1. Introduction
HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus, targets the body's immune system, particularly CD4 cells crucial for fighting infections, leading to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), the advanced stage of HIV infection [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
Transmission occurs through specific bodily fluids like blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. Unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles contaminated with HIV-infected blood, and mother-to-child transmission during childbirth or breastfeeding are common modes.
Once inside the body, HIV infects CD4 cells, using them to replicate and generate more virus. Continuous replication results in a decline in CD4 cell count, weakening the immune system and making the body susceptible to infections and diseases [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
While HIV has no cure, effective management is possible with antiretroviral therapy (ART), a combination of medications suppressing virus replication, reducing viral load, and slowing disease progression. With proper treatment and medical care, individuals with HIV can lead long and healthy lives [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
The HIV genome's sequence can differ among viral isolates because of mutations and genetic diversity. This variability is a key factor in HIV's ability to evade the immune system and develop resistance to antiretroviral drugs. Scientists employ genetic sequencing methods to investigate HIV's genetic diversity and devise approaches for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention [
6,
7,
8].
This work focused on The HIV-1 protease using Molecular Docking methods [
9] throigh SWISS DOCK Server (SwissDock - The online docking web server of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics - Home) [
10].
This viral protease is crucial for cleaving large precursor proteins, called viral polyproteins, into smaller functional proteins necessary for viral maturation and infectivity.
The precise cleavage of these precursor proteins at specific sites by HIV-1 protease is essential for generating structural and functional proteins vital for the assembly of new viral particles. Without the activity of HIV-1 protease, the virus fails to mature properly, leading to significant impairment of its replication [
11,
12,
13].
Given its central role in the viral life cycle, HIV-1 protease has become a prime target for the development of antiretroviral drugs. Protease inhibitors, a class of antiretroviral drugs, specifically target HIV-1 protease, disrupting its proper functioning. By inhibiting the activity of HIV-1 protease, these drugs effectively suppress viral replication, contributing to the management of HIV infection, especially when used in combination therapy [
11,
12,
13].
2. Material and Methods
- -
Structure of Crystal Structure HIV-1virus protease was taken from SWISSDOCK Server (PDB Code:1b6l). Docking investigation was performed automatically by Blind Docking method.
- -
Structure of Crystal Structure Rous sarcoma virus protease was taken from SWISSDOCK Server (PDB Code:1bai). Docking investigation was performed automatically by Blind Docking method.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study, the SWISS DOCK Server [
10] conducted an investigation on several natural compounds targeting HIV-1 protease, a key enzyme in the replication cycle of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). This viral protease is crucial for cleaving large precursor proteins, called viral polyproteins, into smaller functional proteins necessary for viral maturation and infectivity.
The precise cleavage of these precursor proteins at specific sites by HIV-1 protease is essential for generating structural and functional proteins vital for the assembly of new viral particles. Without the activity of HIV-1 protease, the virus fails to mature properly, leading to significant impairment of its replication.
Given its central role in the viral life cycle, HIV-1 protease has become a prime target for the development of antiretroviral drugs. Protease inhibitors, a class of antiretroviral drugs, specifically target HIV-1 protease, disrupting its proper functioning. By inhibiting the activity of HIV-1 protease, these drugs effectively suppress viral replication, contributing to the management of HIV infection, especially when used in combination therapy.
Docking results revealed that Amentoflavone demonstrated excellent binding affinity, with a high estimated ΔG (-10.1 kcal/mol), indicating its potential as an inhibitor of HIV-1 protease. Additionally, Amentoflavone was assessed against Roussarcoma virus protease, exhibiting a similarly high estimated Δ G (-9.93 kcal/mol). These findings are promising, suggesting that this natural compound could serve as a potential candidate against HIV.
