Submitted:
09 February 2024
Posted:
12 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The TRAIL System
2.1. TRAIL-Induced Cell Death
2.2. Comparison of the Proximal Regulatory Mechanisms Governing TRAIL-Induced Cell Death with Other TNFRSF Members
3. Physiological and Physiopathological Functions of TRAIL
3.1. In immune System
3.2. In Diseases
4. Signalling Machinery Associated with TRAIL Non-Canonical Transduction
4.1. Lessons from Fas/CD95 Induced Non-Canonical Signalling (Secondary Complex)
4.1. Calcium Signalling Inducing Cell Motility and Metastasis
4.2. Nuclear DR5 Regulates Both Proliferation and Metastasis
4.3. Caspase-8 Contribution in TRAIL Non-Canonical Signalling
4.4. TRAIL Induce Cancer Metastasis after uPA and c-cbl Regulation
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgements
References
- Wiley, S.R.; Schooley, K.; Smolak, P.J.; Din, W.S.; Huang, C.P.; Nicholl, J.K.; Sutherland, G.R.; Smith, T.D.; Rauch, C.; Smith, C.A. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995, 3, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Ruppert, S.; Donahue, C.J.; Moore, A.; Ashkenazi, A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12687–12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; O’Rourke, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Gentz, R.; Ebner, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 1997, 276, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, M.; Ahmad, M.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Cohen, G.M.; Alnemri, E.S. Identification and molecular cloning of two novel receptors for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25417–25420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Johnson, R.S.; Smolak, P.J.; Waugh, J.Y.; Boiani, N.; Timour, M.S.; Gerhart, M.J.; Schooley, K.A.; Smith, C.A.; et al. TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. Embo J. 1997, 16, 5386–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Bodmer, J.L.; Thome, M.; Hofmann, K.; Holler, N.; Tschopp, J. Characterization of two receptors for TRAIL. FEBS Lett. 1997, 416, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Olson, D.; Tardivel, A.; Browning, B.; Lugovskoy, A.; Gong, D.; Dobles, M.; Hertig, S.; Hofmann, K.; Van Vlijmen, H.; et al. Identification of a new murine tumor necrosis factor receptor locus that contains two novel murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 5444–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.S.; Burns, T.F.; Zhan, Y.; Alnemri, E.S.; El-Deiry, W.S. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the mouse homologue of the KILLER/DR5 tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Boldin, M.P.; Mett, I.L.; Varfolomeev, E.E.; Chumakov, I.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Camonis, J.H.; Wallach, D. Self-association of the “death domains” of the p55 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor and Fas/APO1 prompts signaling for TNF and Fas/APO1 effects. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldin, M.P.; Varfolomeev, E.E.; Pancer, Z.; Mett, I.L.; Camonis, J.H.; Wallach, D. A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7795–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, E.; Kimchi, A.; Wallach, D.; Boldin, M.; Varfolomeev, E. The death domain: a module shared by proteins with diverse cellular functions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995, 20, 342–344. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, K. The modular nature of apoptotic signaling proteins. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 1999, 55, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Ayres, T.M.; Wong, G.H.; Goeddel, D.V. A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 845–853. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, N.; Nagata, S. A novel protein domain required for apoptosis. Mutational analysis of human Fas antigen. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 10932–10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, D.; Lalaoui, N.; Morizot, A.; Solary, E.; Micheau, O. TRAIL in cancer therapy: present and future challenges. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 1299–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, D.; Lalaoui, N.; Morizot, A.; Schneider, P.; Solary, E.; Micheau, O. Differential inhibition of TRAIL-mediated DR5-DISC formation by decoy receptors 1 and 2. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 7046–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, J.P.; Marsters, S.A.; Pitti, R.M.; Gurney, A.; Skubatch, M.; Baldwin, D.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Gray, C.L.; Baker, K.; Wood, W.I.; et al. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 1997, 277, 818–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Lawrence, D.A.; Roy, M.; Kischkel, F.C.; Dowd, P.; Huang, A.; Donahue, C.J.; Sherwood, S.W.; Baldwin, D.T.; et al. Genomic amplification of a decoy receptor for Fas ligand in lung and colon cancer. Nature 1998, 396, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Ni, J.; Yu, G.; Wei, Y.F.; Dixit, V.M. TRUNDD, a new member of the TRAIL receptor family that antagonizes TRAIL signalling. FEBS Lett. 1998, 424, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Ni, J.; Wei, Y.F.; Yu, G.; Gentz, R.; Dixit, V.M. An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 1997, 277, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, M.; Sun, W.; Yang, S.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Lin, L.; Kim, S.; et al. Reduction of decoy receptor 3 enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 2013, 8, e74272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Smolak, P.J.; Walczak, H.; Waugh, J.; Huang, C.P.; DuBose, R.F.; Goodwin, R.G.; Smith, C.A. Cloning and characterization of TRAIL-R3, a novel member of the emerging TRAIL receptor family. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Fernandez-Salas, E.A.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Friess, H.; Amundson, S.; Yin, J.; Meltzer, S.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. The antiapoptotic decoy receptor TRID/TRAIL-R3 is a p53-regulated DNA damage-inducible gene that is overexpressed in primary tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4153–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Dougall, W.C.; Smolak, P.J.; Waugh, J.Y.; Smith, C.A.; Goodwin, R.G. The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 1997, 7, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, F.; Fajoui, Z.E.; Gay, F.; Lalaoui, N.; Parmentier, B.; Chayvialle, J.A.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Micheau, O.; Abello, J.; Saurin, J.C. P53-mediated upregulation of DcR1 impairs oxaliplatin/TRAIL-induced synergistic anti-tumour potential in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizot, A.; Merino, D.; Lalaoui, N.; Jacquemin, G.; Granci, V.; Iessi, E.; Lanneau, D.; Bouyer, F.; Solary, E.; Chauffert, B.; et al. Chemotherapy overcomes TRAIL-R4-mediated TRAIL resistance at the DISC level. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaoui, N.; Morle, A.; Merino, D.; Jacquemin, G.; Iessi, E.; Morizot, A.; Shirley, S.; Robert, B.; Solary, E.; Garrido, C.; et al. TRAIL-R4 promotes tumor growth and resistance to apoptosis in cervical carcinoma HeLa cells through AKT. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaoui, N.; Merino, D.; Morizot, A.; Jacquemin, G.; Granci, V.; Iessi, E.; Solary, E.; Micheau, O. DcR2 PROTECTS CANCER CELLS FROM TRAIL-INDUCED APOPTOSIS BY ACTIVATING Akt. Adv. Tnf Fam. Res. 2011, 691, 745–745. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, J.G.; McDonnell, P.; Burke, M.B.; Deen, K.C.; Lyn, S.; Silverman, C.; Dul, E.; Appelbaum, E.R.; Eichman, C.; DiPrinzio, R.; et al. Osteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14363–14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.; Hasenauer, J.; Pollak, N.; Scheurich, P. Dominant negative effects of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor 4 on TRAIL receptor 1 signaling by formation of heteromeric complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 16576–16587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimondi, E.; Secchiero, P.; Quaroni, A.; Zerbinati, C.; Capitani, S.; Zauli, G. Involvement of TRAIL/TRAIL-receptors in human intestinal cell differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 206, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunalp, S.; Helvaci, D.G.; Oner, A.; Bursali, A.; Conforte, A.; Guner, H.; Karakulah, G.; Szegezdi, E.; Sag, D. TRAIL promotes the polarization of human macrophages toward a proinflammatory M1 phenotype and is associated with increased survival in cancer patients with high tumor macrophage content. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1209249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeuillard, E.; Li, B.; Stumpf, H.E.; Yang, J.; Willhite, J.; Tomlinson, J.L.; Wang, J.; Rohakhtar, F.R.; Simon, V.A.; Graham, R.P.; et al. Noncanonical TRAIL Signaling Promotes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Abundance and Tumor Progression in Cholangiocarcinoma. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, B.; Tonon, F.; Tisato, V.; Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P.; Fabris, B.; Bernardi, S. TRAIL/DR5 pathway promotes AKT phosphorylation, skeletal muscle differentiation, and glucose uptake. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Karstedt, S.; Conti, A.; Nobis, M.; Montinaro, A.; Hartwig, T.; Lemke, J.; Legler, K.; Annewanter, F.; Campbell, A.D.; Taraborrelli, L.; et al. Cancer cell-autonomous TRAIL-R signaling promotes KRAS-driven cancer progression, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse-Wilde, A.; Voloshanenko, O.; Bailey, S.L.; Longton, G.M.; Schaefer, U.; Csernok, A.I.; Schutz, G.; Greiner, E.F.; Kemp, C.J.; Walczak, H. TRAIL-R deficiency in mice enhances lymph node metastasis without affecting primary tumor development. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steitz, A.M.; Schroder, C.; Knuth, I.; Keber, C.U.; Sommerfeld, L.; Finkernagel, F.; Jansen, J.M.; Wagner, U.; Muller-Brusselbach, S.; Worzfeld, T.; et al. TRAIL-dependent apoptosis of peritoneal mesothelial cells by NK cells promotes ovarian cancer invasion. iScience 2023, 26, 108401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauzold, A.; Siegmund, D.; Schniewind, B.; Sipos, B.; Egberts, J.; Zorenkov, D.; Emme, D.; Roder, C.; Kalthoff, H.; Wajant, H. TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7434–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azijli, K.; Yuvaraj, S.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Wurdinger, T.; Dekker, H.; Joore, J.; van Dijk, E.; Quax, W.J.; Peters, G.J.; de Jong, S.; et al. Kinome profiling of non-canonical TRAIL signaling reveals RIP1-Src-STAT3-dependent invasion in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 (Pt 19) Pt 19, 4651–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimura, N.; Isomoto, H.; Bronk, S.F.; Gores, G.J. Trail induces cell migration and invasion in apoptosis-resistant cholangiocarcinoma cells. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 290, G129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Rui, Y.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) promotes trophoblast cell invasion via miR-146a-EGFR/CXCR4 axis: A novel mechanism for preeclampsia? Placenta 2020, 93, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanamee, E.S.; Faustman, D.L. On the TRAIL of Better Therapies: Understanding TNFRSF Structure-Function. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Maecker, H.; Sharp, D.; Lawrence, D.; Renz, M.; Vucic, D.; Ashkenazi, A. Molecular determinants of kinase pathway activation by Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40599–40608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauzold, A.; Wermann, H.; Arlt, A.; Schutze, S.; Schafer, H.; Oestern, S.; Roder, C.; Ungefroren, H.; Lampe, E.; Heinrich, M.; et al. CD95 and TRAIL receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase C and NF-kappaB contributes to apoptosis resistance in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 4258–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajant, H. TRAIL and NFkappaB signaling--a complex relationship. Vitam. Horm. 2004, 67, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shetty, S.; Gladden, J.B.; Henson, E.S.; Hu, X.; Villanueva, J.; Haney, N.; Gibson, S.B. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) up-regulates death receptor 5 (DR5) mediated by NFkappaB activation in epithelial derived cell lines. Apoptosis 2002, 7, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dittmer, M.R.; Blackwell, K.; Workman, L.M.; Hostager, B.; Habelhah, H. TRAIL activates JNK and NF-kappaB through RIP1-dependent and -independent pathways. Cell Signal 2015, 27, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Thome, M.; Burns, K.; Bodmer, J.L.; Hofmann, K.; Kataoka, T.; Holler, N.; Tschopp, J. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity 1997, 7, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.L.; Maeda, S.; Hsu, L.C.; Yagita, H.; Karin, M. Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. TRAIL receptor mediates inflammatory cytokine release in an NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geismann, C.; Erhart, W.; Grohmann, F.; Schreiber, S.; Schneider, G.; Schafer, H.; Arlt, A. TRAIL/NF-kappaB/CX3CL1 Mediated Onco-Immuno Crosstalk Leading to TRAIL Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovich, P.; Higgins, C.A.; Najda, Z.; Longley, D.B.; Martin, S.J. cFLIP(L) acts as a suppressor of TRAIL- and Fas-initiated inflammation by inhibiting assembly of caspase-8/FADD/RIPK1 NF-kappaB-activating complexes. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, R.; Konaka, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Hasegawa, M.; Fukui, M.; Mukaida, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Suda, T. Fas ligand induces cell-autonomous NF-kappaB activation and interleukin-8 production by a mechanism distinct from that of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 46415–46423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Kim, E.J.; Suk, K.; Lee, W.H. Stimulation of Fas (CD95) induces production of pro-inflammatory mediators through ERK/JNK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB in THP-1 cells. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 271, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Teng, F.; Zhang, M. Fas/FasL Complex Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Brain Endothelial Cells Via FADD-FLIP-TRAF-NF-kappaB Pathway. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 71, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuz, S.; Siegmund, D.; Rumpf, J.J.; Samel, D.; Leverkus, M.; Janssen, O.; Hacker, G.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Kracht, M.; Scheurich, P.; et al. NFkappaB activation by Fas is mediated through FADD, caspase-8, and RIP and is inhibited by FLIP. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, B.C.; Legembre, P.; Pietras, E.; Bubici, C.; Franzoso, G.; Peter, M.E. CD95 ligand induces motility and invasiveness of apoptosis-resistant tumor cells. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3175–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legembre, P.; Barnhart, B.C.; Zheng, L.; Vijayan, S.; Straus, S.E.; Puck, J.; Dale, J.K.; Lenardo, M.; Peter, M.E. Induction of apoptosis and activation of NF-kappaB by CD95 require different signalling thresholds. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, T.; Okamoto, K.; Iwata, J.; Shin, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Yasukochi, A.; Nakayama, K.I.; Kadowaki, T.; Tsukuba, T.; Yamamoto, K. Cathepsin E prevents tumor growth and metastasis by catalyzing the proteolytic release of soluble TRAIL from tumor cell surface. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10869–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagolovich, A.V.; Artykov, A.A.; Karmakova, T.A.; Vorontsova, M.S.; Pankratov, A.A.; Andreev-Andrievsky, A.A.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Gasparian, M.E. Genetically Modified DR5-Specific TRAIL Variant DR5-B Revealed Dual Antitumor and Protumoral Effect in Colon Cancer Xenografts and an Improved Pharmacokinetic Profile. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Park, S.M.; Tumanov, A.V.; Hau, A.; Sawada, K.; Feig, C.; Turner, J.R.; Fu, Y.X.; Romero, I.L.; Lengyel, E.; et al. CD95 promotes tumour growth. Nature 2010, 465, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.M.; Martin, S.J. Caspase-8 Acts in a Non-enzymatic Role as a Scaffold for Assembly of a Pro-inflammatory “FADDosome” Complex upon TRAIL Stimulation. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.P.; O’Connor, H.; Henry, C.M.; Davidovich, P.; Clancy, D.M.; Albert, M.L.; Cullen, S.P.; Martin, S.J. TRAIL Receptors Serve as Stress-Associated Molecular Patterns to Promote ER-Stress-Induced Inflammation. Dev. Cell 2020, 52, 714–730 e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Jung, H.; Oh, Y.; Kim, D.; Koh, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Jeon, Y.K.; et al. Soluble Fas ligand drives autoantibody-induced arthritis by binding to DR5/TRAIL-R2. Elife 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, S.; Infante-Duarte, C.; Seeger, B.; Zipp, F. Regulation of soluble and surface-bound TRAIL in human T cells, B cells, and monocytes. Cytokine 2003, 24, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamohara, H.; Matsuyama, W.; Shimozato, O.; Abe, K.; Galligan, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Matsushima, K.; Yoshimura, T. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TRAIL receptor expression in human neutrophils. Immunology 2004, 111, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Matsuzaki, A.; Suminoe, A.; Hattori, H.; Hara, T. Neutrophil-derived TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL): a novel mechanism of antitumor effect by neutrophils. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.P.; Leidal, K.G.; Nauseef, W.M.; Griffith, T.S. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is expressed throughout myeloid development, resulting in a broad distribution among neutrophil granules. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanger, N.A.; Maliszewski, C.R.; Schooley, K.; Griffith, T.S. Human dendritic cells mediate cellular apoptosis via tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartland, S.P.; Genner, S.W.; Martinez, G.J.; Robertson, S.; Kockx, M.; Lin, R.C.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Koay, Y.C.; Manuneedhi Cholan, P.; Kebede, M.A.; et al. TRAIL-Expressing Monocyte/Macrophages Are Critical for Reducing Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. iScience 2019, 12, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, T.S.; Wiley, S.R.; Kubin, M.Z.; Sedger, L.M.; Maliszewski, C.R.; Fanger, N.A. Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecchio, C.; Huber, V.; Scapini, P.; Calzetti, F.; Margotto, D.; Todeschini, G.; Pilla, L.; Martinelli, G.; Pizzolo, G.; Rivoltini, L.; et al. IFNalpha-stimulated neutrophils and monocytes release a soluble form of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo-2 ligand) displaying apoptotic activity on leukemic cells. Blood 2004, 103, 3837–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaas, O.; Vik, R.; Ashkenazi, A.; Espevik, T. Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of APO2 ligand/TRAIL in human monocytes and macrophages. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 51, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Chen, S.L.; Shih, S.C.; Chang, S.J.; Yang, S.L.; Hsieh, J.W.; Cheng, H.C.; Chen, L.J.; Tsao, Y.P. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) promotes tumor cell death by inducing macrophage membrane tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35943–35954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, A.C.; Haux, J.; Steinkjer, B.; Nonstad, U.; Egeberg, K.; Sundan, A.; Ashkenazi, A.; Espevik, T. Regulation of APO-2 ligand/trail expression in NK cells-involvement in NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Cytokine 1999, 11, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamai, L.; Ahmad, M.; Bennett, I.M.; Azzoni, L.; Alnemri, E.S.; Perussia, B. Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity: differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature and mature primary human NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirandola, P.; Ponti, C.; Gobbi, G.; Sponzilli, I.; Vaccarezza, M.; Cocco, L.; Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P.; Manzoli, F.A.; Vitale, M. Activated human NK and CD8+ T cells express both TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TRAIL receptors but are resistant to TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity. Blood 2004, 104, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraza, N.; Malato, Y.; Sander, L.E.; Al-Masaoudi, M.; Freimuth, J.; Riethmacher, D.; Gores, G.J.; Roskams, T.; Liedtke, C.; Trautwein, C. Hepatocyte-specific NEMO deletion promotes NK/NKT cell- and TRAIL-dependent liver damage. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihori, Y.; Kato, K.; Tanaka, M.; Okamoto, T.; Hagiwara, S.; Araki, N.; Kogawa, K.; Kuribayashi, K.; Nakamura, K.; Niitsu, Y. Interleukin-2 gene transfer potentiates the alpha-galactosylceramide-stimulated antitumor effect by the induction of TRAIL in NKT and NK cells in mouse models of subcutaneous and metastatic carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Cretney, E.; Takeda, K.; Wiltrout, R.H.; Sedger, L.M.; Kayagaki, N.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) contributes to interferon gamma-dependent natural killer cell protection from tumor metastasis. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 193, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieda, M.; Nicol, A.; Koezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, A.; Lapteva, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Tokunaga, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kayagaki, N.; Yagita, H.; et al. TRAIL expression by activated human CD4(+)V alpha 24NKT cells induces in vitro and in vivo apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2001, 97, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Santos, L.; Luka, Z.; Wagner, C.; Fernandez-Alvarez, S.; Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Beraza, N. Inhibition of natural killer cells protects the liver against acute injury in the absence of glycine N-methyltransferase. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2012, 56, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, A.; Barreyro, F.J.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Mott, J.L.; Akazawa, Y.; Masuoka, H.C.; Howe, C.L.; Gores, G.J. TRAIL mediates liver injury by the innate immune system in the bile duct-ligated mouse. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2008, 47, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelitsa, L.S.; Weinberg, K.I.; Emanuel, P.D.; Seeger, R.C. Expression of CD1d by myelomonocytic leukemias provides a target for cytotoxic NKT cells. Leukemia 2003, 17, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.W.; Westwood, J.A.; Darcy, P.K.; Sharkey, J.; Tsuji, M.; Franck, R.W.; Porcelli, S.A.; Besra, G.S.; Takeda, K.; Yagita, H.; et al. Combined natural killer T-cell based immunotherapy eradicates established tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7495–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelma, F.; de Niet, A.; Tempelmans Plat-Sinnige, M.J.; Jansen, L.; Takkenberg, R.B.; Reesink, H.W.; Kootstra, N.A.; van Leeuwen, E.M. Natural Killer Cell Characteristics in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Infection Are Associated With HBV Surface Antigen Clearance After Combination Treatment With Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a and Adefovir. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteranderl, C.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Selvakumar, B.; Lecuona, E.; Vadasz, I.; Morty, R.E.; Schmoldt, C.; Bespalowa, J.; Wolff, T.; Pleschka, S.; et al. Macrophage-epithelial paracrine crosstalk inhibits lung edema clearance during influenza infection. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 1566–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Manzoor, S.; Imran, M.; Ashraf, J.; Ashraf, S.; Resham, S.; Ghani, E. Role of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 1 single nucleotide polymorphism in natural clearance and treatment response of HCV infection. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyman, D.; Yalcin, A.D.; Oztoprak, N.; Genc, G.E.; Ozen, N.S.; Kizilates, F.; Berk, H.; Gumuslu, S. Soluble TRAIL levels decreased in chronic hepatitis C treatment with pegylated interferon alpha plus ribavirin: association with viral responses. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5650–5656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gyurkovska, V.; Ivanovska, N. Distinct roles of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in viral and bacterial infections: from pathogenesis to pathogen clearance. Inflamm. Res. : Off. J. Eur. Histamine Res. Society... [Et Al.] 2016, 65, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Alves, L.; Berger, M.D.; Koutsandreas, T.; Kirschke, N.; Lauer, C.; Sporri, R.; Chatziioannou, A.; Corazza, N.; Krebs, P. Non-apoptotic TRAIL function modulates NK cell activity during viral infection. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Hida, S.; Takayanagi, H.; Yokochi, T.; Kayagaki, N.; Takeda, K.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Tanaka, N.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Antiviral response by natural killer cells through TRAIL gene induction by IFN-alpha/beta. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 3138–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warke, R.V.; Martin, K.J.; Giaya, K.; Shaw, S.K.; Rothman, A.L.; Bosch, I. TRAIL is a novel antiviral protein against dengue virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Loewendorf, A.; Wang, Q.; McDonald, B.; Redwood, A.; Benedict, C.A. Inhibition of the TRAIL death receptor by CMV reveals its importance in NK cell-mediated antiviral defense. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacey, M.A.; Marsden, M.; Pham, N.T.; Clare, S.; Dolton, G.; Stack, G.; Jones, E.; Klenerman, P.; Gallimore, A.M.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. Neutrophils recruited by IL-22 in peripheral tissues function as TRAIL-dependent antiviral effectors against MCMV. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.; Tomasec, P.; Aicheler, R.; Loewendorf, A.; Nemcovicova, I.; Wang, E.C.; Stanton, R.J.; Macauley, M.; Norris, P.; Willen, L.; et al. Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein UL141 targets the TRAIL death receptors to thwart host innate antiviral defenses. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, I.S.; Wikstrom, M.E.; Brizard, G.; Coudert, J.D.; Estcourt, M.J.; Manzur, M.; O’Reilly, L.A.; Smyth, M.J.; Trapani, J.A.; Hill, G.R.; et al. TRAIL+ NK cells control CD4+ T cell responses during chronic viral infection to limit autoimmunity. Immunity 2014, 41, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.; Brunetto, M.; Reynolds, G.; Christophides, T.; Kennedy, P.T.; Lampertico, P.; Das, A.; Lopes, A.R.; Borrow, P.; Williams, K.; et al. Cytokines induced during chronic hepatitis B virus infection promote a pathway for NK cell-mediated liver damage. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Smyth, M.J.; Cretney, E.; Hayakawa, Y.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in NK cell-mediated and IFN-gamma-dependent suppression of subcutaneous tumor growth. Cell. Immunol. 2001, 214, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Scheurich, P. TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) and its receptors in tumor surveillance and cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2002, 7, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Smyth, M.J.; Cretney, E.; Hayakawa, Y.; Kayagaki, N.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Critical role for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in immune surveillance against tumor development. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Akiba, H.; Kojima, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Tanner, J.E.; Sayers, T.J.; Seki, N.; Okumura, K.; Yagita, H.; et al. Induction of Tumor-specific T Cell Immunity by Anti-DR5 Antibody Therapy. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Cretney, E.; Hayakawa, Y.; Ota, T.; Akiba, H.; Ogasawara, K.; Yagita, H.; Kinoshita, K.; Okumura, K.; Smyth, M.J. TRAIL identifies immature natural killer cells in newborn mice and adult mouse liver. Blood 2005, 105, 2082–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees, M.; Horak, P.; Schiefer, A.I.; Vanhara, P.; El-Gazzar, A.; Perco, P.; Kiesewetter, B.; Mullauer, L.; Streubel, B.; Raderer, M.; et al. The potential evasion of immune surveillance in mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma by DcR2-mediated up-regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassioli, C.; Baldari, C.T. The Expanding Arsenal of Cytotoxic T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 883010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, T.J.; Ludwig, A.T.; Earel, J.K.; Moore, J.M.; Vanoosten, R.L.; Moses, B.; Leidal, K.; Nauseef, W.M.; Griffith, T.S. Neutrophil stimulation with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) results in the release of functional soluble TRAIL/Apo-2L. Blood 2005, 106, 3474–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamili, F.H.; Bayegi, H.R.; Salmasi, Z.; Sadri, K.; Mahmoudi, M.; Kalantari, M.; Ramezani, M.; Abnous, K. Exosomes derived from TRAIL-engineered mesenchymal stem cells with effective anti-tumor activity in a mouse melanoma model. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmaltz, C.; Alpdogan, O.; Kappel, B.J.; Muriglan, S.J.; Rotolo, J.A.; Ongchin, J.; Willis, L.M.; Greenberg, A.S.; Eng, J.M.; Crawford, J.M.; et al. T cells require TRAIL for optimal graft-versus-tumor activity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamai, L.; Del Zotto, G.; Buccella, F.; Galeotti, L.; Canonico, B.; Luchetti, F.; Papa, S. Cytotoxic functions and susceptibility to apoptosis of human CD56(bright) NK cells differentiated in vitro from CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitors. Cytom. A 2012, 81, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, S.Y.; Lim, G.H.; Park, S.M.; Seo, K.W.; Youn, H.Y. Anti-tumor Effect of Activated Canine B Cells With Interleukin-21 and Anti-B Cell Receptor. Anticancer. Res. 2023, 43, 4007–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, A.A.; Peters, E.; Vodegel, D.; Steenmans, D.; Raimo, M.; Gibbs, S.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Duru, A.D.; Spanholtz, J.; Georgoudaki, A.M. Early TRAIL-engagement elicits potent multimodal targeting of melanoma by CD34(+) progenitor cell-derived NK cells. iScience 2023, 26, 107078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Hayakawa, Y.; Takeda, K.; Yagita, H. New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Labrada, A.; Pesini, C.; Santiago, L.; Hidalgo, S.; Calvo-Perez, A.; Onate, C.; Andres-Tovar, A.; Garzon-Tituana, M.; Uranga-Murillo, I.; Arias, M.A.; et al. All About (NK Cell-Mediated) Death in Two Acts and an Unexpected Encore: Initiation, Execution and Activation of Adaptive Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 896228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, A.; Mule, J.J.; Reichert, C.M.; Shiloni, E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Studies on the anti-tumor efficacy of systemically administered recombinant tumor necrosis factor against several murine tumors in vivo. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, J.; Watanabe-Fukunaga, R.; Adachi, M.; Matsuzawa, A.; Kasugai, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Itoh, N.; Suda, T.; Nagata, S. Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 1993, 364, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavida, B.; Ng, C.P.; Jazirehi, A.; Schiller, G.; Mizutani, Y. Selectivity of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of cancer cells and synergy with drugs: the trail to non-toxic cancer therapeutics (review). Int. J. Oncol. 1999, 15, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, I.F.; Erff, M.; Ashkenazi, A. Direct stimulation of apoptotic signaling by soluble Apo2l/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand leads to selective killing of glioma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Pai, R.C.; Fong, S.; Leung, S.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.A.; Blackie, C.; Chang, L.; McMurtrey, A.E.; Hebert, A.; et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 104, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, S.K.; Harris, L.A.; Xie, D.; Deforge, L.; Totpal, K.; Bussiere, J.; Fox, J.A. Preclinical studies to predict the disposition of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in humans: characterization of in vivo efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Herbst, R.S.; Mendolson, D.S.; Ebbinghaus, S.; Gordon, M.S.; O’Dwyer, M.; Lieberman, G.; Ing, J.; Kurzrock, R.; Novotny, W.; Eckhardt, S.G. A phase I safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) study of recombinant Apo2L/TRAIL, an apoptosis-inducing protein in patients with advanced cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 2, abstr 3013. [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa, K.; Liu, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ohtsuka, T.; Zhang, H.; Mountz, J.D.; Koopman, W.J.; Kimberly, R.P.; et al. Tumoricidal activity of a novel anti-human DR5 monoclonal antibody without hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H.; Miller, R.E.; Ariail, K.; Gliniak, B.; Griffith, T.S.; Kubin, M.; Chin, W.; Jones, J.; Woodward, A.; Le, T.; et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, L.E.; Tschopp, J. The TRAIL to selective tumor death. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurbanov, B.M.; Geilen, C.C.; Fecker, L.F.; Orfanos, C.E.; Eberle, J. Efficient TRAIL-R1/DR4-mediated apoptosis in melanoma cells by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J. Invest. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strater, J.; Hinz, U.; Walczak, H.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Koretz, K.; Herfarth, C.; Moller, P.; Lehnert, T. Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in colon carcinoma: TRAIL-R1 is an independent prognostic parameter. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3734–3740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spierings, D.C.; de Vries, E.G.; Timens, W.; Groen, H.J.; Boezen, H.M.; de Jong, S. Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL death receptors in stage III non-small cell lung cancer tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3397–3405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spierings, D.C.; de Vries, E.G.; Vellenga, E.; van den Heuvel, F.A.; Koornstra, J.J.; Wesseling, J.; Hollema, H.; de Jong, S. Tissue distribution of the death ligand TRAIL and its receptors. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2004, 52, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, R.A.; Turley, H.; Kimberley, F.C.; Liu, X.S.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Ch’En, P.; Xu, X.N.; Jin, B.Q.; Pezzella, F.; Screaton, G.R. Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in normal and malignant tissues. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanlioglu, A.D.; Korcum, A.F.; Pestereli, E.; Erdogan, G.; Karaveli, S.; Savas, B.; Griffith, T.S.; Sanlioglu, S. TRAIL death receptor-4 expression positively correlates with the tumor grade in breast cancer patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 69, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganten, T.M.; Sykora, J.; Koschny, R.; Batke, E.; Aulmann, S.; Mansmann, U.; Stremmel, W.; Sinn, H.P.; Walczak, H. Prognostic significance of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor expression in patients with breast cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 2009, 87, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.F.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.T.; Zhu, J.; Li, T. Expression of TRAIL and its receptor DR5 and their significance in acute leukemia cells. Genet. Mol. Res. : GMR 2015, 14, 18562–18568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, F.; Kruger, S.; Roder, C.; Trauzold, A.; Rocken, C.; Kalthoff, H. The expression of death receptor systems TRAIL-R1/-R2/-R4, CD95 and TNF-R1 and their cognate ligands in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Histol. Histopathol. 2019, 34, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, R.; Bedi, A. Requirement of BAX for TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis of colorectal cancers: synergism with sulindac-mediated inhibition of Bcl-x(L). Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willms, A.; Schittek, H.; Rahn, S.; Sosna, J.; Mert, U.; Adam, D.; Trauzold, A. Impact of p53 status on TRAIL-mediated apoptotic and non-apoptotic signaling in cancer cells. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0214847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheau, O.; Shirley, S.; Dufour, F. Death receptors as targets in cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1723–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, G.E.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Tawadros, F.; Farooqi, A.; Arafat, W.O. Journey of TRAIL from Bench to Bedside and its Potential Role in Immuno-Oncology. Oncol. Rev. 2017, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.J.; Takeda, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Peschon, J.J.; van den Brink, M.R.; Yagita, H. Nature’s TRAIL-On a Path to Cancer Immunotherapy. Immunity 2003, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, D.W.; Shah, K. TRAIL on trial: preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristofano, F.; George, A.; Tajiknia, V.; Ghandali, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Srinivasan, P.; Strandberg, J.; Hahn, M.; Sanchez Sevilla Uruchurtu, A.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of TRAIL death receptors. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, J.L.; Holler, N.; Reynard, S.; Vinciguerra, P.; Schneider, P.; Juo, P.; Blenis, J.; Tschopp, J. TRAIL receptor-2 signals apoptosis through FADD and caspase-8. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kischkel, F.C.; Lawrence, D.A.; Chuntharapai, A.; Schow, P.; Kim, K.J.; Ashkenazi, A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 2000, 12, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.B.; de Vries, E.; Tait, S.W.; Bontjer, I.; Borst, J. TRAIL receptor and CD95 signal to mitochondria via FADD, caspase-8/10, Bid, and Bax but differentially regulate events downstream from truncated Bid. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40760–40767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprick, M.R.; Weigand, M.A.; Rieser, E.; Rauch, C.T.; Juo, P.; Blenis, J.; Krammer, P.H.; Walczak, H. FADD/MORT1 and caspase-8 are recruited to TRAIL receptors 1 and 2 and are essential for apoptosis mediated by TRAIL receptor 2. Immunity 2000, 12, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzio, M.; Stockwell, B.R.; Stennicke, H.R.; Salvesen, G.S.; Dixit, V.M. An induced proximity model for caspase-8 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2926–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boatright, K.M.; Deis, C.; Denault, J.B.; Sutherlin, D.P.; Salvesen, G.S. Activation of caspases-8 and -10 by FLIP(L). Biochem. J. 2004, 382 Pt 2, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boatright, K.M.; Renatus, M.; Scott, F.L.; Sperandio, S.; Shin, H.; Pedersen, I.M.; Ricci, J.E.; Edris, W.A.; Sutherlin, D.P.; Green, D.R.; et al. A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stennicke, H.R.; Jurgensmeier, J.M.; Shin, H.; Deveraux, Q.; Wolf, B.B.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ellerby, H.M.; Ellerby, L.M.; Bredesen, D.; et al. Pro-caspase-3 is a major physiologic target of caspase-8. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 27084–27090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Green, D.R. Protease activation during apoptosis: death by a thousand cuts? Cell 1995, 82, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveeva, A.; Fichtner, M.; McAllister, K.; McCann, C.; Sturrock, M.; Longley, D.B.; Prehn, J.H.M. Heterogeneous responses to low level death receptor activation are explained by random molecular assembly of the Caspase-8 activation platform. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.L.; Gaudet, S.; Albeck, J.G.; Burke, J.M.; Sorger, P.K. Non-genetic origins of cell-to-cell variability in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009, 459, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, C.; Schmitz, I.; Zha, J.; Korsmeyer, S.J.; Krammer, P.H.; Peter, M.E. Differential modulation of apoptosis sensitivity in CD95 type I and type II cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 22532–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Tada-Oikawa, S.; Uchida, A.; Kawanishi, S. TRAIL causes cleavage of bid by caspase-8 and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential resulting in apoptosis in BJAB cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 265, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H.; Bouchon, A.; Stahl, H.; Krammer, P.H. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand retains its apoptosis-inducing capacity on Bcl-2- or Bcl-xL-overexpressing chemotherapy-resistant tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt, Y.; Shaughnessy, P.; Montgomery, W. Apoptosis-induced by TRAIL AND TNF-alpha in human multiple myeloma cells is not blocked by BCL-2. Cytokine 1999, 11, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, S.A.; Walczak, H.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Martin, S.J. Failure of Bcl-2 to block cytochrome c redistribution during TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2000, 471, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, H.; Lawrence, D.; Varfolomeev, E.; Totpal, K.; Morlan, J.; Schow, P.; Fong, S.; Schwall, R.; Sinicropi, D.; Ashkenazi, A. Tumor-cell resistance to death receptor--induced apoptosis through mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 homolog Bax. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, S.; Trauzold, A.; Boenicke, L.; Sandberg, C.; Beckmann, S.; Bayer, E.; Walczak, H.; Kalthoff, H.; Ungefroren, H. Bcl-XL protects pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells against CD95- and TRAIL-receptor-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.C.; Xu, Y.H. Bcl-2 over-expression and activation of protein kinase C suppress the trail-induced apoptosis in Jurkat T cells. Cell Res. 2001, 11, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; O’Neill, K.L.; Gurumurthy, C.B.; Quadros, R.M.; Tu, Y.; Luo, X. Cleavage by Caspase 8 and Mitochondrial Membrane Association Activate the BH3-only Protein Bid during TRAIL-induced Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11843–11851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desagher, S.; Osen-Sand, A.; Nichols, A.; Eskes, R.; Montessuit, S.; Lauper, S.; Maundrell, K.; Antonsson, B.; Martinou, J.C. Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial cytochrome c release during apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Zhao, Y.; Barber, M.J.; Kuharsky, D.K.; Yin, X.M. Bid-induced cytochrome c release is mediated by a pathway independent of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and Bax. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39474–39481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsmeyer, S.J.; Wei, M.C.; Saito, M.; Weiler, S.; Oh, K.J.; Schlesinger, P.H. Pro-apoptotic cascade activates BID, which oligomerizes BAK or BAX into pores that result in the release of cytochrome c. Cell Death Differ. 2000, 7, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiyan, A.M. The apoptosome: heart and soul of the cell death machine. Neoplasia (New York N.Y 1999, 1, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 11549–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acehan, D.; Jiang, X.; Morgan, D.G.; Heuser, J.E.; Wang, X.; Akey, C.W. Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, C.; Timmer, J.; Sperandio, S.; Salvesen, G.S. The apoptosome activates caspase-9 by dimerization. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, N.; Zaru, R.; Micheau, O.; Thome, M.; Attinger, A.; Valitutti, S.; Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Seed, B.; Tschopp, J. Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurette, O.; Rebillard, A.; Huc, L.; Le Moigne, G.; Merino, D.; Micheau, O.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Dimanche-Boitrel, M.T. TRAIL induces receptor-interacting protein 1-dependent and caspase-dependent necrosis-like cell death under acidic extracellular conditions. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Arshad, M.I.; Piquet-Pellorce, C.; Martin-Chouly, C.; Le Moigne-Muller, G.; Van Herreweghe, F.; Takahashi, N.; Sergent, O.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. TRAIL induces necroptosis involving RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent PARP-1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degterev, A.; Hitomi, J.; Germscheid, M.; Ch’en, I.L.; Korkina, O.; Teng, X.; Abbott, D.; Cuny, G.D.; Yuan, C.; Wagner, G.; et al. Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of necrostatins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, K.; Wickliffe, K.E.; Dugger, D.L.; Maltzman, A.; Roose-Girma, M.; Dohse, M.; Komuves, L.; Webster, J.D.; Dixit, V.M. Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature 2019, 574, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheau, O.; Thome, M.; Schneider, P.; Holler, N.; Tschopp, J.; Nicholson, D.W.; Briand, C.; Grutter, M.G. The long form of FLIP is an activator of caspase-8 at the Fas death-inducing signaling complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45162–45171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mompean, M.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Laage, S.; Siemer, A.B.; Bozkurt, G.; Wu, H.; McDermott, A.E. The Structure of the Necrosome RIPK1-RIPK3 Core, a Human Hetero-Amyloid Signaling Complex. Cell 2018, 173, 1244–1253 e1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. The structure of a minimum amyloid fibril core formed by necroptosis-mediating RHIM of human RIPK3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Challa, S.; Moquin, D.; Genga, R.; Ray, T.D.; Guildford, M.; Chan, F.K. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell 2009, 137, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Shao, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, N.; Lu, B.J.; Lin, S.C.; Dong, M.Q.; Han, J. RIP3, an energy metabolism regulator that switches TNF-induced cell death from apoptosis to necrosis. Science 2009, 325, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, S.; Yatim, N.; Werner, M.R.; Tran, H.; Gunja, S.Y.; Tait, S.W.; Albert, M.L.; Green, D.R.; Oberst, A. RIPK1 both positively and negatively regulates RIPK3 oligomerization and necroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Chen, S.; Liao, D.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, W.; Lei, X.; et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell 2012, 148, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, M.J.; Vandenabeele, P. The Ripoptosome: death decision in the cytosol. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Su, L.; Rizo, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, F.S.; Wang, X. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by RIP3. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jitkaew, S.; Cai, Z.; Choksi, S.; Li, Q.; Luo, J.; Liu, Z.G. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2012, 109, 5322–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondelinger, Y.; Declercq, W.; Montessuit, S.; Roelandt, R.; Goncalves, A.; Bruggeman, I.; Hulpiau, P.; Weber, K.; Sehon, C.A.; Marquis, R.W.; et al. MLKL compromises plasma membrane integrity by binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. MLKL regulates necrotic plasma membrane permeabilization. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.M.; Vince, J.E. Post-translational control of RIPK3 and MLKL mediated necroptotic cell death. F1000Research 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wike-Hooley, J.L.; Haveman, J.; Reinhold, H.S. The relevance of tumour pH to the treatment of malignant disease. Radiother. Oncol. 1984, 2, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barja de Quiroga, G. Hypothesis that the acidification of a tissue which takes place during ischemia can lead to tissue hyperoxia during reperfusion due to the Bohr effect. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990, 8, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Gan, I.; Pavlosky, A.; Huang, X.; Fuhrmann, B.; Jevnikar, A.M. Intracellular pH Regulates TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Endothelial Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 1503960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, A.; Bogdanov, A.; Chubenko, V.; Volkov, N.; Moiseenko, F.; Moiseyenko, V. Tumor acidity: From hallmark of cancer to target of treatment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 979154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, V.; Camisaschi, C.; Berzi, A.; Ferro, S.; Lugini, L.; Triulzi, T.; Tuccitto, A.; Tagliabue, E.; Castelli, C.; Rivoltini, L. Cancer acidity: An ultimate frontier of tumor immune escape and a novel target of immunomodulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 43, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.; Acosta-Alvear, D.; Kimmig, P.; Mendez, A.S.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Walter, P.; Ashkenazi, A. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis. Science 2014, 345, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.; Lawrence, D.A.; Ashkenazi, A.; Walter, P. Confirming a critical role for death receptor 5 and caspase-8 in apoptosis induction by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1530–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, F.; Rattier, T.; Constantinescu, A.A.; Zischler, L.; Morle, A.; Ben Mabrouk, H.; Humblin, E.; Jacquemin, G.; Szegezdi, E.; Delacote, F.; et al. TRAIL receptor gene editing unveils TRAIL-R1 as a master player of apoptosis induced by TRAIL and ER stress. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9974–9985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurlaro, R.; Puschel, F.; Leon-Annicchiarico, C.L.; O’Connor, H.; Martin, S.J.; Palou-Gramon, D.; Lucendo, E.; Munoz-Pinedo, C. Glucose Deprivation Induces ATF4-Mediated Apoptosis through TRAIL Death Receptors. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.K.; Lawrence, D.A.; Lu, M.; Tan, J.; Harnoss, J.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Liu, P.; Sandoval, W.; Martin, S.E.; Ashkenazi, A. Coordination between Two Branches of the Unfolded Protein Response Determines Apoptotic Cell Fate. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Marsters, S.A.; Ashkenazi, A.; Walter, P. Misfolded proteins bind and activate death receptor 5 to trigger apoptosis during unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, T.; Fundora, K.A.; Hamamoto, K.; Opozda, D.M.; Liang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Uzun, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Wang, H.G. ER stress elicits non-canonical CASP8 (caspase 8) activation on autophagosomal membranes to induce apoptosis. Autophagy 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, F.; Both, D.; Derks, I.A.M.; Spaargaren, M.; Munoz-Pinedo, C.; Eldering, E. Negligible role of TRAIL death receptors in cell death upon endoplasmic reticulum stress in B-cell malignancies. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glab, J.A.; Doerflinger, M.; Nedeva, C.; Jose, I.; Mbogo, G.W.; Paton, J.C.; Paton, A.W.; Kueh, A.J.; Herold, M.J.; Huang, D.C.; et al. DR5 and caspase-8 are dispensable in ER stress-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havell, E.A.; Fiers, W.; North, R.J. The antitumor function of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), I. Therapeutic action of TNF against an established murine sarcoma is indirect, immunologically dependent, and limited by severe toxicity. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 1067–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.J.; Havell, E.A. The antitumor function of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) II. Analysis of the role of endogenous TNF in endotoxin-induced hemorrhagic necrosis and regression of an established sarcoma. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 167, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensing-Ehl, A.; Frei, K.; Flury, R.; Matiba, B.; Mariani, S.M.; Weller, M.; Aebischer, P.; Krammer, P.H.; Fontana, A. Local Fas/APO-1 (CD95) ligand-mediated tumor cell killing in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 2253–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Yonehara, S.; Ishii, A.; Yonehara, M.; Mizushima, S.; Sameshima, M.; Hase, A.; Seto, Y.; Nagata, S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell 1991, 66, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Suda, T.; Takahashi, T.; Golstein, P.; Nagata, S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell 1993, 75, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leist, M.; Gantner, F.; Bohlinger, I.; Germann, P.G.; Tiegs, G.; Wendel, A. Murine hepatocyte apoptosis induced in vitro and in vivo by TNF-alpha requires transcriptional arrest. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nio, Y.; Zighelboim, J.; Berek, J.; Bonavida, B. Cycloheximide-induced modulation of TNF-mediated cytotoxicity in sensitive and resistant ovarian tumor cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1990, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H.; Haas, E.; Schwenzer, R.; Muhlenbeck, F.; Kreuz, S.; Schubert, G.; Grell, M.; Smith, C.; Scheurich, P. Inhibition of death receptor-mediated gene induction by a cycloheximide-sensitive factor occurs at the level of or upstream of Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24357–24366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Suda, T.; Yatomi, T.; Nakamura, N.; Nagata, S. Lethal effect of recombinant human Fas ligand in mice pretreated with Propionibacterium acnes. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, V.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Galanos, C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchmann, M.; Varfolomeev, E.E.; Hermann, F.; Rueckert, F.; Strand, D.; Koehler, H.; Strand, S.; Lohse, A.W.; Wallach, D.; Galle, P.R. Dominant negative MORT1/FADD rescues mice from CD95 and TNF-induced liver failure. Hepatol. (Baltim. Md. 2003, 37, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichacker, P.Q.; Hoffman, W.D.; Farese, A.; Banks, S.M.; Kuo, G.C.; MacVittie, T.J.; Natanson, C. TNF but not IL-1 in dogs causes lethal lung injury and multiple organ dysfunction similar to human sepsis. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 71, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, L.B.; Emerson, T.E., Jr.; Taylor, F.B., Jr.; Chang, A.C.; Duerr, M.; Peer, G.T.; Flournoy, D.J.; White, G.L.; Kosanke, S.D.; Murray, C.K.; et al. Lethal Staphylococcus aureus-induced shock in primates: prevention of death with anti-TNF antibody. J. Trauma. 1992, 33, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheau, O.; Tschopp, J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003, 114, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.; Huang, J.; Shu, H.B.; Baichwal, V.; Goeddel, D.V. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996, 4, 387–396. [Google Scholar]
- Kelliher, M.A.; Grimm, S.; Ishida, Y.; Kuo, F.; Stanger, B.Z.; Leder, P. The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity 1998, 8, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, A.T.; Bertrand, M.J.M. More to Life than NF-kappaB in TNFR1 Signaling. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Shu, H.B.; Pan, M.G.; Goeddel, D.V. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 1996, 84, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.; Xiong, J.; Goeddel, D.V. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 1995, 81, 495–504. [Google Scholar]
- Varfolomeev, E.E.; Schuchmann, M.; Luria, V.; Chiannilkulchai, N.; Beckmann, J.S.; Mett, I.L.; Rebrikov, D.; Brodianski, V.M.; Kemper, O.C.; Kollet, O.; et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity 1998, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldin, M.P.; Goncharov, T.M.; Goltsev, Y.V.; Wallach, D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell 1996, 85, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhibber-Goel, J.; Coleman-Vaughan, C.; Agrawal, V.; Sawhney, N.; Hickey, E.; Powell, J.C.; McCarthy, J.V. gamma-Secretase Activity Is Required for Regulated Intramembrane Proteolysis of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor 1 and TNF-mediated Pro-apoptotic Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5971–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.K.; Chun, H.J.; Zheng, L.; Siegel, R.M.; Bui, K.L.; Lenardo, M.J. A domain in TNF receptors that mediates ligand-independent receptor assembly and signaling. Science 2000, 288, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albogami, S.; Todd, I.; Negm, O.; Fairclough, L.C.; Tighe, P.J. Mutations in the binding site of TNFR1 PLAD reduce homologous interactions but can enhance antagonism of wild-type TNFR1 activity. Immunology 2021, 164, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Belfetmi, A.; Cai, T.; Xu, B.; Heyninck, K.; Van Den Heede, K.; Buyse, M.A.; Fontana, P.; et al. Autoinhibitory structure of preligand association state implicates a new strategy to attain effective DR5 receptor activation. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, L.; Mruk, K.; Archer, K.; Woelfel, M.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G.; Lenardo, M.J.; Chan, F.K. Preligand assembly domain-mediated ligand- independent association between TRAIL receptor 4 (TR4) and TR2 regulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2005, 102, 18099–18104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.M.; Liu, L.; Tsokos, G.C. Targeted tumor necrosis factor receptor I preligand assembly domain improves skin lesions in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.M.; Zheng, L.; Chan, F.K.; Lenardo, M. Amelioration of inflammatory arthritis by targeting the pre-ligand assembly domain of tumor necrosis factor receptors. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chou, F.C.; Chen, S.J.; Lin, S.H.; Chang, D.M.; Sytwu, H.K. Targeting pre-ligand assembly domain of TNFR1 ameliorates autoimmune diseases - an unrevealed role in downregulation of Th17 cells. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheau, O.; Rizzi, M.; Smulski, C.R. Editorial: TNFR Superfamily Oligomerization and Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 682472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanamee, E.S.; Faustman, D.L. The benefits of clustering in TNF receptor superfamily signaling. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1225704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Fu, T.M.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, L.; Chen, W.; Qiu, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Piai, A.; Fu, Q.; et al. Higher-Order Clustering of the Transmembrane Anchor of DR5 Drives Signaling. Cell 2019, 176, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, C.C.; Lewis, A.K.; Mudaliar, D.J.; Perlmutter, J.D.; Braun, A.R.; Karim, C.B.; Thomas, D.D.; Brody, J.R.; Sachs, J.N. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces death receptor 5 networks that are highly organized. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21265–21278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.K.; Valley, C.C.; Peery, S.L.; Brummel, B.; Braun, A.R.; Karim, C.B.; Sachs, J.N. Death Receptor 5 Networks Require Membrane Cholesterol for Proper Structure and Function. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428 (24 Pt A), 4843–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Fu, Q.; Pan, L.; Piai, A.; Chou, J.J. The Diversity and Similarity of Transmembrane Trimerization of TNF Receptors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 569684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazzette, N.; Cruz, A.C.; Wu, X.; Hammer, J.A.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Siegel, R.M.; Sengupta, P. Super-Resolution Imaging of Fas/CD95 Reorganization Induced by Membrane-Bound Fas Ligand Reveals Nanoscale Clustering Upstream of FADD Recruitment. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, F.L.; Stec, B.; Pop, C.; Dobaczewska, M.K.; Lee, J.J.; Monosov, E.; Robinson, H.; Salvesen, G.S.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Riedl, S.J. The Fas-FADD death domain complex structure unravels signalling by receptor clustering. Nature 2009, 457, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesen, G.S.; Riedl, S.J. Structure of the Fas/FADD complex: a conditional death domain complex mediating signaling by receptor clustering. Cell Cycle (Georget. Tex. 2009, 8, 2723–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.L.; Harrington, H.A. Bistability in apoptosis by receptor clustering. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheau, O. Posttranslational Modifications and Death Receptor Signalling. In TRAIL, Fas Ligand, TNF and TLR3 in Cancer, Micheau, O. Ed.; Springer International Publishing, 2017; pp 247-290.
