1. Introduction
HER2, a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family, plays a crucial role in regulating cell growth and division. Its significance spans across various cancers, with its overexpression often associated with increased tumor aggressiveness. Particularly, HER2 overexpression is frequently observed in specific subtypes of breast cancer [
1,
3].
Breast cancer remains a primary focus of medical research, with continuous efforts directed towards gaining a deeper understanding of its molecular mechanisms, developing targeted therapies, and enhancing patient outcomes. Vigilance, early detection, and comprehensive treatment approaches are pivotal in the battle against breast cancer [
4,
5]
Breast cancer originates from the cells within the breast and represents a complex and heterogeneous disease. It predominantly affects women, beginning typically in the milk-producing glands (lobules) or the ducts responsible for transporting milk from the glands to the nipple. As breast cancer advances, malignant cells have the potential to invade surrounding healthy breast tissue and, in later stages, may spread to distant areas of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.[
6,
7,
8].
The ongoing communication revolves around an extensive investigation facilitated by docking simulations and virtual screening analysis using Autodock Vina. This research delves into the evaluation of numerous natural compounds and drugs and their interactions with the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The objective is to uncover potential binding affinities and molecular interactions, offering insights into the therapeutic possibilities of these compounds concerning HER2, a protein linked to various cancers. The outcomes of this docking simulation and virtual screening analysis hold promise in advancing the exploration of new compounds targeting HER2 for potential therapeutic use [
9,
10].
2. Material and Methods
- Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 was taken from Protein Data Bank (PDB Code:3MZW). Docking investigation was performed by Blind Docking methid by Autodock Vina with Pyrx program, using: Grid box Coordinates of binding Center X ( 31.4377), Y(-40.9558), Z(-6.8609); size_x = 60.4919291639; size_y = 73.9613495255; size_z = 105.705898209.
3. Results and Discussion
Breast cancer originates in the cells of the breast and presents as a complex and diverse ailment. Primarily affecting women, it commonly starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules) or the ducts responsible for carrying milk from the glands to the nipple. As breast cancer progresses, malignant cells can infiltrate nearby healthy breast tissue and, in advanced stages, may metastasize to distant parts of the body via the bloodstream or lymphatic system [
4,
5,
6].
In recent years, there has been increasing focus on identifying new compounds that target human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), a key player in breast cancer progression. This study, based on docking simulation and virtual screening analysis to explore the potential of various compounds in targeting HER2 [
1,
2,
3].
This communication focuses on an extensive investigation utilizing docking simulations and virtual screening analysis with Autodock Vina [
9,
10].
The primary objective is to discern potential binding affinities and molecular interactions, shedding light on the therapeutic potential of these compounds in relation to HER2, a protein associated with multiple cancers. The outcomes of this docking simulation and virtual screening analysis hold the potential to offer valuable insights, contributing to the ongoing exploration of novel compounds targeting HER2 for potential therapeutic applications [
9,
10].
The findings from this docking simulation and virtual screening analysis significantly contribute to the continuous exploration of novel compounds aimed at targeting HER2 for potential therapeutic applications. Specifically, according to the results obtained through Autodock Vina, Acebilustat, Bemcentinib, and Amentoflavone have demonstrated remarkable binding energies, averaging around -10 kcal/mol, when interacting with the HER2 target.
These promising results not only highlight the potential biological role of these compounds but also suggest their potential utility in combating breast cancer.
Table 1.
Comparison of best binding energies scores (kcal/mol) of natural compounds and drugs in complex with Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2, evaluated by Blind Docking method with Pyrx program.
Table 1.
Comparison of best binding energies scores (kcal/mol) of natural compounds and drugs in complex with Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2, evaluated by Blind Docking method with Pyrx program.
| Compounds |
Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| Acebilustat |
-9.6 |
| Amentoflavone |
-9.9 |
| Bemcentinib |
-10.4 |
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked Acebilustat -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Acebilustat. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Acebilustat.
