Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
06 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Particle Size Measurement by spICP-MS
2.4. Porosity Determination
2.5. Particle Size Measurement by SEM
2.6. Detection of Protein-Binding Mesoporous SiO2 Microspheres by spICP-MS
3. Results and Discussion
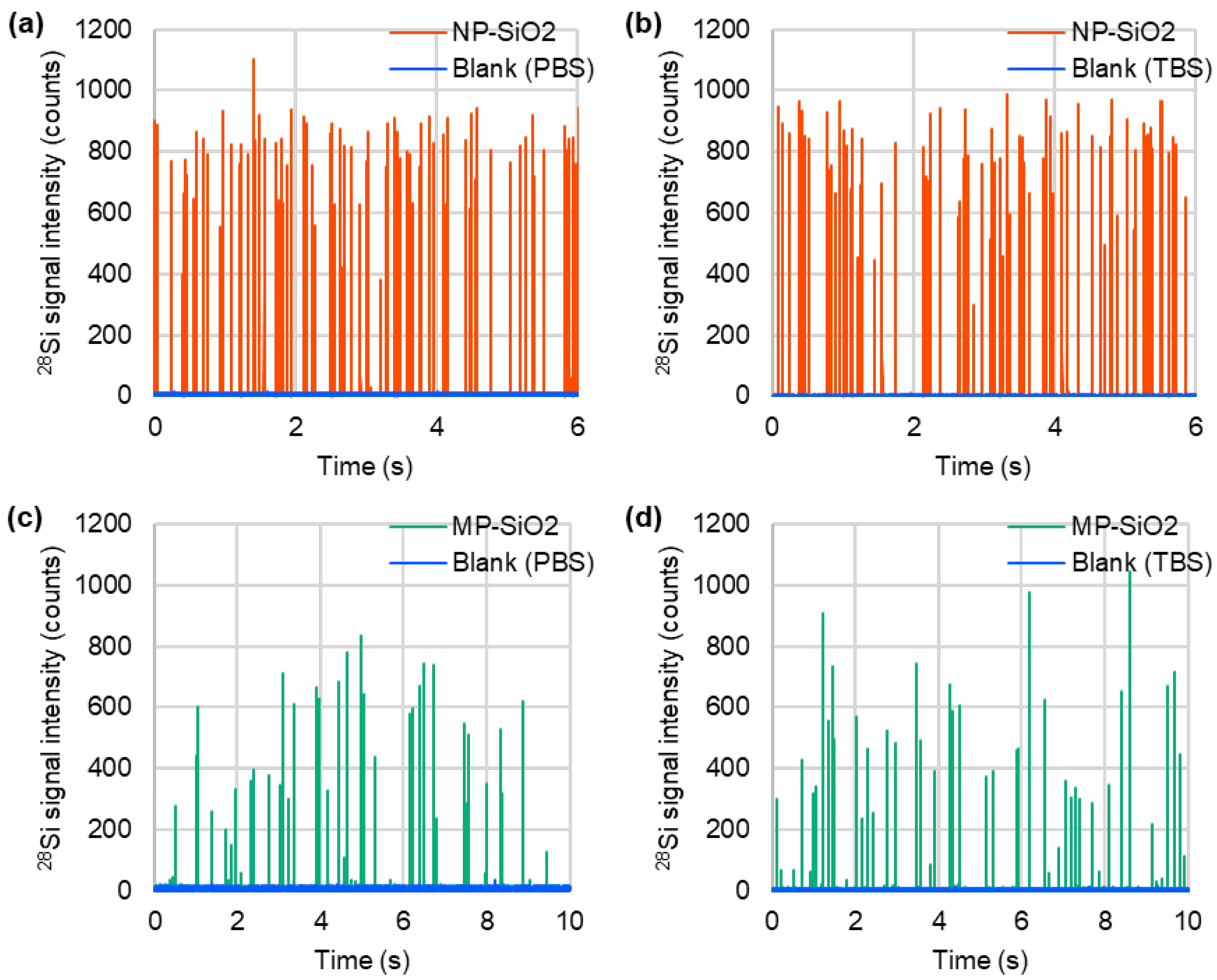
3.1. Particle Size Measurement by spICP-MS and SEM
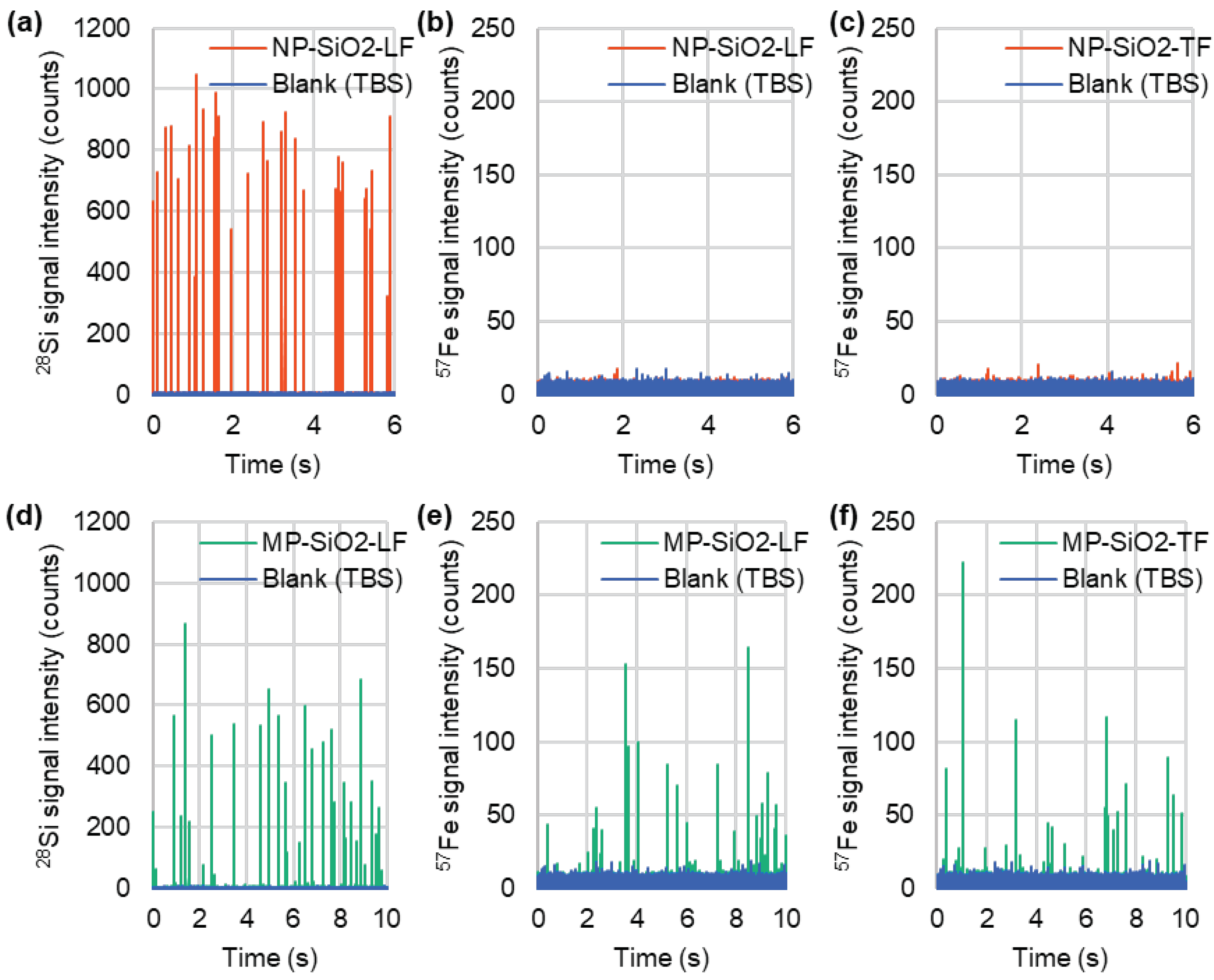
3.2. Detection of Fe-Containing Protein-Binding Mesoporous SiO2 Microspheres by spICP-MS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Close, E.D.; Nwokeoji, A.O.; Milton, D.; Cook, K.; Hindocha, D.M.; Hook, E.C.; Wood, H.; Dickman, M.J. Nucleic acid separations using superficially porous silica particles. J Chromatogr A 2016, 1440, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Ahrens, C.C.; Yu, D.; Ding, Z.; Lim, H.; Li, W. Cell Isolation and Recovery Using Hollow Glass Microspheres Coated with Nanolayered Films for Applications in Resource-Limited Settings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 15265–15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, S.; Baldini, F.; Berneschi, S.; Cosi, F.; Giannetti, A.; Conti, G.N.; Pelli, S.; Righini, G.C.; Tiribilli, B. High-Q polymer-coated microspheres for immunosensing applications. Opt Express 2009, 17, 14694–14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, W. Size-selective separation of DNA fragments by using lysine-functionalized silica particles. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 22029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Aina, V.; Areán, C.O.; Balas, F.; Cauda, V.; Colilla, M.; Delgado, M.R.; Vallet-Regí, M. Studies on MCM-41 mesoporous silica for drug delivery: Effect of particle morphology and amine functionalization. Chem Eng J 2008, 137, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. 3D cubic mesoporous silica microsphere as a carrier for poorly soluble drug carvedilol. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 2012, 147, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, L.P.; Carvalho, L.V.; Lima, F.A.; Quayle, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Tanaka, G.S.; Cabrera, W.H.; Furtado, M.F.; Tambourgi, D.V.; Matos Jdo, R.; et al. Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15: a new effective adjuvant to induce antibody response. Small 2006, 2, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellacherie, M.O.; Li, A.; Lu, B.Y.; Verbeke, C.S.; Gu, L.; Stafford, A.G.; Doherty, E.J.; Mooney, D.J. Single-Shot Mesoporous Silica Rods Scaffold for Induction of Humoral Responses Against Small Antigens. Adv Funct Mater 2020, 30, 2002448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezena, A.G.; Oseliero Filho, P.L.; Cides da Silva, L.C.; Oliveira, C.L.P.; Lopes, J.L.S.; Antonio, N.D.S.; Dettmann, V.F.B.; Akamatsu, M.A.; Martins, T.D.S.; Ribeiro, O.G.; et al. Adjuvant effect of mesoporous silica SBA-15 on anti-diphtheria and anti-tetanus humoral immune response. Biologicals 2022, 80, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño, M.D.; Olesik, J.W.; Barber, A.G.; Challis, K.; Ranville, J.F. Single Particle ICP-MS: Advances toward routine analysis of nanomaterials. Anal Bioanal Chem 2016, 408, 5053–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozhayeva, D.; Engelhard, C. A critical review of single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry – A step towards an ideal method for nanomaterial characterization. J Anal At Spectrom 2020, 35, 1740–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolea, E.; Jimenez, M.S.; Perez-Arantegui, J.; Vidal, J.C.; Bakir, M.; Ben-Jeddou, K.; Gimenez-Ingalaturre, A.C.; Ojeda, D.; Trujillo, C.; Laborda, F. Analytical applications of single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: a comprehensive and critical review. Anal Methods 2021, 13, 2742–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resano, M.; Aramendía, M.; García-Ruiz, E.; Bazo, A.; Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Vanhaecke, F. Living in a transient world: ICP-MS reinvented via time-resolved analysis for monitoring single events. Chem Sci 2022, 13, 4436–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kéri, A.; Sápi, A.; Ungor, D.; Sebők, D.; Csapó, E.; Kónya, Z.; Galbács, G. Porosity determination of nano- and sub-micron particles by single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 2020, 35, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, D.; Feng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Mass spectrometry detection of environmental microplastics: Advances and challenges. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 2024, 170, 117472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Rua-Ibarz, A.; Velimirovic, M.; Tirez, K.; Vanhaecke, F. Detection of microplastics using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) operated in single-event mode. J Anal At Spectrom 2020, 35, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velimirovic, M.; Tirez, K.; Verstraelen, S.; Frijns, E.; Remy, S.; Koppen, G.; Rotander, A.; Bolea-Fernandez, E.; Vanhaecke, F. Mass spectrometry as a powerful analytical tool for the characterization of indoor airborne microplastics and nanoplastics. J Anal At Spectrom 2021, 36, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, F.; Muszyńska, M.; Karasiński, J.; Lev, O.; Halicz, L. Detection of PTFE microparticles by ICP-qMS operated in single-particle mode. J Anal At Spectrom 2022, 37, 2282–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harycki, S.; Gundlach-Graham, A. Characterization of a high-sensitivity ICP-TOFMS instrument for microdroplet, nanoparticle, and microplastic analyses. J Anal At Spectrom 2023, 38, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.-i.; Ikeda, T.; Hiyoshi, N.; Chiba, M.; Yamaguchi, A. Assemblies of two multimeric enzymes using mesoporous silica microspheres toward cascade reaction fields. Biochem Eng J 2022, 182, 108416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.-i.; Baba, T.; Ikeda, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Tsunoda, T.; Yamaguchi, A. Highly Precise and Sensitive Polymerase Chain Reaction Using Mesoporous Silica-Immobilized Enzymes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2022, 14, 29483–29490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, S.-i.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Fujii, S.-i.; Takatsu, A.; Inagaki, K.; Fujimoto, T. High transport efficiency of nanoparticles through a total-consumption sample introduction system and its beneficial application for particle size evaluation in single-particle ICP-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 2017, 409, 1531–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, H.E.; Rogers, N.J.; Jarolimek, C.; Coleman, V.A.; Higgins, C.P.; Ranville, J.F. Determining Transport Efficiency for the Purpose of Counting and Sizing Nanoparticles via Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal Chem 2011, 83, 9361–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Miyashita, S.-i.; Hirata, T. Size Uncertainty in Individual Nanoparticles Measured by Single Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Determination of density by volumetric displacement — Skeleton density by gas pycnometry. 2014, ISO 12154:2014.