- Micheau, O. Regulation of TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Signaling by Glycosylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.W.; Punnoose, E.A.; Januario, T.; Lawrence, D.A.; Pitti, R.M.; Lancaster, K.; Lee, D.; von Goetz, M.; Yee, S.F.; Totpal, K.; et al. Death-receptor O-glycosylation controls tumor-cell sensitivity to the proapoptotic ligand Apo2L/TRAIL. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, T.; Yan, R.; Kim, S.R.; Stowell, S.R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; An, G.; Cummings, R.D.; Ju, T. O-glycans on death receptors in cells modulate their sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through affecting on their stability and oligomerization. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 11786–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, F.; Rattier, T.; Shirley, S.; Picarda, G.; Constantinescu, A.A.; Morle, A.; Zakaria, A.B.; Marcion, G.; Causse, S.; Szegezdi, E.; et al. N-glycosylation of mouse TRAIL-R and human TRAIL-R1 enhances TRAIL-induced death. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estornes, Y.; Dondelinger, Y.; Weber, K.; Bruggeman, I.; Peall, A.; MacFarlane, M.; Lebecque, S.; Vandenabeele, P.; Bertrand, M.J.M. N-glycosylation of mouse TRAIL-R restrains TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatnyeva, O.M.; Kubarenko, A.V.; Weber, C.E.; Pappa, A.; Schwartz-Albiez, R.; Weber, A.N.; Krammer, P.H.; Lavrik, I.N. Modulation of the CD95-induced apoptosis: the role of CD95 N-glycosylation. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Shiraishi, T.; Horinaka, M.; Wakada, M.; Sakai, T. Glycosylation modulates TRAIL-R1/death receptor 4 protein: different regulations of two pro-apoptotic receptors for TRAIL by tunicamycin. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, A.; Merli, S.; Bagnasco, L.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Marino, M.; Cassani, G. Identification of two forms (31-33 and 48 kD) of the urinary soluble p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor that are differentially N- and O-glycosylated. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. : Off. J. Int. Soc. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995, 15, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vreede, G.; Morrison, H.A.; Houser, A.M.; Boileau, R.M.; Andersen, D.; Colombani, J.; Bilder, D. A Drosophila Tumor Suppressor Gene Prevents Tonic TNF Signaling through Receptor N-Glycosylation. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Chi, J.; Zhang, J.; Sui, A.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. N-Acetyl-Glucosamine Sensitizes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis by Activating Death Receptor 5. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; van Roosmalen, I.A.M.; Reis, C.R.; Setroikromo, R.; Quax, W.J. Death receptor 5 is activated by fucosylation in colon cancer cells. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.Y.; Seo, S.U.; Woo, S.M.; Min, K.J.; Byun, H.S.; Hur, G.M.; Kang, S.C.; Kwon, T.K. Oridonin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through GALNT14-mediated DR5 glycosylation. Biochimie 2019, 165, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.E.; Hellbardt, S.; Schwartz-Albiez, R.; Westendorp, M.O.; Walczak, H.; Moldenhauer, G.; Grell, M.; Krammer, P.H. Cell surface sialylation plays a role in modulating sensitivity towards APO-1-mediated apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 1995, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Swindall, A.F.; Kesterson, R.A.; Schoeb, T.R.; Bullard, D.C.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I regulates macrophage apoptosis via alpha2-6 sialylation of the TNFR1 death receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39654–39662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swindall, A.F.; Bellis, S.L. Sialylation of the Fas death receptor by ST6Gal-I provides protection against Fas-mediated apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22982–22990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdbrooks, A.T.; Britain, C.M.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cancer cell survival via sialylation of the TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) death receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Song, Y.K.; Song, J.J.; Siervo-Sassi, R.R.; Kim, H.R.; Li, L.; Spitz, D.R.; Lokshin, A.; Kim, J.H. Reconstitution of galectin-3 alters glutathione content and potentiates TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity by dephosphorylation of Akt. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 288, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, N.; Nakahara, S.; Takenaka, Y.; Fukumori, T.; Hogan, V.; Kanayama, H.O.; Yanagawa, T.; Raz, A. Galectin-3 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by activating Akt in human bladder carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7546–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.I.; Whang, E.E.; Abramson, M.A.; Donner, D.B.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Moore, F.D., Jr.; Ruan, D.T. Galectin-3 regulates apoptosis and doxorubicin chemoresistance in papillary thyroid cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, N.; Byrd, J.C.; Sun, Y.; Ueno, S.; Bresalier, R.S. A galectin-3 sequence polymorphism confers TRAIL sensitivity to human breast cancer cells. Cancer 2011, 117, 4375–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, N.; Byrd, J.C.; Sun, Y.; Hafley, M.; Ramirez, K.; Burks, J.; Bresalier, R.S. Cell-surface galectin-3 confers resistance to TRAIL by impeding trafficking of death receptors in metastatic colon adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksida, T.; Nikolic, I.; Vujicic, M.; Nilsson, U.J.; Leffler, H.; Lukic, M.L.; Stojanovic, I.; Stosic-Grujicic, S. Galectin-3 deficiency protects pancreatic islet cells from cytokine-triggered apoptosis in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, R.R.; Yu, Z.J.; Liang, H.; Shen, S.; Kan, Q. Galectin-1 Modulates the Survival and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Sensitivity in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2015, 30, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Oh, Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, Y.K. DR4-Ser424 O-GlcNAcylation Promotes Sensitization of TRAIL-Tolerant Persisters and TRAIL-Resistant Cancer Cells to Death. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2839–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Z.; Xu, F.; Yuan, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, X.; McDonald, J.M.; Chen, Y. Regulation of pancreatic cancer TRAIL resistance by protein O-GlcNAcylation. Lab. Investig. ; A J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2020, 100, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Pan, X.; Peng, T.; Duan, M.; Du, L.; Zhuang, X.; Cai, X.; Yi, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, S. Auto Arginine-GlcNAcylation Is Crucial for Bacterial Pathogens in Regulating Host Cell Death. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Hu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, X.; Pan, X.; Li, S. Arg-GlcNAcylation on TRADD by NleB and SseK1 Is Crucial for Bacterial Pathogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, L.; Dong, N.; Rong, J.; Gao, W.; Ding, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Pathogen blocks host death receptor signalling by arginine GlcNAcylation of death domains. Nature 2013, 501, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Kim, Y.; Ji, S.; Kim, H.B.; Jung, H.; Yi, E.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Shin, I.; Yang, W.H.; Cho, J.W. O-GlcNAcylation of RIPK1 rescues red blood cells from necroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1160490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossin, A.; Derouet, M.; Abdel-Sater, F.; Hueber, A.O. Palmitoylation of the TRAIL receptor DR4 confers an efficient TRAIL-induced cell death signalling. Biochem. J. 2009, 419, 182, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabandhu, K.; Herincs, Z.; Huault, S.; Dost, B.; Peng, L.; Conchonaud, F.; Marguet, D.; He, H.T.; Hueber, A.O. Palmitoylation is required for efficient Fas cell death signaling. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Tchikov, V.; Schutze, S.; Peter, M.E. Palmitoylation of CD95 facilitates formation of SDS-stable receptor aggregates that initiate apoptosis signaling. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossin, A.; Durivault, J.; Chakhtoura-Feghali, T.; Lounnas, N.; Gagnoux-Palacios, L.; Hueber, A.O. Fas palmitoylation by the palmitoyl acyltransferase DHHC7 regulates Fas stability. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingler, P.; Sarchen, V.; Glatter, T.; Caning, L.; Saggau, C.; Kathayat, R.S.; Dickinson, B.C.; Adam, D.; Schneider-Brachert, W.; Schutze, S.; et al. Palmitoylation is required for TNF-R1 signaling. Cell Commun. Signal 2019, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anel, A.; Bosque, A.; Naval, J.; Pineiro, A.; Larrad, L.; Alava, M.A.; Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J. Apo2L/TRAIL and immune regulation. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, F.; Bernardi, S.; Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P.; Fabris, B. TRAIL modulates the immune system and protects against the development of diabetes. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 680749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sag, D.; Ayyildiz, Z.O.; Gunalp, S.; Wingender, G. The Role of TRAIL/DRs in the Modulation of Immune Cells and Responses. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaletto, C.; Munafo, A.; Di Benedetto, G.; De Francisci, C.; Caraci, F.; Di Mauro, R.; Bucolo, C.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. The immune system on the TRAIL of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Alves, L.; Corazza, N.; Micheau, O.; Krebs, P. The multifaceted role of TRAIL signaling in cancer and immunity. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 5530–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harith, H.H.; Morris, M.J.; Kavurma, M.M. On the TRAIL of obesity and diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remuzgo-Martinez, S.; Genre, F.; Lopez-Mejias, R.; Ubilla, B.; Mijares, V.; Pina, T.; Corrales, A.; Blanco, R.; Martin, J.; Llorca, J.; et al. Expression of osteoprotegerin and its ligands, RANKL and TRAIL, in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fang, Y.; Tu, S.; Chen, H.; Shao, A. Insight into the divergent role of TRAIL in non-neoplastic neurological diseases. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11070–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, E.; Patil, M.S.; Patel, S.; Cartland, S.P.; Kavurma, M.M. The Prognostic, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic Potential of TRAIL Signalling in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosque, A.; Pardo, J.; Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J.; Lasierra, P.; Larrad, L.; Marzo, I.; Naval, J.; Anel, A. Human CD8+ T cell blasts are more sensitive than CD4+ T cell blasts to regulation by APO2L/TRAIL. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Nakayama, M.; Eto, H.; Okumura, K.; Yagita, H. Type I interferons (IFNs) regulate tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression on human T cells: A novel mechanism for the antitumor effects of type I IFNs. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badovinac, V.P.; Messingham, K.A.; Griffith, T.S.; Harty, J.T. TRAIL deficiency delays, but does not prevent, erosion in the quality of “helpless” memory CD8 T cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.M.; Droin, N.M.; Lemmens, E.E.; Pinkoski, M.J.; Bensinger, S.J.; Ehst, B.D.; Griffith, T.S.; Green, D.R.; Schoenberger, S.P. CD4+ T-cell help controls CD8+ T-cell memory via TRAIL-mediated activation-induced cell death. Nature 2005, 434, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, J.A.; Bevan, M.J. TRAIL deficiency does not rescue impaired CD8+ T cell memory generated in the absence of CD4+ T cell help. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4570–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkers, M.C.; Gerlach, C.; Arens, R.; Janssen, E.M.; Fitzgerald, P.; Schumacher, T.N.; Medema, J.P.; Green, D.R.; Schoenberger, S.P. Nab2 regulates secondary CD8+ T-cell responses through control of TRAIL expression. Blood 2012, 119, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Zhang, L.Y.; Devadas, S.; Li, L.; Keegan, A.D.; Shi, Y.F. Reciprocal expression of TRAIL and CD95L in Th1 and Th2 cells: role of apoptosis in T helper subset differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Lorenzo, M.J.; Alava, M.A.; Gamen, S.; Kim, K.J.; Chuntharapai, A.; Pineiro, A.; Naval, J.; Anel, A. Involvement of APO2 ligand/TRAIL in activation-induced death of Jurkat and human peripheral blood T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2714–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.E.; Wolkers, M.C.; Schoenberger, S.P.; Jameson, S.C. The generation of protective memory-like CD8+ T cells during homeostatic proliferation requires CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedger, L.M.; Katewa, A.; Pettersen, A.K.; Osvath, S.R.; Farrell, G.C.; Stewart, G.J.; Bendall, L.J.; Alexander, S.I. Extreme lymphoproliferative disease and fatal autoimmune thrombocytopenia in FasL- and TRAIL-double deficient mice. Blood 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Smyth, M.J.; Kayagaki, N.; Yamaguchi, N.; Kakuta, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in surveillance of tumor metastasis by liver natural killer cells. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, J.M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wu, G.S. The Role of TRAIL in Apoptosis and Immunosurveillance in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaperot, L.; Blum, A.; Manches, O.; Lui, G.; Angel, J.; Molens, J.P.; Plumas, J. Virus or TLR agonists induce TRAIL-mediated cytotoxic activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, T.S.; Brincks, E.L.; Gurung, P.; Kucaba, T.A.; Ferguson, T.A. Systemic immunological tolerance to ocular antigens is mediated by TRAIL-expressing CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.A.; Ni, J.; Pan, G.; Ruben, S.M.; Wei, Y.F.; Pace, J.L.; Hunt, J.S. TRAIL (Apo-2L) and TRAIL receptors in human placentas: implications for immune privilege. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6053–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, A.K.; Sattler, A.; Hahn, E.M.; Hering, N.A.; Arndt, M.; Lauscher, J.C.; Speichinger-Hillenberg, F.; Kotsch, K.; Berg, A.K.; Beyer, K. Immune Phenotypic Characterization of a TRAIL-Knockout Mouse. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacher, M.; Schmidleithner, L.; Simon, M.; Stuve, P.; Sanderink, L.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Wuttke, M.; Schambeck, K.; Ruhland, B.; Hofmann, V.; et al. The effector program of human CD8 T cells supports tissue remodeling. J. Exp. Med. 2024, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyuan, I.T.; Tsai, H.F.; Wu, C.S.; Hsu, P.N. TRAIL suppresses gut inflammation and inhibits colitogeic T-cell activation in experimental colitis via an apoptosis-independent pathway. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyuan, I.T.; Tsai, H.F.; Liao, H.J.; Wu, C.S.; Hsu, P.N. An apoptosis-independent role of TRAIL in suppressing joint inflammation and inhibiting T-cell activation in inflammatory arthritis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Chen, Y.; Goke, R.; Wilmen, A.; Seidel, C.; Goke, A.; Hilliard, B.; Chen, Y. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is an inhibitor of autoimmune inflammation and cell cycle progression. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyuan, I.T.; Hsu, P.N. TRAIL regulates T cell activation and suppresses inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Cao, Z.; Wolf, J.M.; Van Antwerp, M.; Baker, J.R., Jr. Death ligand tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand inhibits experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4721–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Seol, D.W.; Mi, Z.; Robbins, P.D. Intra-articular injection of recombinant TRAIL induces synovial apoptosis and reduces inflammation in a rabbit knee model of arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Hirata, S.; Fukushima, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Ito, T.; Uchino, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Senju, S. Dual effects of TRAIL in suppression of autoimmunity: the inhibition of Th1 cells and the promotion of regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5259–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretney, E.; McQualter, J.L.; Kayagaki, N.; Yagita, H.; Bernard, C.C.; Grewal, I.S.; Ashkenazi, A.; Smyth, M.J. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/Apo2L suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2005, 83, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibaldi, A.; Walczak, H. Death Receptors and Their Ligands in Inflammatory Disease and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, E.E.; Marriott, H.M.; Lawrie, A.; Francis, S.E.; Sabroe, I.; Renshaw, S.A.; Dockrell, D.H.; Whyte, M.K. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) regulates inflammatory neutrophil apoptosis and enhances resolution of inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, S.; Rehkamper, C.; Ferring-Schmitt, S.; Bieber, T.; Tuting, T.; Wenzel, J. Interferon-alpha stimulates TRAIL expression in human keratinocytes and peripheral blood mononuclear cells: implications for the pathogenesis of cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Cudrici, C.; Zernetkina, V.; Niculescu, F.; Rus, H.; Drachenberg, C.; Rus, V. TRAIL, DR4 and DR5 are upregulated in kidneys from patients with lupus nephritis and exert proliferative and proinflammatory effects. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 132, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, I.; Simon, H.U. Alternative functions for TRAIL receptors in eosinophils and neutrophils. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2001, 131, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, N.M.; Zangrilli, J.G.; Steplewski, A.; Hastie, A.; Lindemeyer, R.G.; Planeta, M.A.; Smith, M.K.; Innocent, N.; Musani, A.; Pascual, R.; et al. Differential expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in allergic asthmatics following segmental antigen challenge: evidence for a role of TRAIL in eosinophil survival. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 5986–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckmann, M.; Collison, A.; Simpson, J.L.; Kopp, M.V.; Wark, P.A.; Smyth, M.J.; Yagita, H.; Matthaei, K.I.; Hansbro, N.; Whitehead, B.; et al. Critical link between TRAIL and CCL20 for the activation of TH2 cells and the expression of allergic airway disease. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckmann, M.; Kopp, M.V.; Heinzmann, A.; Mattes, J. Haplotypes covering the TNFSF10 gene are associated with bronchial asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22 Pt 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauli, G.; Pandolfi, A.; Gonelli, A.; Di Pietro, R.; Guarnieri, S.; Ciabattoni, G.; Rana, R.; Vitale, M.; Secchiero, P. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) sequentially upregulates nitric oxide and prostanoid production in primary human endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchiero, P.; Gonelli, A.; Carnevale, E.; Corallini, F.; Rizzardi, C.; Zacchigna, S.; Melato, M.; Zauli, G. Evidence for a proangiogenic activity of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Neoplasia (New York N.Y 2004, 6, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartland, S.P.; Genner, S.W.; Zahoor, A.; Kavurma, M.M. Comparative Evaluation of TRAIL, FGF-2 and VEGF-A-Induced Angiogenesis In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavurma, M.M.; Schoppet, M.; Bobryshev, Y.V.; Khachigian, L.M.; Bennett, M.R. TRAIL stimulates proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells via activation of NF-kappaB and induction of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7754–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Choi, Y.K.; Choe, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Moon, H.E.; Kim, K.W.; Koh, G.Y.; Lee, H.; et al. TRAIL negatively regulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis via caspase-8-mediated enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions. Angiogenesis 2014, 17, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolo, B.A.; Cartland, S.P.; Prado-Lourenco, L.; Griffith, T.S.; Gentile, C.; Ravindran, J.; Azahri, N.S.; Thai, T.; Yeung, A.W.; Thomas, S.R.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Promotes Angiogenesis and Ischemia-Induced Neovascularization Via NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) and Nitric Oxide-Dependent Mechanisms. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, M.L.; Tsai, H.F.; Wu, Y.Y.; Hwa, H.L.; Lee, B.H.; Hsu, P.N. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces osteoclast differentiation from monocyte/macrophage lineage precursor cells. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambandam, Y.; Baird, K.L.; Stroebel, M.; Kowal, E.; Balasubramanian, S.; Reddy, S.V. Microgravity Induction of TRAIL Expression in Preosteoclast Cells Enhances Osteoclast Differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer-Prokop, M.; O’Flaherty, J.; Ross, J.A.; Weyman, C.M. Non-canonical role for the TRAIL receptor DR5/FADD/caspase pathway in the regulation of MyoD expression and skeletal myoblast differentiation. Differentiation 2009, 78, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.L.; Lee, T.A.; Tsai, T.L.; Lin, W.W. TRAIL-induced keratinocyte differentiation requires caspase activation and p63 expression. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, V.; Funcke, J.B.; Keuper, M.; Abd El Hay, M.; Debatin, K.M.; Wabitsch, M.; Fischer-Posovszky, P. TRAIL (TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) inhibits human adipocyte differentiation via caspase-mediated downregulation of adipogenic transcription factors. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, S.H.; Arnold, N.D.; Pickworth, J.A.; Francis, S.E.; Lawrie, A. TRAIL Deficient Mice Are Protected from Sugen/Hypoxia Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Diseases 2014, 2, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.G.; Arnold, N.D.; Chamberlain, J.; Pickworth, J.A.; Paiva, C.; Dawson, S.; Cross, S.; Long, L.; Zhao, L.; Morrell, N.W.; et al. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) reverses experimental pulmonary hypertension. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1919–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, E.; Lu, X.; Zuo, C.; He, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Lv, A. Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Correlate with the Severity of Pulmonary Hypertension. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchiero, P.; Zerbinati, C.; Rimondi, E.; Corallini, F.; Milani, D.; Grill, V.; Forti, G.; Capitani, S.; Zauli, G. TRAIL promotes the survival, migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secchiero, P.; Gonelli, A.; Carnevale, E.; Milani, D.; Pandolfi, A.; Zella, D.; Zauli, G. TRAIL promotes the survival and proliferation of primary human vascular endothelial cells by activating the Akt and ERK pathways. Circulation 2003, 107, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Choi, K.; Ryu, S.W.; Kang, S.W.; Choi, C. TRAIL promotes caspase-dependent pro-inflammatory responses via PKCdelta activation by vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, M.A.; Thomas, T.P.; Grisanti, L.A. Death receptor 5 contributes to cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2019, 136, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Wang, H.C.; Wu, S.J.; Hong, C.J.; Cheng, I.H. Alterations of the Neuroinflammatory Markers IL-6 and TRAIL in Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2015, 5, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, D.; Ferrari-Toninelli, G.; Bonini, S.A.; Sarnico, I.; Benarese, M.; Pizzi, M.; Benussi, L.; Ghidoni, R.; Binetti, G.; Spano, P.; et al. Blockade of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand death receptor DR5 prevents beta-amyloid neurotoxicity. Neuropsychopharmacol. : Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 32, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, D. A new TRAIL in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Brain 2015, 138 Pt 1, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, S.; Ghiso, J.; Rostagno, A. TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5 mediate cerebral microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis induced by oligomeric Alzheimer’s Abeta. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarella, G.; Di Benedetto, G.; Puzzo, D.; Privitera, L.; Loreto, C.; Saccone, S.; Giunta, S.; Palmeri, A.; Bernardini, R. Neutralization of TNFSF10 ameliorates functional outcome in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2015, 138 Pt 1, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartland, S.P.; Harith, H.H.; Genner, S.W.; Dang, L.; Cogger, V.C.; Vellozzi, M.; Di Bartolo, B.A.; Thomas, S.R.; Adams, L.A.; Kavurma, M.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, vascular inflammation and insulin resistance are exacerbated by TRAIL deletion in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Shin, E.; Bae, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Cha, B.S. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor protects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice by targeting TRAIL receptor-mediated lipoapoptosis via modulating hepatic dipeptidyl peptidase-4 expression. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsova, P.; Weng, P.; Salim, W.; Bronk, S.F.; Griffith, T.S.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Gores, G.J. TRAIL Deletion Prevents Liver, but Not Adipose Tissue, Inflammation during Murine Diet-Induced Obesity. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.J.; Wang, P.; Tsabary, G.; Chen, Y.H. Critical roles of TRAIL in hepatic cell death and hepatic inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 113, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, H. Death receptor-ligand systems in cancer, cell death, and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, M.L.; Hsu, P.N.; Liao, H.J.; Lee, B.H.; Tsai, H.F. TRAF-6 dependent signaling pathway is essential for TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces osteoclast differentiation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e38048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.; Prado-Lourenco, L.; Khachigian, L.M.; Bennett, M.R.; Di Bartolo, B.A.; Kavurma, M.M. TRAIL promotes VSMC proliferation and neointima formation in a FGF-2-, Sp1 phosphorylation-, and NFkappaB-dependent manner. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluis, J.M.; Nachbur, U.; Cook, W.D.; Gentle, I.E.; Moujalled, D.; Moulin, M.; Wong, W.W.; Khan, N.; Chau, D.; Callus, B.A.; et al. TAK1 is required for survival of mouse fibroblasts treated with TRAIL, and does so by NF-kappaB dependent induction of cFLIPL. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azijli, K.; Weyhenmeyer, B.; Peters, G.J.; de Jong, S.; Kruyt, F.A. Non-canonical kinase signaling by the death ligand TRAIL in cancer cells: discord in the death receptor family. Cell Death Differ. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekkat, N.; Lombardo, C.M.; Seguin, C.; Lechner, M.C.; Dufour, F.; Nomine, Y.; De Giorgi, M.; Frisch, B.; Micheau, O.; Guichard, G.; et al. Relationship between the agonist activity of synthetic ligands of TRAIL-R2 and their cell surface binding modes. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 15566–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasekharan, S.P.; Koc, M.; Morizot, A.; Micheau, O.; Sorensen, P.H.; Gaide, O.; Andera, L.; Martinou, J.C. TRAIL promotes membrane blebbing, detachment and migration of cells displaying a dysfunctional intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsche, H.; Heilmann, T.; Tower, R.J.; Hauser, C.; von Au, A.; El-Sheikh, D.; Campbell, G.M.; Alp, G.; Schewe, D.; Hubner, S.; et al. TRAIL-R2 promotes skeletal metastasis in a breast cancer xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9502–9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilimanovich, U.; Bumbasirevic, V. TRAIL induces proliferation of human glioma cells by c-FLIPL-mediated activation of ERK1/2. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qin, G.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Wu, P.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, X.; et al. TRAIL promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inducing PD-L1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. : CR 2021, 40, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.M.; Eby, M.; Jasmin, A.; Bookwalter, A.; Murray, J.; Hood, L. Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity 1997, 7, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, I.; Debatin, K.M. TRAIL induces apoptosis and activation of NFkappaB. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1998, 9, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, L.M.; Fox, J.P.; Higgins, C.A.; Majkut, J.; Sessler, T.; McLaughlin, K.; McCann, C.; Roberts, J.Z.; Crawford, N.T.; McDade, S.S.; et al. A revised model of TRAIL-R2 DISC assembly explains how FLIP(L) can inhibit or promote apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, M.; Harper, N.; Snowden, R.T.; Dyer, M.J.; Barnett, G.A.; Pringle, J.H.; Cohen, G.M. Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary B cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6809–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullsack, S.; Rosenthal, A.; Wajant, H.; Siegmund, D. Redundant and receptor-specific activities of TRADD, RIPK1 and FADD in death receptor signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Dang, T.; Che, N.; Yu, H.; Chai, J.; Chen, W. Esophageal cancer cells convert the death signal from TRAIL into a stimulus for survival during acid/bile exposure. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Pobezinskaya, Y.L.; Morgan, M.J.; Liu, Z.G. The role of TRADD in TRAIL-induced apoptosis and signaling. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafont, E.; Kantari-Mimoun, C.; Draber, P.; De Miguel, D.; Hartwig, T.; Reichert, M.; Kupka, S.; Shimizu, Y.; Taraborrelli, L.; Spit, M.; et al. The linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex regulates TRAIL-induced gene activation and cell death. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1147–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H. TRAIL- and TNF-induced signaling complexes-so similar yet so different. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, S.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Krainer, M.; Muller, M.; Jilma, B. LUBAC and ABIN-1 Modulate TRAIL-Based NF-kappaB Induction in Human Embryonic Kidney 293 Cells. Biores Open Access 2018, 7, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Blackwell, K.; Workman, L.M.; Chen, S.; Pope, M.R.; Janz, S.; Habelhah, H. RIP1 Cleavage in the Kinase Domain Regulates TRAIL-Induced NF-kappaB Activation and Lymphoma Survival. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 3324–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, N.; Farrow, S.N.; Kaptein, A.; Cohen, G.M.; MacFarlane, M. Modulation of tumor necrosis factor apoptosis-inducing ligand- induced NF-kappa B activation by inhibition of apical caspases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34743–34752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, S.; Stanger, B.Z.; Leder, P. RIP and FADD: two “death domain”-containing proteins can induce apoptosis by convergent, but dissociable, pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1996, 93, 10923–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Devin, A.; Cook, A.; Keane, M.M.; Kelliher, M.; Lipkowitz, S.; Liu, Z.G. The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 6638–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azijli, K.; Yuvaraj, S.; van Roosmalen, I.; Flach, K.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J.; de Jong, S.; Kruyt, F.A. MAPK p38 and JNK have opposing activities on TRAIL-induced apoptosis activation in NSCLC H460 cells that involves RIP1 and caspase-8 and is mediated by Mcl-1. Apoptosis 2013, 18, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. Tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced chemokine release in both TRAIL-resistant and TRAIL-sensitive cells via nuclear factor kappa B. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.G.; Koo, G.B.; Yu, J.W.; Kim, Y.S. TRADD is critical for resistance to TRAIL-induced cell death through NF-kappaB activation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, F.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Moreno-Caceres, J.; Hernandez-Madrigal, M.; Both, D.; Montironi, C.; Puschel, F.; Nadal, E.; Eldering, E.; Munoz-Pinedo, C. TRAIL receptors promote constitutive and inducible IL-8 secretion in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.T.; Yue, P.; Wang, D.; Tong, J.S.; Chen, Z.G.; Khuri, F.R.; Sun, S.Y. Suppression of death receptor 5 enhances cancer cell invasion and metastasis through activation of caspase-8/TRAF2-mediated signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41324–41338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Jeng, J. Coordinated regulation of two TRAIL-R2/KILLER/DR5 mRNA isoforms by DNA damaging agents, serum and 17beta-estradiol in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2000, 61, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y. Understanding the Role of the Death Receptor 5/FADD/caspase-8 Death Signaling in Cancer Metastasis. Mol. Cell Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ganten, T.M.; Sykora, J.; Koschny, R.; Batke, E.; Aulmann, S.; Mansmann, U.; Stremmel, W.; Sinn, H.P.; Walczak, H. Prognostic significance of tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor expression in patients with breast cancer. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macher-Goeppinger, S.; Aulmann, S.; Tagscherer, K.E.; Wagener, N.; Haferkamp, A.; Penzel, R.; Brauckhoff, A.; Hohenfellner, M.; Sykora, J.; Walczak, H.; et al. Prognostic value of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) and TRAIL receptors in renal cell cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlyakhtina, Y.; Pavet, V.; Gronemeyer, H. Dual role of DR5 in death and survival signaling leads to TRAIL resistance in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legler, D.F.; Micheau, O.; Doucey, M.A.; Tschopp, J.; Bron, C. Recruitment of TNF receptor 1 to lipid rafts is essential for TNFalpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Immunity 2003, 18, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, W.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, C. Redistribution of DR4 and DR5 in lipid rafts accounts for the sensitivity to TRAIL in NSCLC cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, M.; Ascione, B.; Ciarlo, L.; Vona, R.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Gianni, A.M.; Locatelli, S.L.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Malorni, W.; et al. Constitutive localization of DR4 in lipid rafts is mandatory for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in B-cell hematologic malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellail, A.C.; Tse, M.C.; Song, J.H.; Phuphanich, S.; Olson, J.J.; Sun, S.Y.; Hao, C. DR5-mediated DISC controls caspase-8 cleavage and initiation of apoptosis in human glioblastomas. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14 (6A), 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.C.; Duong, H.Q.; Choi, J.E.; Lee, T.B.; Kang, J.H.; Oh, S.H.; Han, S.I. Lipid raft-dependent death receptor 5 (DR5) expression and activation are critical for ursodeoxycholic acid-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmas, D.; Rébé, C.; Micheau, O.; Athias, A.; Gambert, P.; Grazide, S.; laurent, G.; Latruffe, N.; Solary, E. Redistribution of CD95, DR4 and DR5 in rafts accounts for the synergistic toxicity of resveratrol and death receptor ligands in colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8979–8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Tse, M.C.; Bellail, A.; Phuphanich, S.; Khuri, F.; Kneteman, N.M.; Hao, C. Lipid rafts and nonrafts mediate tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic signals in non small cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6946–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, L.S.; Boyd, R.S.; Jukes-Jones, R.; Hughes, M.A.; Robinson, G.L.; Fairall, L.; Schwabe, J.W.; Cain, K.; Macfarlane, M. A death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guegan, J.P.; Ginestier, C.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Ducret, T.; Quignard, J.F.; Vacher, P.; Legembre, P. CD95/Fas and metastatic disease: What does not kill you makes you stronger. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppidi, J.R.; Siegel, R.M. Ligand-independent redistribution of Fas (CD95) into lipid rafts mediates clonotypic T cell death. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppidi, J.R.; Tschopp, J.; Siegel, R.M. Life and death decisions: secondary complexes and lipid rafts in TNF receptor family signal transduction. Immunity 2004, 21, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.M.; Muppidi, J.R.; Sarker, M.; Lobito, A.; Jen, M.; Martin, D.; Straus, S.E.; Lenardo, M.J. SPOTS: signaling protein oligomeric transduction structures are early mediators of death receptor-induced apoptosis at the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 167, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponton, A.; Clement, M.V.; Stamenkovic, I. The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor activates NF-kappaB independently of its cytotoxic function. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8991–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzin, S.; Chaigne-Delalande, B.; Selva, E.; Khadra, N.; Daburon, S.; Contin-Bordes, C.; Blanco, P.; Le Seyec, J.; Ducret, T.; Counillon, L.; et al. The naturally processed CD95L elicits a c-yes/calcium/PI3K-driven cell migration pathway. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malleter, M.; Tauzin, S.; Bessede, A.; Castellano, R.; Goubard, A.; Godey, F.; Leveque, J.; Jezequel, P.; Campion, L.; Campone, M.; et al. CD95L cell surface cleavage triggers a prometastatic signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6711–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monet, M.; Poet, M.; Tauzin, S.; Fouque, A.; Cophignon, A.