Figure 1.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked Acebilustat -9.6 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Acebilustat. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Acebilustat.
Figure 2.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked amentoflavone -9.9 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and amentoflavone. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of amentoflavone.
Figure 2.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked amentoflavone -9.9 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and amentoflavone. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of amentoflavone.
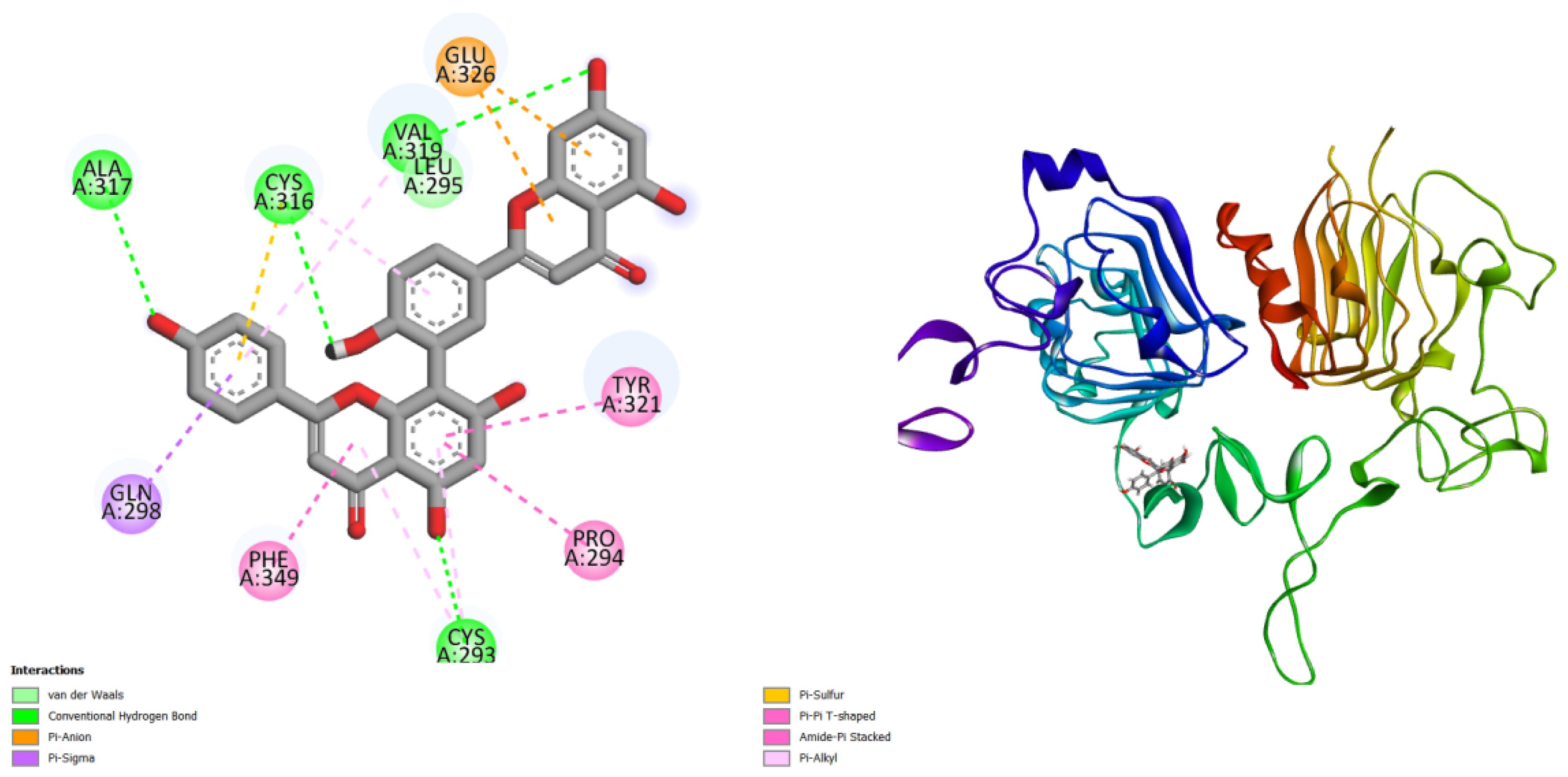
Figure 3.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked Bemcentinib -10.4 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Bemcentinib. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Bemcentinib.
