1. Introduction
The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 is the aetiologic agent of COVID-19, a pandemic disease, which started in China at end of 2019, spread worldwide and caused, as of last December, nearly two billions of infections and seven millions deaths, mostly in elderly subjects with one or more comorbidities [
1]. At least as many deaths as above have been avoided using highly effective, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, which have been generated at an unprecedented speed, though unequally distributed and worldwide available. The construction of most of these vaccines has been based on the Spike (S) constituent of the virus, or its coding DNA or RNA sequences. The S protein is an immunodominant antigen constituted by a trimeric glycoprotein, each monomeric unit of which has two subunits: S1 and S2 mediating binding of the virus to host cell surface (S1) and fusing with cell membrane (S2) [
2].
The S protein plays an essential role in infection and disease. It allows the virus entering the cells and binding the human receptor ACE2, a critical component of blood pressure homeostasis. There is ample evidence that inflammation concurs with virus reproduction in the pathogenesis of the disease, particularly its severe form such as the CRS (cytokine release syndrome). Coherently, it has been shown that inflammation control by pharmacological or immunological interventions greatly benefits the infected patients [
3,
4]. Multiple virus constituents can potentially induce inflammatory response and there is some evidence about the role of the S protein itself as inflammation inducer [
5,
6,
7]. However, mechanisms and molecular determinants of inflammation caused by this glycoprotein are still poorly known.
The saccharide constituent of glycoproteins activates and modulates adaptive and innate responses by interacting with C-type lectin receptors expressed on both lymphocytes and phagocytic or antigen-presenting cells [
8]. The Sars-Cov-2 S protein is extensively decorated by various types of glycans, that appear to be substantially conserved even in distant SARS-CoV-2 variants [
9]. Actually, there are 22 N-glycan sites present on each monomeric S protein subunit and bearing N-glycans of different composition [
9,
10]. It has been reported that circulating mannose-binding lectin (MBL), a collectin acting as pattern recognition in the first line of defense in the pre-immune host, specifically interacts with the active trimer of SARS-CoV-2 S protein through the carbohydrate region domain [
11]. MBL-interaction with S protein activates complement through the lectin pathway, that was considered to be relevant in controlling Covid-19 disease. An association between MBL2 haplotypes or biallelic variants and COVID-19 severity in human patient has been reported [
11].
Considering the number and complexity of receptor/ligand systems whose interactions depends on the glycan moieties and their relevance in anti-pathogen immunity [
8,
12,
13], the biological significance of glycan moieties decorating the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 is an attractive topic for research aimed to ascertain the role of N-glycans in protection from, and/or pathology of, COVID-19.
Along this line of research, we have investigated the immune-modifying properties of two recombinant preparations of the S protein, generated in human Hek293 cells (S-hu) or insect cells (S-in). We focused on S protein capacity of modulating the production of two COVID-19-relevant, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) [
14,
15] in both primary and secondary immune responses, including those to polyclonal, mitogenic activators. To this aim, we used peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy donors whose blood was collected in the pre-pandemic era in order to avoid possible interference of immunity to S protein due to infection or vaccination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sars-Cov-2 S Proteins
Recombinant Sar-Cov-2 S proteins were purchased by SinoBiological, Beijing, China: (S1+S2) produced in baculovirus-insect cells cod. 40589-V08B1 1209 AA MW 134,36 KDa, EC50 binding to ACE2 > 400-1200 ng/ml; (S1+S2) produced in human HEK293 cells cod. 40589-V08H4 1248 AA MW 138,5 KDa EC50 binding to ACE2 > 10-50 ng/ml; S1 produced in human HEK293 cells cod. 40589-V08H 681AA MW 76,5 KDa EC50 binding to ACE2 > 200-600 ng/ml; and S2 produced in human HEK293 cells cod. 40589-V08H1 511 AA MW 56,3 KDa No EC50 binding to ACE2.
2.2. Binding Assay of S Proteins to Concanavalin A
Binding of S proteins to Concanavalin A (Con A) was measured by an in-house ELISA assay. Briefly, polystyrene 96-well plates (Maxisorp, Nunc, USA) were coated and incubated overnight at 4 °C with 100 μl/well of 0.75 μg/ml of S-in, S-hu, and S1 and S2 subunits in PBS. Coated plates were then washed 4 times with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (PBS-T). Plates were blocked for 1 h at 37 °C with 3% BSA (SIGMA, Italy) in PBS-T. After BSA solution removing, in a first set of experiments, the wells of plates coated with S-in- were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with 0.0125 μg/ml of HRP-conjugated Con A (Sigma L-6397) in PBS-T containing 3% BSA, alone or in combination with scalar concentrations of Mannan (S. cerevisiae, Sigma M3640); Destran 1000 (Fluca 31416); Alfa-methyl-mannoside (SIGMA M6882); N-acetil-glucosamine (SIGMA REF. A8625). Con A and oligosaccharides were simultaneously added to the plates. In a second set of experiments, wells of plates coated with S-in, S-hu, S1 or S2 (each at 0.75 μg/ml) were incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with 0.025 ug/ml of HRP-conjugated Con A in PBS-T containing 3% BSA, alone or in combination with 50 μg/ml Mannan added simultaneously to the plates. The plates were then washed 3 times and incubated with TMB-ELISA (Thermoscientific 34028) for 30 min at RT. Color development was stopped with 2 M H2SO4. The binding of Con A to S proteins was revealed by measuring absorbance at 450 nm in a spectrophotometer (MULTISKAN FC, MICROPLATE READER REF. 51119000, Thermo Scientific). Data were presented as the mean of optical density (OD) corrected for background (wells without coated antigen).
2.3. Human PBMC and Cell Cultures
Human studies were performed in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. PBMC were isolated from buffy coat of healthy individuals attending the transfusion center of the Bloodbank of the University “La Sapienza”, Rome, Italy in the years 2016-2017, using density centrifugation. Cells were resuspended in foetal bovine serum (FBS) (Euroclone) containing 10% dimethylsufoxide (SIGMA) and aliquoted at a concentration approximatively of 10-20 x 106 cells per cryovial, frozen overnight at -80°C and transferred to liquid nitrogen storage the following day. Cryopreserved PBMC were thawed in a water bath at 37°C, washed in warmed PBS resuspended at an approximate concentration of 2-3 x 106 cells per ml of RPMI-1640 (Sigma life science) containing 10% heat-inactivated human AB serum, 2mM l-glutamine 10 mM HEPES buffer and 50 U/ml penicillin and 50 μg/ml streptomycin, (complete RPMI-medium) added with 2μl/ml of 25U benzonase (Sigma-Aldrich E1014) (final concentration 50U/ml). Cells were rested at 37°C for 2 hours with 5% CO2 washed and then cultured. After counting, PBMC were cultured at a density 2x106 cells/ml in 96-well plates (final volume 250 µl) or in 48-well plates (0,8-1 ml) in complete RPMI-1640-medium and treated for 72h with the following stimulus: ConA (Sigma-Aldrich C-0412) at 4 µg /ml; agonist anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (clone UCHT1, Invitrogen Life Technologies) at 0.8 µg/ml; full-length non-glycosylated recombinant protein portion of cell surface mannoprotein MP65 (MP65) from Candida abicans (GenScript. Piscataway, NJ) at 1 µg/ml. All stimulations were performed alone or in combination with S-insect (S-in), S-human HEK923 (S-hu) and S1 and S2 Subunits at 5 µg/ml and mannan from Saccharomyces cerevisiae at 10 µg/ml. In some cultures, combination of mannan with S proteins in the presence or absence of anti-CD3 mAb were also performed. At the end of cultures, supernantants were collected and spun free from cell and debries to detect cytokine production, cells were in some experiments used to assay vitality by XTT assay, CD4 and CD8 T cell proliferation by CFSE assay and expression of mannose Receptor on macrophages by flow cytometry
2.4. IFN-γ and IL-6 Quantification
Cytokines were detected in supernatants of cultured PMBC by quantitative sandwich ELISA specific for IFN-γ, or IL-6 (human Quantikine, R&D System, Inc. Minneapolis, MN, USA), in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions. Quantifications were all calculated using a standard curve obtained for each cytokine standard provided by manufacturer.
