The results of compressive strength tests of geopolymer lightweight concrete were subjected to preliminary analysis, and basic statistical measures were determined and presented in
Table 7. The differences between strength values from individual stages of preliminary testing were minor; therefore, in the analysis conducted, they were deemed insignificant.
Based on the results presented in
Table 7, it can be concluded that the highest compressive strength was obtained with an NaOH solution of 300 kg/m
3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm
3, and a curing temperature of 105°C. The average compressive strength was 26.92 MPa, with a relatively low variance of 0.312. The variability of the results with these parameters was very low, at approximately 2.07%. The second-best result was obtained with an NaOH solution of 200 kg/m
3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm
3, and a curing temperature of 65°C. In this case, the average compressive strength was 22.86 MPa, with a variance of 0.508. The variability of the results with these parameters was similarly low, at approximately 3.12%. The samples with the lowest compressive strength had an NaOH solution of 100 kg/m
3, a concentration of 2 mol/dm
3, and a curing temperature of 25°C. The average compressive strength was only 0.33 MPa, with a variance of 0.0083. The variability of the results with these parameters was very high, at approximately 27.52%. The coefficient of variation Vi for each sample, which characterizes the relative variation of the observed variable Y, ranged from 2.07% to 27.52%.
After calculating the regression coefficients, the following equation was obtained to describe the relationship between compressive strength and the indicated factors:
The interpretation of the coefficients of the obtained model leads to the conclusion that an increase in the amount of activator by 1 kg/m3 results in an increase in compressive strength of alkali-activated lightweight concrete by 0.04 MPa, while an increase in activator concentration by 1 mol/dm3 leads to an increase in compressive strength by 1.95 MPa. Additionally, an increase in the curing temperature by 1°C also results in an increase in compressive strength of this geopolymer by approximately 0.14 MPa.
The results in
Table 7 indicate that the highest compressive strengths of lightweight concrete made from alkaline-activated waste materials were obtained in series 8. The mean compressive strength was 26.92, and the standard deviation was 0.5586. These results are based on a small random sample of n=5. The results of random samples are the basis for statistical inference, which may include estimating unknown parameter levels (e.g., expected values) in the general population. Of course, their statistical estimation is done under uncertainty, with a declared probability. Point estimation (which is highly dangerous) or interval estimation can be made, which covers the estimated parameter at the declared level of confidence and is much safer. In this study, a Neyman confidence interval was determined for the expected value of the variable being tested, based on the results obtained in series 8, assuming that the estimator of the estimated parameter is the arithmetic mean obtained in this random sample and with a confidence level of α=0.05:
The determined interval is one of those that cover the expected value of the variable being tested at the declared confidence level. Therefore, the result obtained indicates that with 95% confidence, the mean compressive strength of lightweight concrete made from alkaline-activated waste materials (in the general population) is between 26.14 MPa and 27.70 MPa. An essential part of the conducted analysis is to indicate the absolute and relative precision of estimation, which is necessary for this type of research. The absolute precision of estimation allows us to assess how many units we can be wrong by when determining the confidence interval endpoints.
[MPa]
The relative precision of estimation, expressed in percentages, allows us to decide whether the inference can be considered statistically safe.
The relative precision of estimation is lower than 5%, meaning the inference can be considered entirely safe. Importantly, achieving such a favorable result with such a small random sample is particularly satisfying. Increasing the number of units in random samples leads to a significant increase in estimation precision due to the decrease in the range of random endpoints of confidence intervals.
The results of water absorption tests of geopolymer lightweight concrete were subjected to preliminary analysis, and basic statistical measures were determined and presented in
Table 8.
Based on the results in
Table 8, it can be concluded that the lowest water absorption was achieved with an activator amount of 300 kg/m
3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm
3 and a heating temperature of 105°C. The average water absorption of the tested samples was 14.19%, with a very low variance of 0.07%
2. The diversity of results with these parameters was very low, approximately 1.88%. The second favorable result was obtained with an activator amount of 200 kg/m
3, a concentration of 4 mol/dm
3 and a heating temperature of 105°C. The average water absorption in this case was 14.37%, with a variance of 0.01%
2. The diversity of results with these parameters was very low, approximately 0.72%. The highest absorbability was demonstrated by samples with an activator amount of 100 kg/m
3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm
3 and a heating temperature of 25°C. The average, where the water absorption is as much as 21.65%, with a variance of 0.27%
2. The variation in results with these parameters was around 2.41%, which may indicate the reliability of the results obtained in individual samples. The values of the coefficient of variation Vi for each sample, characterizing the measure of the relative variability of the observed value of the Y variable, range from 0.96% to 14.25%.