- Lee, S.; Bi, X.; Reed, R.B.; Ranville, J.F.; Herckes, P.; Westerhoff, P. Nanoparticle Size Detection Limits by Single Particle ICP-MS for 40 Elements. Environ Sci Technol 2014, 48, 10291–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yang, W.; Tan, H.; Jin, L.; Zhang, L.; Kerns, P.; Dang, Y.; Dissanayake, S.; Schaefer, S.; Liu, B.; et al. Template-free Synthesis of Mesoporous and Crystalline Transition Metal Oxide Nanoplates with Abundant Surface Defects. Matter 2020, 2, 1244–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.-i.; Chiba, M.; Tomon, E.; Tsunoda, T. Synthesis of amino acid using a flow-type microreactor containing enzyme–mesoporous silica microsphere composites. RSC Advances 2014, 4, 9021–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-W.; Chan, W.-T. Calibration of single-particle inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (SP-ICP-MS). J Anal At Spectrom 2015, 30, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesik, J.W.; Gray, P.J. Considerations for measurement of individual nanoparticles or microparticles by ICP-MS: determination of the number of particles and the analyte mass in each particle. J Anal At Spectrom 2012, 27, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, L.A.; Endres, M.C.; Liezers, M.; Ward, J.D.; Eiden, G.C.; Duffin, A.M. Collisional dampening for improved quantification in single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 189, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.C.; Minelli, C.; Tompkins, J.; Stevens, M.M.; Shard, A.G. Emerging Techniques for Submicrometer Particle Sizing Applied to Stöber Silica. Langmuir 2012, 28, 10860–10872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. Porous microsphere and its applications. Int J Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Sokolov, S.V.; Tanner, E.E.L.; Young, N.P.; Compton, R.G. Exploring nanoparticle porosity using nano-impacts: platinum nanoparticle aggregates. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2017, 19, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Zhao, D. Mesoporous titania: From synthesis to application. Nano Today 2012, 7, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, K.; He, X.; Zhang, R. Mesoporous Titanium Dioxide: Synthesis and Applications in Photocatalysis, Energy and Biology. Materials (Basel) 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, N.; Ibarra, I.A.; Humphrey, S.M. High surface area mesoporous Co3O4 from a direct soft template route. J Mater Chem 2012, 22, 12675–12681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sápi, A.; Halasi, G.; Grósz, A.; Kiss, J.; Kéri, A.; Ballai, G.; Galbács, G.; Kukovecz, Á.; Kónya, Z. Designed Pt Promoted 3D Mesoporous Co₃O₄ Catalyst in CO₂ Hydrogenation. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 2019, 19, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, J. A Biodegradation Study of SBA-15 Microparticles in Simulated Body Fluid and in Vivo. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6457–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Setting |
| Plasma and sampling conditions | |
| RF power | 1550 W |
| Plasma gas flow rate | 15 L/min |
| Auxiliary gas flow rate | 0.90 L/min |
| Carrier (nebulizer) gas flow rate | 0.90 L/min |
| Nebulizer pump | 0.10 rps |
| Sampling position | 10.0 mm |
| Cell gas (He) flow rate | 3.0 mL/min |
| Data acquisition | |
| Scanning mode | Peak hopping |
| Data point per peak | 1 point |
| Monitored isotope | 28Si, 57Fe |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





