Submitted:
07 February 2024
Posted:
08 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PGA-K
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Groups
2.4. Evaluation of Biomarkers in Serum
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
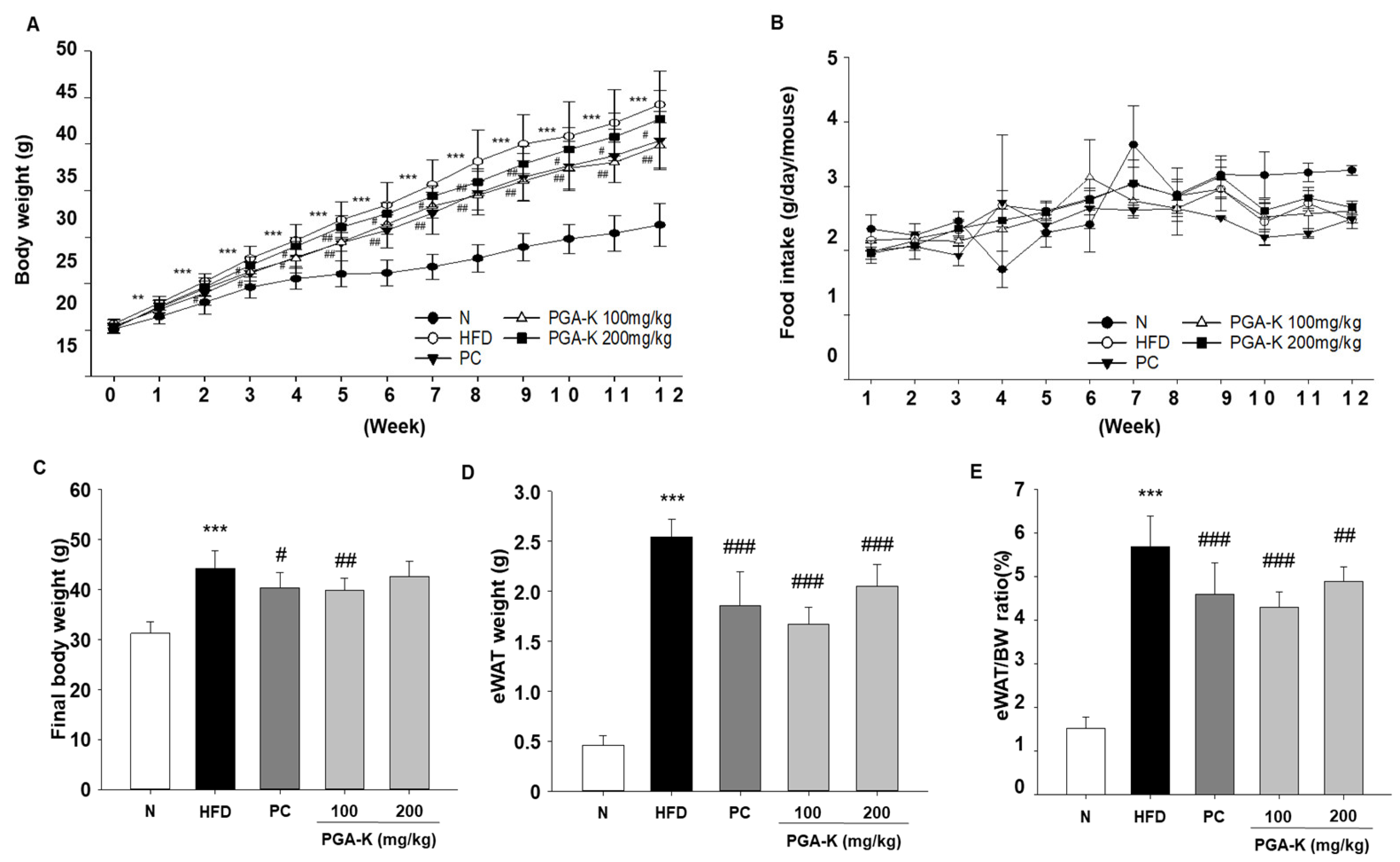
3.1. Effects of PGA-K Administration on Body Weight and Food Intake in HFD-Fed Mice
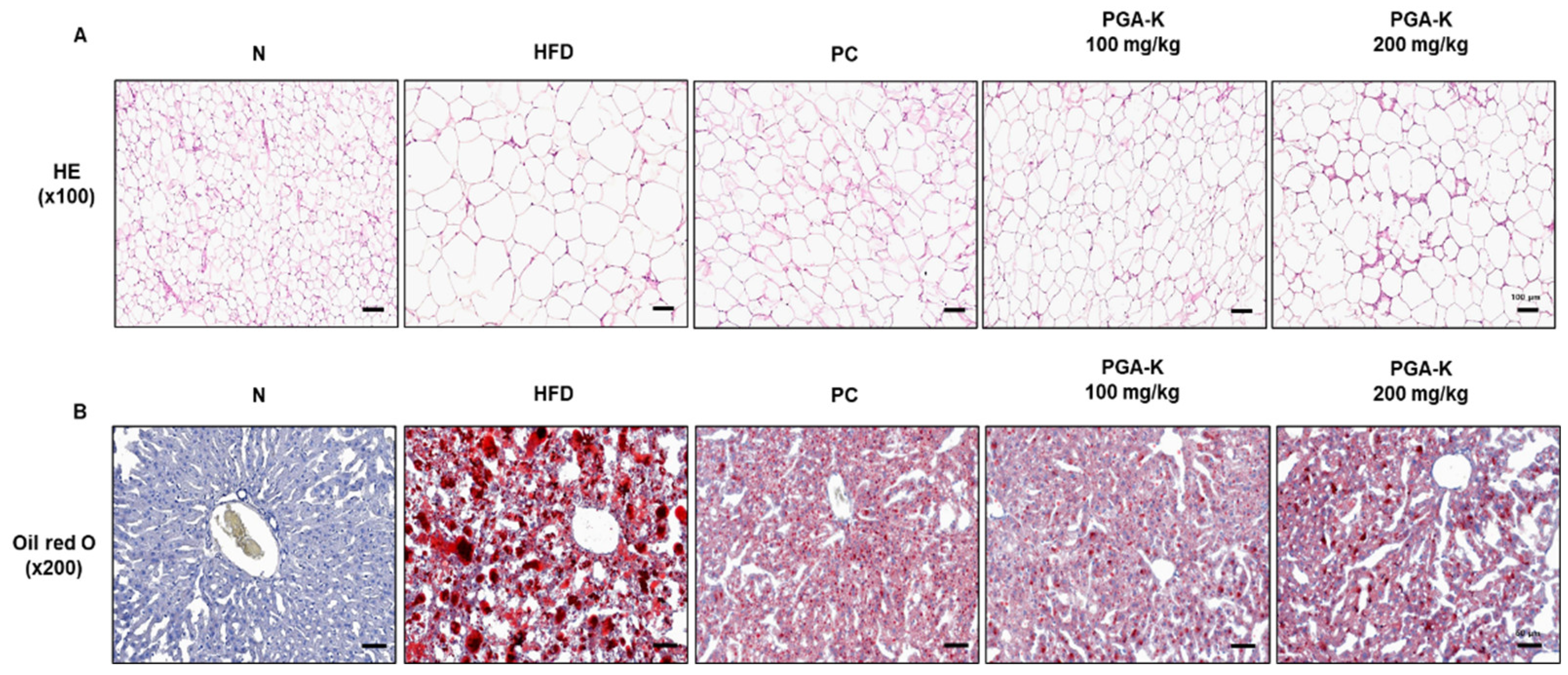
3.2. PGA-K Prevents Adipogenesis and Lipid Accumulation in HFD-Fed Mice
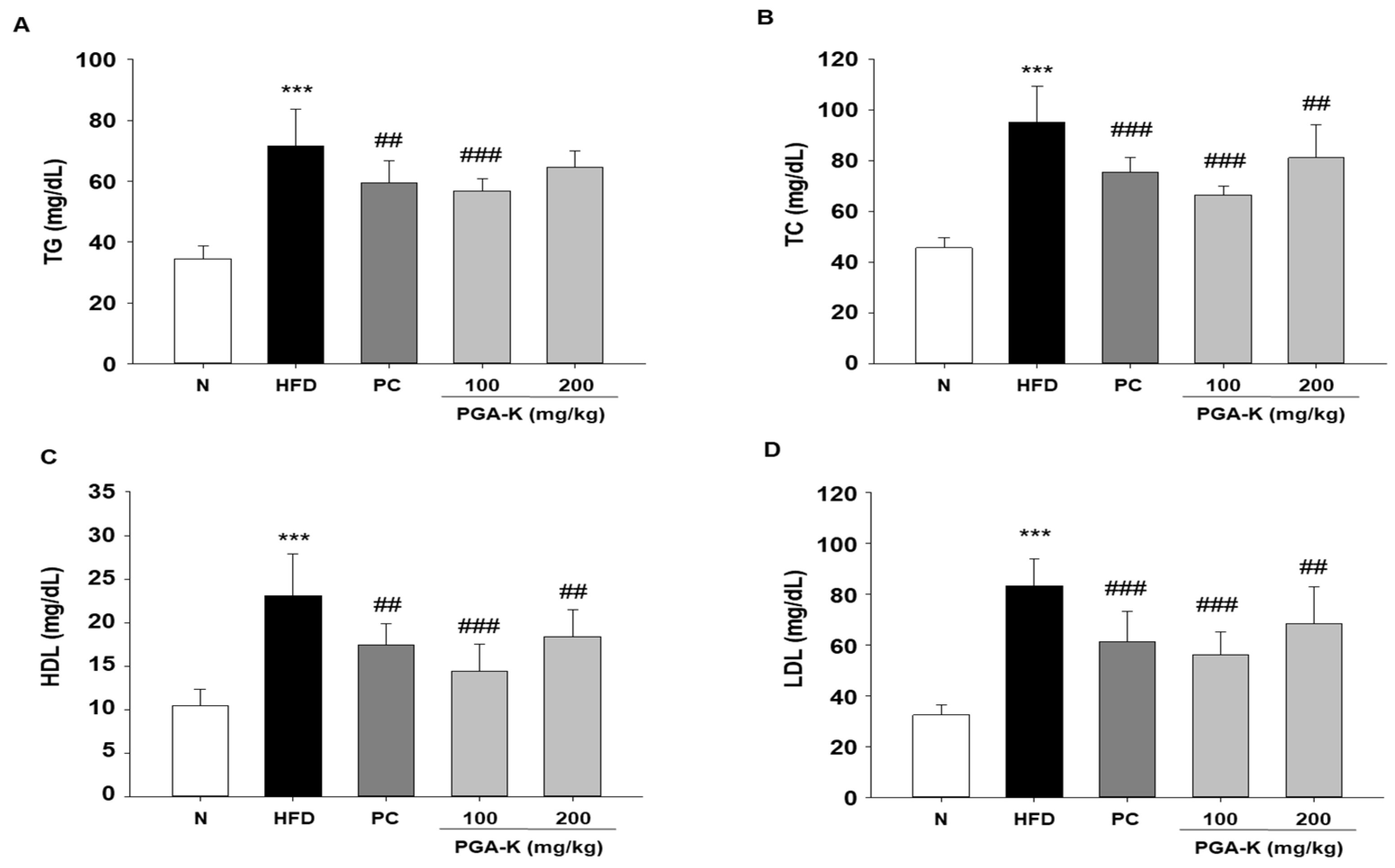
3.3. Effects of PGA-K on Serum Lipid Profiles in HFD-Fed Mice
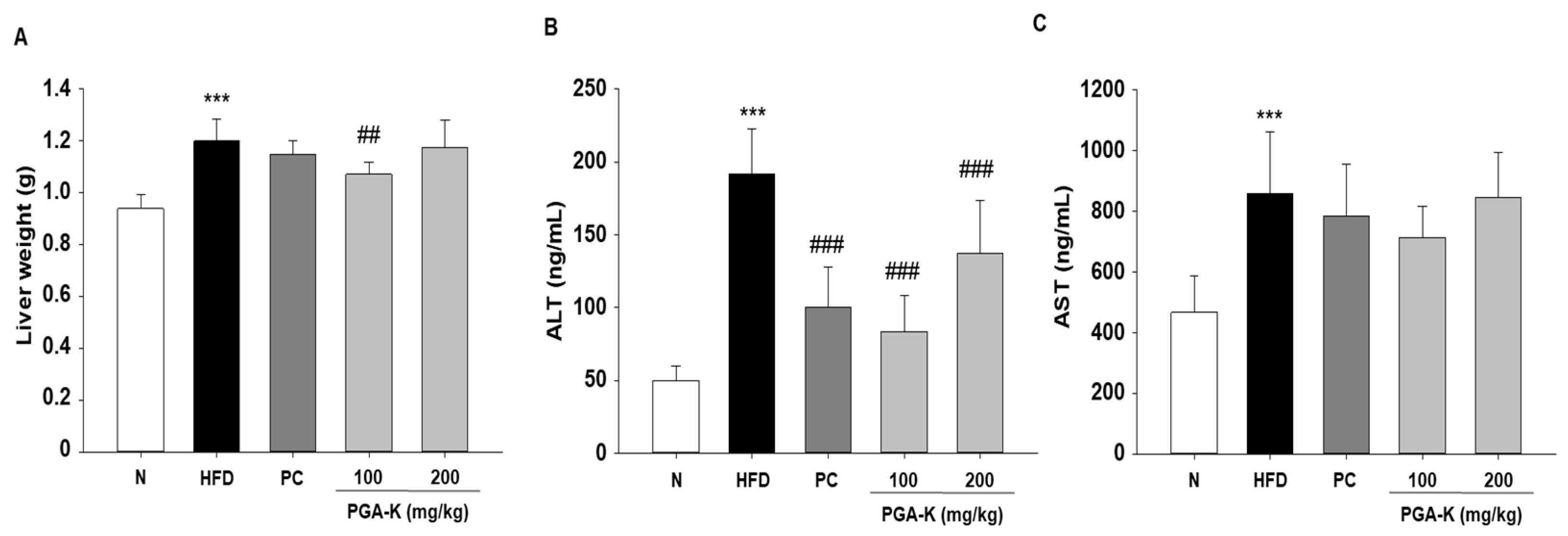
3.4. Effects of PGA-K on Liver Damage in HFD-Fed Mice
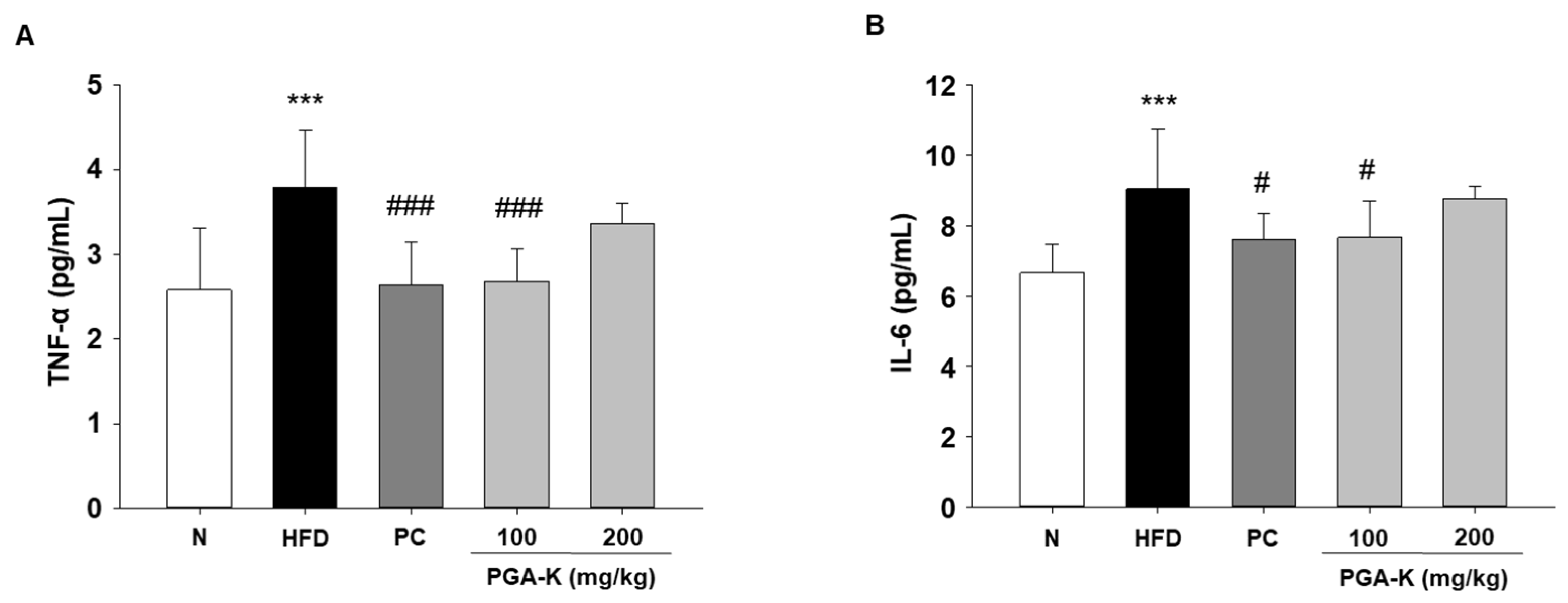
3.5. Effects of PGA-K on HFD-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
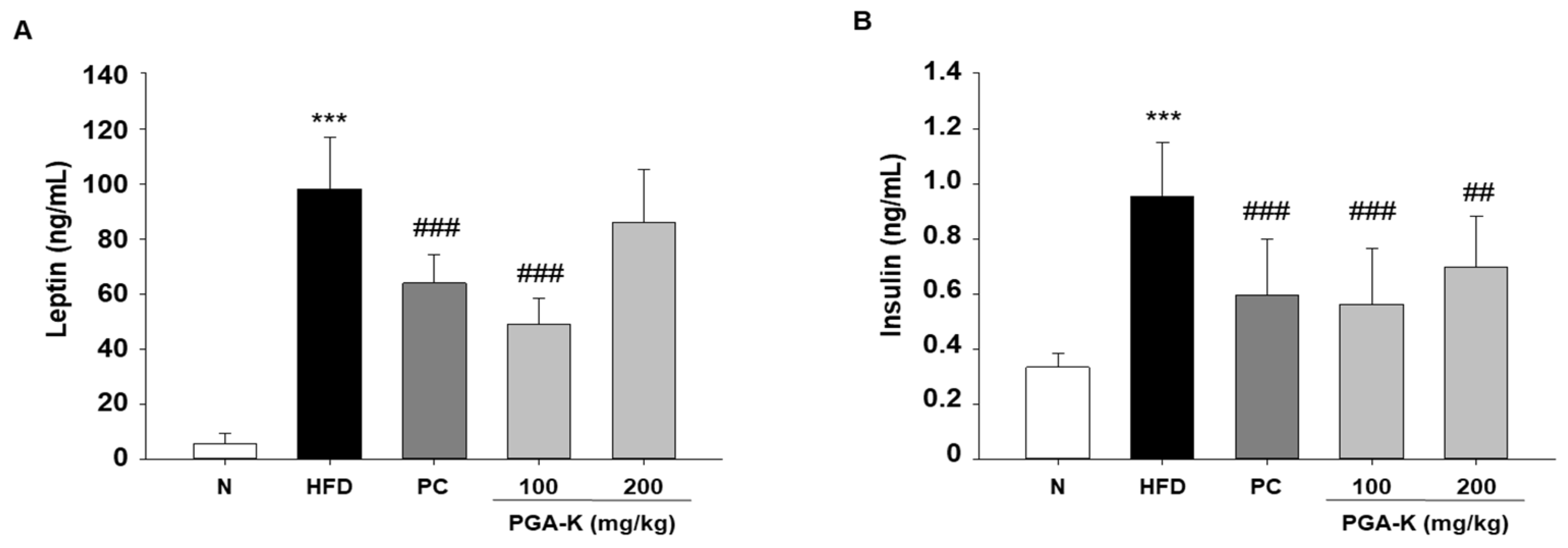
3.6. Effects of PGA-K on HFD-Induced Insulin Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruze, R.; Liu, T.; Zou, X.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, R.; Yin, X.; Xu, Q. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1161521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, H.M.; Song, H.J.; Kang, N.J.; Hwang, D.Y.; Choi, Y.W. Adiposity Reduction by Cucumis melo var. gaettongchamoe Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, A.; Birk, R. Adipose Tissue Hyperplasia and Hypertrophy in Common and Syndromic Obesity-The Case of BBS Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Peltzer, N. Cell death and inflammation during obesity: “Know my methods, WAT(son)”. Cell