2.5. In Vitro Toxicology Assay XTT Based
For XTT assay, PBMC were cultured in complete RPMI medium using an RPMI-1640 without phenol red (Gibco) in 96 well plates, as described above. After 96 h of culture, 50 ul of medium were removed and substituted with fresh RPMI without phenol red containing XTT 1mg/ml (Sigma, In vitro toxicology assay kit XTT based, TOX-2) to reach an amount equal 20% of the culture medium volume. Cells were incubated for further 6 hours before measuring absorbance at a wavelength of 450 nm.
2.6. CFSE Assay
PBMC (107 cells/ml) were stained with CFSE (Invitrogen Life Technologies) at 1 μM in PBS 1%FBS for 10 min at 37°C in the dark then washed and cultured for 3 days (as described above). After culture, cells were washed with FACS buffer and stained for 20 min at 4°C with the following monoclonal antibodies (mAb): PE anti-human CD4 (clone RPA-T4, BD Biosciences), PerCP anti-human CD8 (clone HIT8A, BD Biosciences) and APC anti-human CD3 (clone MEM-57, Immunological Sciences) or the isotype controls. After washing, cells were transferred into FACS tubes and analyzed. The acquisition was performed on a FACSCalibur cytometer (BD Immunocytometry Systems), and the data were analyzed using CellQuest Pro software (BD Immunocytometry Systems, San Jose, CA).
2.7. Mannose Receptor Expression by Flow Cytometry
PMBC were cultured in the presence or absence of S proteins, mannan or their combination for 72 h in complete RPMI medium. In some experiments, after 72 h of culture, the stimulants were added the last 30 minutes of culture before collecting cells for staining. Cultured cells were washed, and then stained for 20 min at 4°C with the following mAbs: PE-Cy5 anti-human CD14 (clone M5E2, BD Biosciences) and APC mouse anti-human CD206 (clone 19.2, BD Pharmingen). After washing, cells were transferred into FACS tubes and analyzed. Before surface staining with specific mAb, the Fc receptors were blocked using purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 (Clone 2.4G2, BD Pharmigen) at a concentration of 5 µg/ml for 10 min at 4°C. Staining of samples with isotype controls was used as a reference to determine positive and negative populations. The acquisition was performed on a FACSCalibur cytometer and the data were analyzed using the Cell Quest Pro software.
2.8. Statistical Analyses
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 software (San Diego, CA). The comparisons between two groups of non-parametric data were analyzed using a Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, parametric data were analyzed by a Paired t test; for multiple comparison, the data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. A p value < 0.05 was taken as indicative of a statistically significant difference.
4. Discussion
In this paper we report findings that highlight the immunomodulatory capacity of the glycan ectodomain of SARS-CoV-2 S proteins generated in insect or human embryo cells, in cultures of human PBMC from pre-pandemic subjects:
i) both S proteins increase IL-6 and IFN-γ production in anti-CD3 mAb-stimulated T cells;
ii) the cell source (insect or human) of S protein determine up-and down-modulation of T cell activation and cytokine production induced by the mitogenic lectin Con A;
iii) the S proteins do not significantly impact cytokine production by memory antigenic responses triggered by a common microbial antigen;
iv) S proteins and the polysaccharide mannan (a polymer, consisting of alpha 1,6 linked mannose chains with alpha 1,2 mannose branches, obtained from the yeast
S. cerevisiae) induce a non-neglectable IL-6 production, probably of non-T cell source, in the unstimulated PBMC cultures of some donors;
v) both the human and, more prominently, the insect S protein cause remarkable expression of CD206, a mannose receptor, which is expressed on typical cells of innate immunity such as the macrophages, dendritic and endothelial cells [
24].
Although we don’t have direct evidence for a role of the glycan constituents present in the S protein, the so-called S protein ectodomain, in the aforesaid immunomodulatory activities, such a role is reasonably attributable to S glycan. In fact, we show here that the S protein strongly binds to Con A and this binding is inhibited by known Con A-ligands, such as the polysaccharide mannan and the alfa-methyl-mannoside. Interestingly, the polysaccharide mannan, substantially mimics, in our model, the immunomodulatory activities shown by the S proteins. It enhances cytokine production by anti-CD3-stimulated T cells, modulates Con A-induced responses, activates PBMC for the production of IL-6 (but not IFN-γ), and caused over expression of the MR on CD14
+ monocytes/macrophages. That the N-glycans of the S proteins are responsible of the immunomodulatory activity here reported is also suggested by the low activity of the S1 and S2 monomeric subunits; which have only a small portion of the N-glycans, when tested in comparison with the trimeric integral S protein at the same dosage. Moreover, the combination of mannan and S proteins does not result in an additive effect on up-regulation of MR expression, suggesting that S proteins use their mannan moieties for MR engagement. Other data of ours are also supportive of a main role of the N-glycan molecules on S protein-induced immunmodulalation in human PBMC cultures. We noticed a different potency of S-in than S-hu proteins at equal dose. Data from a number of authors have established that the N-glycan chains of the S-in protein are remarkable simpler and overall different, as expected, from those of the S-hu protein. They are less complex and with a low or no syalilation [
25]. Differences in degree of polymerization and structure of the mannoside chains could be particularly relevant in explaining our differential data.
Con A, a mannose/glucose-binding lectin isolated from Jack beans (Concanavalia ensiformis), is a well-known T cell mitogen that can activate the immune system, recruit lymphocytes and elicit cytokine production [
17,
18]. Specifically, binding of Con A triggers cross-linking of the TCR complex leading to T cell activation, by activating NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cells), a family of transcription factors, relevant in the development and function of the immune system [
26]. The glycan-binding capacity of lectins determines their mitogenicity, which relies on the lectin affinity for carbohydrates located on immune cell receptors. The Con A ability to activate T cells is also mediated by the activation of various costimulatory molecules e.g., CD28, HEVM but also regulatory molecules such as CTL4 which, interacting with ligands expressed on antigen-presenting cells (e.g., CD80, CD86, CD160), provide or reduce second signal [
17,
18,
27]. The dosage of Con A and its interaction with co-stimulatory or regulatory molecules can determine both activation of effector function or trigger tolerance [
28]. The different up and down modulation of Con A response induced by S-hu and S-in proteins could be due, in addition to a different affinity/avidity for Con A, to the differential activation of costimulatory or regulatory molecules concurring to T cell activation. This interpretation is also in line with opposite effects on mannan-induced co-stimulation of anti-CD3-stimulated PBMC cultures. It is important to consider that Con A, interacting with toll like receptors 2 and 4, determines activation of the innate response, which could play a role in the production of IL-6.