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Vacher, P.; Legembre, P.; Counillon, L. The cleaved FAS ligand activates the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1 through Akt/ROCK1 to stimulate cell motility. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.R.; Thomsen, A.R.; Frevert, C.W.; Pham, U.; Skerrett, S.J.; Kiener, P.A.; Liles, W.C. Fas (CD95) induces proinflammatory cytokine responses by human monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 6209–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Piguet, V.; Valzasina, B.; Lens, S.; Zubler, R.; French, L.; Kindler, V.; Tschopp, J.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Fas engagement induces the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs), the release of interleukin (IL)-1beta, and the production of interferon gamma in the absence of IL-12 during DC-T cell cognate interaction: a new role for Fas ligand in inflammatory responses. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauzold, A.; Roder, C.; Sipos, B.; Karsten, K.; Arlt, A.; Jiang, P.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Siegmund, D.; Muerkoster, S.; Pagerols-Raluy, L.; et al. CD95 and TRAF2 promote invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steller, E.J.; Ritsma, L.; Raats, D.A.; Hoogwater, F.J.; Emmink, B.L.; Govaert, K.M.; Laoukili, J.; Rinkes, I.H.; van Rheenen, J.; Kranenburg, O. The death receptor CD95 activates the cofilin pathway to stimulate tumour cell invasion. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, W.; Lee, C.T.; Desbarats, J. A novel juxtamembrane domain in tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily molecules activates Rac1 and controls neurite growth. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3192–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, X.; Che, X.; Guo, T.; Li, C.; Ma, R.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hou, K.; et al. DR5-Cbl-b/c-Cbl-TRAF2 complex inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis by promoting TRAF2-mediated polyubiquitination of caspase-8 in gastric cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 1733–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalvez, F.; Lawrence, D.; Yang, B.; Yee, S.; Pitti, R.; Marsters, S.; Pham, V.C.; Stephan, J.P.; Lill, J.; Ashkenazi, A. TRAF2 Sets a threshold for extrinsic apoptosis by tagging caspase-8 with a ubiquitin shutoff timer. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Padilla, M.T.; Ren, G.; Gou, X.; Lin, Y. Attenuation of TNFSF10/TRAIL-induced apoptosis by an autophagic survival pathway involving TRAF2- and RIPK1/RIP1-mediated MAPK8/JNK activation. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, T.L.; Emmerich, C.H.; Gerlach, B.; Schmukle, A.C.; Cordier, S.M.; Rieser, E.; Feltham, R.; Vince, J.; Warnken, U.; Wenger, T.; et al. Recruitment of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex stabilizes the TNF-R1 signaling complex and is required for TNF-mediated gene induction. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Budd, R.C.; Holler, N.; Thome, M.; Martinon, F.; Irmler, M.; Burns, K.; Hahne, M.; Kennedy, N.; Kovacsovics, M.; et al. The caspase-8 inhibitor FLIP promotes activation of NF-kappaB and Erk signaling pathways. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, T.; Tschopp, J. N-terminal fragment of c-FLIP(L) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts with TRAF2 and induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Harikumar, K.B.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.; Strub, G.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Maceyka, M.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Kordula, T.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is a missing cofactor for the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAF2. Nature 2010, 465, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Yamada, A.; Katsuta, E.; Aoyagi, T.; Huang, W.C.; Terracina, K.P.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Tsuchida, J.; Yuza, K.; et al. Targeting the SphK1/S1P/S1PR1 Axis That Links Obesity, Chronic Inflammation, and Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noujarede, J.; Carrie, L.; Garcia, V.; Grimont, M.; Eberhardt, A.; Mucher, E.; Genais, M.; Schreuder, A.; Carpentier, S.; Segui, B.; et al. Sphingolipid paracrine signaling impairs keratinocyte adhesion to promote melanoma invasion. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.T.; Yue, P.; Sun, S.Y. DR5 suppression induces sphingosine-1-phosphate-dependent TRAF2 polyubiquitination, leading to activation of JNK/AP-1 and promotion of cancer cell invasion. Cell Commun. Signal 2017, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) induces chemotactic migration of monocytes via a death receptor 4-mediated RhoGTPase pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, A.; Jeong, K.J.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, Y.S. Death receptors 4 and 5 activate Nox1 NADPH oxidase through riboflavin kinase to induce reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptotic cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3313–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, T.; Montinaro, A.; von Karstedt, S.; Sevko, A.; Surinova, S.; Chakravarthy, A.; Taraborrelli, L.; Draber, P.; Lafont, E.; Arce Vargas, F.; et al. The TRAIL-Induced Cancer Secretome Promotes a Tumor-Supportive Immune Microenvironment via CCR2. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhia, B.; Rutten, F.; Nakada, M.; Beaudry, C.; Berens, M.; Kwan, A.; Rutka, J.T. Inhibition of Rho-kinase affects astrocytoma morphology, motility, and invasion through activation of Rac1. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8792–8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustelo, X.R.; Ojeda, V.; Barreira, M.; Sauzeau, V.; Castro-Castro, A. Rac-ing to the plasma membrane: the long and complex work commute of Rac1 during cell signaling. Small GTPases 2012, 3, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miloszewska, J.; Janik, P.; Ostrowski, J. The effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) on calcium (Ca2+) level. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 1991; 39, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Boehning, D.; van Rossum, D.B.; Patterson, R.L.; Snyder, S.H. A peptide inhibitor of cytochrome c/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor binding blocks intrinsic and extrinsic cell death pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2005, 102, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, A.L.; Wang, X.; Stieren, E.S.; Scarbrough, S.G.; Elferink, C.J.; Boehning, D. Requirement of biphasic calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum for Fas-mediated apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 175, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Ouadid-Ahidouch, H.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Remodelling of Ca2+ transport in cancer: how it contributes to cancer hallmarks? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Chen, S.; Hao, J.; Wu, P.; Gu, X.; Wei, H.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J. Roles of calcium signaling in cancer metastasis to bone. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2022, 3, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, N.; Bresson-Bepoldin, L.; Penna, A.; Chaigne-Delalande, B.; Segui, B.; Levade, T.; Vacher, A.M.; Reiffers, J.; Ducret, T.; Moreau, J.F.; et al. CD95 triggers Orai1-mediated localized Ca2+ entry, regulates recruitment of protein kinase C (PKC) beta2, and prevents death-inducing signaling complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2011, 108, 19072–19077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, D.; Lang, I.; Wajant, H. Cell death-independent activities of the death receptors CD95, TRAILR1, and TRAILR2. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1131–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.R.; Chen, P.H.; Bendris, N.; Schmid, S.L. TRAIL-death receptor endocytosis and apoptosis are selectively regulated by dynamin-1 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2017, 114, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiau, K.; Vacher, P.; Micheau, O.; Prouzet-Mauleon, V.; Kroemer, G.; Moosavi, M.A.; Djavaheri-Mergny, M. TRAIL Triggers CRAC-Dependent Calcium Influx and Apoptosis through the Recruitment of Autophagy Proteins to Death-Inducing Signaling Complex. Cells 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.Y.; Lim, S.T.; Cook, W.J.; McDonald, J.M. Calmodulin binding to the Fas death domain. Regulation by Fas activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5661–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Sun, Y.; Nabel, G.J. Regulation of the proinflammatory effects of Fas ligand (CD95L). Science 1998, 282, 1714–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Jing, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; McDonald, J.M.; Chen, Y. Calmodulin mediates Fas-induced FADD-independent survival signaling in pancreatic cancer cells via activation of Src-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 24776–24784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, J.; Agellon, L.B.; Michalak, M. Ca(2+) homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress: An integrated view of calcium signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Chen, C.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, W. Autophagy-related gene 7 (ATG7) and reactive oxygen species/extracellular signal-regulated kinase regulate tetrandrine-induced autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35576–35588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihira, K.; Miki, Y.; Ono, K.; Suzuki, T.; Sasano, H. An inhibition of p62/SQSTM1 caused autophagic cell death of several human carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancy, R.M.; Wang, L.; Schmid, T.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhou, T.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Song, Y. Characterization of the interactions between calmodulin and death receptor 5 in triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. AN INTEGRATED EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL STUDY. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancy, R.M.; Kim, H.; Zhou, T.; Zinn, K.R.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Song, Y. Calmodulin Binding to Death Receptor 5-mediated Death-Inducing Signaling Complex in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, D.; Means, A.R. Calmodulin: a prototypical calcium sensor. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobo, A. The multifunctional role of phospho-calmodulin in pathophysiological processes. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 4011–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Yong, S.; Xu, F.; Zhou, T.; McDonald, J.M.; Chen, Y. Calmodulin antagonists promote TRA-8 therapy of resistant pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25308–25319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminskyy, V.O.; Surova, O.V.; Piskunova, T.; Zborovskaya, I.B.; Tchevkina, E.M.; Andera, L.; Zhivotovsky, B. Upregulation of c-FLIP-short in response to TRAIL promotes survival of NSCLC cells, which could be suppressed by inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cursi, S.; Rufini, A.; Stagni, V.; Condo, I.; Matafora, V.; Bachi, A.; Bonifazi, A.P.; Coppola, L.; Superti-Furga, G.; Testi, R.; et al. Src kinase phosphorylates Caspase-8 on Tyr380: a novel mechanism of apoptosis suppression. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateva, S.R.; Salas, V.; Anguita, E.; Benaim, G.; Villalobo, A. Ca2+/Calmodulin and Apo-Calmodulin Both Bind to and Enhance the Tyrosine Kinase Activity of c-Src. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0128783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pawar, P.; Pan, G.; Ma, L.; Liu, H.; McDonald, J.M. Calmodulin binding to the Fas-mediated death-inducing signaling complex in cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 103, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, T.F.; Samal, A.B.; Bedwell, G.J.; Chen, Y.; Saad, J.S. Structural and biophysical characterization of the interactions between the death domain of Fas receptor and calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21898–21908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, S.; Mielgo, A.; Torres, V.; Teitz, T.; Shields, D.J.; Mikolon, D.; Bogyo, M.; Barila, D.; Lahti, J.M.; Schlaepfer, D.; et al. Caspase-8 association with the focal adhesion complex promotes tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Huangfu, L.; Du, H.; Ji, X.; Xing, X.; Ji, J. Death receptor 5 promotes tumor progression in gastric cancer. FEBS Open Bio 2023, 13, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leithner, K.; Stacher, E.; Wurm, R.; Ploner, F.; Quehenberger, F.; Wohlkoenig, C.; Balint, Z.; Polachova, J.; Olschewski, A.; Samonigg, H.; et al. Nuclear and cytoplasmic death receptor 5 as prognostic factors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2009, 65, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertsch, U.; Roder, C.; Kalthoff, H.; Trauzold, A. Compartmentalization of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptor functions: emerging role of nuclear TRAIL-R2. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Nishina, T.; Nakano, H.; Koyanagi, M.; Takeda, K.; Okumura, K.; Yagita, H. Importin beta1 protein-mediated nuclear localization of death receptor 5 (DR5) limits DR5/tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced cell death of human tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43383–43393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, U.; Adawy, A.; Scharff, E.; Teichmann, P.; Willms, A.; Haselmann, V.; Colmorgen, C.; Lemke, J.; von Karstedt, S.; Fritsch, J.; et al. TRAIL Induces Nuclear Translocation and Chromatin Localization of TRAIL Death Receptors. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselmann, V.; Kurz, A.; Bertsch, U.; Hubner, S.; Olempska-Muller, M.; Fritsch, J.; Hasler, R.; Pickl, A.; Fritsche, H.; Annewanter, F.; et al. Nuclear death receptor TRAIL-R2 inhibits maturation of let-7 and promotes proliferation of pancreatic and other tumor cells. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Shen, H.C.; Rivera Rosado, L.A.; Zhang, Y.; Di, X.; Zhang, B. Mislocalization of death receptors correlates with cellular resistance to their cognate ligands in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Ahmad, R.; Rajabi, H.; Kufe, D. MUC1-C Induces the LIN28B-->LET-7-->HMGA2 Axis to Regulate Self-Renewal in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, W.; Song, J.; Liang, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhu, X.C.; Li, C.; Peng, J.S.; Zheng, J.N. Overexpression of Lin28 inhibits the proliferation, migration and cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis of BGC-823 gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unachukwu, U.; Chada, K.; D’Armiento, J. High Mobility Group AT-Hook 2 (HMGA2) Oncogenicity in Mesenchymal and Epithelial Neoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Powers, J.T.; Einhorn, W.; Hoshida, Y.; Ng, T.L.; Toffanin, S.; O’Sullivan, M.; Lu, J.; Phillips, L.A.; Lockhart, V.L.; et al. Lin28 promotes transformation and is associated with advanced human malignancies. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Shell, S.; Radjabi, A.R.; Schickel, R.; Feig, C.; Boyerinas, B.; Dinulescu, D.M.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. Let-7 prevents early cancer progression by suppressing expression of the embryonic gene HMGA2. Cell Cycle (Georget. Tex. 2007, 6, 2585–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbalaviele, G.; Dunstan, C.R.; Sasaki, A.; Williams, P.J.; Mundy, G.R.; Yoneda, T. E-cadherin expression in human breast cancer cells suppresses the development of osteolytic bone metastases in an experimental metastasis model. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4063–4070. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Behnam Azad, B.; Nimmagadda, S. The intricate role of CXCR4 in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 124, 31–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ni, C.; Chen, W.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Yin, J.; Huang, J.; Qiu, F. Expression of CXCR4 and breast cancer prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Frankenberger, C.A.; Kuo, W.L.; Boelens, M.C.; Eves, E.M.; Cheng, N.; Liang, H.; Li, W.H.; Ishwaran, H.; Minn, A.J.; et al. Signalling pathway for RKIP and Let-7 regulates and predicts metastatic breast cancer. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4500–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Egloff, A.M.; Sen, M.; Grandis, J.R.; Johnson, D.E. Caspase-8 mutations in head and neck cancer confer resistance to death receptor-mediated apoptosis and enhance migration, invasion, and tumor growth. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R.P.; Keller, N.; Barbero, S.; Stupack, D. Caspase-8 as a regulator of tumor cell motility. Curr. Mol. Med. 2014, 14, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, N.; Ozmadenci, D.; Ichim, G.; Stupack, D. Caspase-8 function, and phosphorylation, in cell migration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 82, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, S.; Barila, D.; Mielgo, A.; Stagni, V.; Clair, K.; Stupack, D. Identification of a critical tyrosine residue in caspase 8 that promotes cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13031–13034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contadini, C.; Ferri, A.; Di Martile, M.; Cirotti, C.; Del Bufalo, D.; De Nicola, F.; Pallocca, M.; Fanciulli, M.; Sacco, F.; Donninelli, G.; et al. Caspase-8 as a novel mediator linking Src kinase signaling to enhanced glioblastoma malignancy. Cell Death Differ. 2023, 30, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senft, J.; Helfer, B.; Frisch, S.M. Caspase-8 interacts with the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to regulate cell adhesion and motility. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11505–11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J.; Sondek, J. GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, B.; Boswell, B.C.; Finlay, D.; Cipres, A.; Vuori, K.; Bong Kang, T.; Wallach, D.; Dorfleutner, A.; Lahti, J.M.; Flynn, D.C.; et al. Caspase-8 promotes cell motility and calpain activity under nonapoptotic conditions. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4273–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, Y.G.; Manavathi, B. Focal adhesion dynamics in cellular function and disease. Cell Signal 2021, 85, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzmaier, F.J.; Jean, C.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK in cancer: mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Barron, J.C.; Kostova, I.; Becker, S.; Strebhardt, K. Caspase-8: The double-edged sword. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, B.; Guan, S.; Cheng, W.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hua, Z.C. MiR-7a is an important mediator in Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD)-regulated expression of focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51393–51407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.M.; Rodriguez, Y.A.R.; Jeong, K.; Ahn, E.E.; Lim, S.S. Targeting focal adhesion kinase in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.A.; Mielgo, A.; Barbero, S.; Hsiao, R.; Wilkins, J.A.; Stupack, D.G. Rab5 mediates caspase-8-promoted cell motility and metastasis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, V.A.; Mielgo, A.; Barila, D.; Anderson, D.H.; Stupack, D. Caspase 8 promotes peripheral localization and activation of Rab5. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36280–36289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansalone, C.; Ainsworth, R.I.; Nygaard, G.; Ai, R.; Prideaux, E.B.; Hammaker, D.; Perumal, N.B.; Weichert, K.; Tung, F.; Kodandapani, L.; et al. Caspase-8 Variant G Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Aggressive Behavior. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022, 4, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, C.D.; Pesapane, A.; Formisano, L.; Rosa, R.; D’Amato, V.; Ciciola, P.; Servetto, A.; Marciano, R.; Orsini, R.C.; Monteleone, F.; et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) expression enhances invasion and metastasis in RAS mutated tumors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, T.J.; van Muijen, G.N.; Ruiter, D.J. The plasminogen activation system in tumour invasion and metastasis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 1996, 192, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, V.; Dromard, C.; Rico, A.; Langonne, A.; Gaillard, J.; Guilloton, F.; Casteilla, L.; Sensebe, L. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor interaction with beta1 integrin is required for platelet-derived growth factor-AB-induced human mesenchymal stem/stromal cell migration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarui, T.; Mazar, A.P.; Cines, D.B.; Takada, Y. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (CD87) is a ligand for integrins and mediates cell-cell interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 3983–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiling, J.L.; Byrd, J.C.; Deisz, R.J.; Mizukami, I.F.; Todd, R.F., 3rd; MacDonald, R.G. Binding of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) to the mannose 6-phosphate/insulin-like growth factor II receptor: contrasting interactions of full-length and soluble forms of uPAR. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20628–20637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, C.S.; Kandhukuri, N.; Kondraganti, S.; Gujrati, M.; Olivero, W.C.; Dinh, D.H.; Rao, J.S. RNA interference-mediated simultaneous down-regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and cathepsin B induces caspase-8-mediated apoptosis in SNB19 human glioma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qiu, F.; Liu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhou, P.K.; Wang, Y.; Hua, Z.C. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor regulates apoptotic sensitivity of colon cancer HCT116 cell line to TRAIL via JNK-p53 pathway. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, B.; Darnay, B.; Aggarwal, B.; Dinh, D.H.; Kouraklis, G.; Olivero, W.C.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Glioma cells deficient in urokinase plaminogen activator receptor expression are susceptible to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 4195–4201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, B.; Chen, L.; Ju, Y.; Li, C.; Meng, S. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor inhibits apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer through miR-17/20a suppression of death receptors 4 and 5. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88645–88657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavet, V.; Shlyakhtina, Y.; He, T.; Ceschin, D.G.; Kohonen, P.; Perala, M.; Kallioniemi, O.; Gronemeyer, H. Plasminogen activator urokinase expression reveals TRAIL responsiveness and supports fractional survival of cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.; Mihalcioiu, C.; Rabbani, S.A. Multifaceted Role of the Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) and Its Receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Applications. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Song, J.J. c-Cbl shRNA-expressing adenovirus sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer DU-145 through increases of DR4/5. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; Szczepanski, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; An, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.T.; Alcala, M.A., Jr.; Bartlett, D.L.; Lee, Y.J. c-Cbl-mediated degradation of TRAIL receptors is responsible for the development of the early phase of TRAIL resistance. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Min, K.J.; Choi, K.S.; Kubatka, P.; Kruzliak, P.; Kim, D.E.; Kwon, T.K. Chloroquine enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through up-regulation of DR5 by stabilization of mRNA and protein in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, M.; Pathak, S.K.; Kumawat, K.; Basu, S.; Chatterjee, G.; Pathak, S.; Noguchi, T.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H.; Thien, C.B.; et al. A TNF- and c-Cbl-dependent FLIP(S)-degradation pathway and its function in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced macrophage apoptosis. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; Kim, J.H.; Sun, B.K.; Alcala, M.A., Jr.; Bartlett, D.L.; Lee, Y.J. c-Cbl acts as a mediator of Src-induced activation of the PI3K-Akt signal transduction pathway during TRAIL treatment. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Qu, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y. TRAIL-activated EGFR by Cbl-b-regulated EGFR redistribution in lipid rafts antagonises TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3288–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, D.; Sun, B.K.; Kim, J.H.; Song, J.J. TRAIL/MEKK4/p38/HSP27/Akt survival network is biphasically modulated by the Src/CIN85/c-Cbl complex. Cell Signal 2013, 25, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Hou, K.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sada, K.; Liu, Y. Oxaliplatin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by CBL-regulated death receptor redistribution in lipid rafts. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
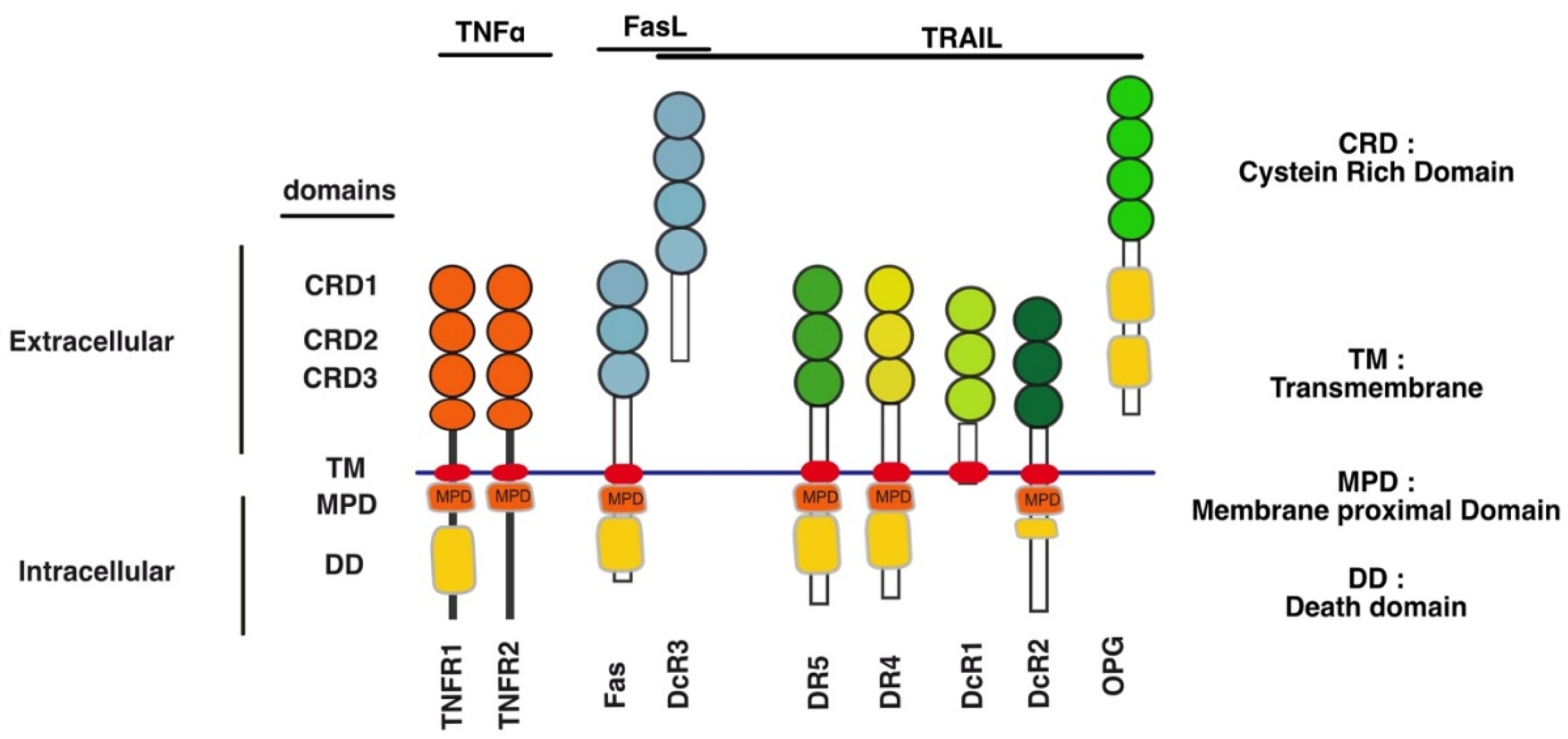
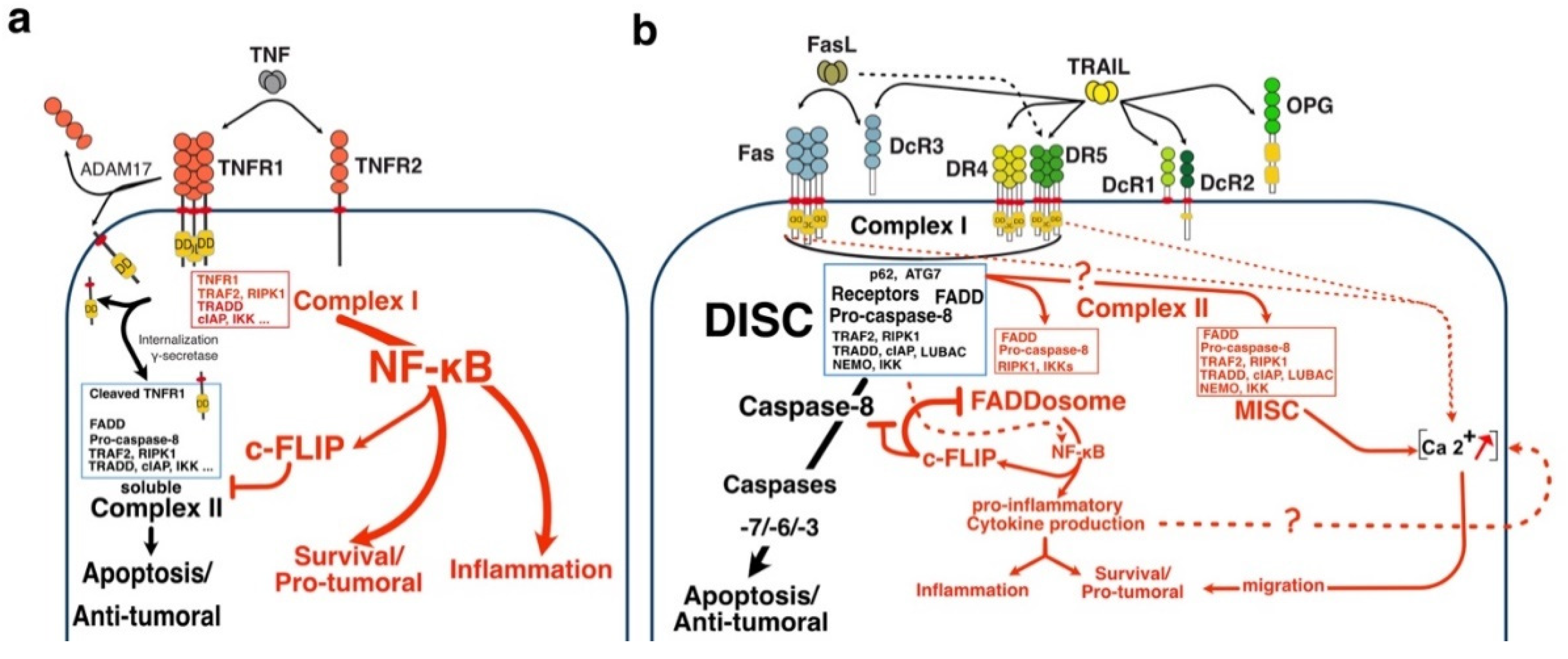
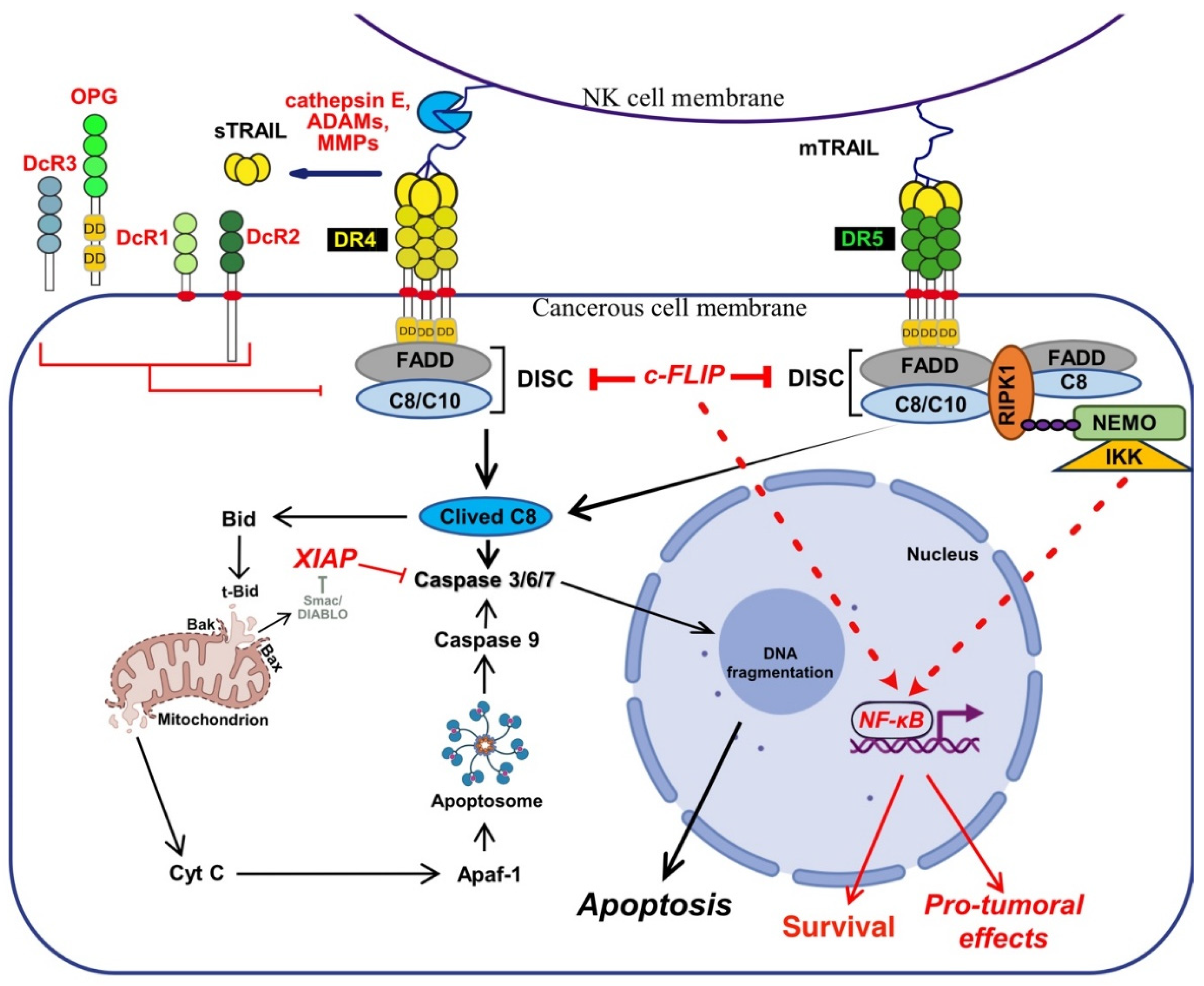
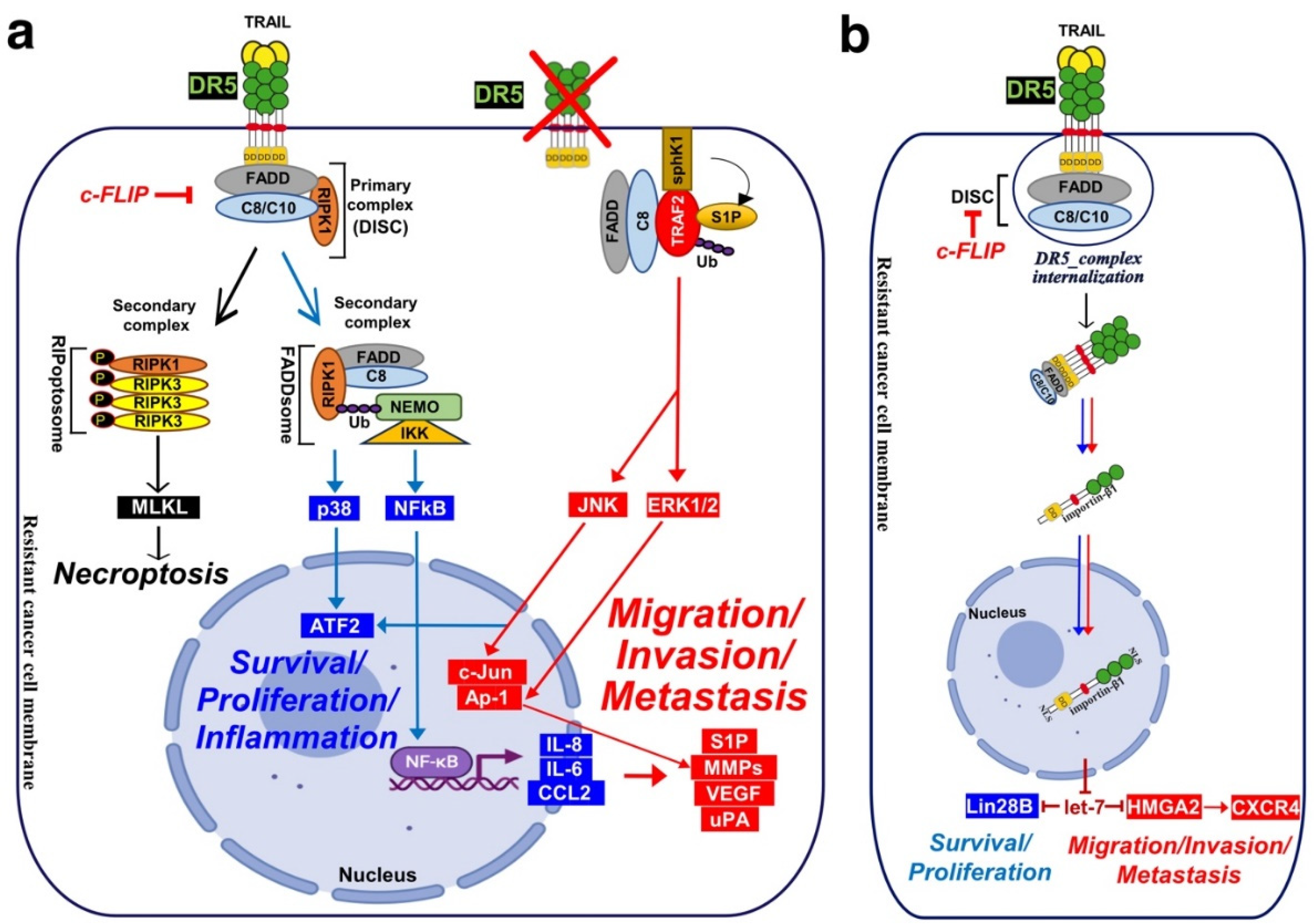
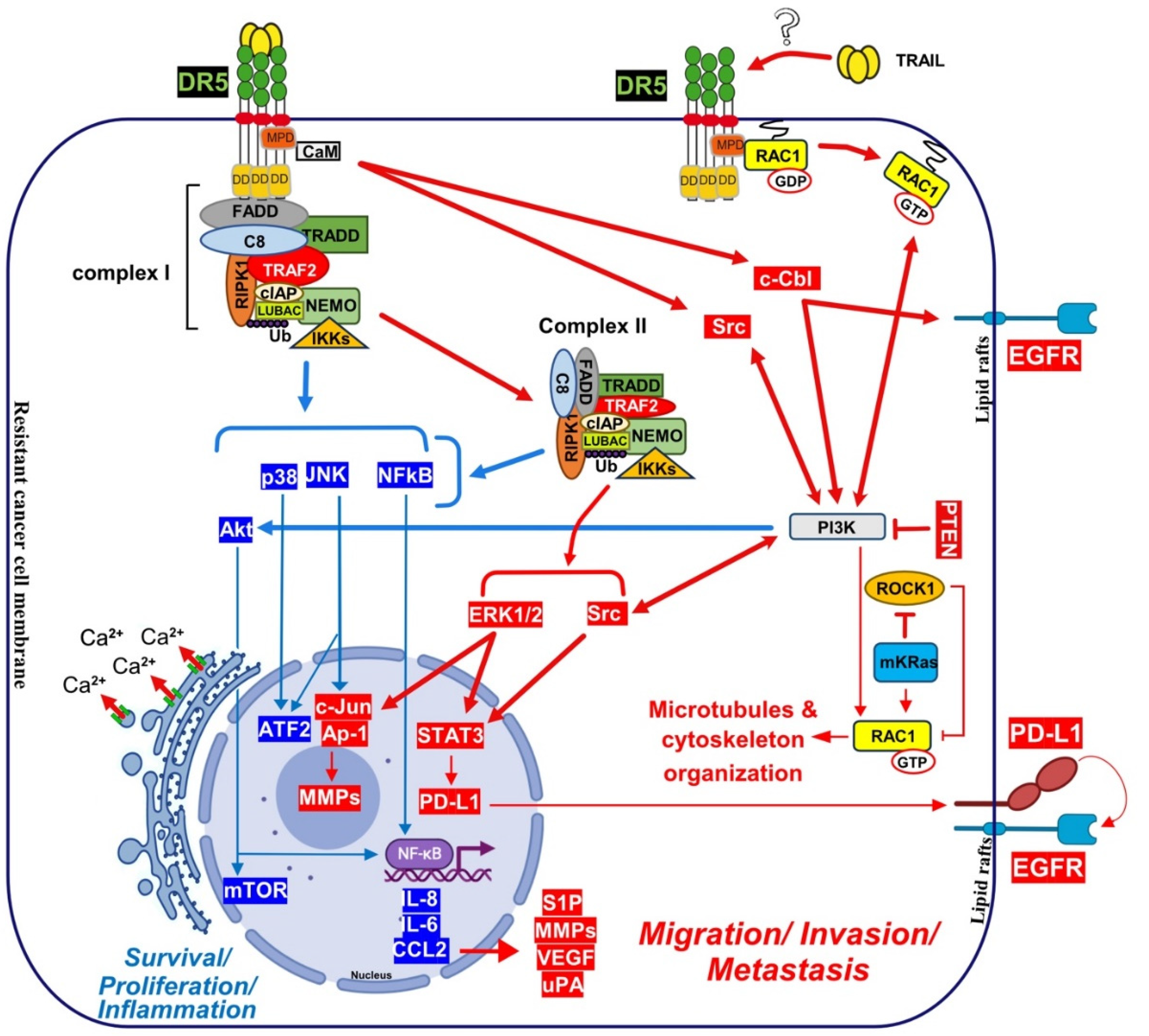
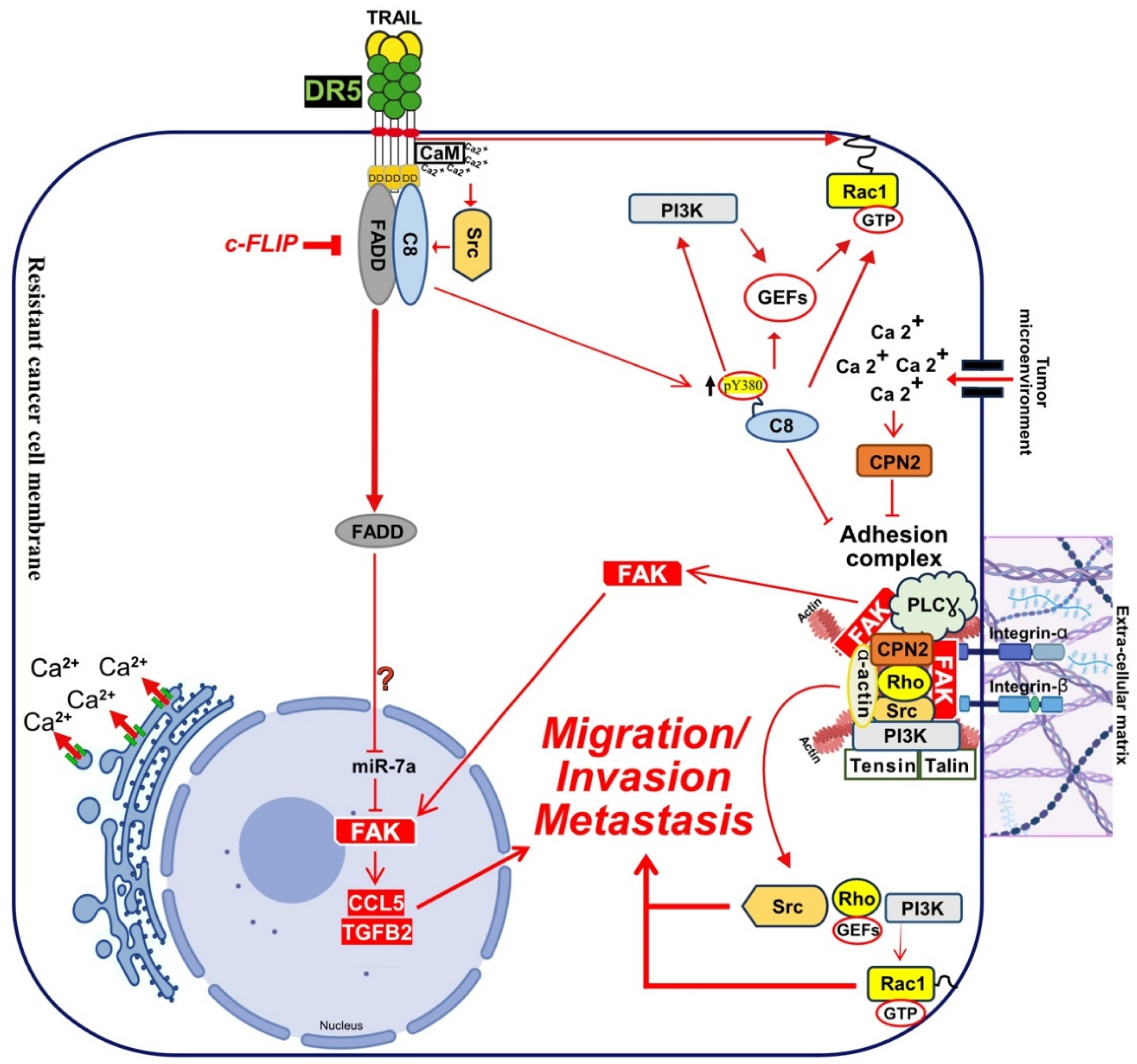
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