Figure 3.
displays the docking outcomes of Structure of Crystal Human Tyrosine kinase-type cell surface receptor HER2 in conjunction with docked Bemcentinib -10.4 kcal mol, within the Ligand Binding Site, as analyzed by Autodock Vina with pyrx program. On the left side, 2D diagrams illustrate the residue interactions between the protein and Bemcentinib. Meanwhile, the right side exhibits the Ligand Binding Site of the protein, highlighting the specific location of Bemcentinib.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the docking simulation and virtual screening analysis conducted in this study have provided valuable insights into potential therapeutic candidates for breast cancer targeting the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). The compounds Acebilustat, Bemcentinib, and Amentoflavone exhibited exceptional binding energies of approximately -10 kcal/mol with HER2, suggesting robust interactions. These findings hold significant promise for the development of novel therapeutic strategies against breast cancer, leveraging the identified compounds’ strong affinities for HER2. The results contribute to the ongoing exploration of effective treatments, particularly in the context of HER2-positive breast cancer.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wolff, A. C., Somerfield, M. R., Dowsett, M., Hammond, M. E. H., Hayes, D. F., McShane, L. M., Allison, K. H. (2023). Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: ASCO–College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 41(22), 3867-3872. [CrossRef]
- Huppert, L. A., Gumusay, O., Idossa, D., & Rugo, H. S. (2023). Systemic therapy for hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative early stage and metastatic breast cancer. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C. J., Hainsworth, J. D., Bose, R., Burris, H. A., Kurzrock, R., Swanton, C., ... & Meric-Bernstam, F. (2024). MyPathway human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 basket study: Pertuzumab+ trastuzumab treatment of a tissue-agnostic cohort of patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-altered advanced solid tumors. [CrossRef]
- Ye, F., Dewanjee, S., Li, Y., Jha, N. K., Chen, Z. S., Kumar, A., & Tang, H. (2023). Advancements in clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast cancer. Molecular cancer, 22(1), 105. [CrossRef]
- Nolan, E., Lindeman, G. J., & Visvader, J. E. (2023). Deciphering breast cancer: from biology to the clinic. Cell. [CrossRef]
- Falato, C., Schettini, F., Pascual, T., Brasó-Maristany, F., & Prat, A. (2023). Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes in hormone receptor-positive and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 112, 102496. [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F., Deluche, E., Lusque, A., Le Bescond, L., Filleron, T., Pradat, Y., ... & André, F. (2023). Trastuzumab deruxtecan in metastatic breast cancer with variable HER2 expression: the phase 2 DAISY trial. Nature medicine, 29(8), 2110-2120. [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F., Deluche, E., Lusque, A., Le Bescond, L., Filleron, T., Pradat, Y., ... & André, F. (2023). Trastuzumab deruxtecan in metastatic breast cancer with variable HER2 expression: the phase 2 DAISY trial. Nature medicine, 29(8), 2110-2120. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X., Ling, M., Lin, Q., Tang, S., Wu, J., & Hu, H. (2023). Effectiveness Analysis of Multiple Initial States Simulated Annealing Algorithm, A Case Study on the Molecular Docking Tool AutoDock Vina. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. [CrossRef]
- Ding, J., Tang, S., Mei, Z., Wang, L., Huang, Q., Hu, H.,& Wu, J. (2023). Vina-GPU 2.0: Further Accelerating AutoDock Vina and Its Derivatives with Graphics Processing Units. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 63(7), 1982-1998. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).