The activation of T lymphocytes with soluble anti-CD3 antibody induces crosslinking with the TCR, but also in this case the activation of a primary response is supported by second signals mediated by co-stimulatory molecules leading to formation of the immunological synapse between T cells and antigen presenting cells [
20,
29]. The sugars play a role in controlling the assembly and stabilization of the complexes in the immunological synapse as well as in protecting them from proteolysis during prolonged T-cell engagement. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that the S proteins and mannan itself-enhance the anti-CD3 mAb response by favoring co-stimulation and the formation of the immunological synapse. However, further studies are required to identify the receptors/ligands expressed on T cells or other immune cells, involved in the S protein-mediated modulatory effects on mitogenic activation of T cells by Con A or soluble anti-CD3 mAb.
The inability of S proteins to modulate the antigenic T cell memory response such as those elicited against a common antigen such as the MP65 of
C. albicans, a known human commensal [
21,
30], may be due to the decreased need for co-stimulation and second signals in the reactivation of an antigenic memory response, as compared to the induction of a primary T response [
31,
32].
Overall, our data on the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines mediated by the S proteins deserve particular consideration in patients treated with anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies [
33] and in all conditions in which saccharide-mediated costimulatory signals are relevant for T cell activation after TCR commitment. Similar caution should be used for experimental Con A-based anticancer therapies [
34,
35] in patients immunized with the current S-protein based, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines or affected by Covid-19. In addition, potential differences between Covid-19 protein vaccine produced in insect cells [
36], and COVID-19 vaccines based on RNA technologies, more similar to protein produced in HEK293, warrant to be studied.
To our knowledge, our report is the first one to show that the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 is able to enhance the CD206, MR expression, an identifying marker of anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. MR is a member of the C-type lectins that serves as a homeostatic receptor by binding and scavenging unwanted mannose N-linked glycoproteins or hormones from circulation. It recycles continuously between the plasma membrane and endosomal compartments in a clathrin-dependent manner [
37]. The MR is expressed at low levels during inflammation and at high levels during the resolution of inflammation, to ensure inflammatory agents are removed from the circulation only at the appropriate time [
38]. In the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the MR could be relevant for the intracellular access of the virus to macrophages and endothelial cells, and their immune activation, suspected to be critical in particularly aggressive forms of Covid-19. Many pathogenic microbes are coated with mannose-containing structures, and the macrophage MR contributes to the intracellular access and phagocytosis of microbial pathogens [
24,
39]. Finally, the extracellular domain of MR is easily solubilized by the metallo proteinases, and this soluble MR induces metainflammation, even enabling IL-6 production by macrophages [
40]. Of note, S-in protein shows a greater affinity/avidity for the MR compared to S-hu protein, similarly to what observed in the binding between S proteins with circulating MLB [
11]. In addition, S-in protein is also more powerful in inducing IL-6 by unstimulated PBMC. Further studies are warranted to determine the possible roles of MR and its soluble form in SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease.
We recognize that our study has a number of limitations. First, a relatively low number of human PBMC donors has been employed, and, as expected, there were non-neglectable, donor to donor differences in the studied immune responses. This was somewhat tempered by a clear, statistically assessable, trend in the donor populations, not blurred by the inevitable background donor differences. Second, no direct proof of the S-glycan constituent involvement in the observed immunomodulatory effects is provided here. Nonetheless, the whole set of our observations clearly suggests for a major role of it in most if not all the reported effects. Third, only two pro-inflammatory cytokines have been studied, and consequently the immunomodulatory setting we describe here, though focused upon two relevant cytokines in COVID-19 pathology, remains partial.
In conclusion, our data reports novel findings that extend our knowledge of the S protein immunobiological activities, highlight the immunological mediation of its glycan ectodomain, and invite further studies to determine their significance in the fight against SARS-CoV-2 and the diseases it causes.
Figure 1.
Spike (S) proteins bind Con A mainly through mannan constituents. (A) Binding of S-in protein (0.75 µg/ml) coated on a microplate and HRP-Con A (0.0125 µg/ml), measured by optical density (O.D.) using an in-house ELISA assay. Scalar concentrations of saccharides (12.5-100 µg/ml) were incubated together with HRP-Con A directly on the S-in protein coated microplate. Data are reported as mean ± sd of two independent experiments run in duplicate. (B) Binding of S-in, S-hu, S1 and S2 proteins (all at 0.75 µg/ml) coated on a microplate and HRP-Con A (0.025 µg/ml) measured by optical density (O.D.) through an in-house ELISA assay. Mannan (50 µg/ml) was incubated together with HRP-Con A directly on the spike-coated microplates. Data are reported as mean ± sd of two independent experiments run in duplicate. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. In panel A, the asterisks indicate the differences respect to the control condition Con A without saccharides. In panel B, only differences in O.D. values between binding of Con A to each specific S proteins in the absence or presence of mannan, and between binding of Con A and S-hu protein versus those of Con A and S1 or S2 subunits are shown.
Figure 1.
Spike (S) proteins bind Con A mainly through mannan constituents. (A) Binding of S-in protein (0.75 µg/ml) coated on a microplate and HRP-Con A (0.0125 µg/ml), measured by optical density (O.D.) using an in-house ELISA assay. Scalar concentrations of saccharides (12.5-100 µg/ml) were incubated together with HRP-Con A directly on the S-in protein coated microplate. Data are reported as mean ± sd of two independent experiments run in duplicate. (B) Binding of S-in, S-hu, S1 and S2 proteins (all at 0.75 µg/ml) coated on a microplate and HRP-Con A (0.025 µg/ml) measured by optical density (O.D.) through an in-house ELISA assay. Mannan (50 µg/ml) was incubated together with HRP-Con A directly on the spike-coated microplates. Data are reported as mean ± sd of two independent experiments run in duplicate. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons post hoc test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. In panel A, the asterisks indicate the differences respect to the control condition Con A without saccharides. In panel B, only differences in O.D. values between binding of Con A to each specific S proteins in the absence or presence of mannan, and between binding of Con A and S-hu protein versus those of Con A and S1 or S2 subunits are shown.