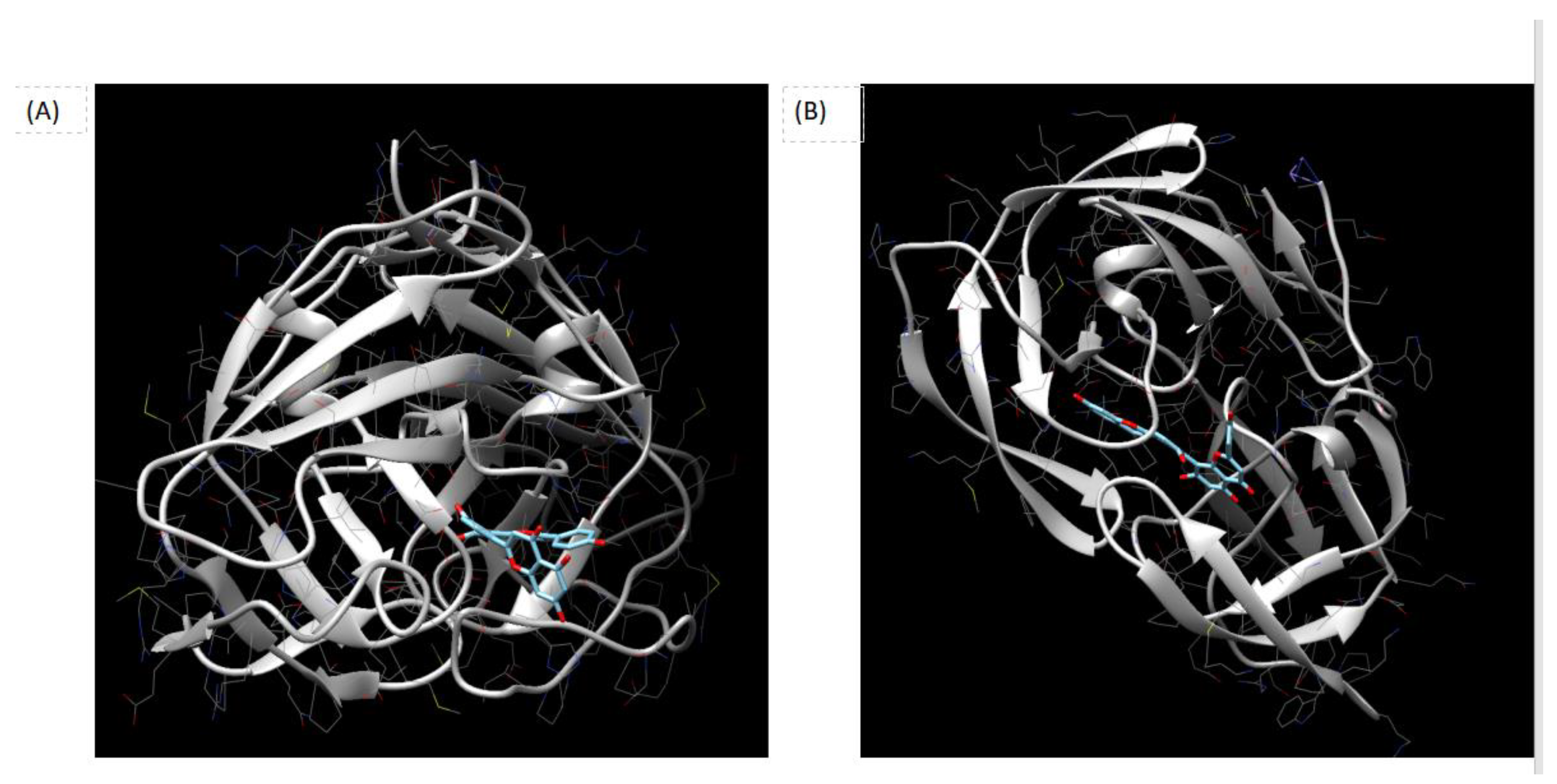
Figure 1 is showed the Docking outcomes of the potential Ligand Binding Site of Amentoflavone in the crystal structures of Rous Sarcoma Virus Protease (RSV Protease) and HIV-1 Protease. Indeed, Panel (A) reportes Crystal structure of Rous Sarcoma Virus Protease (RSV Protease). The potential ligand binding site of Amentoflavone is highlighted in blue. Amentoflavone is docked within the binding site and is represented as a blue-colored molecule. Panel (B) shows Crystal structure of HIV-1 Protease. Similarly, the potential ligand binding site of Amentoflavone is highlighted in blue, and Amentoflavone is docked within this site, shown as a blue-colored molecule. The figure was reproduced using the Chimera program, a molecular visualization software commonly used for analyzing protein structures and ligand interactions.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, this study highlights the potential of natural compounds, particularly Amentoflavone, as inhibitors of HIV-1 protease. The docking results, obtained using the SWISS DOCK Server, demonstrated excellent binding affinity of Amentoflavone with HIV-1 protease, suggesting its potential as an effective inhibitor. Furthermore, Amentoflavone exhibited similar promising results when tested against Roussarcoma virus protease, indicating its broad-spectrum inhibitory activity against viral proteases.