Model coefficients were calculated using the single least squares method. After calculating the values of the regression coefficients, the following form of the equation describing the dependence of compressive strength on the indicated factors was obtained:
Interpreting the coefficients of the obtained model, it can be concluded that an increase in the amount of activator by 1 kg/m3 causes a decrease in the water absorption of lightweight concretes based on alkaline-activated waste raw materials by approximately 0.01%, while the concentration of the activator increases by 1 mol/dm3 causes an increase in the water absorption of concrete by approx. 0.62%, while an increase in the maturing temperature by 1°C causes a decrease in the water absorption of this geopolymer by approx. 0.05%.
The results in
Table 8 clearly indicate the lowest absorption rates for lightweight concrete based on alkaline-activated waste raw materials in series (8), where the average water absorption is 14.19% and the standard deviation is 0.27%. The results of random sample observations, which constitute the basis for statistical inference, allow, among other things, the estimation of an unknown level of a parameter in the general population. At the declared level of probability, an interval estimate of the expected water absorption of geopolymers was made. The results obtained in series (8) were used as the basis for estimation, assuming that the estimator of the estimated parameter is the arithmetic mean obtained in this random sample, and the confidence level is α = 0.05:
The designated interval is one of those that covers the expected value of the tested variable at the declared confidence level. The obtained result means that, with 95% certainty, the average water absorption of lightweight concretes based on alkaline-activated waste raw materials (in the general population) ranges from 13.82% to 14.56%. The absolute precision of the estimate allows us to assess how many units we can be wrong when determining the ends of the confidence interval.
[%]
The relative precision of the estimation, expressed as a percentage, allows you to assess whether the inference can be considered statistically safe.
The level of relative estimation precision is lower than 5%, which means that inference can be considered completely safe.
The results of bulk density tests of geopolymer lightweight concrete were subjected to preliminary analysis, and basic statistical measures were determined and presented in
Table 9.
Based on the results in
Table 9, it can be concluded that the lowest density was obtained with an activator amount of 100 kg/m
3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm
3 and a heating temperature of 25°C. The average density of the tested samples was 1355.76 g/dm
3, with a variance of 241.5680 g/dm
2. The diversity of results with these parameters was very low approx. 1.15%. The second relatively favorable result was obtained with an activator amount of 100 kg/m3, a concentration of 6 mol/dm3 and a heating temperature of 105°C. Medium density in this case is 1387.60 g/dm
3, with a variance of 94.1400 (g/dm
3)
2. The variation in results with these parameters was very low, approximately 0.7%. The highest density was obtained in samples with an activator amount of 300 kg/m
3, a concentration of 2 mol/dm
3 and a heating temperature of 105°C. The average bulk density was obtained as high as 1756.68 g/dm
3, with a variance of 334.8920 (g/dm
3)
2. The variation in results with these parameters was not high and was approximately 1.0417%, which may indicate the reliability of the results obtained in individual samples. The values of the coefficient of variation Vi for each sample, characterizing the measure of the relative variability of the observed value of the variable Y, are ranges from 0.7% to 5.4%.
The regression function determined by a single least squares method, describing the dependence of bulk density on the amount of activator, its concentration and annealing temperature, takes the form:
The interpretation of the coefficients of the obtained model leads to the conclusion that an increase in the amount of activator by 1 kg/m3 causes an increase in the bulk density of lightweight concretes based on alkaline-activated waste raw materials by approximately 0.078 g/dm3, while an increase in the activator concentration by 1 mol/dm3 causes a decrease in density concrete by approx. 23.71 g/dm3. However, an increase in the ripening temperature by every 1°C results in an increase in the density of this geopolymer by approximately 2.245 g/dm3.