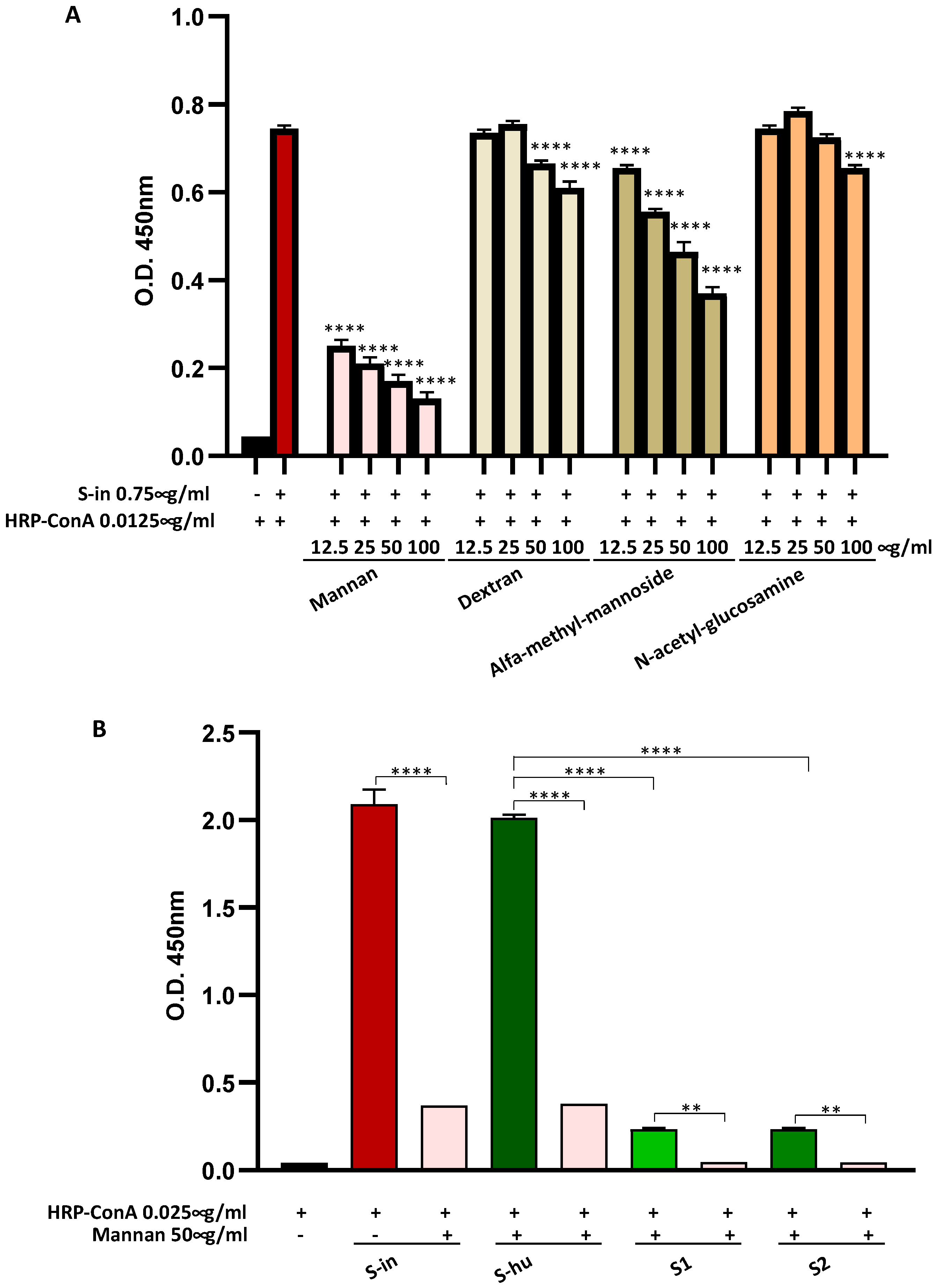
Figure 2.
S-in protein prevents Con A-mediated activation of PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were stimulated or not with Con A (4 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in protein (5 µg/ml) before assaying cell proliferation at 72 h and cytokine production and cell viability at 96 h of culture. To measure T cell proliferation, PBMC were stained with CFSE before being cultured. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC. Cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMC cultured in medium only. Twelve donors in panel A and eleven in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Percentages of CFSElow cells, as measure of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation. Representative density plots gated on CD3+CD4+ or CD3+CD8+ T lymphocytes are shown. Data were analyzed by Cell Quest software. Histograms are mean ± sd of three donors. (D) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combination. (Magnification x 10, scale: 100µm). (E) Live metabolic active PBMC were measured through a colorimetric XTT assay. The violin plots indicated the OD value of formazan dye formed by the activity of mitochondrial dehydrogenases in the sample. Six individual donors were assayed in duplicate. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test, in panels A, B and E (in panel E, the analyses were performed comparing the various groups two by two) and by Paired t test in panel C. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 2.
S-in protein prevents Con A-mediated activation of PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were stimulated or not with Con A (4 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in protein (5 µg/ml) before assaying cell proliferation at 72 h and cytokine production and cell viability at 96 h of culture. To measure T cell proliferation, PBMC were stained with CFSE before being cultured. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC. Cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMC cultured in medium only. Twelve donors in panel A and eleven in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Percentages of CFSElow cells, as measure of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation. Representative density plots gated on CD3+CD4+ or CD3+CD8+ T lymphocytes are shown. Data were analyzed by Cell Quest software. Histograms are mean ± sd of three donors. (D) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combination. (Magnification x 10, scale: 100µm). (E) Live metabolic active PBMC were measured through a colorimetric XTT assay. The violin plots indicated the OD value of formazan dye formed by the activity of mitochondrial dehydrogenases in the sample. Six individual donors were assayed in duplicate. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test, in panels A, B and E (in panel E, the analyses were performed comparing the various groups two by two) and by Paired t test in panel C. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
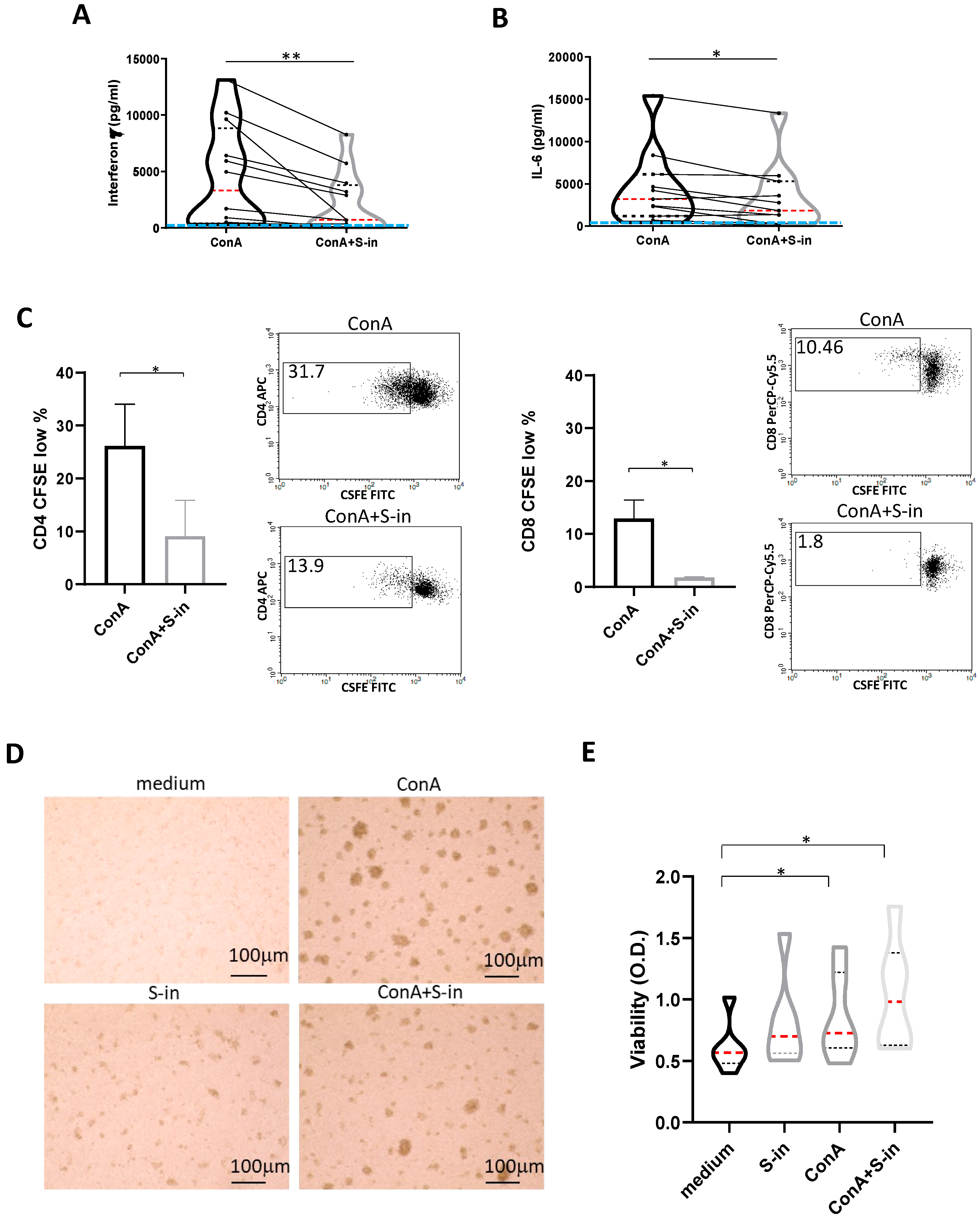
Figure 3.