Death Differ 2023, 30, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, G.; Cimmino, F.; Trinchese, G.; Catapano, A.; Petrella, L.; D’Angelo, M.; Lucchin, L.; Mollica, M.P. From Obesity-Induced Low-Grade Inflammation to Lipotoxicity and Mitochondrial Dysfunction: Altered Multi-Crosstalk between Adipose Tissue and Metabolically Active Organs. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, A.; Gan, R.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Mao, Q.Q.; Zhang, P.Z.; Li, H.B. Effects and mechanisms of edible and medicinal plants on obesity: an updated review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2021, 61, 2061–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, M.S.; Jung, S.; Son, H.Y.; Park, S.; Kang, B.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, C.T.; Kim, Y. Ginger Extract Ameliorates Obesity and Inflammation via Regulating MicroRNA-21/132 Expression and AMPK Activation in White Adipose Tissue. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelczyńska, M.; Moszak, M.; Wesołek, A.; Bogdański, P. The Preventive Mechanisms of Bioactive Food Compounds against Obesity-Induced Inflammation. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mansoori, L.; Al-Jaber, H.; Prince, M.S.; Elrayess, M.A. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines, Growth Factors and Adipokines in Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance. Inflammation 2022, 45, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wu, D.; Qiu, Y. Adipose tissue macrophage in obesity-associated metabolic diseases. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 977485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhorst, A.; Raulien, N.; Wieghofer, P.; Eilers, J.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Bechmann, I.; Gericke, M. Adipocyte death triggers a pro-inflammatory response and induces metabolic activation of resident macrophages. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Chang, K.; Wu, W.; Griffiths, H.R.; Lu, S.; Gao, D. Adipose tissue macrophages as potential targets for obesity and metabolic diseases. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1153915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Prado, F.G.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Karp, S.G.; Soccol, C.R. Fermented Soy Products and Their Potential Health Benefits: A Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Hwang, C.W.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, C.H. Current Perspectives on the Physiological Activities of Fermented Soybean-Derived Cheonggukjang. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopikrishna, T.; Suresh Kumar, H.K.; Perumal, K.; Elangovan, E. Impact of Bacillus in fermented soybean foods on human health. Ann Microbiol 2021, 71, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, W. Enhanced Production of Poly-γ-glutamic Acid by Bacillus subtilis Using Stage-controlled Fermentation and Viscosity Reduction Strategy. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Islam, F.; Ateeq, H.; Asghar, A.; Shah, Y.A.; Ofoedu, C.E.; Chacha, J.S. Nutritional Health Perspective of Natto: A Critical Review. Biochem Res Int 2022, 2022, 5863887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.H.; Noh, H.; Kim, H.W.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Gunter, M.J.; Ferrari, P.; Scalbert, A.; et al. Metabolic tracking of isoflavones in soybean products and biosamples from healthy adults after fermented soybean consumption. Food Chem 2020, 330, 127317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, C.H. Beneficial Effects of Soybean-Derived Bioactive Peptides. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Liew, W.P.; Sulaiman Rahman, H. Antioxidant and Oxidative Stress: A Mutual Interplay in Age-Related Diseases. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Song, J.-L.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Y.; Li, G.-J.; Pang, L. Comparisons of Shuidouchi, Natto, and Cheonggukjang in their physicochemical properties, and antimutagenic and anticancer effects. Food Science and Biotechnology 2013, 22, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Fuentes, F.; Vilahur, G.; Badimon, L.; Palomo, I. Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2013, 2013, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellulu, M.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications. Arch Med Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863, External Resources Crossref (DOI) 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmkun, Y.T. Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes: associations and therapeutic implications. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity 2020, 3611–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojta, I.; Chacińska, M.; Błachnio-Zabielska, A. Obesity, Bioactive Lipids, and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic Adipose Tissue Inflammation Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.B. Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, J.T.; Marsche, G. Obesity-Related Changes in High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism and Function. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakhtoura, M.; Haber, R.; Ghezzawi, M.; Rhayem, C.; Tcheroyan, R.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacotherapy of obesity: an update on the available medications and drugs under investigation. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, C.Y. Anti-Obesity Drugs: A Review about Their Effects and Safety. Diabetes Metab J 2012, 36, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y. Anti-Obesity Drugs: Long-Term Efficacy and Safety: An Updated Review. World J Mens Health 2021, 39, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Huang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhi, C.; Bai, Y.; Che, Q.; Cao, H.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. Anti-Obesity Effect and Mechanism of Chitooligosaccharides Were Revealed Based on Lipidomics in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Noh, E.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kwak, M.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Yang, H.J.; Ryu, M.S.; Seo, H.Y.; Jang, H.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect and Signaling Mechanism of Glycine max Hydrolyzed with Enzymes from Bacillus velezensis KMU01 in a Dextran-Sulfate-Sodium-Induced Colitis Mouse Model. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weggemans, R.M.; Trautwein, E.A. Relation between soy-associated isoflavones and LDL and HDL cholesterol concentrations in humans: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 2003, 57, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.K.; Hong, Y.S.; Sung, Y.A.; Lee, H. The effect of menopause on cardiovascular risk factors according to body mass index in middle-aged Korean women. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Deb, P.K.; Priya, S.; Medina, K.D.; Devi, R.; Walode, S.G.; Rudrapal, M. Dietary Flavonoids: Cardioprotective Potential with Antioxidant Effects and Their Pharmacokinetic, Toxicological and Therapeutic Concerns. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007-2017. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, M.; Zare, M.; Nouripour, F. Effect of Soy and Soy Isoflavones on Obesity-Related Anthropometric Measures: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Adv Nutr 2017, 8, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, M.S.; Yu, O.K.; Cha, Y.S.; Park, T.S. Korean traditional Chungkookjang improves body composition, lipid profiles and atherogenic indices in overweight/obese subjects: a double-blind, randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 2016, 70, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langa, S.; Peirotén, Á.; Curiel, J.A.; de la Bastida, A.R.; Landete, J.M. Isoflavone Metabolism by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Its Application in the Development of Fermented Soy Food with Beneficial Effects on Human Health. Foods 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.K. Effects of Fermented Artemisia annua L. and Salicornia herbacea L. on Inhibition of Obesity In Vitro and In Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, A.; Bhat, A.; Irorere, V.U.; Hill, D.; Williams, C.; Radecka, I. Poly-γ-glutamic acid: production, properties and applications. Microbiology 2015, 161, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogun-Agbaje, O.A.; Odeniyi, O.A.; Odeniyi, M.A. Drug delivery applications of poly-γ-glutamic acid. Futur J Pharm Sci 2 0217, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Qian, W.; Rui, W.; Ke, S.; Sha, L.; Gui, L.; Peng, L.; Hong, X. Effect of dietary poly-γ-glutamic acid on growth, digestive enzyme activity, antioxidant capacity, and TOR pathway gene expression of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Aquaculture Reports 2022, 27, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorena, K.; Jachimowicz-Duda, O.; Ślęzak, D.; Robakowska, M.; Mrugacz, M. Adipokines and Obesity. Potential Link to Metabolic Disorders and Chronic Complications. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, X. The Role of Gut Microbiota in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetes: Lessons from Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