The results of random sample observations, which constitute the basis for statistical inference, allow, among other things, the estimation of an unknown level of a parameter in the general population. At the declared level of probability, an interval estimate of the expected value of the bulk density of geopolymers was made. The results obtained in series (5) were used as the basis for estimation, assuming that the estimator of the estimated parameter is the arithmetic mean obtained in this random sample, and the confidence level is α = 0.05:
The designated interval is one of those that covers the expected value of the tested variable at the declared confidence level. The obtained result means that, with 95% certainty, the average density of lightweight concretes based on alkaline-activated waste raw materials (in the general population) ranges from 1334.19 g/dm3 to 1377.33 g/dm3.
The absolute precision of estimation indicates that when determining the ends of the confidence interval, we may be wrong by [g/dm3]. In turn, the relative precision of estimation equal to allows us to assess whether such inferences can be considered statistically safe.
Lightweight concrete samples based on the fly ash in an amount of 600 kg/m
3, alumino-silicate artificial aggregate activated by a 6 mol/dm
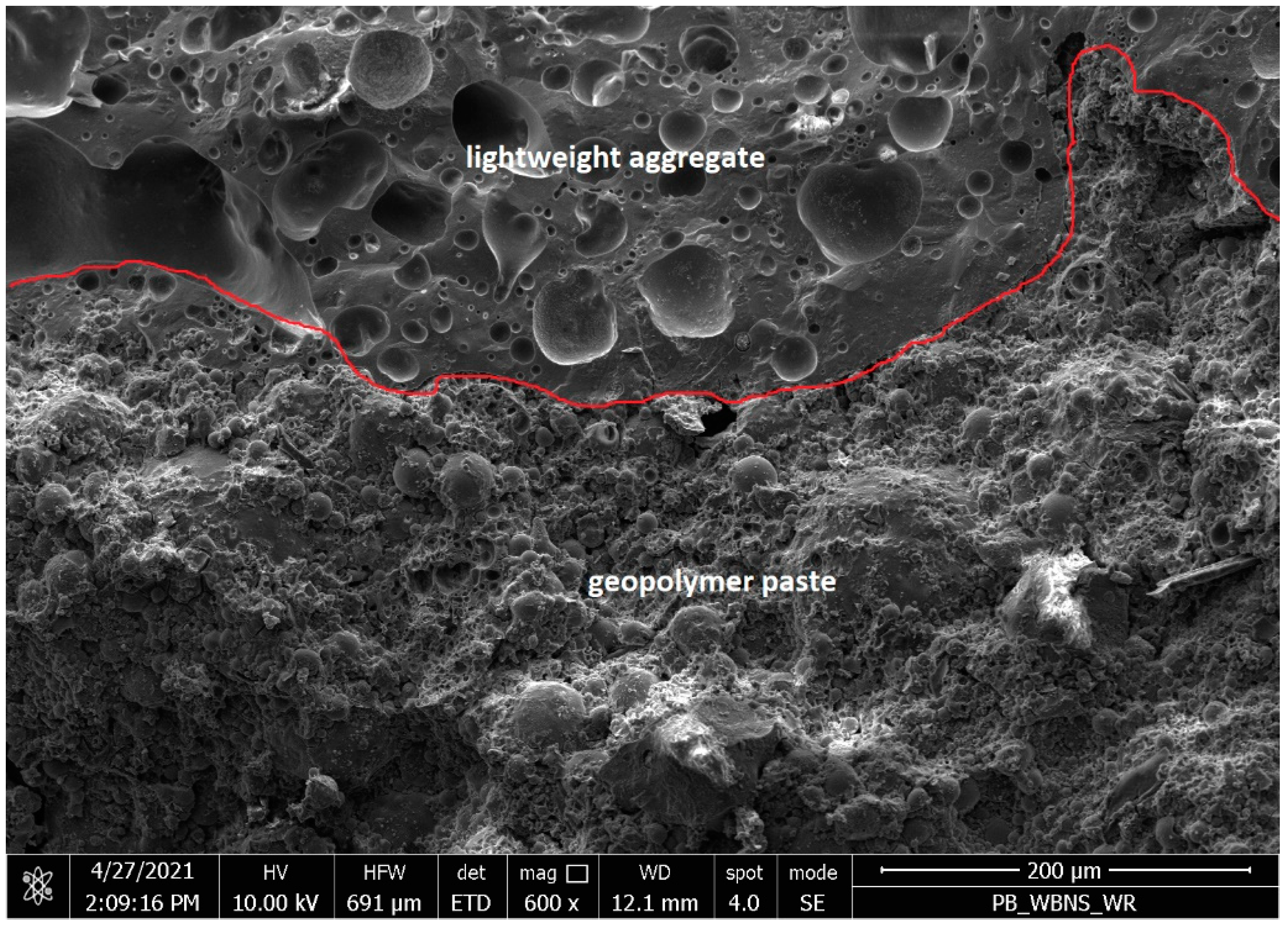
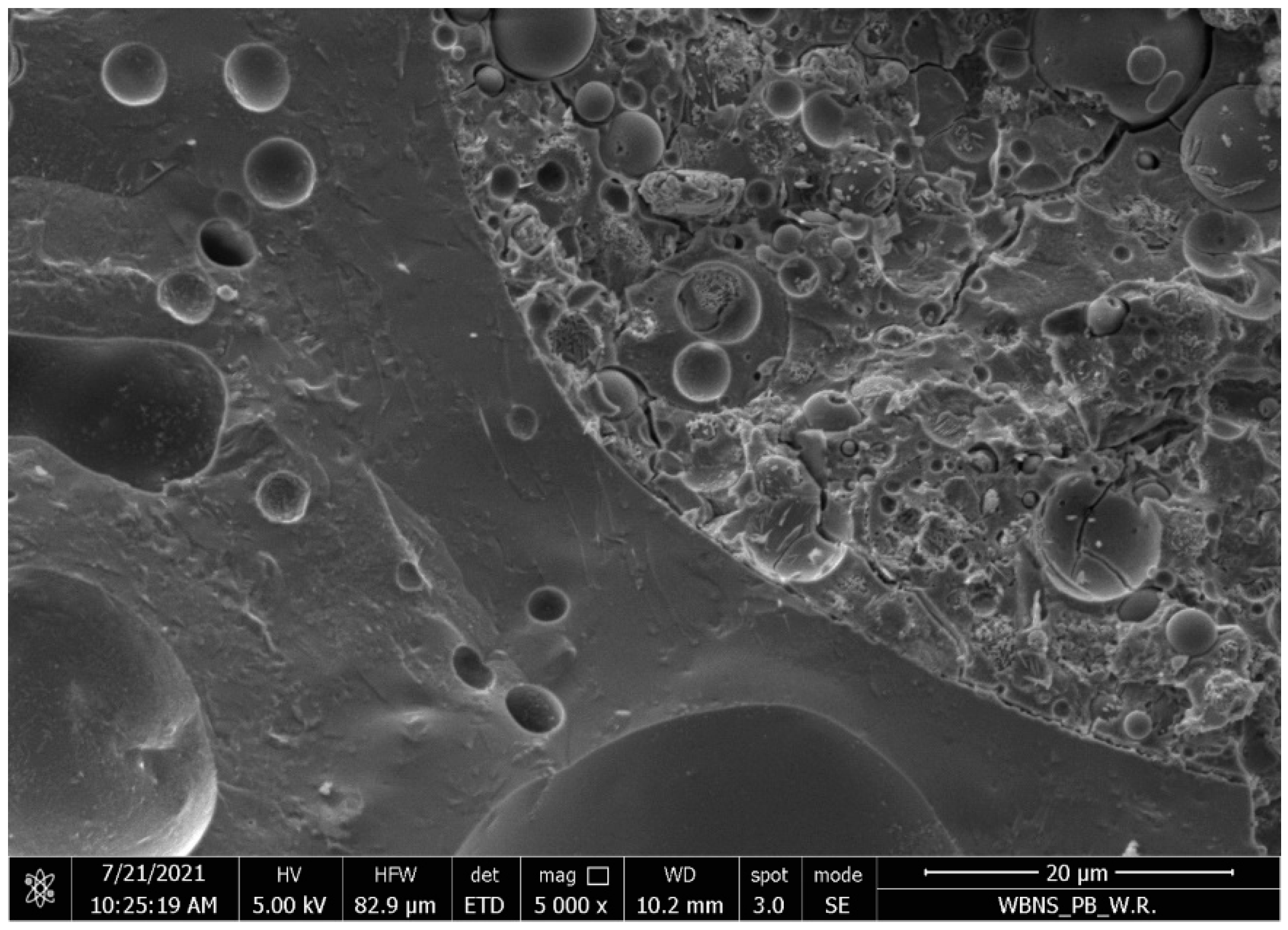
3 alkali solution, and ripened at a temperature of 105°C were also examined under a scanning electron microscope and showed a fine-grained structure with a small amount of micro and macro cracks, as shown in
Figure 6 . The Interfacial Tranzition Zone between the GP and the aggregate was determined to be very good. The majority of the fly ash has reacted. Figure 7 shows samples produced with sodium hydroxide instead of an alkaline solution.