S-hu protein and its S1 and S2 subunits, as well as S. cerevisiae mannan, increase IFN-γ and IL-6 production by Con A-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with Con A (4 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-hu, or S1 or S2 proteins (5 µg/ml) or Mannan from S. cerevisiae (10 µg/ml) for 96 h. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with Con A in the presence or absence of S proteins. Thirteen donors for S-hu protein, and twelve donors for both S1 and S2 in panel A; eleven donors for S-hu protein, and ten donors for both S1 and S2 subunits, in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x10, scale: 100µm). (D) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with Con A in the presence or absence of mannan. Nine donors were assayed in duplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups in panels A, B and D were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 3.
S-hu protein and its S1 and S2 subunits, as well as S. cerevisiae mannan, increase IFN-γ and IL-6 production by Con A-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with Con A (4 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-hu, or S1 or S2 proteins (5 µg/ml) or Mannan from S. cerevisiae (10 µg/ml) for 96 h. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with Con A in the presence or absence of S proteins. Thirteen donors for S-hu protein, and twelve donors for both S1 and S2 in panel A; eleven donors for S-hu protein, and ten donors for both S1 and S2 subunits, in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x10, scale: 100µm). (D) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with Con A in the presence or absence of mannan. Nine donors were assayed in duplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups in panels A, B and D were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
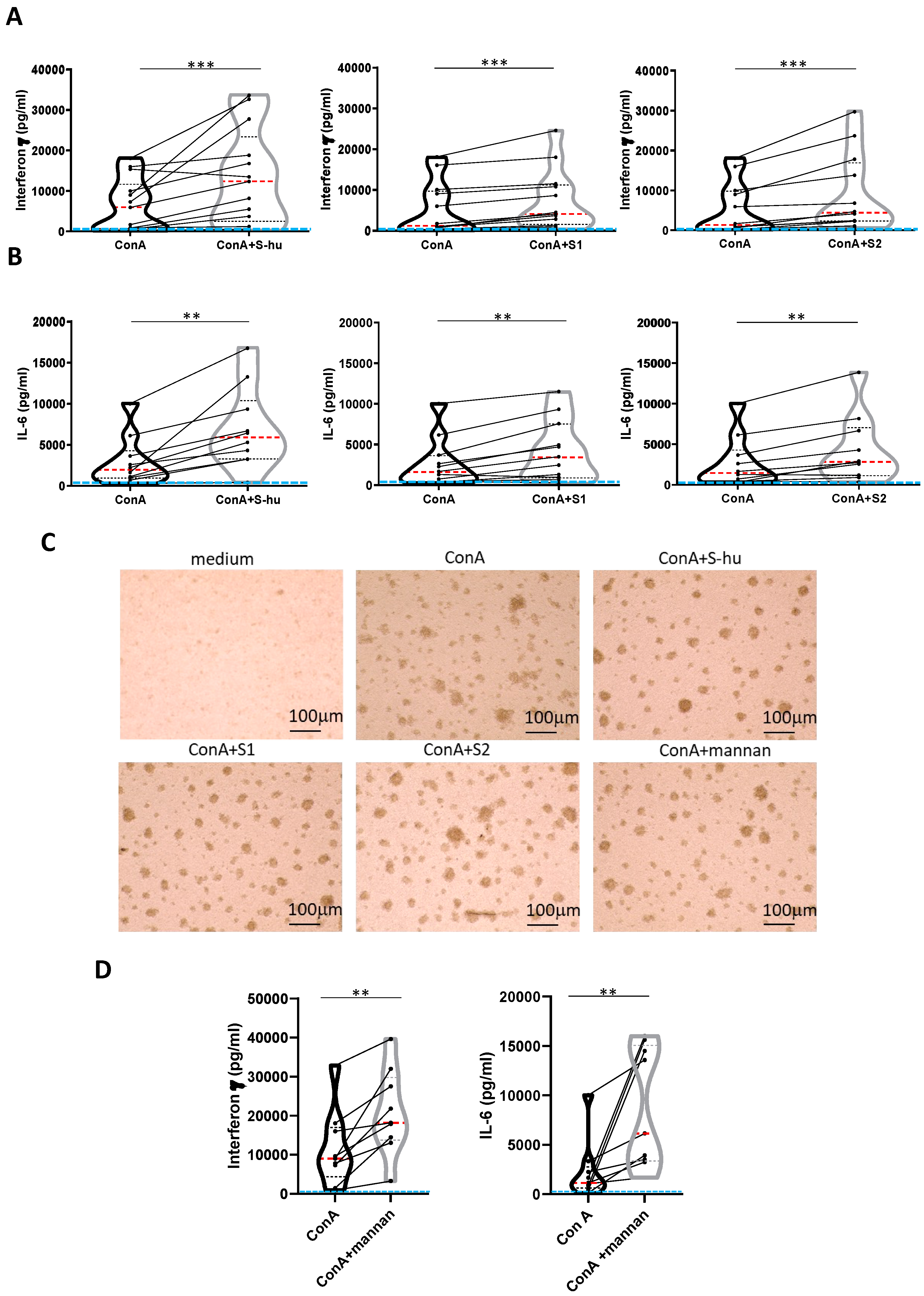
Figure 4.
All S proteins, as well as S. cerevisiae mannan, increase IFN-γ and IL-6 production by anti-CD3 Ab-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with an agonist anti-CD3 Ab (0.8 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in, S-hu, S1 or S2 proteins (all at 5 µg/ml), S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml), or mannan and S proteins combination for 96 h. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with anti-CD3 Ab in the presence or absence of spike proteins. Ten donors for S-in protein, twelve for S-hu protein, nine donors for S1 subunit and nine donors for S2 subunit in panel A; nine donors for S-in protein, eight donors for S-hu protein, six donors for S1 subunit and seven donors for S2 subunit, in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x 10, scale: 100 µm). (D) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with anti-CD3 Ab in the presence or absence of mannan. Seven donors for IFN-γ and IL-6 were assayed in duplicate. Data are plot as mean ± sd of one experiment run in triplicate or quadruplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 4.