These findings underscore the importance of exploring natural compounds as potential therapeutic agents against HIV and other viral infections. Amentoflavone, in particular, shows promise as a natural compound with inhibitory activity against HIV-1 protease, which is crucial for viral replication and infectivity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Christopoulos, K. A., Grochowski, J., Mayorga-Munoz, F., Hickey, M. D., Imbert, E., Szumowski, J. D., ... & Gandhi, M. (2023). First demonstration project of long-acting injectable antiretroviral therapy for persons with and without detectable human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) viremia in an urban HIV clinic. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 76(3), e645-e651. [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J., Mirani, G., & Levison, J. (2023). Providers Have a Responsibility to Discuss Options for Infant Feeding With Pregnant People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus in High-Income Countries. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 76(3), 535-539. [CrossRef]
- Schochetman, G., Subbarao, S., & Kalish, M. L. (2023). Methods for studying genetic variation of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In Viral genome methods (pp. 25-41). CRC Press.
- Schochetman, G., Subbarao, S., & Kalish, M. L. (2023). Methods for studying genetic variation of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). In Viral genome methods (pp. 25-41). CRC Press.
- Perez-Molina, J. A., Crespillo-Andújar, C., Zamora, J., Fernández-Félix, B. M., Gaetano-Gil, A., López-Bernaldo de Quirós, J. C., ... & Berenguer, J. (2023). Contribution of Low CD4 Cell Counts and High Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Viral Load to the Efficacy of Preferred First-Line Antiretroviral Regimens for Treating HIV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 76(11), 2027-2037. [CrossRef]
- Sun, W., Gao, C., Hartana, C. A., Osborn, M. R., Einkauf, K. B., Lian, X., ... & Lichterfeld, M. (2023). Phenotypic signatures of immune selection in HIV-1 reservoir cells. Nature, 614(7947), 309-317. [CrossRef]
- Dufour, C., Ruiz, M. J., Pagliuzza, A., Richard, C., Shahid, A., Fromentin, R., ... & Chomont, N. (2023). Near full-length HIV sequencing in multiple tissues collected postmortem reveals shared clonal expansions across distinct reservoirs during ART. Cell reports, 42(9). [CrossRef]
- Ndashimye, E., Reyes, P. S., & Arts, E. J. (2023). New antiretroviral inhibitors and HIV-1 drug resistance: more focus on 90% HIV-1 isolates?. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 47(1), fuac040. [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, M. T., & Aki-Yalcin, E. (2024). Molecular docking: principles, advances, and its applications in drug discovery. Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 21(3), 480-495. [CrossRef]
- Baysal, Ö., Genç, D., Silme, R. S., Kırboğa, K. K., Çoban, D., Ghafoor, N., ... & Bulut, O. (2023). Targeting Breast Cancer with N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine: Integrating Machine Learning and Cellular Assays for Promising Results. Available at SSRN 4476817.
- Singh, G., Satija, P., Sharma, S., Gupta, S., & Singh, K. N. (2023). Organosilane as potent HIV-1 protease inhibitors and its hybrid silica nanoparticles as a “turn-off” fluorescent sensor for silver ion recognition. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 545, 121263. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A. K., Shahabi, D., Kipfmiller, M., Ghosh, A. K., Johnson, M., Wang, Y. F., ... & Mitsuya, H. (2023). Evaluation of darunavir-derived HIV-1 protease inhibitors incorporating P2′ amide-derivatives: Synthesis, biological evaluation and structural studies. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 83, 129168. [CrossRef]
- Lockbaum, G. J., Rusere, L. N., Henes, M., Kosovrasti, K., Rao, D. N., Spielvogel, E., ... & Ali, A. (2023). HIV-1 protease inhibitors with a P1 phosphonate modification maintain potency against drug-resistant variants by increased interactions with flap residues. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 257, 115501. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).