Figure 5.
Samples of lightweight concrete based on fly ash, activated alkaline alumino-silicate artificial aggregate, of approximately mag 600 x with the contact zone between the lightweight aggregate and the geopolymer paste marked in red.
Figure 5.
Samples of lightweight concrete based on fly ash, activated alkaline alumino-silicate artificial aggregate, of approximately mag 600 x with the contact zone between the lightweight aggregate and the geopolymer paste marked in red.
The best microstructure was obtained by lightweight geopolymer concretes containing 400-600 kg/m3 of the fly ash, corresponding to 200-300 kg/m3 of an alkali solution with a concentration of 4mol/dm3 and a maturation temperature of 105°C. Then we obtain a monolithic combination of polycondensation products with coarse aggregate, with a small number of pores, where a significant amount of fly ash particles undergo polymerization, creating a fine-grained structure of silica and aluminum oxide copolymers and stabilizing metal cations, mainly sodium and calcium, and bound water.
Table 10.
Results of semi-quantitative compositional analyses of sample (8).
Table 10.
Results of semi-quantitative compositional analyses of sample (8).
| Area |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
| Distance from the edge of the aggregate [μm] |
0-80 |
80-160 |
160-240 |
240-320 |
320-400 |
400-480 |
480-560 |
560-640 |
640-720 |
720-800 |
| |
Concentration [% of mass] |
| C |
60,86 |
58,65 |
57,16 |
57,96 |
61,43 |
67,01 |
64,76 |
64,20 |
67,42 |
64,36 |
| Si |
19,99 |
21,99 |
23,08 |
22,60 |
20,82 |
17,96 |
18,56 |
18,97 |
16,82 |
18,68 |
| Al |
7,51 |
8,63 |
9,13 |
9,07 |
8,30 |
7,24 |
7,74 |
7,64 |
7,13 |
7,79 |
| Na |
5,34 |
5,15 |
4,87 |
4,79 |
4,21 |
3,80 |
3,61 |
3,84 |
3,63 |
4,38 |
| Fe |
3,92 |
3,16 |
3,28 |
3,43 |
3,03 |
2,25 |
3,02 |
3,22 |
2,94 |
3,13 |
| Ca |
2,38 |
2,41 |
2,48 |
2,15 |
2,20 |
1,74 |
2,31 |
2,13 |
2,06 |
1,66 |
The analysis of the results of semi-quantitative tests of the composition of the areas of the aggregate-geopolymer grout contact zone in sample of series (8), which was made by the Institute of Construction Technology, showed:
higher overall porosity of the tested sample based on the higher concentration of carbon that comes from the resin filling the air pores;
locally, in the contact zone (0 - 80 μm from the edge of the aggregate) of the tested sample, the pore content was higher;
increased concentration of sodium ions in the area of the contact zone (0 - 80 μm from the edge of the aggregate) of the tested sample compared to greater distances from the aggregate boundary;
in the tested sample, the maximum concentration of silicon and aluminum ions in zone 3 (160 – 240 μm from the edge of the aggregate).