All S proteins, as well as S. cerevisiae mannan, increase IFN-γ and IL-6 production by anti-CD3 Ab-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with an agonist anti-CD3 Ab (0.8 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in, S-hu, S1 or S2 proteins (all at 5 µg/ml), S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml), or mannan and S proteins combination for 96 h. (A-B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with anti-CD3 Ab in the presence or absence of spike proteins. Ten donors for S-in protein, twelve for S-hu protein, nine donors for S1 subunit and nine donors for S2 subunit in panel A; nine donors for S-in protein, eight donors for S-hu protein, six donors for S1 subunit and seven donors for S2 subunit, in panel B were assayed in duplicate. (C) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x 10, scale: 100 µm). (D) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ and IL-6 in culture supernatants of PBMC stimulated with anti-CD3 Ab in the presence or absence of mannan. Seven donors for IFN-γ and IL-6 were assayed in duplicate. Data are plot as mean ± sd of one experiment run in triplicate or quadruplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
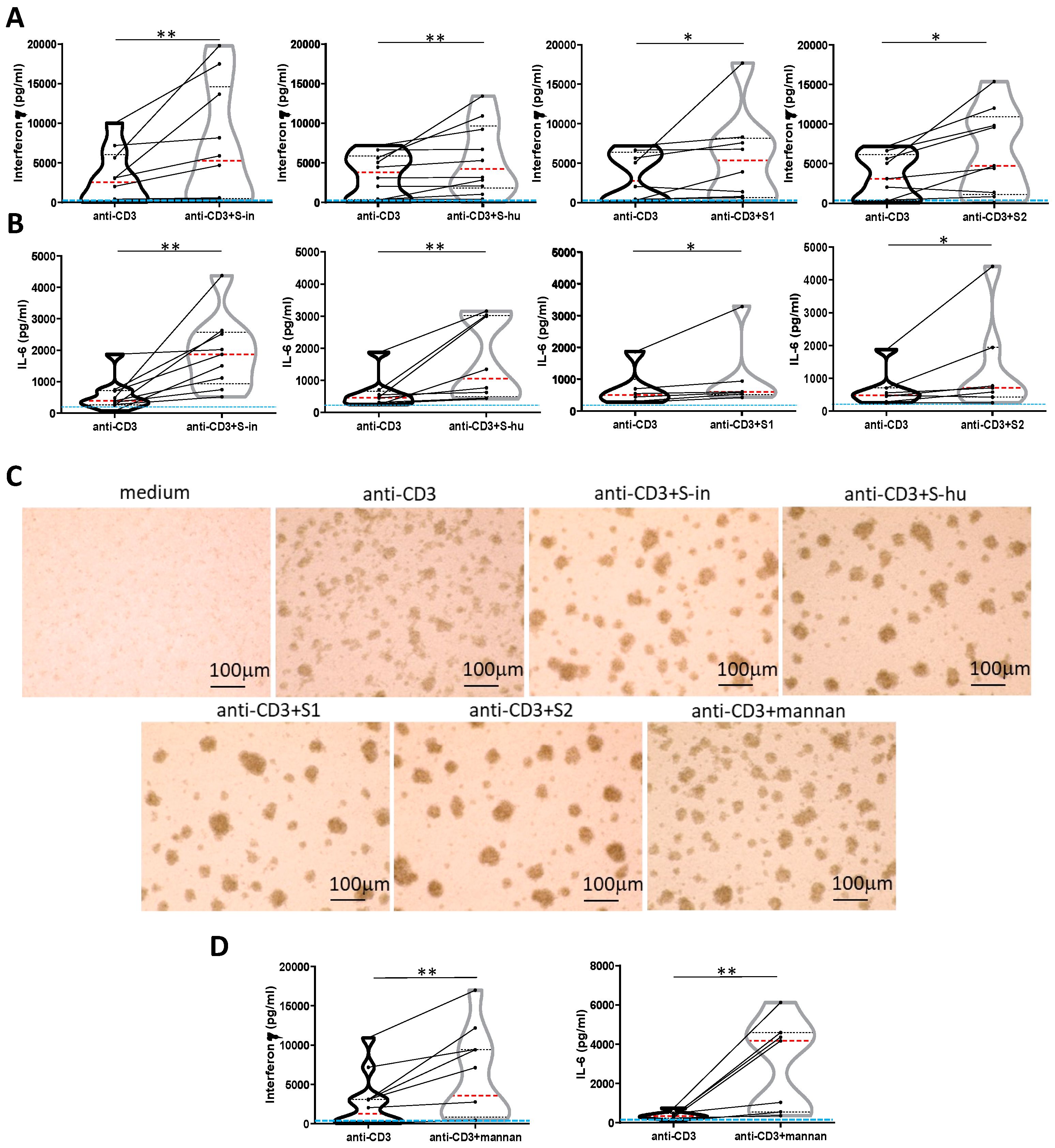
Figure 5.
Neither S proteins nor mannan affect cytokine production by C. albicans antigen MP65-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with recombinant non-glycosylated Candida albicans MP65 protein (1 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in or S-hu proteins (all at 5 µg/ml) or S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) for 96 h. Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants. Fourteen donors for S-in protein, four donors for S-hu protein and five donors for mannan in panel A; ten donors for S-in protein, four donors for S-hu protein and five donors for mannan in panel B were assayed in duplicate. Cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 5.
Neither S proteins nor mannan affect cytokine production by C. albicans antigen MP65-stimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured or not with recombinant non-glycosylated Candida albicans MP65 protein (1 µg/ml) in the presence or absence of S-in or S-hu proteins (all at 5 µg/ml) or S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) for 96 h. Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-6 (B) in culture supernatants. Fourteen donors for S-in protein, four donors for S-hu protein and five donors for mannan in panel A; ten donors for S-in protein, four donors for S-hu protein and five donors for mannan in panel B were assayed in duplicate. Cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. The light blue line indicates the level of IFN-γ or IL-6 found in unstimulated PBMCs cultures. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
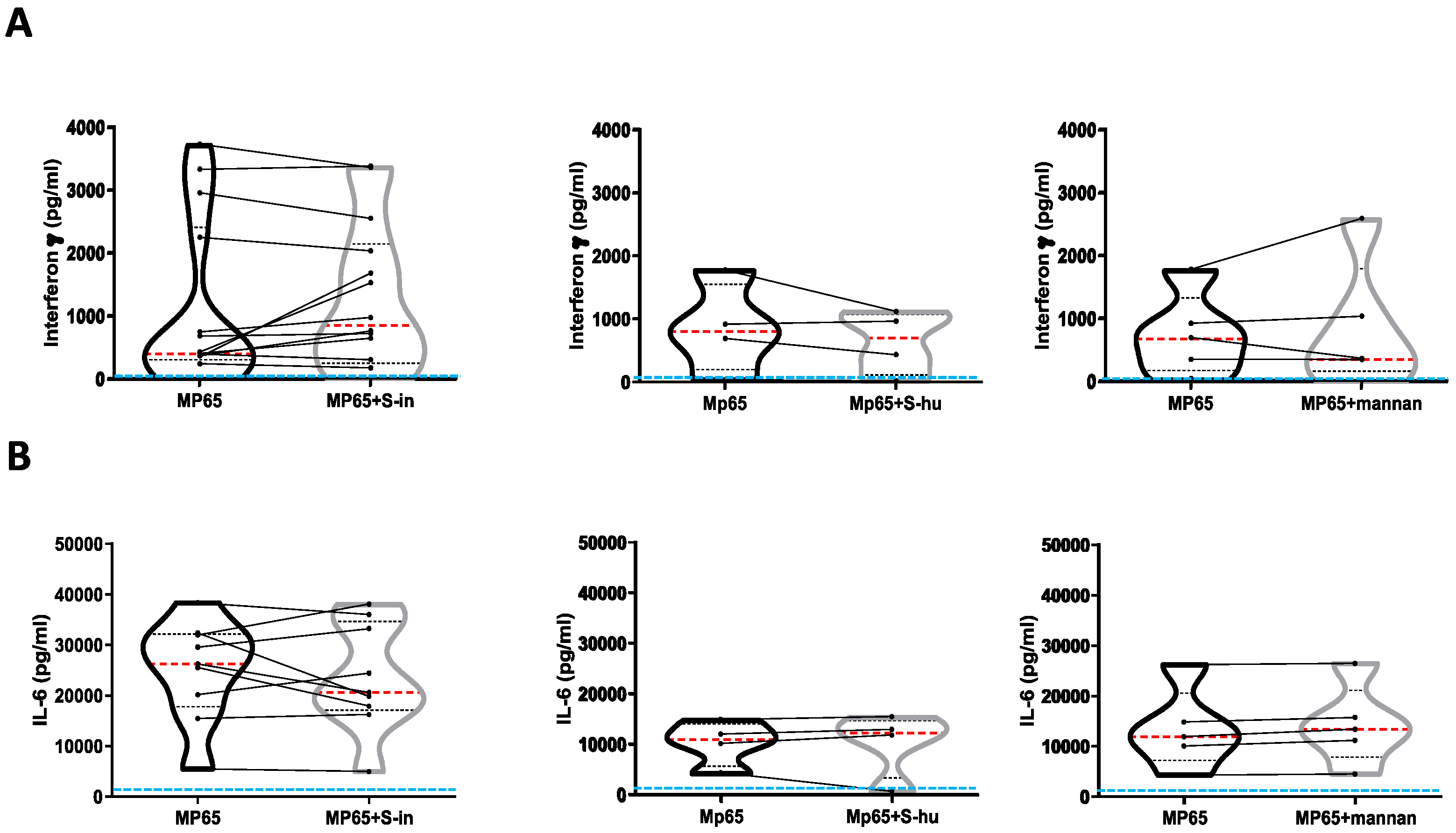
Figure 6.
Both S-in and S-hu proteins, as well as mannan, induce IL-6 production by unstimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured in the presence or absence of S-in, S-hu, S1 or S2 proteins (all at 5 µg/ml) or S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) or combination of S proteins and mannan for 96 h. (A) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of spike proteins. Thirteen donors for S-in protein, ten donors for S-hu protein, eleven donors for S1 subunit and seven donors for S2 subunit were assayed in duplicate. (B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of mannan. Nine donors were assayed in duplicate. (C) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of S-in protein, S-hu protein or mannan and their combination. Eight donors were assayed in duplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. (D) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x10, scale: 100µm). Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. In panels C. the analysis was performed comparing the various groups two by two; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 6.
Both S-in and S-hu proteins, as well as mannan, induce IL-6 production by unstimulated PBMCs. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured in the presence or absence of S-in, S-hu, S1 or S2 proteins (all at 5 µg/ml) or S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) or combination of S proteins and mannan for 96 h. (A) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of spike proteins. Thirteen donors for S-in protein, ten donors for S-hu protein, eleven donors for S1 subunit and seven donors for S2 subunit were assayed in duplicate. (B) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of mannan. Nine donors were assayed in duplicate. (C) Violin plots combined with individual values, showing protein levels of IL-6 in culture supernatants of medium-cultured PBMC in the presence or absence of S-in protein, S-hu protein or mannan and their combination. Eight donors were assayed in duplicate. All cytokines were quantified by specific ELISA kits and tested in duplicate. The red line inside the violin plot indicates the median value. (D) Representative images of PBMC cultures in the presence or absence of various stimuli and their combinations. (Magnification x10, scale: 100µm). Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs test. In panels C. the analysis was performed comparing the various groups two by two; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
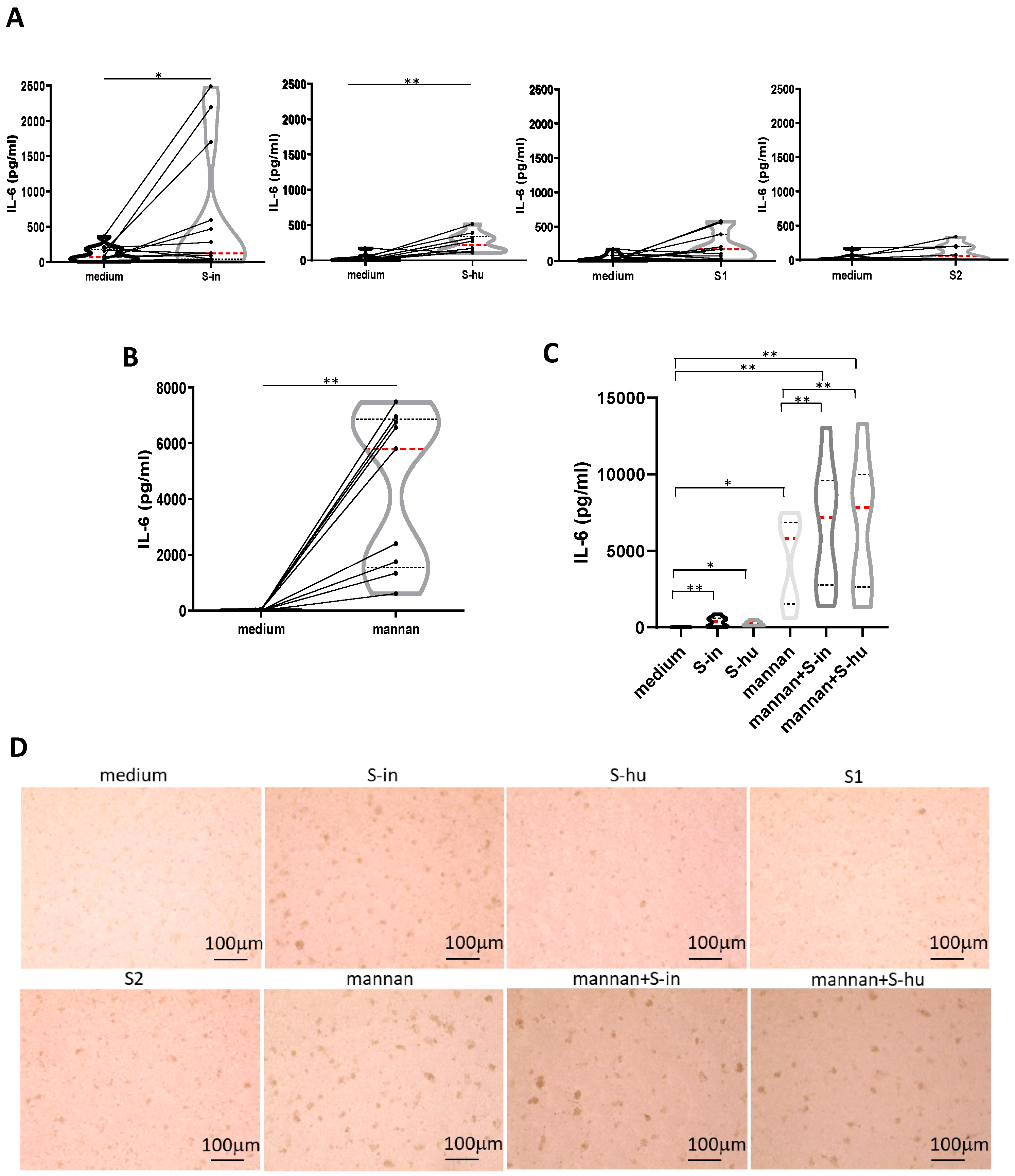
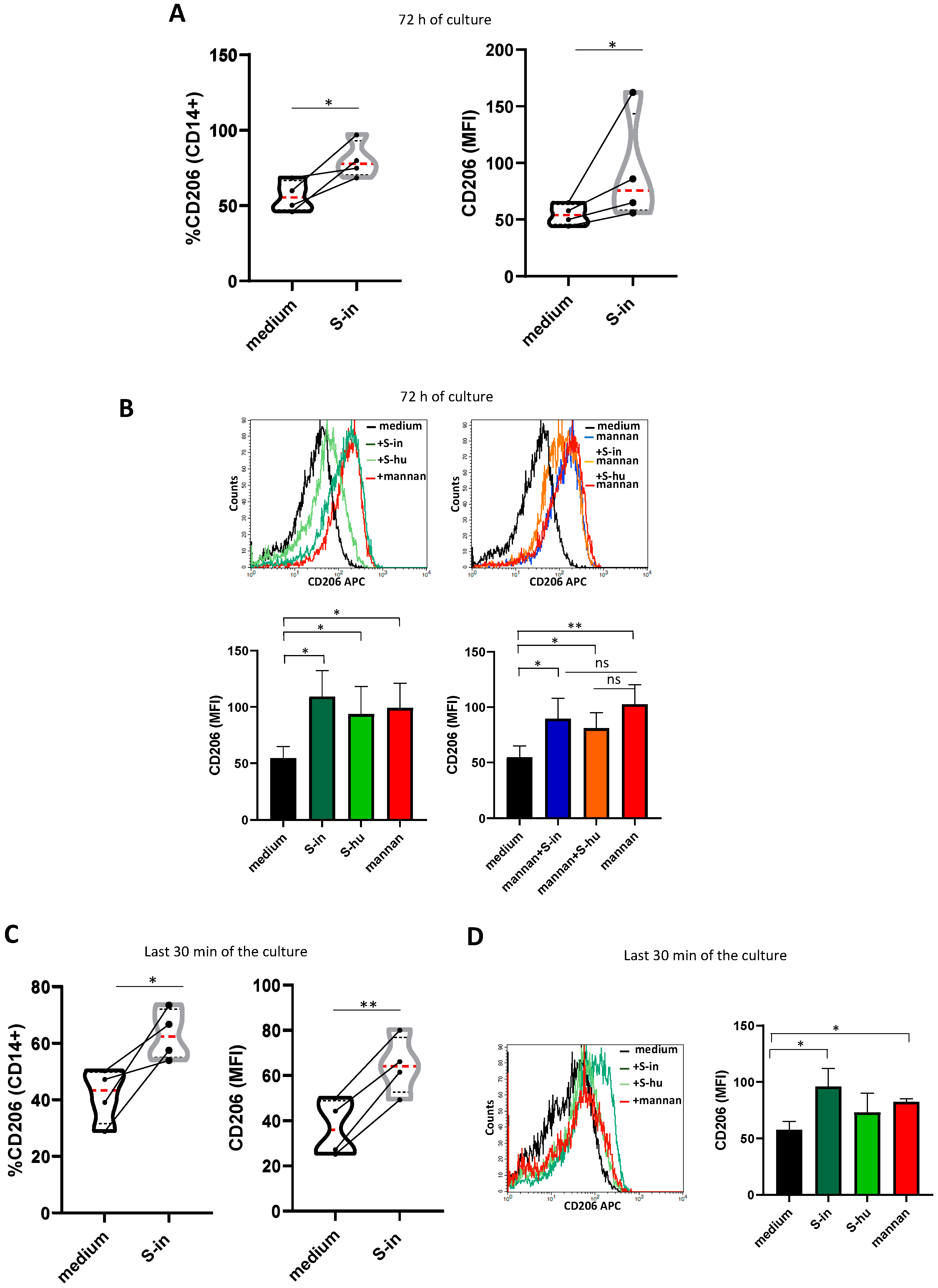
Figure 7.
S proteins as well as mannan upregulate mannose receptor expression on monocytes/macrophages. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured in the presence or absence of S-in and S-hu proteins, (all at 5 µg/ml), S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) or their combination for 72 h before measuring the expression of CD206 on CD14+ monocytes/macrophages by Flow Cytometry. In some conditions, stimuli were added the last 30 min of culture. (A) Violin plots combined with individual values showing the CD206 expression on CD14+ cells of PBMC cultured in the presence or absence of spike-in for 72 h. Four donors were assayed. (B) a representative histogram plot for CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured for 72 h with S-in protein, S-hu protein and mannan (left plots) or their combination (right plots). Histograms represent MFI of CD206 on CD14 positive cells as mean ± sd of 3 donors. (C) Violin plots combined with individual values showing the CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured in medium for 72 h and stimulated or not with S-in protein in the last 30 min of culture. Four donors were assayed. (D) a representative histogram plot for CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured for 72 h and stimulated with S-in protein, S-hu protein or mannan for the last 30 min of culture. Histograms represent MFI of CD206 on CD14 positive cells as mean ± sd of 3 donors. All data were analyzed by Cell Quest software. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Paired t test, in panel B and D the analyses were performed comparing the various groups two by two. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 7.
S proteins as well as mannan upregulate mannose receptor expression on monocytes/macrophages. PBMCs recovered from blood of healthy donors in pre-Sars-Cov-2 pandemic times were cultured in the presence or absence of S-in and S-hu proteins, (all at 5 µg/ml), S. cerevisiae mannan (10 µg/ml) or their combination for 72 h before measuring the expression of CD206 on CD14+ monocytes/macrophages by Flow Cytometry. In some conditions, stimuli were added the last 30 min of culture. (A) Violin plots combined with individual values showing the CD206 expression on CD14+ cells of PBMC cultured in the presence or absence of spike-in for 72 h. Four donors were assayed. (B) a representative histogram plot for CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured for 72 h with S-in protein, S-hu protein and mannan (left plots) or their combination (right plots). Histograms represent MFI of CD206 on CD14 positive cells as mean ± sd of 3 donors. (C) Violin plots combined with individual values showing the CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured in medium for 72 h and stimulated or not with S-in protein in the last 30 min of culture. Four donors were assayed. (D) a representative histogram plot for CD206 expression on CD14+ of PBMC cultured for 72 h and stimulated with S-in protein, S-hu protein or mannan for the last 30 min of culture. Histograms represent MFI of CD206 on CD14 positive cells as mean ± sd of 3 donors. All data were analyzed by Cell Quest software. Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by Paired t test, in panel B and D the analyses were performed comparing the various groups two by two. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.